Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Characterization of sepiolite-gel-based formulations for controlled release of pesticides
Maqueda, C; Partal, P; Villaverde, J; Perez-Rodriguez, JLApplied Clay Science, 46 (2009) 289-295
Show abstract ▽
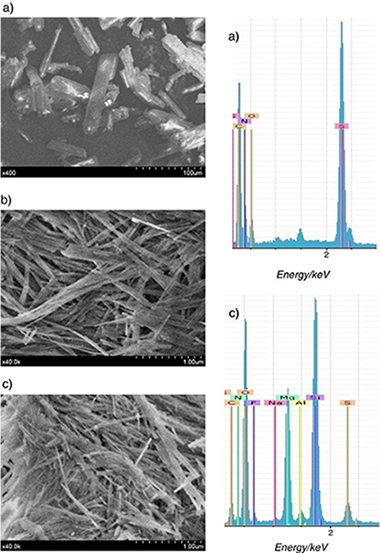
Novel controlled release formulations (CRFs) were developed for reducing leaching of herbicides and contamination of groundwater. The herbicide metribuzin (MTB) was entrapped within a sepiolite-gel matrix using a novel and ultrasound-based technique. Different sepiolite/herbicide matrices (either as a gel or as a powder after freeze-drying) were prepared with pesticide loading between 28.6 and 9.1%. The release of MTB from the control released formulations into water was retarded when compared with commercial formulation (CF), except in the case of the sepiolite-gel-based formulations with lower amounts of sepiolite. The rheological properties and microstructure of these formulations were examined in detail. FTIR spectra showed that there was no evidence of herbicide inside the sepiolite tunnels. The SEM micrograph of the sepiolite-gel-based formulations showed the fibrous morphology typical of sepiolite and no separate particles of MTB were found. However, the chemical analysis by EDX confirmed the presence of S, N, and C, which were attributed to MTB, together with the fibers of sepiolite. Rheological characterization indicated that samples containing MTB develops a microstructure, which is irrespective of concentration above 1 mass % sepiolite. There was a good agreement between the microstructure characteristics and MTB release behavior.
Noviembre, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.08.019
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis and characterization of a plant cutin mimetic polymer
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Heredia, A; Garcia-Segura, R; Benitez, JJPolymer, 50 (2009) 5633-5637
Show abstract ▽

A mimetic polymer of plant cutin have been synthesized from 9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid through a low temperature polycondensation reaction. Reaction conditions (solvent, catalyst, temperature, etc…) were studied and modified to optimize yield and product characteristics. The resulting polyaleurate polymer was characterized by Attenuated Total Reflection-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and solid state 13C-Cross Polarization/Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (13C-CP/MAS NMR). Mechanical and hydrodynamic properties were also investigated. In the average, the product obtained is physically and chemically very similar to plant cutin (a hydrophobic polyester). However, a more detailed analysis of results reveals that polyaleurate framework is more rigid than natural cutin and with additional larger short-range ordered domains. Also, the synthetic polymer displays slightly different mechanical properties with respect to natural cutin. Additional hydrogen bonding within the framework of polyaleurate is considered to be responsible for such experimental observations.
Noviembre, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2009.10.018
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Bonding Structure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-B-C Coatings
Abad, MD; Caceres, D; Pogozhev, YS; Shtansky, DV; Sanchez-Lopez, JCPlasma Processes and Polymers, 6 (2009) S107-S112
Show abstract ▽
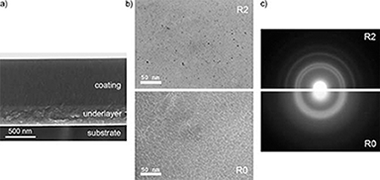
Nanocomposite coatings combining hard phases (TiB2, TiC) with an amorphous carbon (a-C) were developed to provide a good compromise between mechanical and tribological properties for M2 steels used in a wide variety of applications such as cutting tools, bearings and gear mechanisms. A combined d.c.-pulsed and r.f.-magnetron deposition process was used to deposit nanocomposite TiBC/a-C coatings with a variable content of carbon matrix phase. Chemical composition was determined by electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed that the coatings microstructure is rather amorphous with small nanocrystals of TiC and/or TiB2 (not possible to differentiate by diffraction techniques). Investigation of the chemical bonding environment by XPS and EELS allows us to confirm the presence of titanium-boron and titanium-carbon bonds together with free a-C. Coatings exhibited hardness values (H) of 25–29 GPa, effective Young modulus (E*) of 310–350 GPa, H/E* ratios over 0.080 and resistance to plastic deformation (H3/E*2) from 0.15 to 0.20. Tribological properties of the coatings were characterized by a pin-on-disk tribometer using steel and WC balls at high contact stresses (1.1 and 1.4 GPa respectively). Friction coefficients were reduced from 0.6 to 0.2 by increasing the content of free carbon without reduction of the hardness (around 28 GPa), by self-lubricant effects. The tribo-mechanical data are revised according to the phase composition and chemical bonding inside the nanocomposites.
Noviembre, 2009 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200930403
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
The hydrothermal conversion of kaolinite to kalsilite: Influence of time, temperature, and pH
Becerro, AI; Escudero, A; Mantovani, MAmerican Mineralogist, 94 (2009) 11-12
Show abstract ▽
Kalsilite (the low-temperature form of KAlSiO4) is used as the precursor of leucite, an important component in porcelain-fused-to-metal and ceramic-restoration systems, and it has also been proposed as a high-thermal expansion ceramic for bonding to metals. The present study reports the hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of pure kalsilite from kaolinite in subcritical conditions, as well as the characterization of the intermediate products by means of XRD, 29Si and 27Al MAS NMR, IR, SEM, and TEM. Effects of time, temperature, and pH on the reaction products are analyzed. The experimental data indicate that pure kalsilite is obtained after hydrothermal treatment of kaolinite at 300 °C for 12 h in 0.5 M KOH solution. Longer reaction times increase the crystallinity of the structure, whereas lower reaction times give rise to the metastable ABW-type KAlSiO4 polymorph. Lower temperatures are not sufficient to produce kalsilite, but zeolite W is obtained instead as the unique reaction product. Finally, the pH of the aqueous solution in contact with kaolinite is an important parameter for the synthesis of kalsilite, which must be ≥13.70.
Noviembre, 2009 | DOI: 10.2138/am.2009.3284
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Self-Assembling of Er2O3-TiO2 Mixed Oxide Nanoplatelets by a Template-Free Solvothermal Route
Julian-Lopez, B; Martos, M; Ulldemolins, N; Odriozola, JA; Cordoncillo, E; Escribano, PChemistry-A European Journal, 15 (2009) 12426-12434
Show abstract ▽

An easy solvothermal route has been developed to synthesize the first mesoporous Er2O3-TiO2 mixed oxide spherical particles composed of crystalline nanoplatelets, with high surface area and narrow pore size distribution. This synthetic strategy allows the preparation of materials at low temperature with interesting textural properties without the use of surfactants, as well as the control of particle size and shape. TEM and Raman analysis confirm the formation of nanocrystalline Er2O 3-TiO2 mixed oxide. Mesoscopic ordered porosity is reached through the thermal decomposition of organic moieties during the synthetic process, thus leading to a template-free methodology that can be extended to other nanostructured materials. High specific surface areas (up to 313 m 2g-1) and narrow pore size distributions are achieved in comparison to the micrometric material synthesized by the traditional sol-gel route. This study opens new perspectives in the development, by solvothermal methodologies, of multifunctional materials for advanced applications by improving the classical pyrochlore properties (magnetization, heat capacity, catalysis, conductivity, etc.). In particular, since catalytic reactions take place on the surface of catalysts, the high surface area of these materials makes them promising candidates for catalysts. Furthermore, their spherical morphology makes them appropriate for advanced technologies in, for instance, ceramic inkjet printers.
Noviembre, 2009 | DOI: 10.1002/chem.200901423
- ‹ anterior
- 388 of 422
- siguiente ›














