Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Química de Superficies y Catálisis - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Manganese and iron oxides as combustion catalysts of volatile organic compounds
Duran, FG; Barbero, BP; Cadus, LE; Rojas, C; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 92 (2009) 194-201
Show abstract ▽
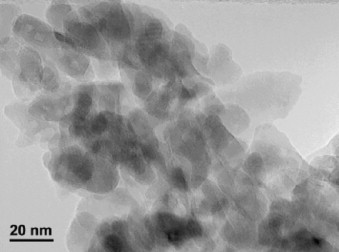
FeMn mixed oxides were prepared by the citrate method with Fe:Mn atomic ratio equal to 1:1, 1:3 and 3:1. The sample was characterized by means of specific surface area measurements, X-ray diffractometry (XRD), temperature programmed desorption of oxygen (O2-DTP), temperature programmed reduction (TPR), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), transmission electron microscopy (TEM and SAED) and high resolution TEM (HREM). The characterization results demonstrated the formation of a Mn2O3–Fe2O3 solid solution. The catalytic performance in ethanol, ethyl acetate and toluene total oxidation on these samples was better than on Fe2O3 and Mn2O3 pure oxides.
Octubre, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.07.010
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Rare-earth disilicate formation under Deep Geological Repository approach conditions
Alba, MD; Chain, P; Orta, MMApplied Clay Science, 46 (2009) 63-68
Show abstract ▽
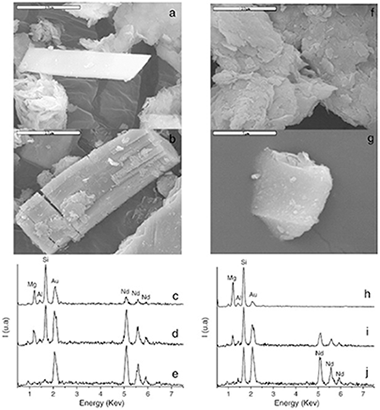
The Deep Geological Repository (DGR) concept involves the placement of long-lived radioactive waste in rooms excavated deep. The major responsibility of the disposal safety falls on the Engineered Barrier System (EBS). The main constituent of EBS is bentonite that prevents the release of radiactive nuclei by physical and chemical mechanisms. The physical mechanism is expected to fault with the weathering of the bentonite while the chemical mechanisms have been only proved at 300 °C. It is the aim of this paper to explore the feasibility of the chemical mechanism at temperatures closer to the DGP conditions and to shed light on the mechanism of transformation of the argillaceous materials of the EBS in rare-earth disilicate phases. Saponite was submitted to hydrothermal reaction at 175 °C and 150 °C with different solutions of REE3+ cations (REE = Sc, Lu, Y, Sm, Nd and La). The products were analyzed by XRD, NMR and electron microscopy. At conditions close to the DGP, the saponite was able to form rare-earth silicates. The formation of the disilicate phase, as final product, needs a set of stages and oxyorthosilicate as precursor.
Septiembre, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.07.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Formation of Nitrogen Functional Groups on Plasma Treated DLC
Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Contreras, L; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 6 (2009) 555-565
Show abstract ▽
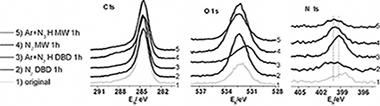
Diamond like carbon (DLC) thin films have been exposed to different nitrogen containing plasmas. A dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) at atmospheric pressure and a microwave discharge (MW) at low pressure using N2 and mixtures Ar + NH3 have been compared. Optical Emission and X-ray Photoelectron spectroscopies, Atomic Force Microscopy and contact angle measurements have been used for this study. A DBD with Ar + NH3 is the most efficient method for DLC functionalization. Films treated with this plasma presented the highest concentration of amine groups as determined by derivatization with 4-chlorobenzaldehyde. All the treated samples underwent a significant aging with time. The efficiency of the different plasmas for DLC functionalization is discussed in the light of the intermediate species detected in the plasma.
Septiembre, 2009 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200900019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Near-ambient X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and kinetic approach to the mechanism of carbon monoxide oxidation over lanthanum substituted cobaltites
Hueso, JL; Martinez-Martinez, D; Caballero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Mun, BS; Salmeron, MCatalysis Communications, 10 (2009) 1898-1902
Show abstract ▽
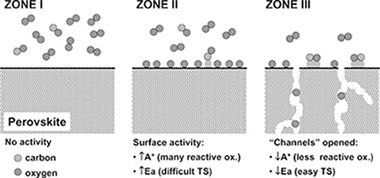
We have studied the oxidation of carbon monoxide over a lanthanum substituted perovskite (La0.5Sr0.5CoO3−d) catalyst prepared by spray pyrolysis. Under the assumption of a first-order kinetics mechanism for CO, it has been found that the activation energy barrier of the reaction changes from ∼80 to ∼40 kJ mol−1 at a threshold temperature of ca. 320 °C. In situ XPS near-ambient pressure (∼0.2 torr) shows that the gas phase oxygen concentration over the sample decreases sharply at ca. 300 °C. These two observations suggest that the oxidation of CO undergoes a change of mechanism at temperatures higher than 300 °C.
Agosto, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2009.06.022
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Reactivity of LaNi1−y Co y O3−δ Perovskite Systems in the Deep Oxidation of Toluene
Pereniguez, R; Hueso, JL; Holgado, JP; Gaillard, F; Caballero, ACatalysis Letters, 131 (2009) 164-169
Show abstract ▽

In the present work we have evaluated the oxidation of toluene over different lanthanum perovskites with a general composition of LaNi1−y Co y O3−δ. These catalysts, prepared by a spray pyrolysis method, have been characterised by XRD, BET and FE-SEM techniques. Additional experiments of temperature programmed desorption of O2, reduction in H2 and X-ray absorption spectroscopy were also performed in order to identify the main surface oxygen species and the reducibility of the different perovskites. The catalytic behaviour toward the oxidation of toluene (as a model for VOCs compounds) was evaluated in the range 100–600 °C, detecting a total conversion for all the samples below 400 °C and higher activities for the cobalt-containing perovskites. The catalytic behaviour of these samples is consistent with a suprafacial mechanism, with the α-type oxygen playing an active role in the oxidation reaction.
Agosto, 2009 | DOI: 10.1007/s10562-009-9968-0
- ‹ anterior
- 391 of 422
- siguiente ›














