Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Comparison between micro-Raman and micro-FTIR spectroscopy techniques for the characterization of pigments from Southern Spain Cultural Heritage
Franquelo, ML; Duran, A; Herrera, LK; de Haro, MCJ; Perez-Rodriguez, JLJournal of Molecular Structure, 924-926 (2009) 404-412
Show abstract ▽
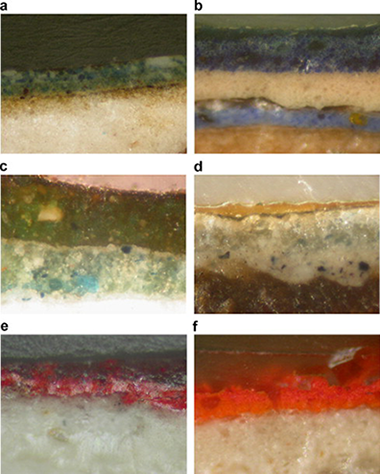
An extensive overview of the complementary use of micro-FTIR and micro-Raman spectroscopy in the Cultural Heritage studies is described in this work.
The samples have been prepared using the cross-section technique. This technique allows the examination of a large portion of a single paint layer in its original condition. A variety of pigments from samples belonging principally to the Cultural Heritage of Southern Spain were characterized by micro-Raman spectroscopy using visible excitation sources and micro-FTIR spectroscopy. The pigments studied comprise blue (azurite, ultramarine blue, Prussian blue), red (vermilion, haematite, red ochre, red lead, etc.), ochre and yellow (goethite, orpiment, realgar, etc.), green (malachite, copper resinate), and white (calcite, gypsum, white lead, titanium white, barite, lithopone) pigments, among others. An orientation is given for their appropriate and unequivocal characterization. Characterization by micro-FTIR and micro-Raman presents difficulties with some pigments. In these cases, analysis by EDX solves most of these doubts. The combined use of both spectroscopic techniques, together with SEM–EDX microanalysis, provides one of the most useful methods in the characterization (and possible dating) of materials used in Cultural Heritage.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.11.041
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Co3O4 + CeO2/SiO2 Catalysts for n-Hexane and CO Oxidation
Todorova, S; Kadinov, G; Tenchev, K; Caballero, A; Holgado, JP; Pereniguez, RCatalysis Letters, 129 (2009) 149-155
Show abstract ▽
Two-component Co–Ce samples deposited onto SiO2 have been prepared, characterized and tested in the reaction of complete n-hexane and CO oxidation. It was established that cerium enhanced the catalytic activity of cobalt in the reaction of n-hexane oxidation, although this depended on the sequence of cobalt and cerium introduction. Co-impregnation of Co and Ce resulted in a close interaction between Co3O4 and CeO2 leading to more surface oxygen species available and, therefore, a better reactivity.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1007/s10562-008-9805-x
Study of ground and unground leached vermiculite
Maqueda, C; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Subrt, J; Murafa, NApplied Clay Science, 44 (2009) 178-184
Show abstract ▽

Grinding of clays modifies their surfaces and can significantly affect their leaching behaviour. The acid reaction of vermiculite from Santa Olalla (Huelva, Spain) with HCl at various concentrations was affected by grinding and acid concentration. The acid leaching of ground vermiculite for 3 min with 1 M HCl solution at 80 °C for 24 h removed MgO and Al2O3 almost completely, leaving a residue containing SiO2 and Fe2O3. X-ray diffraction analysis showed the presence of akaganeite (β-FeOOH) and an amorphous phase (silica). Porosity studies showed a very high specific surface area for ground samples compared with unground vermiculite samples, attributed to the presence of iron in the residue coming from structural iron. High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) confirmed the presence of iron oxyhydroxides embedded in the silica material. The particle morphology of the iron oxides corresponded well to akaganeite microcrystals precipitated from solution. The leached vermiculite residue also contained Cl− and a small amount of Ti4+, which were accumulated into the akaganeite microcrystals.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.01.019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold/hydroxyapatite catalysts: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity to CO oxidation
Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 87 (2009) 245-251
Show abstract ▽
This work reports the synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity for CO oxidation of gold catalysts supported on calcium hydroxyapatite. On both, the hydroxyapatite support and the gold-supported hydroxyapatite catalyst, the CO conversion shows a peak near 100% of conversion at room temperature. The generation of structural vacancies by interaction of CO with the solid provokes the formation of peroxide species in the presence of gaseous oxygen, which seems to be responsible of this high conversion of CO at room temperature. Moreover, the influence of the pre-treatment temperature on the activity has been observed and related with the elimination of carbonate species and the generation of structural defects in the apatite structure, which are able to modify the gold oxidation state.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.016
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribological carbon-based coatings: An AFM and LFM study
Martinez-Martinez, D; Kolodziejczyk, L; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Fernandez, ASurface Science, 603 (2009) 973-979
Show abstract ▽

In this work some carbon-based coatings were studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and lateral force microscopy (LFM) techniques in order to evaluate their microstructure and friction properties at the micro and nanoscale. With this aim, four samples were prepared by magnetron sputtering: an amorphous carbon film (a–C), two nanocomposites TiC/a–C with different phase ratio (∼1:1 and ∼1:3) and a nanocrystalline TiC sample. Additionally, a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) and an amorphous hydrogenated carbon coating (a-C:H) were included to help in the evaluation of the influence of the roughness and the hydrogen presence respectively. The topography (roughness) of the samples was studied by AFM, whereas LFM was used to measure the friction properties at the nanoscale by two different approaches. Firstly, an evaluation of possible friction contrast on the samples was done. This task was performed by subtraction of forward and reverse images and lately confirmed by the study of lateral force profiles in both directions and the histograms of the subtraction images. Secondly, an estimation of the average friction coefficient over the analysed surface of each sample was carried out. To take into account the tip evolution/damaging, mica was used as a reference before and after each sample (hereafter called sandwich method), and samples-to-mica friction ratios were calculated. The LFM was shown to be a useful tool to characterise a mixture of phases with different friction coefficients. In general, the friction ratios seemed to be dominated by the amorphous carbon phase, as it was impossible to distinguish among samples with different proportions of the amorphous phase (friction ratios between 1.5 and 1.75). Nevertheless, it could be concluded that the differences in friction behaviour arose from the chemical aspects (nature of the phase and hydrogen content) rather than surface characteristics, since the roughness (Ra values up to 5.7 nm) does not follow the observed trend. Finally, the Ogletree method was employed in order to calibrate the lateral force and estimate the friction coefficient of our samples. A good agreement was found with macroscopic and literature values going from ∼0.3 for TiC to ∼0.1 for pure carbon.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2009.01.043
- ‹ anterior
- 401 of 422
- siguiente ›














