Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructural characterization of ceramic-intermetallic composites using TEM related techniques
Sayagues, MJ; Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Alcala, MD; Gotor, FJJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 30 (2010) 1765-1774 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.01.039
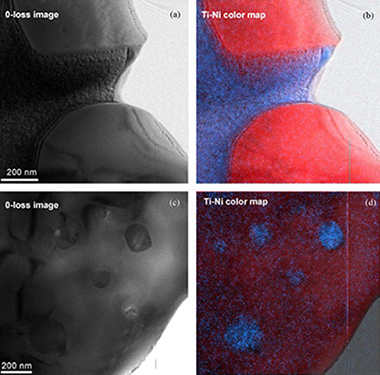
Abstract
TiCxVy/Ni and TiCxNy/Ti-Co composites formed by ceramic and intermetallic binder phases were produced by pressureless sintering at 1400 degrees C from powders synthesized by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process. Four different composites were characterized using high-resolution electron microscopic techniques, in both scanning (SEM, HRSEM) and transmission (TEM, HRTEM, ED, EDS and EELS) modes and using an energy filtered technique (EFTEM) associated with electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). The microcharacterization showed that the ceramic phase with an fcc-cubic structure displayed a short-range order in many crystals detected by diffuse scattering in the ED patterns. This was possibly due to a sequence of C, N, and vacancies of both atoms along certain directions in the structure. On the other hand, even though the binder phase was introduced as metal in the reaction process, it was formed by Ni-Ti or Co-Ti known intermetallic compounds (NiTi2, Ni3Ti, and Co3Ti). An unknown Ni-Ti intermetallic structure with a Ni:Ti ratio close to 2:1 was only found in one of the synthesized composites and displayed a cubic structure with a lattice parameter, a, of about 8.7 angstrom.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.01.039
Identification of cellulose fibres belonging to Spanish cultural heritage using synchrotron high resolution X-ray diffraction
Herrera, LK; Justo, A; Duran, A; de Haro, MCJ; Franquelo, M; Rodriguez, JLPApplied Physics A-Materials Science & Processing, 99 (2010) 391-398 DOI: 10.1007/s00339-010-5626-z
Abstract
A complete characterisation of fibres used in Spanish artwork is necessary to provide a complete knowledge of these natural fibres and their stage of degradation. Textile samples employed as painting supports on canvas and one sample of unprocessed plant material were chosen for this study. All the samples were investigated by synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction (SR-XRD). Flax and cotton have the Cellulose I structure. The values of the crystalline index (CI) were calculated for both types of fibres. The structure of Cellulose IV was associated with the unprocessed plant material. The information obtained by SR-XRD was confirmed by laboratory techniques including scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR).
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s00339-010-5626-z
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
On the microstructure of single wall carbon nanotubes reinforced ceramic matrix composites
Zapata-Solvas, E; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of Materials Science, 45 (2010) 2258-2263 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-009-4126-z
Abstract
A microstructural modelling of the microstructure in single wall carbon nanotubes reinforced alumina ceramics has been developed. The model accounts for the main microstructural features, being quite useful to describe the carbon nanotube distribution along the ceramic matrix. The microstructural analysis derived from this model is found to give a deeper insight into the high-temperature creep of these composites.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-009-4126-z
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
SiOxNy thin films with variable refraction index: Microstructural, chemical and mechanical properties
Godinho, V; de Haro, MCJ; Garcia-Lopez, J; Goossens, V; Terryn, H; Delplancke-Ogletree, MP; Fernandez, AApplied Surface Science, 256 (2010) 4548-4553 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.02.045
Abstract
In this work amorphous silicon oxynitride films with similar composition (ca. Si0.40N0.45O0.10) were deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering from a pure Si target under different N-2-Ar mixtures. Rutherford backscattering (RBS) studies revealed that the coatings presented similar composition but different density. The mechanical properties evaluated by nanoindentation show also a dependence on the deposition conditions that does not correlate with a change in composition. An increase in nitrogen content in the gas phase results in a decrease of hardness and Young's modulus. The microstructural study by high resolution scanning electron microscopy (SEM-FEG) on non-metalized samples allowed the detection of a close porosity in the form of nano-voids (3-15 nm in size), particularly in the coatings prepared under pure N-2 gas. It has been shown how the presence of the close porosity allows tuning the refraction index of the films in a wide range of values without modifying significantly the chemical, thermal and mechanical stability of the film.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.02.045
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Permanent magnetism in phosphine- and chlorine-capped gold: from clusters to nanoparticles
Munoz-Marquez, MA; Guerrero, E; Fernandez, A; Crespo, P; Hernando, A; Lucena, R; Conesa, JCJournal of Nanoparticle Research, 12 (2010) 1307-1318 DOI: 10.1007/s11051-010-9862-0

Abstract
Magnetometry results have shown that gold NPs (similar to 2 nm in size) protected with phosphine and chlorine ligands exhibit permanent magnetism. When the NPs size decreases down to the subnanometric size range, e.g. undecagold atom clusters, the permanent magnetism disappears. The near edge structure of the X-ray absorption spectroscopy data points out that charge transfer between gold and the capping system occurs in both cases. These results strongly suggest that nearly metallic Au bonds are also required for the induction of a magnetic response. Electron paramagnetic resonance observations indicate that the contribution to magnetism from eventual iron impurities can be disregarded.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s11051-010-9862-0
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
The Effect of Water on Particle Size, Porosity and the Rate of Drug Release From Implanted Titania Reservoirs
Lopez, T; Ortiz, E; Alexander-Katz, R; Odriozola, JA; Quintana, P; Gonzalez, RD; Lottici, PP; Marino, LGJournal of Biomedical Materials Research Part-B Applied Biomaterials, 93B (2010) 401-406 DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.31595

Abstract
The implantation of controlled drug release devices represents a new strategy in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders Sol-gel titania implants filled with valproic acid, have been used for this purpose to treat induced epilepsy in rats The kinetics of the drug release depend on. (a) porosity, (b) chemical interactions between valproic acid and surface hydroxyl groups of titania, (c) particle size, and (d) particle size agglomerates The concentration of water used in the hydrolysis reaction is an important variable in the degree of porosity, hydroxylation, and structural defects of the nanostructured titanium oxide reservoir The titanium n-butoxide/water ratio was systematically varied during the sol-gel synthesis, while maintaining the amount of valproic acid constant. Characterization studies were performed using DTA-TGA, FTIR, Raman, TEM, SEM, BET, and in vitro release kinetic measurements The particle agglomerate size and porosity were found to depend on the amount of water used in the sol-gel reactio.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.31595
Reactividad de Sólidos
A new model for the kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of polymers driven by random scission
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMPolymer Degradation and Stability, 95 (2010) 733-739 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.02.017
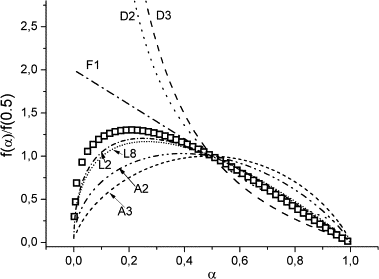
Abstract
In this paper, a series of f(alpha) kinetic equations able to describe the random scission degradation of polymers is formulated in such a way that the reaction rate of the thermal degradation of polymers that go through a random scission mechanism can be directly related to the reacted fraction. The proposed equations are validated by a study of the thermal degradation of poly(butylene terephthalate) (PBT). The combined kinetic analysis of thermal degradation curves of this polymer obtained under different thermal pathways have shown that the proposed equation fits all these curves while other conventional models used in literature do not.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.02.017
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Excitation transfer mechanism along the visible to the Near-IR in rhodamine J-heteroaggregates
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Toudert, J; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, AChemical Communications, 46 (2010) 4372-4374 DOI: 10.1039/c0cc00087f
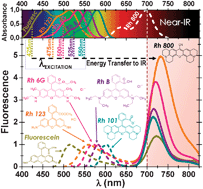
Abstract
An enhanced fluorescent emission of the dye Rhodamine 800 in the Near-IR is observed in the presence of other xanthene dye molecules (RhX) when they are hosted in different matrices due to the formation of a new type of fluorescent J-heteroaggregates.
This enhanced emission of the acceptor occurs despite the low spectral overlapping and the low quantum yield of Rh800.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/c0cc00087f
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
N- and/or W-(co)doped TiO2-anatase catalysts: Effect of the calcination treatment on photoactivity
Kubacka, A; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 95 (2010) 238-244 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.12.028
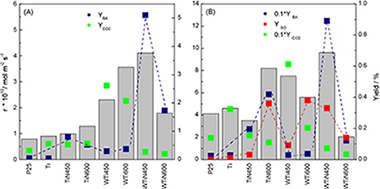
Abstract
A series of nanosized W,N-codoped and single-doped N- and W-anatase-TiO2 catalysts have been prepared by a microemulsion method and calcined at different temperatures. The activity in the sunlight selective photo-oxidation of toluene and styrene has been correlated with structural, electronic, and surface examinations of the catalysts done with the help of XRD-Rietveld, N-2 physisorption, X-ray photoelectron, infrared, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and UV-vis spectroscopies. Irrespective of the reaction, W,N-codoped nanocatalysts showed an enhanced photoactivity with respect to bare anatase and single-doped N-TiO2 and W-TiO2 materials. A strong W-N synergistic interaction appears to play a decisive role in driving the excellent photoactivity performance of W,N-codoped materials by affecting (i) electronic properties, particularly maximizing the anatase band gap decrease and enhancing the subsequent visible light photon absorption, and (ii) surface properties, in turn related to the formation of OH radicals upon light excitation. The maximum photoactivity is reached by calcination at 450 degrees C and is concomitantly observed with a near complete selectivity to partial oxidation products. Higher calcination temperatures yielded solids with significantly inferior photocatalytic performance. The properties of the W-N interaction are discussed as a function of the calcination temperature.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.12.028
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Non-destructive depth compositional profiles by XPS peak-shape analysis
Lopez-Santos, MC; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAnalytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 396 (2010) 2757-2768 DOI: 10.1007/s00216-009-3312-9

Abstract
The measured peak shape and intensity of the photoemitted signal in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) experiments (elastic and inelastic parts included) are strongly correlated, through electron-transport theory, with the depth distribution of photoelectron emitters within the analyzed surface. This is the basis of so-called XPS peak-shape analysis (also known as the Tougaard method) for non-destructive determination of compositional in-depth (up to 6-8 nm) profiles. This review describes the theoretical basis and reliability of this procedure for quantifying amounts and distributions of material within a surface. The possibilities of this kind of analysis are illustrated with several case examples related to the study of the initial steps of thin-film growth and the modifications induced in polymer surfaces after plasma treatments.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s00216-009-3312-9
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Catalytic nanomedicine: Functionalisation of nanostructured cryptomelane
Lopez, T; Ortiz, E; Alvarez, M; Manjarrez, J; Montes, M; Navarro, P; Odriozola, JAMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 120 (2010) 518-525 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.11.049
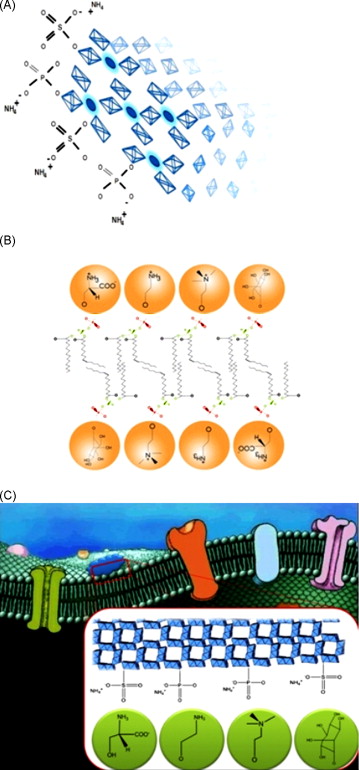
Abstract
Nanostructured cryptomelanes (KMn8O16) were synthesized from manganese sulphate and manganese acetate precursors by the reflux method. The respectively obtained samples, CRYSO4 and CRYAc, were functionalised with hydroxyl, ammonium, sulphate and phosphate groups in order to modify the biocompatibility and surface properties of cryptomelane. Characterization by FTIR and XRD confirmed bond formation of CRY-NH, CRY=S=O, CRY-NH, and CRY=PO4. In both functionalise samples (CRYSO4-F and CRYAc-F), IR bands occurred at 1399 cm(-1), corresponding to the sulphate species, and 1106 cm(-1), related to phosphate vibrations; along with the OH and NH characteristic vibration bands in the high energy region. Biocompatibility of functionalised samples was tested by implantation of cryptomelane reservoir in the basolateral amygdala and caudal nucleus of Wistar rats using stereotactic surgery. The brains of the rats were processed in order to evaluate any damage associated with the implant. The results showed that functionalised cryptomelanes did not cause tissue damage or inflammation while not functionalised cryptomelanes caused cell death.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.11.049
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
One-Step Dry Method for the Synthesis of Supported Single-Crystalline Organic Nanowires Formed by pi-Conjugated Molecules
Borras, A; Groning, O; Aguirre, M; Gramm, F; Groning, PLangmuir, 26 (2010) 5763-5771 DOI: 10.1021/la1003758
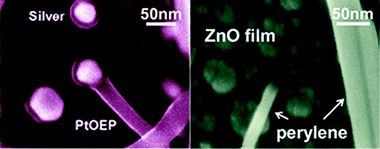
Abstract
We present for the first time a general vacuum process for the growth of supported organic nanowires formed by pi-conjugated molecules, including metalloporphyrins, metallophthalocyanines, and perylenes. This methodology consists on a one-step physical vapor deposition of the pi-conjugated molecules. The synthesis is carried out at controlled temperature on substrates with tailor morphology which allows the growth or organic nanowires in the form of squared nanofibers and nanobelts. The study of the nanowires by electron diffraction and HRTEM combining with the results of a theoretical analysis of the possible arrangement of the pi-conjugated molecules along the nanowires reveals that the nanowires show a columnar structure along the fiber axis consisting of pi-stacked molecules having a herringbone-like arrangement. The formation of these nanowires on different substrates demonstrates that the growth mechanism is independent of the substrate chemical composition. An in-depth phenomenological study of the Formation of the nanowires drives us to propose a growth mechanism based on a crystallization process. Furthermore, the growth method allows the fabrication of two particular ID heterostructures: binary and open core@shell organic nanofibers.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/la1003758
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Gas phase photocatalytic oxidation of toluene using highly active Pt doped TiO2
Colon, G; Maicu, M; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, MJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 320 (2010) 14-18 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2009.12.009

Abstract
Platinum doped TiO2 materials were studied for the gas phase photocatalytic degradation of toluene. Platinum deposition was achieved by photodeposition method over TiO2 prepared by means of a sol-gel route. The effect of sulphuric acid pretreatment on the further platinisation process has been extensively studied. From the wide structural and surface analysis of the catalysts an interesting synergetic effect has been demonstrated. The previous sulphate treatment over TiO2 leads to improved dispersion of the Pt which presents a lower aggregation and homogeneous cluster size. This fact, together with the adequate control of anatase structural and surface parameter due to the sulphate treatment, renders a good photocatalytic performance for toluene oxidation reaction. The highest reaction rates and CO2 selectivities have been obtained for Pt-S-TiO2 samples.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2009.12.009
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Surface Functionalization, Oxygen Depth Profiles, and Wetting Behavior of PET Treated with Different Nitrogen Plasmas
Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2 (2010) 980-990 DOI: 10.1021/am100052w
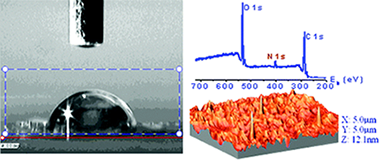
Abstract
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plates have been exposed to different nitrogen containing plasmas with the purpose of incorporating nitrogen functional groups on its surface. Results with a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) at atmospheric pressure and a microwave discharge (MW) at reduced pressure and those using an atom source working under ultrahigh vacuum conditions have been compared for N-2 and mixtures Ar + NH3 as plasma gases. The functional groups have been monitored by X-ray Photoemission Spectroscopy (XPS). Nondestructive oxygen and carbon depth profiles for the plasma treated and one month aged samples have been determined by means of the nondestructive Tougaard's method of XPS background analysis. The surface topography of the treated samples has been examined by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), while the surface tension has been determined by measuring the static contact angles of water and iodomethane. It has been found that the DBD with a mixture of Ar+NH3 is the most efficient treatment for nitrogen and amine group functionalization as determined by derivatization by reaction with chlorobenzaldehyde. It is also realized that the nitrogen functional groups do not contribute significantly to the observed increase in surface tension of plasma treated PET.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/am100052w
Materiales Avanzados
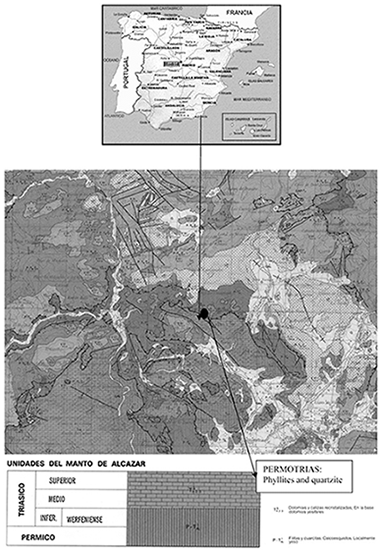
Physical and geotechnical properties of clay phyllites
Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Romero, EApplied Clay Science, 48 (2010) 307-318 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.12.022
Abstract
An experimental programme is presented with the aim of characterising - from physical, microstructural and geotechnical perspectives - the main properties of compacted clay phyllites. These clay phyllites are widely used as waterproofing material for roofs in the Alpujarra (Andalusia, Spain), as sealing liners in irrigation ponds, and as core material of small earthen zoned dams. An exhaustive physical-characterisation programme on the powder fraction has been followed using X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), chemical analysis by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), thermal analysis, particle-size distribution analysis, consistency limits, and density of solid particles. From a microstructural standpoint, mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) tests, as well as nitrogen-adsorption tests, were carried out to characterise the pore network and surface area of the material in both natural and compacted states. The geotechnical characterisation programme on the compacted material was focused on the water-permeability and water-retention properties, the volume change on soaking (swelling or collapse), the compressibility on loading, the shear-strength properties, and the mechanical-penetration properties. In this way, an important physical and hydro-mechanical data base is provided, which could help in evaluating the suitability for using this material in a wide range of earthen constructions (liners, road subgrades, embankments, core material in zoned dams). It has been found that the material contains illite, chlorite and quartz as the main components, and feldspar, iron oxide and interstratified illite-smectite as minor ones. Despite the presence of active clay minerals, the compacted material did not display an important swelling on soaking at low stresses, as a consequence of its low specific surface and low water-retention ability. The material exhibited good compaction properties and, consequently, low water permeability plus a stiff response on loading. Nevertheless, despite the low porosity attained on the dry-side compaction, the material underwent some collapse on soaking at stresses greater than 100 kPa.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.12.022
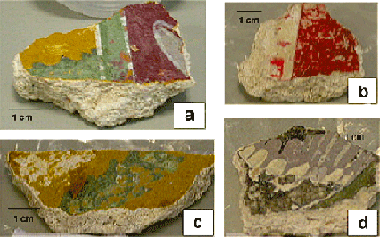
Determination of pigments and binders in Pompeian wall paintings using synchrotron radiation - High-resolution X-ray powder diffraction and conventional spectroscopy-chromatography
Duran, A; De Haro, MCJ; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Franquelo, ML; Herrera, LK; Justo, AArchaeometry, 52 (2010) 286-307 DOI: 10.1111/j.1475-4754.2009.00478.x
Abstract
The employment of synchrotron techniques complemented by conventional laboratory systems has allowed us to deepen and improve our knowledge of Roman wall painting procedures. The palette identified in wall paintings from Pompeii and Herculaneum from the second century bc includes goethite, hematite, cinnabar, glauconite, Egyptian blue, and other components such as calcite and aragonite. Proof of the use of organic binders is provided by FTIR and PY-GC/MS. Therefore, the possibility of the use of 'a secco' techniques cannot be ruled out. Pigments in wall paintings are usually found in small percentages and conventional X-ray diffractometers do not detect them. Synchrotron radiation - high-resolution X-ray powder diffraction has allowed identification with only a few micrograms of sample.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1475-4754.2009.00478.x
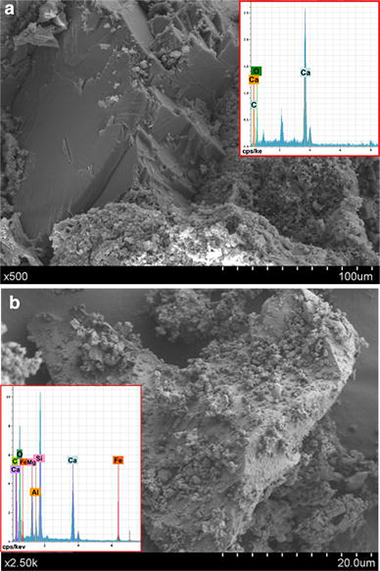
A thermal study approach to roman age wall painting mortars
Duran, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Poyato, J; Perez-Rodriguez, JLJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 99 (2010) 803-809 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-009-0667-2
Abstract
Roman ancient mortars have been widely studied, in connection with both diagnosis and application required for restoring. Thermoanalytical experiments performed on mortars from Pompeii and Herculaneum provided a very good understanding of the technology employed. The mortars from Pompeii were obtained by the proper mixing of lime and marble grains while mortars of Herculaneum by lime and silicates compounds. The position of the endothermic peak of calcite decomposition showed important variations in the different samples studied, which was assigned to the different crystallinity and particle sizes. Experiments under CO2 flow confirmed the presence of magnesium calcium carbonates.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-009-0667-2
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructural characterization of copper based alloys produced by reactive milling
Palma, R; Sepulveda, A; Zuniga, A; Donoso, E; Dianez, MJ; Criado, JMRevista de Metalurgia, 46 (1010) 197-205 DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.2010.v46.i3
Abstract
The micro and nanostructure of Cu-Al, Cu-V and Cu-Ti alloys produced by reactive milling were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Samples with different milling times (t = 0, 10, 20 and 30 h) were considered. The grain size, dislocation density and residual microstrain were evaluated form the XRD data using the Williamson-Hall and Klug-Alexander methods. The evolution of texture as a function of milling time was also studied using XRD. It was found, using TEM, that the grain size and dispersoid size were nanometric in all three alloys considered.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.2010.v46.i3
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Evaluation of Different Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Configurations As an Alternative Technology for Green C-1 Chemistry in the Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane and the Direct Decomposition of Methanol
Rico, VJ; Hueso, JL; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry A, 114 (2010) 4009-4016 DOI: 10.1021/jp100346q
Abstract
Carbon dioxide reforming of methane and direct decomposition of methanol have been investigated using dielectric harrier discharges (DBD)) at atmospheric pressure and reduced working temperatures. Two different plasma reactor configurations are compared and especial attention is paid to the influence of the surface roughness of the electrodes oil the conversion yields in the first plasma device. The influence of different filling gap dielectric materials (i.e., Al2O3 of BaTiO3) in the second packed configuration has been also evaluated. Depending on the experimental conditions of applied voltage, residence time of reactants. feed ratios, or factor configuration. different conversion yields are achieved ranging front 20 to 80% in the case of methane and 7-45% for the carbon dioxide. The direct decomposition of methanol reaches 60-100% Under similar experimental conditions. Interestingly, the selectivity toward the production of hydrogen and carbon monoxide is kept almost constant under all the experimental conditions, and the formation of longer hydrocarbon chains of coke is a byproduct is not detected. The maximum efficiency yields are observed for the packed-bed reactor configuration containing alumina for both reaction processes (similar to 1 mol H-2 per kilowatt hour for dry reforming of methane and similar to 4.5 mol H-2, per kilowatt hour for direct decomposition of methanol).
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp100346q
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structural characterization of polyhydroxy fatty acid nanoparticles related to plant lipid biopolyesters
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Dominguez, E; Luna, M; Benitez, JJ; Heredia, AChemistry and Physics of Lipids, 163 (2010) 329-333 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2010.01.006
Abstract
In the present work, we report the physico-chemical properties and structural characteristics of special polyhydroxy fatty acid nanoparticles after their fusion by means of attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and light microscopy. All the characteristics and properties investigated have an important degree of similarity to the native plant cutin, the main biopolymer present in the plant cuticles. The supramolecular organization of these polymerized prime nanoparticles after their interaction on cellulose substrate and isolated cuticle samples, simulating the in vivo conditions in epidermal plant cells, strongly suggests a growth of these nanoparticles after a self-assembly process.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2010.01.006
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Application of Micro-X-ray Fluorescence Analysis for the Characterization of Industrial Wastes
Alba, MD; Aparicio, P; Benitez, JM; Castro, MA; Diaz, M; Orta, MMIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 49 (2010) 2348-2352 DOI: 10.1021/ie901716w
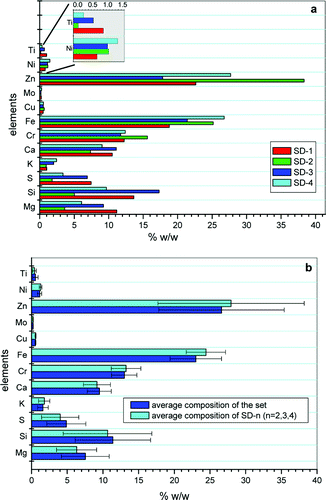
Abstract
The issue of how to improve product quality and product yield in a short period of time is becoming more critical in many industries. Thus, shorter delay times between laboratory analysis and process correction are important in process control. Elimination of sample handling and operator Manipulation is desirable. The present article proposes micro-X-ray fluorescence (mu XRF) as an economical control method for industrial product quality with a minimum time cost. Samples from different industrial processes have been chosen and analyzed by XRF and mu XRF, The results show that the two techniques give similar results and that mu XRF allows the waste to be classified and is able to detect problems in the production process.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/ie901716w
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Theoretical Analysis of the Performance of One-Dimensional Photonic Crystal-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Lozano, G; Colodrero, S; Caulier, O; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 3681-3687 DOI: 10.1021/jp9096315
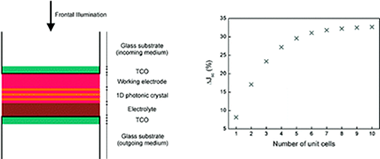
Abstract
A simple analytical model that allows designing one-dimensional photonic crystal based dye sensitized solar cells of optimized performance, accounting for the actual optical features of the device, is herein presented. Based on the theoretical description of the effect of coupling such Bragg mirrors to the light harvesting electrode, recently reported experimental values of the spectral dependence of incident photon to current conversion efficiency attained for such Structures are fairly reproduced and rationalized. A thorough analysis or them in terms of the interplay between the effect of the electrode thickness and the characteristics of the Bragg reflection, such as intensity, spectral position, and width, is provided. Predictions on the maximum enhancement factors expected for realistic Structures are also presented.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp9096315
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Magnetometry and electron paramagnetic resonance studies of phosphine- and thiol-capped gold nanoparticles
Guerrero, E; Munoz-Marquez, MA; Fernandez, A; Crespo, P; Hernando, A; Lucena, R; Conesa, JCJournal of Applied Physics, 107 (2010) 064303-064309 DOI: 10.1063/1.3327414

Abstract
In the last years, the number of studies performed by wholly independent research groups that confirm the permanent magnetism, first observed in our research lab, for thiol-capped Au nanoparticles (NPs) has rapidly increased. Throughout the years, the initial magnetometry studies have been completed with element-specific magnetization measurements based on, for example, the x-ray magnetic circular dichroism technique that have allowed the identification of gold as the magnetic moment carrier. In the research work here presented, we have focused our efforts in the evaluation of the magnetic behavior and iron impurities content in the synthesized samples by means of superconducting quantum interference device magnetometry and electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometry, respectively. As a result, hysteresis cycles typical of a ferromagnetic material have been measured from nominally iron-free gold NPs protected with thiol, phosphine, and chlorine ligands. It is also observed that for samples containing both, capped gold NPs and highly diluted iron concentrations, the magnetic behavior of the NPs is not affected by the presence of paramagnetic iron impurities. The hysteresis cycles reported for phosphine-chlorine-capped gold NPs confirm that the magnetic behavior is not exclusively for the metal-thiol system.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1063/1.3327414
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Room-Temperature Reaction of Oxygen with Gold: An In situ Ambient-Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Investigation
Jiang, P; Porsgaard, S; Borondics, F; Kober, M; Caballero, A; Bluhm, H; Besenbacher, F; Salmeron, MJournal of the American Chemical Society, 132 (2010) 2858-2859 DOI: 10.1021/ja909987j
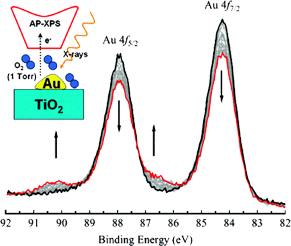
Abstract
The interaction of O-2 with gold foil and gold nanoparticles grown by thermal deposition on TiO2(110) was studied by in situ ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy at room temperature. No spontaneous dissociation of O-2 was observed either on Au foil or oil Au nanoparticles up to 1 Torr of O-2. X-ray irradiation, however, is very effective in promoting gold oxidation on both surfaces in the presence of O-2. Our results help reconcile recent conflicting experimental observations regarding the activation of molecular oxygen, which is a crucial issue in Au catalyzed oxidation reactions.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/ja909987j
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanosynthesis of Hf1-xZrxB2 Solid Solution and Hf1-xZrxB2/SiC Composite Powders
Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Alcala, MD; Gotor, FJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 93 (2010) 696-702 DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03484.x
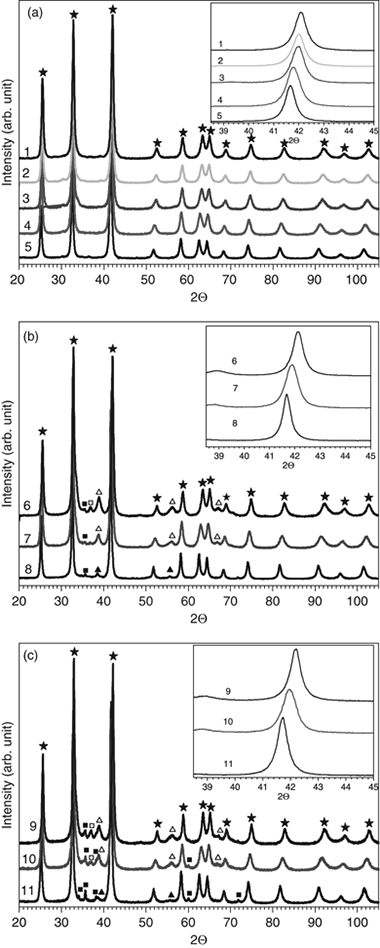
Abstract
The synthesis of solid solutions in the HfB2-ZrB2 system was conducted by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) processes under an inert atmosphere from elemental mixtures of Hf, Zr, and B. The stoichiometry of the Hf1-xZrxB2 solid solution phase was controlled by adjusting the Hf/Zr/B atomic ratio in the starting mixture. Composite materials with SiC were achieved by adding the required amount of SiC to the Hf/Zr/B reactant mixture. The presence of up to 20 vol% of SiC did not inhibit the MSR process. Longer milling times were required to ignite the mixture. Small amounts of the refractory phases ZrC or HfC were observed in the composite powders. The chemical composition, structure, and microstructure of products were studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, electron diffraction, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. This complete characterization confirmed the formation of P6/mmm hexagonal diboride phases with a submicrometric microstructure. The determination of the chemical composition and lattice parameters ascertained the formation of solid solutions with good chemical homogeneity in the HfB2-ZrB2 system.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03484.x
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Active and Optically Transparent Tetracationic Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films
Castillero, P; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Cano, M; Pedrosa, JM; Roales, J; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2 (2010) 712-721 DOI: 10.1021/am900746q
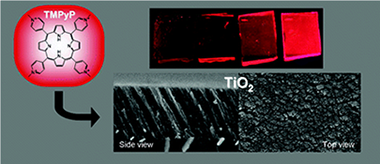
Abstract
Fluorescent tetracationic porphyrin (TMPyP) molecules have been incorporated into optically transparent TiO2 thin films acting as a host material. The films, with a columnar structure and open pores, were prepared by electron evaporation at glancing angles (GAPVD). The open porosity of the films has been estimated by measuring a water adsorption isotherm with a quartz crystal monitor. TMPyP molecules were infiltrated in the host thin films by their immersion into water solutions at controlled values of pH. The state of the adsorbed molecules, the infiltration efficiency, and the adsorption kinetics were assessed by analyzing the optical response of the films by UV-vis absorption and fluorescence techniques. The infiltration efficiency was directly correlated with the acidity of the medium, increasing at basic pHs as expected from simple considerations based on the concepts of the point of zero charge (PZC) developed for colloidal oxides. By a quantitative evaluation based on the analysis of the UV spectra, the infiltration process has been described by a Langmuir type adsorption isotherm and an Elovich-like kinetics. The accessibility of the infiltrated molecules in the TMPyP/TiO2 composite films is assessed by following the changes of their optical properties when exposed to the acid vapors and their subsequent recovery with time.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/am900746q
Reactividad de Sólidos
Spark Plasma Sintering of Ultrafine TiCxN1-x Powders Synthesized by a Mechanically Induced Self-Sustaining Reaction
Borrell, A; Fernandez, A; Torrecillas, R; Cordoba, JM; Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 93 (2010) 2252-2256 DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.03735.x
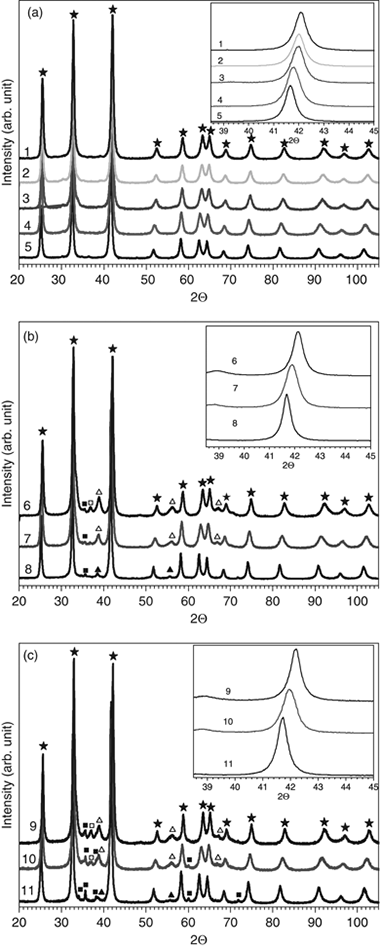
Abstract
High-purity, nanometer-sized titanium carbonitride powders, TiCxN1-x, were obtained with a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) in a high-energy planetary ball mill from a mixture of titanium and different carbon precursors under a nitrogen atmosphere. A promising method for developing dense TiCxN1-x materials is the coupling of MSR with the spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique. The powders were sintered at different temperatures to provide a completely dense monolithic ceramic (> 99% theoretical density). In this work, the influence of the carbon precursor and SPS treatment on the material microstructures were studied, and the main mechanical properties of the end material were evaluated.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.03735.x
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Morphological evolution of pulsed laser deposited ZrO2 thin films
Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Prieto-Lopez, LO; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; de la Cruz, W; Rudolph, H; Habraken, FHPM; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Applied Physics, 107 (2010) 54311-54320 DOI: 10.1063/1.3318604
Abstract
Morphological evolution of ZrO2 thin films deposited during pulsed laser deposition of Zr in O-2 atmosphere has been experimentally studied at two different film deposition temperatures, 300 and 873 K. The roughness exponent, alpha, the growth exponent, beta, the coarsening exponent, 1/z, and the exponent defining the evolution of the characteristic wavelength of the surface, p, for depositions at 300 K amounted to beta = 1.0 +/- 0.1, alpha = 0.4 +/- 0.1, 1/z = 0.34 +/- 0.03, and p = 0.49 +/- 0.03, whereas for depositions carried out at 873 K amounted to beta = 0.3 +/- 0.3, alpha = 0.4 +/- 0.2, and 1/z = 0.0 +/- 0.2. Experimental error becomes important due to the flat morphology of the films inherent to the deposition technique. The change in the surface topography with the film temperature has been studied with the help of a simple Monte Carlo model which indicates the existence of two different growth regimes: a shadowing dominated growth, occurring at low temperatures, characterized by calculated values beta = 1.00 +/- 0.04, alpha = 0.50 +/- 0.04, p = 0.46 +/- 0.01, and 1/z = 0.35 +/- 0.02 and a diffusion dominated growth that takes place at high temperatures as well as at low deposition rates, characterized by calculated values beta = 0.15 +/- 0.08, alpha = 0.33 +/- 0.04, and 1/z = 0.33 +/- 0.07. The good agreement obtained between the experimental and simulated parameters is discussed within the frame of the general characteristics of the deposition method.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1063/1.3318604
Seville City Hall Chapter Room ceiling decoration
Duran, A; Robador, MD; de Haro, MCJ; Herrera, LK; Gimena, P; Perez-Rodriguez, JLMateriales de Construcción, 60 (2010) 83-95 DOI: 10.3989/mc.2010.45107
Abstract
El objetivo de este trabajo es el estudio de diferentes aspectos, como el color, la composición química y las fases mineralógicas presentes en los diferentes materiales que forman la ornamentación del techo de la Sala Capitular del Ayuntamiento de Sevilla, mediante métodos físicos y químicos. Nuestros resultados muestran que el dorado fue realizado sobre una capa de bol previamente depositada sobre una lámina de blanco de plomo que cubría un estrato de calcita. Posteriormente, y probablemente debido a alteraciones en el dorado original, el techo fue de nuevo dorado usando una técnica similar. En el siglo XIX, casi todo el techo, excepto las zonas con inscripciones, fue blanqueado usando una mezcla de calcita y blanco de plomo. Se empleó plata para cubrir la espada del rey Juan I (casetón 27). Finísimas láminas de oro se usaron para decorar los atributos reales: coronas, cinturones, cetros, espadas y rosarios. En diferentes partes de la decoración fueron detectados pigmentos como azurita, malaquita, bermellón y negro de humo. La composición del mortero de la estructura era a base de cal y dolomita molida.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.3989/mc.2010.45107
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Oxidation State and Local Structure of Ti-Based Additives in the Reactive Hydride Composite 2LiBH(4) + MgH2
Deprez, E; Muñoz-Marquez, MA; Roldan, MA; Prestipino, C; Palomares, FJ; Minella, CB; Bosenberg, U; Dornheim, M; Bormann, R; Fernandez, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 3309-3317 DOI: 10.1021/jp910955r
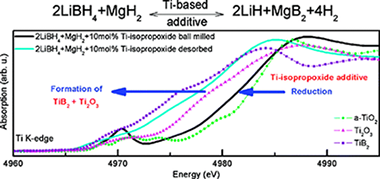
Abstract
Nowadays, the technological utilization of reactive hydride composites (RHC) Lis hydrogen storage materials is limited by their reaction kinetics. However, addition of transition-metal-based additives, for instance titanium isopropoxide (Ti-iso), to the 2LiBH(4)+MgH2 system, results in a significant improvement of sorption kinetics. In this work, the evolution of chemical state and local structure of the Ti-based additive has been investigated by means of X-ray absorption (XAS) and photoemission (XPS) spectroscopy. X-ray absorption near-edge Structure (XANES) its well as extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis have been Undertaken at the Ti K-edge. The measurements reveal the formation of a highly dispersed and disordered TiO2-like phase during ball milling. During first desorption reduced titanium oxide and titanium boride are formed and remain stable upon cycling. The Surface analysis performed by XPS shows that the reduction processes of the Ti-based additive during first desorption IS Coupled to the migration of the Ti species front the surface to the bulk of the material. Several factors, related to favoring heterogeneous nucleation of MgB2 and the increase of interfacial area through grain refinement are proposed as potential driving force, among other effects, for the observed kinetic improvement.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp910955r
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
In situ spectroscopic detection of SMSI effect in a Ni/CeO2 system: hydrogen-induced burial and dig out of metallic nickel
Caballero, A; Holgado, JP; Gonzalez-delaCruz, VM; Habas, SE; Herranz, T; Salmeron, MChemical Communications, 46 (2010) 1097-1099 DOI: 10.1039/b920803h
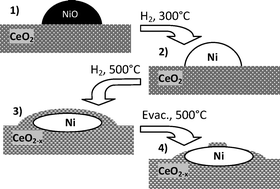
Abstract
In situ APPES technique demonstrates that the strong metal support interaction effect (SMSI) in the Ni-ceria system is associated with the decoration and burial of metallic particles by the partially reduced support, a phenomenon reversible by evacuation at high temperature of the previously absorbed hydrogen.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/b920803h
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Lanthanide sorption on smectitic clays in presence of cement leachates
Galunin, E; Alba, MD; Santos, MJ; Abrao, T; Vidal, MGeochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74 (2010) 862-875 DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.11.003
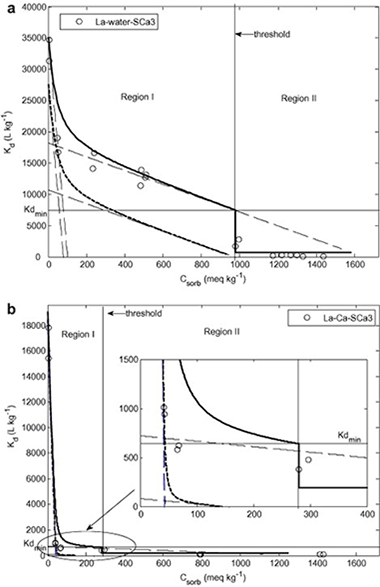
Abstract
Due to their potential retention capacity, clay minerals have been proposed for use in the engineered barriers for the storage of high-level radioactive actinides in deep geological waste repositories. However, there is still a lack of data on the sorption of actinides in clays in conditions simulating those of the repositories. The present article examines the sorption of two lanthanides (actinide analogues) in a set of smectitic clays (FEBEX bentonite, MX80 bentonite, hectorite, saponite, Otay montmorillonite, and Texas montmorillonite). Distribution coefficients (K-d) were determined in two media: water and 0.02 mol L-1 Ca, the latter representing the cement leachates that may modify the chemical composition of the water in contact with the clay. The K-d values of the lanthanides used in the experiments (La and Lu) varied greatly (25-50 000 L kg(-1)) depending on the ionic medium (higher values in water than in the Ca medium), the initial lanthanide concentration (up to three orders of magnitude decrease inversely with lanthanide concentration), and the examined clay (up to one order of magnitude for the same lanthanide and sorption medium). Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms were used to fit sorption data to allow comparison of the sorption parameters among smectites. The model based on the two-site Langmuir isotherms provided the best fit of the sorption data, confirming the existence of sorption sites with different binding energies. The sites with higher sorption affinity were about 6% of the total sorption capacity in the water medium, and up to 17% in the Ca medium, although in this latter site sorption selectivity was lower. The wide range of K-d values obtained regarding the factors examined indicated that the retention properties of the clays should also be considered when selecting a suitable clay for engineered barriers.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.11.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Air- and Light-Stable Superhydrophobic Colored Surfaces Based on Supported Organic Nanowires
Borras, A; Groning, P; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARLangmuir, 26 (2010) 1487-1492 DOI: 10.1021/la903701j

Abstract
In this work, we report oil it new type of superhydrophobic material consisting of supported organic nanowires prepared by vacuum deposition, Different intensely colored surfaces with water contact angles its high its 180 degrees call be Fabricated depending oil the composition. morphology, and density of the nanowires. These surfaces are stable in air and under intense light irradiation. The wettability properties of coatings made of metalloporphyrins and metallophthalocyanines nanowires as well as other heterostructured binary and open core@shell nanowires are studied.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/la903701j
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Complete n-hexane oxidation over supported Mn-Co catalysts
Todorova, S; Kolev, H; Holgado, JP; Kadinov, G; Bonev, C; Pereniguez, R; Caballero, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 94 (2010) 46-54 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.10.019

Abstract
Two series of Co-Mn samples were prepared by impregnation of silica with aqueous solutions or Co(NO3)(2)center dot 6H(2)O and/or Mn(NO3)(2)center dot 6H(2)O. Cobalt oxide was the predominant phase in one of the series and manganese was used as the promoter. The major component in the second series was manganese oxide and Co was the promoter. The prepared samples were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), temperature-programmed reduction (TPR), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and tested in the reaction of complete n-hexane oxidation. The catalytic activity of both single component cobalt and manganese samples was similar, however, a combination between the two elements changed significantly the activity and this depended on the method of preparation. Catalysts prepared by a common solution of Co- and Mn nitrates manifested a considerable increase in activity as a result of very low crystallinity of the supported metal oxide phases, partial enrichment of the surface with cobalt and uniform distribution of oxide agglomerates on the support.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.10.019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Synthesis, characterization, and photoactivity of InTaO4 and In0.9Ni0.1TaO4 thin films prepared by electron evaporation
Rico, VJ; Frutos, F; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Gonzales-Elipe, ARJournal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 28 (2010) 127-134 DOI: 10.1116/1.3273597
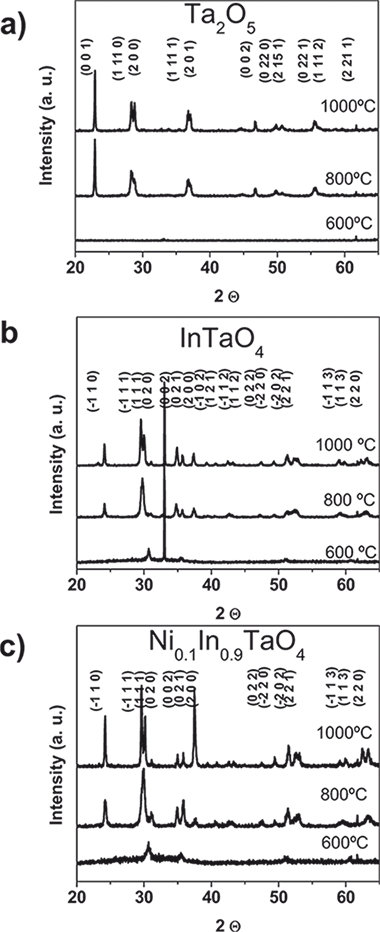
Abstract
InTaO4 and In0.9Ni0.1TaO4 thin films have been prepared by electron evaporation of successive layers of the single oxide components and posterior annealing at T > 800 degrees C. The annealed thin films presented the monoclinic crystallographic structure typical of these mixed oxides. The electrical and optical behaviors of the films, assessed by C-V measurements, surface conductivity as a function of temperature, and UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, indicate that these oxides are wide band gap semiconductors with a variable dielectric constant depending on the annealing conditions. By reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy some electronic states have been found in the gap at an energy that is compatible with the activation energy deduced from the conductivity versus 1/T plots for these oxides. The photoactivity of these materials has been assessed by looking to the evolution of the wetting contact angle as a function of the irradiation time. All the films became superhydrophilic when irradiated with UV light, while the In0.9Ni0.1TaO4 thin films also presented a small partial decrease in wetting angle when irradiated with visible photons.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1116/1.3273597
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Doping level effect on sunlight-driven W,N-co-doped TiO2-anatase photo-catalysts for aromatic hydrocarbon partial oxidation
Kubacka, A; Bachiller-Baeza, B; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 93 (2010) 274-281 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.09.039
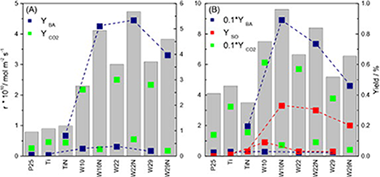
Abstract
A series of nanosized W,N-co-doped anatase TiO2 catalysts with different dopant contents has been prepared by a microemulsion method and examined in the sunlight selective photo-oxidation of toluene and styrene. The activity results have been correlated with structural, electronic, and surface examinations of the catalysts done with the help of XRD-Rietveld, N-2 physisorption and NH3 chemisorption-calorimetry, XPS, Infrared, and UV-visible spectroscopies. Irrespective of the reaction, a consistent reaction rate enhancement with respect to titania (nano-TiO2, P25) references and W-doped TiO2 systems is observed for single-phase anatase W,N-co-doped samples. This is likely linked with the decrease of the band gap energy decrease and results from a combined W-N cooperative effect on structural properties of the anatase network. W,N simultaneous presence also makes a drastic effect on selectivity, maximizing the yield to partial oxidation products. This appears related with surface properties of the materials.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.09.039
Reactividad de Sólidos - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
The Multistep Nature of the Kaolinite Dehydroxylation: Kinetics and Mechanism
Ortega, A; Macias, M; Gotor, FJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 93 (2010) 197-203 DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03328.x
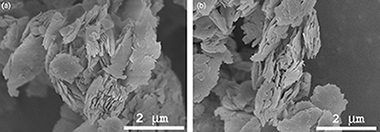
Abstract
The thermal dehydroxylation of kaolinite has been reexamined using small sample weights, a homogeneous particle size distribution and high-vacuum conditions in order to reduce the influences of heat and mass-transfer phenomena. The controlled rate thermal analysis (CRTA) technique, which was specially developed to minimize the pressure and temperature gradients through the sample, was employed to carry out meaningful kinetic experiments. Two advanced isoconversional methods, the Vyazovkin and the Galwey methods, were used complementarily to determine the dependence of the activation energy on the degree of conversion. For this purpose, the Vyazovkin method has been adapted to CRTA experiments. It was demonstrated that there are at least two different stages, revealing the multistep nature of this reaction. The activation energy for the first step, which is assigned to nucleation and the growth of nuclei, decreases from 100 to 75 kJ/mol. The second stage corresponds to a diffusion process and the activation energy rises to 120 kJ/mol because of the metakaolinite formation, which closes the interlamellar channels and leaves isolated patches of kaolinite from which the water escapes with difficulty.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03328.x
Microscopic and spectroscopic techniques for the study of paper supports and textile used in the binding of hispano-arabic manuscripts from Al-Andalus: A transition model in the 15th century
Espejo, T; Duran, A; Lopez-Montes, A; Blanc, RJournal of Cultural Heritage, 11 (2010) 50-58 DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2009.01.007

Abstract
This work focuses on the study of paper and textiles used in the binding of a series of manuscripts that share some specific characteristics that lead us to speculate on the possibility of a transitional codicological typology from the Arabic to the Christian book in Al-Andalus during the 15th century. The books we analyzed belong to the collection of the Historical Archive of Malaga, the Archive of Sacromonte Abbey, in Granada, the School of Arabic Studies and the Library of P.P. Escolapios, also in Granada. Paper physical study was performed by microscopic and spectroscopic techniques. A routine and objective method, Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, was employed and proved to be a useful technique for the characterization of cellulosic fibres, main component of paper from the boards and the envelope flap pasteboards, and the fabric lining from the cover. The results of our research will help us to date, identify and study the evolution of the techniques, proving that the materials and innovations of the Italian paper manufacturing processes were perfectly known in the south of modern day Spain, before the Christian Reconquest.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2009.01.007
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Determination of the decay rate constant for hepatocytes immobilized in alginate microcapsules
Leal-Egana, A; Diaz-Cuenca, A; Bader, AJournal of Micoencapsulation, 27 (2010) 86-93 DOI: 10.3109/02652040903050550
Abstract
Primary mouse hepatocytes (between 10-250 cells per capsule) were immobilized within 1.0% w/v alginate microbeads. The textural properties of the alginate matrix were characterized and a full protocol based upon the measurement of the initial rate of Resazurin reduction was studied and standardized. Using this method, the decay rate constant (K-d = 0.45 +/- 0.01 days(-1)) and the time in which the cell viability decreases in half (VI50 = 37 +/- 0.7 h) have been measured. The method was compared with the analysis of cell vitality using Calcein A/M and Ethidium Homodimer I. Differences between the two methods were found in the viability profile due to the significant presence of double stained cells along the culture time. According to the author's knowledge, this is the first report of a systematic study and determination of the K-d value for immobilized hepatocytes, incorporating a wide range of cell concentrations within the alginate matrix.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.3109/02652040903050550
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Chemical and electronic characterization of cobalt in a lanthanum perovskite. Effects of strontium substitution
Hueso, JL; Holgado, JP; Pereniguez, R; Mun, S; Salmeron, M; Caballero, AJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 183 (2010) 27-32 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2009.10.008
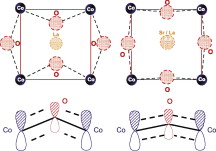
Abstract
Two different cobaltites, LaCoO3 and La0.5Sr0.5CoO3-delta, have been prepared and characterized by means of high energy Co K-edge and low energy O K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). Even though half of the La(III) is substituted by Sr(II), little or no changes call be detected in the formal oxidation state of cobalt atoms. The presence of strontium cations induces two main effects in the chemical and electronic state of the perovskite. The charge balance with Sr(II) species is reached by the formation of oxygen vacancies throughout the network, which explains the well-known increase in the reactivity of this Substituted perovskite. O K-edge XAS experiments show that the Sr(II) species induce the transitions of d electrons of cobalt cations from low to high Spill Configuration. We propose that this change in Spill Multiplicity is induced by two cooperative effects: the oxygen vacancies. creating five coordinated cobalt atoms, and the bigger size of Sr(II) cations, aligning the Co-O-Co atoms, and favoring the overlapping of pi-symmetry cobalt and oxygen orbitals, reducing the splitting energy of e(g) and t(2g) levels.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2009.10.008
- ‹ anterior
- 49 of 54
- siguiente ›














