Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Reactividad de Sólidos
A recurrent error which needs to be resolved
Ortega, AThermochimica Acta, 491 (2009) 116-117 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2009.02.009
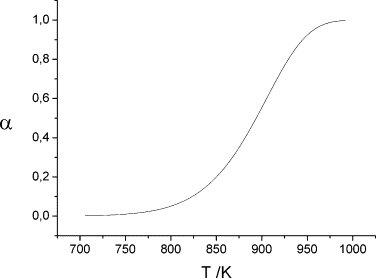
Abstract
The recent paper by Jankovic et al. [B. Janković, B. Adnađevic, J. Jovanović; Thermochimica Acta 452 (2007) 106] and other similar papers have raised a problem which needs to be resolved. These authors use the method of Kennedy and Clark [J.A. Kennedy, S.M. Clark, Thermochimica Acta 307 (1997) 27] which is conceptually erroneous; this is analyzed in this paper.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2009.02.009
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Effect of Sulfate Pretreatment on Gold-Modified TiO2 for Photocatalytic Applications
Hidalgo, MC; Maicu, M; Navio, JA; Colon, GJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 12840-12847 DOI: 10.1021/jp903432p

Abstract
The influence of sulfated pretreatment of TiO2 on the structure, morphology, and dispersion of gold and photocatalytic properties of Au/TiO2 were studied. Notable enhancements in the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 were achieved by deposition of gold onto samples that had previously undergone sulfate treatment followed by high temperature calcination. The enhancement in activity can be attributed to the stronger bonding and improved electronic communication between gold particles and TiO2 on defect rich surfaces as are found on sulfated samples after calcination at 700 °C. Two different methods for gold deposition were evaluated: chemical reduction by citrate and photodeposition. The citrate method produced more homogeneous and smaller gold particles with a better dispersion than photodeposition, which lead to greater increases in activity in the photocatalytic degradation of phenol when the former method was used for deposition on both sulfated and nonsulfated TiO2. The combination of sulfate pretreatment and gold deposition by chemical reduction was shown to be a good strategy to obtain gold/titania catalysts possessing homogeneous particle size and dispersion of the metal and a strong bonding between the Au and the TiO2 surface.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp903432p
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrical characteristics of mixed Zr–Si oxide thin films prepared by ion beam induced chemical vapor deposition at room temperature
Ferrer, FJ; Frutos, F; Garcia-Lopez, J; Jimenez, C; Yubero, FThin Solid Films, 517 (2009) 5446-5452 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2009.01.099
Abstract
Mixed Zr–Si oxide thin films have been prepared at room temperature by ion beam decomposition of organometallic volatile precursors. The films were flat and amorphous. They did not present phase segregation of the pure single oxides. A significant amount of impurities (–C–, –CHx, –OH, and other radicals coming from partially decomposed precursors) remained incorporated in the films after the deposition process. This effect is minimized if the Ar content in the O2/Ar bombarding gas is maximized. Static permittivity and breakdown electrical field of the films were determined by capacitance–voltage and current–voltage electrical measurements. It is found that the static permittivity increases non-linearly from ~ 4 for pure SiO2 to ~ 15 for pure ZrO2. Most of the dielectric failures in the films were due to extrinsic breakdown failures. The maximum breakdown electrical field decreases from ~ 10.5 MV/cm for pure SiO2 to ~ 45 MV/cm for pure ZrO2. These characteristics are justified by high impurity content of the thin films. In addition, the analysis of the conduction mechanisms in the formed dielectrics is consistent to Schottky and Poole-Frenkel emission for low and high electric fields applied, respectively.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2009.01.099
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
ZnO activation by using activated carbon as a support: Characterisation and photoreactivity
Melian, EP; Diaz, OG; Rodriguez, JMD; Colon, G; Arana, J; Melian, JH; Navio, JA; Pena, JPApplied Catalysis A-General, 364 (2009) 176-181 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.05.042

Abstract
The effect of the mixing ZnO with different portions of activated carbon (AC) has been studied. The resulting catalysts were characterised and evaluated in the photocatalytic decomposition of aqueous pollutants. Changes in the catalyst colour and in the FTIR vibration bands of the surface hydroxyl groups were recorded. νOH vibrations were shifted to lower wavenumbers as AC loading increased, demonstrating modification of the acid-base character of the catalysts. Laser scattering studies showed that AC loading leads to smaller ZnO particles. BET surface area measurements and scanning electron micrograph (SEM) analysis showed agglomeration of ZnO particle pores in the AC structure.
Results showed that in addition to a synergistic effect of the AC-ZnO combination, AC content modifies the ZnO particle properties and consequently photocatalytic behaviour. This was evident in phenol degradation experiments where changes in the concentration profiles of the catechol and hydroquinone degradation intermediates, were observed. However, the AC-ZnO catalysts were less efficient than pure ZnO in the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol (DCP). This seems to be due to the strong adsorption of the DCP molecule on AC, resulting in lower diffusion to the catalytic ZnO and thus a lower rate of photocatalysis.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.05.042
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanoindentation of TiO2 thin films with different microstructures
Gaillard, Y; Rico, VJ; Jimenez-Pique, E; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 42 (2009) 145305 DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/42/14/145305
Abstract
A series of nanoindentation tests has been carried out with TiO2 films produced by physical vapour deposition (PVD) under different conditions. Films with different microstructures and crystallographic structures have been prepared by changing experimental parameters such as the temperature of the substrate, the deposition angle (by the so-called glancing angle physical vapour deposition, GAPVD) or by exposing the growing film to a beam of accelerated ions. The obtained results of hardness and Young's modulus depict interesting correlations with the microstructure and structure of the films providing a general picture for the relationships between these characteristics and their mechanical properties. Different models have been used to extract Young's modulus and hardness parameters from the experimental nanoindentation curves. The obtained results are critically discussed to ascertain the ranges of validity of each procedure according to the type of sample investigated.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/42/14/145305
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Degradation of n-Butyl tin Chlorides in Waters. A Comparative Assessment of the Process by Photo-assisted and Chemical- treatment Methods
Navio, JA; Cerrillos, C; Macias, MJournal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 12 (2009) 158-163 DOI: ---
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
FTIR study of photocatalytic degradation of 2-propanol in gas phase with different TiO2 catalysts
Arana, J; Alonso, AP; Rodriguez, JMD; Colon, G; Navio, JA; Pena, JPApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 89 (2009) 204-213 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.11.027
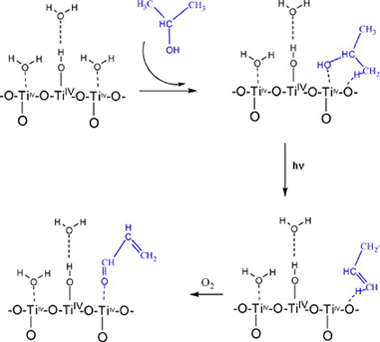
Abstract
The photocatalytic efficiency of different TiO 2 catalysts in the degradation of 2-propanol in gas phase has been studied. The obtained efficiencies have been compared considering the distribution of rutile-anatase phases, surface area, particle size, distribution of surface hydroxyl groups and Brönsted or Lewis acid centres. The catalysts used were Degussa-P25 (TiO 2-P25), Hombikat, Millennium, Kemira and s/g-TiO 2, a catalyst prepared by a sol-gel method. The best photocatalytic behaviours have been obtained with those catalysts with higher surface area and the presence of only anatase phase (Hombikat and Millennium). A progressive deactivation of TiO 2-P25 and s/g-TiO 2 has been observed during the photocatalytic process. FTIR studies indicated that degradation mechanisms depended on the catalyst employed. Deactivation processes observed in TiO 2-P25 have been correlated with the formation of carboxylates.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.11.027
Study of degradation processes of metals used in some artworks from the cultural heritage of Andalusia, Spain
Duran, A; Herrera, LK; de Haro, MCJ; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Justo, ARevista de Metalurgia, 45 (2009) 277-286 DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.0827
Abstract
The study of the alteration processes of metals, such as lead, bronze, iron and tin-mercury alloys, used in some of the
most important chosen artefacts of Andalusian Cultural Heritage is the main objective of this paper. Hydrocerussite
and cerussite were detected in lead seals stored in a hole of cardboard. Bronze is altered to atacamite by environmental
contamination, which is also responsible for the formation of rust from iron. Corrosion of the tin-mercury surface
of amalgam mirrors produces tin monoxide and tin dioxide and releases liquid mercury from the solid phase.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.0827
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Stability of phyllosilicates in Ca(OH)2 solution: Influence of layer nature, octahedral occupation, presence of tetrahedral Al and degree of crystallinity
Mantovani, M; Escudero, A; Alba, MD; Becerro, AIApplied Geochemistry, 24 (2009) 1251-1260 DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.03.012
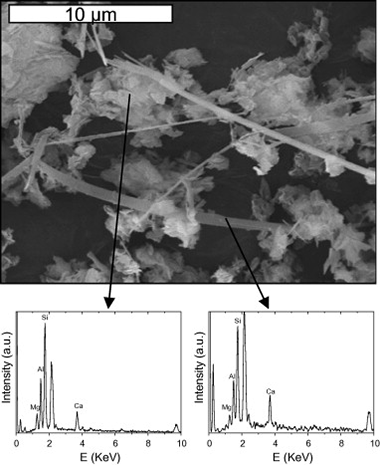
Abstract
This paper presents the results of a comprehensive investigation of the interaction of layered silicates with Ca(OH)2 in hydrothermal conditions. The study is intended to evaluate the stability of the clay buffer in radioactive waste repositories, at the intermediate stages of concrete leaching, when the pH is controlled by the dissolution of portlandite. The influence of layer nature, octahedral occupation, presence of tetrahedral Al and degree of crystallinity will be assessed by analysing the behaviour of a set of well-selected phyllosilicates and using the combined capabilities of 29Si and 27Al MAS-NMR spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction and SEM/EDX. The results show that the main factor affecting the stability of the clay is the octahedral occupation, so that trioctahedral phyllosilicates are much more stable than dioctahedral ones. The nature and expandability of the layer does not seem to much influence the stability of the clay, so that a 2:1 expandable phyllosilicate shows the same stability as a chemically analogous 1:1 non-expandable phyllosilicate. However other factors like the poor crystallinity of the starting material or the presence of Al in the tetrahedral sheet of trioctahedral phyllosilicates weaken the clay structure in alkaline conditions and favour the transformation towards other phases.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.03.012
Study of the gilding technique used in polychromed stones and ceramics by dedicated laboratory-made micro X-ray diffraction and complementary techniques
Duran, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; de Haro, MCJAnalytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 394 (2009) 1671-1677 DOI: 10.1007/s00216-009-2836-3
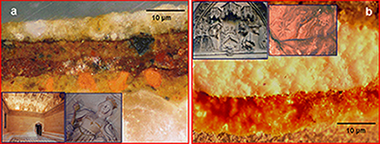
Abstract
This work describes the use of a new dedicated laboratory-made micro X-ray diffraction system for detecting the phases present in cross-sections of artworks. As an example, the phases present in samples from gilding ceramics and stone sculptures from the heritage of Seville (Spain) were successfully detected using this new system, which takes advantage of various devices developed for synchrotron radiation, and is complemented by the information provided by other techniques.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1007/s00216-009-2836-3
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Light generation at the anomalous dispersion high energy range of a nonlinear opal film
Botey, M; Maymo, M; Molinos-Gomez, A; Dorado, L; Depine, RA; Lozano, G; Mihi, A; Miguez, H; Martorell, JOptics Express, 17 (2009) 12210-12216 DOI: 10.1364/OE.17.012210
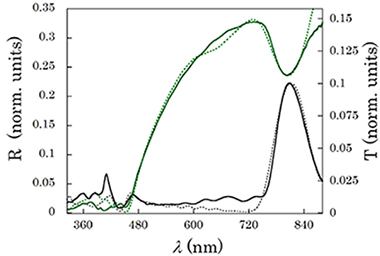
Abstract
We study experimentally and theoretically light propagation and generation at the high energy range of a close-packed fcc photonic crystal of polystyrene spheres coated with a nonlinear material. We observe an enhancement of the second harmonic generation of light that may be explained on the basis of amplification effects arising from propagation at anomalous group velocities. Theoretical calculations are performed to support this assumption. The vector KKR method we use allows us to determine, from the linear response of the crystal, the behavior of the group velocity in our finite photonic structures when losses introduced by absorption or scattering by defects are taken into account assuming a nonzero imaginary part for the dielectric constant. In such structures, we predict large variations of the group velocity for wavelengths on the order or smaller than the lattice constant of the structure, where an anomalous group velocity behavior is associated with the flat bands of the photonic band structure. We find that a direct relation may be established between the group velocity reduction and the enhancement of a light generation processes such as the second harmonic generation we consider. However, frequencies for which the enhancement is found, in the finite photonic crystals we use, do not necessarily coincide with the frequencies of flat high energy bands.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1364/OE.17.012210
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Chemical State of Nitrogen and Visible Surface and Schottky Barrier Driven Photoactivities of N-Doped TiO2 Thin Films
Romero-Gomez, P; Rico, V; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 13341-13351 DOI: 10.1021/jp9024816
Abstract
N-doped TiO2 thin films have been prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition and by physical vapor deposition by adding nitrogen or ammonia to the gas phase. Different sets of N-doped TiO2 thin films have been obtained by changing the preparation conditions during the deposition. The samples have been characterized by X-ray diffraction, Raman, UV−vis spectroscopy, and X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS). By changing the preparation conditions, different structures, microstructures, and degrees and types of doping have been obtained and some relationships have been established between these film properties and their visible light photoactivity. The N1s XP spectra of the samples are characterized by three main features, one tentatively attributed to Ti−N (i.e., nitride with a binding energy (BE) of 396.1 eV) and two others with BEs of 399.3 and 400.7 eV, tentatively attributed to nitrogen bonded simultaneously to titanium and oxygen atoms (i.e., Ti−N−O like species). By controlling the deposition conditions it is possible to prepare samples with only one of these species as majority component. It has been shown that only the samples with Ti−N−O like species show surface photoactivity being able to change their wetting angle when they are illuminated with visible light. The presence of these species and an additional complex structure formed by a mixture of anatase and rutile phases is an additional condition that is fulfilled by the thin films that also present photocatalytic activity with visible light (i.e., surface and Schottky barrier driven photoactivities). The relationships existing between the reduction state of the samples and the formation of Ti−N or Ti−N−O like species are also discussed.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp9024816
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Deposition of Al-Fe pillared bentonites and gold supported Al-Fe pillared bentonites on metallic monoliths for catalytic oxidation reactions
Martinez, LM; Dominguez, MI; Sanabria, N; Hernandez, WY; Moreno, S; Molina, R; Odriozola, JA; Centeno, MAApplied Catalysis A-General, 364 (2009) 166-173 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.05.046

Abstract
Al-Fe pillared bentonite and gold supported on Al-Fe pillared bentonite catalysts deposed on Fecralloy monoliths have been prepared, characterized and tested in two oxidation reactions: gaseous oxidation of CO and phenol oxidation in aqueous medium. The deposition of the solid on the metallic substrate does not alter its structural characteristics. The use of monoliths improves the activity in both reactions and offers the additional advantage to facilitate the separation of the catalyst from the reaction medium.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.05.046
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Thermal Evolution of WC/C Nanostructured Coatings by Raman and In Situ XRD Analysis
El Mrabet, S; Abad, MD; Lopez-Cartes, C; Martinez-Martinez, D; Sanchez-Lopez, JCPlasma Processes and Polymers, 6 (2009) S444-S449 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200931004
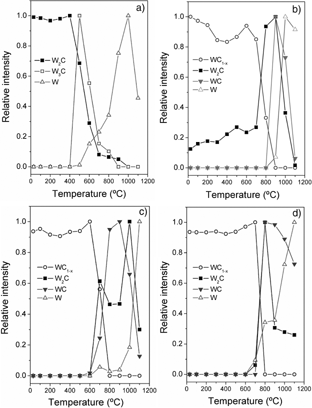
Abstract
In this work, a series of WC/C nanostructured films were deposited on silicon substrates by changing the ratio of sputtering power applied to graphite and WC magnetron sources (PC/PWC: 0, 0.1, 0.5, 1). The thermal stability of WC/C coatings was followed in situ by means of X-ray diffraction measurements up to 1 100 °C in vacuum (10−1 Pa). Initially, the film microstructure is composed of nanocrystalline WC1−x and W2C phases. As the PC/PWC ratio increases the crystallinity decreases, and WC1−x becomes the predominant phase from PC/PWC = 0.1. The results show that the structural evolution with temperature of all studied layers depends essentially on their initial phase and chemical composition (determined by the synthesis conditions: ratio PC/PWC). The coating deposited at PC/PWC = 0 reveals a transformation of W2C phase into W and W3C phases at 400 °C. However, the samples with PC/PWC greater than 0 exhibits an improved thermal stability up to 600–700 °C where the WC1−x begins to transform into W2C and WC phases. At 900 °C, WC is the predominant phase, especially for those coatings prepared with higher ratios. Further annealing above 1 000 °C yields W as the foremost phase. The thermal behaviour was later studied by means of Raman spectroscopy measurements at certain temperatures where the main changes in phase composition were observed. Particularly, a fitting analysis was carried out on the D and G bands typical of disordered and amorphous carbon. The changes induced during heating are discussed in terms of the positions of D and G lines, and full width at half maximum (FWHM).
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200931004
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Application of 29Si and 27Al MAS NMR Spectroscopy to the Study of the Reaction Mechanism of Kaolinite to Illite/Muscovite
Mantovani, M; Escudero, A; Becerro, AIClays and Clay Minerals, 57 (2009) 302-310 DOI: 10.1346/CCMN.2009.0570303
Abstract
Understanding the mechanisms for illitization of clay minerals has important applications in reconstructing geologic histories and determining the origins of physical and chemical characteristics of buried sediments. While many studies have been carried out on this topic, few have focused on the mechanism of illite formation from kaolinite. The purpose of this study was to investigate more deeply the illitization of kaolinite in KOH solution at a high solid/liquid ratio (1000 mg/mL). X-ray diffraction (XRD) and infrared spectroscopy were used to follow the formation of new crystalline phases and the composition of the octahedral sheet, while the transformation of the Si and Al local environments was analyzed by 29Si and 27Al magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MAS NMR). The results revealed that the first reaction stage consists of the diffusion of Al from the octahedral to the tetrahedral sheet of the kaolinite TO layers, giving rise to the precursors of the illite/muscovite nuclei. Combination of XRD with 27Al MAS NMR measurements indicated that a minimum amount of tetrahedral Al is required in the original TO layer before condensation of a second tetrahedral sheet occurs to complete the formation of the illite/muscovite TOT layers.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1346/CCMN.2009.0570303
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Determination of nitrogen partitioning coefficients in superduplex stainless steels by NRA using a nuclear microprobe
Munoz, C; Morilla, Y; Lopez, JG; Paul, A; Odriozola, JANuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 267 (2009) 2208-2211 DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2009.03.093

Abstract
Superduplex stainless steels (SDSSs) combine the good mechanical behavior and the high corrosion resistance of the ferrite (α-Fe) and austenite (γ-Fe) phases. The SDSSs properties depend strongly on the partitioning of the elements that form the alloy. The ferrite is generally enriched in P, Si, Cr and Mo while the content of Ni, Mn, Cu and N in the austenite phase is higher. Nitrogen is known to be a strong austenite stabilizer and its presence increases the strength and the pitting corrosion resistance of the stainless steels. While the global nitrogen content in SDSSs can be readily determined using elemental analyzers, it cannot be measured at a microscopic scale.
In this work, the nuclear microprobe of the Centro Nacional de Aceleradores (Sevilla) was used to obtain the quantitative distribution of nitrogen in SDSSs. A deuteron beam of 1.8 MeV was employed to determine the overall elemental concentration of the matrix by deuteron-induced X-ray emission, whereas the nitrogen partitioning coefficients were obtained by using the 14N(d, α0)12C nuclear reaction. Mappings of this element show that the nitrogen ratio between the ferrite and austenite phases ranges from 0.3 to 0.6 in the analyzed samples.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2009.03.093
Materiales Avanzados
Phyllites used as waterproofing layer materials for greenhouses crops in Spain: multivariate statistical analysis applied to their classification based on X-ray fluorescence analysis
Garzon, E; Garcia-Rodriguez, IG; Ruiz-Conde, A; Sanchez-Soto, PJX-Ray Spectrometry, 38 (2009) 429-438 DOI: 10.1002/xrs.1199
Abstract
The results are presented for the chemical characterization carried out with 53 raw material samples with phyllosilicates from outcrops located between the provinces of Almería and Granada (SE Spain) in order to use them as waterproof layers under the floors of greenhouses. For this purpose, the samples have been studied by these techniques: X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), X-Ray Fluorescence (WDXRF), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), chemical analysis by energy-dispersive X-Ray detection (EDX), and thermogravimetry. To isolate groups of phyllite samples with similar chemical profiles and correlations between the samples, the WDXRF data (11 chemical elements) have been processed using the methodology of exploratory multivariate statistical analyses: cluster analysis, main-component analysis, and discriminating canon analysis. This study was performed as a screening test and as a means of finding similarities and correlations among all 53 phyllite samples, allowing the isolation of groups of phyllite samples with similar chemical profiles. The results indicate that the 53 phyllite samples can be divided into two main groups. The first group is subdivided into two subgroups (1 and 2), one of which includes most of the samples. The latter is further classified into three blocks with the same chemical composition. This allows to search for the raw material with potentially the best waterproof characteristics within the five groups. The classification is of validity as a screening test for subsequent experimental determinations concerning the physical properties of these samples.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1002/xrs.1199
Materiales Coloidales
M-Doped Al2TiO5 (M=Cr, Mn, Co) Solid Solutions and their Use as Ceramic Pigments
Dondi, M; Lyubenova, TS; Carda, JB; Ocaña, MJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 92 (2009) 1972-1980 DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03172.x
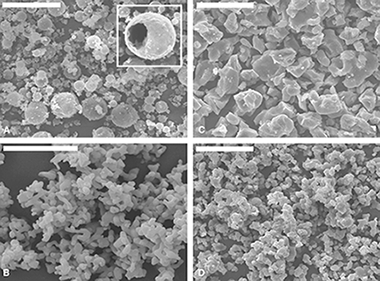
Abstract
New ceramic pigments based on the tialite (Al2TiO5) structure, doped with Co (pink), Cr (green), or Mn (brown), were prepared through the pyrolysis of aerosols followed by calcination of the obtained powders at 1400°C. The expected decomposition of Al2TiO5 into a mixture of Al2O3 and TiO2 on refiring was inhibited by Cr-doping and also by co-doping with Mg the Mn- or Co-doped samples. Microstructure and phase evolution during pigment preparation were monitored by scanning electron microscopy and XRPD. Unit cell parameters of tialite were determined by Rietveld refinement of the X-ray diffraction patterns, revealing in all cases the formation of solid solutions where the solubility of dopants in the Al2TiO5 lattice followed the trend Co<Mn<Cr. The valence state and possible location of dopants in the tialite lattice were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectra and diffuse reflectance spectroscopies, which suggested the presence of Cr3+ ions in a large interstitial site of the tialite lattice with a distorted octahedral geometry, and of Mn3+ and Co2+ ions in the Al3+ octahedral sites of the tialite lattice in the former case, and in both Al3+ and Ti4+ octahedral sites in the latter. Testing the ceramic glazes assessed the technological behavior of pigments, which found that the color stability was reasonably good for the Mn-doped tialite and the Cr-doped pigment, although the latter suffered a small loss of green hue. The Co-doped pigment was found to be not stable in glazes, undergoing a cobalt-leaching effect.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03172.x
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Chemical Reactions in 2D: Self-Assembly and Self-Esterification of 9(10),16-Dihydroxypalmitic Acid on Mica Surface
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; San-Miguel, MA; Sansom, MSP; Heredia, A; Benitez, JJLangmuir, 25 (2009) 6869-6874 DOI: 10.1021/la9001412
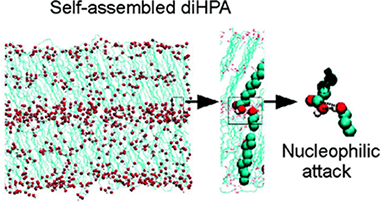
Abstract
9(10),16-Dihydroxypalmitic acid (diHPA) is a particularly interesting polyhydroxylated fatty acid (1) because it is the main monomer of cutin, the most abundant biopolyester in nature, and (2) because the presence of a terminal and a secondary hydroxyl group in midchain positions provides an excellent model to study their intermolecular interactions in a confined phase such as self-assembled layers. In this study we have combined atomic force microscopy (AFM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FT-IR) spectroscopy, as well as molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to conclude that the self-assembling of diHPA molecules on mica is a layer by layer process following a Brunauer−Emmett−Teller (BET) type isotherm and with the first layer growing much faster than the rest. Interactions between secondary hydroxyls reinforce the cohesive energy of the monolayer, while the presence of the terminal hydroxyl group is necessary to trigger the multilayered growth. Besides, XPS and ATR-FT-IR spectroscopies clearly indicate that spontaneous self-esterification occurs upon self-assembling. The esterification reaction is a prerequisite to propose a self-assembly route for the biosynthesis of cutin in nature. Molecular dynamics simulations have shown that internal molecular reorganization within the self-assembled layers provides the appropriate intermolecular orientation to facilitate the nucleophilic attack and the release of a water molecule required by the esterification reaction.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/la9001412
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Fibrous MnO2 Nanoparticles with (2 × 2) Tunnel Structures. Catalytic Activity in the Total Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds
Dominguez, MI; Navarro, P; Romero-Sarria, F; Frias, D; Cruz, SA; Delgado, JJ; Centeno, MA; Montes, M; Odriozola, JAJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 9 (2009) 3837-3842 DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2009.NS76
Abstract
Manganese oxides having 2 × 2 tunnel structures (cryptomelanes) have been synthesized by a milling method in order to test their efficiency as catalysts for the abatement of volatile organic compounds, using toluene as probe molecule. These materials present excellent textural properties, arising from the nanofiber morphology and were active for toluene total oxidation. DRIFTS of the adsorbed phase allow proposing the role of lattice oxygen in the catalytic reaction.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2009.NS76
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth of Crystalline TiO2 by Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
Borras, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Widmer, R; Rico, VJ; Justo, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARCrystal Growth & Design, 9 (2009) 2868-2876 DOI: 10.1021/cg9001779

Abstract
TiO2 thin films in the form of anatase have been prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) at 523 K as the substrate temperature and a low working pressure. The study of the microstructure and texture of the films at different stages of deposition show that their growth follows the Kolmogorov’s model developed to describe the evolution of crystalline films from a saturated homogeneous medium. An additional characteristic feature of the growth process by PECVD is the formation of different crystalline domains, particularly at low deposition rates. The effects of this parameter and of the characteristics of the substrate on the growing process are also addressed.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/cg9001779
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
W,N-Codoped TiO2-Anatase: A Sunlight-Operated Catalyst for Efficient and Selective Aromatic Hydrocarbons Photo-Oxidation
Kubacka, A; Bachiller-Baeza, B; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 8553-8555 DOI: 10.1021/jp902618g
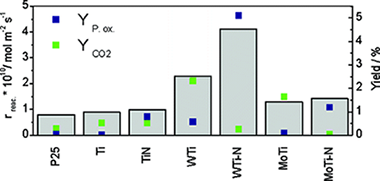
Abstract
New W,N-doped TiO2 anatase-based materials are synthesized having both unprecedent high activity and selectivity in the gas-phase partial oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons using sunlight as excitation energy and molecular oxygen as oxidant.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp902618g
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Integration of methanol steam reforming and combustion in a microchannel reactor for H2 production: A CFD simulation study
Arzamendi, G; Dieguez, PM; Montes, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Gandia, LMCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 25-31 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.034

Abstract
A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) study of the thermal integration of the steam reforming of methanol (SRM) and the combustion of methanol in a catalytic microchannel reactor is presented. This issue is of interest for in situ H2 production for portable power units based on low-temperature PEM fuel cells. Three-dimensional simulations have been carried out under relevant conditions for the SRM reaction that have shown that microreactors allow achieving complete methanol reforming and combustion at space velocities as high as 50,000 h−1, with selectivities for H2 above 99% at relatively low temperatures in the 270–290 °C range.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.034
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Cationic (V, Mo, Nb, W) doping of TiO2–anatase: A real alternative for visible light-driven photocatalysts
Kubacka, A; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 286-292 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.028

Abstract
In this article we investigate the structure–activity link of anatase-type Ti–M (M = V, Mo, Nb, and W) mixed oxides used for toluene photo-oxidation under sunlight-type excitation. An analysis of the local and long-range structural and electronic characteristics of the mixed oxides show that only structurally highly homogeneous anatase-type oxides with electronic properties exclusively leading to a band gap decrease drive to efficient visible light-driven photocatalysts. Within our microemulsion preparation method, this only occurs for Ti–V and Ti–W series of samples. The isoelectronic (V4+) substitution of Ti4+ ions at the anatase lattice is characterized by a low solubility limit (ca. 2.5 at. %), and drives to a limited modification of the band gap and to a moderate enhancement of the photo-activity with respect to bare titania reference systems. W presence at anatase cation positions occurs with concomitant presence of cation vacancies derived by the charge imbalance between the W6+ and Ti4+ species. A unique W-vacancy local arrangement is detected by the structural characterization, leading to both an important band gap decrease and enhancement of the photo-activity upon sunlight excitation.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.028
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
High deposition rates of uniform films in tetramethylsilane-based plasmas generated by elementary microwave sources in matrix configuration
Latrasse, L; Lacoste, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Bes, A; Rayar, M; Pelletier, JSurface and Coatings Technology, 203 (2009) 2343-2349 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.02.121
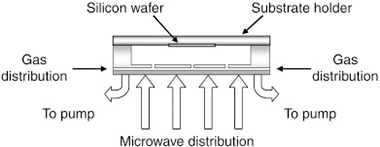
Abstract
Plasma scaling up can be achieved by distributing elementary microwave plasma sources on planar rectangular networks. These so-called matrix plasmas can generate uniform sheets of plasma over a wide argon pressure range, from 7.5 to 750 Pa, with densities between 1012 and 1013 cm− 3. In order to estimate the capabilities of matrix plasmas for PACVD processing in terms of deposition rate and uniformity, SiOCH and SiNCH films were deposited using TMS (tetramethylsilane), as the organic gas precursor of silicon, mixed with oxygen or nitrogen flows. Plasmas of O2 / TMS and N2 / TMS gas mixtures can be sustained between 5 and 25 Pa. Variations in the deposition rate as a function of microwave power and nitrogen partial pressure are reported. Thickness uniformity of SiOCH and SiNCH films was measured across a silicon wafer. The obtained deposition rates exceed 1.3 μm/min and the films present a uniformity better than 5% on 75 mm diameter silicon wafers. Composition of the films has also been analyzed by XPS as a function of process parameters: microwave input power, composition of gas mixture, and N2 partial pressure. In particular, these analyses have shown a very low yield of nitrogen incorporation when using N2 gas as nitrogen precursor and high Si and Si–Si bonding contents in the films, probably due to a strong fragmentation of the TMS precursor in the high density plasma.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.02.121
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Wetting angles and photocatalytic activities of illuminated TiO2 thin films
Rico, V; Romero, P; Hueso, JL; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 347-354 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.037

Abstract
TiO2 thin films have been prepared by physical vapour deposition (PVD) and plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD) to study the UV-induced photo-activity of this material. Wetting angle variations and photo-catalytic activity for the degradation of dyes upon UV illumination have been compared for thin films with different crystalline structure (amorphous, rutile and anatase), microstructure (columnar, compact, etc.) and porosities as estimated from the values of their refraction indices and their direct assessment with a quartz crystal monitor. The surface of the thin films became superhydrophilic upon UV light irradiation and then it recovered its original state by keeping the samples in the dark. Wetting angle decays follow very similar kinetics for amorphous and crystalline films, independently of their actual porosities. By contrast the photo-catalytic activity was very dependent on the crystalline structure of the films (anatase > rutile > amorphous) and on their porosities. The different behaviour depicted by the films with regard to these two properties suggests that they respond to different though related mechanisms and that they cannot be considered as equivalent when trying to prove the photo-activity of TiO2.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.037
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Thermal Stability and Oxidation Resistance of Nanocomposite TiC/a-C Protective Coatings
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Gago, R; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCPlasma Processes and Polymers, 6 (2009) S462-S467 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200931002

Abstract
Nanocomposite films composed by small crystallites of hard phases embedded in an amorphous lubricant matrix have been extensively studied as protective coatings. These kinds of coatings have often to work in extreme environments, exposed to high temperatures (above 800–900 °C), and/or oxidizing/corrosive atmospheres, which may resist. As a result, it is important to study the behavior of such coatings at high temperatures (thermal stability) and in the presence of oxygen (oxidation resistance). In this sense, we have selected a TiC/a-C nanocomposite coating with good mechanical and tribological properties in order to do several thermal tests under three different environments: high vacuum (10−6 mbar), low vacuum (10−1 mbar), and air. Our observations allow us to establish that the film microstructure is stable at least up to 1 000 °C in high vacuum. When oxygen is present, the practical temperature of use is reduced at 700 °C (low partial pressure) and 300 °C (air) by formation of Ti oxides and C removal.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200931002
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Molding with nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals: a route to flexible and transferable Bragg mirrors of high dielectric contrast
Calvo, ME; Sobrado, OS; Lozano, G; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry, 19 (2009) 3144-3148 DOI: 10.1039/B902090J
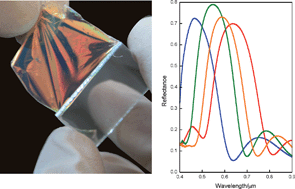
Abstract
Self-standing, flexible Bragg mirror films of high refractive index contrast and showing intense and wide Bragg peaks are herein presented. Nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals are used as templates to infiltrate a polymer, which provides the multilayer with mechanical stability while preserving the dielectric contrast existing in the mold. Such films can be lifted off the substrate and used to coat another surface of arbitrary shape.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1039/B902090J
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
AISI 304 Austenitic stainless steels monoliths for catalytic applications
Martinez, LM; Sanz, O; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 148 (2009) 191-200 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.12.030

Abstract
The thermal treatments of austenitic stainless steels monoliths were studied in order to generate a highly homogeneous and rough oxide scale strongly attached to the base alloy, which will subsequently ensure the good adherence of the catalysts. In this work it has been shown that the morphology, integrity and homogeneity of the scale are strongly influenced by the temperature and time of treatment. Washcoating method was used to deposit on the monolith surface a Au/CeO2 catalyst. The drying procedure turned out to be the most critical variable for the adherence and homogeneity of the catalytic ceria layer, while the ceria colloid concentrations in the starting aqueous dispersion seems to have only a threshold effect. The monolithic reactors containing Au/CeO2 layers are active in the oxidation of CO.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.12.030
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Molecular dynamics simulation of the effect of pH on the adsorption of rhodamine laser dyes on TiO2 hydroxylated surfaces
Hamad, S; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Mejias, JA; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMolecular Simulation, 35 (2009) 1140-1151 DOI: 10.1080/08927020903108083
Abstract
We have carried out a study of adsorption, on the (1 0 1) surface of anatase TiO2, of two industrially relevant rhodamine molecules [rhodamine 6G (R6G) and rhodamine 800 (R800)] employing molecular dynamics. These theoretical studies have shown that R6G must adsorb on surfaces under basic conditions. Moreover, the adsorption of this molecule shows a strong dependence upon the pH of the system, i.e. under basic conditions the adsorption energy is quite high, under neutral conditions the adsorption energy is lower and under acidic conditions an even lower adsorption energy indicates that there must be very little adsorption under such conditions. By contrast, for R800, there is little dependence of the adsorption energy upon the pH, suggesting that the amount of adsorption of these molecules is little affected by this parameter. These theoretical results are in qualitative agreement with the experimental results consisting of the incorporation of these dye molecules into porous thin films.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1080/08927020903108083
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribological carbon-based coatings: An AFM and LFM study
Martinez-Martinez, D; Kolodziejczyk, L; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Fernandez, ASurface Science, 603 (2009) 973-979 DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2009.01.043

Abstract
In this work some carbon-based coatings were studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and lateral force microscopy (LFM) techniques in order to evaluate their microstructure and friction properties at the micro and nanoscale. With this aim, four samples were prepared by magnetron sputtering: an amorphous carbon film (a–C), two nanocomposites TiC/a–C with different phase ratio (∼1:1 and ∼1:3) and a nanocrystalline TiC sample. Additionally, a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) and an amorphous hydrogenated carbon coating (a-C:H) were included to help in the evaluation of the influence of the roughness and the hydrogen presence respectively. The topography (roughness) of the samples was studied by AFM, whereas LFM was used to measure the friction properties at the nanoscale by two different approaches. Firstly, an evaluation of possible friction contrast on the samples was done. This task was performed by subtraction of forward and reverse images and lately confirmed by the study of lateral force profiles in both directions and the histograms of the subtraction images. Secondly, an estimation of the average friction coefficient over the analysed surface of each sample was carried out. To take into account the tip evolution/damaging, mica was used as a reference before and after each sample (hereafter called sandwich method), and samples-to-mica friction ratios were calculated. The LFM was shown to be a useful tool to characterise a mixture of phases with different friction coefficients. In general, the friction ratios seemed to be dominated by the amorphous carbon phase, as it was impossible to distinguish among samples with different proportions of the amorphous phase (friction ratios between 1.5 and 1.75). Nevertheless, it could be concluded that the differences in friction behaviour arose from the chemical aspects (nature of the phase and hydrogen content) rather than surface characteristics, since the roughness (Ra values up to 5.7 nm) does not follow the observed trend. Finally, the Ogletree method was employed in order to calibrate the lateral force and estimate the friction coefficient of our samples. A good agreement was found with macroscopic and literature values going from ∼0.3 for TiC to ∼0.1 for pure carbon.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2009.01.043
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold/hydroxyapatite catalysts: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity to CO oxidation
Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 87 (2009) 245-251 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.016
Abstract
This work reports the synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity for CO oxidation of gold catalysts supported on calcium hydroxyapatite. On both, the hydroxyapatite support and the gold-supported hydroxyapatite catalyst, the CO conversion shows a peak near 100% of conversion at room temperature. The generation of structural vacancies by interaction of CO with the solid provokes the formation of peroxide species in the presence of gaseous oxygen, which seems to be responsible of this high conversion of CO at room temperature. Moreover, the influence of the pre-treatment temperature on the activity has been observed and related with the elimination of carbonate species and the generation of structural defects in the apatite structure, which are able to modify the gold oxidation state.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.016
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthesis and Characterization of Ce1−xEuxO2−x/2 Mixed Oxides and Their Catalytic Activities for CO Oxidation
Hernandez, WY; Centeno, MA; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2012) 5629-5635 DOI: 10.1021/jp8092989

Abstract
A series of Ce1−xEuxO2−x/2 mixed oxides was synthesized by coprecipitation. The solids were characterized by means of XRF, SBET, XRD, UV−vis, and Raman techniques, and their catalytic activities toward CO oxidation were tested. A solid solution, with CeO2 F-type structure, is formed for europium contents (measured as Eu2O3 by XRF) ≤20% wt. For higher contents, the solid solution is not formed, but a physical mixture is detected. The existence of oxygen vacancies in the solids with Eu2O3 contents between 3 and 17% wt was demonstrated by the presence of bands at 532 and 1275 cm−1 in their Raman spectra. The catalytic performances of the solids correlate with the amount of these punctual defects in the solid solution.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp8092989
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Surface nanostructuring of TiO2 thin films by ion beam irradiation
Romero-Gomez, P; Palmero, A; Yubero, F; Vinnichenko, M; Kolitsch, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARScripta Materialia, 60 (2009) 574-577 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.12.014

Abstract
This work reports a procedure to modify the surface nanostructure of TiO2 anatase thin films through ion beam irradiation with energies in the keV range. Irradiation with N+ ions leads to the formation of a layer with voids at a depth similar to the ion-projected range. By setting the ion-projected range a few tens of nanometers below the surface of the film, well-ordered nanorods appear aligned with the angle of incidence of the ion beam. Slightly different results were obtained by using heavier (S+) and lighter (B+) ions under similar conditions.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.12.014
Sonication induced redox reactions of the Ojén (Andalucía, Spain) vermiculite
Poyato, J; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Ramirez-Valle, V; Lerf, A; Wagner, FEUltrasonics Sonochemistry, 16 (2009) 570-576 DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2008.12.009
Abstract
Sonication in a 1:1 mixture (volume ratio) of water and concentrated H2O2 (30%) is a soft method for particle size reduction of phyllosilicate minerals like vermiculites. Repeated sonication causes a particle size reduction to about 70 nm for the Santa Olalla and to 45 nm for the Ojén-vermiculite. In this context the question arises whether the strong oxidising effect of the hydrogen peroxide affects the oxidation state of the iron in the vermiculites. Therefore, the Fe3+/Fetotal ratio before and after sonication was determined by means of Mössbauer spectroscopy. Whereas this ratio was found to remain almost constant in the Santa Olalla vermiculite, it increased from 0.79 to 0.85 in case of the Ojén sample. In the latter case, the oxidation is accompanied by a decrease of the layer charge.
Surprisingly, sonication in pure water leads to a decrease of the Fe3+/Fetotal ratio in the case of the Ojén-vermiculite, i.e., to an increase of the Fe2+ fraction to roughly twice the value before sonication. Again the Fe3+/Fetotal ratio of the Santa Olalla vermiculite remains unchanged. The surface area SBET of the reduced Ojén-vermiculite amounts to 50 m2/g, which is close to the value obtained in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. The results presented should be taken as a warning that particle size reduction by sonication may be accompanied by a change of the redox state and the layer charge of the material.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2008.12.009
Comparison between micro-Raman and micro-FTIR spectroscopy techniques for the characterization of pigments from Southern Spain Cultural Heritage
Franquelo, ML; Duran, A; Herrera, LK; de Haro, MCJ; Perez-Rodriguez, JLJournal of Molecular Structure, 924-926 (2009) 404-412 DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.11.041
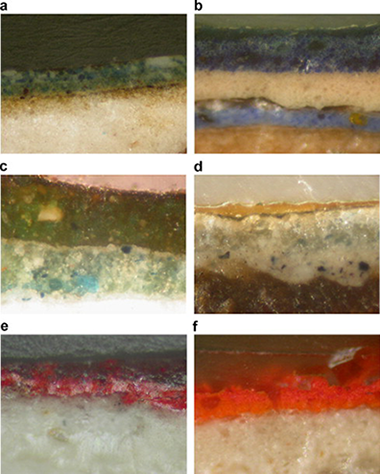
Abstract
An extensive overview of the complementary use of micro-FTIR and micro-Raman spectroscopy in the Cultural Heritage studies is described in this work.
The samples have been prepared using the cross-section technique. This technique allows the examination of a large portion of a single paint layer in its original condition. A variety of pigments from samples belonging principally to the Cultural Heritage of Southern Spain were characterized by micro-Raman spectroscopy using visible excitation sources and micro-FTIR spectroscopy. The pigments studied comprise blue (azurite, ultramarine blue, Prussian blue), red (vermilion, haematite, red ochre, red lead, etc.), ochre and yellow (goethite, orpiment, realgar, etc.), green (malachite, copper resinate), and white (calcite, gypsum, white lead, titanium white, barite, lithopone) pigments, among others. An orientation is given for their appropriate and unequivocal characterization. Characterization by micro-FTIR and micro-Raman presents difficulties with some pigments. In these cases, analysis by EDX solves most of these doubts. The combined use of both spectroscopic techniques, together with SEM–EDX microanalysis, provides one of the most useful methods in the characterization (and possible dating) of materials used in Cultural Heritage.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.11.041
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Co3O4 + CeO2/SiO2 Catalysts for n-Hexane and CO Oxidation
Todorova, S; Kadinov, G; Tenchev, K; Caballero, A; Holgado, JP; Pereniguez, RCatalysis Letters, 129 (2009) 149-155 DOI: 10.1007/s10562-008-9805-x
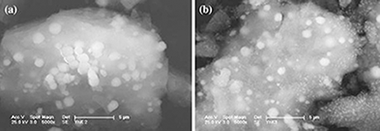
Abstract
Two-component Co–Ce samples deposited onto SiO2 have been prepared, characterized and tested in the reaction of complete n-hexane and CO oxidation. It was established that cerium enhanced the catalytic activity of cobalt in the reaction of n-hexane oxidation, although this depended on the sequence of cobalt and cerium introduction. Co-impregnation of Co and Ce resulted in a close interaction between Co3O4 and CeO2 leading to more surface oxygen species available and, therefore, a better reactivity.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1007/s10562-008-9805-x
Study of ground and unground leached vermiculite
Maqueda, C; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Subrt, J; Murafa, NApplied Clay Science, 44 (2009) 178-184 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.01.019

Abstract
Grinding of clays modifies their surfaces and can significantly affect their leaching behaviour. The acid reaction of vermiculite from Santa Olalla (Huelva, Spain) with HCl at various concentrations was affected by grinding and acid concentration. The acid leaching of ground vermiculite for 3 min with 1 M HCl solution at 80 °C for 24 h removed MgO and Al2O3 almost completely, leaving a residue containing SiO2 and Fe2O3. X-ray diffraction analysis showed the presence of akaganeite (β-FeOOH) and an amorphous phase (silica). Porosity studies showed a very high specific surface area for ground samples compared with unground vermiculite samples, attributed to the presence of iron in the residue coming from structural iron. High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) confirmed the presence of iron oxyhydroxides embedded in the silica material. The particle morphology of the iron oxides corresponded well to akaganeite microcrystals precipitated from solution. The leached vermiculite residue also contained Cl− and a small amount of Ti4+, which were accumulated into the akaganeite microcrystals.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.01.019
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Reactividad de Sólidos
Properties of Ti(C,N) cermets synthesized by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Cordoba, JM; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Aviles, MA; Alcala, MD; Gotor, FJJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 29 (2012) 1173-1182 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.08.019
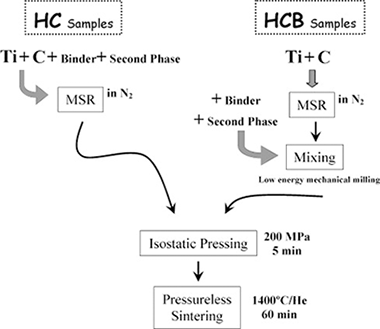
Abstract
The properties of TiCxN1−x/(Ni or Co) cermets sintered by a pressureless method from powder mixtures, and obtained for the first time by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction process (MSR), were studied. The hardness, toughness, friction and wear coefficients, and oxidation resistance were determined. It was shown that cermets obtained from powdered materials synthesized in one single MSR step possessed improved mechanical properties, similar to those obtained in cermets with more complex bulk compositions. Higher wear resistances were observed in cermets whose hard phase was richer in carbon. The oxidation resistance of the cermets depended primarily on the binder composition. This resistance was better for those cermets with cobalt as the binder. Superior oxidation resistance was displayed when small amounts of W or Mo were incorporated into the binder.
Abril, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.08.019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study by grazing incident diffraction and surface spectroscopy of amalgams from ancient mirrors
Herrera, LK; Duran, A; Franquelo, ML; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Espinos, JP; Rubio-Zuazo, J; Castro, GR; Justo, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JLCentral European Journal of Chemistry, 7 (2009) 47-53 DOI: 10.2478/s11532-008-0089-1

Abstract
Characterization of four amalgam surfaces, with different alteration degrees from Andalusia historical mirrors, has been carried out by grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD), and other spectroscopic techniques (SEM/EDX, XPS, and REELS). The combination of all these techniques allows determining the corrosion state of the amalgams. The results show that the amalgams are composed in all cases of a binary alloy of tin and mercury. As mercury has high vapour pressure at RT, it slowly segregates and eventually evaporates, it leaves finely divided particles of tin that easily can be oxidize, forming tin monoxide (SnO) and tin dioxide (SnO2). In one of the samples, most of the amalgam remains unoxidized, since Hg0.1Sn0.9 and metallic Sn phases are the major components; in two other samples, Hg0.1Sn0.9 and Sn phases are not detected while SnO2 and SnO phases appear. Finally, in the last studied sample, only SnO2 phase is detected. The surface analyses of these samples by XPS show that, for most of them an unique chemical species (Sn4+) is found.
Marzo, 2009 | DOI: 10.2478/s11532-008-0089-1
- ‹ anterior
- 51 of 54
- siguiente ›














