Artículos SCI
2022
2022
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2/WO3 nanocomposite from sonochemical-microwave assisted synthesis for the photodegradation of ciprofloxacin and oxytetracycline antibiotics under UV and sunlight
Moghni, N; Boutoumi, H; Khalaf, H; Makaoui, N; Colon, GJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A-Chemistry, 428 (2022) 113848
Show abstract ▽
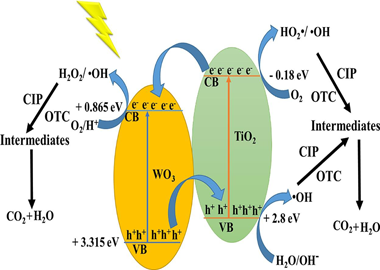
The TiO2/WO3 photocatalysts were prepared by a simple assisted sonochemical -microwave combination. The wide surface and structural characterization of synthesized material confirmed that the adopted preparation method resulted in nanoparticulated crystallite anatase phase of TiO2 with a large surface area (> 200 m(2)/g), and the dispersion of WO3 on the surface of TiO2. The photoactivity was assessed for the photodegradation of ciprofloxacin (CIP) and oxytetracycline (OTC) antibiotics under UV and sunlight irradiation. The mineralization rate, toxicity assessment, pollutant concentration effect on photodegradation efficiency, and reusability potential under sunlight were all investigated. Results showed that TiO2 doped with 5 wt% of WO3 exhibited the best photocatalytic activity under UV (100% degradation) and solar light. Rate constants for CIP and OTC degradation showed that TiO2/WO3 significantly improved with respect to bare TiO2. The antibacterial study revealed that the photodegraded solutions became less toxic than the initial CIP and OTC solutions showing a significant decrease in the inhibition zone diameter and mineralization rates. The prepared TiO2/WO3 maintained high performances in the presence of high concentrations of pollutants as well as good stability after four consecutive uses. The increased photocatalytic activity is attributed to the incorporation of WO3, which extends the light absorption range and decreases the rate of electron -hole recombination.
Junio, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2022.113848
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Evidence of new Ni-O-K catalytic sites with superior stability for methane dry reforming
Azancot, L; Blay, V; Blay-Roger, R; Bobadilla, LF; Penkova, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 307 (2022) 121148
Show abstract ▽
Liquid fuels produced via Fischer-Tropsch synthesis from biomass-derived syngas constitute an attractive and sustainable energy vector for the transportation sector. This study focuses on the role of potassium as a promoter in Ni-based catalysts for reducing coke deposition during catalytic dry reforming. The study provides a new structural link between catalytic performance and physicochemical properties. We identify new Ni-O-K chemical states associated with high stability in the reforming process, evidenced by different characterization techniques. The nickel particles form a core surrounded by a Ni-O-K phase layer (Ni@Ni-O-K) during the reduction of the catalyst. This phase likely presents an alkali-nickelate-type structure, in which nickel is stabilized in oxidation state + 3. The Ni-O-K formation induces essential changes in the electronic, physical, structural, and morphological properties of the catalysts, notably enhancing their long-term stability in dry reforming. This work thus provides new directions for designing more efficient catalysts for sustainable gas-to-liquids processes.
Junio, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121148
Materiales Avanzados
Synthesis and characterization of alkali-activated materials containing biomass fly ash and metakaolin: effect of the soluble salt content of the residue
Jurado-Contreras, S; Bonet-Martínez, E; Sánchez-Soto, PJ; Gencel, O; Eliche-Quesada, DArchives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 22 (2022) 121
Show abstract ▽
The present study investigates the production and characterization of alkali-activated bricks prepared with mixing metakaolin (MK) and biomass fly ash from the combustion of a mix of pine pruning, forest residues and energy crops (BFA). To use this low cost and high availability waste, different specimens were prepared by mixing MK with different proportions of BFA (25, 50 and 75 wt%). Specimens containing only metakaolin and biomass fly ash were produced for the purpose of comparison. Effects of the alkali content of biomass fly ash, after a washing pretreatment (WBFA), as well as the concentration of NaOH solution on the physical, mechanical and microstructural properties of the alkali-activated bricks were studied. It was observed that up to 50 wt% addition of the residue increases compressive strength of alkali-activated bricks. Alkalinity and soluble salts in fly ash have a positive effect, leading materials with the improved mechanical properties. Concentration of NaOH 8 M or higher is required to obtain optimum mechanical properties. The compressive strength increases from 23.0 MPa for the control bricks to 44.0 and 37.2 MPa with the addition of 50 wt% BFA and WBFA, respectively, indicating an increase of more than 60%. Therefore, the use of biomass fly ash provides additional alkali (K) sources that could improve the dissolution of MK resulting in high polycondensation. However, to obtain optimum mechanical properties, the amount of BFA cannot be above 50 wt%.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1007/s43452-022-00444-2
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Versatile Ni-Ru catalysts for gas phase CO2 conversion: Bringing closer dry reforming, reverse water gas shift and methanation to enable end-products flexibility
Merkouri, LP; le Sache, E; Pastor-Perez, L; Duyar, MS; Reina, TRFuel, 315 (2022) 123097
Show abstract ▽
Advanced catalytic materials able to catalyse more than one reaction efficiently are needed within the CO2 utilisation schemes to benefit from end-products flexibility. In this study, the combination of Ni and Ru (15 and 1 wt%, respectively) was tested in three reactions, i.e. dry reforming of methane (DRM), reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) and CO2 methanation. A stability experiment with one cycle of CO2 methanation-RWGS-DRM was carried out. Outstanding stability was revealed for the CO2 hydrogenation reactions and as regards the DRM, coke formation started after 10 h on stream. Overall, this research showcases that a multicomponent Ni-Ru/CeO2 -Al2O3 catalyst is an unprecedent versatile system for gas phase CO2 recycling. Beyond its excellent performance, our switchable catalyst allows a fine control of end-products selectivity.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.123097
Materiales Coloidales
Neodymium doped lanthanide fluoride nanoparticles as contrast agents for luminescent bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Calderon-Olvera, RM; Cantelar, E; Corral, A; Balcerzyk, M; De la Fuente, JM; Ocaña, MBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Ceramica y Vidrio, 61 (2022) 540-549
Show abstract ▽
The synthesis of uniform neodymium-doped lanthanum trifluoride nanoparticles with lenticular shape and a mean diameter around 45 nm by using a homogeneous precipitation method is reported. The luminescent properties of the synthesized samples in terms of their emission spectra and emission lifetime are analyzed as a function of the Nd content to find the optimum phosphor and its suitability for luminescent imaging in the second biological window. The X-ray attenuation properties of the optimum phosphor are evaluated to investigate their additional ability as contrast agent for X-ray computed tomography. Finally, the colloidal stability of the obtained nanoparticles in physiological medium and their cytotoxicity are also analyzed to assess their aptness for in vivo bioimaging applications.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2021.07.004
- ‹ anterior
- 59 of 420
- siguiente ›














