Artículos SCI
2022
2022
Reactividad de Sólidos
The SrCO3/SrO system for thermochemical energy storage at ultra-high temperature
Amghar, N; Ortiz, C; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Maqueda, LP; Jimenez, PESSolar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 238 (2022) 111632
Show abstract ▽
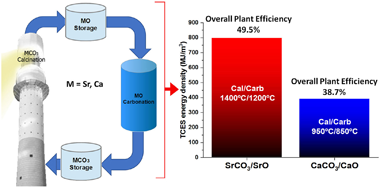
Thermochemical energy storage (TCES) has attracted interest in the last years due to the possibility of attaining high energy densities, seasonal storage capacity and greater efficiencies than currently commercial thermal energy storage systems using molten salts. This work analyses the potential of an ultra-high temperature TCES system based on the SrCO3/SrO system. The process relies upon the reversible decomposition of SrCO3 into SrO and CO2. As proposed in previous works for the integration of the Ca-Looping process to store energy in CSP plants, both the calcination (endothermic) and carbonation (exothermic) reactions are carried out in a closed CO2 loop. At these conditions, the required temperature to attain full calcination in short residence times is around 1400 degrees C whereas carbonation takes place at about 1200 degrees C. Using this process, the energy density potentially achievable by the storage material is very high (around 2000 MJ/m(3)) while the ultra-high carbonation temperature would improve thermoelectric efficiency. The enhancement of the multicycle performance of the SrCO3/SrO system using refractory additives is also explored. Even though current commercial CSP plants with tower technology cannot yet operate at these ultra-high temperatures, recent advances in the development of high-temperature solar receivers could allow operation at 1400 degrees C in the medium term. Finally, a conceptual model of the integration of the SrCO3/SrO system in a CSP plant supports higher overall efficiency and energy density, but lower solar-to-electric efficiency due to thermal losses.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2022.111632
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Influence of Femtosecond Laser Modification on Biomechanical and Biofunctional Behavior of Porous Titanium Substrates
Beltran, AM; Giner, M; Rodríguez, A; Trueba, P; Rodríguez-Albelo, LM; Vázquez-Gámez, MA; Godinho, V; Alcudia, A; Amado, JM; López-Santos, C; Yadir, TMaterials, 15 (2022) 2969
Show abstract ▽
Bone resorption and inadequate osseointegration are considered the main problems of titanium implants. In this investigation, the texture and surface roughness of porous titanium samples obtained by the space holder technique were modified with a femtosecond Yb-doped fiber laser. Different percentages of porosity (30, 40, 50, and 60 vol.%) and particle range size (100-200 and 355-500 mu m) were compared with fully-dense samples obtained by conventional powder metallurgy. After femtosecond laser treatment the formation of a rough surface with micro-columns and micro-holes occurred for all the studied substrates. The surface was covered by ripples over the micro-metric structures. This work evaluates both the influence of the macro-pores inherent to the spacer particles, as well as the micro-columns and the texture generated with the laser, on the wettability of the surface, the cell behavior (adhesion and proliferation of osteoblasts), micro-hardness (instrumented micro-indentation test, P-h curves) and scratch resistance. The titanium sample with 30 vol.% and a pore range size of 100-200 mu m was the best candidate for the replacement of small damaged cortical bone tissues, based on its better biomechanical (stiffness and yield strength) and biofunctional balance (bone in-growth and in vitro osseointegration).
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.3390/ma15092969
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Characterization of Re-Mo/ZSM-5 catalysts: How Re improves the performance of Mo in the methane dehydroaromatization reaction
Lopez-Martin, A; Sini, MF; Cutrufello, MG; Caballero, A; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 304 (2022) 120960
Show abstract ▽
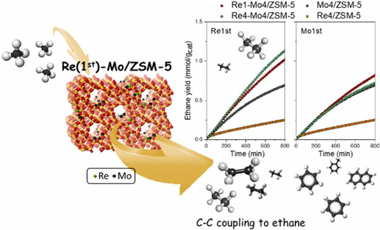
In this study, the promoting effect of rhenium addition as a co-dopant on Mo/ZSM-5 catalysts system has been analysed. Hence, bimetallic (Re-Mo/ZSM-5) catalysts have been synthesized using a sequential impregnation methodology. The catalytic performance for direct aromatization of methane reaction has been determined and correlated with their physical and chemical state combining multiple characterization techniques. An important synergy between Mo and Re, affected by the sequential impregnation, has been observed. Thus, Re1-Mo4/ZSM-5 in which Re has been incorporated first shows notably higher aromatic yields and stability against deactivation. Characterization results suggest that catalytic enhancement is due to the important effect of Re presence in close interaction with Mo. Improved evolution of ethane through C-C coupling would be correlated to this catalytic performance. As we discuss, Mo nature and location in the bimetallic systems are strongly conditioned by Re and the impregnation sequence and favours such intermediate step.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120960
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Mesoporous Silica-Based Nanoparticles as Non-Viral Gene Delivery Platform for Treating Retinitis Pigmentosa
Valdes-Sanchez, L; Borrego-González, S; Montero-Sanchez, A; Massalini, S; De la Cerda, B; Díaz-Cuenca, A; Díaz-Corrales, FJJournal of Clinical Medicine, 11 (2022) 2170
Show abstract ▽
Background: Gene therapy is a therapeutic possibility for retinitis pigmentosa (RP), in which therapeutic transgenes are currently delivered to the retina by adeno-associated viral vectors (AAVs). Although their safety and efficacy have been demonstrated in both clinical and preclinical settings, AAVs present some technical handicaps, such as limited cargo capacity and possible immunogenicity in repetitive doses. The development of alternative, non-viral delivery platforms like nanoparticles is of great interest to extend the application of gene therapy for RP. Methods: Amino-functionalized mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles (N-MSiNPs) were synthesized, physico-chemically characterized, and evaluated as gene delivery systems for human cells in vitro and for retinal cells in vivo. Transgene expression was evaluated by WB and immunofluorescence. The safety evaluation of mice subjected to subretinal injection was assessed by ophthalmological tests (electroretinogram, funduscopy, tomography, and optokinetic test). Results: N-MSiNPs delivered transgenes to human cells in vitro and to retinal cells in vivo. No adverse effects were detected for the integrity of the retinal tissue or the visual function of treated eyes. N-MSiNPs were able to deliver a therapeutic transgene candidate for RP, PRPF31, both in vitro and in vivo. Conclusions: N-MSiNPs are safe for retinal delivery and thus a potential alternative to viral vectors.
Abril, 2022 | DOI: 10.3390/jcm11082170
Composition and technological features of ceramics manufactured by Benito de Valladares in the seventeenth century from the Alcazar Palace in Seville, Spain
Pérez-Rodríguez, J.L.; Robador, M.D.; Duran, A.European Physical Journal Plus, 137 (2022) 469
Show abstract ▽
The walls of the Alcazar Palace in Seville have been covered with ceramic tiles of different styles that were manufactured with different techniques. Several studies have been carried out on these ceramics, but no interest has been paid to the tiles manufactured by the workshop of the Valladares family, one of the most productive ceramic workshops in Triana (Seville). In this work, tiles that were made in the Valladares workshop are studied for the first time. The tiles from the Cenador del Leon built in 1645-1646 were chosen. The experimental studies suggest that the ceramic body was manufactured with silico-calcareous clay. This raw material was heated to a temperature of ca. 900 degrees C. A nondestructive and on-site analytical procedure was applied first. Microsamples were also taken and studied through microanalytical techniques. The maiolica style was used by Benito de Valladares for tile manufacture. The glaze phases were constituted by two layers. The pigments and doping elements used to obtain different colors were characterized. Valladares' work is considered as a continuation of Augusta's work; therefore, a comparison between both ceramists has been realized to better understand the ceramics production in southern Spain during the sixteenth to seventeenth centuries.
Abril, 2022 | DOI: 10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02669-9
- ‹ anterior
- 61 of 420
- siguiente ›














