Artículos SCI
2022
2022
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
3D-printed structured catalysts for CO2 methanation reaction: Advancing of gyroid-based geometries
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Baena-Moreno, F; De Miguel, JCN; Miah, KUM; Arroyo-Torralvo, F; Ossenbrink, R; Odriozola, JA; Benzinger, W; Hensel, A; Wenka, A; Arellano-García, HEnergy Conversion and Management, 258 (2022) 115464
Show abstract ▽
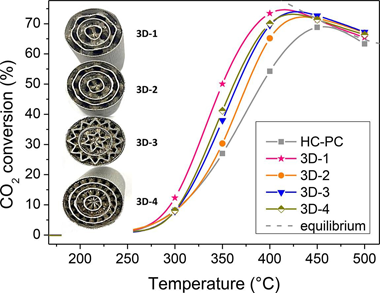
This work investigates the CO2 methanation rate of structured catalysts by tuning the geometr y of 3D-printed metal Fluid Guiding Elements (FGEs) structures based on periodically variable pseudo-gyroid geometries. The enhanced performance showed by the structured catalytic systems is mostly associated with the capability of the FGEs substrate geometries for efficient heat usages. Thus, variations on the channels diameter resulted in ca. 25% greater CO2 conversions values at intermediate temperature ranges. The highest void fraction evidenced in the best performing catalyst (3D-1) favored the radial heat transfer and resulted in significantly enhanced catalytic activity, achieving close to equilibrium (75%) conversions at 400 ? and 120 mL/min. For the 3D-1 catalyst, a mathematical model based on an experimental design was developed thus enabling the estimation of its behavior as a function of temperature, spatial velocity, hydrogen to carbon dioxide (H-2/CO2) ratio, and inlet CO2 concentration. Its optimal operating conditions were established under 3 different scenarios: 1) no restrictions, 2) minimum H-2:CO2 ratios, and 3) minimum temperatures and H-2/CO2 ratio. For instance, for the lattest scenario, the best CO2 methanation conditions require operating at 431 ?, 200 mL/min, H-2/CO2 = 3 M ratio, and inlet CO2 concentration = 10 %.
Abril, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.enconman.2022.115464
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
QUEELS: Software to calculate the energy loss processes in TEELS, REELS, XPS and AES including effects of the core hole
Tougaard, S; Pauly, N; Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis, 54 (2022) 820-833
Show abstract ▽
We present the user-friendly and freely available software package QUEELS (QUantitative analysis of Electron Energy Losses at Surfaces) that allows to calculate effective inelastic scattering cross sections within the dielectric response description, for swift electrons travelling nearby surfaces in several environments. We briefly describe the underlying theoretical models and illustrate its use to evaluate the distribution of energy losses taking place in electron spectroscopies like transmission electron energy loss spectroscopy (TEELS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) and reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy (REELS), which are widely used for material analysis. This includes the intrinsic excitations due to the core hole in XPS and AES.
Abril, 2022 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.7095
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Fast photodegradation of rhodamine B and caffeine using ZnO-hydroxyapatite composites under UV-light illumination
KarimTanji, J.A.Navio, Abdellah Chaqroune, Jamal Naja, F.Puga, M.C.Hidalgo, AbdelhakKherbecheCatalysis Today, 388 (2022) 176-186
Show abstract ▽
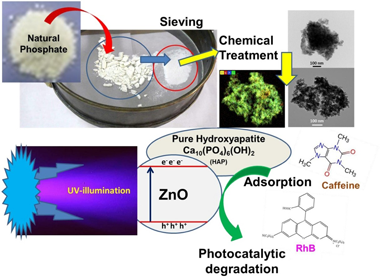
Zinc oxide-hydroxyapatite composites were prepared using wet impregnation method. Firstly, a natural phosphate ore rich in silica and calcium phosphate was sieved to separate silica phase from phosphate phase. Then, through a chemical precipitation method, a pure hydroxyapatite (HAP) was obtained, which was used as a support for ZnO immobilization and applied for the photodegradation of two toxic contaminants: a transparent molecule (caffeine) and dye molecule (rhodamine B). During the present work two weight ratio percentages of zinc oxide were used: 25 wt.% and 50 wt.% of ZnO relative to HAP. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), BET surface area (SBET), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM-EDS) and by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM-STEM). The immobilization of ZnO on HAP surface followed by thermal treatment at 400 °C for 2 h to get a homogenous dispersion of ZnO on the hydroxyapatite support. At high ZnO impregnation percentage, photodegradation performances of ZnO-HAP under UV illumination were fast and superior than the ZnO photocatalyst alone. The results showed that due to the presence of HAP, the conversion of both molecules became faster and greater, since it promotes the synergic phenomena of adsorption and photocatalysis. The toxicity of the treated substrate solutions obtained in the corn kernels germination test indicated a low toxicity after the photodegradation processes, probably due to a high mineralization degree.
Abril, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.07.044
Reactividad de Sólidos
Highly uniform Y3Al2Ga3O12-based nanophosphors for persistent luminescence bioimaging in the visible and NIR regions
Arroyo, E; Herrero, BT; De la Fuente, JM; Ocaña, M; Becerro, AIInorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 9 (2022) 2454-2461
Show abstract ▽
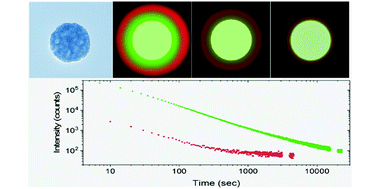
In the last few years, persistent phosphors with a garnet crystal structure have attracted a great deal of interest for a plethora of applications ranging from bioimaging to anti-counterfeiting technologies. However, the development of synthesis methods to fabricate uniform garnet-based micro and nanoparticles, that are needed for such applications, is not mature at all. This study reports the synthesis of highly uniform yttrium aluminum gallium garnet nanospheres. The method is based on homogeneous precipitation in a polyol medium followed by silica coating and calcination. The nanoparticles resulting after silica removal were also uniform and were easily functionalized with polyacrylic acid. The colloidal stability of the latter in physiological media and their biocompatibility were analyzed. The luminescence of the particles, doped with Ce3+, Cr3+, and Nd3+, was studied by recording emission and excitation spectra and persistent luminescence decay curves. Due to their uniform morphology, high colloidal stability, absence of toxicity, and persistent emission in the visible and near-infrared regions, the reported nanospheres show great potential as persistent luminescent bioimaging probes. In addition, the synthesis method paves the way for future use of this persistent material in other applications that require the phosphor to be in the form of highly uniform nanoparticles.
Abril, 2022 | DOI: 10.1039/d2qi00480a
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Z-scheme WO3/PANI heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light: A depth experimental and DFT studies
Y. Naciri; A.Hsini; A.Bouziani; K.Tanji; B.El Ibrahimi; M.N.Ghazza; B. Bakiz; A.Albourine; A.Benlhachemi; J.A. NavíoChemosphere, 292 (2022) 133468
Show abstract ▽
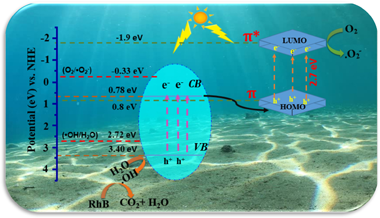
A WO3@PANI heterojunction photocatalyst with a various mass ratio of polyaniline to WO3 was obtained via the in situ oxidative deposition polymerization of aniline monomer in the presence of WO3 powder. The characterization of WO3@PANI composites was carried via X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), ultraviolet–visible diffuse reflection spectroscopy (DRS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL). The photocatalytic efficiency of WO3@PANI photocatalysts was assessed by following the decomposition of the Rhodamine B (RhB) dye under visible light irradiation (λ >420 nm). The results evidenced the high efficiency of the WO3@PANI (0.5 wt %) nanocomposite in the photocatalytic degradation of RhB (90% within 120 min) under visible light irradiation 3.6 times compared to pure WO3. The synergistic effect between PANI and WO3 is the reason for the increased photogenerated carrier separation. The superior photocatalytic performance of the WO3@PANI catalyst was ascribed to the increased visible light in the visible range and the efficient charge carrier separation. Furthermore, the Density Functional Theory study (DFT) of WO3@PANI was performed at the molecular level, to find its internal nature for the tuning of photocatalytic efficiency. The DFT results indicated that the chemical bonds connected the solid-solid contact interfaces between WO3 and PANI. Finally, a plausible photocatalytic mechanism of WO3@PANI (0.5 wt %) performance under visible light illumination is suggested to guide additional photocatalytic activity development.
Abril, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133468
- ‹ anterior
- 63 of 420
- siguiente ›














