Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Materiales Coloidales
White, blue, violet, and other colors from Tm3+/Tb3+/Eu3+ co-doped polymorph SrAl2O4 films, deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique
Calderon-Olvera, RM; Garcia-Hipolito, M; Alvarez-Fregoso, O; Alvarez-Perez, MA; Baez-Rodriguez, A; Ramos-Brito, F; Garcia-Velasco, AC; Falcony, COpticalls Materials
Show abstract ▽
SrAl2O4: Tm3+, SrAl2O4: (Tb3+; Eu3+) and SrAl2O4: (Tb3+; Eu3+; Tm3+) films were deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis (USP) method at 550. C and subsequently heat-treated at 800 degrees C. XRD characterization showed a monoclinic/hexagonal polymorph phase of these films with orthorhombic Sr4Al14O25 as secondary phase. The incorporation of Tm3+ ions in strontium aluminate host lattice generated emissions of blue color for photoluminescence and violet color for cathodoluminescence. The violet emission was associated to the electronic transition from I-1(6) energy level of Tm3+. Photoluminescence of the SrAl2O4: (Tb3+; Eu3+) films resulted in two different colors, white emission was observed when excited with 210 nm and bluish-white emission was achieved by exciting with 275, and 286 nm. When three dopant ions (Tm3+; Tb3+; Eu3+) were incorporated inside strontium aluminate host lattice, it was observed (exciting under 252 nm) white photoluminescence emission (x = 0.3377, y = 0.3294); for excitation wavelengths (lambda(exc)) = 262, 315 and 375 nm, emissions in different shades of blue-green were achieved. Quantum efficiencies between 48 and 57% were obtained.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111737
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Designed organomicaceous materials for efficient adsorption of iodine
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9 (2021) 106577
Show abstract ▽
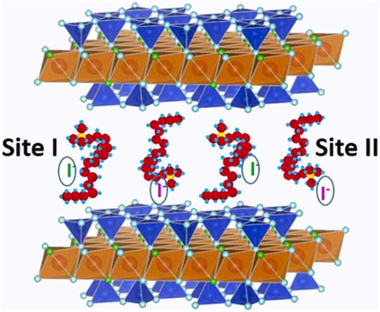
The anionic iodine I-129 has a significant contribution to overall long-term dose resulting from the nuclear waste storage and its immobilization by clay barrier is crucial. Organoclays have been tested as ideal adsorption materials, being the clay layer charge and the length and type of organic molecules the most relevant parameters affecting the adsorption. In this work, a family of designed organomicas are explored in term of iodine adsorption capacity. Their adsorption capacities were always higher than that of the traditional clays and organoclays. C-18-M4 shows a maximum monolayer adsorption capacity one order of magnitude higher than natural organoclays, with a free energy typical of physical adsorption and adsorption sites of high affinity. However, its surface is not homogeneous in terms of stability constant according to the Scatchard adsorption parameters. Hence, this study can provide a guidance for the design and construction of ultrahigh-capacity iodine adsorbents.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106577
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
LaFeO3 Modified with Ni for Hydrogen Evolution Via Photocatalytic Glucose Reforming in Liquid Phase
G. Iervolino; V. Vaiano; D. Sannino; F. Puga; J.A. Navío; M.C. HidalgoCatalysts, 11 (2021) 1558
Show abstract ▽
In this work, the optimization of Ni amount on LaFeO3 photocatalyst was studied in the photocatalytic molecular hydrogen production from glucose aqueous solution under UV light irradiation. LaFeO3 was synthesized via solution combustion synthesis and different amount of Ni were dispersed on LaFeO3 surface through deposition method in aqueous solution and using NaBH4 as reducing agent. The prepared samples were characterized with different techniques: Raman spectroscopy, UltraViolet-Visible Diffuse Reflectance Spettroscopy (UV–Vis-DRS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), Transmission Electron microscopy (TEM), and Scanning Electron microscopy (SEM) analyses. For all the investigated photocatalysts, the presence of Ni on perovskite surface resulted in a better activity compared to pure LaFeO3. In particular, it is possible to identify an optimal amount of Ni for which it is possible to obtain the best hydrogen production. Specifically, the results showed that the optimal Ni amount was equal to nominal 0.12 wt% (0.12Ni/LaFeO3), for which the photocatalytic H2 production was equal to 2574 μmol/L after 4 h of UV irradiation. The influence of different of photocatalyst dosage and initial glucose concentration was also evaluated. The results of the optimization of operating parameters indicated that the highest molecular hydrogen production was achieved on 0.12Ni/LaFeO3 sample with 1.5 g/L of catalyst dosage and 1000 ppm initial glucose concentration. To determine the reactive species that play the most significant role in the photocatalytic hydrogen production, photocatalytic tests in the presence of different radical scavengers were performed. The results showed that •OH radical plays a significant role in the photocatalytic conversion of glucose in H2. Moreover, photocatalytic tests carried out with D2O instead of H2O evidenced the role of water molecules in the photocatalytic production of molecular hydrogen in glucose aqueous solution.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/catal11121558
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
In Situ DRIFTS-MS Methanol Adsorption Study onto Supported NiSn Nanoparticles: Mechanistic Implications in Methanol Steam Reforming
Bobadilla, LF; Azancot, L; Ivanova, S; Delgado, JJ; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Roger, ACNanomaterials, 11 (2021) 3234
Show abstract ▽
Methanol adsorption over both supported NiSn Nps and analogous NiSn catalyst prepared by impregnation was studied by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) to gain insights into the basis of hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming. Different intermediate species such as methoxides with different geometry (bridge and monodentate) and formate species were identified after methanol adsorption and thermal desorption. It is proposed that these species are the most involved in the methanol steam reforming reaction and the major presence of metal-support interface sites in supported NiSn Nps leads to higher production of hydrogen. On the basis of these results, a plausible reaction mechanism was elucidated through the correlation between the thermal stability of these species and the evolution of the effluent gas released. In addition, it was demonstrated that DME is a secondary product generated by condensation of methoxides over the acid sites of alumina support in an acid-catalyzed reaction.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/nano11123234
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Mechanical Performances of Isolated Cuticles Along Tomato Fruit Growth and Ripening
Benitez, JJ; Guzman-Puyol, S; Vilaplana, F; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Dominguez, E; Heredia, AFrontiers in Chemistry, 12 (2021) 787839
Show abstract ▽
The cuticle is the most external layer that protects fruits from the environment and constitutes the first shield against physical impacts. The preservation of its mechanical integrity is essential to avoid the access to epidermal cell walls and to prevent mass loss and damage that affect the commercial quality of fruits. The rheology of the cuticle is also very important to respond to the size modification along fruit growth and to regulate the diffusion of molecules from and toward the atmosphere. The mechanical performance of cuticles is regulated by the amount and assembly of its components (mainly cutin, polysaccharides, and waxes). In tomato fruit cuticles, phenolics, a minor cuticle component, have been found to have a strong influence on their mechanical behavior. To fully characterize the biomechanics of tomato fruit cuticle, transient creep, uniaxial tests, and multi strain dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) measurements have been carried out. Two well-differentiated stages have been identified. At early stages of growth, characterized by a low phenolic content, the cuticle displays a soft elastic behavior. Upon increased phenolic accumulation during ripening, a progressive stiffening is observed. The increment of viscoelasticity in ripe fruit cuticles has also been associated with the presence of these compounds. The transition from the soft elastic to the more rigid viscoelastic regime can be explained by the cooperative association of phenolics with both the cutin and the polysaccharide fractions.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.787839
- ‹ anterior
- 71 of 420
- siguiente ›














