Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Materiales Coloidales
NaY(MoO4)(2)-based nanoparticles: synthesis, luminescence and photocatalytic properties
Nunez, NO; Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Calderon-Olvera, RM; Becerro, AI; Colon, G; Ocana, MDalton Transactions, 50 (2021) 16539-16547
Show abstract ▽
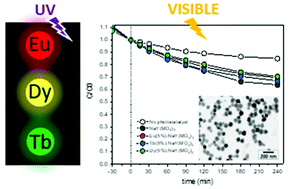
Abstract
We report on a novel synthesis method, which produces NaY(MoO4)(2) nanoparticles having an almost spherical shape and hydrophilic character. The procedure is also suitable for the preparation of NaY(MoO4)(2)-based nanophosphors by doping this host with lanthanide cations (Eu3+, Tb3+ and Dy3+), which, under UV illumination, exhibit intense luminescence whose color is determined by the selected doping cation (red for Eu3+, green for Tb3+ and yellow for Dy3+). The effects of the cations doping level on the luminescent properties are analyzed in terms of emission intensities and luminescent lifetime, to find the optimum phosphors. Finally, the performance of these nanophosphors and that of the undoped system for the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B, used as a model compound, is also analyzed.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1dt02365a
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Extraction of microstructural parameters from sculptured thin films nanoindentation
Gaillard, Y; Jimenez-Pique, E; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSurface & Coatings Technology, 425 (2021) 127696
Show abstract ▽
This work deals with the indentation analysis of nanocolumnar thin films and the difficulties encountered to deduce relevant mechanical parameters by this methodology. SiO2 thin films prepared by physical vapour oblique angle deposition with different nanocolumnar microstructures have been subjected to indentation analysis. Despite the fact that the films had been made of the same material, deposited on the same substrate and had similar thickness, their indentation responses were different and depended on their particular microstructure. It has been also realised that the measured hardness and elastic modulus variation with the indentation depth were length scale dependent and that there is not a unique analytical thin-film nanoindentation model to extract the mechanical properties from the experimental nanoindentation curves. To overcome these limitations a numerical finite element model (FEM) of the nanocolumnar coatings has been built to figure out the contributions of the different physical phenomena intervening in the indentation process. This FEM simulation relies on a description of the elasto-plastic microstructural units of the coatings and the contact friction interactions between them. Based on this simulation a parametrical representation, incorporating two length scales and the contributions of densification and/or the buckling of nanocolumnar units, has been developed to account for the evolution of the apparent elastic modulus deduced from numerical indentation tests. A Hall-Petch modification of this description considering two length scales instead of the common approximation considering a single length scale has rendered the best agreement with the elastic values determined experimentally. Although, at the present stage, the particular microstructure of the films can not be deduced from the evolution of their elastic moduli with the indentation depth, the obtained results and their interpretation constitute a first though essential step for the elaboration of an inverse analysis methodology capable of correlating microstructure and elastic response of nanocolumnar coatings.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127696
Reactividad de Sólidos
Pure perovskite BiFeO3-BaTiO3 ceramics prepared by reaction flash sintering of Bi2O3-Fe2O3-BaTiO3 mixed powders
Taibi, A; Chaguetmi, S; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Perejón, A; García, JE; Satha, H; Pérez-Maqueda, LACeramics International, 47 (2021) 26947-26954
Show abstract ▽
In this work, the 0.67BiFeO(3)-0.33BaTiO(3) ferroelectric ceramic was prepared by Reaction Flash Sintering (RFS). This preparation technique combines synthesis and sintering in a single Flash experiment. The starting oxides reacted during the flash to produce a stoichiometric well-sintered solid solution at a temperature of 858 degrees C by applying a modest field of 35 V cm(-1). The process takes place in a matter of seconds, which allows obtaining a pure perovskite structure without secondary phases. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results show the mixture of rhombohedral and pseudocubic phases expected for a composition that lies within a morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) region, since a significant splitting is observed in the reflections at 2 theta values of 39 degrees and 56.5 degrees. The microstructure exhibit a peculiar bimodal grain size distribution that determines the electrical properties. As compared with previous results, flash-prepared 0.67BiFeO(3)-0.33BaTiO(3) evidences smaller grain size, as well as slightly lower remanent polarization (P-r) and smaller coercive field (E-c) under similar electric fields. It is also demonstrated that the preparation by RFS provides benefits regarding electrical energy consumption.
Octubre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.06.108
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Photonic sensor systems for the identification of hydrocarbons and crude oils in static and flow conditions
Gil-Rostra, J; Quintero-Moreno, S; Rico, VJ; Yubero, F; Sanza, FJ; Casquel, R; Gallo-Valverde, E; Jara-Galan, ME; Sanz-Sanz, P; Holgado, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 344 (2021) 130265
Show abstract ▽
Identification of hydrocarbons and crude oils is typically carried out with samples that, taken from natural sources or refineries, must be brought to the laboratory for their analysis with rather sophisticated instruments. Alternatively, "in situ" procedures have been also developed for this purpose. In this work, we propose the use of a series of several sensor systems based on photonic transducers in the form of chips for the identification and classification of crude oils and hydrocarbons through the determination of their refractive index in the visible and absorption in the near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Two of the photonic transducers rely on modifications of a Bragg microcavity and they monitor the changes in visible light interference phenomena that occur in response to the variation of the refractive index of oils. The third one, in the form of a dielectric mirror, monitors the near infrared absorption of crude oils and hydrocarbons through the recording of a transflectance spectrum. The capacity of these transducers for crude oil identification is proved by the analysis of a series of oils and distilled fractions that have been properly identified and classified as a function of their density and partition of long hydrocarbon chains. The three photonic transducers are operated with optical fibers and can be used in static and dynamic modes, this latter under conditions that are especially well-suited for "insitu" analysis of oil streams in real facilities. The proved resistance of the chips to high pressure and temperature conditions supports their suitability to withstand harsh working environments as those existing in extraction wells.
Octubre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2021.130265
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma-Assisted Deposition of TiO2 3D Nanomembranes: Selective Wetting, Superomniphobicity, and Self-Cleaning
Montes, L; Roman, JM; Garcia-Casas, X; Castillo-Seoane, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Borras, AAdvanced Materials Interfaces (2021) 2100767
Show abstract ▽
Fabrication of tunable wetting surfaces is sought for the last years given its importance on energy, biomaterials and antimicrobials, water purification, microfluidics, and smart surfaces. Liquid management on surfaces mainly depends on the control at the micro- and nanoscale of both roughness and chemical composition. Herein, the combination of a soft-template method and plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition is presented for the synthesis of TiO2 nanofibers on porous substrates such as cellulose and stainless-steel membranes. The protocol, carried out under mild conditions, produces 3D nanomembranes with superhydrophobicity and oleophilicity that are tested as microliter water/oil filters. Photoactivation of TiO2 by UV illumination provides a straightforward approach for wetting tunability that converts the surface into amphiphilic. A final chemical modification of the TiO2 nanofibers by embedding them in an elastomeric polymeric shell and by fluorine-based grafting opens the path toward the formation of superomniphobic and self-cleaning surfaces with long-lasting lifetimes. Thus, a reliable procedure is demonstrated for the fabrication of TiO2 nanofibers, which allows the modification of porous supports and provides an innovative route for the development of 3D nanomembranes with under design wetting. This protocol is extendable to alternative metal oxides, metals, and core@shell nanoarchitectures with potential multifunctionalities.
Octubre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/admi.202100767
- ‹ anterior
- 75 of 420
- siguiente ›














