Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles and the role of the synthesis method on their physical and chemical properties
Uribe-Lopez, MC; Hidalgo-Lopez, MC; Lopez-Gonzalez, R; Frias-Marquez, DM; Nunez-Nogueira, G; Hernandez-Castillo, D; Alvarez-Lemus, MAJournal of Photochemistry & Photobiology, A: Chemistry, 404 (2021) 112866
Show abstract ▽

In the present study, we report on the effect of the synthesis method in the photoactivity of ZnO-NPs. The nanoparticles were prepared by precipitation and sol-gel procedures using zinc nitrate and zinc (II) acetylacetonate as ZnO precursors, respectively. The obtained samples were named as ZnO-PP (precipitation method) and ZnO-SG (sol-gel method). The powders were calcined at 500 degrees C and further characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy, X-ray Powder Diffraction, N-2 adsorption, thermal analysis, Diffuse Reflectance UV-Vis spectroscopy, and Electron Microscopy. Both methods of synthesis lead to formation of pure ZnO with hexagonal-wurtzite crystalline structures with average crystallite sizes similar to 30 nm. The specific surface area was affected by the synthesis method, since SBET values were 5 m(2)/g and 13 m(2)/g for sol-gel and precipitation method, respectively. The electron microscopy revealed significant changes in morphology for the obtained nanoparticles, as sol-gel directed the hexagonal rod-like geometries (similar to 50 nm in diameter) while quasi-spherical nanoparticles (similar to 100 nm in diameter) were formed using precipitation method. Photocatalytic activity was estimated by degrading phenol (50 ppm) as probe molecule under UVA irradiation (lambda = 356 nm), the results demonstrated that ZnO-PP reached 100 % of degradation after 120 min and 90 % of the pollutant was mineralized, whereas for ZnO-SG the results were 80 % and 48 % respectively. Fluorescence test using terephthalic acid (TA) demonstrated higher formation of OH center dot radicals for ZnO synthesized by precipitation method, which could explain the higher photodegradation and mineralization observed. These results support that even slight differences in physical and chemical properties of ZnO, have a significant impact on the photocatalytic performance of such nanoparticles.
Enero, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112866
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Elucidating the Promotional Effect of Cerium in the Dry Reforming of Methane
Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Lopez-Martin, A; Ramirez, A; Gascon, J; Caballero, AChemcatchem, 13 (2021) 553-563
Show abstract ▽
A series of Ni-Ce catalysts supported on SBA-15 has been prepared by co-impregnation, extensively characterized and evaluated in the carbon dioxide reforming of methane (DRM). The characterization by TEM, XRD and TPR has allowed us to determine the effect of metal loading on metal dispersion. Cerium was found to improve nickel location inside the mesopores of SBA-15 and to suppress coke formation during the DRM reaction. The analysis by XPS allowed us to associate the high cerium dispersion with the presence of low-coordinated Ce3+ sites, being main responsible for its promotional effect. A combination of XAS and XPS has permitted us to determine the physicochemical properties of metals under reduction conditions. The low nickel coordination number determined by XAS in N-Ce doped systems after reduction suggests the generation of very small nickel particles which showed greater catalytic activity and stability in the reaction, and a remarkable resistance to coke formation.
Enero, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.202001527
Materiales Coloidales
Dysprosium and Holmium Vanadate Nanoprobes as High-Performance Contrast Agents for High-Field Magnetic Resonance and Computed Tomography Imaging
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Nunez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Fernandez-Afonso, Y; de la Fuente, JM; Balcerzyk, M; Ocana, MInorganic Chemistry, 60 (2021) 152-160
Show abstract ▽
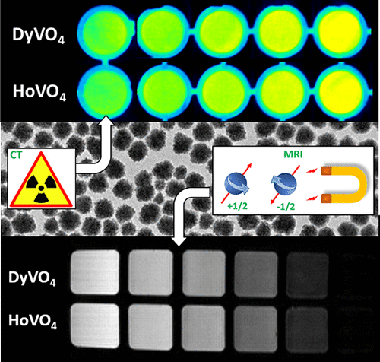
We describe a wet chemical method for the synthesis of uniform and well-dispersed dysprosium vanadate (DyVO4) and holmium vanadate (HoVO4) nanoparticles with an almost spherical shape and a mean size of ∼60 nm and their functionalization with poly(acrylic acid). The transverse magnetic relaxivity of both systems at 9.4 T is analyzed on the basis of magnetic susceptibility and magnetization measurements in order to evaluate their potential for application as high-field MRI contrast agents. In addition, the X-ray attenuation properties of these systems are also studied to determine their capabilities as computed tomography contrast agent. Finally, the colloidal stability under physiological pH conditions and the cytotoxicity of the functionalized NPs are also addressed to assess their suitability for bioimaging applications.
Enero, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c02601
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Enhanced Directional Light Extraction from Patterned Rare-Earth Phosphor Films
Cabello-Olmo, E; Molet, P; Mihi, A; Lozano, G; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 9 (2021) 2001611
Show abstract ▽
The combination of light‐emitting diodes (LEDs) and rare earth (RE) phosphors as color‐converting layers comprises the basis of solid‐state lighting. Indeed, most LED lamps include a photoluminescent coating made of phosphor material, i.e., crystalline matrix suitably doped with RE elements, to produce white light from a blue or ultraviolet LED chip. Transparent phosphor‐based films constitute starting materials for new refined emitters that allow different photonic designs to be implemented. Among the different photonic strategies typically employed to tune or enhance emission, surface texturing has proved its versatility and feasibility in a wide range of materials and devices. However, most of the nanofabrication techniques cannot be applied to RE phosphors directly because of their chemical stability or because of their cost. The first monolithic patterned structure of down‐shifting nanophosphors with square arrays of nanoholes with different lattice parameters is reported in this study. It is shown that a low‐cost soft‐nanolithography procedure can be applied to red‐emitting nanophosphors (GdVO4:Eu3+ nanocrystals) to tune their emission properties, attaining a twofold directional enhancement of the emitted light at predesigned emission wavelengths in specific directions.
Enero, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.202001611
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Disentangling Electron–Phonon Coupling and Thermal Expansion Effects in the Band Gap Renormalization of Perovskite Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Francisco-Lóprez, A.; Baker, A.J., Petrozza, A.; Calvo, M.E.; Goñi, A.R.; Míguez, H.Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 12 (2021) 569-575
Show abstract ▽
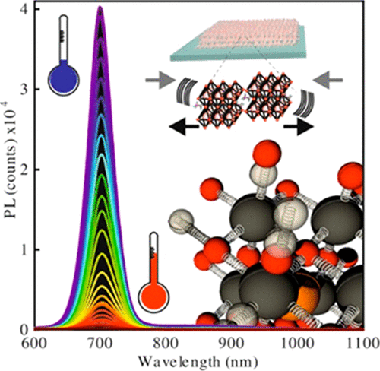
The complex electron–phonon interaction occurring in bulk lead halide perovskites gives rise to anomalous temperature dependences, like the widening of the electronic band gap as temperature increases. However, possible confinement effects on the electron–phonon coupling in the nanocrystalline version of these materials remain unexplored. Herein, we study the temperature (ranging from 80 K to ambient) and hydrostatic pressure (from atmospheric to 0.6 GPa) dependence of the photoluminescence of ligand-free methylammonium lead triiodide nanocrystals with controlled sizes embedded in a porous silica matrix. This analysis allowed us to disentangle the effects of thermal expansion and electron–phonon interaction. As the crystallite size decreases, the electron–phonon contribution to the gap renormalization gains in importance. We provide a plausible explanation for this observation in terms of quantum confinement effects, showing that neither thermal expansion nor electron–phonon coupling effects may be disregarded when analyzing the temperature dependence of the optoelectronic properties of perovskite lead halide nanocrystals.
Enero, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03042
- ‹ anterior
- 97 of 420
- siguiente ›














