Scientific Papers in SCI
2019
2019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Antibacterial Nanostructured Ti Coatings by Magnetron Sputtering: From Laboratory Scales to Industrial Reactors
Alvarez, R; Munoz-Pina, S; Gonzalez, MU; Izquierdo-Barba, I; Fernandez-Martinez, I; Rico, V; Arcos, D; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Palmero, A; Vallet-Regi, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Garcia-Martin, JMNanomaterials, 9 (2019) art. 1217
Show abstract ▽
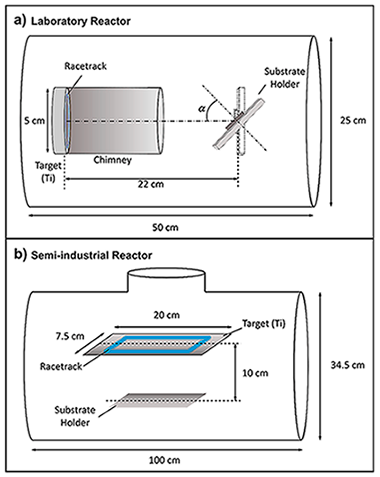
Based on an already tested laboratory procedure, a new magnetron sputtering methodology to simultaneously coat two-sides of large area implants (up to similar to 15 cm(2)) with Ti nanocolumns in industrial reactors has been developed. By analyzing the required growth conditions in a laboratory setup, a new geometry and methodology have been proposed and tested in a semi-industrial scale reactor. A bone plate (DePuy Synthes) and a pseudo-rectangular bone plate extracted from a patient were coated following the new methodology, obtaining that their osteoblast proliferation efficiency and antibacterial functionality were equivalent to the coatings grown in the laboratory reactor on small areas. In particular, two kinds of experiments were performed: Analysis of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation, and osteoblasts-bacteria competitive in vitro growth scenarios. In all these cases, the coatings show an opposite behavior toward osteoblast and bacterial proliferation, demonstrating that the proposed methodology represents a valid approach for industrial production and practical application of nanostructured titanium coatings.
September, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/nano9091217
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Montmorillonite-stabilized gold nanoparticles for nitrophenol reduction
Chenouf, M; Megias-Sayago, C; Ammari, F; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAComptes Rendus Chimie, 22 (2019) 621-627
Show abstract ▽
Two gold-based catalysts were obtained by Au chemical reduction of the HAuCl(4 )precursor. The resulting nanoparticles were stabilized and immobilized on montmorillonite (Mt) and montmorillonite-ceria (Mt/CeO2). All prepared catalysts were active in 4-nitrophenol to aminophenol reduction at room temperature. Synergy between montmorillonite and ceria is postulated in such a way that the montmorillonite phase hinders particle growth either by influencing the nucleation behavior of gold or by increasing the number of nucleation sites and raising the overall dispersion. The role of the ceria support, on the other hand, may be associated with the 4-NP adsorption at the ceria-gold interface, stabilizing the reaction intermediate and hence lowering the activation barrier for the reduction of 4-NP to 4-AP.
September, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.crci.2019.07.005
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Applications and potentialities of Atomic Force Microscopy in fossil and extant plant cuticle characterization
Benitez, JJ; Guzman-Puyol, S; Dominguez, E; Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAReview of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 268 (2019) 125-132
Show abstract ▽
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) is a versatile technique of surface characterization, providing accurate information about the topography and other wide variety of magnitudes at submicron scale. It is extensively utilized in materials science, but its use in other disciplines such as paleobotany is infrequent. In this review, we introduce the main concepts of AFM to paleobotanists, comparing the characteristics of this technique to common electronic and optical microscopies. Then, main works with extant plants, in particular plant cuticles, are described. Finally, realistic applications with fossils are reviewed and their potential use in the characterization of plant fossils discussed. AFM is proposed as a complementary technique to common microscopies to characterize plant cuticle fine details at nanoscale.
September, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2019.06.015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
SiOx by magnetron sputtered revisited: Tailoring the photonic properties of multilayers
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alvarez, R; Espinos, JP; Rico, V; Gil-Rostra, J; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARApplied Surface Science, 488 (2019) 791-800
Show abstract ▽
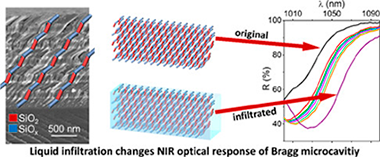
Traditionally porous silicon based photonic structures have been prepared by electrochemically etching of silicon. In this work, porous multilayers of nanocolumnar SiOx and SiO2 thin films acting as near infrared (NIR) 1D-photonic nanostructures are prepared by magnetron sputtering deposition at oblique angles (MS-OA). Simultaneous control of porosity and stoichiometry of the stacked films is achieved by adjusting the deposition angle and oxygen partial pressure according to a parametric formula. This new methodologoy is proved for the synthesis of SiOx thin films with x close to 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6 and nanostructures varying from compact (at 0 degrees deposition angle) to highly porous and nanocolumnar (at 70 degrees and 85 degrees deposition angles). The strict control of composition, structure and nanostructure provided by this technique permits a fine tuning of the absorption edge and refraction index at 1500 nm of the porous films and their manufacturing in the form of SiOx-SiO2 porous multilayers acting as near infrared (NIR) 1D-photonic structures with well-defined optofluidic responses. Liquid tunable NIR Bragg mirrors and Bragg microcavities for liquid sensing applications are presented as proof of concept of the possibilities of this MS-OA manufacturing method as an alternative to the conventional electrochemical fabrication of silicon based photonic structures.
September, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.273
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Extraordinary visible photocatalytic activity of a Co0.2Zn0.8O system studied in the Remazol BB oxidation
KarimTanji; J.A.Navio; Jamal Naja; M.C.Hidalgo; Abdellah Chaqroune; C.Jaramillo-Páez; Abdelhak KherbecheJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 382 (2019) 111877
Show abstract ▽
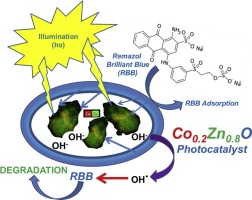
Nanoparticles of CoxZn1-xO system with a nominal composition of x=0.2 were synthesized by the Solution Combustion Method (SCM). Structural and morphological studies as well as the chemical composition of the material were widely investigated by different techniques. Photocatalytic activity under UV and Visible illumination was studied by means of the Remazol Brilliant Blue dye (RBB) oxidation reaction. The effect of different experimental parameters, such as the initial dye concentration, photocatalyst mass, pH or hydrogen peroxide concentration on the RBB discoloration under UV irradiation was studied. Optimal experimental conditions were found to be a photocatalyst mass of 1 g.L-1, dye concentration of 20 mg.L-1 and solution pH of 11. Hydrogen peroxide addition was found to have no effect in the photocatalytic behavior of the material in the range of concentration studied (0 to 6•10-4 M). The optimal parameters were chosen to investigate the degradation of RBB under UV-illumination and just visible illumination. It was observed that the UV-photocatalytic property of pristine ZnO for the RBB removal was scarcely improved after cobalt-incorporation, whereas the effect of cobalt incorporation into ZnO greatly enhanced the RBB conversion under visible illumination. Even more interesting is that, under same experimental conditions, the visible efficiency of the Co-ZnO system is the same that the one showed under UV illumination, i.e. the system does not loose efficiency when illuminated only with visible light.
September, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.111877
- ‹ previous
- 117 of 410
- next ›














