Scientific Papers in SCI
2022
2022
Materiales Avanzados
Study of a Waste Kaolin as Raw Material for Mullite Ceramics and Mullite Refractories by Reaction Sintering
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Eliche-Quesada, D; Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Garzon, EMaterials, 15 (2022) 583
Show abstract ▽
A deposit of raw kaolin, located in West Andalusia (Spain), was studied in this work using a representative sample. The methods of characterization were X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), particle size analysis by sieving and sedimentation, and thermal analysis. The ceramic properties were determined. A sample of commercial kaolin from Burela (Lugo, Spain), with applications in the ceramic industry, was used in some determinations for comparison purposes. The kaolin deposit has been produced by alteration of feldspar-rich rocks. This raw kaolin was applied as an additive in local manufactures of ceramics and refractories. However, there is not previous studies concerning its characteristics and firing properties. Thus, the meaning of this investigation was to conduct a scientific study on this subject and to evaluate the possibilities of application. The raw kaolin was washed for the beneficiation of the rock using water to increase the kaolinite content of the resultant material. The results indicated that the kaolinite content of the raw material was 20 wt % as determined by XRD, showing ~23 wt % of particles lower than 63 mu m. The kaolinite content of the fraction lower than 63 mu m was 50 wt %. Thus, an improvement of the kaolinite content of this raw kaolin was produced by wet separation. However, the kaolin was considered as a waste kaolin, with microcline, muscovite and quartz identified by XRD. Thermal analyses by Thermo-Dilatometry (TD), Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Thermo-Gravimetry (TG) allowed observe kaolinite thermal decomposition, quartz phase transition and sintering effects. Pressed samples of this raw kaolin, the fraction lower than 63 mu m obtained by water washing and the raw kaolin ground using a hammer mill were fired at several temperatures in the range 1000-1500 & DEG;C for 2 h. The ceramic properties of all these samples were determined and compared. The results showed the progressive linear firing shrinkage by sintering in these samples, with a maximum value of ~9% in the fraction lower than 63 mu m. In general, water absorption capacity of the fired samples showed a decrease from ~18-20% at 1050 & DEG;C up to almost zero after firing at 1300 & DEG;C, followed by an increase of the experimental values. The open porosity was almost zero after firing at 1350 & DEG;C for 2 h and the bulk density reached a maximum value of 2.40 g/cm(3) as observed in the ground raw kaolin sample. The XRD examination of fired samples indicated that they are composed by mullite, from kaolinite thermal decomposition, and quartz, present in the raw sample, as main crystalline phases besides a vitreous phase. Fully-densified or vitrified materials were obtained by firing at 1300-1350 & DEG;C for 2 h. In a second step of this research, it was examined the promising application of the previous study to increase the amount of mullite by incorporation of alumina (alpha-alumina) to this kaolin sample. Firing of mixtures, prepared using this kaolin and alpha-alumina under wet processing conditions, produced the increase of mullite in relative proportion by reaction sintering at temperatures higher than 1500 & DEG;C for 2 h. Consequently, a mullite refractory can be prepared using this kaolin. This processing of high-alumina refractories is favoured by a previous size separation, which increases the kaolinite content, or better a grinding treatment of the raw kaolin.
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.3390/ma15020583
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma engineering of microstructured piezo-Triboelectric hybrid nanogenerators for wide bandwidth vibration energy harvesting
Garcia-Casas, X; Ghaffarinehad, A; Aparicio, FJ; Castillo-Seoane, J; Lopez-Santos, C; Espinos, JP; Cotrino, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, ANano Energy, 91 (2022) 106673
Show abstract ▽
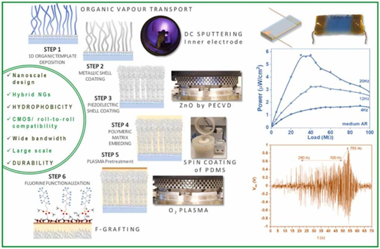
We introduce herein the advanced application of low-pressure plasma procedures for the development of piezo and triboelectric mode I hybrid nanogenerators. Thus, plasma assisted deposition and functionalization methods are presented as key enabling technologies for the nanoscale design of ZnO polycrystalline shells, the formation of conducting metallic cores in core@shell nanowires, and for the solventless surface modification of polymeric coatings and matrixes. We show how the perfluorinated chains grafting of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) provides a reliable approach to increase the hydrophobicity and surface charges at the same time that keeping the PDMS mechanical properties. In this way, we produce efficient Ag/ZnO convoluted piezoelectric nanogenerators supported on flexible substrates and embedded in PDMS compatible with a contact-separation triboelectric architecture. Factors like crystalline texture, ZnO thickness, nanowires aspect ratio, and surface chemical modification of the PDMS are explored to optimize the power output of the nanogenerators aimed for harvesting from low-frequency vibrations. Just by manual triggering, the hybrid device can charge a capacitor to switch on an array of color LEDs. Outstandingly, this simple three-layer architecture allows for harvesting vibration energy in a wide bandwidth, thus, we show the performance characteristics for frequencies between 1 Hz and 50 Hz and demonstrate the successful activation of the system up to ca. 800 Hz.
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106673
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Visible light photodegradation of blue basic 41 using cobalt doped ZnO: Box–Behnken optimization and DFT calculation
K. Tanji; M. Zouheir; Y. Naciri; H. Ahmoum; A. Hsini; O. Mertah; A. El Gaidoumi; J.A. Navio; M.C. Hidalgo; A KherbecheJournal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 19 (2022) 2779-2794
Show abstract ▽
CoxZn1−xO system (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.2) was synthesized using the solution combustion method with urea as a fuel source. Photocatalytic tests were performed under visible light to assess the Basic Blue 41 (BB41) conversion. Various characterization techniques, including XRD, FT-IR analysis, SEM, EDS, XRF, BET-surface area, and DRS were used to investigate the composition, structure, and morphology of the synthesized catalysts. In addition, the density functional theory calculation was used in order to study the electronic properties of the ZnO structure. The Box–Behnken model was valid for describing the degradation of BB41 dye according to the analysis of variances results. A maximum conversion of 100% for BB41 dye has been reached with high mineralization and important removal of chemical oxygen demand. The optimum conditions for BB41 conversion are reported. On the other hand, the reuse tests of the best catalyst showed high-performance stability after five cycles. Furthermore, the activity of superoxide ions (O2·−) and hydroxyl radicals (OH.) as the spices responsible for BB41 dye conversion was well confirmed by the free radicals scavenging tests. The use of Box–Behnken optimization and DFT calculation applied to the synthesized catalysts proves to be a very suitable procedure to establish the operating conditions under which the synthesis strategy of the CoxZn1−xO catalyst in its activity in the visible region performs an excellent efficiency for the degradation of organic dyes and makes contributions to the current literature related to the field of environmental technology.
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.1007/s13738-022-02496-w
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Performance of AISI 316L-stainless steel foams towards the formation of graphene related nanomaterials by catalytic decomposition of methane at high temperature
Cazana, F; Latorre, N; Tarifa, P; Royo, CJ; Sebastian, V; Romeo, E; Centeno, MA; Monzon, ACatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 236-246
Show abstract ▽
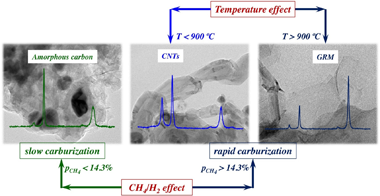
This work explores the preparation of graphene-related materials (GRMs) grown on stainless steel foams via catalytic decomposition of methane (CDM). The main active phases for the reaction are the Fe nanoparticles segregated from the stainless-steel after the activation stage of the foam. The effect of the feed composition and reaction temperature has been studied in order to maximize the productivity, stability and selectivity to GRMs. The maximum productivity attained was 0.116 g(C)/g(foam) h operating at 950 degrees C with a feed ratio of CH4/H-2 = 3 (42.9 %CH4:14.3 %H-2). The carbonaceous nanomaterials (CNMs) obtained were characterized by X-Ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy and by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. The parameters of the kinetic model developed are directly related to the relevant stages of the process, including carburization, diffusion-precipitation and deactivation-regeneration. The balance among these sequential stages determines the overall performance of the activated foam. In conditions of rapid carburization of the Fe NPs (p(CH4) > 14 %), the productivity to CNMs is favoured, avoiding an initial deactivation of the active sites by fouling with amorphous carbon. After a rapid carburization, the selectivity to the different CNMs is governed by the ratio CH4/H-2, and mainly by the temperature. Thus, the formation of GRMs, mainly Few Layer Graphene (FLG) and even graphene, is favoured at temperatures above 900 degrees C. At lower temperatures, carbon nanotubes are formed.
January, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.12.003
2021
2021
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Mechanical Performances of Isolated Cuticles Along Tomato Fruit Growth and Ripening
Benitez, JJ; Guzman-Puyol, S; Vilaplana, F; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Dominguez, E; Heredia, AFrontiers in Chemistry, 12 (2021) 787839
Show abstract ▽
The cuticle is the most external layer that protects fruits from the environment and constitutes the first shield against physical impacts. The preservation of its mechanical integrity is essential to avoid the access to epidermal cell walls and to prevent mass loss and damage that affect the commercial quality of fruits. The rheology of the cuticle is also very important to respond to the size modification along fruit growth and to regulate the diffusion of molecules from and toward the atmosphere. The mechanical performance of cuticles is regulated by the amount and assembly of its components (mainly cutin, polysaccharides, and waxes). In tomato fruit cuticles, phenolics, a minor cuticle component, have been found to have a strong influence on their mechanical behavior. To fully characterize the biomechanics of tomato fruit cuticle, transient creep, uniaxial tests, and multi strain dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) measurements have been carried out. Two well-differentiated stages have been identified. At early stages of growth, characterized by a low phenolic content, the cuticle displays a soft elastic behavior. Upon increased phenolic accumulation during ripening, a progressive stiffening is observed. The increment of viscoelasticity in ripe fruit cuticles has also been associated with the presence of these compounds. The transition from the soft elastic to the more rigid viscoelastic regime can be explained by the cooperative association of phenolics with both the cutin and the polysaccharide fractions.
December, 2021 | DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.787839
- ‹ previous
- 61 of 410
- next ›














