Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Zinc Polyaleuritate Ionomer Coatings as a Sustainable, Alternative Technology for Bisphenol A-Free Metal Packaging
Morselli, D; Cataldi, P; Paul, UC; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Scarpellini, A; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia, A; Valentini, P; Pompa, PP; Marrero-López, D; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 9 (2021) 15484-15495
Show abstract ▽
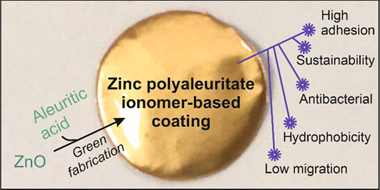
Sustainable coatings for metal food packaging were prepared from ZnO nanoparticles (obtained by the thermal decomposition of zinc acetate) and a naturally occurring polyhydroxylated fatty acid named aleuritic (or 9,10,16-trihydroxy-hexadecanoic) acid. Both components reacted, originating under specific conditions zinc polyaleuritate ionomers. The polymerization of aleuritic acid into polyaleuritate by a solvent-free, melt polycondensation reaction was investigated at different times (15, 30, 45, and 60 min), temperatures (140, 160, 180, and 200 degrees C), and proportions of zinc oxide and aleuritic acid (0:100, 5:95, 10:90, and 50:50, w/w). Kinetic rate constants calculated by infrared spectroscopy decreased with the amount of Zn due to the consumption of reactive carboxyl groups, while the activation energy of the polymerization decreased as a consequence of the catalyst effect of the metal. The adhesion and hardness of coatings were determined from scratch tests, obtaining values similar to robust polymers with high adherence. Water contact angles were typical of hydrophobic materials with values >= 94 degrees. Both mechanical properties and wettability were better than those of bisphenol A (BPA)-based resins and most likely are related to the low migration values determined using a hydrophilic food simulant. The presence of zinc provided a certain degree of antibacterial properties. The performance of the coatings against corrosion was studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy at different immersion times in an aqueous solution of NaCl. Considering the features of these biobased lacquers, they can be potential materials for bisphenol A-free metal packaging.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c04815
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic Treatment of Stained Wastewater Coming from Handicraft Factories. A Case Study at the Pilot Plant Level
Murcia Mesa, JJ; Hernández Niño, JS; González, W; Rojas, H; Hidalgo, MC; Navío, JAWater, 13 (2021) 2705
Show abstract ▽
UV/H2O2 process and TiO2-based photocatalysis were studied in the present work. The effectiveness of these methods was tested in the treatment of effluents taken from handicraft factories. Microorganisms, dyes, and different organic pollutants were detected in the industrial effluents. The experimental procedure for the wastewater treatment was carried out in a patented sunlight reactor on a pilot plant scale. From this study, UV/H2O2 was found to be the best treatment for dye elimination. The optimal peroxide dosage for the degradation of dyes and the elimination of bacteria was 0.07 M. In this case, 70.80% of discoloration was achieved after 7 h of sunlight exposure, under an average sunlight intensity of 3.42 W/m2. The photocatalytic treatment based on TiO2 achieved the highest elimination of coliform bacteria and the lowest TOC value; however, the presence of this material in the reactor had a detrimental effect on the overall elimination of dyes. A combination of both UV/H2O2 and TiO2 treatments significantly improves the dyes discoloration, the elimination of bacteria, and the organic compounds degradation. Some of the results of this study were presented at the 4th Congreso Colombiano de Procesos Avanzados de Oxidación, 4CCPAOx.
October, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/w13192705
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Development of a novel PANI@WO3 hybrid composite and its application as a promising adsorbent for Cr(VI) ions removal
Abdelghani Hsinia, Yassine Naciri, Mohamed Laabd, Asmae Bouziani, J.A.Navío, F.Puga, Rabah Boukherroub, Rajae Lakhmiri, Abdallah AlbourineJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9 (2021) 105885
Show abstract ▽
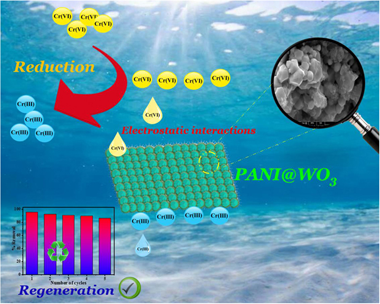
In the current study, an in-situ oxidative polymerization method was used to synthesize polyaniline-coated tungsten trioxide biphasic composite (PANI@WO3). The as-developed composite material properties were elucidated using different characterization tools such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), N2 sorption-desorption isotherm, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The PANI@WO3 was further applied to remove hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) from aqueous solutions. The results demonstrated that the optimal removal efficacy was achieved at pH 2. Meanwhile, the pseudo-second-order kinetic and isotherm of the Langmuir model were fitted for Cr(VI) adsorption. Cr(VI) amount of 549.37 mg·g−1 was the maximum capacity of adsorption attained for PANI@WO3, which is significantly higher than that of existing adsorbents. From a thermodynamic point of view, the Cr(VI) adsorption process occurred spontaneously and endothermically. Importantly, PANI@WO3 still exhibited an excellent adsorption capability after five regeneration cycles, indicating the potential reusability of the PANI@WO3 composite. XPS analysis of PANI@WO3 surface after adsorption of Cr(VI) confirmed its adsorption and concomitant reduction into Cr(III) ions. The transfer of mass phenomenon, electrostatic attraction, and reduction reaction were the primary processes for Cr(VI) ions elimination. These findings revealed that the synthesized PANI@WO3 exhibited a high potential for wastewater treatment containing Cr(VI).
October, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105885
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Mechanically Switchable Wetting Petal Effect in Self-Patterned Nanocolumnar Films on Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
Parra-Barranco, J; Lopez-Santos, C; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, ANanomaterials, 11 (2021) 2566
Show abstract ▽
Switchable mechanically induced changes in the wetting behavior of surfaces are of paramount importance for advanced microfluidic, self-cleaning and biomedical applications. In this work we show that the well-known polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer develops self-patterning when it is coated with nanostructured TiO2 films prepared by physical vapor deposition at glancing angles and subsequently subjected to a mechanical deformation. Thus, unlike the disordered wrinkled surfaces typically created by deformation of the bare elastomer, well-ordered and aligned micro-scaled grooves form on TiO2/PDMS after the first post-deposition bending or stretching event. These regularly patterned surfaces can be reversibly modified by mechanical deformation, thereby inducing a switchable and reversible wetting petal effect and the sliding of liquid droplets. When performed in a dynamic way, this mechanical actuation produces a unique capacity of liquid droplets (water and diiodomethane) transport and tweezing, this latter through their selective capture and release depending on their volume and chemical characteristics. Scanning electron and atomic force microscopy studies of the strained samples showed that a dual-scale roughness, a parallel alignment of patterned grooves and their reversible widening upon deformation, are critical factors controlling this singular sliding behavior and the possibility to tailor their response by the appropriate manufacturing of surface structures.
October, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/nano11102566
Reactividad de Sólidos
Relevance of Particle Size Distribution to Kinetic Analysis: The Case of Thermal Dehydroxylation of Kaolinite
Arcenegui-Troya, J;Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAProcesses, 9 (2021) 1852
Show abstract ▽
Kinetic models used for the kinetic analysis of solid-state reactions assume ideal conditions that are very rarely fulfilled by real processes. One of the assumptions of these ideal models is that all sample particles have an identical size, while most real samples have an inherent particle size distribution (PSD). In this study, the influence of particle size distribution, including bimodal PSD, in kinetic analysis is investigated. Thus, it is observed that PSD can mislead the identification of the kinetic model followed by the reaction and even induce complex thermoanalytical curves that could be misinterpreted in terms of complex kinetics or intermediate species. For instance, in the case of a bimodal PSD, kinetics is affected up to the point that the process resembles a reaction driven by a multi-step mechanism. A procedure for considering the PSD in the kinetic analysis is presented and evaluated experimentally by studying the thermal dehydroxylation of kaolinite. This process, which does not fit any of the common ideal kinetic models proposed in the literature, was analyzed considering PSD influence. However, when PSD is taken into account, the process can be successfully described by a 3-D diffusion model (Jander's equation). Therefore, it is concluded that the deviations from ideal models for this dehydroxylation process could be explained in terms of PSD.
October, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/pr9101852
- ‹ previous
- 66 of 410
- next ›














