Scientific Papers in SCI
2019
2019
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Extraordinary visible photocatalytic activity of a Co0.2Zn0.8O system studied in the Remazol BB oxidation
KarimTanji; J.A.Navio; Jamal Naja; M.C.Hidalgo; Abdellah Chaqroune; C.Jaramillo-Páez; Abdelhak KherbecheJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 382 (2019) 111877 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.111877

Abstract
Nanoparticles of CoxZn1-xO system with a nominal composition of x=0.2 were synthesized by the Solution Combustion Method (SCM). Structural and morphological studies as well as the chemical composition of the material were widely investigated by different techniques. Photocatalytic activity under UV and Visible illumination was studied by means of the Remazol Brilliant Blue dye (RBB) oxidation reaction. The effect of different experimental parameters, such as the initial dye concentration, photocatalyst mass, pH or hydrogen peroxide concentration on the RBB discoloration under UV irradiation was studied. Optimal experimental conditions were found to be a photocatalyst mass of 1 g.L-1, dye concentration of 20 mg.L-1 and solution pH of 11. Hydrogen peroxide addition was found to have no effect in the photocatalytic behavior of the material in the range of concentration studied (0 to 6•10-4 M). The optimal parameters were chosen to investigate the degradation of RBB under UV-illumination and just visible illumination. It was observed that the UV-photocatalytic property of pristine ZnO for the RBB removal was scarcely improved after cobalt-incorporation, whereas the effect of cobalt incorporation into ZnO greatly enhanced the RBB conversion under visible illumination. Even more interesting is that, under same experimental conditions, the visible efficiency of the Co-ZnO system is the same that the one showed under UV illumination, i.e. the system does not loose efficiency when illuminated only with visible light.
September, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.111877
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Insoluble and Thermostable Polyhydroxyesters From a Renewable Natural Occurring Polyhydroxylated Fatty Acid
Benitez, JJ; Guzman-Puyol, S; Cruz-Carrillo, MA; Ceseracciu, L; Moreno, AG; Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 7 (2019) art. 643 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00643
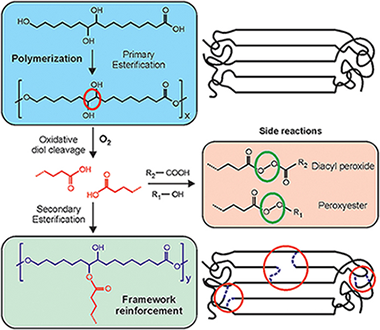
Abstract
To explore the potential of long chain polyhydroxyalkanoates as non-toxic food packaging materials, the characterization of polyesters prepared from a natural occurring polyhydroxylated C16 carboxylic acid (9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic or aleuritic acid) has been addressed. Such monomer has been selected to elucidate the reactivity of primary and secondary hydroxyl groups and their contribution to the structure and properties of the polyester. Resulting polyaleuritate films have been produced using an open mold in one-step, solvent-free self-polycondensation in melt state and directly in air to evaluate the effect of oxygen in their final physical and chemical properties. These polymers are amorphous, insoluble, and thermostable, being therefore suitable for solvent, and heat resistant barrier materials. Structurally, most of primary hydroxyls are involved in ester bonds, but there is some branching arising from the partial participation of secondary O-H groups. The oxidative cleavage of the vicinal diol moiety and a subsequent secondary esterification had a noticeable effect on the amorphization and stiffening of the polyester by branching and densification of the ester bond network. A derivation of such structural modification was the surface compaction and the reduction of permeability to water molecules. The addition of Ti(OiPr)(4) as a catalyst had a moderate effect, likely because of a poor diffusion within the melt, but noticeably accelerated both the secondary esterification and the oxidative processes. Primary esterification was a high conversion bulk reaction while oxidation and secondary esterification was restricted to nearby regions of the air exposed side of cast films. The reason was a progressive hindering of oxygen diffusion as the reaction progresses and a self-regulation of the altered layer growth. Despite such a reduced extent, the oxidized layer noticeably increased the UV-vis light blockage capacity. In general, characterized physical properties suggest a high potential of these polyaleuritate polyesters as food preserving materials.
September, 2019 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00643
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Montmorillonite-stabilized gold nanoparticles for nitrophenol reduction
Chenouf, M; Megias-Sayago, C; Ammari, F; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAComptes Rendus Chimie, 22 (2019) 621-627 DOI: 10.1016/j.crci.2019.07.005
Abstract
Two gold-based catalysts were obtained by Au chemical reduction of the HAuCl(4 )precursor. The resulting nanoparticles were stabilized and immobilized on montmorillonite (Mt) and montmorillonite-ceria (Mt/CeO2). All prepared catalysts were active in 4-nitrophenol to aminophenol reduction at room temperature. Synergy between montmorillonite and ceria is postulated in such a way that the montmorillonite phase hinders particle growth either by influencing the nucleation behavior of gold or by increasing the number of nucleation sites and raising the overall dispersion. The role of the ceria support, on the other hand, may be associated with the 4-NP adsorption at the ceria-gold interface, stabilizing the reaction intermediate and hence lowering the activation barrier for the reduction of 4-NP to 4-AP.
September, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.crci.2019.07.005
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Correlation of Structure and Performance of Hard Carbons as Anodes for Sodium Ion Batteries
Gomez-Martin, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ruttert, M; Winter, M; Placke, T; Ramirez-Rico, JChemistry of Materials, 31 (2019) 7288-7299 DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b01768

Abstract
Hard carbons are the material of choice as negative electrode in sodium ion batteries. Despite being extensively studied, there is still debate regarding the mechanisms responsible for storage in low- and high-potential regions. This work presents a comprehensive approach to elucidate the involved storage mechanisms when Na ions insert into such disordered structures. Synchrotron X-ray total scattering experiments were performed to access quantitative information on atomic ordering in these materials at the nanoscale. Results prove that hard carbons undergo an atomic rearrangement as the graphene layers cross-link at intermediate temperatures (1200-1600 degrees C), resulting in an increase of the average interplanar distance up to 1400 degrees C, followed by a progressive decrease. This increase correlates with the positive trend in the reversible capacity of biomass-derived carbons when processed up to 1200-1600 degrees C due to an increased capacity at low potential (<= 0.1 V vs Na/Na+). A decrease in achievable sloping capacity with increasing heat-treatment temperature arises from larger crystalline domains and a lower concentration of defects. The observed correlation between structural parameters and electrochemical properties clearly supports that the main storage of Na ions into a hard-carbon structure is based on an adsorption-intercalation mechanism.
September, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b01768
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Antibacterial Nanostructured Ti Coatings by Magnetron Sputtering: From Laboratory Scales to Industrial Reactors
Alvarez, R; Munoz-Pina, S; Gonzalez, MU; Izquierdo-Barba, I; Fernandez-Martinez, I; Rico, V; Arcos, D; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Palmero, A; Vallet-Regi, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Garcia-Martin, JMNanomaterials, 9 (2019) art. 1217 DOI: 10.3390/nano9091217

Abstract
Based on an already tested laboratory procedure, a new magnetron sputtering methodology to simultaneously coat two-sides of large area implants (up to similar to 15 cm(2)) with Ti nanocolumns in industrial reactors has been developed. By analyzing the required growth conditions in a laboratory setup, a new geometry and methodology have been proposed and tested in a semi-industrial scale reactor. A bone plate (DePuy Synthes) and a pseudo-rectangular bone plate extracted from a patient were coated following the new methodology, obtaining that their osteoblast proliferation efficiency and antibacterial functionality were equivalent to the coatings grown in the laboratory reactor on small areas. In particular, two kinds of experiments were performed: Analysis of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation, and osteoblasts-bacteria competitive in vitro growth scenarios. In all these cases, the coatings show an opposite behavior toward osteoblast and bacterial proliferation, demonstrating that the proposed methodology represents a valid approach for industrial production and practical application of nanostructured titanium coatings.
September, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/nano9091217
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
MTA HP Repair stimulates in vitro an homogeneous calcium phosphate phase coating deposition
Jiménez-Sánchez, M.D.C.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Díaz-Cuenca, A.Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, 11 (2019) e322-e326 DOI: 10.4317/jced.55661

Abstract
Background: To study the mineralization capacity in vitro of the bioceramic endodontic material MTA HP Repair. Material and Methods: Bioactivity evaluation in vitro was carried out, by soaking processed cement disk in simulated body fluid (SBF) during 168 h. The cement surface was studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX). Release to the SBF media of ionic degradation products was monitored using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Results: FT-IR showed increasing formation of phosphate phase bands at 1097, 960, 607 and 570 cm -1 with prolonged SBF soaking. FEG-SEM analysis reveals that HP produces a effectively surface covering consisting in homogeneous spherical phosphate phase aggregates with an average diameter of 0.5 -1 .0 μm. EDX analysis comparing un-treated (hydrated), 24 h and 72 h SBF treated surfaces of MTA HP Repair revealed phosphate deposition after 24 h, with high phosphorous/silicon element ratio signal measured after 24 h, indicating a very high phosphate phase deposition for this material. Conclusions: The study shows that MTA HP Repair produces a quick and effective bioactive response in vitro in terms of crystalline calcium phosphate surface coating formation. The high bioactive response of MTA HP Repair makes it an interesting candidate for endodontic use as repair cement.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.4317/jced.55661
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Physicochemical parameters - hydration performance relationship of the new endodontic cement MTA Repair HP
Jiménez-Sánchez, M.D.C.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Díaz-Cuenca, A.Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, 11 (2019) e739-e744 DOI: 10.4317/jced.56013

Abstract
Background: To characterize the chemical composition and textural parameters of the MTA Repair HP precursor powder and their influence to hydration performance. Material and Methods: Un-hydrated precursor material was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), laser diffraction (LD), N2 physisorption and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM). Setting time was assessed according to ASTM specification C 266. Hydrated material was analysed by XRD, FT-IR, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis and FEG-SEM. Results: Ca3SiO5 and Ca2SiO4, in addition to CaWO4 as radiopacifier are the main compositional phases. Other measured parameters indicate high specific surface area of 4.8 m2 g-1, high aluminium content of 1.7 wt.% and low initial and final setting times of 12 and 199 min, respectively. Singular microstructural features consisting of high aspect ratio nanoparticles are main constituents of un-hydrated precursor. Besides, FEM-SEM observation shows notably growth of hexagonal shaped plate-like morphologies homogeneously distributed along the sample during hydration process. Conclusions: The short setting time measured for HP Repair, is correlated with high surface area of precursor powder, high Al content and the absence of compositional sulphate phases.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.4317/jced.56013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bio-based composite fibers from pine essential oil and PLA/PBAT polymer blend. Morphological, physicochemical, thermal and mechanical characterization
Hernandez-Lopez, M; Correa-Pacheco, ZN; Bautista-Banos, S; Zavaleta-Avejar, L; Benitez-Jimenez, JJ; Sabino-Gutierrez, MA; Ortega-Gudino, PMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 234 (2019) 345-353 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.01.034
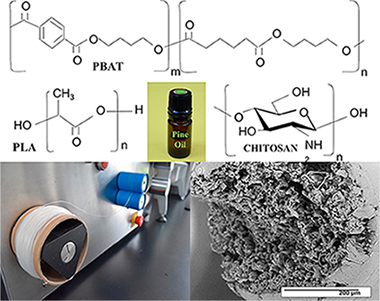
Abstract
Biodegradable aliphatic polyesters are an alternative to reduce the use of synthetic plastic materials that cause severe damage to the environment. Formulations based on poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), were mixed in a 60:40 ratio, adding different concentrations of pine essential oil through the use of extrusion technology to obtain biodegradable polymer fibers. Some formulations were coated with chitosan. All the elaborated fibers were characterized by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy-Attenuated Total Reflection (FTIR-ATR), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and mechanical properties. The SEM studies showed that the PBAT improves the tenacity and provides greater elasticity promoting the interaction between the blends phases with fibril formation. In the FTIR-ATR analysis, compatibility between the blends was observed due to a possible interaction of the carbonyl group of PBAT with PLA. The DSC and the mechanical properties showed partial miscibility of the blends, indicating, that the plasticizing action of the essential oil gave greater mobility, flexibility, less rigidity and crystallization in the blends. A lower Young's modulus and greater elongation at break was also observed.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.01.034
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Support effects on NiO-based catalysts for the oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of ethane
Delgado, D; Sanchis, R; Cecilia, JA; Rodriguez-Castellon, E; Caballero, A; Solsona, B; Nieto, JMLCatalysis Today, 333 (2019) 10-16 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.07.010

Abstract
We report on the effect of NiO-support interactions on the chemical nature of Ni species in a series of supported NiO catalysts for the ODH of ethane. SiO2, TiO2-anatase, a high surface area TiO2 and a porous clay hetero-structure (PCH) with TiO2 and SiO2 pillars were used as supports, which led to a selectivity to ethylene in the range 30-90% over supported NiO catalysts. The catalysts were characterized by means of XRD, N-2-Adsorption, H-2-TPR, XPS and in situ (under H-2 reductive atmosphere) and ex situ XAS spectroscopy. The catalytic performance of supported materials is discussed in terms of their reducibility and specific reduction kinetics, but also taking into account the specific chemical nature of Ni species on each catalyst. The influence of the particle size and the presence of Ni and O vacancies on the catalytic performance in the ODH of ethane is inferred.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.07.010
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Au/Al2O3 - Efficient catalyst for 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidation to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid
Megias-Sayago, C; Lolli, A; Ivanova, S; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 333 (2019) 169-175 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.04.024

Abstract
The catalytic activity of a simple Au/Al2O3 catalytic system prepared by the direct anionic exchange (DAE) method was evaluated in the selective 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) oxidation under mild conditions, using molecular oxygen as the oxidant. The influence of the HMF/NaOH ratio and reaction time on product yield and distribution were studied and discussed in detail. Extremely high activity and selectivity were observed in mild conditions, with 99% of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) production at full HMF conversion after 4 h with the use of only 4 equivalents of NaOH at 70 degrees C. Catalyst viability and stability were verified by repeating the cycle up to five times. Changes in the nature of the support were also contemplated by introducing some ceria fraction, i.e. 20 wt%.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.04.024
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanically induced combustion synthesis and thermoelectric properties of nanostructured strontium hexaboride (SrB6)
Jalaly, M; Khosroshahi, BK; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJ; Yamini, SA; Failamani, F; Mori, TCeramics International, 45 (2019) 14426-14431 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.163
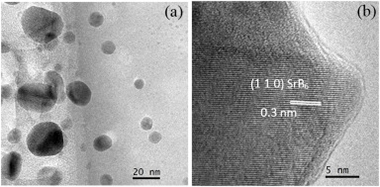
Abstract
The nanoparticles of strontium hexaboride (SrB6) were synthesized by a mechanically induced magnesiothermic combustion in the Mg/B2O3/SrO system. Ignition time in this system was recorded to be 23 min of milling. X-ray diffraction(XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) techniques were used to characterize the combustion product. Thermal analysis was employed to assess the formation mechanism. It was revealed that Mg initially reduced B2O3 in a combustive manner to generate elemental boron and a large amount of heat, resulting in the reduction of SrO by Mg at high temperature. The in-situ formed elemental Sr and B react immediately to generate SrB6. Thermoelectric properties of consolidated SrB6, including thermal conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity, and figure-of-merit were evaluated at the temperature range of 300–873 K.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.163
Materiales Coloidales
Luminescence and X-ray Absorption Properties of Uniform Eu3+:(H3O)Lu3F10 Nanoprobes
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Balcerzyk, M; Ocana, MNanomaterials, 9 (2019) 1153 DOI: 10.3390/nano9081153

Abstract
Due to the high atomic number of lutetium and the low phonon energy of the fluoride matrix, Lu-based fluoride nanoparticles doped with active lanthanide ions are potential candidates as bioprobes in both X-ray computed tomography and luminescent imaging. This paper shows a method for the fabrication of uniform, water-dispersible Eu3+:(H3O)Lu3F10 nanoparticles doped with different Eu contents. Their luminescent properties were studied by means of excitation and emission spectra as well as decay curves. The X-ray attenuation capacity of the phosphor showing the highest emission intensity was subsequently analyzed and compared with a commercial contrast agent. The results indicated that the 10% Eu3+-doped (H3O)Lu3F10 nanoparticles fabricated with the proposed polyol-based method are good candidates to be used as dual probes for luminescent imaging and X-ray computed tomography.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/nano9081153
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Natural abundance O-17 MAS NMR and DFT simulations: New insights into the atomic structure of designed micas
Pavon, E; Osuna, FJ; Alba, MD; Delevoye, LSolid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 100 (2019) 45-51 DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2019.03.006
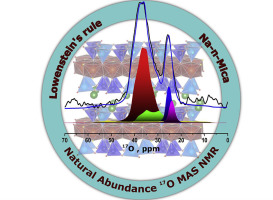
Abstract
Combining O-17 Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) NMR at natural abundance with DFT calculations is a promising methodology to shed light on the structure and disorder in tetrahedral sheets of designed micas with enhanced properties. Among brittle micas, synthetic mica is an important alternative to natural ones with a swelling sheet-like structure that results in many applications, by exploiting unique characteristics. Lowenstein's rule is one of the main chemical factor that determines the atomic structure of aluminosilicates and furthermore their properties. In the present article, O-17 MAS NMR spectroscopy is used to validate (or not) the agreement of the Lowenstein's rule with the distribution of Si and Al sites in the tetrahedral sheets of synthetic micas. O-17 MAS spectra of synthetic high-charged micas exhibit two regions of signals that revealed two distinguishable oxygen environments, namely Si-O-X (with X = Si, Al-tet , Mg) and Al-tet -O-Y (Y=Mg or Al-tet). DFT calculations were also conducted to obtain the O-17 chemical shift and other NMR features like the quadrupolar coupling constant, C-Q, for all of the oxygen environments encountered in the two model structures, one respecting the Lowenstein's rule and the other involving Al-tet -O-Al-tet and Si-O-Si environments. Our DFT calculations support the O-17 assignment, by confirming that Al-tet -O-3Mg and Al tet -O-Al tet oxygen environments show chemical shifts under 30 ppm and more important, with quadrupolar coupling constants of about 1 MHz, in line with the spectral observation. By quantifying the O-17 MAS NMR spectra at natural abundance, we demonstrate that one of the synthetic mica compositions does not meet the Lowenstein's rule.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2019.03.006
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Carbon Supported Gold Nanoparticles for the Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol
Molina, HR; Munoz, JLS; Leal, MID; Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Gallego, MNC; Odriozola, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 7 (2019) 548 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00548
Abstract
This work is a detailed study on how to optimize gold colloids preparation and their deposition to very different in nature carbon materials. The change of the continuous phase and its dielectric constant is used to assure the good dispersion of the hydrophilic/hydrophobic carbons and the successful transfer of the preformed small size colloids to their surface. The sintering behavior of the particles during the calcination step is also studied and the optimal conditions to reduce to a minimum the particle size increase during the protecting agent removal phase are found. The as prepared catalysts have been tested in a relevant reaction in the field of environmental catalysis such as the reduction of 4-nitrophenol leading to promising results. Overall, this work proposes an important methodology to follow when a carbonaceous material are selected as catalyst supports for green chemistry reactions.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00548
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Higher hydration performance and bioactive response of the new endodontic bioactive cement MTA HP repair compared with ProRoot MTA white and NeoMTA plus
Jimenez-Sanchez, Maria Del Carmen; Segura-Egea, Juan Jose; Diaz-Cuenca, AranzazuJournal of biomedical materials research. Part B, Applied biomaterials, 107 (2019) 2109-2120 DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34304

Abstract
The aim of this study was to characterize the hydration performance and the bioactive response of the new bioactive endodontic cement MTA HP repair (HP), comparing its physicochemical parameters with those of ProRoot MTA White (Pro) and NeoMTA Plus (Neo). Un-hydrated precursor materials were characterized by X-ray fluorescence, laser diffraction, N2 physisorption and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM). Setting time was assessed according to ASTM specification C 266. Hydrated materials were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and (FEG-SEM). Bioactivity evaluation in vitro was carried out, by soaking processed cement disk in simulated body fluid (SBF) during 168 h. The cements surface was studied by FT-IR, FEG-SEM, and energy dispersive X-ray. Release to the SBF media of ionic degradation products was monitored using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. HP showed shorter initial setting time compared to Pro and Neo and produce a quick and effective bioactive response in vitro in terms of phosphate phase surface coating formation. This higher bioactive response for HP is correlated with increasing calcium aluminate content, increasing surface area of un-hydrated powder precursor and the increasing release capacity of Si ionic products of the final hydrated product. The higher bioactive response of MTA HP repair highlights this material, as very interesting to further investigate its performance to improve the outcome of vital pulp therapy procedures.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34304
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Noble Metal Supported on Activated Carbon for "Hydrogen Free" HDO Reactions: Exploring Economically Advantageous Routes for Biomass Valorisation
Jin, W; Santos, JL; Pastor-Perez, L; Gu, S; Centeno, MA; Reina, TRChemcatchem (2019) 4434-4441 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900841

Abstract
An innovative route for bio‐compounds upgrading via “hydrogen‐free” hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) is proposed and evaluated using guaiacol as a model compound in a high‐pressure batch reactor. Experimental results showed that noble metal supported on activated carbon catalysts are able to conduct tandem multiple steps including water splitting and subsequent HDO. The activity of Ru/C catalyst is superior to other studied catalysts (i. e. Au/C, Pd/C and Rh/C) in our water‐only HDO reaction system. The greater dispersion and smaller metal particle size confirmed by the TEM micrographs accounts for the better performance of Ru/C. This material also presents excellent levels of stability as demonstrated in multiple recyclability runs. Overall, the proposed novel approach confirmed the viability of oxygenated bio‐compounds upgrading in a water‐only reaction system suppressing the need of external H2 supply and can be rendered as a fundamental finding for the economical biomass valorisation to produce added value bio‐fuels.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900841
Structural and compositional analysis of Co-based coatings after catalytic tests for the sodium borohydride hydrolysis
Beltran, AMMaterials Research Express, 6 (2019) art. 085511 DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab1e27
Abstract
The use of Co-based catalysts for the sodium borohydride hydrolysis for hydrogen production is a well-known process as a source of clean energy, although its mechanisms are still under discussion. With the aim of acquiring a deeper knowledge about this catalytic process, three different catalysts (Co, CoC and CoB) were deposited as a thin film layer by magnetron sputtering onto a polymeric membrane, used as a substrate and analyzed by advance transmission and scanning-transmission electron microscopy techniques (STEM). Structural and compositional characterizations, by electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), have been performed on the coatings before and after their use as catalysts on the sodium borohydride reaction for 90 min, to check the production of hydrogen. Results have shown the formation of CoxB nanoflakes and other Co-based compounds over the catalysts and related to their catalytic activity. Knowing the changes in the structure and composition of the catalysts is key to understanding their catalytic behavior, activity and durability. Among the analyzed catalysts, the Co-C presents better activity during the first cycles, which is related to a larger formation of CoxB.
August, 2019 · DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab1e27
Química de Superficies y Catálisis - Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the preparation method in the metal-support interaction and reducibility of Ni-Mg-Al based catalysts for methane steam reforming
Azancot, L; Bobadilla, LF; Santos, JL; Cordoba, JM; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44 (2019) 19827-19840 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.05.167
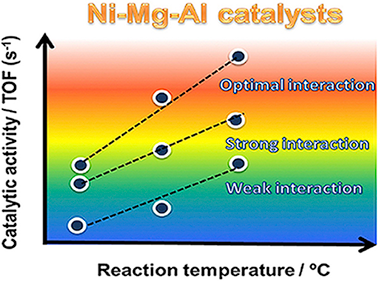
Abstract
Ni-Mg-Al based catalysts were prepared using different preparation methods (impregnation, impregnation-coprecipitation and coprecipitation) and tested in steam reforming of methane. The differences observed in catalytic activity were directly correlated to the physicochemical properties and the different degree of Ni-Mg-Al interaction. The reducibility results showed that the catalyst prepared by the impregnation-coprecipitation method presented the most optimal metal-support interaction to reduce the NiO preserving the Ni-0 particles highly dispersed on the support surface. These results demonstrate that the structure and catalytic performance of Ni-Mg-Al based catalysts can be tuned by controlling the metal-support interaction through of the preparation method.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.05.167
Laboratory multi-technique study of Spanish decorated leather from the 12th to 14th centuries
Franquelo, ML; Duran, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JLSpectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 218 (2019) 331-341 DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.04.012

Abstract
This work comprises an exhaustive study of Spanish decorative leathers dating from the 12th to 14th centuries. These paintings are considered a key example of a crucible of artistic styles: Gothic, Islamic and Florentine Trecento. The goal of this work was to use the scientific information provided by a number of experimental techniques – namely EDX, micro-FTIR, micro-Raman and micro-XRD – to assess the dating of the wooden vault, leather preparation and filling fibres. Another goal was to assess the artistic technique based on the characterization of pigments and the differentiation between original materials and those added throughout its history. Gypsum was the original preparation layer extended over the leather. A new preparation stratum was added in further interventions with the artwork. The original pictorial materials and those used during refurbishments have been identified. Original pigments were: red lead, Mars red, red lake, cinnabar, lapis lazuli, red ochres, raw sienna, white lead and charcoal black. Gilding was also found. Pigments added during restoration were: barite, emerald green, rutile, anatase, Mars red, cadmium red, lithopone, cadmium yellow, charcoal black and orpiment.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.04.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma Enabled Conformal and Damage Free Encapsulation of Fragile Molecular Matter: from Surface-Supported to On-Device Nanostructures
Alcaire, M; Aparicio, FJ; Obrero, J; Lopez-Santos, C; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Frutos, F; Ostrikov, K; Borras, A; Barranco, AAdvanced Functional Materials, (2019) art. 1903535 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201903535
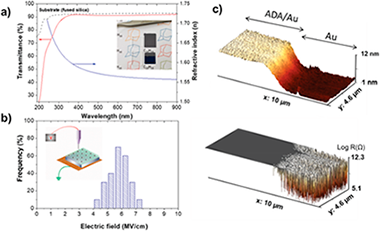
Abstract
Damage-free encapsulation of molecular structures with functional nanolayers is crucial to protect nanodevices from environmental exposure. With nanoscale electronic, optoelectronic, photonic, sensing, and other nanodevices based on atomically thin and fragile organic matter shrinking in size, it becomes increasingly challenging to develop nanoencapsulation that is simultaneously conformal at atomic scale and does not damage fragile molecular networks, while delivering added device functionality. This work presents an effective, plasma-enabled, potentially universal approach to produce highly conformal multifunctional organic films to encapsulate atomically thin graphene layers and metalorganic nanowires, without affecting their molecular structure and atomic bonding. Deposition of adamantane precursor and gentle remote plasma chemical vapor deposition are synergized to assemble molecular fragments and cage-like building blocks and completely encapsulate not only the molecular structures, but also the growth substrates and device elements upon nanowire integration. The films are insulating, transparent, and conformal at sub-nanometer scale even on near-tip high-curvature areas of high-aspect-ratio nanowires. The encapsulated structures are multifunctional and provide effective electric isolation, chemical and environmental protection, and transparency in the near-UV-visible-near-infrared range. This single-step, solvent-free remote-plasma approach preserves and guides molecular building blocks thus opening new avenues for precise, atomically conformal nanofabrication of fragile nanoscale matter with multiple functionalities.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201903535
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Au/CeO2-ZnO/Al2O3 as Versatile Catalysts for Oxidation Reactions: Application in Gas/Liquid Environmental Processes
Megias-Sayago, C; Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Odriozola, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 7 (2019) art. 504 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00504

Abstract
The present work showcases the versatility of nanogold systems supported on Zn-doped ceria when applied in two important environmental processes, the total CO oxidation, and the liquid phase oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid. In the CO oxidation the suitability of these materials is clearly demonstrated achieving full conversions even at sub-ambient conditions. Regarding the glucose oxidation our materials display high conversion values (always over 50%) and very importantly full or almost full selectivity toward gluconic acid-an added value platform chemical in the context of biomass upgrading routes. The key factors controlling the successful performance on both reactions are carefully discussed and compared to previous studies in literature. To our knowledge this is one of the very few works in catalysis by gold combining liquid and gas phase reactions and represents a step forward in the flexible behavior of nano gold catalysts.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00504
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Large gap atmospheric pressure barrier discharges using ferroelectric materials
Navascues, P.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A. R.; Cotrino, J.; Gomez-Ramirez, A.Plasma Sources Sciences & Tecnology, 28 (2019) 075002 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6595/ab28ce
Abstract
This work reports a phenomenological comparative study of atmospheric pressure barrier plasmas using ferroelectric (ferroelectric barrier discharge (FBD)) and dielectric (dielectric barrier discharge (DBD)) plates to moderate the discharge. For FBD operation and large inter-electrode distances, experiments with helium carried out in a parallel plate reactor as a function of applied voltage have shown an enhancement of one order of magnitude in the charge transferred through the circuit. In a similar way to DBDs, FBDs rendered a laterally localized arrangement of discrete columnar discharges with a pattern distribution and an overall current intensity that depended on operation conditions. However, unlike the regular columnar pattern found for DBD operation, discharge columns in the FBD mode appear randomly and inhomogeneously distributed on the ferroelectric surface. This geometrical behavior of FBD plasma columns, as well as the singular variation of current with applied voltage and the particular shape characteristics of the current discharge curves have been accounted for by the high capacity of ferroelectric surfaces to randomly accumulate charge and to promote the emission of secondary electrons in the presence of a plasma.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6595/ab28ce
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Does grain size have an influence on intrinsic mechanical properties and conduction mechanism of near fully-dense boron carbide ceramics?
Moshtaghioun, BM; Laguna-Bercero, MA; Gomez-Garcia, D; Pena, JIJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 795 (2019) 408-415 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.037
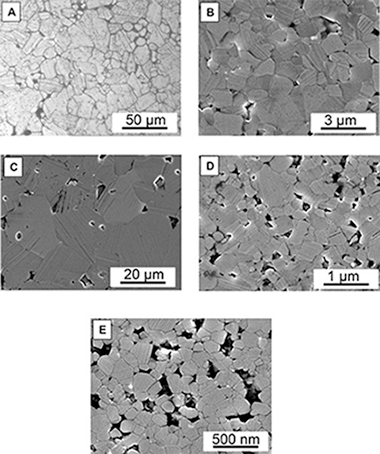
Abstract
This work is concentrated on getting a reply to the following question: how does the grain size of boron carbide specimens influence on their mechanical and electrical response? It is a common issue that both essential properties are usually affected by the grain boundaries. To this purpose, a set of near fully-dense boron carbide specimens were prepared by spark plasma sintering. In order to reduce residual porosity and grain-size effects, nanoindentation tests at room temperature were conducted. DC conductivity was measured through four-point test technique from room temperature up to 800 °C. The results show that hardness can reach values as high as ∼60 GPa and plasticity onset takes place at around 23 GPa by dislocation nucleation. Regarding the conductivity, it is found that grain boundaries can block the mobility of bipolarons in an effective way. A simple additive law is provided to account for the resistivity of boron carbide polycrystals.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.037
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effects of Boron Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-Co Based Cermets
Chicardi, E; Martinez, FJGMetals, 9 (2019) art. 787 DOI: 10.3390/met9070787
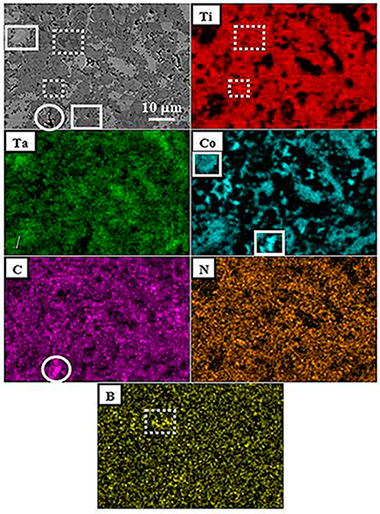
Abstract
In this work, a titanium-tantalum carbonitride based cermet, with cobalt as the binder phase and boron as a sintering additive, was developed by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction process using two different methodologies. The boron additive was added to prevent the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds generally formed during the liquid phase sintering step due to the excessive ceramic dissolution into the molten binder phase. A systematic study was carried out to understand the effects of boron addition on the nature of the phases, microstructure, and mechanical properties of cermets. With the boron addition, the formation of two different boride solid solutions, i. e., (Ti, Ta)B-2 and (Ti, Ta)(3)B-4, was observed. Moreover, the nature of the binder was also modified, from the (Ti, Ta)Co-2 brittle intermetallic compound (for cermets without boron addition) to ductile and tough (Ti, Ta)Co-3 and alpha-Co phases (for cermets with boron addition). These modifications caused, as a general trend, the increase of hardness and toughness in cermets.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/met9070787
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bionanocomposites based on chitosan intercalation in designed swelling high-charged micas
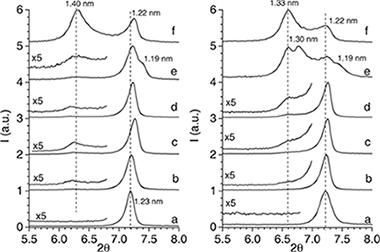
Alba, MD; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Perdigon, AC; Raffin, FScientific Reports, 9 (2019) art. 10265 DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46495-z
Abstract
Bionanocomposites based on layered inorganic components, as clays, and polymers of biological origin, as chitosan, have a major impact in medical and environmental fields, being economical and environmentally friendly materials. Na-Mn micas (n = 2 and 4) with controlled surface charge, high cation exchange capacity and swelling behaviour, are attractive inorganic composite components that exhibit improved adsorption properties compared to other inorganic solids which makes them potentially useful for bionanocomposites. The goal of this research was to explore the potential use of those synthetic brittle micas to form eco-friendly bionanocomposites with chitosan biopolymer. Hence, chitosan-mica bionanocomposites were prepared by ion-exchange reaction between chitosan solution and synthetic high charge mica. X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermal analysis, MAS-NMR spectroscopy and zeta-potential have been employed for bionanocomposites characterization. The results showed that the adsorption of chitosan is effective, although a chitosan portion remains in the outer surface being hydrogen-bonded to the tetrahedral sheet of the silicate.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46495-z
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
On‐Surface Synthesis and Characterization of Acene‐Based Nanoribbons Incorporating Four‐Membered Rings
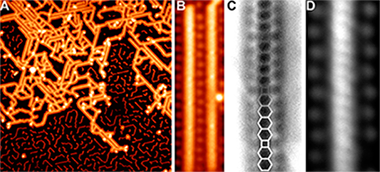
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Dienel, T; Nicolai, A; Kharche, N; Liang, LB; Daniels, C; Meunier, V; Liu, JZ; Feng, XL; Mullen, K; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Groning, O; Ruffieux, P; Fasel, RChemistry-A European Journal DOI: 10.1002/chem.201901410
Abstract
A bottom up method for the synthesis of unique tetracene-based nanoribbons, which incorporate cyclobutadiene moieties as linkers between the acene segments, is reported. These structures were achieved through the formal [2+2] cycloaddition reaction of ortho-functionalized tetracene precursor monomers. The formation mechanism and the electronic and magnetic properties of these nanoribbons were comprehensively studied by means of a multitechnique approach. Ultra-high vacuum scanning tunneling microscopy showed the occurrence of metal-coordinated nanostructures at room temperature and their evolution into nanoribbons through formal [2+2] cycloaddition at 475 K. Frequency-shift non-contact atomic force microscopy images clearly proved the presence of bridging cyclobutadiene moieties upon covalent coupling of activated tetracene molecules. Insight into the electronic and vibrational properties of the so-formed ribbons was obtained by scanning tunneling microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and theoretical calculations. Magnetic properties were addressed from a computational point of view, allowing us to propose promising candidates to magnetic acene-based ribbons incorporating four-membered rings. The reported findings will increase the understanding and availability of new graphene-based nanoribbons with high potential in future spintronics.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/chem.201901410
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
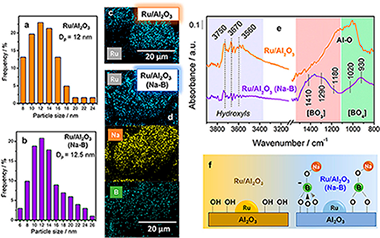
Size-tailored Ru nanoparticles deposited over gamma-Al2O3 for the CO2 methanation reaction
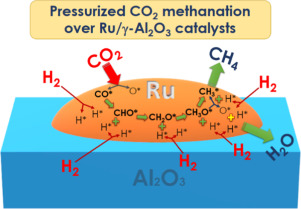
Navarro-Jaen, S; Navarro, JC; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JAApplied Surface Science, 483 (2019) 750-761 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.248
Abstract
By means of the polyol method, a series of 5 wt% Ru/Al2O3 catalysts was synthesized controlling the particle size of the ruthenium species. The physico-chemical characterization demonstrated the successful particle size control of the Ru species, in such a way that higher the Ru/PVP ratio, higher the Ru particle size. Moreover, there are evidences that suggest preferential growth of the RuO2 clusters depending on the Ru/PVP ratio. Regarding the catalytic activity during the CO2 methanation, the total conversion and the CH4 yield increased with the particle size of Ru. Nevertheless, a considerable enhancement of the catalytic performance of the most active system was evidenced at 4 bar, demonstrating the improvement of the thermodynamics (superior total conversion) and kinetics (superior reaction rate) of the CO2 methanation at pressures above the atmospheric one. Finally, the in situ DRIFTS study allowed to establish that CO2 was dissociated to CO* and O* species on the metallic Ru particles, followed by the consecutive hydrogenation of CO* towards CHO*, CH2O*, CH3O*, and finally CH4 molecules, which were further desorbed from the catalyst. Thus from the mechanistic point of view, a suitable particle size of the Ru nanoparticles along with the high-pressure effects results in the enhancement of the availability of hydrogen and consequently in the formation of CHxO species that enhance the cleavage of the C-O bond, which is the rate-determining step of the overall CO2 methanation process.
July, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.248
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B dye over a novel Zn3(PO4)2/BiPO4 catalyst
Naciri,Y.;Chennah,A.;Jaramillo-Páez,C.;Navío,J.A.;Bakiz, B.;Taoufyq,A.;Ezahri,M.;Villain,S.;Guinneton,F.;Benlhachemi,A.Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7 (2019) 103075 DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103075

Abstract
In this work, a facile method was used to synthesize the Zn3(PO4)2/BiPO4 composite photocatalysts with different Bi contents followed by heat treatment at 900 °C for 3 h. The as-prepared samples were studied by a variety of characterization techniques including X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) combined with energy dispersive X-ray diffraction (EDX), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). The UV–vis spectroscopy was used to analyze the evolution of Rhodamine B discoloration in presence of the synthesized phosphate photocatalysts. The XRD, SEM-EDX, TEM, DRS and XPS analyses confirmed the formation of heterojunction structure between both materials, during the process of co-precipitation and ulterior heat treatment. The photocatalytic tests showed that photocatalytic ability of the 70% Bi-Zn3(PO4)2 composites was higher than that of pure Zn3(PO4)2 and BiPO4 after 1 h of UV-illumination. The obviously enhanced photocatalytic activity of the 70% Bi-Zn3(PO4)2 sample could be mainly attributed to the formation of the heterojunction, accelerating the separation of photogenerated charge carriers. A plausible mechanism of the photocatalytic degradation of RhB on Zn3(PO4)2/BiPO4 composites is proposed. The reduction in the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) revealed the mineralization of dye along with color removal. Thus, it can be suggested that the 70% Bi-Zn3(PO4)2 can serve as a promising photocatalyst in the degradation of organic contaminants under UV light.
June, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103075
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Multifunctional antimicrobial chlorhexidine polymers by remote plasma assisted vacuum deposition
Mora-Boza, A; Aparicio, FJ; Alcaire, M; Lopez-Santos, C; Espinos, JP; Torres-Lagares, D; Borras, A; Barranco, AFrontiers of chemical science and engineering, 13 (2019) 330-339 DOI: 10.1007/s11705-019-1803-6

Abstract
Novel antibacterial materials for implants and medical instruments are essential to develop practical strategies to stop the spread of healthcare associated infections. This study presents the synthesis of multifunctional antibacterial nanocoatings on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) by remote plasma assisted deposition of sublimated chlorhexidine powders at low pressure and room temperature. The obtained materials present effective antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli K12, either by contact killing and antibacterial adhesion or by biocide agents release depending on the synthetic parameters. In addition, these multifunctional coatings allow the endure hydrophilization of the hydrophobic PDMS surface, thereby improving their biocompatibility. Importantly, cell-viability tests conducted on these materials also prove their non-cytotoxicity, opening a way for the integration of this type of functional plasma films in biomedical devices.
June, 2019 · DOI: 10.1007/s11705-019-1803-6
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
2D compositional self-patterning in magnetron sputtered thin films
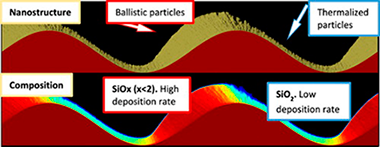
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alvarez, R; Rico, V; Espinos, JP; Lopez-Santos, MC; Solis, J; Siegel, J; del Campo, A; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARApplied Surface Science, 480 (2019) 115-121 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.206
Abstract
Unlike topography patterning, widely used for numerous applications and produced by means of different technologies, there are no simple procedures to achieve surface compositional patterning at nanometric scales. In this work we have developed a simple method for 2D patterning the composition of thin films. The method relies on the magnetron sputtering deposition at oblique angles onto patterned substrates made by laser induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS). The method feasibility has been demonstrated by depositing SiOx thin films onto LIPSS structures generated in Cr layers. A heterogeneous and aligned distribution of O/Si ratios (and different Sin+ chemical states) along the LIPSS structure in length scales of some hundreds nm's has been proven by angle resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and a patterned arrangement of composition monitored by atomic force microscopy-Raman analysis. The obtained results are explained by the predictions of a Monte Carlo simulation of this deposition process and open the way for the tailored one-step fabrication of surface devices with patterned compositions.
June, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.206
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Comprehensive Experimental and Theoretical Study of the CO plus NO Reaction Catalyzed by Au/Ni Nanoparticles
Kyriakou, G; Marquez, AM; Holgado, JP; Taylor, MJ; Wheatley, AEH; Mehta, JP; Sanz, JF; Beaumont, SK; Lambert, RMACS Catalysis, 9 (2019) 4919-4929 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b05154
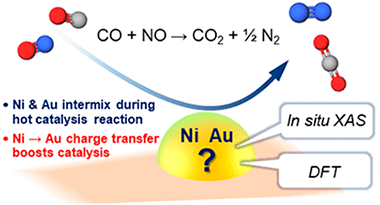
Abstract
The catalytic and structural properties of five different nanoparticle catalysts with varying Au/Ni composition were studied by six different methods, including in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The as-prepared materials contained substantial amounts of residual capping agent arising from the commonly used synthetic procedure. Thorough removal of this material by oxidation was essential for the acquisition of valid catalytic data. All catalysts were highly selective toward N-2 formation, with 50-50 Au:Ni material being best of all. In situ X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy showed that although Au acted to moderate the oxidation state of Ni, there was no clear correlation between catalytic activity and nickel oxidation state. However, in situ extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy showed a good correlation between Au Ni coordination number (highest for Ni50Au50) and catalytic activity. Importantly, these measurements also demonstrated substantial and reversible Au/Ni intermixing as a function of temperature between 550 degrees C (reaction temperature) and 150 degrees C, underlining the importance of in situ methods to the correct interpretation of reaction data. DFT calculations on smooth, stepped, monometallic and bimetallic surfaces showed that N + N recombination rather than NO dissociation was always rate-determining and that the activation barrier to recombination reaction decreased with increased Au content, thus accounting for the experimental observations. Across the entire composition range, the oxidation state of Ni did not correlate with activity, in disagreement with earlier work, and theory showed that NiO itself should be catalytically inert. Au-Ni interactions were of paramount importance in promoting N + N recombination, the rate-limiting step.
June, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b05154
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Exchange bias and two steps magnetization reversal in porous Co/CoO layer
Ovejero, JG; Godinho, V; Lacroix, B; Garcia, MA; Hernando, A; Fernandez, AMaterials & Design, 171 (2019) 107691 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107691
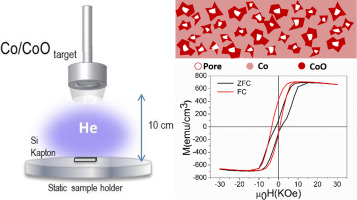
Abstract
In this paper Co/CoO thick layers (hundreds of nanometers) of different porosity and oxidation degree were prepared in a magnetron sputtering deposition processby tailoring the DC sputtering power, as well as the process gas and target composition. The control of the synthesis parameters allowed the nanostructuration of the films with a singular distribution of closed pores and a controlled amount of CoO. We observed an exchange bias field of 2.8 KOe for porous Co/CoO composites, similar to Co/CoO bilayers but for coatings thicker than 300 nm. Besides, it was observed that the coating presents bistable magnetic features when cooled under zero field conditions as a result of the unusual exchange coupling.
June, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107691
Materiales Avanzados
Microbiological induced carbonate (CaCO3) precipitation using clay phyllites to replace chemical stabilizers (cement or lime)
Morales, L; Garzon, E; Romero, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Clay Science, 174 (2019) 15-28 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.03.018
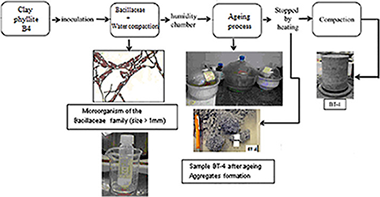
Abstract
The objective of the present study is to develop a biotechnological tool for a new application of clay phyllites as stabilized materials in linear works replacing chemical stabilizer (e.g. cement or lime) by natural cement, formed by precipitated calcium carbonate generated by microorganisms of the Bacillaceae family (Bacilluspasteurii). Part of the development process conducting a chemical and mineralogical characterization and an examination of physical and hydromechanical properties. The results of this study show that the effect of bacteria on clay phyllites increases the calcium carbonate content, specific surface area and plasticity values. These increased values are caused by the addition of a non-plastic component to clay phyllites resulting in a more aggregated structure through the precipitation of calcium carbonate from the bacteria, ultimately filling the pores of this material. Microbiological treatments on clay phyllites tends to aggregate the original particles, creating aggregates that are partially associated with the formation of calcium carbonate. Said process is influenced by the curing and compaction procedures conducted on samples, which also cause breakage of carbonated structures formed during treatment. As a result of this breaking process of aggregates, some compaction energy is lost and the treated samples do not reach the maximum dry density of the natural state for the same level of compaction energy applied. Treated samples display a slightly larger friction angle with no cohesion, consistent with filling properties and denser condition. Compressibility is consistently lower than that of the natural state. Comparison of collapse data showsthat the occurrence and amount of collapse are controlled by the as-compacted dry density. It is also determined that higher compaction effort is even more effective than increasing the amount of bacteria introduced to stabilize the sample for the filling of pores (size ranges 3–50 μm) with calcium carbonate. However, the post-ageing compaction destroys the initial binding/cementation effect.
June, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.03.018
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Coupling of WO3 with anatase TiO2 sample with high {001} facet exposition: Effect on the photocatalytic properties
Lara, M.A.; Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Navío, J.A.; Sánchez-Cid, P.; Hidalgo, M.C.Catalysis Today, 328 (2019) 142-148 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.012
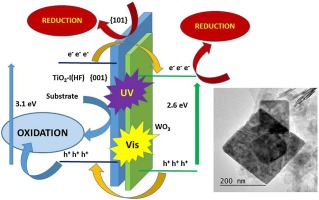
Abstract
A highly faceted {001} TiO2 catalyst was hydrothermally synthesized by using Ti(IV)-isopropoxide precursor with aqueous HF addition. WO3 was synthesized by following a reported method. Coupled TiO2-WO3 samples were synthesized by adding the corresponding amount of WO3 to fluorinated TiO2 gel followed by a hydrothermal treatment. Additionally the synthesized systems were characterized by using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) and N2-adsorption (BET) for specific surface area determination. The photocatalytic activity of the single and coupled oxides was measured by means of three model reactions: the photo-oxidation of phenol (as a colourless substrate) and methyl orange (as a dye) and the photoreduction of Cr(VI) as K2Cr2O7. The coupling of WO3 with a highly faceted {001} TiO2 makes it possible to optimize the photocatalytic properties of the faceted material. In fact, {001} faceted TiO2 by itself presents a substantial improvement with respect to commercial TiO2(P25), as it can implement its photoactivity after the incorporation of WO3 with promising results, which can reduce the limitations of TiO2 in terms of its photoactivity, taking advantage of a higher percentage of solar radiation.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Liquid switchable radial polarization converters made of sculptured thin films
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rico, VJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Arteaga, O; Bertran, E; Serna, R; Gonzalez-Elip, AR; Yubero, FApplied Surface Science, 475 (2019) 230-236 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.200
Abstract
A radial polarization converter is a super-structured optical retarder that converts a conventional linearly polarized light beam into a structured beam with radial or azimuthal polarization. We present a new type of these sophisticated optical elements, which is made of porous nanostructured sculptured single thin films or multilayers prepared by physical vapor deposition at an oblique angle. They are bestowed with an axisymmetric retardation activity (with the fast axis in a radial configuration). In particular, a Bragg microcavity multilayer that exhibits a tunable transmission peak in the visible range with a retardance of up to 0.35 rad has been fabricated using this methodology. Owing to the highly porous structure of this type of thin films and multilayers, their retardance could be switched off by liquid infiltration. These results prove the possibility of developing wavelength dependent (through multilayer optical design) and switchable (through vapor condensation or liquid infiltration within the pore structure) radial polarization converters by means of oblique angle physical vapor deposition.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.200
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Hydrophobicity, Freezing Delay, and Morphology of Laser-Treated Aluminum Surfaces
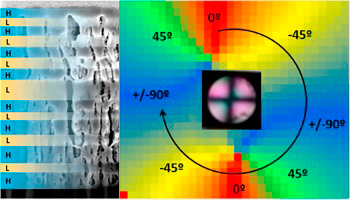
Rico, VJ; Lopez-Santos, C; Villagra, M; Espinos, JP; de la Fuente, GF; Angurel, LA; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARLangmuir, 35 (2019) 6483-6491 DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00457
Abstract
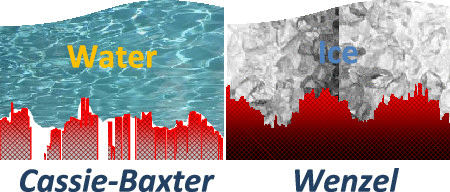
Until recently, superhydrophobicity was considered as a hint to predict surface icephobicity, an association of concepts that is by no means universal and that has been proven to depend on different experimental factors and material properties, including the actual morphology and chemical state of surfaces. This work presents a systematic study of the wetting and freezing properties of aluminum Al6061, a common material widely used in aviation, after being subjected to nanosecond pulsed IR laser treatments to modify its surface roughness and morphology. All treated samples, independent of their surface finishing state, presented initially an unstable hydrophilic wetting behavior that naturally evolved with time to reach hydrophobicity or even superhydrophobicity. To stabilize the surface state and to bestow the samples with a permanent and stable hydrophobic character, laser-treated surfaces were covered with a thin layer of CFx prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. A systematic comparison between freezing delay (FD) and wetting properties of water droplets onto these plasma-/polymer-modified laser-treated surfaces that, under conditions where a heterogeneous nucleation mechanism prevails, surface morphology rather than the actual value of the surface roughness parameter the key feature for long FD times. In particular, it is found that surface morphologies rendering a Cassie-Baxter wetting regime longer FDs than those characterized by a Wenzel-like wetting state. It is that laser treatment, with or without additional coverage with thin CFx coatings, affects wetting and ice formation behaviors and might be an efficient procedure to mitigate icing problems on metal surfaces.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00457
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
BixTiyOz-Fe multiphase systems with excellent photocatalytic performance in the visible
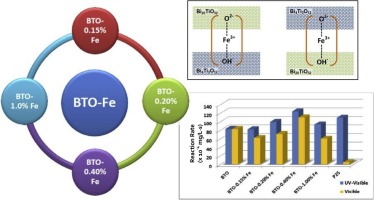
Zambrano, P.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Catalysis Today, 328 (2019) 136-141 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.032
Abstract
New photocatalysts based on bismuth titanates doped with iron with outstanding visible photocatalytic activity were prepared by a facile hydrothermal method followed by incipient wetness impregnation. The starting material was composed by three phases; majority of Bi20TiO32 closely interconnected to Bi4Ti3O12 and amorphous TiO2. Fe doping increased the already very high visible activity of the original material. The high visible activity showed by these materials could be ascribed to a combination of several features; i.e. low band gap energy value (as low as 1.78 eV), a structure allowing a good separation path for visible photogenerated electron-holes pairs and a relatively high surface area. Fe doping could be acting as bonding paths for the bismuth titanates phases, and the amount of Fe on the surface was found to be a crucial parameter on the photocatalytic activity of the materials. Visible activity of the best photocatalyst was superior to UV-Activity of commercial TiO2 P25 used as reference in same experimental conditions.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.032
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Surface nickel particles generated by exsolution from a perovskite structure
Aguero, FN; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, MA; Cadus, LEJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 273 (2019) 75-80 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2019.02.036

Abstract
LaAl1-xNixO3 (with x = 0.05 and 0.2) perovskite oxides were successfully synthesized and its behavior under reduction atmosphere was studied. HRTEM and STEM studies, coupled to HAADF and EDX detection, allowed to evidence the Ni exsolution process to the surface of the solid and to build nano-catalytic centers. The size of these centers is independent of the reduction conditions in the range studied. The high specific surface of the raw material, its porosity and the structure defects could be responsible of the low temperature at which the exsolution process starts. The content of Ni dopants allows the control of Ni centers size on the surface and the synthesis method provides Ni-nanoparticles strongly anchored to the resultant support.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2019.02.036
Amber imitation? Two unusual cases of Pinus resin-coated beads in Iberian Late Prehistory (3rd and 2nd millennia BC)
Odriozola, CP; Cordero, JAG; Daura, J; Sanz, M; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Aviles, MAPLoS One, 14 (2019) e0215469 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215469

Abstract
A group of beads from the artificial cave of La Molina (Lora de Estepa, Sevilla) and Cova del Gegant (Sitges, Barcelona) were made from a biogenic raw material and intentionally covered by a layer of resin. This is the first time this type of treatment has been documented on elements of adornment in the Late Prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula. The composition and nature of the coatings are analysed and the symbolic role of such alterations and imitations of prehistoric adornments is discussed.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215469
Reactividad de Sólidos
Manufacturing optimisation of an original nanostructured (beta plus gamma)-TiNbTa material
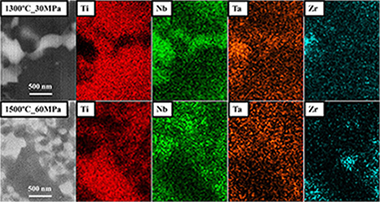
Garcia-Garrido, C; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, C; Torrecillas, R; Perez-Pozo, L; Salvo, C; Chicardi, EJournal of Materials Research and Technology-JMR&T, 8 (2019) 2573-2585 DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.03.004
Abstract
An original (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material was manufactured by an optimised powder metallurgy treatment, based on a mechanical alloying (MA) synthesis, carried out at low energy, and a subsequently field assisted consolidation technique, the pulsed electric current sintering (PECS). The successful development of this (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material was possible by the optimisation of the milling time (60 h) for the MA synthesis and the load and sintering temperature for the PECS (30 MPa and 1500 degrees C), as key parameters. Furthermore, the selected heating and cooling rates were 500 degrees C min(-1) and free cooling, respectively, to help maintain the lowest particle size and to avoid the formation of a detrimental high stiffness, hexagonal (alpha)-Ti alloy. All these optimised experimental conditions enabled the production of a full densified (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material, with partially nanostructured areas and two TiNbTa alloys, with a body centred cubic (beta) and a novel face-centred cubic (gamma) structures. The interesting microstructural characteristics gives the material high hardness and mechanical strength that, together with the known low elastic modulus for the beta-Ti alloys, makes them suitable for their use as potential biomaterials for bone replacement implants.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.03.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Phosphate-type supports for the design of WGS catalysts
Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 244 (2019) 853-862 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.022
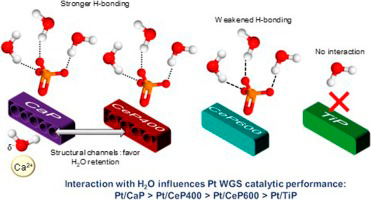
Abstract
The importance of water availability during the WGS reaction has been extensively reported. Thus, the search of new supports able to interact with the water molecule is of great importance. In this work, a series of phosphate type supports containing Ce, Ca and Ti have been studied, demonstrating that water interaction with the support is closely related to the textural properties, surface composition and crystal structure of the solids. Additionally, DRIFTS results showed that different interaction mechanisms with the water molecule occur depending on the support. The system containing Ca dissociates the water molecule and interacts with it via the phosphate and Ca2+ ions. However, the Ce systems retain water in its molecular form, which interacts with the solids via hydrogen bonding with the phosphate groups. On the other hand, the Ti system experiences a loss of phosphorous, presenting a low degree of interaction with the water molecule. Additionally, the behavior of the supports with water has been successfully related to the WGS catalytic activity of the corresponding phosphate supported Pt catalysts.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.022
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
3D core-multishell piezoelectric nanogenerators
A. Nicolas Filippin; Juan R.Sanchez-Valencia; Xabier Garcia-Casas; Victor Lopez-Flores; Manuel Macias-Montero; Fabian Frutos; Angel Barranco; Ana BorrasNano Energy, 58 (2019) 476-483 DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.047
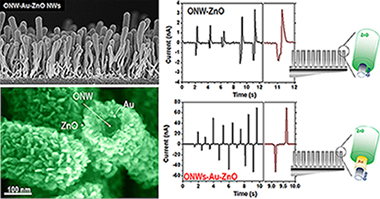
Abstract
The thin film configuration presents obvious practical advantages over the 1D implementation in energy harvesting systems such as easily manufacturing and processing, and long-lasting and stable devices. However, ZnO-based piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) generally rely on the exploitation of single-crystalline nanowires because of their self-orientation in the c-axis direction and ability to accommodate long deformations resulting in high piezoelectric performance. Herein, we show an innovative approach to produce PENGs by combining polycrystalline ZnO layers fabricated at room temperature by plasma-assisted deposition with supported small-molecule organic nanowires (ONWs) acting as 1D scaffolds. Such hybrid nanostructures present convoluted core-shell morphology, formed by a single-crystalline organic nanowire conformally surrounded by a poly-crystalline ZnO shell and combine the organic core mechanical properties with the ZnO layer piezoelectric response. In a step forward towards the integration of multiple functions within a single wire, we have also developed ONW-Au-ZnO nanoarchitectures including a gold shell acting as inner electrode achieving output piezo-voltages up to 170 mV. The synergistic combination of functionalities in the ONW-Au-ZnO devices promotes an enhanced performance generating piezo-currents one order of magnitude larger than the ONW-ZnO nanowires and superior to the thin film nanogenerators for equivalent and higher thicknesses.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.047
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Low molecular weight epsilon-caprolactone-p-coumaric acid copolymers as potential biomaterials for skin regeneration applications
Contardi, M; Alfaro-Pulido, A; Picone, P; Guzman-Puyol, S; Goldoni, L; Benitez, J; Heredia, A; Barthel, MJ; Ceseracciu, L; Cusimano, G; Brancato, OR; Di Carlo, M; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAPLoS One, 14 (2019) e0214956 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214956
Abstract
epsilon-caprolactone-p-coumaric acid copolymers at different mole ratios (epsilon-caprolactone: p-coumaric acid 1:0, 10:1, 8:1, 6:1, 4:1, and 2:1) were synthesized by melt-polycondensation and using 4-dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid as catalyst. Chemical analysis by NMR and GPC showed that copolyesters were formed with decreasing molecular weight as p-coumaric acid content was increased. Physical characteristics, such as thermal and mechanical properties, as well as water uptake and water permeability, depended on the mole fraction of p-coumaric acid. The p-coumarate repetitive units increased the antioxidant capacity of the copolymers, showing antibacterial activity against the common pathogen Escherichia coli. In addition, all the synthesized copolyesters, except the one with the highest concentration of the phenolic acid, were cytocompatible and hemocompatible, thus becoming potentially useful for skin regeneration applications.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214956
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Powder and Nanotubes Titania Modified by Dye Sensitization as Photocatalysts for the Organic Pollutants Elimination
Murcia, JJ; Avila-Martinez, EG; Rojas, H; Cubillos, J; Ivanova, S; Penkova, A; Laguna, OHNanomaterials, 9 (2019) 517 DOI: 10.3390/nano9040517
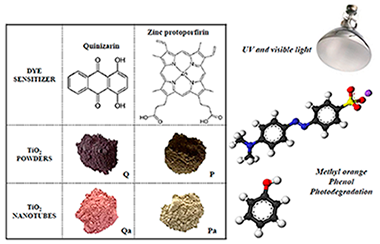
Abstract
In this study, titanium dioxide powder obtained by the sol-gel method and TiO2 nanotubes, were prepared. In order to increase the TiO2 photoactivity, the powders and nanotubes obtained were modified by dye sensitization treatment during the oxide synthesis. The sensitizers applied were Quinizarin (Q) and Zinc protoporphyrin (P). The materials synthesized were extensively characterized and it was found that the dye sensitization treatment leads to modify the optical and surface properties of Titania. It was also found that the effectiveness of the dye-sensitized catalysts in the phenol and methyl orange (MO) photodegradation strongly depends on the dye sensitizer employed. Thus, the highest degradation rate for MO was obtained over the conventional Q-TiO2 photocatalyst. In the case of the nanotubes series, the most effective photocatalyst in the MO degradation was based on TiO2-nanotubes sensitized with the dye protoporfirin (ZnP). Selected catalysts were also tested in the phenol and MO photodegradation under visible light and it was observed that these samples are also active under this radiation.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/nano9040517
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Effect of support oxygen storage capacity on the catalytic performance of Rh nanoparticles for CO2 reforming of methane
Yentekakis, IV; Goula, G; Hatzisymeon, M; Betsi-Argyropoulou, I; Botzolaki, G; Kousi, K; Kondarides, DI; Taylor, MJ; Parlett, CMA; Osatiashtiani, A; Kyriakou, G; Holgado, JP; Lambert, RMApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 243 (2019) 490-501 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.048
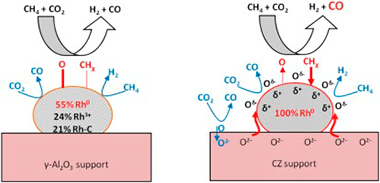
Abstract
The effects of the metal oxide support on the activity, selectivity, resistance to carbon deposition and high temperature oxidative aging on the Rh-catalyzed dry reforming of methane (DRM) were investigated. Three Rh catalysts supported on oxides characterized by very different oxygen storage capacities and labilities (gamma-Al2O3, alumina-ceria-zirconia (ACZ) and ceria-zirconia (CZ)) were studied in the temperature interval 400-750 degrees C under both integral and differential reaction conditions. ACZ and CZ promoted CO2 conversion, yielding CO enriched synthesis gas. Detailed characterization of these materials, including state of the art XPS measurements obtained via sample transfer between reaction cell and spectrometer chamber, provided clear insight into the factors that determine catalytic performance. The principal Rh species detected by post reaction XPS was Rh, its relative content decreasing in the order Rh/CZ(100%) > Rh/ACZ(72%) > Fth/gamma Al2O3(55%). The catalytic activity followed the same order, demonstrating unambiguously that Rh is indeed the key active site. Moreover, the presence of CZ in the support served to maintain Rh in the metallic state and minimize carbon deposition under reaction conditions. Carbon deposition, low in all cases, increased in the order Rh/CZ < Rh/ACZ < Rh/gamma-Al2O3 consistent with a bi-functional reaction mechanism whereby backspillover of labile lattice O2- contributes to carbon oxidation, stabilization of Rh and modification of its surface chemistry; the resulting O vacancies in the support providing centers for dissociative adsorption of CO2. The lower apparent activation energy observed with CZ-containing samples suggests that CZ is a promising support component for use in low temperature DRM.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.048
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Operando Spectroscopic Evidence of the Induced Effect of Residual Species in the Reaction Intermediates during CO2 Hydrogenation over Ruthenium Nanoparticles
Navarro-Jaen, S; Szego, A; Bobadilla, LF; Laguna, OH; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemcatchem, 11 (2019) 2063-2068 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900101
Abstract
In this work, we present a highly active catalyst based on Ru nanoparticles dispersed on alumina, which showed an unexpected activity for CO2 methanation. This exceptional catalytic behavior was attributed to the presence of residual species that remained on the surface after synthesis. Furthermore, through Operando DRIFTS (diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy) measurements it was demonstrated that these remaining species provoked an induced effect on the nature of the surface intermediates spectroscopically observed, and consequently on their mechanistic role during the pathway of the CO2 hydrogenation to methane.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900101
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Differences in the Catalytic Behavior of Au-Metalized TiO2 Systems During Phenol Photo-Degradation and CO Oxidation
Oscar H. Laguna; Julie J. Murcia; Hugo Rojas; Cesar Jaramillo-Paez; Jose A. Navío; Maria C. HidalgoCatalysts, 9 (2019) 331 DOI: 10.3390/catal9040331
Abstract
For this present work, a series of Au-metallized TiO2 catalysts were synthesized and characterized in order to compare their performance in two different catalytic environments: the phenol degradation that occurs during the liquid phase and in the CO oxidation phase, which proceeds the gas phase. The obtained materials were analyzed by different techniques such as XRF, SBET, XRD, TEM, XPS, and UV-Vis DRS. Although the metallization was not totally efficient in all cases, the amount of noble metal loaded depended strongly on the deposition time. Furthermore, the differences in the amount of loaded gold were important factors influencing the physicochemical properties of the catalysts, and consequently, their performances in the studied reactors. The addition of gold represented a considerable increase in the phenol conversion when compared with that of the TiO2, despite the small amount of noble metal loaded. However, this was not the case in the CO oxidation reaction. Beyond the differences in the phase where the reaction occurred, the loss of catalytic activity during the CO oxidation reaction was directly related to the sintering of the gold nanoparticles.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/catal9040331
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of heat treatment on apatite coatings deposited on pre-calcified titanium substrates
Beltran, AM; Martin-Santana, Y; Gonzalez, JE; Montealegre-Melendez, I; Gonzalez, E; Peon-Aves, E; Gotor, FJ; Torres, YInternational Journal of Materials Research, 110 (2019) 351-358 DOI: 10.3139/146.111746
Abstract
Titanium and its alloys are considered interesting materials for endosseous implants. However, they still present drawbacks related to their in-vivo behavior that can be overcome by coatings, such as apatite. This work focuses on the deposition of apatite coatings on commercially pure titanium (grade II) substrates previously pre-calcified. The influence of the temperature used in the thermal treatment on the microstructure and tribo-mechanical surface properties was analyzed. The coatings were structurally and chemically characterized and their tribo-mechanical behavior was evaluated. The nano-apatite coatings were only formed on surfaces with successive treatments in NaOH and CaCl2 solutions. In addition, scratch tests showed that after the heat treatment the nanoapatite coatings had high bond strength to the substrate.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.3139/146.111746
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser-induced coloration of ceramic tiles covered with magnetron sputtered precursor layers
Rico, VJ; Lahoz, R; Rey-Garcia, F; de Francisco, I; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; de la Fuente, GF; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1589-1598 DOI: 10.1111/jace.16022

Abstract
This paper reports a new methodology for the coloring of glazed ceramic tiles consisting of the near infrared pulsed laser processing of copper containing oxide coatings prepared by magnetron sputtering. As a second approach, the employ for the same purpose of a novel laser furnace technique is also described. Changing the laser parameters and using the laser furnace to treat the tiles at high temperature during irradiation has resulted in a wide color palette. The optical characterization of the modified tiles by UV-Vis spectroscopy has been complemented with their microstructural and compositional analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), and Time Of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (TOF-SIMS). The chemical composition of the surface was obtained by X-ray Photoemission Spectroscopy (XPS) and its structure determined by X?ray diffraction (XRD). The chemical resistance was characterized by several tests following the norm ISO 10545-13. Color changes have been attributed to surface microstructural and chemical transformations that have been accounted for by simple models involving different ablation, melting, diffusion, and segregation/agglomeration phenomena depending on the laser treatments employed.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.16022
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
UV and visible-light driven photocatalytic removal of caffeine using ZnO modified with different noble metals (Pt, Ag and Au)
Vaiano, V.; Jaramillo-Paez, C.A.; Matarangolo, M.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Materials Research Bulletin, 112 (2019) 251-260 DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.12.034

Abstract
In this work, ZnO photocatalyst was modified with different noble metals (Pt, Ag and Au) through photodeposition method and then characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, BET, UV–vis DRS, FESEM, and XPS). The addition of noble metals produces important changes in the light absorption properties with a significant absorbance in the visible region due to the existence of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) observed at about 450 nm and 550 nm for ZnO modified with Ag and Au, respectively. The morphology of the samples was studied by TEM and the size ranges of the different metals were estimated. Noble metal nanoparticles were in every case heterogeneously deposited on the larger ZnO particles. All the prepared photocatalysts were tested in the photocatalytic removal of caffeine (toxic and persistent emerging compound) under UV and visible light irradiation. It was observed an enhancement of photocatalytic caffeine removal from aqueous solutions under UV light irradiation with the increase of metal content (from 0.5 to 1 wt %) for ZnO modified with Ag and Au (Ag/ZnO and Au/ZnO). In particular, Ag/ZnO and Au/ZnO with higher Ag and Au content (1 wt %) allowed to achieve the almost complete caffeine degradation after only 30 min and a TOC removal higher than 90% after 4 h of UV light irradiation. These two photocatalysts were investigated also under visible light irradiation and it was found that their photocatalytic performances were strongly enhanced in presence of visible light compared to unmodified ZnO. In particular, Ag/ZnO photocatalyst was able to reach the complete caffeine degradation and a TOC removal of about 70% after 4 h of visible light irradiation.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.12.034
Reactividad de Sólidos
Tribological behavior of graphene nanoplatelet reinforced 3YTZP composites
Gutierrez-Mora, F; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 39 (2019) 1381-1388 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.11.005

Abstract
The tribological behavior of graphene nanoplatelet (GNP) reinforced 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (3YTZP) composites with different GNP content (2.5, 5 and 10 vol%) was analyzed and discussed. Their dry sliding behavior was studied using a ball-on-disk geometry with zirconia balls as counterparts, using loads between 2 and 20 N at ambient conditions and compared to the behavior of a monolithic 3YTZP ceramic used as a reference material. The composites showed lower friction coefficients and higher wear resistance than the monolithic 3YTZP. An outstanding performance was achieved at 10 N, where the friction coefficient decreased from 0.6 to 0.3 and the wear rates decreased 3 orders of magnitude in comparison with the monolithic ceramic. A layer adhered to the worn surface was found for all the composites, but it did not acted as a lubricating film. The composites with the lowest GNP content showed an overall improved tribological behavior.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.11.005
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
CuxCo3-xO4 ultra-thin film as efficient anodic catalysts for anion exchange membrane water electrolysers
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, F; de Lucas-Consuegra, AJournal of Power Sources, 415 (2019) 136-144 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.01.056
Abstract
CuxCo3-xO4 ultra-thin films, deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles have been used as anodic catalysts in anion exchange membrane water electrolysers. It has been demonstrated that the used deposition procedure provides porous and amorphous samples with a strict control of the total catalyst load and Co/Cu ratio. Electrocatalytic tests showed a maximum performance for the oxygen evolution reaction at Co/Cu atomic ratio around 1.8. The optimized anodic catalyst presented a long-term stability confirmed by accelerated lifetime tests together with the chemical surface analysis of the used samples. The effect of the crystallization of a single layer CuxCo3-xO4 and a multilayer (CuO/Co3O4)(n) anodic catalyst samples was also investigated. The observed loss of catalytic performance found in both cases may prove that a particular local chemical environment around the Co and Cu sites acts as an efficient catalytic site for the oxygen evolution reaction. A catalyst film with the optimum Co/Cu atomic ratio was incorporated into a Membrane Electrode Assembly, using a sputtered Ni film as cathode. Current density values up to 100 mA cm(-2) at 2.0 V were obtained in 1.0 M KOH electrolyte. Upon normalization by the amount of catalyst, this performance is one of the highest reported in literature.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.01.056
Technological evolution of ceramic glazes in the renaissance: In situ analysis of tiles in the Alcazar (Seville, Spain)
de Viguerie, Laurence; Robador, Maria D.; Castaing, Jacques; Perez-Rodriguez, Jose L.; Walter, Philippe; Bouquillon, AnneJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1402-1413 DOI: 10.1111/jace.15955
Abstract
The Alcazar Palace (Seville, Spain) is famous for its ceramic decorations; 16th century wall tiles of different typologies have been analyzed in order to relate the manufacturing process of their colored glazes to the evolving technologies of the Renaissance. Chemical and mineralogical compositions have been determined in situ by nondestructive X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction on arista ceramics in the Cenador de Carlos Quinto, and majolica ceramics in the Palacio Gotico and the Royal oratory. The arista style belongs to the local Hispano-Moresque ceramic tradition. Majolica tiles have the complex microstructures of glazes from Italy. The two types are clearly differentiated by their typology, morphology (curved vs flat surface), and also microstructure (single vs multi-layers), glaze chemistry, and use of different coloring agents. Moreover, we found different glaze chemistries in the investigated majolicas, which correspond to different artists and/or practices.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.15955
Reactividad de Sólidos
A theoretical study of the bonding capabilities of the zinc-zinc double bond
Ayala, R; Galindo, AInternational Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 119 (2019) e25823 DOI: 10.1002/qua.25823
Abstract
The theoretical knowledge about the zinc-zinc bond has been recently expanded after the proposal of a zinc-zinc double bond in several [Zn-2(L)(4)] compounds (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2017, 56, 10151-10155). Prompted by these results, we have selected the [Zn-2(CO)(4)] species, isolobally related to ethylene, and theoretically investigated the possible (2)-Zn-2-coordination to several first-row transition metal fragments. The [Zn-2(CO)(4)] coordination to the metal fragment produces an elongation of the dizinc bond and a concomitant pyramidalization of the [Zn(CO)(2)] unit. These structural parameters are indicative of -backdonation from the metal to the coordinated dizinc moiety, as occurred with ethylene ligand. A quantum theory of atoms in molecules study of the ZnZn bond shows a decrease of (BCP), delta(2)(BCP) (ZnZn) and delocalization indexes (Zn,Zn), relative to corresponding values in the parent [Zn-2(CO)(4)] molecule. The ZnZn and MZn bonds in these [((2)-Zn-2(CO)(4))M(L)(n)] complexes can be described as shared interactions with an important covalent component where the ZnZn bond is preserved, albeit weakened, upon coordination.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/qua.25823
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Promoting effect of CeO2, ZrO2 and Ce/Zr mixed oxides on Co/gamma-Al2O3 catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
Garcilaso, V; Barrientos, J; Bobadilla, LF; Laguna, OH; Boutonnet, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JARenewable Energy, 132 (2019) 1141-1150 DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.080
Abstract
A series of cobalt-based catalysts have been synthesized using as support gamma-Al2O3 promoted by ceria/zirconia mixed oxides with a variable Ce/Zr molar ratio. The obtained catalysts demonstrated oxide promotion results in the protection of the major textural properties, especially for Zr-rich solids. Reducibility of cobalt species was enhanced by the presence of mixed oxides. The chemical composition of the oxide promoter influenced not only physicochemical properties of final catalysts but also determined their performance during the reaction. In this sense, Zr-rich systems presented a superior catalytic performance both in total conversion and in selectivity towards long chain hydrocarbons. The observed Zr-promotion effect could be explained by two significant contributions: firstly, the partial inhibition of Co-Al spinel compound formation by the presence of Zr-rich phases which enhances the availability of Co actives site and secondly, Zr-associate acidic sites promote higher hydrocarbons selectivity.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.080
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Combining dietary phenolic antioxidants with polyvinylpyrrolidone: transparent biopolymer films based on p-coumaric acid for controlled release
Contardi, M; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Guzman-Puyol, S; Summa, M; Benitez, JJ; Goldoni, L; Caputo, G; Cusimano, G; Picone, P; Di Carlo, M; Bertorelli, R; Athanassioua, A; Bayer, ISJournal of Materials Chemistry B, 7 (2019) 1384-1396 DOI: 10.1039/c8tb03017k
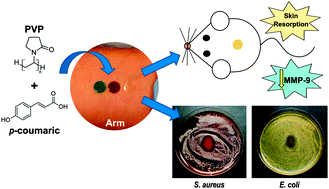
Abstract
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) has probably been one of the most utilized pharmaceutical polymers with applications ranging from a blood plasma substitute to nanoparticle drug delivery, since its synthesis in 1939. It is a highly biocompatible, non-toxic and transparent film forming polymer. Although high solubility of PVP in aqueous environment is advantageous, it still poses several problems for some applications in which sustained targeting and release are needed or hydrophobic drug inclusion and delivery systems are to be designed. In this study, we demonstrate that a common dietary phenolic antioxidant, p-coumaric acid (PCA), can be combined with PVP covering a wide range of molar ratios by solution blending in ethanol, forming new transparent biomaterial films with antiseptic and antioxidant properties. PCA not only acts as an effective natural plasticizer but also establishes H-bonds with PVP increasing its resistance to water dissolution. PCA could be released in a sustained manner up to a period of 3 days depending on the PVP/ PCA molar ratio. Sustained drug delivery potential of the films was studied using methylene blue and carminic acid as model drugs, indicating that the release can be controlled. Antioxidant and remodeling properties of the films were evaluated in vitro by free radical cation scavenging assay and in vivo on a murine model, respectively. Furthermore, the material resorption of films was slower as PCA concentration increased, as observed from the in vivo full-thickness excision model. Finally, the antibacterial activity of the films against common pathogens such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus and the effective reduction of inflammatory agents such as matrix metallopeptidases were demonstrated. All these properties suggest that these new transparent PVP/ PCA films can find a plethora of applications in pharmaceutical sciences including skin and wound care.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1039/c8tb03017k
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Transparent and Robust All-Cellulose Nanocomposite Packaging Materials Prepared in a Mixture of Trifluoroacetic Acid and Trifluoroacetic Anhydride
Guzman-Puyol, S; Ceseracciu, L; Tedeschi, G; Marras, S; Scarpellini, A; Benitez, JJ; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JANanomaterials, 9 (2019) 368 DOI: 10.3390/nano9030368
Abstract
All-cellulose composites with a potential application as food packaging films were prepared by dissolving microcrystalline cellulose in a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic anhydride, adding cellulose nanofibers, and evaporating the solvents. First, the effect of the solvents on the morphology, structure, and thermal properties of the nanofibers was evaluated by atomic force microscopy (AFM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), respectively. An important reduction in the crystallinity was observed. Then, the optical, morphological, mechanical, and water barrier properties of the nanocomposites were determined. In general, the final properties of the composites depended on the nanocellulose content. Thus, although the transparency decreased with the amount of cellulose nanofibers due to increased light scattering, normalized transmittance values were higher than 80% in all the cases. On the other hand, the best mechanical properties were achieved for concentrations of nanofibers between 5 and 9 wt.%. At higher concentrations, the cellulose nanofibers aggregated and/or folded, decreasing the mechanical parameters as confirmed analytically by modeling of the composite Young's modulus. Finally, regarding the water barrier properties, water uptake was not affected by the presence of cellulose nanofibers while water permeability was reduced because of the higher tortuosity induced by the nanocelluloses. In view of such properties, these materials are suggested as food packaging films.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/nano9030368
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
The impact of photocatalytic Ag/TiO2 and Ag/N-TiO2 nanoparticles on human keratinocytes and epithelial lung cells
Rebleanu, D; Gaidau, C; Voicu, G; Constantinescu, CA; Sanchez, CM; Rojas, TC; Carvalho, S; Calin, MToxicology, 416 (2019) 30-43 DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2019.01.013
Abstract
The potential human health risks following the exposure to inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) is a very important issue for their application in leather finishing industry. The aim of our study was to investigate the cytotoxic effect of silver (Ag)/titanium dioxide (TiO2) NPs on human cells. Photocatalytic NPs were prepared by electrochemical deposition of Ag on the surface of TiO2 and nitrogen (N)-TiO2 NPs and, subsequently, physicochemical characterized. Then, a set of experiments have been performed to study the cytotoxicity and cell death mechanisms involved, the changes in cell morphology and the production of ROS induced in human keratinocytes (HaCaT) and human lung epithelial cells (A549) by exposure to NPs. Moreover, the changes in major signaling pathways and the inflammatory response induced by Ag/N-TiO2 NPs in A549 cells were investigated. The data showed that cell death by late apoptosis/necrosis is induced in cells as function of the dose and the type of NPs and is characterized by morphological changes and cytoskeletal disorganization and an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. The exposure of A549 cells to Ag/N-TiO2 NPs determine the activation of ERK1/2 MAP-kinase pathway and the release of pro-inflammatory mediators CXCL1, GM-CSF and MIF, known to be involved in the recruitment of circulating neutrophils and monocytes.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2019.01.013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Controlled thermolysis of MIL-101(Fe, Cr) for synthesis of FexOy/porous carbon as negative electrode and Cr2O3/porous carbon as positive electrode of supercapacitor
Farisabadi, A; Moradi, M; Hajati, S; Kiani, MA; Espinos, JPApplied Surface Science, 469 (2019) 192-203 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.053
Abstract
In the present study, two kinds of metal oxide/carbon nanocomposite were prepared through calcination of MIL-101(Fe, Cr). The morphological and structural properties of the specimens were investigated using X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller analysis, energy dispersive Xray spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The electrode materials were also electrochemically investigated using cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge-discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy techniques in 6 M KOH electrolyte. Because of synergistic effect of metal oxides and carbon, the obtained samples showed excellent performance; in a way that Cr2O3/C and Fe Oy/C showed high specific capacitance of 420 F g(-1) and 114 F g(-1) at current density of 2 A g(-1), respectively. The Cr2O3/C electrode also displayed high rate capability even at scan rate of 1500 mV s(-1). Moreover, we successfully developed an asymmetric supercapacitor in which Cr2O3/C served as positive electrode and Fe Oy/C served as negative electrode. The asymmetric device can deliver an energy density of 9.6 W h kg(-1) and power density of 8000 W kg(-1), with 93% capacitance retention after 3000 charge-discharge cycles. These outcomes show that the MOF-derived metal oxide/carbon composite can be regarded as a promising development for advanced electrode materials for applying in supercapacitors.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.053
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
XPS primary excitation spectra of Zn 2p, Fe 2p, and Ce 3d from ZnO, α‐Fe2O3, and CeO2
Pauly, N.; Yubero, F.; Espinós, J.P.; Tougaard, S.Surface and Interface Analysis, 51 (2019) 353-360 DOI: 10.1002/sia.6587

Abstract
Metal oxides are important for current development in nanotechnology. X‐ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS) is a widely used technique to study the oxidation states of metals, and a basic understanding of the photoexcitation process is important to obtain the full information from XPS. We have studied core level excitations of Zn 2p, Fe 2p, and Ce 3d photoelectron emissions from ZnO, α‐Fe2O3, and CeO2. Using an effective energy‐differential XPS inelastic‐scattering cross section evaluated within the semiclassical dielectric response model for XPS, we analysed the experimental spectra to determine the corresponding primary excitation spectra, ie, the initial excitation processes. We find that simple emission (Zn 2p) as well as complex multiplet photoemission spectra (Fe 2p and Ce 3d) can be quantitatively analysed with our procedure. Moreover, for α‐Fe2O3, it is possible to use the software package CTM4XAS (Charge Transfer Multiplet program for X‐ray Absorption Spectroscopy) to calculate its primary excitation spectrum within a quantum mechanical model, and it was found to be in good agreement with the spectrum determined by analysis of the experiment.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/sia.6587
- ‹ previous
- 13 of 37
- next ›














