Scientific Papers in SCI
2019
2019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Multifunctional antimicrobial chlorhexidine polymers by remote plasma assisted vacuum deposition
Mora-Boza, A; Aparicio, FJ; Alcaire, M; Lopez-Santos, C; Espinos, JP; Torres-Lagares, D; Borras, A; Barranco, AFrontiers of chemical science and engineering, 13 (2019) 330-339 DOI: 10.1007/s11705-019-1803-6

Abstract
Novel antibacterial materials for implants and medical instruments are essential to develop practical strategies to stop the spread of healthcare associated infections. This study presents the synthesis of multifunctional antibacterial nanocoatings on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) by remote plasma assisted deposition of sublimated chlorhexidine powders at low pressure and room temperature. The obtained materials present effective antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli K12, either by contact killing and antibacterial adhesion or by biocide agents release depending on the synthetic parameters. In addition, these multifunctional coatings allow the endure hydrophilization of the hydrophobic PDMS surface, thereby improving their biocompatibility. Importantly, cell-viability tests conducted on these materials also prove their non-cytotoxicity, opening a way for the integration of this type of functional plasma films in biomedical devices.
June, 2019 · DOI: 10.1007/s11705-019-1803-6
Amber imitation? Two unusual cases of Pinus resin-coated beads in Iberian Late Prehistory (3rd and 2nd millennia BC)
Odriozola, CP; Cordero, JAG; Daura, J; Sanz, M; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Aviles, MAPLoS One, 14 (2019) e0215469 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215469

Abstract
A group of beads from the artificial cave of La Molina (Lora de Estepa, Sevilla) and Cova del Gegant (Sitges, Barcelona) were made from a biogenic raw material and intentionally covered by a layer of resin. This is the first time this type of treatment has been documented on elements of adornment in the Late Prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula. The composition and nature of the coatings are analysed and the symbolic role of such alterations and imitations of prehistoric adornments is discussed.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215469
Reactividad de Sólidos
Manufacturing optimisation of an original nanostructured (beta plus gamma)-TiNbTa material
Garcia-Garrido, C; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, C; Torrecillas, R; Perez-Pozo, L; Salvo, C; Chicardi, EJournal of Materials Research and Technology-JMR&T, 8 (2019) 2573-2585 DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.03.004
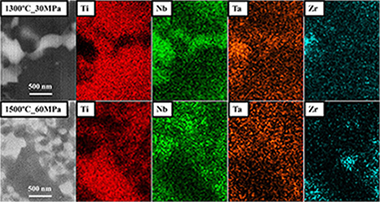
Abstract
An original (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material was manufactured by an optimised powder metallurgy treatment, based on a mechanical alloying (MA) synthesis, carried out at low energy, and a subsequently field assisted consolidation technique, the pulsed electric current sintering (PECS). The successful development of this (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material was possible by the optimisation of the milling time (60 h) for the MA synthesis and the load and sintering temperature for the PECS (30 MPa and 1500 degrees C), as key parameters. Furthermore, the selected heating and cooling rates were 500 degrees C min(-1) and free cooling, respectively, to help maintain the lowest particle size and to avoid the formation of a detrimental high stiffness, hexagonal (alpha)-Ti alloy. All these optimised experimental conditions enabled the production of a full densified (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material, with partially nanostructured areas and two TiNbTa alloys, with a body centred cubic (beta) and a novel face-centred cubic (gamma) structures. The interesting microstructural characteristics gives the material high hardness and mechanical strength that, together with the known low elastic modulus for the beta-Ti alloys, makes them suitable for their use as potential biomaterials for bone replacement implants.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.03.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Phosphate-type supports for the design of WGS catalysts
Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 244 (2019) 853-862 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.022
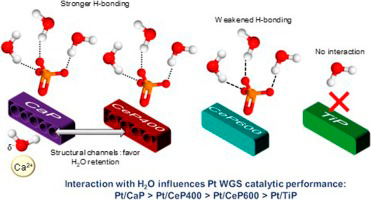
Abstract
The importance of water availability during the WGS reaction has been extensively reported. Thus, the search of new supports able to interact with the water molecule is of great importance. In this work, a series of phosphate type supports containing Ce, Ca and Ti have been studied, demonstrating that water interaction with the support is closely related to the textural properties, surface composition and crystal structure of the solids. Additionally, DRIFTS results showed that different interaction mechanisms with the water molecule occur depending on the support. The system containing Ca dissociates the water molecule and interacts with it via the phosphate and Ca2+ ions. However, the Ce systems retain water in its molecular form, which interacts with the solids via hydrogen bonding with the phosphate groups. On the other hand, the Ti system experiences a loss of phosphorous, presenting a low degree of interaction with the water molecule. Additionally, the behavior of the supports with water has been successfully related to the WGS catalytic activity of the corresponding phosphate supported Pt catalysts.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.022
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Coupling of WO3 with anatase TiO2 sample with high {001} facet exposition: Effect on the photocatalytic properties
Lara, M.A.; Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Navío, J.A.; Sánchez-Cid, P.; Hidalgo, M.C.Catalysis Today, 328 (2019) 142-148 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.012
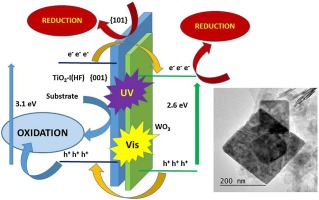
Abstract
A highly faceted {001} TiO2 catalyst was hydrothermally synthesized by using Ti(IV)-isopropoxide precursor with aqueous HF addition. WO3 was synthesized by following a reported method. Coupled TiO2-WO3 samples were synthesized by adding the corresponding amount of WO3 to fluorinated TiO2 gel followed by a hydrothermal treatment. Additionally the synthesized systems were characterized by using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) and N2-adsorption (BET) for specific surface area determination. The photocatalytic activity of the single and coupled oxides was measured by means of three model reactions: the photo-oxidation of phenol (as a colourless substrate) and methyl orange (as a dye) and the photoreduction of Cr(VI) as K2Cr2O7. The coupling of WO3 with a highly faceted {001} TiO2 makes it possible to optimize the photocatalytic properties of the faceted material. In fact, {001} faceted TiO2 by itself presents a substantial improvement with respect to commercial TiO2(P25), as it can implement its photoactivity after the incorporation of WO3 with promising results, which can reduce the limitations of TiO2 in terms of its photoactivity, taking advantage of a higher percentage of solar radiation.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Liquid switchable radial polarization converters made of sculptured thin films
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rico, VJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Arteaga, O; Bertran, E; Serna, R; Gonzalez-Elip, AR; Yubero, FApplied Surface Science, 475 (2019) 230-236 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.200
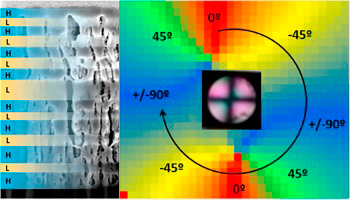
Abstract
A radial polarization converter is a super-structured optical retarder that converts a conventional linearly polarized light beam into a structured beam with radial or azimuthal polarization. We present a new type of these sophisticated optical elements, which is made of porous nanostructured sculptured single thin films or multilayers prepared by physical vapor deposition at an oblique angle. They are bestowed with an axisymmetric retardation activity (with the fast axis in a radial configuration). In particular, a Bragg microcavity multilayer that exhibits a tunable transmission peak in the visible range with a retardance of up to 0.35 rad has been fabricated using this methodology. Owing to the highly porous structure of this type of thin films and multilayers, their retardance could be switched off by liquid infiltration. These results prove the possibility of developing wavelength dependent (through multilayer optical design) and switchable (through vapor condensation or liquid infiltration within the pore structure) radial polarization converters by means of oblique angle physical vapor deposition.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.200
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Hydrophobicity, Freezing Delay, and Morphology of Laser-Treated Aluminum Surfaces
Rico, VJ; Lopez-Santos, C; Villagra, M; Espinos, JP; de la Fuente, GF; Angurel, LA; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARLangmuir, 35 (2019) 6483-6491 DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00457
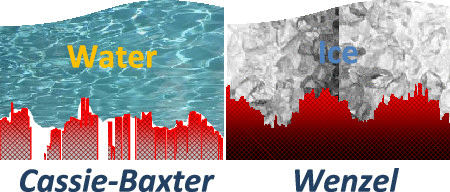
Abstract
Until recently, superhydrophobicity was considered as a hint to predict surface icephobicity, an association of concepts that is by no means universal and that has been proven to depend on different experimental factors and material properties, including the actual morphology and chemical state of surfaces. This work presents a systematic study of the wetting and freezing properties of aluminum Al6061, a common material widely used in aviation, after being subjected to nanosecond pulsed IR laser treatments to modify its surface roughness and morphology. All treated samples, independent of their surface finishing state, presented initially an unstable hydrophilic wetting behavior that naturally evolved with time to reach hydrophobicity or even superhydrophobicity. To stabilize the surface state and to bestow the samples with a permanent and stable hydrophobic character, laser-treated surfaces were covered with a thin layer of CFx prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. A systematic comparison between freezing delay (FD) and wetting properties of water droplets onto these plasma-/polymer-modified laser-treated surfaces that, under conditions where a heterogeneous nucleation mechanism prevails, surface morphology rather than the actual value of the surface roughness parameter the key feature for long FD times. In particular, it is found that surface morphologies rendering a Cassie-Baxter wetting regime longer FDs than those characterized by a Wenzel-like wetting state. It is that laser treatment, with or without additional coverage with thin CFx coatings, affects wetting and ice formation behaviors and might be an efficient procedure to mitigate icing problems on metal surfaces.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00457
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
BixTiyOz-Fe multiphase systems with excellent photocatalytic performance in the visible
Zambrano, P.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Catalysis Today, 328 (2019) 136-141 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.032
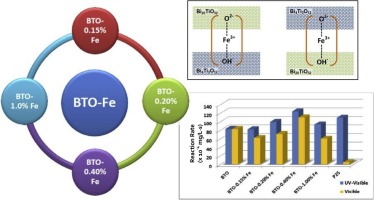
Abstract
New photocatalysts based on bismuth titanates doped with iron with outstanding visible photocatalytic activity were prepared by a facile hydrothermal method followed by incipient wetness impregnation. The starting material was composed by three phases; majority of Bi20TiO32 closely interconnected to Bi4Ti3O12 and amorphous TiO2. Fe doping increased the already very high visible activity of the original material. The high visible activity showed by these materials could be ascribed to a combination of several features; i.e. low band gap energy value (as low as 1.78 eV), a structure allowing a good separation path for visible photogenerated electron-holes pairs and a relatively high surface area. Fe doping could be acting as bonding paths for the bismuth titanates phases, and the amount of Fe on the surface was found to be a crucial parameter on the photocatalytic activity of the materials. Visible activity of the best photocatalyst was superior to UV-Activity of commercial TiO2 P25 used as reference in same experimental conditions.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.032
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Surface nickel particles generated by exsolution from a perovskite structure
Aguero, FN; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, MA; Cadus, LEJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 273 (2019) 75-80 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2019.02.036

Abstract
LaAl1-xNixO3 (with x = 0.05 and 0.2) perovskite oxides were successfully synthesized and its behavior under reduction atmosphere was studied. HRTEM and STEM studies, coupled to HAADF and EDX detection, allowed to evidence the Ni exsolution process to the surface of the solid and to build nano-catalytic centers. The size of these centers is independent of the reduction conditions in the range studied. The high specific surface of the raw material, its porosity and the structure defects could be responsible of the low temperature at which the exsolution process starts. The content of Ni dopants allows the control of Ni centers size on the surface and the synthesis method provides Ni-nanoparticles strongly anchored to the resultant support.
May, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2019.02.036
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Differences in the Catalytic Behavior of Au-Metalized TiO2 Systems During Phenol Photo-Degradation and CO Oxidation
Oscar H. Laguna; Julie J. Murcia; Hugo Rojas; Cesar Jaramillo-Paez; Jose A. Navío; Maria C. HidalgoCatalysts, 9 (2019) 331 DOI: 10.3390/catal9040331
Abstract
For this present work, a series of Au-metallized TiO2 catalysts were synthesized and characterized in order to compare their performance in two different catalytic environments: the phenol degradation that occurs during the liquid phase and in the CO oxidation phase, which proceeds the gas phase. The obtained materials were analyzed by different techniques such as XRF, SBET, XRD, TEM, XPS, and UV-Vis DRS. Although the metallization was not totally efficient in all cases, the amount of noble metal loaded depended strongly on the deposition time. Furthermore, the differences in the amount of loaded gold were important factors influencing the physicochemical properties of the catalysts, and consequently, their performances in the studied reactors. The addition of gold represented a considerable increase in the phenol conversion when compared with that of the TiO2, despite the small amount of noble metal loaded. However, this was not the case in the CO oxidation reaction. Beyond the differences in the phase where the reaction occurred, the loss of catalytic activity during the CO oxidation reaction was directly related to the sintering of the gold nanoparticles.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/catal9040331
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
UV and visible-light driven photocatalytic removal of caffeine using ZnO modified with different noble metals (Pt, Ag and Au)
Vaiano, V.; Jaramillo-Paez, C.A.; Matarangolo, M.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Materials Research Bulletin, 112 (2019) 251-260 DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.12.034

Abstract
In this work, ZnO photocatalyst was modified with different noble metals (Pt, Ag and Au) through photodeposition method and then characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, BET, UV–vis DRS, FESEM, and XPS). The addition of noble metals produces important changes in the light absorption properties with a significant absorbance in the visible region due to the existence of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) observed at about 450 nm and 550 nm for ZnO modified with Ag and Au, respectively. The morphology of the samples was studied by TEM and the size ranges of the different metals were estimated. Noble metal nanoparticles were in every case heterogeneously deposited on the larger ZnO particles. All the prepared photocatalysts were tested in the photocatalytic removal of caffeine (toxic and persistent emerging compound) under UV and visible light irradiation. It was observed an enhancement of photocatalytic caffeine removal from aqueous solutions under UV light irradiation with the increase of metal content (from 0.5 to 1 wt %) for ZnO modified with Ag and Au (Ag/ZnO and Au/ZnO). In particular, Ag/ZnO and Au/ZnO with higher Ag and Au content (1 wt %) allowed to achieve the almost complete caffeine degradation after only 30 min and a TOC removal higher than 90% after 4 h of UV light irradiation. These two photocatalysts were investigated also under visible light irradiation and it was found that their photocatalytic performances were strongly enhanced in presence of visible light compared to unmodified ZnO. In particular, Ag/ZnO photocatalyst was able to reach the complete caffeine degradation and a TOC removal of about 70% after 4 h of visible light irradiation.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.12.034
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of heat treatment on apatite coatings deposited on pre-calcified titanium substrates
Beltran, AM; Martin-Santana, Y; Gonzalez, JE; Montealegre-Melendez, I; Gonzalez, E; Peon-Aves, E; Gotor, FJ; Torres, YInternational Journal of Materials Research, 110 (2019) 351-358 DOI: 10.3139/146.111746
Abstract
Titanium and its alloys are considered interesting materials for endosseous implants. However, they still present drawbacks related to their in-vivo behavior that can be overcome by coatings, such as apatite. This work focuses on the deposition of apatite coatings on commercially pure titanium (grade II) substrates previously pre-calcified. The influence of the temperature used in the thermal treatment on the microstructure and tribo-mechanical surface properties was analyzed. The coatings were structurally and chemically characterized and their tribo-mechanical behavior was evaluated. The nano-apatite coatings were only formed on surfaces with successive treatments in NaOH and CaCl2 solutions. In addition, scratch tests showed that after the heat treatment the nanoapatite coatings had high bond strength to the substrate.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.3139/146.111746
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser-induced coloration of ceramic tiles covered with magnetron sputtered precursor layers
Rico, VJ; Lahoz, R; Rey-Garcia, F; de Francisco, I; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; de la Fuente, GF; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1589-1598 DOI: 10.1111/jace.16022

Abstract
This paper reports a new methodology for the coloring of glazed ceramic tiles consisting of the near infrared pulsed laser processing of copper containing oxide coatings prepared by magnetron sputtering. As a second approach, the employ for the same purpose of a novel laser furnace technique is also described. Changing the laser parameters and using the laser furnace to treat the tiles at high temperature during irradiation has resulted in a wide color palette. The optical characterization of the modified tiles by UV-Vis spectroscopy has been complemented with their microstructural and compositional analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), and Time Of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (TOF-SIMS). The chemical composition of the surface was obtained by X-ray Photoemission Spectroscopy (XPS) and its structure determined by X?ray diffraction (XRD). The chemical resistance was characterized by several tests following the norm ISO 10545-13. Color changes have been attributed to surface microstructural and chemical transformations that have been accounted for by simple models involving different ablation, melting, diffusion, and segregation/agglomeration phenomena depending on the laser treatments employed.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.16022
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
3D core-multishell piezoelectric nanogenerators
A. Nicolas Filippin; Juan R.Sanchez-Valencia; Xabier Garcia-Casas; Victor Lopez-Flores; Manuel Macias-Montero; Fabian Frutos; Angel Barranco; Ana BorrasNano Energy, 58 (2019) 476-483 DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.047
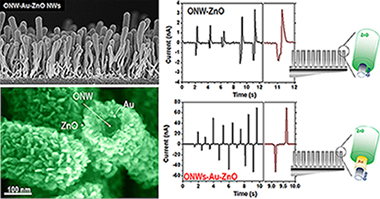
Abstract
The thin film configuration presents obvious practical advantages over the 1D implementation in energy harvesting systems such as easily manufacturing and processing, and long-lasting and stable devices. However, ZnO-based piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) generally rely on the exploitation of single-crystalline nanowires because of their self-orientation in the c-axis direction and ability to accommodate long deformations resulting in high piezoelectric performance. Herein, we show an innovative approach to produce PENGs by combining polycrystalline ZnO layers fabricated at room temperature by plasma-assisted deposition with supported small-molecule organic nanowires (ONWs) acting as 1D scaffolds. Such hybrid nanostructures present convoluted core-shell morphology, formed by a single-crystalline organic nanowire conformally surrounded by a poly-crystalline ZnO shell and combine the organic core mechanical properties with the ZnO layer piezoelectric response. In a step forward towards the integration of multiple functions within a single wire, we have also developed ONW-Au-ZnO nanoarchitectures including a gold shell acting as inner electrode achieving output piezo-voltages up to 170 mV. The synergistic combination of functionalities in the ONW-Au-ZnO devices promotes an enhanced performance generating piezo-currents one order of magnitude larger than the ONW-ZnO nanowires and superior to the thin film nanogenerators for equivalent and higher thicknesses.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.047
Reactividad de Sólidos
Tribological behavior of graphene nanoplatelet reinforced 3YTZP composites
Gutierrez-Mora, F; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 39 (2019) 1381-1388 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.11.005

Abstract
The tribological behavior of graphene nanoplatelet (GNP) reinforced 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (3YTZP) composites with different GNP content (2.5, 5 and 10 vol%) was analyzed and discussed. Their dry sliding behavior was studied using a ball-on-disk geometry with zirconia balls as counterparts, using loads between 2 and 20 N at ambient conditions and compared to the behavior of a monolithic 3YTZP ceramic used as a reference material. The composites showed lower friction coefficients and higher wear resistance than the monolithic 3YTZP. An outstanding performance was achieved at 10 N, where the friction coefficient decreased from 0.6 to 0.3 and the wear rates decreased 3 orders of magnitude in comparison with the monolithic ceramic. A layer adhered to the worn surface was found for all the composites, but it did not acted as a lubricating film. The composites with the lowest GNP content showed an overall improved tribological behavior.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.11.005
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Low molecular weight epsilon-caprolactone-p-coumaric acid copolymers as potential biomaterials for skin regeneration applications
Contardi, M; Alfaro-Pulido, A; Picone, P; Guzman-Puyol, S; Goldoni, L; Benitez, J; Heredia, A; Barthel, MJ; Ceseracciu, L; Cusimano, G; Brancato, OR; Di Carlo, M; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAPLoS One, 14 (2019) e0214956 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214956
Abstract
epsilon-caprolactone-p-coumaric acid copolymers at different mole ratios (epsilon-caprolactone: p-coumaric acid 1:0, 10:1, 8:1, 6:1, 4:1, and 2:1) were synthesized by melt-polycondensation and using 4-dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid as catalyst. Chemical analysis by NMR and GPC showed that copolyesters were formed with decreasing molecular weight as p-coumaric acid content was increased. Physical characteristics, such as thermal and mechanical properties, as well as water uptake and water permeability, depended on the mole fraction of p-coumaric acid. The p-coumarate repetitive units increased the antioxidant capacity of the copolymers, showing antibacterial activity against the common pathogen Escherichia coli. In addition, all the synthesized copolyesters, except the one with the highest concentration of the phenolic acid, were cytocompatible and hemocompatible, thus becoming potentially useful for skin regeneration applications.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214956
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Effect of support oxygen storage capacity on the catalytic performance of Rh nanoparticles for CO2 reforming of methane
Yentekakis, IV; Goula, G; Hatzisymeon, M; Betsi-Argyropoulou, I; Botzolaki, G; Kousi, K; Kondarides, DI; Taylor, MJ; Parlett, CMA; Osatiashtiani, A; Kyriakou, G; Holgado, JP; Lambert, RMApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 243 (2019) 490-501 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.048
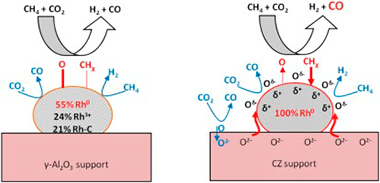
Abstract
The effects of the metal oxide support on the activity, selectivity, resistance to carbon deposition and high temperature oxidative aging on the Rh-catalyzed dry reforming of methane (DRM) were investigated. Three Rh catalysts supported on oxides characterized by very different oxygen storage capacities and labilities (gamma-Al2O3, alumina-ceria-zirconia (ACZ) and ceria-zirconia (CZ)) were studied in the temperature interval 400-750 degrees C under both integral and differential reaction conditions. ACZ and CZ promoted CO2 conversion, yielding CO enriched synthesis gas. Detailed characterization of these materials, including state of the art XPS measurements obtained via sample transfer between reaction cell and spectrometer chamber, provided clear insight into the factors that determine catalytic performance. The principal Rh species detected by post reaction XPS was Rh, its relative content decreasing in the order Rh/CZ(100%) > Rh/ACZ(72%) > Fth/gamma Al2O3(55%). The catalytic activity followed the same order, demonstrating unambiguously that Rh is indeed the key active site. Moreover, the presence of CZ in the support served to maintain Rh in the metallic state and minimize carbon deposition under reaction conditions. Carbon deposition, low in all cases, increased in the order Rh/CZ < Rh/ACZ < Rh/gamma-Al2O3 consistent with a bi-functional reaction mechanism whereby backspillover of labile lattice O2- contributes to carbon oxidation, stabilization of Rh and modification of its surface chemistry; the resulting O vacancies in the support providing centers for dissociative adsorption of CO2. The lower apparent activation energy observed with CZ-containing samples suggests that CZ is a promising support component for use in low temperature DRM.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.048
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Powder and Nanotubes Titania Modified by Dye Sensitization as Photocatalysts for the Organic Pollutants Elimination
Murcia, JJ; Avila-Martinez, EG; Rojas, H; Cubillos, J; Ivanova, S; Penkova, A; Laguna, OHNanomaterials, 9 (2019) 517 DOI: 10.3390/nano9040517
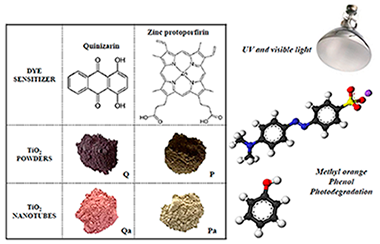
Abstract
In this study, titanium dioxide powder obtained by the sol-gel method and TiO2 nanotubes, were prepared. In order to increase the TiO2 photoactivity, the powders and nanotubes obtained were modified by dye sensitization treatment during the oxide synthesis. The sensitizers applied were Quinizarin (Q) and Zinc protoporphyrin (P). The materials synthesized were extensively characterized and it was found that the dye sensitization treatment leads to modify the optical and surface properties of Titania. It was also found that the effectiveness of the dye-sensitized catalysts in the phenol and methyl orange (MO) photodegradation strongly depends on the dye sensitizer employed. Thus, the highest degradation rate for MO was obtained over the conventional Q-TiO2 photocatalyst. In the case of the nanotubes series, the most effective photocatalyst in the MO degradation was based on TiO2-nanotubes sensitized with the dye protoporfirin (ZnP). Selected catalysts were also tested in the phenol and MO photodegradation under visible light and it was observed that these samples are also active under this radiation.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/nano9040517
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Operando Spectroscopic Evidence of the Induced Effect of Residual Species in the Reaction Intermediates during CO2 Hydrogenation over Ruthenium Nanoparticles
Navarro-Jaen, S; Szego, A; Bobadilla, LF; Laguna, OH; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemcatchem, 11 (2019) 2063-2068 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900101
Abstract
In this work, we present a highly active catalyst based on Ru nanoparticles dispersed on alumina, which showed an unexpected activity for CO2 methanation. This exceptional catalytic behavior was attributed to the presence of residual species that remained on the surface after synthesis. Furthermore, through Operando DRIFTS (diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy) measurements it was demonstrated that these remaining species provoked an induced effect on the nature of the surface intermediates spectroscopically observed, and consequently on their mechanistic role during the pathway of the CO2 hydrogenation to methane.
April, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900101
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Synthesis of sol-gel pyrophyllite/TiO2 heterostructures: Effect of calcination temperature and methanol washing on photocatalytic activity
El Gaidoumi, A.; Doña Rodríguez, J.M.; Pulido Melián, E.; González-Díaz, O.M.; Navío Santos, J.M.; El Bali, B.; Kherbeche, A.Surfaces and Interfaces, 14 (2019) 19-25 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfin.2018.10.003
Abstract
We successfully synthesized an efficient photoactive pyrophyllite/TiO2 heterostructures using a sol-gel route at ambient temperature. The samples were prepared by exfoliation of a pyrophyllite layered-type clay by TiO2. The prepared samples exhibited strong photocatalytic activity for the degradation of phenol. The heterostructure PTi750 (SBET = 16.58 m2/g) calcined at 750 °C, in which the mixed phases of anatase and rutile exist (52.2% anatase/10.7% rutile), showed the highest photocatalytic activity against commercial TiO2Aeroxide P25. The methanol washed PTi750 was 5 times faster than the corresponding unwashed sample; phenol was totally degraded with a TOC reduction of 89.2%. The materials have been characterized by: X-ray diffraction (XRD), Diffuse reflectance UV–vis spectrophotometry (UV–Vis DRS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and BET specific surface area.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfin.2018.10.003
Reactividad de Sólidos
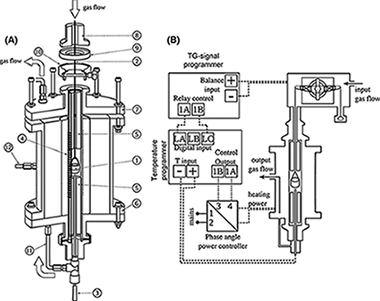
Sample-Controlled analysis under high pressure for accelerated process studies
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Soria-Hoyo, C; Valverde, JM; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1338-1346 DOI: 10.1111/jace.15960
Abstract
The potential of controlled rate thermal analysis (CRTA) for studying high-pressure gas-solid processes has been evaluated. CRTA is a type of smart temperature program based on a feedback system that uses any experimental signal related to the process evolution for commanding the temperature evolution. In this work, an instrument that uses the gravimetric signal for CRTA control has been designed and used for the study of two high-pressure gas-solid reactions: the highly exothermic thermal oxidation of TiC under high pressure of oxygen and the reduction in Fe2O3 under high pressure of hydrogen. Advantages of CRTA for discriminating overlapping processes and appraising kinetic reaction mechanisms are shown.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.15960
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Tamm Plasmons Directionally Enhance Rare-Earth Nanophosphor Emission
Geng, DL; Cabello-Olmo, E; Lozano, G; Miguez, HACS Photonics, 6 (2019) 634-641 DOI: 10.1021/acsphotonics.8b01407
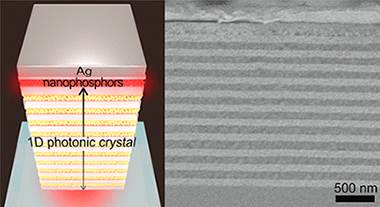
Abstract
Rare-earth-based phosphors are the materials on which current solid-state lighting technology is built. However, their large crystal size impedes the tuning, optimization, or manipulation of emitted light that can be achieved by their integration in nanophotonic architectures. Herein we demonstrate a hybrid plasmonic-photonic architecture capable of both channeling in a specific direction and enhancing by eight times the emission radiated by a macroscopically wide layer of nanophosphors. In order to do so, a slab of rare-earth-based nanocrystals is inserted between a dielectric multilayer and a metal film, following a rational design that optimizes the coupling of nanophosphor emission to collective modes sustained by the metal-dielectric system. Our approach is advantageous for the optimization of solid-state lighting systems.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acsphotonics.8b01407
Reactividad de Sólidos
Anisotropic lattice expansion determined during flash sintering of BiFeO3 by in-situ energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction
Wassel, MAB; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Charalambous, H; Perejon, A; Jha, SK; Okasinski, J; Tsakalakos, TScripta Materialia, 162 (2019) 286-291 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.11.028
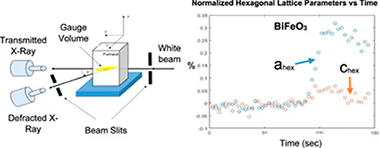
Abstract
BiFeO3 has a Curie temperature (T-c) of 825 degrees C, making it difficult to sinter using conventional methods while maintaining the purity of the material, as unavoidably secondary phases appear at temperatures above T-c Flash sintering is a relatively new technique that saves time and energy compared to other sintering methods. BiFeO3 was flash sintered at 500 degrees C to achieve 90% densification. In-situ energy dispersive X-ray diffraction (EDXRD) revealed that the material did not undergo any phase transformation, having been sintered well below the Tc. Interestingly, anisotropic lattice expansion in the material was observed when the sample was exposed to the electric field.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.11.028
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Test of a He-3 target for transfer reactions in inverse kinematics
Carozzi, G; Valiente-Dobon, JJ; Gadea, A; Siciliano, M; Mengoni, D; Fernandez, A; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; Di Nitto, ANuovo cimento c-colloquia and communications in physics, 42 (2019) 94 DOI: 10.1393/ncc/i2019-19094-9
Abstract
With the aim of studying exotic nuclei close to the proton dripline, an innovative He-3 target was produced and tested in a collaboration between the Materials Science Institute of Seville (Spain) and the Legnaro National Laboratories (Italy). The target was manufactured with a new technique that aims to reduce the costs while providing high quality targets. The target was tested at the Legnaro National Laboratories. The results of this test are presented in this contribution.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1393/ncc/i2019-19094-9
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Trapping of Gas Bubbles in Water at a Finite Distance below a Water-Solid Interface
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Thiyam, P; Miguez, H; Parsons, DF; Brevik, I; Bostrom, MLangmuir, 35 (2019) 4218-4223 DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b04176
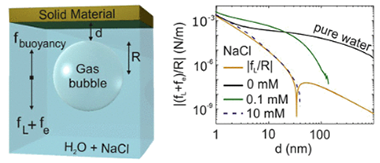
Abstract
Gas bubbles in a water-filled cavity move upward because of buoyancy. Near the roof, additional forces come into play, such as Lifshitz, double layer, and hydrodynamic forces. Below uncharged metallic surfaces, repulsive Lifshitz forces combined with buoyancy forces provide a way to trap micrometer-sized bubbles. We demonstrate how bubbles of this size can be stably trapped at experimentally accessible distances, the distances being tunable with the surface material. By contrast, large bubbles (>= 100 mu m) are usually pushed toward the roof by buoyancy forces and adhere to the surface. Gas bubbles with radii ranging from 1 to 10 mu m can be trapped at equilibrium distances from 190 to 35 nm. As a model for rock, sand grains, and biosurfaces, we consider dielectric materials such as silica and polystyrene, whereas aluminium, gold, and silver are the examples of metal surfaces. Finally, we demonstrate that the presence of surface charges further strengthens the trapping by inducing ion adsorption forces.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b04176
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Promoting effect of CeO2, ZrO2 and Ce/Zr mixed oxides on Co/gamma-Al2O3 catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
Garcilaso, V; Barrientos, J; Bobadilla, LF; Laguna, OH; Boutonnet, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JARenewable Energy, 132 (2019) 1141-1150 DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.080
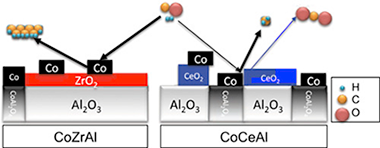
Abstract
A series of cobalt-based catalysts have been synthesized using as support gamma-Al2O3 promoted by ceria/zirconia mixed oxides with a variable Ce/Zr molar ratio. The obtained catalysts demonstrated oxide promotion results in the protection of the major textural properties, especially for Zr-rich solids. Reducibility of cobalt species was enhanced by the presence of mixed oxides. The chemical composition of the oxide promoter influenced not only physicochemical properties of final catalysts but also determined their performance during the reaction. In this sense, Zr-rich systems presented a superior catalytic performance both in total conversion and in selectivity towards long chain hydrocarbons. The observed Zr-promotion effect could be explained by two significant contributions: firstly, the partial inhibition of Co-Al spinel compound formation by the presence of Zr-rich phases which enhances the availability of Co actives site and secondly, Zr-associate acidic sites promote higher hydrocarbons selectivity.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.080
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
CuxCo3-xO4 ultra-thin film as efficient anodic catalysts for anion exchange membrane water electrolysers
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, F; de Lucas-Consuegra, AJournal of Power Sources, 415 (2019) 136-144 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.01.056
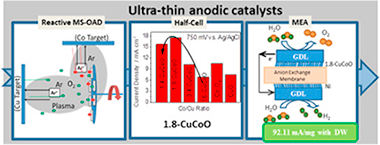
Abstract
CuxCo3-xO4 ultra-thin films, deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles have been used as anodic catalysts in anion exchange membrane water electrolysers. It has been demonstrated that the used deposition procedure provides porous and amorphous samples with a strict control of the total catalyst load and Co/Cu ratio. Electrocatalytic tests showed a maximum performance for the oxygen evolution reaction at Co/Cu atomic ratio around 1.8. The optimized anodic catalyst presented a long-term stability confirmed by accelerated lifetime tests together with the chemical surface analysis of the used samples. The effect of the crystallization of a single layer CuxCo3-xO4 and a multilayer (CuO/Co3O4)(n) anodic catalyst samples was also investigated. The observed loss of catalytic performance found in both cases may prove that a particular local chemical environment around the Co and Cu sites acts as an efficient catalytic site for the oxygen evolution reaction. A catalyst film with the optimum Co/Cu atomic ratio was incorporated into a Membrane Electrode Assembly, using a sputtered Ni film as cathode. Current density values up to 100 mA cm(-2) at 2.0 V were obtained in 1.0 M KOH electrolyte. Upon normalization by the amount of catalyst, this performance is one of the highest reported in literature.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.01.056
Technological evolution of ceramic glazes in the renaissance: In situ analysis of tiles in the Alcazar (Seville, Spain)
de Viguerie, Laurence; Robador, Maria D.; Castaing, Jacques; Perez-Rodriguez, Jose L.; Walter, Philippe; Bouquillon, AnneJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1402-1413 DOI: 10.1111/jace.15955
Abstract
The Alcazar Palace (Seville, Spain) is famous for its ceramic decorations; 16th century wall tiles of different typologies have been analyzed in order to relate the manufacturing process of their colored glazes to the evolving technologies of the Renaissance. Chemical and mineralogical compositions have been determined in situ by nondestructive X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction on arista ceramics in the Cenador de Carlos Quinto, and majolica ceramics in the Palacio Gotico and the Royal oratory. The arista style belongs to the local Hispano-Moresque ceramic tradition. Majolica tiles have the complex microstructures of glazes from Italy. The two types are clearly differentiated by their typology, morphology (curved vs flat surface), and also microstructure (single vs multi-layers), glaze chemistry, and use of different coloring agents. Moreover, we found different glaze chemistries in the investigated majolicas, which correspond to different artists and/or practices.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.15955
Reactividad de Sólidos
A theoretical study of the bonding capabilities of the zinc-zinc double bond
Ayala, R; Galindo, AInternational Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 119 (2019) e25823 DOI: 10.1002/qua.25823
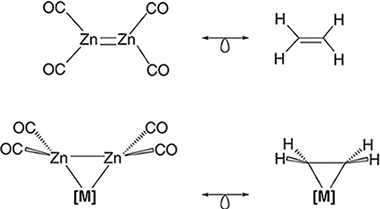
Abstract
The theoretical knowledge about the zinc-zinc bond has been recently expanded after the proposal of a zinc-zinc double bond in several [Zn-2(L)(4)] compounds (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2017, 56, 10151-10155). Prompted by these results, we have selected the [Zn-2(CO)(4)] species, isolobally related to ethylene, and theoretically investigated the possible (2)-Zn-2-coordination to several first-row transition metal fragments. The [Zn-2(CO)(4)] coordination to the metal fragment produces an elongation of the dizinc bond and a concomitant pyramidalization of the [Zn(CO)(2)] unit. These structural parameters are indicative of -backdonation from the metal to the coordinated dizinc moiety, as occurred with ethylene ligand. A quantum theory of atoms in molecules study of the ZnZn bond shows a decrease of (BCP), delta(2)(BCP) (ZnZn) and delocalization indexes (Zn,Zn), relative to corresponding values in the parent [Zn-2(CO)(4)] molecule. The ZnZn and MZn bonds in these [((2)-Zn-2(CO)(4))M(L)(n)] complexes can be described as shared interactions with an important covalent component where the ZnZn bond is preserved, albeit weakened, upon coordination.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/qua.25823
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Combining dietary phenolic antioxidants with polyvinylpyrrolidone: transparent biopolymer films based on p-coumaric acid for controlled release
Contardi, M; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Guzman-Puyol, S; Summa, M; Benitez, JJ; Goldoni, L; Caputo, G; Cusimano, G; Picone, P; Di Carlo, M; Bertorelli, R; Athanassioua, A; Bayer, ISJournal of Materials Chemistry B, 7 (2019) 1384-1396 DOI: 10.1039/c8tb03017k
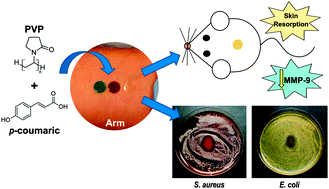
Abstract
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) has probably been one of the most utilized pharmaceutical polymers with applications ranging from a blood plasma substitute to nanoparticle drug delivery, since its synthesis in 1939. It is a highly biocompatible, non-toxic and transparent film forming polymer. Although high solubility of PVP in aqueous environment is advantageous, it still poses several problems for some applications in which sustained targeting and release are needed or hydrophobic drug inclusion and delivery systems are to be designed. In this study, we demonstrate that a common dietary phenolic antioxidant, p-coumaric acid (PCA), can be combined with PVP covering a wide range of molar ratios by solution blending in ethanol, forming new transparent biomaterial films with antiseptic and antioxidant properties. PCA not only acts as an effective natural plasticizer but also establishes H-bonds with PVP increasing its resistance to water dissolution. PCA could be released in a sustained manner up to a period of 3 days depending on the PVP/ PCA molar ratio. Sustained drug delivery potential of the films was studied using methylene blue and carminic acid as model drugs, indicating that the release can be controlled. Antioxidant and remodeling properties of the films were evaluated in vitro by free radical cation scavenging assay and in vivo on a murine model, respectively. Furthermore, the material resorption of films was slower as PCA concentration increased, as observed from the in vivo full-thickness excision model. Finally, the antibacterial activity of the films against common pathogens such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus and the effective reduction of inflammatory agents such as matrix metallopeptidases were demonstrated. All these properties suggest that these new transparent PVP/ PCA films can find a plethora of applications in pharmaceutical sciences including skin and wound care.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1039/c8tb03017k
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Transparent and Robust All-Cellulose Nanocomposite Packaging Materials Prepared in a Mixture of Trifluoroacetic Acid and Trifluoroacetic Anhydride
Guzman-Puyol, S; Ceseracciu, L; Tedeschi, G; Marras, S; Scarpellini, A; Benitez, JJ; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JANanomaterials, 9 (2019) 368 DOI: 10.3390/nano9030368
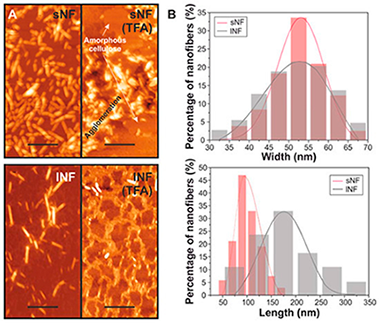
Abstract
All-cellulose composites with a potential application as food packaging films were prepared by dissolving microcrystalline cellulose in a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic anhydride, adding cellulose nanofibers, and evaporating the solvents. First, the effect of the solvents on the morphology, structure, and thermal properties of the nanofibers was evaluated by atomic force microscopy (AFM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), respectively. An important reduction in the crystallinity was observed. Then, the optical, morphological, mechanical, and water barrier properties of the nanocomposites were determined. In general, the final properties of the composites depended on the nanocellulose content. Thus, although the transparency decreased with the amount of cellulose nanofibers due to increased light scattering, normalized transmittance values were higher than 80% in all the cases. On the other hand, the best mechanical properties were achieved for concentrations of nanofibers between 5 and 9 wt.%. At higher concentrations, the cellulose nanofibers aggregated and/or folded, decreasing the mechanical parameters as confirmed analytically by modeling of the composite Young's modulus. Finally, regarding the water barrier properties, water uptake was not affected by the presence of cellulose nanofibers while water permeability was reduced because of the higher tortuosity induced by the nanocelluloses. In view of such properties, these materials are suggested as food packaging films.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/nano9030368
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
The impact of photocatalytic Ag/TiO2 and Ag/N-TiO2 nanoparticles on human keratinocytes and epithelial lung cells
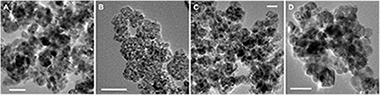
Rebleanu, D; Gaidau, C; Voicu, G; Constantinescu, CA; Sanchez, CM; Rojas, TC; Carvalho, S; Calin, MToxicology, 416 (2019) 30-43 DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2019.01.013
Abstract
The potential human health risks following the exposure to inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) is a very important issue for their application in leather finishing industry. The aim of our study was to investigate the cytotoxic effect of silver (Ag)/titanium dioxide (TiO2) NPs on human cells. Photocatalytic NPs were prepared by electrochemical deposition of Ag on the surface of TiO2 and nitrogen (N)-TiO2 NPs and, subsequently, physicochemical characterized. Then, a set of experiments have been performed to study the cytotoxicity and cell death mechanisms involved, the changes in cell morphology and the production of ROS induced in human keratinocytes (HaCaT) and human lung epithelial cells (A549) by exposure to NPs. Moreover, the changes in major signaling pathways and the inflammatory response induced by Ag/N-TiO2 NPs in A549 cells were investigated. The data showed that cell death by late apoptosis/necrosis is induced in cells as function of the dose and the type of NPs and is characterized by morphological changes and cytoskeletal disorganization and an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. The exposure of A549 cells to Ag/N-TiO2 NPs determine the activation of ERK1/2 MAP-kinase pathway and the release of pro-inflammatory mediators CXCL1, GM-CSF and MIF, known to be involved in the recruitment of circulating neutrophils and monocytes.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2019.01.013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Controlled thermolysis of MIL-101(Fe, Cr) for synthesis of FexOy/porous carbon as negative electrode and Cr2O3/porous carbon as positive electrode of supercapacitor
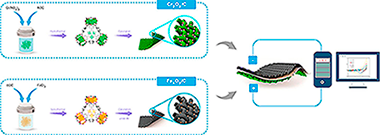
Farisabadi, A; Moradi, M; Hajati, S; Kiani, MA; Espinos, JPApplied Surface Science, 469 (2019) 192-203 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.053
Abstract
In the present study, two kinds of metal oxide/carbon nanocomposite were prepared through calcination of MIL-101(Fe, Cr). The morphological and structural properties of the specimens were investigated using X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller analysis, energy dispersive Xray spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The electrode materials were also electrochemically investigated using cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge-discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy techniques in 6 M KOH electrolyte. Because of synergistic effect of metal oxides and carbon, the obtained samples showed excellent performance; in a way that Cr2O3/C and Fe Oy/C showed high specific capacitance of 420 F g(-1) and 114 F g(-1) at current density of 2 A g(-1), respectively. The Cr2O3/C electrode also displayed high rate capability even at scan rate of 1500 mV s(-1). Moreover, we successfully developed an asymmetric supercapacitor in which Cr2O3/C served as positive electrode and Fe Oy/C served as negative electrode. The asymmetric device can deliver an energy density of 9.6 W h kg(-1) and power density of 8000 W kg(-1), with 93% capacitance retention after 3000 charge-discharge cycles. These outcomes show that the MOF-derived metal oxide/carbon composite can be regarded as a promising development for advanced electrode materials for applying in supercapacitors.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.053
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Comparative studies on electrochemical energy storage of NiFe-S nanoflake and NiFe-OH towards aqueous supercapacitor
Naseri, M; Moradi, M; Hajati, S; Espinos, JP; Kiani, MAJournal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 30 (2019) 4499-4510 DOI: 10.1007/s10854-019-00738-x

Abstract
In this study, electrochemical energy storage performances of an efficient Ni-Fe sulfide and hydroxide supported on porous nickel foam are compared. X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-rayphotoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) results confirmed the formation of Ni-Fe-S and Ni-Fe-OH electrodes. In addition, Brunauer-Emmett Teller (BET) was used to determine the specific surface area of the prepared materials. Moreover, the morphologies were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The brilliant characteristics of Ni-Fe-S could be attributed to transport acceleration in electrolyte ions and electrons, occurrence of redox reactions as well as the higher conductivity of the sample. From stand point of comparison, the capacitance of Ni-Fe-S is more than that of Ni-Fe-OH. Therefore, the exchange of O2- with S2- in Ni-Fe-OH lattice obviously improves the electrochemical performance. The as-fabricated Ni-Fe sulfide electrode exhibits a tremendous specific capacitance of 884.9Fg(-1) at 1A g(-1). Furthermore, an assembled asymmetric supercapacitor device using the activated carbon as negative electrode and this smart configuration (Ni-Fe-S) as positive electrode also provided a maximum specific power and specific energy of 8000Wkg(-1), 37.9 Whkg(-1), respectively. Also, it shows cycling stability with 88.8% capacitance retention after 1700 cycles in aqueous electrolyte, demonstrating its potential application in the next-generation high-performance supercapacitors used for energy storage.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1007/s10854-019-00738-x
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
XPS primary excitation spectra of Zn 2p, Fe 2p, and Ce 3d from ZnO, α‐Fe2O3, and CeO2
Pauly, N.; Yubero, F.; Espinós, J.P.; Tougaard, S.Surface and Interface Analysis, 51 (2019) 353-360 DOI: 10.1002/sia.6587

Abstract
Metal oxides are important for current development in nanotechnology. X‐ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS) is a widely used technique to study the oxidation states of metals, and a basic understanding of the photoexcitation process is important to obtain the full information from XPS. We have studied core level excitations of Zn 2p, Fe 2p, and Ce 3d photoelectron emissions from ZnO, α‐Fe2O3, and CeO2. Using an effective energy‐differential XPS inelastic‐scattering cross section evaluated within the semiclassical dielectric response model for XPS, we analysed the experimental spectra to determine the corresponding primary excitation spectra, ie, the initial excitation processes. We find that simple emission (Zn 2p) as well as complex multiplet photoemission spectra (Fe 2p and Ce 3d) can be quantitatively analysed with our procedure. Moreover, for α‐Fe2O3, it is possible to use the software package CTM4XAS (Charge Transfer Multiplet program for X‐ray Absorption Spectroscopy) to calculate its primary excitation spectrum within a quantum mechanical model, and it was found to be in good agreement with the spectrum determined by analysis of the experiment.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/sia.6587
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Sustainable polycondensation of multifunctional fatty acids from tomato pomace agro-waste catalyzed by tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate
J.A. Heredia-Guerrero, G. Caputo, S. Guzmán-Puyol, G. Tedeschi, A. Heredia, L. Ceseracciu, J.J. Benítez, A. AthanassiouMaterials Today Sustainability, 3-4 (2019) 100004 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2018.12.001
Abstract
Bioplastics were prepared from the fatty fraction (i.e., unsaturated and polyhydroxylated fatty acids) of tomato pomace agro-wastes. Aliphatic polyesters were synthesized at different temperatures (125, 150, and 175 °C), reaction times (0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 3, 5, and 7 h), and amounts of tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate (0, 0.02, 0.05, and 0.10 mmol) used as a catalyst. The rate constants and activation energies were calculated from infrared spectra. The right combination of reaction temperature and amount of catalyst improved the reaction kinetics (apparent k from ∼1 to ∼8.5 h−1), whereas the activation energy was reduced from ∼39 without catalyst to ∼28 kJ/mol when tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate was present. Glass transitions between ca. −25 and ∼0 °C were measured by differential scanning calorimetry, strictly depending on the degree of polymerization. The amorphous character of the samples was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. Young's modulus and hardness were calculated from indentation tests and were typical of soft materials, although increased as the polycondensation reaction progressed. High water-contact angles (maximum value ∼109°) and low water uptakes (minimum value ∼2.1%) were determined. Physical properties were compared with those of common man-made plastics and polymers, finding that these tomato pomace bioplastics could be their realistic alternatives.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2018.12.001
Reactividad de Sólidos - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Microstructure, interfaces and properties of 3YTZP ceramic composites with 10 and 20 vol% different graphene-based nanostructures as fillers
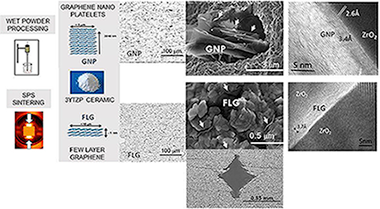
Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Rojas, TC; Jimenez-Pique, E; Lopez-Pernia, C; Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, AJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 777 (2019) 213-224 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.336
Abstract
The graphene family comprises not only single layer graphene but also graphene-based nanomaterials (GBN), with remarkably different number of layers, lateral dimension and price. In this work, two of these GBN, namely graphene nanoplatelets (GNP) with n similar to 15-30 layers and few-layer graphene (FLG) with n < 3 layers have been evaluated as fillers in 3 mol% yttria stabilized tetragonal zirconia (3YTZP) ceramic composites. Composites with 10 and 20 vol% GNP or FLG have been fabricated by wet powder processing and spark plasma sintering (SPS) and the influence of the content and number of layers of the graphene-based filler has been assessed. For both graphene-based fillers, an intermediate zirconia oxycarbide has been detected in the grain boundaries. The lower stacking degree and much more homogeneous distribution of the FLG, revealed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), can improve load transfer between the GBNs and the ceramic matrix. However, high FLG contents lower densification of the composites, due partly to the larger FLG interplanar spacing also estimated by TEM. The hardness (both Vickers and nanoindentation) and the elastic modulus decrease with increased GBN content and with improved graphene dispersion. The FLG greatly inhibit the crack propagation that occur perpendicular to their preferential orientation plane. The composites with thinner FLG have higher electrical conductivity than those with GNP. The highest electrical conductivity is achieved by composites with 20 vol% FLG in the direction perpendicular to the compression axis during sintering, sigma(perpendicular to) = 3400 +/- 500 Sm-1.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.336
Degradation processes of historic metal threads used in some Spanish and Portuguese ornamentation pieces
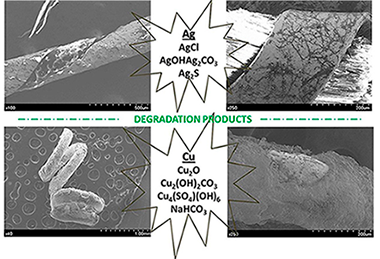
Duran, A; Perez-Maqueda, R; Perez-Rodriguez, JLJournal of Cultural Heritage, 36 (2019) 135-142 DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2018.09.006
Abstract
The degradation processes that occurred on metal threads applied in the embroidery used for clothing and in the ornamentation of sculptures, the Sevillian Holy Week processions, and Portuguese and Spanish palace and museum are thoroughly analyzed. Some threads from the 14th and 18–19th centuries were considered. In the metal threads, sulphur- and chlorine-based compounds were detected either individually or together, depending on the degradation process. Basic silver carbonate, sodium bicarbonate and copper-based compounds were also observed. The different degradation processes were attributed to different factors, such as environmental contamination, degradation of the fibrous cores, and inadequate cleaning and/or mechanical treatments.
March, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2018.09.006
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
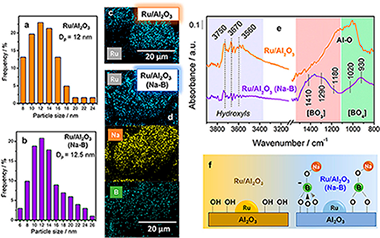
Does shaping catalysts modify active phase sites? A comprehensive in situ FTIR spectroscopic study on the performance of a model Ru/Al2O3 catalyst for the CO methanation
Bobadilla, LF; Munoz-Murillo, A; Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 357 (2019) 248-257 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.166

Abstract
Routinely, it seems assumed that the catalytic layer coated on monoliths and microchannel reactors preserve the properties of the initial powder catalyst. However, this assumption should be reasonably demonstrated since the set of chemical and physical manipulations involved in the preparation of these catalytic devices hardly does not alter the surface of the starting catalyst powders. This work aims to evaluate the transformations that takes place in a model Ru/Al2O3 catalyst during a typical slurry preparation procedure and their impact on the catalytic performance for the CO methanation reaction and the selective methanation of CO in CO2-rich reformate gases. For this purpose, we have conducted an in situ comprehensive study by means of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) in which the nature of the species present on the surface of the catalyst during CO hydrogenation was analyzed. This study reveals that during the preparation of the slurry the starting Ru/Al2O3 catalyst suffers a redispersion of metallic Ru particles and more surface hydroxyls are created by the incorporation of additional alumina. These modifications have a noticeable influence in the catalytic performance and despite their importance, these aspects have been poorly considered in other studies.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.166
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Urban wastewater treatment by using Ag/ZnO and Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts
J.J. Murcia, L.G. Arias Bolivar, H.A. Rojas Sarmiento, E.G. Ávila Martínez, C. Jaramillo Páez, M.A. Lara, J.A. Navío Santos, M.C. Hidalgo LópezEnvironmental Science and Pollution Research (2018) 1-9 DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-1592-3

Abstract
In this study, the treatment of wastewater coming from a river highly polluted with domestic and industrial effluents was evaluated. For this purpose, series of photocatalysts obtained by ZnO and TiO2 modification were evaluated. The effect of metal addition and Ti precursor (in the case of the titania series) over the physicochemical and photocatalytic properties of the materials obtained was also analyzed. The evaluation of the photocatalytic activity showed that semiconductor modification and precursor used in the materials synthesis are important factors influencing the physicochemical and therefore the photocatalytic properties of the materials obtained. The water samples analyzed in the present work were taken from a highly polluted river, and it was found that the effectiveness of the photocatalytic treatment increases when the reaction time increases and for both, wastewater samples and isolated Escherichia coli strain follow the next order Pt/TiO2 << ZnO. It was also observed that biochemical and chemical demand oxygen and turbidity significantly decrease after treatment, thus indicating that photocatalysis is a non-selective technology, which can lead to recover wastewater containing different pollutants.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-1592-3
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effects of the speed ratio on the efficiency of planetary mills
Real, C; Gotor FJHeliyon, 5 (2019) e01227 DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01227
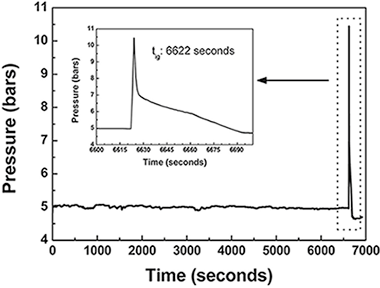
Abstract
The ignition time (tig) of the mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process involving the formation of TiB2 from Ti/2B elemental mixtures was used to study the influence of the ratio (k = -ωv/ωd) between the rotational speed of the supporting disc (ωd) and vials (ωv) on the milling efficiency of a Pulverisette 4 planetary mill. The variation of the inverse of the ignition time (1/tig), which is directly related to the milling power provided by the planetary mill, with the process conditions has shown that it is not possible to find a single k value as optimal independently of the experimental conditions used (ωd and the ball-to-powder ratio, BPR). Moreover, it was observed that the lowest milling efficiency (longer tig values) was found for k = 1, which is the usual value employed in routine laboratory works. The best efficiencies were found for the larger k values (2.5 or 3). At lower ωd, the shortest tig was obtained for k = 2.5 and at higher ωd for k = 3, independently of BPR.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01227
Reactividad de Sólidos
High-performance and low-cost macroporous calcium oxide based materials for thermochemical energy storage in concentrated solar power plants
Jimenez, PES; Perejon, A; Guerrero, MB; Valverde, JM; Ortiz, C; Maqueda, LAPApplied Energy, 235 (2019) 543-552 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.131
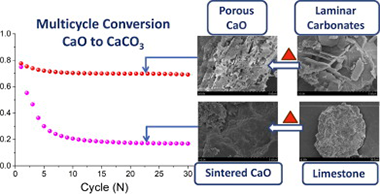
Abstract
High energy density, cycling stability, low cost and scalability are the main features required for thermochemical energy storage systems to achieve a feasible integration in Concentrating Solar Power plants (CSP). While no system has been found to fully satisfy all these requirements, the reversible CaO/CaCO3 carbonation reaction (CaL) is one of the most promising since CaO natural precursors are affordable and earth-abundant. However, CaO particles progressively deactivate due to sintering-induced morphological changes during repeated carbonation and calcinations cycles. In this work, we have prepared acicular calcium and magnesium acetate precursors using a simple, cost-effective and easily scalable technique that requires just the natural minerals and acetic acid, thereby avoiding expensive reactants and environmentally unfriendly solvents. Upon thermal decomposition, these precursors yield a stable porous structure comprised of well dispersed MgO nanoparticles coating the CaO/CaCO3 grains that is resistant to pore-plugging and sintering while at the same time exhibits high long term effective conversion. Process simulations show that the employment of these materials could significantly improve the overall CSP-CaL efficiency at the industrial level.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.131
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth of nanocolumnar thin films on patterned substrates at oblique angles
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Munoz-Pina, S; Alcala, G; Alvarez, R; Lacroix, B; Santos, AJ; Cuevas-Maraver, J; Rico, V; Gago, R; Vazquez, L; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, APlasma Processes and Polymers, 16 (2019) e1800135 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201800135

Abstract
The influence of one dimensional substrate patterns on the nanocolumnar growth of thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles is theoretically and experimentally studied. A well-established growth model has been used to study the interplay between the substrate topography and the thin film morphology. A critical thickness has been defined, below which the columnar growth is modulated by the substrate topography, while for thicknesses above, the impact of substrate features is progressively lost in two stages; first columns grown on taller features take over neighboring ones, and later the film morphology evolves independently of substrate features. These results have been experimentally tested by analyzing the nanocolumnar growth of SiO2 thin films on ion-induced patterned substrates.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201800135
Reactividad de Sólidos
Electrical properties of bismuth ferrites: Bi2Fe4O9 and Bi25FeO39
Perejon, A; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; West, AR; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 39 (2019) 330-339 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.09.008
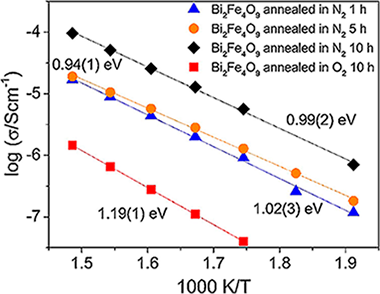
Abstract
Bi2Fe4O9 was prepared by solid-state reaction and the electrical properties measured by impedance spectroscopy. After annealing in O-2 at 900 degrees C, Bi2Fe4O9 is an electrically-homogeneous insulator. Its high frequency permittivity is constant (similar to 14.1) over the temperature range 300-400 degrees C and shows no evidence of incipient ferroelectricity at lower temperatures. On annealing in N-2 at 900 degrees C, the pellets gradually decompose.
Bi25FeO39 was prepared by both solid-state reaction and mechanosynthesis. It showed a modest amount of mixed conduction of both oxide ions and holes. Impedance analysis showed a complex response that best fitted an equivalent circuit consisting of a parallel combination of long-range conduction and short range dielectric relaxation elements.
The electrical conductivity of both Bi-2 Fe4O9 and Bi25FeO39 is less than that of BiFeO3 prepared by solid-state reaction, which indicates that any leakage conductivity of BiFeO3 is not due to the possible presence of small amounts of these secondary phases.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.09.008
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of a cubic Ti(BCN) advanced ceramic by a solid-gas mechanochemical reaction
Chicardi, E; Garcia-Garrido, C; Beltran, AM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJCeramics International, 45 (2019) 3878-3885 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.11.060
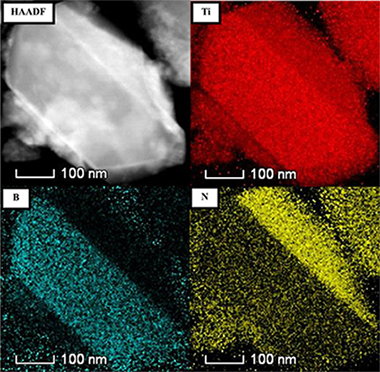
Abstract
In this work, a titanium boron carbonitride advanced ceramic was successfully synthesised by a solid-gas mechanochemical reaction in a planetary ball mill from a mixture of elemental Ti, B, and C under nitrogen atmosphere. This material, with a general formula of Ti(BCN), exhibits a face-centred cubic structure (NaCl type) that is analogous to Ti(CN). This phase was gradually formed with sufficient milling time as a result of diffusional processes, which were permitted by the reduction of the energy in the system caused by the decrease in the spinning rate of the planetary ball mill. In contrast, under more energetic milling conditions, a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) took place, leading to the formation of a TiB2-Ti(CN) ceramic composite. The microstructural characterisation revealed that Ti(BCN) was composed of ceramic particles constituted of misoriented nanocrystalline domains. B, C and N were optimally distributed in the Ti(BCN) phase. The TiB2-Ti (CN) ceramic composite was composed of micrometric and nanometric particles homogeneously distributed. Additionally, the nitrogen content obtained for Ti(BCN) was higher than for the Ti(CN) phase in the composite material.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.11.060
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Eu3+ Luminescence in High Charge Mica: An In Situ Probe for the Encapsulation of Radioactive Waste in Geological Repositories
Martin-Rodriguez, R; Aguado, F; Alba, MD; Valiente, R; Perdigon, ACACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 11 (4) (2019) 7559-7565 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b20030
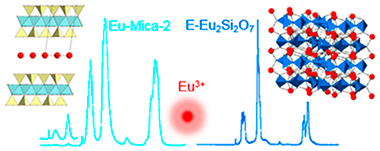
Abstract
Isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in deep geological repositories (DGR) through a multibarrier concept is the most accepted approach to ensure long-term safety. Clay minerals are one of the most promising materials to be used as engineered barriers. In particular, high charge micas, as components of the engineered barrier, show superselectivity for some radioactive isotopes and a large adsorption capacity, which is almost twice that of the other low charge aluminosilicates. In addition, high charge micas are optimum candidates for decontamination of nuclear waste through two different mechanisms; namely an ion exchange reaction and a nonreversible mechanism involving the formation of new stable crystalline phases under hydrothermal conditions. In this work, we report a new in situ optical sensor based on the incorporation of Eu3+ in these high charge micas for tracking the long-term physical-chemical behavior of HLW contaminants in DRG under mild hydrothermal conditions. The incorporation of Eu3+ into the interlayer space of the mica originates a well resolved green and red luminescence, from both the 5D1 and 5D0 excited states, respectively. The formation of new crystalline phases under hydrothermal conditions involves important changes in the Eu3+ emission spectra and lifetime. The most interesting features of Eu3+ luminescence to be used as an optical sensor are (1) the presence or absence of the Eu3+ green emission from the 5D1 excited state, (2) the energy shift of the 5D0 → 7F0 transition, (3) the crystal-field splitting of the 7F1 Eu3+ level, and (4) the observed luminescence lifetimes, which are directly related to the interaction mechanisms between the lanthanide ions and the silicate network.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b20030
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Mesoporous pyrophyllite–titania nanocomposites: synthesis and activity in phenol photocatalytic degradation
A. El Gaidoumi; J.M. Doña-Rodríguez; E. Pulido Melián; O.M. González-Díaz; B. El Bali; J.A. Navío; A. KherbecheResearch on Chemical Intermediates, 45 (2019) 333-353 DOI: 10.1007/s11164-018-3605-8

Abstract
Pyrophyllite–TiO2 nanocomposite PTi750 was successfully synthesized using a sol–gel method at ambient temperature based on exfoliation of the pyrophyllite layered clay by incorporation of the TiO2 precursor titanium(IV) t-butoxide. PTi750 exhibited higher photocatalytic activity in phenol degradation compared with commercial TiO2 Aeroxide P25. Ag-photodeposited PTi750 was more photoactive than PTi750, exhibiting detoxification, total degradation, and good mineralization of polluted solution and excellent stability after five reuses at optimal conditions in terms of the parameters pH, H2O2 concentration, and photocatalyst amount. The nanocomposites were investigated using several techniques, viz. diffuse-reflectance ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectrophotometry, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) specific surface area measurements.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1007/s11164-018-3605-8
Reactividad de Sólidos
Tailoring the Band Gap in the ZnS/ZnSe System: Solid Solutions by a Mechanically Induced Self-Sustaining Reaction
Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJInorganic Chemistry, 58 (2019) 2565-2575 DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b03183
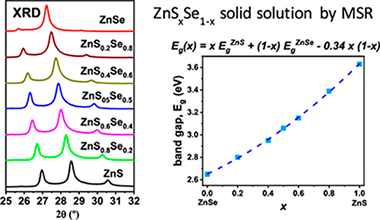
Abstract
The complete ZnSxSe1-x solid solution was successfully obtained by the mechanochemical process denoted as a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction. Excellent control of the chemical stoichiometry of the solid solution was possible by adjusting the atomic ratio of the starting Zn/S/Se elemental mixture subjected to milling. A mixture of both wurtzite-2H (hexagonal) and zinc blende (cubic) structures was always obtained, although for a similar milling time the proportion of the zinc blende structure increased with the Se content in the solid solution. However, wurtzite was the major phase for S-rich compositions when milling was stopped just after ignition. It was demonstrated that milling induces the wurtzite-to-zinc blende phase transition. The 8H hexagonal polytype was also observed in samples subjected to long milling times. Variation of the lattice parameters for both structures with the x value in the solid solution presented an excellent linearity, confirming the validity of Vegard's law. However, variation of the band-gap energy (E-g) with x was not perfectly linear, and a small bowing parameter of 0.34 was obtained. It was possible to tune the E-g value between those of the end members of the solid solution in a continuous manner by adjusting the stoichiometry of the solid solution. The morphology and crystalline domain size can also be controlled by adjusting, in this case, the postignition milling time of the mechanochemical process.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b03183
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid over TiO2(B)/anatase nanobelts and Au-TiO2(B)/anatase nanobelts
Chenchana, A.; Nemamcha, A.; Moumeni, H.; Doña Rodríguez, J.M.; Araña, J.; Navío, J.A.; González Díaz, O.; Pulido Melián, E.Applied Surface Science, 467-468 (2019) 1076-1087 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.175
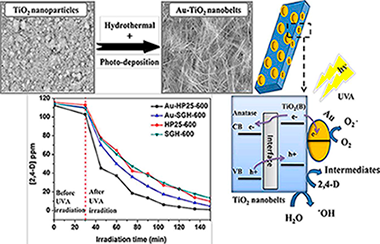
Abstract
In this work, novel TiO2-based nanobelts with various phases were synthesized: biphasic TiO2(B)/anatase, pure TiO2(B) and pure anatase. These catalysts were obtained via hydrothermal reaction using two nanoparticulated TiO2 photocatalysts as precursors: Aeroxide TiO2 P25 (P25) and TiO2 synthesized via a sol-gel process (SG). In addition, the surface of the photocatalysts was modified with gold using a photodeposition method. A characterization study of the different photocatalysts was performed with X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), UV–Vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectrum analysis (XPS) and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller measurements (BET). The photocatalytic reaction of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) was investigated under UVA irradiation. A toxicity analysis was performed with the marine bioluminescent bacteria Vibrio fischeri. The highest 2,4-D removal efficiency of 99.2% was obtained with the biphasic Au-TiO2(TiO2(B)/anatase) nanobelts with anatase as predominant phase. Toxicity was mainly due to the intermediate 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) which was eliminated in 4 h. The TiO2 nanobelt phase structure is shown to have a significant effect on photocatalytic activity.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.175
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study of the Interface of the Early Stages of Growth under Quasi-Equilibrium Conditions of ZnO on Graphene/Cu and Graphite
Morales, C; Black, A; Urbanos, FJ; Granados, D; Mendez, J; del Campo, A; Yubero, F; Soriano, LAdvanced Materials Interfaces, 6 (2019) art. 1801689 DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801689
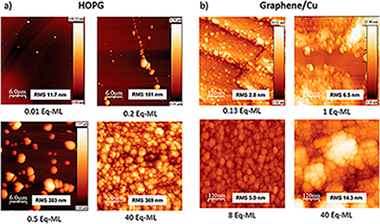
Abstract
The study of the early stages of growth of ZnO on graphene supported on Cu and on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite by means of reactive thermal evaporation of metallic Zn at room temperature is presented. This growth method allows to go in depth in the study of the fundamental interaction between ZnO and graphene at the interface in quasi-equilibrium conditions. Quantitative, chemical, and morphological analysis is performed using photoemission spectroscopy, atomic force, and scanning microscopies as experimental characterization techniques and factor analysis and inelastic peak shape analysis as modeling techniques. The growth of ZnO on a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite substrate is also studied using the same growth method for comparison. The results show that, in spite that the first atomic layer of both substrates is identical, the growth kinetics and morphology of the deposits are completely different. A model for the kinetics of the growth of ZnO on both substrates is proposed.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801689
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical combustion synthesis of vanadium carbide (VC), niobium carbide (NbC) and tantalum carbide (TaC) nanoparticles
Jalaly, M; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 79 (2019) 177-184 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.12.011
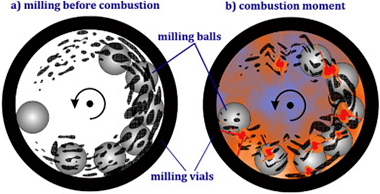
Abstract
The nanoparticles of vanadium, niobium, and tantalum carbides were synthesized by a mechanically induced magnesiothermic combustion in the separate Mg/V2O5/C, Mg/Nb2O5/C, and Mg/Ta2O5/C systems. Initial materials in these systems ignited after short milling times of 10, 10, and 23 min, respectively. X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and elemental mapping techniques were employed to characterize the combustion products. In this process, magnesium reduces initial oxides to generate elemental V/Nb/Ta to react with carbon, forming the carbide phases.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.12.011
Reactividad de Sólidos
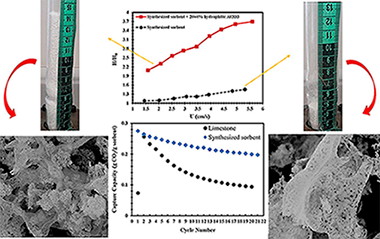
Multicycle CO2 capture activity and fluidizability of Al-based synthesized CaO sorbents
Azimi, B; Tahmasebpoor, M; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 358 (2019) 679-690 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.061
Abstract
CaO-based materials have been identified as promising sorbents for highly efficient pre-combustion and post-combustion CO2 capture in fluidized beds operated at high temperatures by means of the Calcium Looping (CaL) process. However, Ca-based sorbents suffer from a decline of the capture capacity over multiple sorption/desorption cycles, mainly due to sintering, and from a markedly heterogeneous fluidization behavior due to the strength of interparticle attractive forces as compared to particle weight. The present study is focused on the development of novel synthetic CaO/Al2O3 sorbents for CO2capture with enhanced CaL performance and fluidizability by dry mixing with flow conditioner nanopowders. The influence of initial precursors on the sorbents multicycle activity at realistic CaL conditions has been investigated. The formation of a stable Ca9Al6O18 mixed-phase during the preparation of the sorbents promotes the multicycle capture capacity. The type of Ca and Al precursors, either soluble or insoluble, can significantly affect the dispersion of this stabilizer (Ca9Al6O18) in the sorbent matrix and, consequently, may affect the carbonation activity of the materials. The sorbent prepared from soluble aluminum nitrate and calcium nitrate precursors by sol-gel method exhibits a very stable multicycle capture capacity with a capture capacity around 0.2 g of CO2/g of sorbent after 21 cycles keeping a 72% of its initial capture capacity. The fluidizability of this promising sorbent was also investigated as affected by the addition of three different flow conditioners. Fluidization experiments confirmed the positive effect of using hydrophilic alumina and hydrophobic silica nanoparticles on improving the fluidizability of the synthesized sorbents.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.061
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Catalytic Efficiency of Cu-Supported Pyrophyllite in Heterogeneous Catalytic Oxidation of Phenol
El Gaidoumi, A.; Doña-Rodríguez, J.M.; Pulido Melián, E.; González-Díaz, O.M.; Navío, J.A.; El Bali, B.; Kherbeche, A.Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, (2019) 1-13 DOI: 10.1007/s13369-019-03757-2
Abstract
The copper-impregnated pyrophyllite (Cu/RC) was prepared and used as catalyst in catalytic wet peroxide oxidation (CWPO) of phenol. The catalyst was prepared by impregnation of copper (2.5 wt%) into pyrophyllite-type clay and characterized by X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The optimum operation conditions for CWPO of phenol over Cu/RC were determined by investigating the effects of pH, temperature, catalyst amount, and hydrogen peroxide concentration. Stability of the Cu/RC catalyst and toxicity of treated solution were studied, by measuring the copper concentration leached out from the catalyst and the inhibition of Vibrio fischeri bacteria bioluminescence, respectively. The probable degradation mechanism of phenol over Cu/RC was considered by HPLC analysis. The obtained results showed that Cu/RC achieved highest activity (total phenol degradation and 80% TOC reduction) and detoxification with remarkable low copper leaching concentration (0.006 mg\,L−1)mg\,L−1) at optimized conditions (pH == 3, T=50∘T=50∘C, 2 g\,L−1g\,L−1 catalyst amount, 50 mg L−1L−1phenol concentration and 7.45 mmol\,L−1mmol\,L−1 hydrogen peroxide concentration during 4 h). Meanwhile, few intermediates with low concentration were observed by the HPLC analysis for the CWPO of phenol. The Cu/RC catalyst showed a good activity after five successive runs (88% of degradation and 73% mineralization) at optimized conditions.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1007/s13369-019-03757-2
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Immobilization of Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles on Various Ceria-Based Oxides: Influence of the Protecting Agent on the Glucose Oxidation Reaction
Chenouf, M; Megias-Sayago, C; Ammari, F; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysts, 9 (2019) 125 DOI: 10.3390/catal9020125
Abstract
The influence of the protecting agent's nature on gold particle size and dispersion was studied in this work over a series of gold-based catalysts. CO and glucose oxidation were chosen as catalytic reactions to determine the catalyst's structure-activity relationship. The nature of the support appeared to be the predominant factor for the increase in activity, as the oxygen mobility was decisive for the CO oxidation in the same way that the Lewis acidity was decisive for the glucose oxidation. For the same catalyst composition, the use of montmorillonite as the stabilizing agent resulted in better catalytic performance.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/catal9020125
Amber, beads and social interaction in the Late Prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula: an update
Odriozola, CP; Sousa, AC; Mataloto, R; Boaventura, R; Andrade, M; Garcia, RV; Garrido-Cordero, JA; Rodriguez, E; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Aviles, MA; Daura, J; Sanz, M; Riquelme, JAArchaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 11 (2019) 567-595 DOI: 10.1007/s12520-017-0549-7
Abstract
The identification of archaeological amber has been used in Iberian prehistory to evidence long-distance exchanges and engage Iberia in networks that connect western Europe with central and northern Europe, the emergence of social complexity, and the consolidation of trade networks. However, until now, no comprehensive analytical study of the Iberian amber has been produced to support any of the interpretive models currently in use. This paper approaches the analysis of Iberian Peninsula amber artefacts by considering their provenance (based on FTIR characterization), chronology, and spatial relationship with other exotica. Our work increases the number of analyzed artefacts to 156 (24%), out of the c. 647 currently known for the Iberian Peninsula. Based on these new data and a review of Murillo-Barroso and Martinon-Torres (2012), this overview outlines amber consumption patterns from the 6th to 2nd millennia BCE and demonstrates long-distance amber exchange connecting Iberia with the Mediterranean region from the Neolithic period onwards.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1007/s12520-017-0549-7
Reactividad de Sólidos
Insight into the BiFeO3 flash sintering process by in-situ energy dispersive X-ray diffraction (ED-XRD)
Perez-Maqueda, LA; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Wassel, MA; Jha, SK; Perejon, A; Charalambous, H; Okasinski, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Tsakalakos, TCeramics International, 45 (2019) 2828-2834 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.293
Abstract
The sintering mechanism of BiFeO3 has been investigated in-situ by energy dispersive X-ray diffraction (ED-XRD) using a high-energy white collimated X-ray beam from the Advanced Photon Source (Argonne National Laboratories). Such radiation is very penetrating thereby allowing measurements of the sample even when placed inside the flash sintering set up. Additionally, the fast ED-XRD measurements permit monitoring the flash sintering process by providing information about phase composition and sample temperature in real time. Moreover, profile scans, obtained by moving the stage vertically while recording the ED-XRD spectra, permit investigating the homogeneity of the flash for the entire length of the sample. All experiments have been complemented by ex-situ studies. It has been concluded that flash sintering of BiFeO3 is a homogeneous process without any directionality effects. Furthermore, flash sintering takes place at quite low temperatures (below the Tc ≈ 830 °C), which may be related to the high quality of the samples, as pure, highly insulating ceramics without evidence of secondary phases with a homogenous nanostructured grain size distribution are obtained by this technique. Moreover, it is also evidenced that the rapid heating of the sample does not seem to justify, at least by itself, the densification process. Therefore, it appears that the electric current should play a role in the enhanced mobility during the sintering process.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.293
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Environmentally Tight TiO2-SiO2 Porous 1D-Photonic Structures
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Rico, V; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Materials Interfaces, 6 (2019) art. 1801212 DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801212
Abstract
Although thin film porosity is the basis of many optical sensors, it can be deleterious for a stable optical behavior of passive optical elements due to the condensation of water and other vapors in their pores. This paper proposes a new strategy for the magnetron sputtering (MS) fabrication of environmentally tight SiO2-TiO2 porous multilayers. Thin films of these two oxides deposited in an oblique angle configuration (MS-OAD) present a nanocolumnar and highly porous nanostructure and, as a consequence, experience significant changes in their optical properties when exposed to water vapor. Similarly, the optical properties of Bragg reflectors and Bragg microcavities made of the stacking of porous and compact SiO2 and TiO2 thin films experience reversible changes when these 1D-photonic structures are exposed to water pressure. A key finding of this work is that a very thin capping layer of SiO2 deposited on the surface of porous SiO2 films in the stack, at the interlayer between the two oxides, efficiently seals the pores making the photonic structures environmentally tight. This capping layer approach is a useful strategy to incorporate porosity as an additional parameter to design the optical behavior of planar photonic structures while preserving optical and environmental stability.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801212
Reactividad de Sólidos
Production of Ag-ZnO powders by hot mechanochemical processing
Guzman, D; Aguilar, C; Rojas, P; Criado, JM; Dianez, MJ; Espinoza, R; Guzman, A; Martinez, CTransactions of nonferrous metals society of China, 29 (2019) 365-373 DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64946-0
Abstract
Ag-CdO composites are still one of the most commonly used electrical contact materials in low-voltage applications owing to their excellent electrical and mechanical properties. Nevertheless, considering the restriction on using Cd due to its toxicity, it is necessary to find alternative materials that can replace these composites. In this study, the synthesis of Ag-ZnO alloys from Ag-Zn solid solutions was investigated by hot mechanochemical processing. The hot mechanochemical processing was conducted in a modified attritor mill at 138 degrees C under flowing O-2 at 1200 cm(3)/min for 3.0 h. The microstructure and phase evolution were investigated using X-ray diffractometry, field emission gun scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The results suggest that it is possible to complete the oxidation of Ag-Zn solid solution by hot mechanochemical processing at a low temperature and short time. This novel synthesis route can produce Ag-ZnO composites with a homogeneous distribution of nanoscale ZnO precipitates, which is impossible to achieve using the conventional material processing methods. Considering the fact that the fundamental approach to improving electric contact material performance resides in obtaining uniform dispersion of the second-phase in the Ag matrix, this new processing route could open the possibility for Ag-ZnO composites to replace non-environmentally friendly Ag-CdO.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64946-0
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Fluorinated and Platinized Titania as Effective Materials in the Photocatalytic Treatment of Dyestuffs and Stained Wastewater Coming from Handicrafts Factories
Murcia, J.J.; Cely, A.C.; Rojas, H.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navío, J.A.Catalysts, 9 (2019) 179 DOI: 10.3390/catal9020179
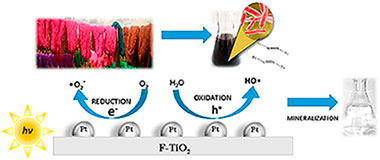
Abstract
In this study, commercial and lab-prepared TiO2 were modified by fluorination and platinum photodeposition; and the effect of these modifications over the physicochemical and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 was evaluated. It was found that F and Pt addition leads to the modification of the optical and textural properties of TiO2. The materials prepared were tested in the photocatalytic degradation of different organic dyestuffs such as methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO); the degradation of commercial anilines employed in the staining of natural fibers was also evaluated. Photocatalysis was also studied in this work as an eco-friendly treatment of wastewater coming from handicrafts factories. In general it was observed that the effectiveness of the photocatalytic treatment strongly depends on the substrate to be degraded, thus, fluorinated and platinized commercial Titania (Pt-F-P25) showed the best photocatalytic performance in the MB and MO photodegradation and in contrast, in the case of the anilines the highest degradation was obtained over commercial TiO2 fluorinated (F-P25). These results can be explained by differences observed in the structure and in the adsorption of these dyestuffs over the photocatalysts surfaces. F-P25 photocatalyst also demonstrated to be the best material for the treatment of real wastewater coming from handicrafts factories.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/catal9020179
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
An innovative approach for micro/nano structuring plasma polymer films
Thiry, D; Vinx, N; Aparicio, FJ; Moerman, D; Lazzaroni, R; Cossement, D; Snyders, RThin Solid Films, 672 (2019) 26-32 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2018.12.050
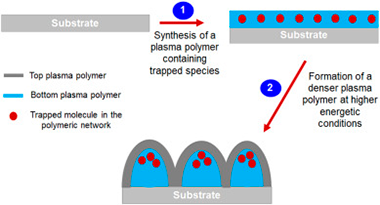
Abstract
This work aims at presenting an innovative method for tailoring the morphology of functionalized plasma polymer films (PPF). The approach is based on the formation of a plasma polymer bilayer system in which the two layers differ by their chemical composition and cross-linking degree. As a case study, propanethiol-based plasma polymer films have been investigated. As revealed by a much higher S/C ratio than in the propanethiol precursor (i.e. 0.83 vs 0.33), it has been demonstrated that the bottom layer contains a large fraction of trapped sulfur-based molecules (e.g. H2S). When further covered by a denser PPF formed at higher energetic conditions, a three-dimensional morphological reorganization takes place giving rise to the micro/nano structuration of the organic material. The shape, the dimensions as well as the density of the generated structures are found to depend on the thickness of both coatings involved in the bilayer structure, offering a great flexibility for surface engineering. Annealing experiments unambiguously confirm the major role played by the sulfur-based trapped molecules for inducing the reshaping process. The whole set of data clearly paves the way for the development of an innovative approach for finely tailoring the morphology of functionalized PPF at the micro/nano scale.
February, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2018.12.050
- ‹ previous
- 14 of 37
- next ›














