Scientific Papers in SCI
2015
2015
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Biocompatible Films with Tailored Spectral Response for Prevention of DNA Damage in Skin Cells
Nunez-Lozano, R; Pimentel, B; Castro-Smirnov, JR; Calvo, ME; Miguez, H; de la Cueva-Mendez, GAdvanced Healthcare Materials, 4 (2015) 1944-1948 DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201500223
Abstract
A hybrid nanostructured organic–inorganic biocompatible film capable of efficiently blocking a preselected range of ultraviolet light is designed to match the genotoxic action spectrum of human epithelial cells. This stack protects cultured human skin cells from UV-induced DNA lesions. As the shielding mechanism relies exclusively on reflection, the secondary effects due to absorption harmful radiation are prevented
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201500223
Materiales Avanzados
Phyllite clay-cement composites having improved engineering properties and material applications
Garzon, E; Cano, M; O'Kelly, BC; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Clay Science, 114 (2015) 229-233 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.06.006
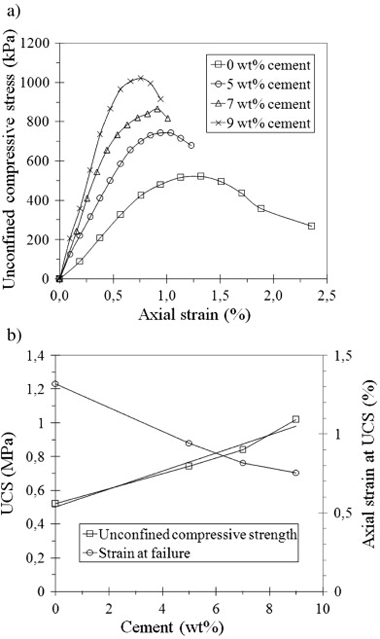
Abstract
Phyllite clays contain clay minerals (chlorite, illite and mixed-layer illite smectite), quartz and feldspars. In this experimental laboratory study, new composites of phyllite clay and cement (5, 7 and 9 wt.%) were prepared and tested to determine their Atterberg limits, dry density and optimum water content for modified Proctor (MP) compaction, California Bearing ratio, swelling potential after soakage in water, unconfined compressive strength (UCS) and water-permeability coefficient. From the mixes investigated, the composite with 5 wt.% cement was deemed most suitable for certain construction material applications, having a plasticity index of 10.5%, maximum dry density of 2.17 Mg/m3 and optimum water content of 8% for MP compaction (undergoing no swelling under soakage), a UCS of 0.74 MPa, and a very low permeability coefficient value of 7.4 × 10− 11 m/s. Potential material applications for these new composites include for building construction, roofs, and flexible pavements.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.06.006
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Microstructure of mixed oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Gil-Rostra, J; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Ferrer, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, FThin Solid Films, 591 (2015) 330-335 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.01.058
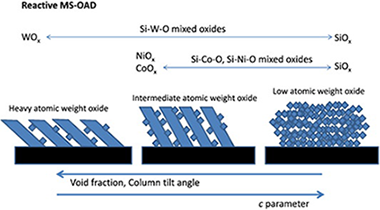
Abstract
Several mixed oxide thin film series of samples (Si–Co–O, Si–Ni–O, Si–W–O) have been prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at oblique angle geometries. The paper focuses on the description of microstructure of the films as a function of their stoichiometry. It is found that for identical process parameters (gas mixture, pressure, magnetron-substrate distance, incidence angle of the vapour flux, etc.) the tilt angle of the developed columnar microstructure and the film porosity is strongly dependent on the stoichiometry of the films. The results are discussed in the framework of several theoretical models on this topic.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.01.058
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Facile Synthesis of Decahedral Particles of Anatase TiO2 with Exposed {001} Facets
Perales-Martinez, IA; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, V; Obregon-Alfaro, S; Lee, SWJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 15 (2015) 7351-7356 DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10578
Abstract
This paper reports a facile synthesis of decahedral particles of anatase TiO2 dominated by {101} and {001} faces. The decahedral particles has been enhanced by means a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method using TiF4 as a titanium precursor and HF as capping agent to promote oriented growth and formation of {001} faces in only 4 h. The prepared samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, high resolution of transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The morphology of anatase TiO2 particles is consisted of near-perfect-truncated-bipyramid-shape. Reaction time is a key factor to obtain truncated-bipyramid-shaped particles with sharp and well-defined edges. Reaction times longer than 4 h induce irregular particles. Decahedral anatase TiO2 particles are truncated bypiramid crystals which have eight {101} and two {001} facets at top/bottom surfaces. The average size of decahedral anatase TiO2 particles are similar to 250 nm for the samples obtained without applying the microwave irradiation and similar to 350 nm for reaction 4 h.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10578
Materiales Coloidales
Uniform Poly(acrylic acid)-Functionalized Lanthanide-Doped LaVO4 Nanophosphors with High Colloidal Stability and Biocompatibility
Nunez, NO; Zambrano, P; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cantelar, E; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 27 (2015) 4546-4554 DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201500265
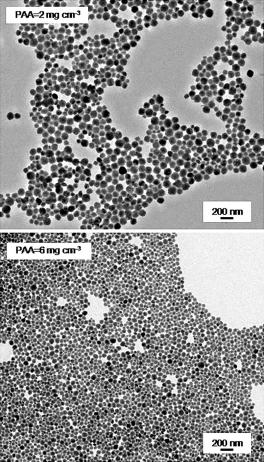
Abstract
Ln-doped (Ln = Eu or Nd) LaVO4 nanoparticles functionalized with poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) were prepared from lanthanide and vanadate precursors in the presence of PAA by a simple one-pot method that consists of a homogeneous precipitation reaction in ethylene glycol/water at a moderate temperature (120 degrees C). The size of the nanoparticles could be modified in the 40-70 nm range by adjusting the amount of PAA added. The effects of the Eu and Nd contents of these nanomaterials on theirs optical properties (emission intensity and lifetime) were also analyzed to find the optimum nanophosphors. Finally, the nanoparticles showed negligible cytotoxicity for Vero cells at concentrations up to 0.05 mgmL(-1) and a high colloidal stability in physiological buffer solutions; therefore, they satisfy the most important requirements for in vitro biotechnological applications.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201500265
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Boosting the activity of a Au/CeO2/Al2O3 catalyst for the WGS reaction
Reina, T. R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Catalysis Today, 253 (2015) 149-154 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.01.041
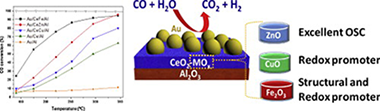
Abstract
Herein a strategy to design highly efficient Au/CeO2/Al2O3 based WGS catalysts is proposed. The inclusion of transition metals, namely Fe, Cu and Zn as CeO2 dopant is considered. All the promoters successfully increased the WGS performance of the undoped sample. The activity improvement can be correlated to structural and/or redox features induced by the dopants. The comparative characterization of the doped samples by means of XRD, Raman spectroscopy and OSC evaluation permits an accurate understanding of the boosted WGS activity arising from the Ce-promoter interaction. This study establishes distinction among both, structural and redox sources of promotion and provides a useful strategy to develop highly active Au/CeO2 based catalysts for the WGS reaction.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.01.041
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Boosting the visible-light photoactivity of Bi2WO6 using acidic carbon additives
Carmona, RJ; Velasco, LF; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Ania, COApplied Catalysis A-General, 505 (2015) 467-477 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.05.011
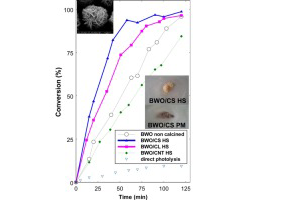
Abstract
We have explored the role of the physicohemical properties of carbon materials as additives to bismuth tungstate on its structure, optical properties, and photocatalytic activity for the degradation of rhodamine B under visible light. For this purpose, C/Bi2WO6 hybrid composites were prepared following two different routes: (i) physical mixture of the catalyst components, and (ii) one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of the semiconductor in the presence of the carbon additive. Three carbons with different properties were selected as additives: biomass-derived activated carbon, carbon nanotubes and carbon spheres obtained from polysaccharides. Data has shown the outstanding role of the acidic/basic nature of the carbon additive, and of the synthetic method on the photocatalytic performance of the resulting composites. For a given additive, the degradation rate of RhB is greatly improved for the catalysts prepared through a one-step hydrothermal synthesis, where there is low shielding effect of the carbon matrix. Carbon additives of acidic nature boost the surface acidity of the hybrid photocatalyst, thereby enhancing the photodegradation of RhB under visible light via a coupled mechanism (photosensitization, semiconductor photocatalysis and carbon-photon mediated reactions).
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.05.011
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Specific features of the electrical properties in partially graphitized porous biocarbons of beech wood
Popov, VV; Orlova, TS; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the solid state, 57 (2015) 1746-1751 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783415090280
Abstract
The electrical and galvanomagnetic properties of partially graphitized highly porous bioC(Ni) biocarbon matrices produced by pyrolysis (carbonization) of beech wood at temperatures T (carb) = 850-1600A degrees C in the presence of a Ni-containing catalyst have been studied in comparison with their microstructural features. The temperature dependences of the resistivity, the magnetoresistance, and the Hall coefficient have been measured in the temperature range of 4.2-300 K in magnetic fields to 28 kOe. It has been shown that an additional graphite phase introduction into samples with T (carb) a parts per thousand yen 1000A degrees C results in an increase in the carrier mobility by a factor of 2-3, whereas the carrier (hole) concentration remains within similar to 10(20) cm(-3), as in biocarbons obtained without catalyst. An analysis of experimental data has demonstrated that the features of the conductivity and magnetoresistance of these samples are described by quantum corrections related to their structural features, i.e., the formation of a globular graphite phase of nano- and submicrometer sizes in the amorphous matrix. The quantum corrections to the conductivity decrease with increasing carbonization temperature, which indicates an increase in the degree of structure ordering and is in good agreement with microstructural data.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783415090280
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Physiological Degradation Mechanisms of PLGA Membrane Films under Oxygen Plasma Treatment
Lopez-Santos, C; Terriza, A; Portoles, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal fo Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 20446–20452 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05011
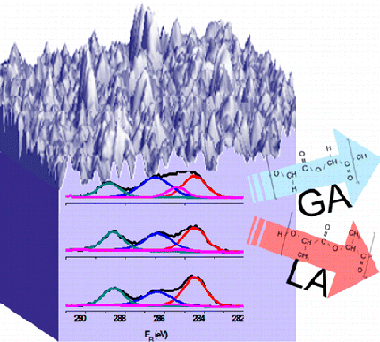
Abstract
Degradation under simulated physiological conditions of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) (PLGA) copolymer membrane films subjected to an oxygen plasma treatment compared to its “as prepared” state has been studied by gas cluster ion beam assisted X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy for chemical depth profiling analysis. This investigation is complemented with atomic force microscopy, weight loss measurements, and visual inspection of the films at the different stages of the degradation process. The obtained results show that the carbon functional groups of the PLGA membrane films undergo a heterogeneous hydrolytic degradation to different rates depending on the plasma pretreatment. The content of glycolic groups (GA) in untreated PLGA samples immersed for 3 weeks in a phosphate-buffered saline solution decreased at the surface, whereas the ratio between glycolic and lactic units (LA) did not vary in the inner regions (∼400 nm depth) of the degraded membrane films. By contrast, oxygen plasma pretreatment enhances the degradation efficiency and causes that both lactic and glycolic functional components decreased at the surface and in the interior of the film, although with less prevalence for the lactic units that present a comparatively higher resistance to degradation.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05011
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Microreactors technology for hydrogen purification: Effect of the catalytic layer thickness on CuOx/CeO2-coated microchannel reactors for the PROX reaction
Laguna, O. H.; Castano, M. Gonzalez; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Chemical Engineering Journal, 271 (2015) 45-52 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.023
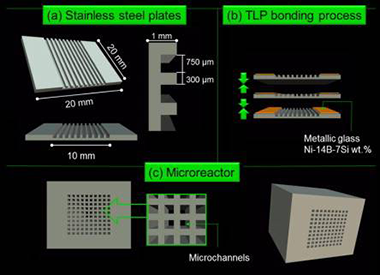
Abstract
Two blocks of microreactors composed by 100 microchannels and coated, respectively, with 150 and 300 mg of a CuOx/CeO2 catalyst, were prepared and tested in the preferential oxidation of CO in presence of H2 (PROX). The deposition of different amount of catalyst resulted in different catalytic layer thicknesses thus modifying the catalytic performances of the microreactor. The evaluation of the main reaction variables (the space velocity, the O2-to-CO ratio and the presence of H2O and/or CO2 in the stream) was performed over both microreactors and compared to that of the parent powder catalyst. The least loaded microreactor, with a coating thickness around 10 μm, presented the highest CO conversion and selectivity levels at temperatures below 160 °C. This result evidences (i) the improvement of the catalytic performances got by the structuration of the powder catalyst and (ii) the importance of the selection of the adequate thickness of the catalytic layer on the microreactor, which have not to exceed and optimal value. An adequate coating thickness allows minimizing the mass and heat transport limitations, thus resulting in the enhancement of the catalytic performance during the PROX reaction.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.023
Reactividad de Sólidos
Photocatalytic Properties of TiO2 Thin Films Modified with Ag and Pt Nanoparticles Deposited by Gas Flow Sputtering
Maicu, M; Gloss, D; Frach, P; Hecker, D; Gerlach, G; Cordoba, JMJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 15 (2015) 6478-6486 DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10873
Abstract
In this work, a gas flow sputtering (GFS) process which allows the production and deposition of metal nanoparticles (NPs) in a vacuum environment is described. Aim of the study is to prove the potential of this technology for the fabrication of new TiO2 films with enhanced photocatalytic properties. For this purpose, Ag and Pt NPs have been produced and deposited on photocatalytic float glass coated with TiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering. The influence of the process parameters and of the metal amount on the final properties of the particles (quantity, size, size distribution, oxidation state etc.,) was widely investigated. Moreover, the effect of the NPs on the photocatalytic activity of the resulting materials was evaluated for the case of the decomposition of stearic acid (SA) during UV-A irradiation. The reduction of the water contact angle (WCA) during the irradiation period was measured in order to test the photo-induced super-hydrophilicity (PSH).
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10873
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Direct observation of doping incorporation pathways in self-catalytic GaMnAs
Kasama, T.; Thuvander, M.; Siusys, A.; Gontard, L. C.; Kovacs, A.; Yazdi, S.; Duchamp, M.; Gustafsson, A.; Dunin-Borkowski, R. E.; Sadowski, J.Journal of Applied Physics, 118 (2015) 054302 DOI: 10.1063/1.4927623
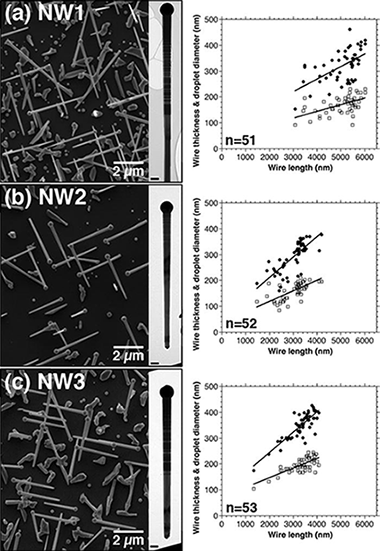
Abstract
Doping mechanisms of Mn in GaAs nanowires (NWs) that have been grown self-catalytically at 600 °C by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) are investigated using advanced electron microscopy techniques and atom probe tomography. Mn is found to be incorporated primarily in the form of non-magnetic tetragonal Ga0.82Mn0.18 nanocrystals in Ga catalyst droplets at the ends of the NWs, while trace amounts of Mn (22 ± 4 at. ppm) are also distributed randomly in the NW bodies without forming clusters or precipitates. The nanocrystals are likely to form after switching off the reaction in the MBE chamber, since they are partially embedded in neck regions of the NWs. The Ga0.82Mn0.18 nanocrystals and the low Mn concentration in the NW bodies are insufficient to induce a ferromagnetic phase transition, suggesting that it is difficult to have high Mn contents in GaAs even in 1-D NW growth via the vapor-liquid-solid process.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1063/1.4927623
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Viability of adding gypsum and calcite for remediation of metal-contaminated soil: laboratory and pilot plant scales
Gonzalez-Nunez, R; Alba, MD; Vidal, M; Rigol, AInternational Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 12 (2015) 2697-2710 DOI: 10.1007/s13762-014-0671-3
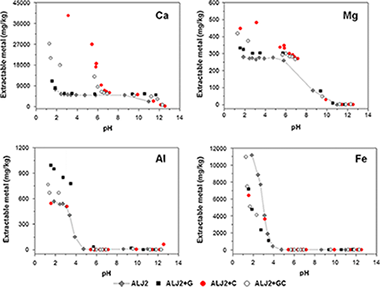
Abstract
The effect of adding waste materials (gypsum and calcite) for the remediation of a soil contaminated by pyritic minerals was examined. Materials were characterised in terms of their acid neutralisation capacity (ANC), sorption capacity and structural components. Their effect on the contaminant leaching in soil + material mixtures over a wide range of pH was also evaluated. Results at laboratory and pilot plant scales were compared to account for the potential variability in the material efficiency when applied at larger scale. The use of gypsum permitted its valorisation, although calcite was a more effective amendment because its addition led to a greater increase in the pH and acid neutralisation capacity, and thus in the sorption capacity in the resulting soil + material mixture. In the same way, when the combination of gypsum + calcite was added to the soil, it led to an increase in the pH from 2.5 to 6.9 and in the ANC from −86 to 1,513 meq/kg. As a result, the concentration of extractable heavy metals and As was reduced, and they were successfully immobilised both at laboratory and at pilot plant scales. Thus, the use of these materials induced a significant reduction in the contaminant mobility and permitted the valorisation of waste materials.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1007/s13762-014-0671-3
Materiales Coloidales
BaGa4O7, a new A3BC10O20 crystalline phase: synthesis, structural determination and luminescence properties
Boyer, Marina; Veron, Emmanuel; Becerro, Ana Isabel; Porcher, Florence; Suchomel, Matthew R.; Matzen, Guy; Allix, MathieuCrystEngComm, 17 (2015) 6127-6135 DOI: 10.1039/C5CE01101A
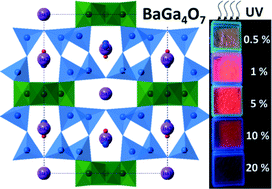
Abstract
The synthesis, structural determination and luminescence properties of a new barium gallate, BaGa4O7, are reported. This crystalline material can uniquely be obtained by direct cooling from the molten state. The crystallographic structure was determined using a combination of electron, synchrotron and neutron powder diffraction data. BaGa4O7 crystallizes in the monoclinic I2/mspace group with a = 15.0688(1) Å, b = 11.7091(1) Å, c = 5.1429(2) Å and β = 91.0452(2)° and can be described as an original member of the A3BC10O20 family. Atypical for this A3BC10O20structural framework, BaGa4O7 is found to contain exclusively divalent and trivalent cations. In order to maintain overall electroneutrality, disordered defect-type partial substitution of gallium and oxygen ions on barium sites occurs within the pentagonal channels of BaGa4O7. Thanks to the flexibility of this structural framework, BaGa4O7 can be heavily doped with europium and thus is shown to exhibit strong orange-red luminescence emission at 618 nm under 393 nm excitation.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C5CE01101A
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Absorption Enhancement in Organic-Inorganic Halide Perovskite Films with Embedded Plasmonic Gold Nanoparticles
Carretero-Palacios, S; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 18635-18640 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06473
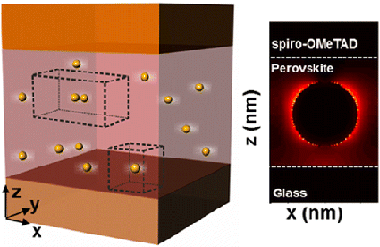
Abstract
We report on the numerical analysis of solar absorption enhancement in organic-inorganic halide perovskite films embedding plasmonic gold nanoparticles. The effect of particle size and concentration is analyzed in realistic systems in which random particle location within the perovskite film and the eventual formation of dimers are also taken into account. We find a maximum integrated solar absorption enhancement of similar to 10% in perovskite films of 200 nm thickness and similar to 6% in 300 nm films, with spheres of radii 60 and 90 nm, respectively, in volume concentrations of around 10% in both cases. We show that the presence of dimers boosts the absorption enhancement up to,similar to 12% in the thinnest films considered. Absorption reinforcement arises from a double contribution of plasmonic near-field and scattering effects, whose respective weight can be discriminated and evaluated from the simulations.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06473
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Rapid Legionella pneumophila determination based on a disposable core–shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles immunoplatform
Martin, M; Salazar, P; Jimenez, C; Lecuona, M; Ramos, MJ; Ode, J; Alcoba, J; Roche, R; Villalonga, R; Campuzano, S; Pingarron, JM; Gonzalez-Mora, JLAnalytica Chimica Acta, 887 (2015) 51-58 DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.05.048
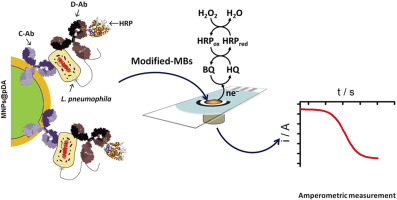
Abstract
A novel amperometric magnetoimmunoassay, based on the use of core–shell magnetic nanoparticles and screen-printed carbon electrodes, was developed for the selective determination of Legionella pneumophila SG1. A specific capture antibody (Ab) was linked to the poly(dopamine)–modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs@pDA-Ab) and incubated with bacteria. The captured bacteria were sandwiched using the antibody labeled with horseradish peroxidase (Ab-HRP), and the resulting MNPs@pDA-Ab-Legionella neumophila-Ab-HRP were captured by a magnetic field on the electrode surface. The amperometric response measured at −0.15 V vs. Ag pseudo-reference electrode of the SPCE after the addition of H2O2 in the presence of hydroquinone (HQ) was used as transduction signal. The achieved limit of detection, without pre-concentration or pre-enrichment steps, was 104 Colony Forming Units (CFUs) mL−1. The method showed a good selectivity and the MNPs@pDA-Ab exhibited a good stability during 30 days. The possibility of detecting L. pneumophila at 10 CFU mL−1 level in less than 3 h, after performing a membrane-based preconcentration step, was also demonstrated.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.05.048
Reactividad de Sólidos
Preparation of phase pure, dense fine grained ceramics by conventional and spark plasma sintering of La-substituted BiFeO3 nanoparticles
Perejon, Antonio; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Poyato, Rosalia; Maso, Nahum; West, Anthony R.; Criado, Jose M.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 35 (2015) 2283-2293 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.01.030
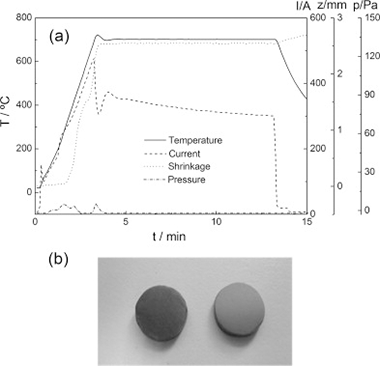
Abstract
High density ceramics of the system Bi1-xLaxFeO3, 0 <= x <= 0.15, have been prepared starting from nanoparticles obtained by mechanosynthesis. The ceramics have been sintered conventionally at 850 degrees C and by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Sintering conditions have been optimized to obtain single phase ceramics, and the microstructure of the ceramics has been compared. Ceramics prepared conventionally present grain sizes from 5 mu m to less than 1 mu m, whereas grain sizes by SPS are in the range from 50 to 100 nm, which demonstrates that it is possible to obtain nanostructured ceramics of La-substituted BiFeO3 using mechanosynthesis followed by SPS at low temperature (625-650 degrees C). The as-prepared SPS ceramics show low resistivity, indicating some reduction in the samples. However, after an oxidative anneal in air, ceramics are highly insulating at room temperature and electrically homogeneous. The high quality of the ceramics has also been demonstrated by XRD, EDX, Raman and DSC.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.01.030
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanical and electrical properties of low SWNT content 3YTZP composites
Poyato, R; Macias-Delgado, J; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 35 (2015) 2351-2359 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.02.022
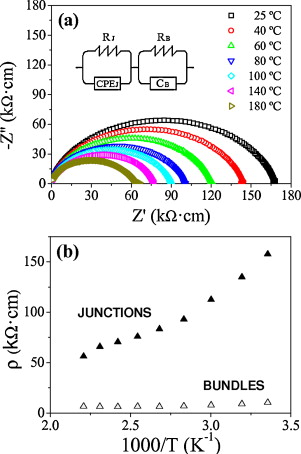
Abstract
Fully dense 3 mol% Y2O3-ZrO2 (3YTZP) composites with low single wall carbon nanotube content (0.5, 1 and 1.5 vol% SWNT) were prepared by colloidal processing and spark plasma sintering (SPS). SWNT were distributed at ceramic grain boundaries and also into agglomerates. Characterization of SWNT agglomerates indicated that increase in SWNT vol% does not imply an increase in agglomeration. SWNT agglomerate density was related to the evolution of hardness and fracture toughness with SWNT vol%. Electrical properties of the composites were characterized in a wide temperature range, and percolation threshold was estimated. A model allowing separation of the individual SWNT bundles contribution to resistance from the resistance due to junctions between bundles was proposed for composites with a percolating SWNT network.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.02.022
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Ultraviolet Pretreatment of Titanium Dioxide and Tin-Doped Indium Oxide Surfaces as a Promoter of the Adsorption of Organic Molecules in Dry Deposition Processes: Light Patterning of Organic Nanowires
Oulad-Zian, Y; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Parra-Barranco, J; Hamad, S; Espinos, JP; Barranco, A; Ferrer, J; Coll, M; Borras, ALangmuir, 31 (2015) 8294-8302 DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01572
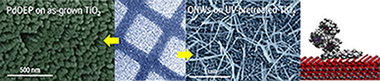
Abstract
In this article we present the preactivation of TiO2 and ITO by UV irradiation under ambient conditions as a tool to enhance the incorporation of organic molecules on these oxides by evaporation at low pressures. The deposition of p-stacked molecules on TiO2 and ITO at controlled substrate temperature and in the presence of Ar is thoroughly followed by SEM, UV-vis, XRD, RBS, and photoluminescence spectroscopy, and the effect is exploited for the patterning formation of small-molecule organic nanowires (ONWs). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) in situ experiments and molecular dynamics simulations add critical information to fully elucidate the mechanism behind the increase in the number of adsorption centers for the organic molecules. Finally, the formation of hybrid organic/inorganic semiconductors is also explored as a result of the controlled vacuum sublimation of organic molecules on the open thin film microstructure of mesoporous TiO2.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01572
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Modulating Low Energy Ion Plasma Fluxes for the Growth of Nanoporous Thin Films
Alvarez, Rafael; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Ferrer, Francisco J.; Rico, Victor; Cotrino, Jose; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Palmero, AlbertoPlasma Processes and Polymers, 12 (2015) 719-724 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201400209
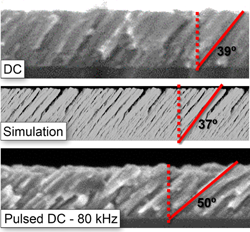
Abstract
The growth of nanoporous layers by plasma-assisted deposition techniques is strongly mediated by the ion fluxes in the reactor. To analyze their influence we have deposited different nanostructured thin films by the magnetron sputtering technique at oblique angles, modulating the ion fluxes in the plasma by tuning the frequency of the electromagnetic signal from pure DC to 160 kHz DC pulsed mode. In the DC case, ions possess energies below 5 eV and do not induce noticeable changes in the film structure. However, when the signal is pulsed, ions with energies up to 40 eV impinge on the film, decreasing the porosity of the layers and tilting down the porous/nanocolumnar structures. As a result, we demonstrate that the overall porosity of the layers and the tilt angle of the columns can be tailored as two independent morphological quantities.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201400209
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Removing the effects of the "dark matter" in tomography
Gontard, Lionel C.Ultramicroscopy, 154 (2015) 64-72 DOI: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2015.03.017
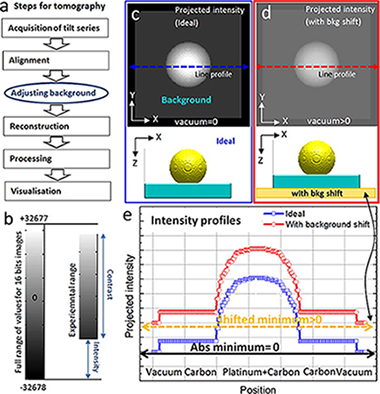
Abstract
Electron tomography (ET) using different imaging modes has been progressively consolidating its position as a key tool in materials science. The fidelity of a tomographic reconstruction, or tomogram, is affected by several experimental factors. Most often, an unrealistic cloud of intensity that does not correspond to a real material phase of the specimen ("dark matter") blurs the tomograms and enhances artefacts arising from the missing wedge (MW). Here we show that by simple preprocessing of the background level of any tomographic tilt series, it is possible to minimise the negative effects of that "dark matter". Iterative reconstruction algorithms converge better, leading to tomograms with fewer streaking artefacts from the MW, more contrast, and increased accuracy. The conclusions are valid irrespective of the imaging mode used, and the methodology improves the segmentation and visualisation of tomograms of both crystalline and amorphous materials. We show examples of HAADF STEM and BF TEM tomography.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2015.03.017
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic propylene epoxidation on Bi2WO6-based photocatalysts
Murcia-Lopez, S.; Vaiano, V.; Sannino, D.; Hidalgo, M. C.; Navio, J. A.Research on Chemical Intermediates, 41 (2015) 4199-4212 DOI: 10.1007/s11164-013-1523-3
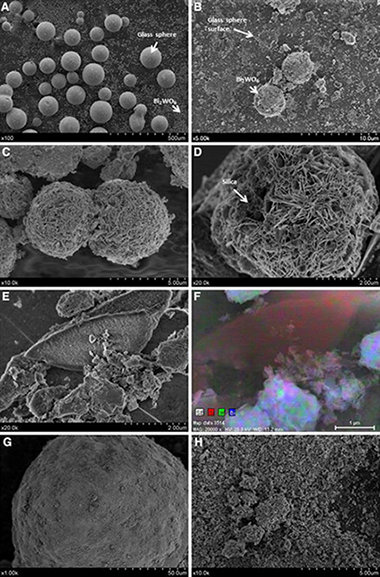
Abstract
The photocatalytic epoxidation of propylene (PR) with molecular oxygen was carried out in a fluidized-bed reactor with several Bi2WO6-based materials under UV-A illumination. Three different photocatalysts were tested: one of single Bi2WO6 and two of coupled Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructures, thus showing that a mixed system of Bi2WO6 with commercial TiO2 Degussa-P25 leads to the best combination of conversion and PO selectivity. Then, direct support on glass spheres and silica gel was made, being a good alternative for improving the Bi2WO6 performance. Additionally, several reaction conditions of temperature and PR to O-2 feed ratio were studied.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1007/s11164-013-1523-3
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
On the origin of the photocatalytic activity improvement of BIVO4 through rare earth tridoping
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis A-General, 501 (2015) 56-62 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.04.032
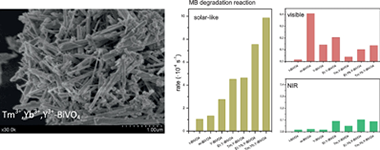
Abstract
Rare earth (Tm3+/Er3+,Yb3+,Y3+) tri-doped BiVO4 have been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of methylene blue and O-2 evolution reactions. The improved photocatalytic performance has been attained by multiple approach of the overall photocatalytic mechanism. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Y3+ induces the stabilization of the tetragonal phase probably due to its substitutional incorporation in the BiVO4 lattice. Moreover, the extensive doping with rare earth ions such as Yb3+ and Er3+/Tm3+ t-BiVO4 evidenced that important structural, electronic changes as well as the luminescence properties were also exalted. Ternary doping clearly prompts the higher photocatalytic activities. A more packed tetragonal structure in conjunction leading to improved charge carriers mobility, with the observed visible and NIR photoactivities of t-BiVO4 could be the responsible of the improved photocatalytic activity under solar-like irradiation.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.04.032
Study of coatings by thermal analysis in a monument built with calcarenite
Luisa Franquelo, Maria; Dolores Robador, Maria; Luis Perez-Rodriguez, JoseJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 121 (2015) 195-201 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-015-4432-4
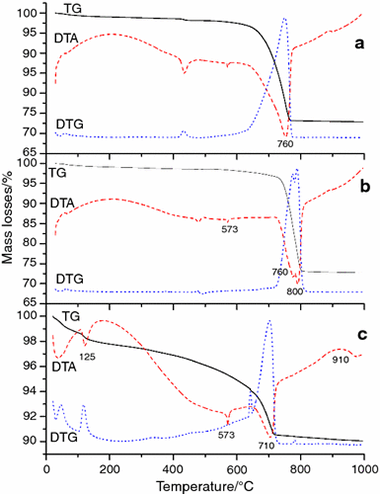
Abstract
In this research, characterization of materials either added during restoration or formed by environmental contamination in the Seville City Hall, built with calcarenite stone, was investigated by thermal methods. Three different mortars for restoration have been characterized: (a) lime micro-mortar for internal consolidation of mortar itself, (b) mortar for reconstruction of deteriorated areas and (c) mortar with Portland cement. Acrylate polymer as consolidant and protection used was characterized. Addition of gypsum or “white cement” has been also applied in the restoration. Altered materials as black crusts constituted by gypsum, calcite and organic compound were determined by thermal analysis. Patina with high concentration of hydrated calcium oxalate, and the transformation mechanism of calcium oxalate into calcium carbonate and formation of calcium oxide produced by decomposition of the calcite were also characterized in the studied monument by thermal analysis. The patina with hydrated calcium oxalate produced by high biological activity was also studied.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-015-4432-4
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
New Copper wide range nanosensor electrode prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles for the non-enzimatic determination of glucose
Salazar, P; Rico, V; Rodriguez-Amaro, R; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochimica Acta, 169 (2015) 195-201 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.092
Abstract
In this work a novel Cu nanostructured electrode is presented. Cu tilted nanocolumnar and porous thin films have been prepared by physical vapor deposition (PVD) in an oblique angle configuration and characterized by different techniques. Cyclic voltammetry and amperometry were used to study the sensing ability of the copper films deposited on ITO to quantitatively determine glucose and to optimize the experimental conditions of detection. Scanning electron microscopy data revealed that the film microstructure consists of tilted nanocolumns of around 70 nm of diameter and an inclination of 65° with respect to the surface normal that extend through the total thickness of the layer of ca. 300 nm. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman, used to determine the oxidation state of Cu, revealed that an oxy/hydroxide external layer formed around the nanocolumns is the active phase responsible for the electrocatalytic detection of glucose. Under optimized conditions, the CuO/Cu nanoporous/ITO electrode presented a sensitivity of 1.41 A mol dm−3 cm−2 (R2:0.999) with a limit of detection of 0.36 μmol dm−3 and a reproducibility of 3.42%.The selectivity of the proposed sensor was checked against various interferences, including physiological compounds, different sugars and ethanol, thereby showing excellent anti-interference properties. The CuO/Cu nanoporous/ITO electrode was also used successfully to determine glucose in blood samples showing a performance comparable to that of a commercial glucometer. An extended working range covering from 1 to 5 × 10−3 mol dm−3 was determined for these sensor films which, in this way, could be applied for different analytical purposes including agro industrial liquids.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.092
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A novel and improved surfactant-modified Prussian Blue electrode for amperometric detection of free chlorine in water
Salazar, Pedro; Martin, Miriam; Garcia-Garcia, Francisco J.; Luis Gonzalez-Mora, Jose; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 213 (2015) 116-123 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.02.092
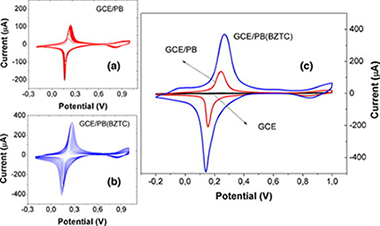
Abstract
A surfactant-modified Prussian Blue (PB) electrochemical sensor has been developed. Benzethonium was used to assist the electrodeposition of PB onto a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). The surface coverage ( [View the MathML source] ) was 7.75 × 10−8 mol cm−2, five times higher than the value obtained in the absence of surfactant, and the film thickness of ca. 123 nm. SEM, EDX, Raman were used to characterize the electrodes while their electrochemical analysis proved a superior performance for the surfactant modified PB film. Cyclic voltammetry and amperometry were used to study the sensor ability to detect chlorine, and the main experimental variables were optimized. Under optimized conditions, the sensor presented a sensitivity of 12 μA ppm−1 cm−2, a linear range from 9 ppb to 10 ppm and a reproducibility of 4.2%. For the first time, we proved the sensor performance for real applications. Thus, chlorine was determined in tap water and the obtained concentrations validated with a standard colorimetric method. The obtained results showed that our sensor is highly performant and reliable for applications involving determinations of environmental residual chlorine.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.02.092
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanocolumnar 1-dimensional TiO2 photoanodes deposited by PVD-OAD for perovskite solar cell fabrication
Javier Ramos, F.; Oliva-Ramirez, Manuel; Nazeeruddin, Mohammad Khaja; Graetzel, Michael; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Ahmad, ShahzadaJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 3 (2015) 13291-13298 DOI: 10.1039/c5ta02238j
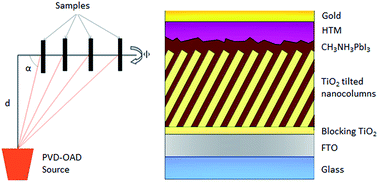
Abstract
Perovskite solar cells have attracted increasing interest among the photovoltaic community in the last few years owing to their unique properties and high efficiency. In the present work, we report the fabrication of perovskite solar cells based on highly ordered 1-dimensional porous TiO2 photoanodes, which are uniform on a large area. These nanocolumnar porous TiO2 photoanodes were deposited by physical vapor deposition in an oblique angle configuration (PVD-OAD) by varying the zenithal angle between the target and the substrate normal. Perovskite infiltration into these 1-dimensional nanocolumnar structures was homogeneous through the entire thickness of the porous layer as revealed by secondary ion mass spectroscopy studies. The fabricated solar cells, with an optimized thickness of the photoanode and with industrially accepted methods, will pave the way for easy implementation on a large scale.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/c5ta02238j
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Fabrication of Optical Multi layer Devices from Porous Silicon Coatings with Closed Porosity by Magnetron Sputtering
Caballero-Hernandez, Jaime; Godinho, Vanda; Lacroix, Bertrand; Jimenez de Haro, Maria C.; Jamon, Damien; Fernandez, AsuncionACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7 (2015) 13880-13897 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b02356
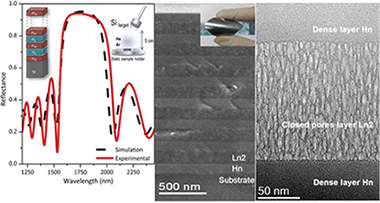
Abstract
The fabrication of single-material photonic-multilayer devices is explored using a new methodology to produce porous silicon layers by magnetron sputtering. Our bottom-up methodology produces highly stable amorphous porous silicon films with a controlled refractive index using magnetron sputtering and incorporating a large amount of deposition gas inside the closed pores. The influence of the substrate bias on the formation of the closed porosity was explored here for the first time when He was used as the deposition gas. We successfully simulated, designed, and characterized Bragg reflectors and an optical microcavity that integrates these porous layers. The sharp interfaces between the dense and porous layers combined with the adequate control of the refractive index and thickness allowed for excellent agreement between the simulation and the experiments. The versatility of the magnetron sputtering technique allowed for the preparation of these structures for a wide range of substrates such as polymers while also taking advantage of the oblique angle deposition to prepare Bragg reflectors with a controlled lateral gradient in the stop band wavelengths.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b02356
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Environmental Effects on the Photophysics of Organic-Inorganic Halide Perovskites
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Anaya, M; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 6 (2015) 2200-2205 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b00785
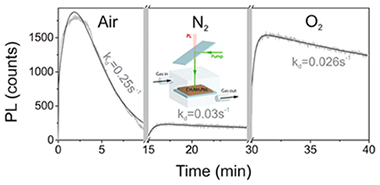
Abstract
The photophysical properties of films of organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites under different ambient conditions are herein reported. We demonstrate that their luminescent properties are determined by the interplay between photoinduced activation and darkening processes, which strongly depend on the atmosphere surrounding the samples. We have isolated oxygen and moisture as the key elements in each process, activation and darkening, both of which involve the interaction with photogenerated carriers. These findings show that environmental factors play a key role in the performance of lead halide perovskites as efficient luminescent materials.
June, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b00785
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Core-shell polydopamine magnetic nanoparticles as sorbent in micro-dispersive solid-phase extraction for the determination of estrogenic compounds in water samples prior to high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis
Socas-Rodriguez, B; Hernandez-Borges, J; Salazar, P; Martin, M; Rodriguez-Delgado, MAJournal of Chromatography A, 1397 (2015) 1-10 DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.04.010

Abstract
In this work, core-shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles (m-NPs) were prepared and characterized in our laboratory and applied as sorbents for the magnetic-micro solid phase extraction (m-mu SPE) of twelve estrogenic compounds of interest (i.e. 17 alpha-estradiol, 17 beta-estradiol, estrone, hexestrol, 17 alpha-ethynylestradiol, diethylstibestrol, dienestrol, zearalenone, alpha-zearalanol,beta-zearalanol, alpha-zearalenol and beta-zearalenol) from different water samples. Separation, determination and quantification were achieved by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to ion trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization. NPs@poly(dopamine) were synthesized by a chemical coprecipitation procedure and characterized by different surface characterization techniques (X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, transmission and scanning electron microscopy, infrared and Raman spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry, microelectrophoresis and adsorption/desorption isotherms). Parameters affecting the extraction efficiency of m-mu SPE (i.e. polymerization time, pH of the sample, extraction and elution conditions) were studied and optimized. The methodology was validated for Milli-Q, mineral, tap and wastewater using 2-methoxyestradiol as internal standard, obtaining recoveries ranging from 70 to 119% with relative standard deviation values lower than 20% and limits of quantification in the range 0.02-1.1 mu g/L.
June, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.04.010
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
A novel two-steps solvothermal synthesis of nanosized BiPO4 with enhanced photocatalytic activity
Zhang, YF; Sillanpaa, M; Obregon, S; Colon, GJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 402 (2015) 92-99 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2015.03.011
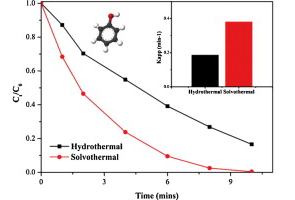
Abstract
Nano-sized BiPO4 has been successfully synthesized via a novel designed two-steps solvothermal route using ethylene glycol as solvent. Comparing with traditional hydrothermal method, the novel approach could readily prepare BiPO4 with shorter time. The photocatalytic activity of prepared BiPO4 has been tested via degradation of methylene blue (MB) under light irradiation. The experimental results show that the BiPO4 prepared by novel route had enhanced photocatalytic activity and the synthetic parameters also impact the reaction rate meaningfully. Finally, the obtained samples have been widely characterized by means of powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS) and Fourier transformed infrared (FTIR) spectra. BiPO4 prepared by this novel approach have a particles size below 100 nm, which is a big improvement by comparing with previous works (few micrometer). The effect of EG during the formation of BiPO4 has been discussed and a possible formation mechanism is proposed.
June, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2015.03.011
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Island-type growth of Au–Pt heterodimers: direct visualization of misfit dislocations and strain-relief mechanisms
Garcia-Negrete, CA; Knappett, BR; Schmidt, FP; Rojas, TC; Wheatley, AEH; Hofer, F; Fernandez, ARSC Advances, 5 (2015) 55262-55268 DOI: 10.1039/C5RA09808D
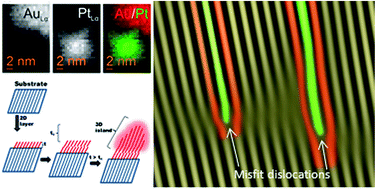
Abstract
Structural and analytical characterization related to the formation mechanism of Au–Pt heterodimers from polyhedral Pt nanocrystals is reported. The observation of specific lattice strain effects and the emergence of misfit dislocations point to the relevance of the Stranski–Krastanov growth mode as a means of explaining the previously reported dimerisation reaction between Au and Pt. Two size-dependent strain relief mechanisms were identified. For dimers grown from 4.7 nm seeds, the mechanism is related to bulk lattice strain accumulation at {111} planes along with lattice relaxation effects on other crystalline planes. However, for dimers grown from 11.2 nm seed sizes, the formation of misfit dislocations proved to be a highly efficient mechanism by which to release interface mismatch strain. Nanoscale chemical mapping at Au–Pt interfaces also revealed Au–Pt alloying to be unlikely under the mild temperature conditions employed in this work for Au–Pt heterodimer synthesis.
June, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C5RA09808D
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
H-2 oxidation as criterion for PrOx catalyst selection: Examples based on Au-Co-O-x-supported systems
Reina, TR; Megias-Sayago, C; Florez, AP; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Catalysis, 326 (2015) 161-171 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.03.015
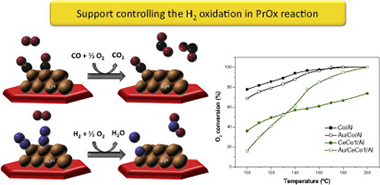
Abstract
A new approach for understanding PrOx reaction over gold catalysts is proposed in this work. The competition between H-2 and CO oxidation has been studied over a series of Au/MOx/Al2O3 (M = Ce and Co) catalysts in simulated post-reforming gas stream, containing H2O and CO2 for H-2 cleanup goals. The catalysts' behavior is correlated to their oxygen storage capacity, redox behavior, and oxidation ability. The estimation of the reaction rates reveals that in these solids the H-2 combustion, the selectivity limiting factor in the PrOx process, is mainly controlled by the support and not by the gold presence. The possible use of the hydrogen oxidation reaction as a catalyst selection criterion is discussed.
June, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.03.015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Porous, robust highly conducting Ni-YSZ thin film anodes prepared by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles for application as anodes and buffer layers in solid oxide fuel cells
Garcia-Garcia, Francisco J.; Yubero, Francisco; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Balomenou, Stella P.; Tsiplakides, Dimitris; Petrakopoulou, Ioanna; Lambert, Richard M.Inernational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40 (2015) 7382-7387 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.04.001
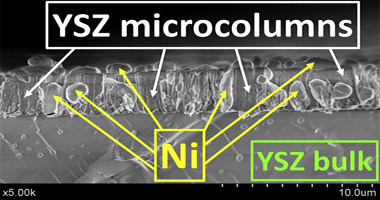
Abstract
Uniform, highly porous, columnar thin films incorporating YSZ and NiO prepared by magnetron sputtering with deposition at glancing incidence exhibited stoichiometries close to that of the Y-Zr-Ni sputter target. Characterization by means of SEM, XRD, XPS and RBS revealed that the uniformly distributed nickel component in the as-deposited films consisted of NiO, and that the YSZ component was essentially amorphous. Annealing such films at 850 degrees C in hydrogen resulted in crystallization of the YSZ phase with preservation of the columnar morphology, while the NiO underwent reduction to metallic Ni, which partially segregated to the film surface. The hydrogen-annealed thin film anodes exhibited high conductivity, comparable to that of conventionally-prepared anodes, in both hydrogen and hydrogen/water mixtures at temperatures relevant to SOFC operation. They were also robust against strain-induced separation from the substrate under limited thermal cycling in both oxidizing and reducing atmospheres and are promising candidates for use as anodes in their own right and as strain-accommodating buffer layers between conventional anodes and the electrolyte for use in SOFC applications.
June, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.04.001
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Uranium immobilization by FEBEX bentonite and steel barriers in hydrothermal conditions
Villa-Alfageme, M; Hurtado, S; El Mrabet, S; Pazos, MC; Castro, MA; Alba, MDChemical Engineering Journal, 269 (2015) 279-287 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.134
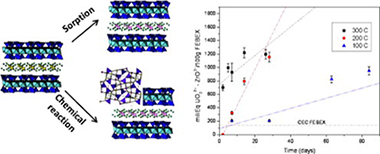
Abstract
FEBEX clay is considered a reference material in engineered barriers for safe storage of nuclear waste and uranium is a minor component of high-level radioactive waste (HLRW) and a main component of the spent nuclear fuel (SNF). Here, the kinetics of reaction of uranium with FEBEX was investigated in addition to the uranium immobilisation ability and the structural analysis of the reaction products. Hydrothermal treatments were accomplished with UO22+ and tetravalent actinide simulator ZrO2+, also present in HLRW. The quantification of the reaction was performed through gamma spectrometry of uranium. Two mechanisms for UO22+ retention by FEBEX were detected: adsorption and formation of stable and insoluble new phases. The structural analyses performed using ZrO2+, confirmed the uranium adsorption and the presence of new phases, ZrO2 and Zr(SiO4), that emphasise the existence of a chemical reaction with the bentonite. The analysis of the velocity of reaction uranium-clay minerals revealed temperature dependence. An exponential fitting suggested that the removal of uranium from solution at temperatures over 200 °C could be completed in less than a year. For lower temperatures, several years are needed. Milliequivalents of UO22+ immobilised by the clay depended on temperature and time and were over cation exchange capacity (CEC) of FEBEX even at 100 °C (reaching 600% of CEC). The reaction with steel, also temperature dependent, was finally analysed. At 200 °C 40–70% of uranium reacted with steel. But only 30–15% reacted at 300 °C and 100 °C. The reactions provide a stable immobilisation mechanism for uranium even when its sorption and swelling capacities fail. Our experiments will be of particular interest for very deep borehole disposals were higher temperatures and pressures are expected.
June, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.134
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Fine Tuning the Emission Properties of Nanoemitters in Multilayered Structures by Deterministic Control of their Local Photonic Environment
Alberto Jiménez-Solano, Juan Francisco Galisteo-López and Hernán MíguezSmall, 11 (2015) 2727-2732 DOI: 10.1002/smll.201402898
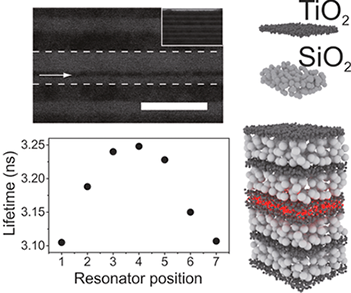
Abstract
Deterministic control on the dynamics of organic nanoemitters is achieved through precise control of its photonic environment. Resonators are fabricated by a combination of spin- and dip-coating techniques, which allows placement of the emitters at different positions within the sample, thus acting as a probe of the local density of states.
June, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/smll.201402898
Reactividad de Sólidos
In Situ Synthesis of a ZrB2-Based Composite Powder Using a Mechanochemical Reaction for the Zircon/Magnesium/Boron Oxide/Graphite System
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MSS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 12 (2015) 551-559 DOI: 10.1111/ijac.12202
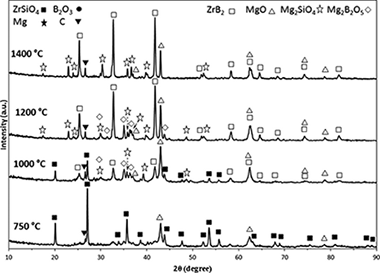
Abstract
A ZrSiO4/B2O3/Mg/C system was used to synthesize a ZrB2-based composite through a high-energy ball milling process. As a result of the milling process, a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) was achieved in this system. A composite powder of ZrB2-SiC-ZrC was prepared in situ by a magnesiothermic reduction with an ignition time of approximately 6min. The mechanism for the formation of the product was investigated by studying the relevant subreactions, the stoichiometric amount of B2O3, and thermal analysis.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.1111/ijac.12202
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Free-Base Carboxyphenyl Porphyrin Films Using a TiO2 Columnar Matrix: Characterization and Application as NO2 Sensors
Roales, Javier; Pedrosa, Jose M.; Guillen, Maria G.; Lopes-Costa, Tania; Castillero, Pedro; Barranco, Angel; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Sensors, 15 (2015) 11118-11132 DOI: 10.3390/s150511118
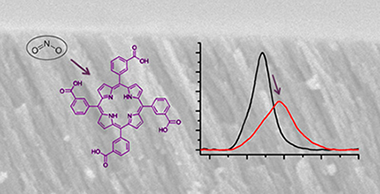
Abstract
The anchoring effect on free-base carboxyphenyl porphyrin films using TiO2 microstructured columns as a host matrix and its influence on NO2 sensing have been studied in this work. Three porphyrins have been used: 5-(4-carboxyphenyl)10,15,20-triphenyl-21H,23H-porphyrin (MCTPP); 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)-21H,23H-porphyrin (p-TCPP); and 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(3-carboxyphenyl)-21H,23H-porphyrin (m-TCPP). The analysis of UV-Vis spectra of MCTPP/TiO2, p-TCPP/TiO2 and m-TCPP/TiO2 composite films has revealed that m-TCPP/TiO2 films are the most stable, showing less aggregation than the other porphyrins. IR spectroscopy has shown that m-TCPP is bound to TiO2 through its four carboxylic acid groups, while p-TCPP is anchored by only one or two of these groups. MCTPP can only be bound by one carboxylic acid. Consequently, the binding of p-TCPP and MCTPP to the substrate allows them to form aggregates, whereas the more fixed anchoring of m-TCPP reduces this effect. The exposure of MCTPP/TiO2, p-TCPP/TiO2 and m-TCPP/TiO2 films to NO2 has resulted in important changes in their UV-Vis spectra, revealing good sensing capabilities in all cases. The improved stability of films made with m-TCPP suggests this molecule as the best candidate among our set of porphyrins for the fabrication of NO2 sensors. Moreover, their concentration-dependent responses upon exposure to low concentrations of NO2 confirm the potential of m-TCPP as a NO2 sensor.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.3390/s150511118
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
The role of silver nanoparticles functionalized on TiO2 for photocatalytic disinfection of harmful algae
Lee, Soo-Wohn; Obregon, S.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, V.RSC Advances, 5 (2015) 44470-44475 DOI: 10.1039/C5RA08313C
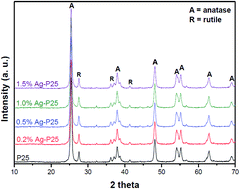
Abstract
Silver loaded TiO2 samples were prepared by photodeposition of different amounts of Ag+ ions over commercial titanium dioxide (Evonik TiO2 P25) in aqueous media without the presence of sacrificial agents. The obtained photocatalysts were characterized by several techniques such as X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) in order to correlate the effect of the silver amount on the photocatalytic properties of the final nanocomposite. The effect of the silver nanoparticles on the photocatalytic behaviour of TiO2 was evaluated by means of the photodegradation of methyl orange dye and the inactivation of noxious algae Tetraselmis suecicaand Amphidium carterae under continuous exposure of low power irradiation UV-light. The sample with 1.5% wt of silver nanoparticles showed the highest photocatalytic elimination of the azo dye and both algae types. According to the results, the cells were deformed during the photocatalytic process by the attack of highly reactive species such as hydroxyl radicals, H2O2 and superoxide ions generated on the TiO2 surface. The algae cells were not regenerated by themselves after the photocatalytic process due the high degree of fragmentation that they suffered during the light irradiation.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C5RA08313C
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrochemical activation of an oblique angle deposited Cu catalyst film for H-2 production
Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Valverde, JL; de Lucas-Consuegra, ACatalysis Science & Technology, 5 (2015) 2203-2214 DOI: 10.1039/c4cy01524j
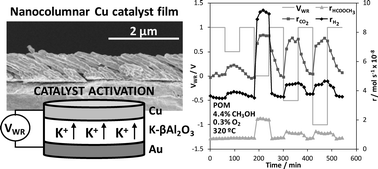
Abstract
A novel Cu catalyst film was prepared by oblique angle physical vapour deposition (OAD) on a K-βAl2O3 solid electrolyte (alkaline ionic conductor) for catalytic/electrocatalytic purposes. This technique allowed us to obtain a highly porous and electrically conductive Cu catalyst electrode which was tested in the partial oxidation of methanol (POM) reaction for H2 production and its catalytic activity was in situ enhanced via electrochemical promotion of catalysis (EPOC). The electropromotional effect was reversible and reproducible, and allowed us to increase both hydrogen and methyl formate production rates by almost three times under optimal promotion conditions (320 °C, 2.2 × 10−7 mol of K+ transferred). The observed promotional effect was attributed to a decrease in the Cu catalyst work function as a consequence of the controlled migration of electropositive K+ ions which favoured the chemisorption of electron acceptor molecules (O2) at the expense of the electron donor ones (CH3OH). Under the reaction conditions these ions formed some kinds of potassium surface compounds as demonstrated by SEM, EDX and XPS post-reaction characterization analyses. The obtained results demonstrate the interest of the used catalyst-electrode preparation technique for the electrochemical activation of non-noble metal catalyst films.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/c4cy01524j
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético - Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Theory and Practice: Bulk Synthesis of C3B and its H2- and Li-Storage Capacity
King, TC; Matthews, PD; Glass, H; Cormack, JA; Holgado, JP; Leskes, M; Griffin, JM; Scherman, OA; Barker, PD; Grey, CP; Dutton, SE; Lambert, RM; Tustin, G; Alavi, A; Wright, DSAngewandte Chemie International Edition, 54 (2015) 5919-5923 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201412200
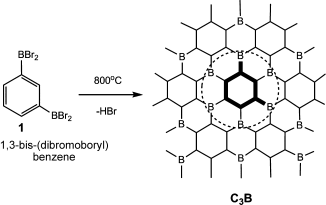
Abstract
Previous theoretical studies of C3B have suggested that boron-doped graphite is a promising H2- and Li-storage material, with large maximum capacities. These characteristics could lead to exciting applications as a lightweight H2-storage material for automotive engines and as an anode in a new generation of batteries. However, for these applications to be realized a synthetic route to bulk C3B must be developed. Here we show the thermolysis of a single-source precursor (1,3-(BBr2)2C6H4) to produce graphitic C3B, thus allowing the characteristics of this elusive material to be tested for the first time. C3B was found to be compositionally uniform but turbostratically disordered. Contrary to theoretical expectations, the H2- and Li-storage capacities are lower than anticipated, results that can partially be explained by the disordered nature of the material. This work suggests that to model the properties of graphitic materials more realistically, the possibility of disorder must be considered.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/anie.201412200
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
STEM-in-SEM high resolution imaging of gold nanoparticles and bivalve tissues in bioaccumulation experiments
C.A. García-Negrete; M.C. Jiménez de Haro; J. Blasco; M. Soto; A. FernándezAnalyst, 140 (2015) 3082-3089 DOI: 10.1039/C4AN01643B
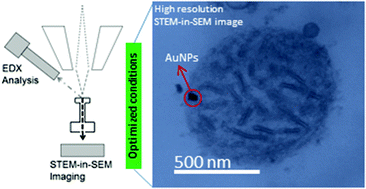
Abstract
The methodology termed scanning transmission electron microscopy in scanning electron microscopy (STEM-in-SEM) has been used in this work to study the uptake of citrate stabilized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) (average particle sizes of 23.5 ± 4.0 nm) into tissue samples uponin vitro exposure of the dissected gills of the Ruditapes philippinarum marine bivalve to the nanoparticle suspensions. The STEM-in-SEM methodology has been optimized for achieving optimum resolution under SEM low voltage operating conditions (20–30 kV). Based on scanning microscope assessments and resolution testing (SMART), resolutions well below 10 nm were appropriately achieved by working at magnifications over 100k×, with experimental sample thickness between 300 and 200 nm. These relatively thick slices appear to be stable under the beam and help avoid NP displacement during cutting. We herein show that both localizing of the internalized nanoparticles and imaging of ultrastructural disturbances in gill tissues are strongly accessible due to the improved resolution, even at sample thicknesses higher than those normally employed in standard TEM techniques at higher voltages. Ultrastructural imaging of bio-nano features in bioaccumulation experiments have been demonstrated in this study.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C4AN01643B
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Mono and bimetallic Cu-Ni structured catalysts for the water gas shift reaction
O. Arbeláez, T.R. Reina, S. Ivanova, F. Bustamante, A.L. Villa, M.A. Centeno, J.A. OdriozolaApplied Catalysis A-General, 497 (2015) 1-9 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.02.041
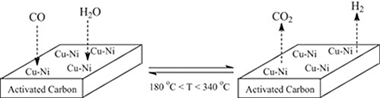
Abstract
The water-gas shift (WGS) reaction over structured Cu, Ni, and bimetallic Cu-Ni supported on active carbon (AC) catalysts was investigated. The structured catalysts were prepared in pellets form and applied in the medium range WGS reaction. A good activity in the 180–350 °C temperature range was registered being the bimetallic Cu-Ni:2-1/AC catalyst the best catalyst. The presence of Cu mitigates the methanation activity of Ni favoring the shift process. In addition the active carbon gasification reaction was not observed for the Cu-containing catalyst converting the active carbon in a very convenient support for the WGS reaction. The stability of the bimetallic Cu-Ni:2-1/AC catalyst under continuous operation conditions, as well as its tolerance towards start/stop cycles was also evaluated.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.02.041
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Anisotropic In-Plane Conductivity and Dichroic Gold Plasmon Resonance in Plasma-Assisted ITO Thin Films e-Beam-Evaporated at Oblique Angles
Parra-Barranco, Julian; Garcia-Garcia, Francisco J.; Rico, Victor; Borras, Ana; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Frutos, Fabian; Barranco, Angel; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7 (2015) 10993-11001 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b02197
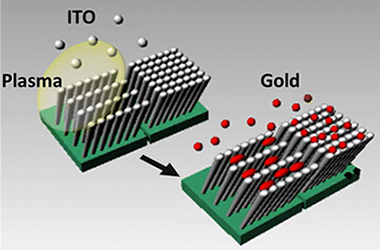
Abstract
ITO thin films have been prepared by electron beam evaporation at oblique angles (OA), directly and while assisting their growth with a downstream plasma. The films microstructure, characterized by scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and glancing incidence small-angle X-ray scattering, consisted of tilted and separated nanostructures. In the plasma assisted films, the tilting angle decreased and the nanocolumns became associated in the form of bundles along the direction perpendicular to the flux of evaporated material. The annealed films presented different in-depth and sheet resistivity as confirmed by scanning conductivity measurements taken for the individual nanocolumns. In addition, for the plasma-assisted thin films, two different sheet resistance values were determined by measuring along the nanocolumn bundles or the perpendicular to it. This in-plane anisotropy induces the electrochemical deposition of elongated gold nanostructures. The obtained Au-ITO composite thin films were characterized by anisotropic plasmon resonance absorption and a dichroic behavior when examined with linearly polarized light.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b02197
Reactividad de Sólidos
Toughening of complete solid solution cermets by graphite addition
Chicardi, E; Torres, Y; Sayagues, MJ; Medri, V; Melandri, C; Cordoba, JM; Gotor, FJChemical Engineering Journal, 267 (2015) 297-305 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.022
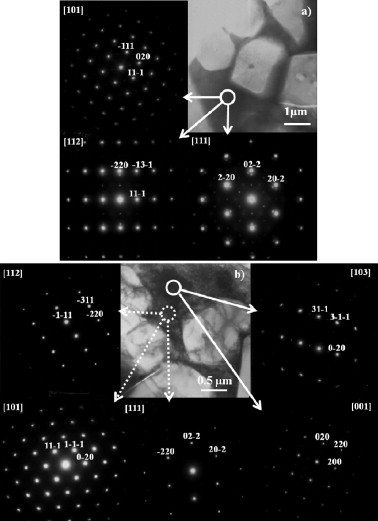
Abstract
(Ti0.95Ta0.05)(C0.5N0.5)-Co complete solid solution cermets (CSCs) were developed by a mechanochemical synthesis process and a pressureless sintering method. The effect of different percentages of graphite used as a sintering additive on the nature of the binder phase and the mechanical properties of the cermets was investigated. Microstructural and mechanical characterisations were carried out by X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Vickers hardness, indentation fracture toughness and nanoindentation. The addition of graphite modified the carbon activity during sintering, reducing the dissolution of carbonitride ceramic particles into the molten binder. The amount of Ti and Ta remaining in the binder after sintering gradually decreased as the amount of graphite added increased, which induced a change in the nature of the binder phase. When no graphite was added, the binder consisted of the brittle TixTa1−xCo2 intermetallic phase. With the increase in the amount of graphite added, the formation of more ductile phases, such as TixTa1−xCo3 and α-Co, was observed, causing a significant improvement in the toughness of the cermets.
May, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.022
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Self-lubricity of WSex nanocomposite coatings
S. Dominguez-Meister; M. Conte; A. Igartua; T.C. Rojas; J.C. Sánchez-LópezACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7 (2015) 7979-7986 DOI: 10.1021/am508939s
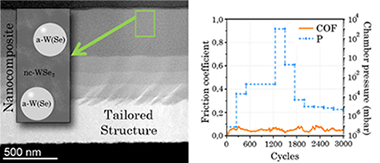
Abstract
Transition metal chalcogenides with lamellar structure are known for their use in tribological applications although limited to vacuum due to their easy degradation in the presence of oxygen and/or moisture. Here we present a tailored WSex coating with low friction (0.07) and low wear rates (3 × 10–7 mm3 Nm–1) even in ambient air. To understand the low friction behavior and lower chemical reactivity a tribological study is carried out in a high-vacuum tribometer under variable pressure (atmospheric pressure to 1 × 10–8 mbar). A detailed investigation of the film nanostructure and composition by advanced transmission electron microscopy techniques with nanoscale resolution determined that the topmost layer is formed by nanocrystals of WSe2 embedded in an amorphous matrix richer in W, a-W(Se). After the friction test, an increased crystalline order and orientation of WSe2 lamellas along the sliding direction were observed in the interfacial region. On the basis of high angle annular dark field, scanning transmission electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray analysis, the release of W atoms from the interstitial basal planes of the a-W(Se) phase is proposed. These W atoms reaching the surface, play a sacrificial role preventing the lubricant WSe2 phase from oxidation. The increase of the WSe2 crystalline order and the buffer effect of W capturing oxygen atoms would explain the enhanced chemical and tribological response of this designed nanocomposite material.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/am508939s
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
An Optically Controlled Microscale Elevator Using Plasmonic Janus Particles
Nedev, S; Carretero-Palacios, S; Kuhler, P; Lohmuller, T; Urban, AS; Anderson, LJE; Feldmann, JACS Photonics, 2 (2015) 491-496 DOI: 10.1021/ph500371z
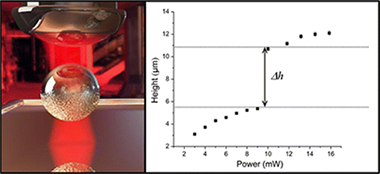
Abstract
In this article, we report how Janus particles, composed of a silica sphere with a gold half-shell, can be not only stably trapped by optical tweezers but also displaced controllably along the axis of the laser beam through a complex interplay between optical and thermal forces. Scattering forces orient the asymmetric particle, while strong absorption on the metal side induces a thermal gradient, resulting in particle motion. An increase in the laser power leads to an upward motion of the particle, while a decrease leads to a downward motion. We study this reversible axial displacement, including a hysteretic jump in the particle position that is a result of the complex pattern of a tightly focused laser beam structure above the focal plane. As a first application we simultaneously trap a spherical gold nanoparticle and show that we can control the distance between the two particles inside the trap. This photonic micron-scale “elevator” is a promising tool for thermal force studies, remote sensing, and optical and thermal micromanipulation experiments.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/ph500371z
Reactividad de Sólidos
Morphological changes on graphene nanoplatelets induced during dispersion into an epoxy resin by different methods
Moriche, R; Prolongo, SG; Sanchez, M; Jimenez-Suarez, A; Sayagues, MJ; Urena, AComposites Part B-Engineering, 72 (2015) 199-205 DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.12.012
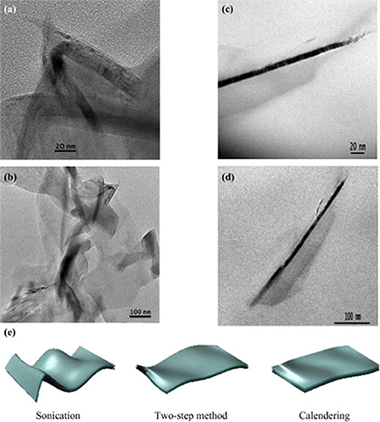
Abstract
A structural analysis demonstrating how the manufacturing method of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) into a polymer matrix can strongly modify the GNPs morphology and, consequently, their properties, was carried out. Three different methods based on sonication and high shear forces were used to elucidate defects induction and possible size diminution. Manufacturing methods including high shear forces caused the extension of the GNPs while sonication induces wrinkling of the sheets. Residual stresses are induced in the nanoplatelets structure showing an increase in the Raman intensities ratios I-D/I-G and I-D/I-G when a major cycles number of calendering are applied.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.12.012
Materiales Coloidales
Biosynthesis of silver fine particles and particles decorated with nanoparticles using the extract of Illicium verum (star anise) seeds
Luna, Carlos; Chavez, V. H. G.; Diaz Barriga-Castro, Enrique; Nunez, Nuria O.; Mendoza-Resendez, RaquelSpectrochimica Acta Part A-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 141 (2015) 43-50 DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.12.076
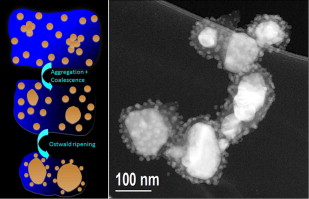
Abstract
Given the upsurge of new technologies based on nanomaterials, the development of sustainable methods to obtain functional nanostructures has become an imperative task. In this matter, several recent researches have shown that the biodegradable natural antioxidants of several plant extracts can be used simultaneously as reducing and stabilizing agents in the wet chemical synthesis of metallic nanoparticles, opening new opportunities to design greener synthesis. However, the challenge of these new techniques is to produce stable colloidal nanoparticles with controlled particle uniformity, size, shape and aggregation state, in similar manner than the well-established synthetic methods. In the present work, colloidal metallic silver nanoparticles have been synthesized using silver nitrate and extracts of Illicium verum (star anise) seeds at room temperature in a facile one-step procedure. The resulting products were colloidal suspensions of two populations of silver nanoparticles, one of them with particle sizes of few nanometers and the other with particles of tens of nm. Strikingly, the variation of the AgNO3/extract weight ratio in the reaction medium yielded to the variation of the spatial distribution of the nanoparticles: high AgNO3/extract concentration ratios yielded to randomly dispersed particles, whereas for lower AgNO3/extract ratios, the biggest particles appeared coated with the finest nanoparticles.-This biosynthesized colloidal system, with controlled particle aggregation states, presents plasmonic and SERS properties with potential applications in molecular sensors and nanophotonic devices.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.12.076
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanically induced self-propagating reaction of vanadium carbonitride
Roldan, MA; Alcala, MD; Real, CCeramics International, 41 (2015) 4688-4695 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.12.016
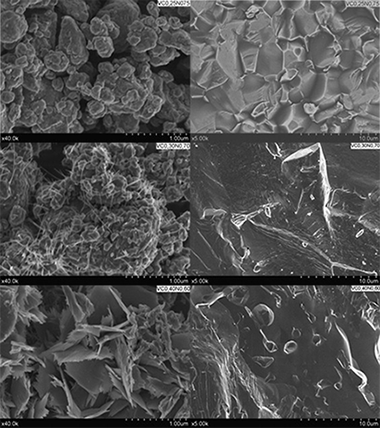
Abstract
Vanadium carbonitrides (VCxN1-x) were prepared via mechanosynthesis from mixtures of elemental vanadium and carbon with different V/C atomic ratios under a nitrogen atmosphere using a high-energy ball mill. We obtained the full composition range of carbonitrides at room temperature. The products were characterized using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and electron energy loss spectroscopy. The results showed particle-sized products with high sinterability and very high microhardness.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.12.016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Self-Assembling of Tetradecylammonium Chain on Swelling High Charge Micas (Na-Mica-3 and Na-Mica-2): Effect of Alkylammonium Concentration and Mica Layer Charge
Pazos, MC; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDLangmuir, 31 (2015) 4394-4401 DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00224
Abstract
A family of tetradecylammonium micas is synthesized using synthetic swelling micas with high layer charge (NanSi8-nAln,Mg6F4O20 center dot XH2O, where n = 2 and 3) exchanged with tetradecylammonium cations. The molecular arrangement of the surfactant is,elucidated on the basis of XRD patterns and DTA. The ordering conformation of the surfactant molecules into the interlayer space of Micas is investigated by IR/FT, C-13, Al-27, and Si-29 MAS NMR. The structural arrangement of the tetradecylammonium cation in the interlayer space of high-charge micas is more sensitive to the effect of the mica layer charge at high concentration. The surfactant arrangement is found to follow the bilayer-paraffin model for all values of layer charge and surfactant concentration. However, at initial concentration below the mica CEC, a lateral monolayer is also observed. The amount of ordered conformation all-trans is directly proportional to the layer charge and surfactant concentration.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00224
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 over platinised Bi2WO6-based materials
Murcia-Lopez, S; Vaiano, V; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Sannino, DPhotochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 14 (2015) 678-685 DOI: 10.1039/c4pp00407h
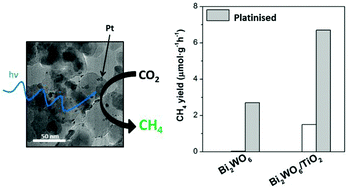
Abstract
The photocatalytic reduction of CO2 with H2O to produce CH4 in the gas phase was carried out in the presence of two Bi2WO6-based materials. For this purpose, single Bi2WO6 and a coupled Bi2WO6-TiO2 system were synthesised and metallised with Pt, through a Pt photodeposition method. Then, the samples were characterised and the photocatalytic activity was evaluated in a continuous fluidised-bed reactor irradiated with UV light. Single Bi2WO6 presents an interesting behaviour under H2O rich conditions. In particular, the metallisation improves the material's performance for CH4 formation, while the TiO2 addition to Bi2WO6 increases the CH4 yield only at low H2O/CO2 ratio. The Bi2WO6-TiO2 system metallised with a Pt photocatalyst displayed the highest CH4 yield among all the prepared photocatalysts. The stability of the system can be enhanced through the addition of a blue phosphor to the reactant mixture, especially under H2O rich conditions.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/c4pp00407h
Reactividad de Sólidos
Applications of sample-controlled thermal analysis (SCTA) to kinetic analysis and synthesis of materials
Perez-Maqueda, L. A.; Criado, J. M.; Sanchez-Jimenez, P. E.; Dianez, M. J.Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 120 (2015) 45-51 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-014-4176-6
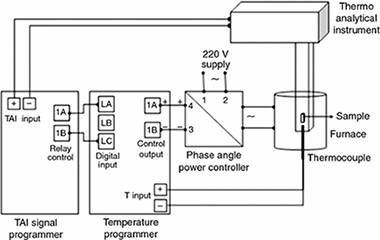
Abstract
The advantages of the sample-controlled thermal analysis (SCTA) for both the kinetic analysis of solid-state reactions and the synthesis of materials are reviewed. This method implies an intelligent control of the temperature by the solid-state reaction under study in such a way that the reaction rate as a function of the time fits a profile previously defined by the user. It has been shown that SCTA has important advantages for discriminating the kinetic model of solid-state reactions as compared with conventional rising temperature methods. Moreover, the advantages of SCTA methods for synthesising materials with controlled texture and structure are analysed.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-014-4176-6
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Hydrogen production through sodium borohydride ethanolysis
Arzac, GM; Fernandez, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40 (2015) 5326-5332 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.01.115
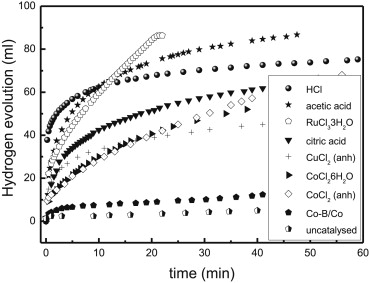
Abstract
In this work, sodium borohydride (SB) ethanolysis was explored for the first time as a method to generate hydrogen for Polymer Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Ethanolysis by-product was characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, X-Ray Diffraction, and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Metal and acid catalysts were tested. RuCl3 center dot 3H(2)O was the best metal catalyst. Acetic acid was selected for the study because of its effectiveness, low cost and relative greenness. The maximum gravimetric hydrogen density obtained was 2.1% wt. The addition of water produces an increase in hydrogen generation rate and a decrease in conversion. The use of ethanol-methanol mixtures produces an increase in reaction rates in absence of catalyst. As a proof of concept the reaction was performed in a small reactor which operates by the addition of ethanolic acetic acid solutions to solid SB (in the form of granules). The reactor produces stable and constant hydrogen generation in the range of 20-80 ml min(-1) during 1 h at constant temperature (around 27-35 degrees.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.01.115
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Pectin-Lipid Self-Assembly: Influence on the Formation of Polyhydroxy Fatty Acids Nanoparticles
Guzman-Puyol, Susana; Jesus Benitez, Jose; Dominguez, Eva; Bayer, Ilker Sefik; Cingolani, Roberto; Athanassiou, Athanassia; Heredia, Antonio; Heredia-Guerrero, Jose AlejandroPLoS One, 10 (2015) e0124639 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124639
Abstract
Nanoparticles, named cutinsomes, have been prepared from aleuritic (9,10,16-trihidroxipalmitic) acid and tomato fruit cutin monomers (a mixture of mainly 9(10), 16-dihydroxypalmitic acid (85%, w/w) and 16-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid (7.5%, w/w)) with pectin in aqueous solution. The process of formation of the nanoparticles of aleuritic acid plus pectin has been monitored by UV-Vis spectrophotometry, while their chemical and morphological characterization was analyzed by ATR-FTIR, TEM, and non-contact AFM. The structure of these nanoparticles can be described as a lipid core with a pectin shell. Pectin facilitated the formation of nanoparticles, by inducing their aggregation in branched chains and favoring the condensation between lipid monomers. Also, pectin determined the self-assembly of cutinsomes on highly ordered pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) surfaces, causing their opening and forming interconnected structures. In the case of cutin monomers, the nanoparticles are fused, and the condensation of the hydroxy fatty acids is strongly affected by the presence of the polysaccharide. The interaction of pectin with polyhydroxylated fatty acids could be related to an initial step in the formation of the plant biopolyester cutin.
April, 2015 · DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124639
Materiales Coloidales
Up-conversion in Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped LaPO4 submicron-sized spheres
Garcia-Sevillano, J.; Cantelar, E.; Cusso, F.; Ocana, M.Optical Materials, 41 (2015) 104-107 DOI: 10.1016/j.optmat.2014.10.022
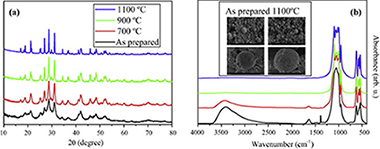
Abstract
Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped materials have been extensively used for imaging in biomedical applications using either visible up-converted (UC) or near-infrared (NIR) emissions. The UC spectrum is composed mainly by two Erbium emissions in the green (2H11/2:4S3/2 → 4I15/2) and red (4F9/2 → 4I15/2) spectral range, while the NIR spectrum includes Er3+ (λ ∼ 1.5 μm, 4I13/2 → 4I15/2) and Er3+/Yb3+ (λ ∼ 980 nm, 2F5/2 → 2F7/2(Yb3+):4I11/2 → 4I15/2 (Er3+)) transitions; which relative intensities are dependent on several physical parameters. In the present work, we present the preparation and optical characterization of Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped LaPO4 submicron-sized spheres. The luminescence (CW and pulsed) characteristics, after different post-annealing treatments, are studied. It is found that such treatments strongly increment the emission efficiency, possibly due to the suppression of residual impurities. After calcination at 1100 °C the material behaves as an excellent UC and NIR–NIR wavelength converter.
March, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.optmat.2014.10.022
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
High N-content a-C:N films elaborated by femtosecond PLD with plasma assistance
Maddi, C; Donnet, C; Loir, AS; Tite, T; Barnier, V; Rojas, TC; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Wolski, K; Garrelie, FApplied Surface Science, 332 (2015) 346-353 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.123
Abstract
Amorphous carbon nitride (a-C:N) thin films are a interesting class of carbon-based electrode materials. Therefore, synthesis and characterization of these materials have found lot of interest in environmental analytical microsystems. Herein, we report the nitrogen-doped amorphous carbon thin film elaboration by femtosecond pulsed laser deposition (fs-PLD) both with and without a plasma assistance. The chemical composition and atomic bonding configuration of the films were investigated by multi-wavelength (MW) Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS). The highest nitrogen content, 28 at.%, was obtained with plasma assistance. The I(D)/I(G) ratio and the G peak position increased as a function of nitrogen concentration, whereas the dispersion and full width at half maximum (FWHM) of G peak decreased. This indicates more ordered graphitic like structures in the films both in terms of topological and structural, depending on the nitrogen content. EELS investigations were correlated with MW Raman results. The interpretation of XPS spectra of carbon nitride films remains a challenge. Plasma assisted PLD in the femtosecond regime led to a significant high nitrogen concentration, which is highlighted on the basis of collisional processes in the carbon plasma plume interacting with the nitrogen plasma.
March, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.123
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis temperature effect on Na-Mica-4 crystallinity and heteroatom distribution
Naranjo, M; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 204 (2015) 282-288 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.11.026
Abstract
The discovery of swelling brittle mica, Na-Mica-4, has been one of the most significant advances in the pursuit for a material with high ion-exchange capacity. For technical applications, the control of the phase evolution during the synthesis is crucial. The main aim of this study was to investigate the effect of Na-Mica-4 synthesis temperature on the crystalline phase evolution, Si–Al distribution in the tetrahedral sheet, the Al occupancy between tetrahedral and octahedral sites and their effects on the interlayer space composition. The synthesis temperature range between 600 °C and 900 °C was explored. At low temperature (600 °C), the precursors were transformed in a low-charged swelling 2:1 phyllosilicate, saponite type, which was progressively aluminum enriched with temperature. The high-charged swelling mica was completely formed at 700 °C, although a minor anhydrous contribution remained up to 850 °C. Up to 800 °C, silicates and fluorides secondary phases were detected as a minor contribution.
March, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.11.026
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Transmission electron microscopy of thiol-capped Au clusters on C: Structure and electron irradiation effects
Lionel C. Gontard, Rafal E. Dunin-BorkowskiMicron DOI: 10.1016/j.micron.2014.12.001
Abstract
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy is used to study interactions between thiol-capped Au clusters and amorphous C support films. The morphologies of the clusters are found to depend both on their size and on the local structure of the underlying C. When the C is amorphous, larger Au clusters are crystalline, while smaller clusters are typically disordered. When the C is graphitic, the Au particles adopt either elongated shapes that maximize their contact with the edge of the C film or planar arrays when they contain few Au atoms. We demonstrate the influence of electron beam irradiation on the structure, shape and stability of the Au clusters, as well as on the formation of holes bounded by terraces of graphitic lamellae in the underlying C.
March, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micron.2014.12.001
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Nanolevitation Phenomena in Real Plane-Parallel Systems Due to the Balance between Casimir and Gravity Forces
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 5663-5670 DOI: 10.1021/jp511851z
Abstract
We report on the theoretical analysis of equilibrium distances in real plane-parallel systems under the influence of Casimir and gravity forces at thermal equilibrium. Due to the balance between these forces, thin films of Teflon, silica, or polystyrene in a single-layer configuration and immersed in glycerol stand over a silicon substrate at certain stable or unstable positions depending on the material and the slab thickness. Hybrid systems containing silica and polystyrene, materials which display Casimir forces and equilibrium distances of opposite nature when considered individually, are analyzed in either bilayer arrangements or as composite systems made of a homogeneous matrix with small inclusions inside. For each configuration, equilibrium distances and their stability can be adjusted by fine-tuning of the volume occupied by each material. We find the specific conditions under which nanolevitation of realistic films should be observed. Our results indicate that thin films of real materials in plane-parallel configurations can be used to control suspension or stiction phenomena at the nanoscale.
March, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/jp511851z
- ‹ previous
- 23 of 37
- next ›














