Scientific Papers in SCI
2016
2016
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A novel 3D absorption correction method for quantitative EDX-STEM tomography
Burdet, P; Saghi, Z; Filippin, AN; Borras, A; Midgley, PAUltramicroscopy, 160 (2016) 118-129 DOI: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2015.09.012
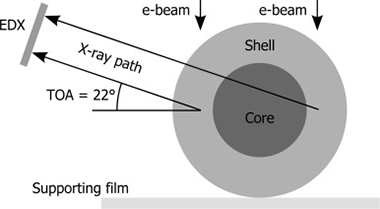
Abstract
This paper presents a novel 3D method to correct for absorption in energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) microanalysis of heterogeneous samples of unknown structure and composition. By using STEM-based tomography coupled with EDX, an initial 3D reconstruction is used to extract the location of generated X-rays as well as the X-ray path through the sample to the surface. The absorption correction needed to retrieve the generated X-ray intensity is then calculated voxel-by-voxel estimating the different compositions encountered by the X-ray. The method is applied to a core/shell nanowire containing carbon and oxygen, two elements generating highly absorbed low energy X-rays. Absorption is shown to cause major reconstruction artefacts, in the form of an incomplete recovery of the oxide and an erroneous presence of carbon in the shell. By applying the correction method, these artefacts are greatly reduced. The accuracy of the method is assessed using reference X-ray lines with low absorption.
January, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2015.09.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optofluidic Modulation of Self-Associated Nanostructural Units Forming Planar Bragg Microcavities
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Barranco, A; Loffler, M; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Nano, 10 (2016) 1256-1264 DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b06625
Abstract
Bragg microcavities (BMs) formed by the successive stacking of nanocolumnar porous SiO2 and TiO2 layers with slanted, zigzag, chiral, and vertical configurations are prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles while azimuthally varying the substrate orientation during the multilayer growth. The slanted and zigzag BMs act as wavelength-selective optical retarders when they are illuminated with linearly polarized light, while no polarization dependence is observed for the chiral and vertical cavities. This distinct optical behavior is attributed to a self-nanostructuration mechanism involving a fence-bundling association of nanocolumns as observed by focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy in the slanted and zigzag microcavities. The outstanding retarder response of the optically active BMs can be effectively modulated by dynamic infiltration of nano- and mesopores with liquids of different refraction indices acting as a switch of the polarization behavior. The unprecedented polarization and tunable optofluidic properties of these nanostructured photonic systems have been successfully simulated with a simple model that assumes a certain birefringence for the individual stacked layers and accounts for the light interference phenomena developed in the BMs. The possibilities of this type of self-arranged nanostructured and optically active BMs for liquid sensing and monitoring applications are discussed.
January, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b06625
Reactividad de Sólidos
High temperature oxidation resistance of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets
Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Gotor, FJCorrosion Science, 102 (2016) 125-136 DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.10.001
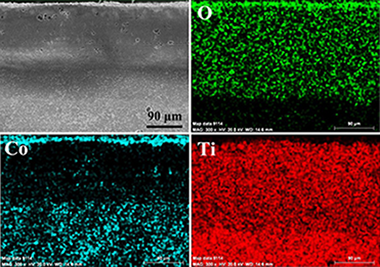
Abstract
Cermets based on titanium-tantalum carbonitride were oxidized in static air between 800 degrees C and 1100 degrees C for 48 h. The thermogravimetric and microstructural study showed an outstanding reduction in the oxidation of more than 90% when the Ta content was increased. In cermets with low Ta content, the formation of a thin CoO/Co3O4 outer layer tends to disappear by reacting with the underlying rutile phase, which emerges at the surface. However, in cermets with higher Ta content, the formation of an external titanate layer, observed even at a low temperature, appears to prevent the oxygen diffusion and the oxidation progression.
January, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.10.001
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of tin additions on the precipitation processes in a Cu-Ni-Zn alloys
Donoso, EC; Dianez, MJ; Criado, JM; Espinoza, R; Mosquera, ERevista de Metalurgia, 52 (2016) e060 DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.060
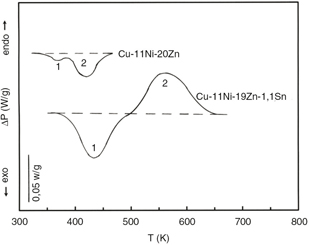
Abstract
Influence of tin additions on the precipitation processes in a Cu-Ni-Zn alloys. The influence of 1.1 wt% tin additions on the precipitation hardening of Cu-11 wt% Ni-20 wt% Zn alloy was studied by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), microhardeness measurements and High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM). The calorimetric curves, in the range of temperatures analyzed, show the presence of two exothermic reactions in the ternary alloy, associated to the short-range-order development assisted by migration of excess vacancies. On the other hand, one exothermic and one endothermic reaction are observed in the quaternary alloy, associated to the formation and dissolution of Cu2NiZn precipitates, respectively. It has been show that an addition of 1.1% tin plays an important role in the formation of Cu2NiZn precipitates, responsible for the precipitation hardening of the ternary alloy.
January, 2016 · DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.060
2015
2015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
"In Operando" X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Analysis of Structural Changes During Electrochemical Cycling of WO3 and WxSiyOz Amorphous Electrochromic Thin Film Cathodes
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Chaboy, JJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 644-652 DOI: 10.1021/jp508377v
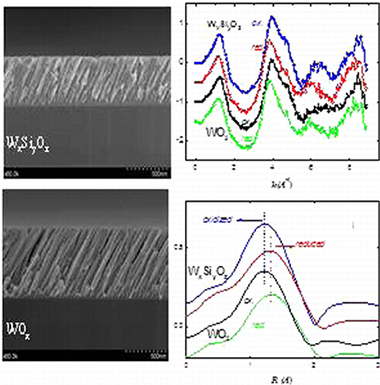
Abstract
This work reports a X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) study under in operando conditions of the structural and chemical changes undergone by WO3 and WxSiyOz thin films used as electrochromic cathodes. The electrochromic films were prepared by magnetron sputtering deposition at oblique angles and then characterized by a large variety of techniques. The voltammograms and chronoamperometric diagrams in both aqueous and organic electrolyte media revealed a total reversibility of the electrochromic behavior, a low response time, and a high coloration efficiency for the two types of thin films. The in operando X-ray absorption study of the films working in aqueous solutions revealed that when they were electrochemically cycled the average WO distances reversibly varied by a Delta d of 0.06 and 0.08 angstrom for, respectively, WO3 and WxSiyOz. These changes are discussed by assuming the reduction of W6+ cations and the transformation of W-O double bonds into single WO bond structures during the electrochemical cycling of the films.
January, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/jp508377v
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical properties of zirconium oxynitride films: The effect of composition, electronic and crystalline structures
Carvalho, P; Borges, J; Rodrigues, MS; Barradas, NP; Alves, E; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Cunha, L; Marques, L; Vasilevskiy, MI; Vaz, FApplied Surface Science, 358 (2015) 660-669 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.09.129
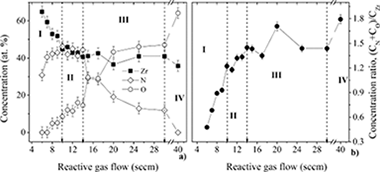
Abstract
This work is devoted to the investigation of zirconium oxynitride (ZrOxNy) films with varied optical responses prompted by the variations in their compositional and structural properties. The films were prepared by dc reactive magnetron sputtering of Zr, using Ar and a reactive gas mixture of N-2 + O-2 ( 17:3). The colour of the films changed from metallic-like, very bright yellow-pale and golden yellow, for low gas flows to red-brownish for intermediate gas flows. Associated to this colour change there was a significant decrease of brightness. With further increase of the reactive gas flow, the colour of the samples changed from red-brownish to dark blue or even to interference colourations. The variations in composition disclosed the existence of four different zones, which were found to be closely related with the variations in the crystalline structure. XRD analysis revealed the change from a B1 NaCl face-centred cubic zirconium nitride-type phase for films prepared with low reactive gas flows, towards a poorly crystallized over-stoichiometric nitride phase, which may be similar to that of Zr3N4 with some probable oxygen inclusions within nitrogen positions, for films prepared with intermediate reactive gas flows. For high reactive gas flows, the films developed an oxynitride-type phase, similar to that of gamma-Zr2ON2 with some oxygen atoms occupying some of the nitrogen positions, evolving to a ZrO2 monoclinic type structure within the zone where films were prepared with relatively high reactive gas flows. The analysis carried out by reflected electron energy loss spectroscopy (REELS) revealed a continuous depopulation of the d-band and an opening of an energy gap between the valence band (2p) and the Fermi level close to 5 eV. The ZrN-based coatings (zone land II) presented intrinsic colourations, with a decrease in brightness and a colour change from bright yellow to golden yellow, red brownish and dark blue. Associated to these changes, there was also a shift of the reflectivity minimum to lower energies, with the increase of the non-metallic content. The samples lying in the two last zones (zone III, oxynitride and zone IV, oxide films) revealed a typical semi-transparent-optical behaviour showing interference-like colourations only due to the complete depopulation of the d band at the Fermi level. The samples lying in these zones presented also an increase of the optical bandgap from 2 to 3.6 eV.
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.09.129
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Study of the phenol photocatalytic degradation over TiO2 modified by sulfation, fluorination, and platinum nanoparticles photodeposition
Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Arana, J; Dona-Rodriguez, JMApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 179 (2015) 305-312 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.05.040
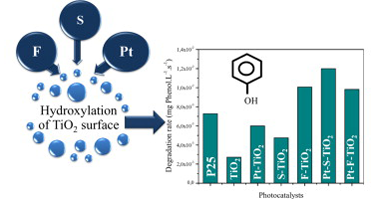
Abstract
In this work, titanium dioxide has been modified by sulfation, fluorination and simultaneous Pt nanoparticles deposition; the influence of these treatments on the photocatalytic activity of this oxide has been studied. A complete characterization study was carried out and it was observed that sulfation, fluorination and metallization were important factors influencing the TiO2 properties. The photocatalytic activity of the materials prepared was evaluated in the phenol degradation and it was found that TiO2fluorination significantly increased the phenol photodegradation rate, compared with bare TiO2, sulfated TiO2 or the commercial TiO2 Degussa P25. It was also found that Pt photodeposition on sulphated TiO2 notably increased the photocatalytic activity of this oxide, while Pt on fluorinated TiO2 did not modify significantly the phenol photodegradation rate.
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.05.040
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
High-temperature deformation of fully-dense fine-grained boron carbide ceramics: Experimental facts and modeling
Moshtaghioun, BM; Garcia, DG; Rodriguez, ADMaterials & Design, 88 (2015) 287-293 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.08.134
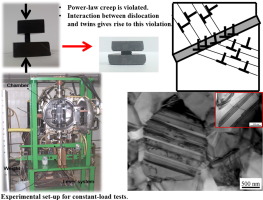
Abstract
Boron carbide ceramics are the hardest material in Nature after diamond and the cubic phase of boron nitride. Due to this fact, their room-temperature fracture properties are the object of intense research. Paradoxically, high-temperature deformation is essentially unknown, because very high temperatures and stresses are necessarily required and high-quality specimens have not been available until recently. In this paper, the high-temperature compressive creep of fine-grained boron carbide polycrystals is reported. The breakdown of the classical power-law for high-temperature plasticity in ceramics is found. An analytical model is proposed. The model assumes that deformation is produced by dislocation glide. However, since the formation of twins is energetically favorable in this material and they act as strong barriers for dislocation glide, their motion turns to become progressively more difficult as elongation proceeds. The combination of increasing twin barriers and dislocations in mutual interaction is proposed to be the mechanism for high-temperature plasticity in this material. The model is validated with the experimental results. Final elongation of boron carbide specimens is reported to be over 100%, although this material cannot be described as a superplastic ceramic.
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.08.134
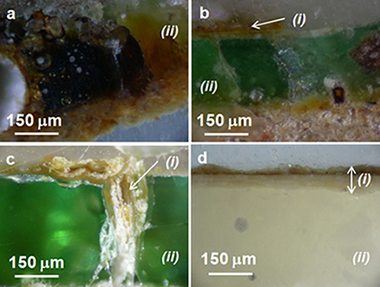
Ceramics from the Alcazar Palace in Seville (Spain) dated between the 11th and 15th centuries: Compositions, technological features and degradation processes
Garofano, I; Robador, MD; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Castaing, J; Pacheco, C; Duran, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 35 (2015) 4307-4319 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.07.033
Abstract
For the purpose of chemical characterization, a selection of 29 ceramic fragments from the 11th to 15th century has been made from materials excavated in the Seville Alcazar Palace. The PIXE elemental analysis results indicated that the ceramic bodies can be divided into four groups. The XRD identification of the phases present in the bodies revealed differences in the firing temperatures. The PIXE analysis of the glazes revealed variable PbO and SnO2 contents. The latter component was not detected in all the glazes. Cu, Co, Mn, Fe and Sb elements were associated with green, blue, black and yellow colours, respectively. Some glazes were covered by iridescent layers constituted by lead carbonate and phosphates due to alteration of the glazes. It was also possible to detail the microstructure and composition of the ultimate surface layers responsible for the lustre effect observed in two of the ceramic samples using PIXE and Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS).
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.07.033
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
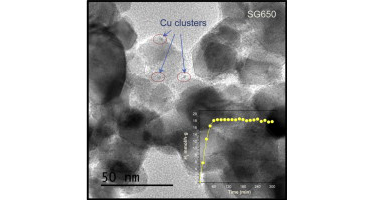
Cu–TiO2 systems for the photocatalytic H2 production: Influence of structural and surface support features
Obregon, S; Munoz-Batista, MJ; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Kubacka, A; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 179 (2015) 468-478 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.05.043
Abstract
The influence of different TiO2 supports on the Cu active species has been studied. It was found that the photocatalytic H2 evolution is highly affected by the structural and electronic features of surface Cu species. Thus, metal dispersion and oxidation state appears strongly conditioned by the structural and surface properties of the TiO2 support. We have examined three TiO2 supports prepared by different synthetic methods; sol–gel, hydrothermal and microemulsion. In addition, we have induced structural and surface modifications by sulfate pretreatment over freshly prepared TiO2 precursors and subsequent calcination. Notably different copper dispersion and oxidation state is obtained by using these different TiO2 supports. From the wide structural and surface analysis of the catalysts we are able to propose that the occurrence of highly disperse Cu2+ species, the sample surface area as well as the crystallinity of the TiO2 support are directly related to the photocatalytic activity for H2 production reaction.
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.05.043
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Efficient synthesis of ammonia from N-2 and H-2 alone in a ferroelectric packed-bed DBD reactor
Gomez-Ramirez, A; Cotrino, J; Lambert, RM; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Sources Science and Technology, 24 (2015) 065011 DOI: 10.1088/0963-0252/24/6/065011
Abstract
A detailed study of ammonia synthesis from hydrogen and nitrogen in a planar dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactor was carried out. Electrical parameters were systematically varied, including applied voltage and frequency, electrode gap, and type of ferroelectric material (BaTiO3 versus PZT). For selected operating conditions, power consumption and plasma electron density were estimated from Lissajous diagrams and by application of the Bolsig + model, respectively. Optical emission spectroscopy was used to follow the evolution of plasma species (NH*, N*, N-2(+) and N-2*) as a function of applied voltage with both types of ferroelectric material. PZT gave both greater energy efficiency and higher ammonia yield than BaTiO3: 0.9 g NH3 kWh(-1) and 2.7% single pass N-2 conversion, respectively. This performance is substantially superior to previously published findings on DBD synthesis of NH3 from N-2 and H-2 alone. The influence of electrical working parameters, the beneficial effect of PZT and the importance of controlling reactant residence time are rationalized in a reaction model that takes account of the principal process variables
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1088/0963-0252/24/6/065011
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
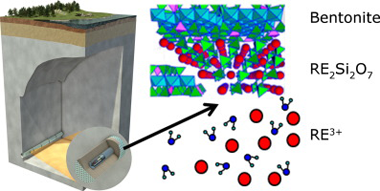
Impact of hydrothermal treatment of FEBEX and MX80 bentonites in water, HNO3 and Lu(NO3)(3) media: Implications for radioactive waste control
Osuna, FJ; Chain, P; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 118 (2015) 48-55 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.08.036
Abstract
Engineered barriers of deep geological repositories (DGR) are commonly constructed with bentonite. FEBEX and MX80 bentonites have been selected by different countries as reference materials for the sealing of repositories; however, their chemical reactivity with high-level long-lived radioactive wastes (HLRW) under subcritical conditions had not been explored before. The hydrothermal stability in neutral and acid media and chemical reactivity in contact with an actinide analogous compound were both studied. The long-range and short-range structural changes were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance and scanning electron microscopy. Both bentonites have exhibited a good stability in neutral and acid media and have generated a new phase immobilizing the actinide analogous compound. The extent of the chemical reaction is higher in MX80 bentonite than in FEBEX bentonite.
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.08.036
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
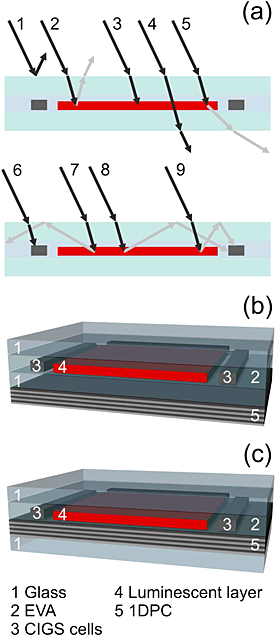
Design and realization of transparent solar modules based on luminescent solar concentrators integrating nanostructured photonic crystals
Jimenez-Solano, A; Delgado-Sanchez, JM; Calvo, ME; Miranda-Munoz, JM; Lozano, G; Sancho, D; Sanchez-Cortezon, E; Miguez, HProgress in Photovoltaics, 23 (2015) 1785-1792 DOI: 10.1002/pip.2621
Abstract
Herein, we present a prototype of a photovoltaic module that combines a luminescent solar concentrator integrating one-dimensional photonic crystals and in-plane CuInGaSe2 (CIGS) solar cells. Highly uniform and wide-area nanostructured multilayers with photonic crystal properties were deposited by a cost-efficient and scalable liquid processing amenable to large-scale fabrication. Their role is to both maximize light absorption in the targeted spectral range, determined by the fluorophore employed, and minimize losses caused by emission at angles within the escape cone of the planar concentrator. From a structural perspective, the porous nature of the layers facilitates the integration with the thermoplastic polymers typically used to encapsulate and seal these modules. Judicious design of the module geometry, as well as of the optical properties of the dielectric mirrors employed, allows optimizing light guiding and hence photovoltaic performance while preserving a great deal of transparency. Optimized in-plane designs like the one herein proposed are of relevance for building integrated photovoltaics, as ease of fabrication, long-term stability and improved performance are simultaneously achieved.
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/pip.2621
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructure and impedance spectroscopy of 3YTZP/SWNT ceramic nanocomposites
Poyato, R; Macias-Delgado, J; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ACeramics International, 41 (2015) 12861-12868 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.06.123
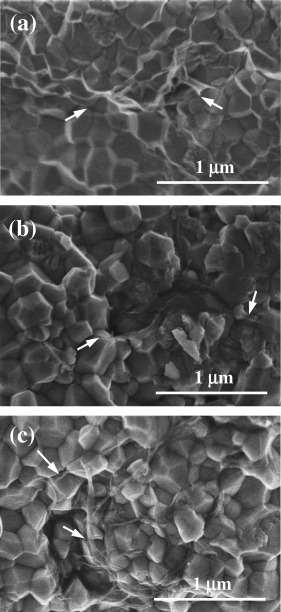
Abstract
This work provides new insights on microstructure and electrical properties of 3 mol% Y2O3-ZrO2 (3YTZP) composites with 0.5, 1, and 1.5 vol% single walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs). The composites were spark plasma sintered (SPS) in identical conditions at 1250 degrees C from powder prepared by two different processing routines, with the aim of optimizing the SWNTs dispersion throughout the ceramic matrix. High densification and submicrometric grain size were achieved in all the composites. Electrical properties of the composites were characterized in a wide temperature range, and modeling of the impedance properties was approached by means of an equivalent circuit that allows separation of the individual SWNT bundles contribution to resistance from the resistance due to junctions between bundles. Effects of the homogeneous distribution of SWNTs at the ceramic grain boundaries on the crystalline phases, percolation threshold, total conductivity and evolution of junctions' resistivity with temperature were analyzed and discussed.
December, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.06.123
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma reforming of methane in a tunable ferroelectric packed-bed dielectric barrier discharge reactor
Montoro-Damas, AM; Brey, JJ; Rodriguez, MA; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Cotrino, JJournal of Power Sources, 296 (2015) 268-275 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.07.038
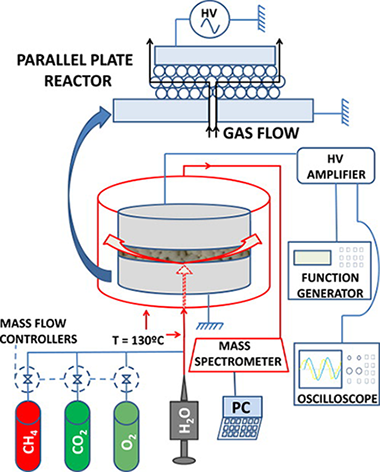
Abstract
In a tunable circular parallel plate dielectric barrier discharge reactor with pellets of a ferroelectric material separating the electrodes we investigate the plasma reforming of methane trying to maximize both the reaction yield and the energetic efficiency of the process. The geometrical configuration of the reactor (gap between electrodes, active electrode area) and the ferroelectric pellet size have been systematically varied to determine their influence on the process efficiency. The comparison between wet (with H2O as reactant), oxidative (with O2), and dry (with CO2) reforming reactions reveals a higher efficiency for the former with CO + H2 as main reaction products. The maximum energetic efficiency EE, defined as the produced number of litres of H2 per kWh, found for optimized working conditions at low-level applied power is higher than the up to date best-known results. A comprehensive discussion of the influence of the different parameters affecting the reaction yield is carried out.
November, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.07.038
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Atomic scale characterization of SiO2/4H-SiC interfaces in MOSFETs devices
Beltran, AM; Duguay, S; Strenger, C; Bauer, AJ; Cristiano, F; Schamm-Chardon, SSolid State Communications, 221 (2015) 28-32 DOI: 10.1016/j.ssc.2015.08.017
Abstract
The breakthrough of 4H-SiC MOSFETs is stemmed mainly due to the mobility degradation in their channel in spite of the good physical intrinsic material properties. Here, two different n-channel 4H-SiC MOSFETs are characterized in order to analyze the elemental composition at the SiC/SiO2 interface and its relationship to their electrical properties. Elemental distribution analyses performed by EELS reveal the existence of a transition layer between the SiC and the SiO2 regions of the same width for both MOSFETs despite a factor of nearly two between their electron mobility. Additional 3D compositional mapping by atom probe tomography corroborates these results, particularly the absence of an anomalous carbon distribution around the SiC/SiO2interface.
November, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ssc.2015.08.017
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Simultaneous Production of CH4 and H-2 from Photocatalytic Reforming of Glucose Aqueous Solution on Sulfated Pd-TiO2 Catalysts
Vaiano, V; Iervolino, G; Sarno, G; Sannino, D; Rizzo, L; Mesa, JJM; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JAOil & Gas Science and Technology-Revue D IFP Energies Nouvelles, 70 (2015) 891-902 DOI: 10.2516/ogst/2014062
Abstract
In this work, the simultaneous production of CH4 and H-2 from photocatalytic reforming of glucose aqueous solution on Pd-TiO2 catalysts under UV light irradiation by Light-Emitting Diodes (LED) was investigated. The Pd-TiO2 catalysts were prepared by the photodeposition method. The Pd content was in the range 0.5-2 wt% and a photodeposition time in the range 15-120 min was used. Pd-TiO2 powders were extensively characterized by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), SBET, X-Ray Fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), UV-Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectra (UV-Vis DRS), TEM and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). It was found that the lower Pd loading (0.5 wt%) and 120 min of photodeposition time allowed us to obtain homogeneously distributed metal nanoparticles of small size; it was also observed that the increase in the metal loading and deposition time led to increasing the Pd-0 species effectively deposited on the sulfated TiO2 surface. Particle size and the oxidation state of the palladium were the main factors influencing the photocatalytic activity and selectivity. The presence of palladium on the sulfated titania surface enhanced the H-2 and CH4 production. In fact, on the catalyst with 0.5 wt% Pd loading and 120 min of photodeposition time, H-2 production of about 26 lmol was obtained after 3 h of irradiation time, higher than that obtained with titania without Pd (about 8.5 lmol). The same result was obtained for the methane production. The initial pH of the solution strongly affected the selectivity of the system. In more acidic conditions, the production of H-2 was enhanced, while the CH4 formation was higher under alkaline conditions.
November, 2015 · DOI: 10.2516/ogst/2014062
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Adaptable Ultraviolet Reflecting Polymeric Multilayer Coatings of High Refractive Index Contrast
Smirnov, JRC; Ito, M; Calvo, ME; Lopez-Lopez, C; Jimenez-Solano, A; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Zavala-Rivera, P; Tanaka, K; Sivaniah, E; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 3 (2015) 1633-1639 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201500209
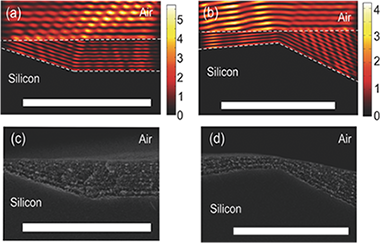
Abstract
A synthetic route is demonstrated to build purely polymeric nanostructured multilayer coatings, adaptable to arbitrary surfaces, and capable of efficiently blocking by reflection a targeted and tunable ultraviolet (UV) range. Reflection properties are determined by optical interference between UV light beams reflected at the interfaces between polystyrene layers of different porosity and hence refractive index. As no dopant absorber intervenes in the shielding effect, polymer degradation effects are prevented. Alternated porosity results from the modulation of photochemical effects at the few tens of nanometers length scale, combined with the collective osmotic shock induced during the processing of the precursor diblock copolymer film. Experimental evidence of the application of this method to coat rough surfaces with smooth and conformal UV protecting films is provided.
November, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201500209
Green pigments of Roman mural paintings from Seville Alcazar
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; de Haro, MDJ; Siguenza, B; Martinez-Blanes, JMApplied Clay Science, 116 (2015) 211-219 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.03.016
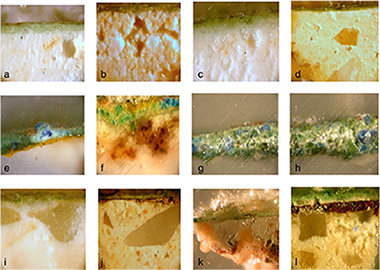
Abstract
We report here a study of 30 fragments of green wall paintings from Roman times found in the Patio de Banderas excavation in Seville Alcazar. The sample characterisation was realised using optical microscopy, colourimetry, infrared and micro-Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The study of these pigments is important because it can help determine the source or the pictorial technique used. The samples studied in this work have been divided into two groups, according to the composition of their green pigments. In the first group, celadonite has been characterised as the primary component of the green colour; chlorite was also detected. Particles constituted by chromium accompanied by aluminium, iron and zinc were found in all studied samples of this group. Chlorite and chromium oxide could also be responsible for the green colour. The presence of chromium suggested the presence of green colour pigment from Verona. In the second group, a mixture of celadonite and glauconite was detected and could be responsible for the green colour observed. The addition of refracting material such as Egyptian blue was also used. A mixture of Egyptian green and Egyptian blue together with celadonite and glauconite was also found. Four classes of intonaco were recognised and classified based upon the composition of the aggregates.
November, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.03.016
Reactividad de Sólidos
A new model of the carbonator reactor in the calcium looping technology for post-combustion CO2 capture
Ortiz, C; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Becerra, JA; Perez-Maqueda, LAFuel, 160 (2015) 328-338 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.07.095
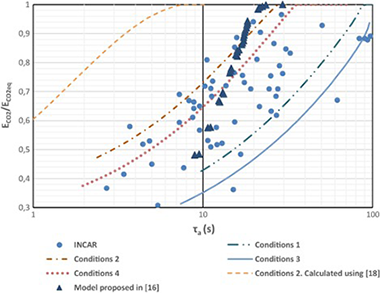
Abstract
The Ca-Looping (CaL) process is considered as a promising technology for CO2 post-combustion capture in power generation plants yielding a minor penalty on plant performance as compared with other capture technologies such as conventional amine-based capture systems. This manuscript presents a new carbonator reactor model based on lab-scale multicyclic CaO conversion results, which take into account realistic CaO regeneration conditions that necessarily involve calcination under high CO2 partial pressure and high temperature. Under these conditions, CaO conversion in the diffusion controlled stage is a relevant contribution to the carbonation degree during typical residence times. The main novelty of the model proposed in the present work is the consideration of the capture efficiency in the diffusion controlled phase of carbonation. It is demonstrated that increasing the residence time by a few minutes in the carbonator yields a significant improvement of the capture efficiency. Model predictions are shown to agree with experimental results retrieved from pilot-scale tests. The new model allows a more accurate evaluation and prediction of carbonator’s performance over a wider range of residence times. The results obtained may be relevant for the optimization of CaL operation parameters to be used in real power plants.
November, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.07.095
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Enhancement of stability and photoactivity of TiO2 coatings on annular glass reactors to remove emerging pollutants from waters
Espino-Estevez, MR; Fernandez-Rodriguez, C; Gonzalez-Diaz, OM; Navio, JA; Fernandez-Hevia, D; Dona-Rodriguez, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 279 (2015) 488-497 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.038
Abstract
TiO2 coatings of highly photoactive lab-made titania were prepared on the outer wall of the inner tube of a glass tubular reactor by dip-coating method. The effect of decreasing the size of the aggregates to improve adhesion and photoactivity of the coatings to degrade phenol, diclofenac and isoproturon was also investigated. Chemical disaggregation of the TiO2 particles resulted in a lower aggregate size, between 0.1 and 1 μm, than mechanical disaggregation, between 1 and 10 μm. The results of the adhesion tape test showed that either milling of aggregate material with a planetary mill or chemical stabilization of the particles were necessary to obtain TiO2 coatings on glass tube with acceptable quality to be used in water treatment applications. SEM images showed that coatings prepared after milling the TiO2 suspension were more homogeneous without surface aggregates. The degree of adhesion of the coatings after increasing the roughness of the support by abrasive blasting was also evaluated. Adhesion to the substrate was slightly lower when using the modified support. The photoactivity results showed that the coatings prepared after wet milling of catalyst during 30 min and after chemical disaggregation were more efficient in terms of degradation and mineralization when using phenol as model molecule. Subsequent studies with two emerging pollutants, diclofenac and isoproturon, also showed enhanced efficiency of these coatings. The reusability of the TiO2 coatings was also evaluated and a promising photocatalytic performance was observed with a very low variation of the decay rate after five consecutive usages.
November, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.038
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Single-step fabrication process of 1-D photonic crystals coupled to nanocolumnar TiO2 layers to improve DSC efficiency
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Colodrero, S; Miguez, H; Gonzalez-Elipe, AROptics Express, 23 (2015) A1642-A1650 DOI: 10.1364/OE.23.0A1642
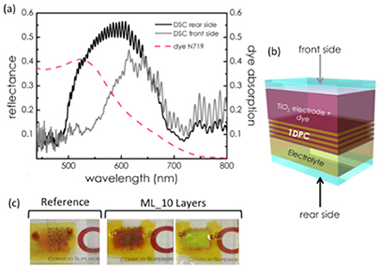
Abstract
The present work proposes the use of a TiO2 electrode coupled to a one-dimensional photonic crystal (1DPC), all formed by the sequential deposition of nanocolumnar thin films by physical vapor oblique angle deposition (PV-OAD), to enhance the optical and electrical performance of DSCs while transparency is preserved. We demonstrate that this approach allows building an architecture combining a non-dispersive 3 µm of TiO2 electrode and 1 µm TiO2-SiO2 1DPC, both columnar, in a single-step process. The incorporation of the photonic structure is responsible for a rise of 30% in photovoltaic efficiency, as compared with a transparent cell with a single TiO2 electrode. Detailed analysis of the spectral dependence of the photocurrent demonstrates that the 1DPC improves light harvesting efficiency by both back reflection and optical cavity modes confinement within the TiO2 films, thus increasing the overall performance of the cell.
November, 2015 · DOI: 10.1364/OE.23.0A1642
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synergy between gold and oxygen vacancies in gold supported on Zr-doped ceria catalysts for the CO oxidation
Laguna, OH; Perez, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 176 (2015) 385-395 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.019
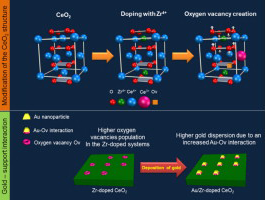
Abstract
The CO oxidation activity of 1 wt.% gold catalysts prepared by deposition-precipitation on a series of ceria doped with Zr supports was studied. The supports (10, 25 and 50 Zr at.%) were synthesized by a pseudo sol-gel method through the thermal decomposition of the corresponding metallic propionates. All the prepared solids were characterized by means of XRF, BET, XRD, Raman spectroscopy, SEM, and H-2-TPR. Solid solution was obtained in all mixed systems, while the segregation of different Ce-Zr oxides was observed for the solid with the 50 Zr at.%. The oxygen vacancies population and the amount of easier reducible Ce4+ species in the solids increase with the Zr content. No major textural or structural modifications were detected after gold deposition, although a strong Au-support interaction was generated. Such interaction is strongly influenced by the nucleation of gold deposits on the oxygen vacancies and consequently the amount of Zr inserted in the ceria network also determines the dispersion of gold. The presence of gold eases the surface reduction at lower temperatures, and as higher the amount of Zr in the gold catalysts, higher the CO conversion at low temperatures, probably due to the enhancement of the electronic transfer at the surface of the catalysts.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.019
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Role of Y in the oxidation resistance of CrAlYN coatings
Dominguez-Meister, S; El Mrabet, S; Escobar-Galindo, R; Mariscal, A; de Haro, CJ; Justo, A; Brizuela, M; Rojas, TC; Sanchez-Lopez, JCApplied Surface Science, 363 (2015) 504-511 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.099
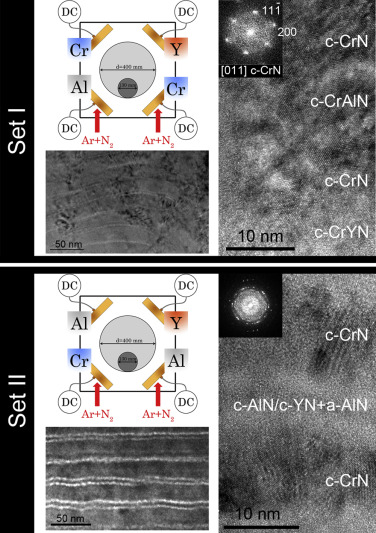
Abstract
CrAlYN coatings with different aluminum (4–12 at.%) and yttrium (2–5 at.%) contents are deposited by d.c. reactive magnetron sputtering on silicon and M2 steel substrates using metallic targets and Ar/N2 mixtures. The influence of the nanostructure and chemical elemental distribution on the oxidation resistance after heating in air at 1000 °C is studied by means of cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy (X-SEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy (GD-OES). The sequential exposure to the metallic targets during the synthesis leads to a multilayer structure where concentration of metallic elements (Cr, Al and Y) is changing periodically. A good oxidation resistance is observed when Al- and Y-rich regions are separated by well-defined CrN layers, maintaining crystalline coherence along the columnar structure. This protective behavior is independent of the type of substrate and corresponds to the formation of a thin mixed (Al, Cr)-oxide scale that protects the film underneath. The GD-OES and XRD analysis have demonstrated that Y acts as a reactive element, blocking the Fe and C atoms diffusion from the steel and favoring higher Al/Cr ratio in the passivation layer after heating. The coating with Y content around 4 at.% exhibited the best performance with a thinner oxide scale, a delay in the CrN decomposition and transformation to Cr2N, and a more effective Fe and C blocking.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.099
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
"In situ" XPS studies of laser-induced surface nitridation and oxidation of tantalum
Lahoz, R; Espinos, JP; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; de la Fuente, GFJournal of Materials Research, 30 (2015) 2967-2976 DOI: 10.1557/jmr.2015.190
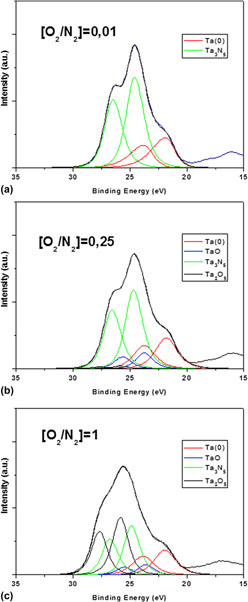
Abstract
This work studies the nitridation of Ta by laser irradiation by means of x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The study has been carried out under "in situ" conditions by controlling the nitrogen partial pressure, the presence of traces of oxygen, and the irradiance of the laser. It is found that a thin layer of Ta2O5 is directly obtained when irradiating in the presence of oxygen, while a Ta3N5 surface compound and some minor contributions of nonstoichiometric phases are formed in the presence of nitrogen. For O-2:N-2 mixtures at 0.1 Pa, preferential nitride formation occurs up to a ratio of 1:4, while Ta2O5 starts to be predominant for ratios above this value. The air stability of the tantalum nitride layer formed by laser irradiation and the surface topography of the irradiated metal are also studied. The possible factors determining this behavior are discussed.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1557/jmr.2015.190
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Amperometric magnetobiosensors using poly(dopamine)-modified Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for the detection of phenolic compounds
Martin, M; Salazar, P; Campuzano, S; Villalonga, R; Pingarron, JM; Gonzalez-Mora, JLAnalytical Methods, 7 (2015) 8801-8808 DOI: 10.1039/C5AY01996F
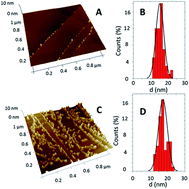
Abstract
The synthesis of poly(dopamine)-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) and their application in preparing electrochemical enzyme biosensors that are useful to detect phenolic compounds is reported in this work. MNPs of about 16 nm were synthesized by a co-precipitation method and conveniently modified with poly(dopamine). Non-modified and modified MNPs were characterized using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Raman and infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was covalently immobilized onto the surface of the poly(dopamine)-modified MNPs via Michael addition and/or Schiff base formation and used to construct a biosensor for phenolic compounds by capturing the HRP-modified-nanoparticles onto the surface of a magnetic-modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Cyclic voltammetry and amperometry were used to study the electrochemical and analytical properties of the biosensor using hydroquinone (HQ) as a redox probe. Among the different phenolic compounds studied, the biosensor exhibited higher sensitivity for HQ, 1.38 A M−1 cm−2, with limits of detection and quantification of 0.3 and 1.86 μM, respectively. The analytical biosensor performance for HQ and 2-aminophenol compared advantageously with those of previous phenolic biosensors reported in the literature.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C5AY01996F
Materiales Avanzados
An improved method for determining the external specific surface area and the plasticity index of clayey samples based on a simplified method for non-swelling fine-grained soils
Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Clay Science, 115 (2015) 97-107 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.07.015
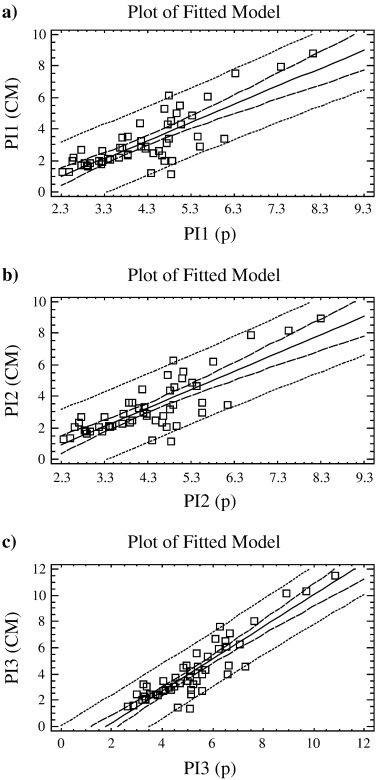
Abstract
Previous studies have used the clay content of soils for estimating the specific surface areas and different correlations have been found, including plasticity-value correlations. Based on several assumptions, Dolinar (2012) proposed a simplified method for determining the external specific surface area of non-swelling fine-grained soils. An equation relates the external specific surface area (BET-nitrogen) with percentage of clay fraction (< 2 μm), determined by hydrometer method, and plasticity index (Atterberg).
In this work, based on that simplified method, the authors have developed an improved method for determining the external specific surface area of fine-grained clay samples. Instead of percentage of clay fraction, it was proposed to use the clay mineral content estimated by XRD methods. From an analysis of previous Dolinars results, the calculated and measured values of external specific surface area were studied for a group of non-swelling and fine-grained soil samples (Dolinar's samples), five non-swelling clayey samples and data samples from the literature. Additionally, an estimation of the plasticity index (Atterberg) has been also considered in this improved method. Both these methods, simplified and improved, were tested and compared using all these samples. It demonstrated the practical application of both these methods for an estimation of external specific surface area and plasticity index. However, in the present research two models were considered to determine the specific surface areas (BET and Langmuir) and the influence of several sources of errors in these predictions was discussed. The predictions were found more accurate when specific surface area from Langmuir's model is considered. It is concluded that the present research will be useful for the prediction of external specific surface area and plasticity index of non-swelling clayey materials and to dispose of theoretical practical relationships between clay mineralogy and geotechnical properties of valuable interest.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.07.015
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Full solution processed mesostructured optical resonators integrating colloidal semiconductor quantum dots
Calvo, ME; Hidalgo, N; Schierholz, R; Kovacs, A; Fernandez, A; Bellino, MG; Soler-Illia, GJAA; Miguez, HNanoscale, 7 (2015) 16583-16589 DOI: 10.1039/C5NR03977K
Abstract
Herein we show a solution based synthetic pathway to obtain a resonant optical cavity with embedded colloidal semiconductor quantum dots (CSQDs). The optical cavity pore network, surrounded by two dense Bragg mirrors, was designed ad hoc to selectively host the quantum dots, while uncontrolled infiltration of those in the rest of the layered structure was prevented. Coupling between the optical resonant modes of the host and the natural emission of the embedded nanoparticles gives rise to the fine tuning of the luminescence spectrum extracted from the ensemble. Our approach overcomes, without the need for an encapsulating agent and exclusively by solution processing, the difficulties that arise from the low thermal and chemical stability of the CSQDs. It opens the route to achieving precise control over their location and hence over the spectral properties of light emitted by these widely employed nanomaterials. Furthermore, as the porosity of the cavity is preserved after infiltration, the system remains responsive to environmental changes, which provides an added value to the proposed structure.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C5NR03977K
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Synergistic strategies for the preparation of highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells on plastic substrates: combination of chemical and physical sintering
Li, Y; Yoo, K; Lee, DK; Kim, JY; Son, HJ; Kim, JH; Lee, CH; Miguez, H; Ko, MJRSC Advances, 5 (2015) 76795-76803 DOI: 10.1039/C5RA10290A
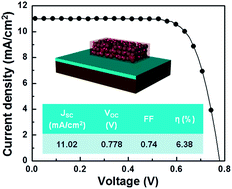
Abstract
Preparation of well-interconnected TiO2 electrodes at low temperature is critical for the fabrication of highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) on plastic substrates. Herein we explore a synergistic approach using a combination of chemical and physical sintering. We formulate a binder-free TiO2 paste based on “nanoglue” as the chemical sintering agent, and use it to construct a photoelectrode on plastic by low-temperature physical compression to further improve the connectivity of TiO2 films. We systematically investigated the factors affecting the photovoltaic performance and found the conditions to achieve electron diffusion lengths as long as 25 μm and charge collection efficiencies as high as 95%, as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements indicate. We apply this approach to obtain a DSC deposited on plastic displaying 6.4% power conversion efficiency based on commercial P25 titania particles.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C5RA10290A
Reactividad de Sólidos
Structural, Optical, and Electrical Characterization of Yttrium-Substituted BiFeO3 Ceramics Prepared by Mechanical Activation
Perejon, A; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAInorganic Chemistry, 54 (2015) 9876-9884 DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b01654
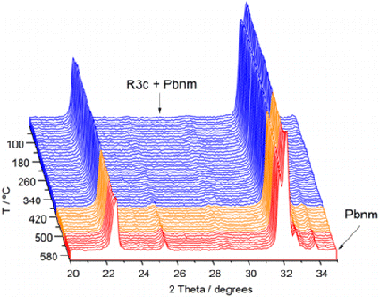
Abstract
Ceramics of Bi1-xYxFeO3 solid solutions (x = 0.02, 0.07, and 0.10) have been prepared by mechanical activation followed by sintering. The effect of yttrium content on the structural, electrical, and optical properties of the materials has been studied. Thus, single-phase solid solutions with rhombohedral R3c structure have been achieved for x = 0.02 and 0.07, while for x = 0.10 the main R3c phase has been detected together with a small amount of the orthorhombic Pbnm phase. Multiferroic properties of the samples, studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), showed that both T-N and T-C (temperatures of the antiferromagnetic paramagnetic and ferroelectric-paraelectric transitions, respectively) decrease with increasing yttrium content. The nature of the ferroelectric paraelectric transition has been studied by temperature-dependent X-ray diffraction (XRD), which revealed rhombohedral R3c to orthorhombic Pbnm phase transitions for x = 0.07 and 0.10. On the other hand, for x = 0.02 the high-temperature phase was indexed as Pnma. Optical properties of the samples, as studied by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, showed low optical band gap that decreases with increasing yttrium content. Prepared ceramics were highly insulating at room temperature and electrically homogeneous, as assayed by impedance spectroscopy, and the conductivity increased with x.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b01654
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Oxodiperoxomolybdenum complex immobilized onto ionic liquid modified SBA-15 as an effective catalysis for sulfide oxidation to sulfoxides using hydrogen peroxide
Carrasco, Carlos J.; Montilla, Francisco; Bobadilla, Luis; Ivanova, Svetlana; Antonio Odriozola, Jose; Galindo, AgustinCatalysis Today, 255 (2015) 102-108 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.10.053
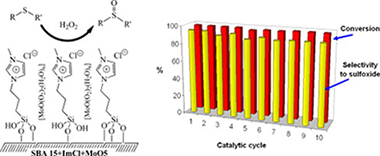
Abstract
A supported ionic-liquid-phase (SILP) was prepared by the reaction of 1-methyl-3-(3-(triethoxysilyl) propyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride with a mesoporous SBA-15 silica and then an oxodiperoxomolybdenum complex was immobilized onto the obtained SILP. The resulting material, identified as SBA-15 + ImCl+ MoO5, was characterized by solid state NMR (H-1, C-13 and Si-29), and their textural and thermogravimetric properties were determined. The SBA-15 + ImCl+ MoO5 material was investigated as catalyst for the oxidation of methylphenylsulfide, as model reaction, with aqueous hydrogen peroxide as oxidant at room temperature. The presence of the molybdenum species was crucial for achieving good conversions and methanol was selected as the best solvent (conversion of 95% and selectivity toward sulfoxide 98%). The optimized reaction conditions were applied for the oxidation of several selected sulfides. In general, good catalytic activity and selectivity to sulfoxide were obtained and, remarkably, the selectivity toward sulfoxide is higher than those observed in the study of the same process carried out in [C(4)min][PF6] (C(4)mim = 1-buty1-3-methylimidazolium) and catalyzed by a molecular molybdenum complex, under the same reaction conditions. The importance of the IL-functionalization in the SBA-15 material was evidenced by recycling experiments. The SBA-15 + ImCl+ MoO5 catalyst was used for the sulfoxidation of the methylphenylsulfide substrate for ten reaction cycles without a significant change in conversion, selectivity to sulfoxide and molybdenum content.
October, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.10.053
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Biocompatible Films with Tailored Spectral Response for Prevention of DNA Damage in Skin Cells
Nunez-Lozano, R; Pimentel, B; Castro-Smirnov, JR; Calvo, ME; Miguez, H; de la Cueva-Mendez, GAdvanced Healthcare Materials, 4 (2015) 1944-1948 DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201500223
Abstract
A hybrid nanostructured organic–inorganic biocompatible film capable of efficiently blocking a preselected range of ultraviolet light is designed to match the genotoxic action spectrum of human epithelial cells. This stack protects cultured human skin cells from UV-induced DNA lesions. As the shielding mechanism relies exclusively on reflection, the secondary effects due to absorption harmful radiation are prevented
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201500223
Materiales Avanzados
Phyllite clay-cement composites having improved engineering properties and material applications
Garzon, E; Cano, M; O'Kelly, BC; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Clay Science, 114 (2015) 229-233 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.06.006
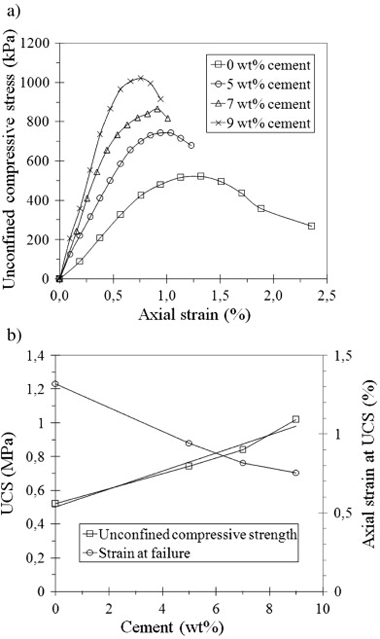
Abstract
Phyllite clays contain clay minerals (chlorite, illite and mixed-layer illite smectite), quartz and feldspars. In this experimental laboratory study, new composites of phyllite clay and cement (5, 7 and 9 wt.%) were prepared and tested to determine their Atterberg limits, dry density and optimum water content for modified Proctor (MP) compaction, California Bearing ratio, swelling potential after soakage in water, unconfined compressive strength (UCS) and water-permeability coefficient. From the mixes investigated, the composite with 5 wt.% cement was deemed most suitable for certain construction material applications, having a plasticity index of 10.5%, maximum dry density of 2.17 Mg/m3 and optimum water content of 8% for MP compaction (undergoing no swelling under soakage), a UCS of 0.74 MPa, and a very low permeability coefficient value of 7.4 × 10− 11 m/s. Potential material applications for these new composites include for building construction, roofs, and flexible pavements.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.06.006
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Microstructure of mixed oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Gil-Rostra, J; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Ferrer, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, FThin Solid Films, 591 (2015) 330-335 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.01.058
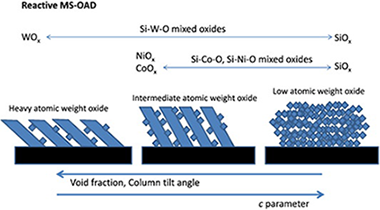
Abstract
Several mixed oxide thin film series of samples (Si–Co–O, Si–Ni–O, Si–W–O) have been prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at oblique angle geometries. The paper focuses on the description of microstructure of the films as a function of their stoichiometry. It is found that for identical process parameters (gas mixture, pressure, magnetron-substrate distance, incidence angle of the vapour flux, etc.) the tilt angle of the developed columnar microstructure and the film porosity is strongly dependent on the stoichiometry of the films. The results are discussed in the framework of several theoretical models on this topic.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.01.058
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Facile Synthesis of Decahedral Particles of Anatase TiO2 with Exposed {001} Facets
Perales-Martinez, IA; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, V; Obregon-Alfaro, S; Lee, SWJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 15 (2015) 7351-7356 DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10578
Abstract
This paper reports a facile synthesis of decahedral particles of anatase TiO2 dominated by {101} and {001} faces. The decahedral particles has been enhanced by means a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method using TiF4 as a titanium precursor and HF as capping agent to promote oriented growth and formation of {001} faces in only 4 h. The prepared samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, high resolution of transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The morphology of anatase TiO2 particles is consisted of near-perfect-truncated-bipyramid-shape. Reaction time is a key factor to obtain truncated-bipyramid-shaped particles with sharp and well-defined edges. Reaction times longer than 4 h induce irregular particles. Decahedral anatase TiO2 particles are truncated bypiramid crystals which have eight {101} and two {001} facets at top/bottom surfaces. The average size of decahedral anatase TiO2 particles are similar to 250 nm for the samples obtained without applying the microwave irradiation and similar to 350 nm for reaction 4 h.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10578
Materiales Coloidales
Uniform Poly(acrylic acid)-Functionalized Lanthanide-Doped LaVO4 Nanophosphors with High Colloidal Stability and Biocompatibility
Nunez, NO; Zambrano, P; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cantelar, E; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 27 (2015) 4546-4554 DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201500265
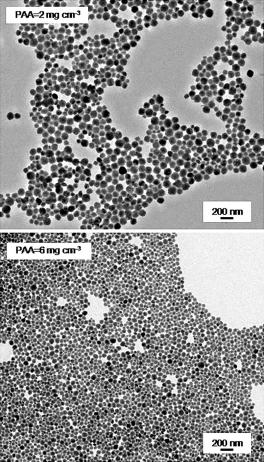
Abstract
Ln-doped (Ln = Eu or Nd) LaVO4 nanoparticles functionalized with poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) were prepared from lanthanide and vanadate precursors in the presence of PAA by a simple one-pot method that consists of a homogeneous precipitation reaction in ethylene glycol/water at a moderate temperature (120 degrees C). The size of the nanoparticles could be modified in the 40-70 nm range by adjusting the amount of PAA added. The effects of the Eu and Nd contents of these nanomaterials on theirs optical properties (emission intensity and lifetime) were also analyzed to find the optimum nanophosphors. Finally, the nanoparticles showed negligible cytotoxicity for Vero cells at concentrations up to 0.05 mgmL(-1) and a high colloidal stability in physiological buffer solutions; therefore, they satisfy the most important requirements for in vitro biotechnological applications.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201500265
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Microreactors technology for hydrogen purification: Effect of the catalytic layer thickness on CuOx/CeO2-coated microchannel reactors for the PROX reaction
Laguna, O. H.; Castano, M. Gonzalez; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Chemical Engineering Journal, 271 (2015) 45-52 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.023
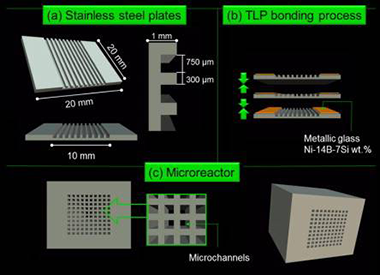
Abstract
Two blocks of microreactors composed by 100 microchannels and coated, respectively, with 150 and 300 mg of a CuOx/CeO2 catalyst, were prepared and tested in the preferential oxidation of CO in presence of H2 (PROX). The deposition of different amount of catalyst resulted in different catalytic layer thicknesses thus modifying the catalytic performances of the microreactor. The evaluation of the main reaction variables (the space velocity, the O2-to-CO ratio and the presence of H2O and/or CO2 in the stream) was performed over both microreactors and compared to that of the parent powder catalyst. The least loaded microreactor, with a coating thickness around 10 μm, presented the highest CO conversion and selectivity levels at temperatures below 160 °C. This result evidences (i) the improvement of the catalytic performances got by the structuration of the powder catalyst and (ii) the importance of the selection of the adequate thickness of the catalytic layer on the microreactor, which have not to exceed and optimal value. An adequate coating thickness allows minimizing the mass and heat transport limitations, thus resulting in the enhancement of the catalytic performance during the PROX reaction.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.023
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
A comparative study of Bi2WO6, CeO2, and TiO2 as catalysts for selective photo-oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds
Lopez-Tenllado, FJ; Murcia-Lopez, S; Gomez, DM; Marinas, A; Marinas, JM; Urbano, FJ; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MC; Gatica, JMApplied Catalysis A-General, 505 (2015) 375-381 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.08.013
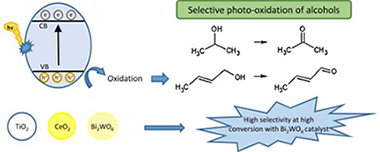
Abstract
Several semiconductors based on ceria or bismuth tungstate were tested for selective oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds in a search for photocatalysts more selective than TiO2. Gas-phase selective photo-oxidation of propan-2-ol to acetone and liquid-phase transformation of 2-buten-1-ol (crotyl alcohol) to 2-butenal (crotonaldehyde) were studied as test reactions. In both processes the highest selectivities were achieved with Bi2WO6-based solids. Further studies on crotyl alcohol transformation evidenced the lower adsorption of the aldehyde on these systems which could minimize the decrease in crotyl alcohol yield observed for TiO2 or CeO2 at high conversions. Incorporation of titania (5% molar) to the Bi2WO6 system increased the reaction rate significantly whereas the aldehyde yield remained high.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.08.013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Specific features of the electrical properties in partially graphitized porous biocarbons of beech wood
Popov, VV; Orlova, TS; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the solid state, 57 (2015) 1746-1751 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783415090280
Abstract
The electrical and galvanomagnetic properties of partially graphitized highly porous bioC(Ni) biocarbon matrices produced by pyrolysis (carbonization) of beech wood at temperatures T (carb) = 850-1600A degrees C in the presence of a Ni-containing catalyst have been studied in comparison with their microstructural features. The temperature dependences of the resistivity, the magnetoresistance, and the Hall coefficient have been measured in the temperature range of 4.2-300 K in magnetic fields to 28 kOe. It has been shown that an additional graphite phase introduction into samples with T (carb) a parts per thousand yen 1000A degrees C results in an increase in the carrier mobility by a factor of 2-3, whereas the carrier (hole) concentration remains within similar to 10(20) cm(-3), as in biocarbons obtained without catalyst. An analysis of experimental data has demonstrated that the features of the conductivity and magnetoresistance of these samples are described by quantum corrections related to their structural features, i.e., the formation of a globular graphite phase of nano- and submicrometer sizes in the amorphous matrix. The quantum corrections to the conductivity decrease with increasing carbonization temperature, which indicates an increase in the degree of structure ordering and is in good agreement with microstructural data.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783415090280
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Physiological Degradation Mechanisms of PLGA Membrane Films under Oxygen Plasma Treatment
Lopez-Santos, C; Terriza, A; Portoles, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal fo Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 20446–20452 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05011
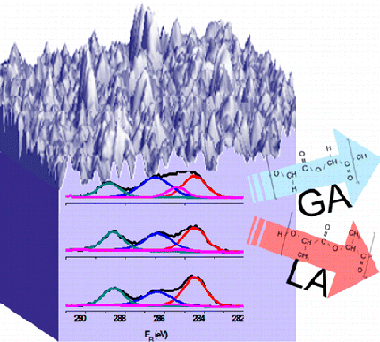
Abstract
Degradation under simulated physiological conditions of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) (PLGA) copolymer membrane films subjected to an oxygen plasma treatment compared to its “as prepared” state has been studied by gas cluster ion beam assisted X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy for chemical depth profiling analysis. This investigation is complemented with atomic force microscopy, weight loss measurements, and visual inspection of the films at the different stages of the degradation process. The obtained results show that the carbon functional groups of the PLGA membrane films undergo a heterogeneous hydrolytic degradation to different rates depending on the plasma pretreatment. The content of glycolic groups (GA) in untreated PLGA samples immersed for 3 weeks in a phosphate-buffered saline solution decreased at the surface, whereas the ratio between glycolic and lactic units (LA) did not vary in the inner regions (∼400 nm depth) of the degraded membrane films. By contrast, oxygen plasma pretreatment enhances the degradation efficiency and causes that both lactic and glycolic functional components decreased at the surface and in the interior of the film, although with less prevalence for the lactic units that present a comparatively higher resistance to degradation.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05011
Reactividad de Sólidos
Photocatalytic Properties of TiO2 Thin Films Modified with Ag and Pt Nanoparticles Deposited by Gas Flow Sputtering
Maicu, M; Gloss, D; Frach, P; Hecker, D; Gerlach, G; Cordoba, JMJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 15 (2015) 6478-6486 DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10873
Abstract
In this work, a gas flow sputtering (GFS) process which allows the production and deposition of metal nanoparticles (NPs) in a vacuum environment is described. Aim of the study is to prove the potential of this technology for the fabrication of new TiO2 films with enhanced photocatalytic properties. For this purpose, Ag and Pt NPs have been produced and deposited on photocatalytic float glass coated with TiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering. The influence of the process parameters and of the metal amount on the final properties of the particles (quantity, size, size distribution, oxidation state etc.,) was widely investigated. Moreover, the effect of the NPs on the photocatalytic activity of the resulting materials was evaluated for the case of the decomposition of stearic acid (SA) during UV-A irradiation. The reduction of the water contact angle (WCA) during the irradiation period was measured in order to test the photo-induced super-hydrophilicity (PSH).
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10873
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Boosting the activity of a Au/CeO2/Al2O3 catalyst for the WGS reaction
Reina, T. R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Catalysis Today, 253 (2015) 149-154 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.01.041
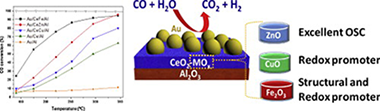
Abstract
Herein a strategy to design highly efficient Au/CeO2/Al2O3 based WGS catalysts is proposed. The inclusion of transition metals, namely Fe, Cu and Zn as CeO2 dopant is considered. All the promoters successfully increased the WGS performance of the undoped sample. The activity improvement can be correlated to structural and/or redox features induced by the dopants. The comparative characterization of the doped samples by means of XRD, Raman spectroscopy and OSC evaluation permits an accurate understanding of the boosted WGS activity arising from the Ce-promoter interaction. This study establishes distinction among both, structural and redox sources of promotion and provides a useful strategy to develop highly active Au/CeO2 based catalysts for the WGS reaction.
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.01.041
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Boosting the visible-light photoactivity of Bi2WO6 using acidic carbon additives
Carmona, RJ; Velasco, LF; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Ania, COApplied Catalysis A-General, 505 (2015) 467-477 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.05.011
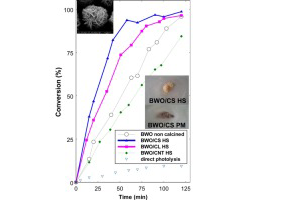
Abstract
We have explored the role of the physicohemical properties of carbon materials as additives to bismuth tungstate on its structure, optical properties, and photocatalytic activity for the degradation of rhodamine B under visible light. For this purpose, C/Bi2WO6 hybrid composites were prepared following two different routes: (i) physical mixture of the catalyst components, and (ii) one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of the semiconductor in the presence of the carbon additive. Three carbons with different properties were selected as additives: biomass-derived activated carbon, carbon nanotubes and carbon spheres obtained from polysaccharides. Data has shown the outstanding role of the acidic/basic nature of the carbon additive, and of the synthetic method on the photocatalytic performance of the resulting composites. For a given additive, the degradation rate of RhB is greatly improved for the catalysts prepared through a one-step hydrothermal synthesis, where there is low shielding effect of the carbon matrix. Carbon additives of acidic nature boost the surface acidity of the hybrid photocatalyst, thereby enhancing the photodegradation of RhB under visible light via a coupled mechanism (photosensitization, semiconductor photocatalysis and carbon-photon mediated reactions).
September, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.05.011
Materiales Coloidales
BaGa4O7, a new A3BC10O20 crystalline phase: synthesis, structural determination and luminescence properties
Boyer, Marina; Veron, Emmanuel; Becerro, Ana Isabel; Porcher, Florence; Suchomel, Matthew R.; Matzen, Guy; Allix, MathieuCrystEngComm, 17 (2015) 6127-6135 DOI: 10.1039/C5CE01101A
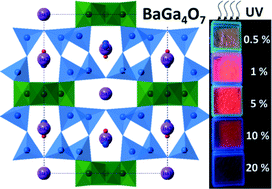
Abstract
The synthesis, structural determination and luminescence properties of a new barium gallate, BaGa4O7, are reported. This crystalline material can uniquely be obtained by direct cooling from the molten state. The crystallographic structure was determined using a combination of electron, synchrotron and neutron powder diffraction data. BaGa4O7 crystallizes in the monoclinic I2/mspace group with a = 15.0688(1) Å, b = 11.7091(1) Å, c = 5.1429(2) Å and β = 91.0452(2)° and can be described as an original member of the A3BC10O20 family. Atypical for this A3BC10O20structural framework, BaGa4O7 is found to contain exclusively divalent and trivalent cations. In order to maintain overall electroneutrality, disordered defect-type partial substitution of gallium and oxygen ions on barium sites occurs within the pentagonal channels of BaGa4O7. Thanks to the flexibility of this structural framework, BaGa4O7 can be heavily doped with europium and thus is shown to exhibit strong orange-red luminescence emission at 618 nm under 393 nm excitation.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C5CE01101A
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Absorption Enhancement in Organic-Inorganic Halide Perovskite Films with Embedded Plasmonic Gold Nanoparticles
Carretero-Palacios, S; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 18635-18640 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06473
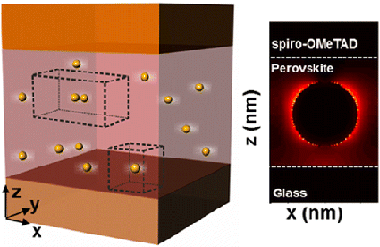
Abstract
We report on the numerical analysis of solar absorption enhancement in organic-inorganic halide perovskite films embedding plasmonic gold nanoparticles. The effect of particle size and concentration is analyzed in realistic systems in which random particle location within the perovskite film and the eventual formation of dimers are also taken into account. We find a maximum integrated solar absorption enhancement of similar to 10% in perovskite films of 200 nm thickness and similar to 6% in 300 nm films, with spheres of radii 60 and 90 nm, respectively, in volume concentrations of around 10% in both cases. We show that the presence of dimers boosts the absorption enhancement up to,similar to 12% in the thinnest films considered. Absorption reinforcement arises from a double contribution of plasmonic near-field and scattering effects, whose respective weight can be discriminated and evaluated from the simulations.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06473
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Rapid Legionella pneumophila determination based on a disposable core–shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles immunoplatform
Martin, M; Salazar, P; Jimenez, C; Lecuona, M; Ramos, MJ; Ode, J; Alcoba, J; Roche, R; Villalonga, R; Campuzano, S; Pingarron, JM; Gonzalez-Mora, JLAnalytica Chimica Acta, 887 (2015) 51-58 DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.05.048
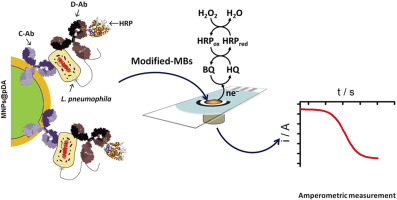
Abstract
A novel amperometric magnetoimmunoassay, based on the use of core–shell magnetic nanoparticles and screen-printed carbon electrodes, was developed for the selective determination of Legionella pneumophila SG1. A specific capture antibody (Ab) was linked to the poly(dopamine)–modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs@pDA-Ab) and incubated with bacteria. The captured bacteria were sandwiched using the antibody labeled with horseradish peroxidase (Ab-HRP), and the resulting MNPs@pDA-Ab-Legionella neumophila-Ab-HRP were captured by a magnetic field on the electrode surface. The amperometric response measured at −0.15 V vs. Ag pseudo-reference electrode of the SPCE after the addition of H2O2 in the presence of hydroquinone (HQ) was used as transduction signal. The achieved limit of detection, without pre-concentration or pre-enrichment steps, was 104 Colony Forming Units (CFUs) mL−1. The method showed a good selectivity and the MNPs@pDA-Ab exhibited a good stability during 30 days. The possibility of detecting L. pneumophila at 10 CFU mL−1 level in less than 3 h, after performing a membrane-based preconcentration step, was also demonstrated.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.05.048
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Direct observation of doping incorporation pathways in self-catalytic GaMnAs
Kasama, T.; Thuvander, M.; Siusys, A.; Gontard, L. C.; Kovacs, A.; Yazdi, S.; Duchamp, M.; Gustafsson, A.; Dunin-Borkowski, R. E.; Sadowski, J.Journal of Applied Physics, 118 (2015) 054302 DOI: 10.1063/1.4927623
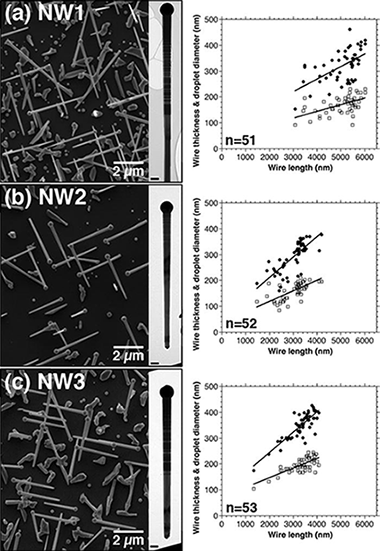
Abstract
Doping mechanisms of Mn in GaAs nanowires (NWs) that have been grown self-catalytically at 600 °C by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) are investigated using advanced electron microscopy techniques and atom probe tomography. Mn is found to be incorporated primarily in the form of non-magnetic tetragonal Ga0.82Mn0.18 nanocrystals in Ga catalyst droplets at the ends of the NWs, while trace amounts of Mn (22 ± 4 at. ppm) are also distributed randomly in the NW bodies without forming clusters or precipitates. The nanocrystals are likely to form after switching off the reaction in the MBE chamber, since they are partially embedded in neck regions of the NWs. The Ga0.82Mn0.18 nanocrystals and the low Mn concentration in the NW bodies are insufficient to induce a ferromagnetic phase transition, suggesting that it is difficult to have high Mn contents in GaAs even in 1-D NW growth via the vapor-liquid-solid process.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1063/1.4927623
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Viability of adding gypsum and calcite for remediation of metal-contaminated soil: laboratory and pilot plant scales
Gonzalez-Nunez, R; Alba, MD; Vidal, M; Rigol, AInternational Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 12 (2015) 2697-2710 DOI: 10.1007/s13762-014-0671-3
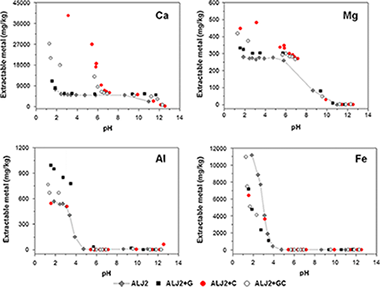
Abstract
The effect of adding waste materials (gypsum and calcite) for the remediation of a soil contaminated by pyritic minerals was examined. Materials were characterised in terms of their acid neutralisation capacity (ANC), sorption capacity and structural components. Their effect on the contaminant leaching in soil + material mixtures over a wide range of pH was also evaluated. Results at laboratory and pilot plant scales were compared to account for the potential variability in the material efficiency when applied at larger scale. The use of gypsum permitted its valorisation, although calcite was a more effective amendment because its addition led to a greater increase in the pH and acid neutralisation capacity, and thus in the sorption capacity in the resulting soil + material mixture. In the same way, when the combination of gypsum + calcite was added to the soil, it led to an increase in the pH from 2.5 to 6.9 and in the ANC from −86 to 1,513 meq/kg. As a result, the concentration of extractable heavy metals and As was reduced, and they were successfully immobilised both at laboratory and at pilot plant scales. Thus, the use of these materials induced a significant reduction in the contaminant mobility and permitted the valorisation of waste materials.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1007/s13762-014-0671-3
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Ultraviolet Pretreatment of Titanium Dioxide and Tin-Doped Indium Oxide Surfaces as a Promoter of the Adsorption of Organic Molecules in Dry Deposition Processes: Light Patterning of Organic Nanowires
Oulad-Zian, Y; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Parra-Barranco, J; Hamad, S; Espinos, JP; Barranco, A; Ferrer, J; Coll, M; Borras, ALangmuir, 31 (2015) 8294-8302 DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01572
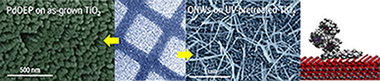
Abstract
In this article we present the preactivation of TiO2 and ITO by UV irradiation under ambient conditions as a tool to enhance the incorporation of organic molecules on these oxides by evaporation at low pressures. The deposition of p-stacked molecules on TiO2 and ITO at controlled substrate temperature and in the presence of Ar is thoroughly followed by SEM, UV-vis, XRD, RBS, and photoluminescence spectroscopy, and the effect is exploited for the patterning formation of small-molecule organic nanowires (ONWs). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) in situ experiments and molecular dynamics simulations add critical information to fully elucidate the mechanism behind the increase in the number of adsorption centers for the organic molecules. Finally, the formation of hybrid organic/inorganic semiconductors is also explored as a result of the controlled vacuum sublimation of organic molecules on the open thin film microstructure of mesoporous TiO2.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01572
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Modulating Low Energy Ion Plasma Fluxes for the Growth of Nanoporous Thin Films
Alvarez, Rafael; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Ferrer, Francisco J.; Rico, Victor; Cotrino, Jose; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Palmero, AlbertoPlasma Processes and Polymers, 12 (2015) 719-724 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201400209
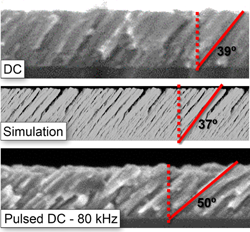
Abstract
The growth of nanoporous layers by plasma-assisted deposition techniques is strongly mediated by the ion fluxes in the reactor. To analyze their influence we have deposited different nanostructured thin films by the magnetron sputtering technique at oblique angles, modulating the ion fluxes in the plasma by tuning the frequency of the electromagnetic signal from pure DC to 160 kHz DC pulsed mode. In the DC case, ions possess energies below 5 eV and do not induce noticeable changes in the film structure. However, when the signal is pulsed, ions with energies up to 40 eV impinge on the film, decreasing the porosity of the layers and tilting down the porous/nanocolumnar structures. As a result, we demonstrate that the overall porosity of the layers and the tilt angle of the columns can be tailored as two independent morphological quantities.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201400209
Reactividad de Sólidos
Preparation of phase pure, dense fine grained ceramics by conventional and spark plasma sintering of La-substituted BiFeO3 nanoparticles
Perejon, Antonio; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Poyato, Rosalia; Maso, Nahum; West, Anthony R.; Criado, Jose M.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 35 (2015) 2283-2293 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.01.030
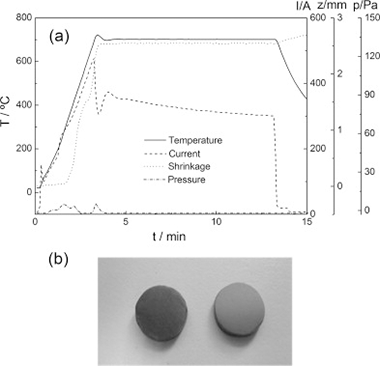
Abstract
High density ceramics of the system Bi1-xLaxFeO3, 0 <= x <= 0.15, have been prepared starting from nanoparticles obtained by mechanosynthesis. The ceramics have been sintered conventionally at 850 degrees C and by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Sintering conditions have been optimized to obtain single phase ceramics, and the microstructure of the ceramics has been compared. Ceramics prepared conventionally present grain sizes from 5 mu m to less than 1 mu m, whereas grain sizes by SPS are in the range from 50 to 100 nm, which demonstrates that it is possible to obtain nanostructured ceramics of La-substituted BiFeO3 using mechanosynthesis followed by SPS at low temperature (625-650 degrees C). The as-prepared SPS ceramics show low resistivity, indicating some reduction in the samples. However, after an oxidative anneal in air, ceramics are highly insulating at room temperature and electrically homogeneous. The high quality of the ceramics has also been demonstrated by XRD, EDX, Raman and DSC.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.01.030
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanical and electrical properties of low SWNT content 3YTZP composites
Poyato, R; Macias-Delgado, J; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 35 (2015) 2351-2359 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.02.022
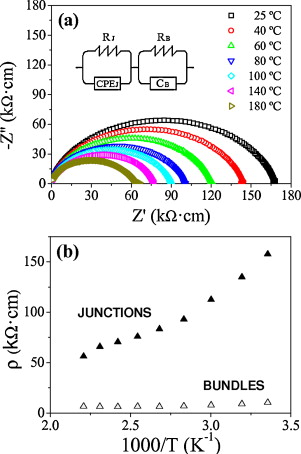
Abstract
Fully dense 3 mol% Y2O3-ZrO2 (3YTZP) composites with low single wall carbon nanotube content (0.5, 1 and 1.5 vol% SWNT) were prepared by colloidal processing and spark plasma sintering (SPS). SWNT were distributed at ceramic grain boundaries and also into agglomerates. Characterization of SWNT agglomerates indicated that increase in SWNT vol% does not imply an increase in agglomeration. SWNT agglomerate density was related to the evolution of hardness and fracture toughness with SWNT vol%. Electrical properties of the composites were characterized in a wide temperature range, and percolation threshold was estimated. A model allowing separation of the individual SWNT bundles contribution to resistance from the resistance due to junctions between bundles was proposed for composites with a percolating SWNT network.
August, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.02.022
Study of coatings by thermal analysis in a monument built with calcarenite
Luisa Franquelo, Maria; Dolores Robador, Maria; Luis Perez-Rodriguez, JoseJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 121 (2015) 195-201 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-015-4432-4
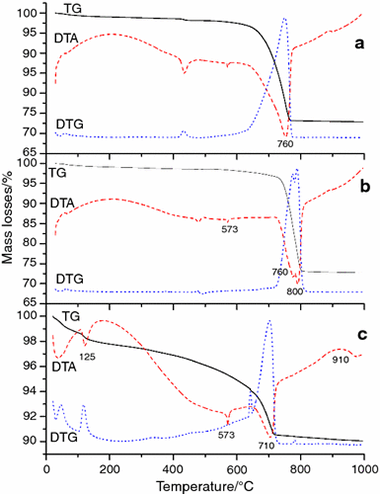
Abstract
In this research, characterization of materials either added during restoration or formed by environmental contamination in the Seville City Hall, built with calcarenite stone, was investigated by thermal methods. Three different mortars for restoration have been characterized: (a) lime micro-mortar for internal consolidation of mortar itself, (b) mortar for reconstruction of deteriorated areas and (c) mortar with Portland cement. Acrylate polymer as consolidant and protection used was characterized. Addition of gypsum or “white cement” has been also applied in the restoration. Altered materials as black crusts constituted by gypsum, calcite and organic compound were determined by thermal analysis. Patina with high concentration of hydrated calcium oxalate, and the transformation mechanism of calcium oxalate into calcium carbonate and formation of calcium oxide produced by decomposition of the calcite were also characterized in the studied monument by thermal analysis. The patina with hydrated calcium oxalate produced by high biological activity was also studied.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-015-4432-4
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
New Copper wide range nanosensor electrode prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles for the non-enzimatic determination of glucose
Salazar, P; Rico, V; Rodriguez-Amaro, R; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochimica Acta, 169 (2015) 195-201 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.092
Abstract
In this work a novel Cu nanostructured electrode is presented. Cu tilted nanocolumnar and porous thin films have been prepared by physical vapor deposition (PVD) in an oblique angle configuration and characterized by different techniques. Cyclic voltammetry and amperometry were used to study the sensing ability of the copper films deposited on ITO to quantitatively determine glucose and to optimize the experimental conditions of detection. Scanning electron microscopy data revealed that the film microstructure consists of tilted nanocolumns of around 70 nm of diameter and an inclination of 65° with respect to the surface normal that extend through the total thickness of the layer of ca. 300 nm. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman, used to determine the oxidation state of Cu, revealed that an oxy/hydroxide external layer formed around the nanocolumns is the active phase responsible for the electrocatalytic detection of glucose. Under optimized conditions, the CuO/Cu nanoporous/ITO electrode presented a sensitivity of 1.41 A mol dm−3 cm−2 (R2:0.999) with a limit of detection of 0.36 μmol dm−3 and a reproducibility of 3.42%.The selectivity of the proposed sensor was checked against various interferences, including physiological compounds, different sugars and ethanol, thereby showing excellent anti-interference properties. The CuO/Cu nanoporous/ITO electrode was also used successfully to determine glucose in blood samples showing a performance comparable to that of a commercial glucometer. An extended working range covering from 1 to 5 × 10−3 mol dm−3 was determined for these sensor films which, in this way, could be applied for different analytical purposes including agro industrial liquids.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.092
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A novel and improved surfactant-modified Prussian Blue electrode for amperometric detection of free chlorine in water
Salazar, Pedro; Martin, Miriam; Garcia-Garcia, Francisco J.; Luis Gonzalez-Mora, Jose; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 213 (2015) 116-123 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.02.092
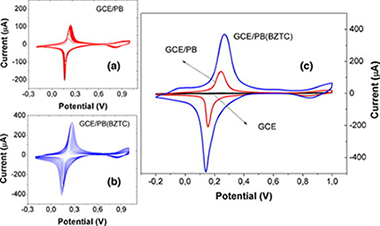
Abstract
A surfactant-modified Prussian Blue (PB) electrochemical sensor has been developed. Benzethonium was used to assist the electrodeposition of PB onto a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). The surface coverage ( [View the MathML source] ) was 7.75 × 10−8 mol cm−2, five times higher than the value obtained in the absence of surfactant, and the film thickness of ca. 123 nm. SEM, EDX, Raman were used to characterize the electrodes while their electrochemical analysis proved a superior performance for the surfactant modified PB film. Cyclic voltammetry and amperometry were used to study the sensor ability to detect chlorine, and the main experimental variables were optimized. Under optimized conditions, the sensor presented a sensitivity of 12 μA ppm−1 cm−2, a linear range from 9 ppb to 10 ppm and a reproducibility of 4.2%. For the first time, we proved the sensor performance for real applications. Thus, chlorine was determined in tap water and the obtained concentrations validated with a standard colorimetric method. The obtained results showed that our sensor is highly performant and reliable for applications involving determinations of environmental residual chlorine.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.02.092
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Removing the effects of the "dark matter" in tomography
Gontard, Lionel C.Ultramicroscopy, 154 (2015) 64-72 DOI: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2015.03.017
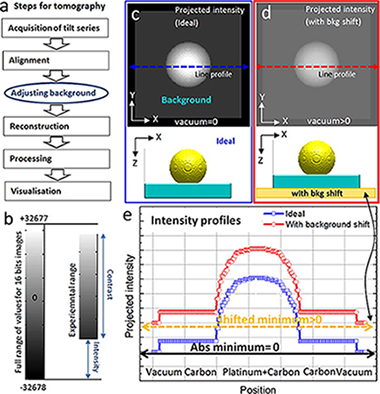
Abstract
Electron tomography (ET) using different imaging modes has been progressively consolidating its position as a key tool in materials science. The fidelity of a tomographic reconstruction, or tomogram, is affected by several experimental factors. Most often, an unrealistic cloud of intensity that does not correspond to a real material phase of the specimen ("dark matter") blurs the tomograms and enhances artefacts arising from the missing wedge (MW). Here we show that by simple preprocessing of the background level of any tomographic tilt series, it is possible to minimise the negative effects of that "dark matter". Iterative reconstruction algorithms converge better, leading to tomograms with fewer streaking artefacts from the MW, more contrast, and increased accuracy. The conclusions are valid irrespective of the imaging mode used, and the methodology improves the segmentation and visualisation of tomograms of both crystalline and amorphous materials. We show examples of HAADF STEM and BF TEM tomography.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2015.03.017
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic propylene epoxidation on Bi2WO6-based photocatalysts
Murcia-Lopez, S.; Vaiano, V.; Sannino, D.; Hidalgo, M. C.; Navio, J. A.Research on Chemical Intermediates, 41 (2015) 4199-4212 DOI: 10.1007/s11164-013-1523-3
Abstract
The photocatalytic epoxidation of propylene (PR) with molecular oxygen was carried out in a fluidized-bed reactor with several Bi2WO6-based materials under UV-A illumination. Three different photocatalysts were tested: one of single Bi2WO6 and two of coupled Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructures, thus showing that a mixed system of Bi2WO6 with commercial TiO2 Degussa-P25 leads to the best combination of conversion and PO selectivity. Then, direct support on glass spheres and silica gel was made, being a good alternative for improving the Bi2WO6 performance. Additionally, several reaction conditions of temperature and PR to O-2 feed ratio were studied.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1007/s11164-013-1523-3
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
On the origin of the photocatalytic activity improvement of BIVO4 through rare earth tridoping
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis A-General, 501 (2015) 56-62 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.04.032
Abstract
Rare earth (Tm3+/Er3+,Yb3+,Y3+) tri-doped BiVO4 have been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of methylene blue and O-2 evolution reactions. The improved photocatalytic performance has been attained by multiple approach of the overall photocatalytic mechanism. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Y3+ induces the stabilization of the tetragonal phase probably due to its substitutional incorporation in the BiVO4 lattice. Moreover, the extensive doping with rare earth ions such as Yb3+ and Er3+/Tm3+ t-BiVO4 evidenced that important structural, electronic changes as well as the luminescence properties were also exalted. Ternary doping clearly prompts the higher photocatalytic activities. A more packed tetragonal structure in conjunction leading to improved charge carriers mobility, with the observed visible and NIR photoactivities of t-BiVO4 could be the responsible of the improved photocatalytic activity under solar-like irradiation.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.04.032
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanocolumnar 1-dimensional TiO2 photoanodes deposited by PVD-OAD for perovskite solar cell fabrication
Javier Ramos, F.; Oliva-Ramirez, Manuel; Nazeeruddin, Mohammad Khaja; Graetzel, Michael; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Ahmad, ShahzadaJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 3 (2015) 13291-13298 DOI: 10.1039/c5ta02238j
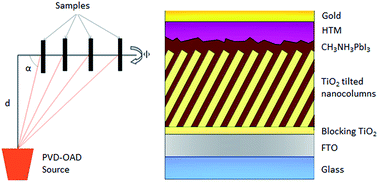
Abstract
Perovskite solar cells have attracted increasing interest among the photovoltaic community in the last few years owing to their unique properties and high efficiency. In the present work, we report the fabrication of perovskite solar cells based on highly ordered 1-dimensional porous TiO2 photoanodes, which are uniform on a large area. These nanocolumnar porous TiO2 photoanodes were deposited by physical vapor deposition in an oblique angle configuration (PVD-OAD) by varying the zenithal angle between the target and the substrate normal. Perovskite infiltration into these 1-dimensional nanocolumnar structures was homogeneous through the entire thickness of the porous layer as revealed by secondary ion mass spectroscopy studies. The fabricated solar cells, with an optimized thickness of the photoanode and with industrially accepted methods, will pave the way for easy implementation on a large scale.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/c5ta02238j
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Fabrication of Optical Multi layer Devices from Porous Silicon Coatings with Closed Porosity by Magnetron Sputtering
Caballero-Hernandez, Jaime; Godinho, Vanda; Lacroix, Bertrand; Jimenez de Haro, Maria C.; Jamon, Damien; Fernandez, AsuncionACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7 (2015) 13880-13897 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b02356
Abstract
The fabrication of single-material photonic-multilayer devices is explored using a new methodology to produce porous silicon layers by magnetron sputtering. Our bottom-up methodology produces highly stable amorphous porous silicon films with a controlled refractive index using magnetron sputtering and incorporating a large amount of deposition gas inside the closed pores. The influence of the substrate bias on the formation of the closed porosity was explored here for the first time when He was used as the deposition gas. We successfully simulated, designed, and characterized Bragg reflectors and an optical microcavity that integrates these porous layers. The sharp interfaces between the dense and porous layers combined with the adequate control of the refractive index and thickness allowed for excellent agreement between the simulation and the experiments. The versatility of the magnetron sputtering technique allowed for the preparation of these structures for a wide range of substrates such as polymers while also taking advantage of the oblique angle deposition to prepare Bragg reflectors with a controlled lateral gradient in the stop band wavelengths.
July, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b02356
- ‹ previous
- 22 of 37
- next ›














