Scientific Papers in SCI
2016
2016
Materiales Coloidales
Confinement and surface effects on the physical properties of rhombohedral-shape hematite (alpha-Fe2O3) nanocrystals
Luna, C; Cuan-Guerra, AD; Barriga-Castro, ED; Nunez, NO; Mendoza-Resendez, RMaterials Research Bulletin, 80 (2016) 44-52 DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.03.029
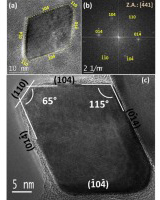
Abstract
Morphological, microstructural and vibrational properties of hematite (alpha-Fe2O3) nanocrystals with a rhombohedral shape and rounded edges, obtained by forced hydrolysis of iron(III) solutions under a fast nucleation, have been investigated in detail as a function of aging time. These studies allowed us to propose a detailed formation mechanism and revealed that these nanocrystals are composed of four {104} side facets, two {110} faces at the edges of the long diagonal of the nanocrystals and two {-441} facets as the top and bottom faces. Also, the presence of nanoscopic pores and fissures was evidenced. The vibrational bands of such nanocrystals were shifted to lower frequencies in comparison with bulk hematite ones as the nanocrystal size was reduced due to phonon confinement effects. Also, the indirect and direct transition band gaps displayed interesting dependences on the aging time arising from quantum confinementand surface effects
August, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.03.029
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Effect of TiO2-Pd and TiO2-Ag on the photocatalytic oxidation of diclofenac, isoproturon and phenol
Espino-Estevez, MR; Fernandez-Rodriguez, C; Gonzalez-Diaz, OM; Arana, J; Espinos, JP; Ortega-Mendez, JA; Dona-Rodriguez, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 298 (2016) 82-95 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.016
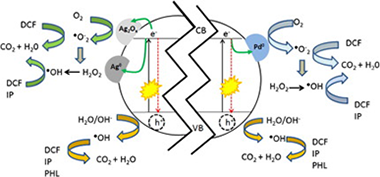
Abstract
The effects of silver and palladium metals on the photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac sodium salt (DCF), isoproturon (IP) and phenol (PHL) in water over lab-made TiO2 synthesized following a sol-gel method were investigated. Silver and palladium catalysts were prepared by photodeposition at 1 wt.% of loading metal. The resulting materials were characterized through BET, XRD, TEM, SEM, XPS and DRS-UV-Vis. The photodeposition test conditions of both metals determined their final oxidation state, with reduced particles of palladium and silver as well as silver oxides found on the catalysts. The results showed that the type of metal had different effects on the photodegradation mechanism depending on the nature of the pollutants. Accordingly, the highest degradation rate for IP and DCF was obtained when using the catalyst photodeposited with palladium and for PHL the catalyst photodeposited with silver. The photodegradation intermediates of PHL, DCF and IP were also identified.
August, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Constant rate thermal analysis of a dehydrogenation reaction
Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Murafa, N; Subrt, JRSC Advances, 6 (2016) 81454-81460 DOI: 10.1039/C6RA10157G
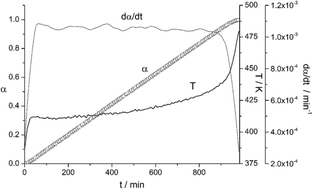
Abstract
The Constant Rate Thermal Analysis (CRTA) procedure has been employed for the first time to study the kinetics of MgH2 dehydrogenation by thermogravimetry under high vacuum. CRTA implies controlling the temperature in such a way that the decomposition rate is maintained constant all over the process, employing the mass change as the experimental signal proportional to the reaction rate. The CRTA curves present a higher resolution power to discriminate the kinetic model obeyed by the reaction in comparison with conventional heating rate curves. The combined kinetic analysis has been applied to obtain the kinetic parameters, which show that MgH2 decomposition under high vacuum obeys first-order kinetics (F1). It has been proposed that the dehydrogenation of MgH2 under high vacuum takes place by instantaneous nucleation in the border line of the bidimensional crystallites followed by the growth of the nuclei.
July, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/C6RA10157G
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Unbroken Perovskite: Interplay of Morphology, Electro-optical Properties, and Ionic Movement
Correa-Baena, JP; Anaya, M; Lozano, G; Tress, W; Domanski, K; Saliba, M; Matsui, T; Jacobsson, TJ; Calvo, ME; Abate, A; Gratzel, M; Miguez, H; Hagfeldt, AAdvanced Materials, 28 (2016) 5031-5037 DOI: 10.1002/adma.201600624
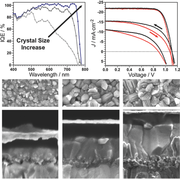
Abstract
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite materials have risen up as leading components for light-harvesting applications. However, to date many questions are still open concerning the operation of perovskite solar cells (PSCs). A systematic analysis of the interplay among structural features, optoelectronic performance, and ionic movement behavior for FA(0.83)MA(0.17)Pb(I0.83Br0.17)(3) PSCs is presented, which yield high power conversion efficiencies up to 20.8%.
July, 2016 · DOI: 10.1002/adma.201600624
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic removal of patent blue V dye on Au-TiO2 and Pt-TiO2 catalysts
Vaiano, V; Iervolino, G; Sannino, D; Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Ciambelli, P; Navio, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 188 (2016) 134-146 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.001
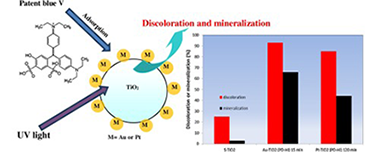
Abstract
In this work it was studied the efficiency of a photocatalytic process for the removal of patent blue V. This dye is very difficult to remove by conventional treatments such as adsorption or coagulation therefore the photocatalytic process is a very interesting alternative for the removal this dye mainly because it does not require expensive oxidants and it can be carried out at mild temperatures and pressures. In this work it was tested the efficiency of Au-TiO2 and Pt-TiO2 photocatalysts in the Patent blue V removal. The Au-TiO2 catalysts were prepared by two different methods: chemical reduction and photochemical deposition; Pt-TiO2 catalysts were obtained only by photochemical deposition. In the synthesis of the catalysts prepared by photochemical deposition, it was evaluated the influence of some parameters, such as deposition time and the intensity of the light source over the physicochemical properties and photocatalytic activity of the materials obtained. An analysis of the effect of the catalyst dosage and initial patent blue V concentration over the dye degradation efficiency was also attempted.
In general, it was observed that the presence of Au or Pt on TiO2 enhances the patent blue V photodegradation; it was found that noble metal particle size and distribution on TiO2 surface are important factors influencing the dye removal. The highest dye degradation was obtained over the Au-TiO2 catalyst prepared by photochemical deposition, using high light intensity and 15 min of deposition time during the synthesis. A discoloration and a total organic carbon (TOC) removal of 93 and 67% respectively, were obtained over this material after 180 min of UV irradiation. These values are higher than that the obtained on S-TiO2 (discoloration and TOC removal of about 25% and 3%, respectively).
July, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.001
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic hydrogen production from degradation of glucose over fluorinated and platinized TiO2 catalysts
Iervolino, G; Vaiano, V; Murcia, JJ; Rizzo, L; Ventre, G; Pepe, G; Campiglia, P; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Sannino, DJournal of Catalysis, 339 (2016) 47-56 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2016.03.032
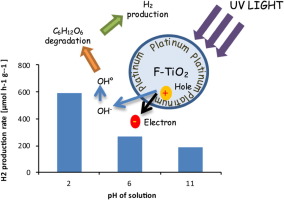
Abstract
The present work reports the renewable hydrogen production by photocatalytic degradation of glucose over commercial and home prepared TiO2 modified by the simultaneous presence of fluorine and Pt (Pt-F-TiO2). The obtained materials were widely characterized by different techniques (XRD, SBF, UV-Vis DRS, XRF, SEM and TEM) and it was found that surface area, anatase/rutile ratio and the distribution and size of the platinum particles are important factors influencing the effectiveness of these materials in the H-2 production. The photocatalytic H-2 production from the glucose solution was 97 mu mol of H-2 after 3 h of irradiation on home prepared TiO2 modified by F and Pt addition, while a lower value corresponding to 31 mu mol of H-2 was obtained on commercial TiO2 modified by F and Pt, after 3 h of irradiation. The hydrogen production rate increased by decreasing the initial pH of solution reaching the highest value of about 590 mu mol h(-1) g(-1) after 3 h of irradiation time at pH = 2. Accordingly, sugar containing wastewaters from food industry has the potential for producing hydrogen by photocatalytic process while removing organics before disposal or reuse.
July, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2016.03.032
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
In vitro stimulation of MC3T3-E1cells and sustained drug delivery by a hierarchical nanostructured SiO2-CaO-P2O5 scaffold
Ramiro-Gutierrez, ML; Santos-Ruiz, L; Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Becerra, J; Diaz-Cuenca, AMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 229 (2016) 31-43 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.04.018
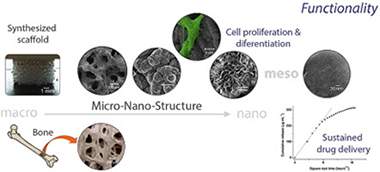
Abstract
A hierarchical scaffold, SP1_h_HA, consisting of a biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite surface coating growth onto a reticulated structure having a nano-organized porous texture was fabricated and functionally studied in vitro using osteoprogenitor cells. Three scaffold materials (designated as SP0_l, SP0_h and SP1_h) were also prepared through modifications of the processing variables as control materials. The scaffolds were characterized showing well-interconnected micron-sized voids and a nano (4–6 nm)-organized porosity. In order to evaluate potential local risks and performance over mammalian cells the scaffolds were studied in comparison with a commercial clinical grade scaffold material, ProOsteon® 500R. MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblast viability was evaluated using the resazurin assay and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM), showing in all cases good proliferative response. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) production and analysis of the differentiation marker osteocalcin (OC), both in non-osteoinductive and osteoinductive media, were assessed using colorimetric and RT-PCR methods. The implementation of the new scaffold processing variables enhanced ALP activity with respect to the SP0_l control material. The cell proliferation, ALP activity, and mRNA OC expression response to SP1_h_HA scaffold were higher than those observed after the use of ProOsteon® 500R. In addition, SP1_h_HA scaffold showed a two stage sustained release of gentamicin sulfate (GS) instead of the quick release shown by ProOsteon® 500R. These results suggest that our synthesized scaffold could be effective for antibiotic delivery and bone regeneration and a better option than ProOsteon® 500R.
July, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.04.018
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Synthesis, characterization and performance of robust poison resistant ultrathin film yttria stabilized zirconia nickel anodes for application in solid electrolyte fuel cells
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lambert, RMJournal of Power Sources, 324 (2016) 679-686 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.05.124
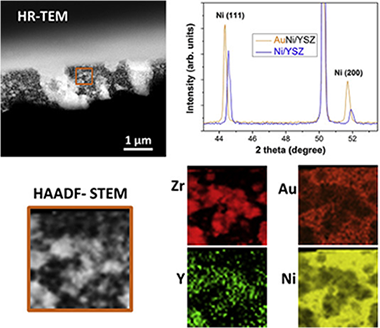
Abstract
We report on the synthesis of undoped ∼5 μm YSZ-Ni porous thin films prepared by reactive pulsed DC magnetron sputtering at an oblique angle of incidence. Pre-calcination of the amorphous unmodified precursor layers followed by reduction produces a film consisting of uniformly distributed tilted columnar aggregates having extensive three-phase boundaries and favorable gas diffusion characteristics. Similarly prepared films doped with 1.2 at.% Au are also porous and contain highly dispersed gold present as Ni-Au alloy particles whose surfaces are strongly enriched with Au. With hydrogen as fuel, the performance of the undoped thin film anodes is comparable to that of 10–20 times thicker typical commercial anodes. With a 1:1 steam/carbon feed, the un-doped anode cell current rapidly falls to zero after 60 h. In striking contrast, the initial performance of the Au-doped anode is much higher and remains unaffected after 170 h. Under deliberately harsh conditions the performance of the Au-doped anodes decreases progressively, almost certainly due to carbon deposition. Even so, the cell maintains some activity after 3 days operation in dramatic contrast with the un-doped anode, which stops working after only three hours of use. The implications and possible practical application of these findings are discussed.
July, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.05.124
Reactividad de Sólidos
Targeted multifunctional tannic acid nanoparticles
Aguilera, J. R.; Venegas, V.; Oliva, J. M.; Sayagues, M. J.; de Miguel, M.; Sanchez-Alcazar, J. A.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, M.; Zaderenko, A. P.RSC Advances, 9 (2016) 108611-108620 DOI: 10.1039/c5ra19405a
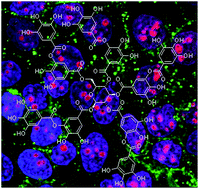
Abstract
Tannic acid (TA) has multiple effects against cancer, being especially promising in those types that overexpress the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), as TA modulates its activation and downstream signaling pathways, triggering apoptosis. Nonetheless, despite the important role of this receptor in the pathogenesis and progression of a wide variety of tumors, no TA systems targeted to this receptor have been described yet. In this work, we synthesize, characterize by physico-chemical techniques and study the cytotoxic effect and cell uptake of TA nanoparticles targeted to EGFR in both tumoral and normal human skin cells. Our nanoparticles exhibited an extremely high entrapment efficiency, and were only toxic for the tumoral cells. The uptake assay demonstrated that nanoparticles are able to enter the cells through a receptor-mediated mechanism. Furthermore, we have included fluorescent markers in these nanoparticles to combine imaging and therapeutic applications, thus building effectively a multifunctional tool for biomedicine.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/c5ra19405a
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Stress measurement using area detectors: a theoretical and experimental comparison of different methods in ferritic steel using a portable X-ray apparatus
Ramirez-Rico, J; Lee, SY; Ling, JJ; Noyan, ICJournal of Materials Science, 51 (2016) 5343-5355 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-016-9837-3
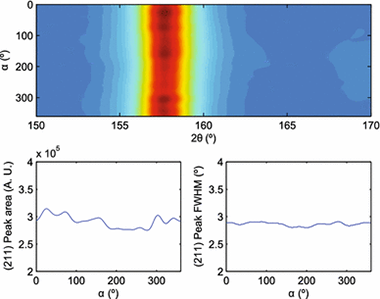
Abstract
Using area detectors for stress determination by diffraction methods in a single exposure greatly simplifies the measurement process and permits the design of portable systems without complex sample cradles or moving parts. An additional advantage is the ability to see the entire or a large fraction of the Debye ring and thus determine texture and grain size effects before analysis. The two methods most commonly used to obtain stress from a single Debye ring are the so-called cosαcosαand full-ring fitting methods, which employ least-squares procedures to determine the stress from the distortion of a Debye ring by probing a set of scattering vector simultaneously. The widely applied sin2ψsin2ψ method, in contrast, requires sample rotations to probe a different subset of scattering vector orientations. In this paper, we first present a description of the different methods under the same formalism and using a unified set of coordinates that are suited to area detectors normal to the incident beam, highlighting the similarities and differences between them. We further characterize these methods by means of in situ measurements in carbon steel tube samples, using a portable detector in reflection geometry. We show that, in the absence of plastic flow, the different methods yield basically the same results and are equivalent. An analysis of possible sources of errors and their impact in the final stress values is also presented.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1007/s10853-016-9837-3
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermal conductivity of Fe graphitized wood derived carbon
Ramirez-Rico, J; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Popov, VV; Orlova, TSMaterials & Design, 99 (2016) 528-534 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.03.070
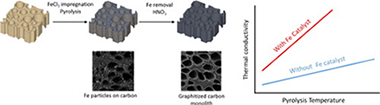
Abstract
Graphitic porous carbon materials from pyrolysis of wood precursors were obtained by means of a nanosized Fe catalyst, and their microstructure and electrical and thermal transport properties investigated. Thermal and electrical conductivity of graphitized carbon materials increase with the pyrolysis temperature, indicating a relationship between the degree of graphitization and thus in crystallite size with transport properties in the resulting carbon scaffolds. Evaluation of the experimental results indicate that thermal conductivity is mainly through phonons and increases with the temperature in Fe-catalyzed carbons suggesting that the mean free path of phonons in the material is small and defect scattering dominates over phonon-phonon interactions in the range from room temperature to 800 °C.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.03.070
Reactividad de Sólidos
Template-Assisted Hydrothermal Growth of Aligned Zinc Oxide Nanowires for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Applications
Ou, C; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Datta, A; Boughey, FL; Whiter, RA; Sahonta, SL; Kar-Narayan, SACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8 (2016) 13678-13683 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b04041
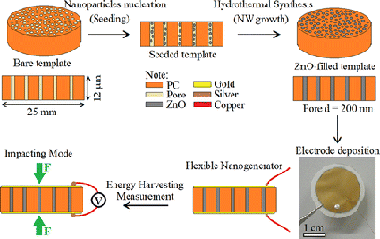
Abstract
A flexible and robust piezoelectric nanogenerator (NG) based on a polymer-ceramic nanocomposite structure has been successfully fabricated via a cost-effective and scalable template assisted hydrothermal synthesis method. Vertically aligned arrays of dense and uniform zinc oxide (ZnO) nanowires (NWs) with high aspect ratio (diameter similar to 250 nm, length similar to 12 mu m) were grown within nanoporous polycarbonate (PC) templates. The energy conversion efficiency was found to be similar to 4.2%, which is comparable to previously reported values for ZnO NWs. The resulting NG is found to have excellent fatigue performance, being relatively immune to detrimental environmental factors and mechanical failure, as the constituent ZnO NWs remain embedded and protected inside the polymer matrix.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b04041
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemically synthesized nanocrystalline ternary CuInSe2 chalcogenide semiconductor
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Kovac, J; Kovac, J; Bujnakova, Z; Briancin, J; Zorkovska, A; Balaz, P; Ficeriova, JMaterials Letters, 173 (2016) 182-186 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2016.03.051

Abstract
The synthesis of nanocrystalline ternary CuInSe2 particles prepared by high-energy milling in a planetary mill in an argon atmosphere from copper, indium and selenium was reported. CuInSe2 particles crystallize in the tetragonal structure with the crystallite size of about 30.5 nm. The Raman spectrum of CuInSe2 nanoparticles shows a strong peak at 176 cm−1 corresponds to the A1 phonon mode of tetragonal CuInSe2 chalcopyrite. HRTEM measurements also revealed the presence of nanocrystals with the size of 10–20 nm with the tendency to form agglomerates. The optical absorption study shows that nanoparticles have direct optical band gap energy of 1.8 eV. The quantum size effect of the particles was confirmed also by PL measurement.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2016.03.051
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
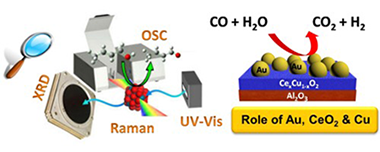
The role of Au, Cu & CeO2 and their interactions for an enhanced WGS performance
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 187 (2016) 98-107 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.01.031
Abstract
The WGS reaction over multicomponent Au/Ce1-xCuxO2/Al2O3 catalysts is studied in this work. The systems are carefully designed aiming to take advantage of every active phase included in the formulation: gold, ceria and copper. Special emphasis is given to the CeO2-CuO synergy and its influence on the displayed catalytic performance with and without gold. To this aim a meaningful correlation between the physicochemical properties of the mixed materials and their activity/stability is proposed. In general terms the developed catalysts present high activity under realistic WGS reaction conditions, with fairly good long term stability. In addition, the systems successfully withstand start-up/shut-downs situations, indispensable requisite for real applications in the field of pure hydrogen production for fuel cell goals.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.01.031
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Metallic nanostructures for efficient LED lighting
Lozano, G; Rodriguez, SRK; Verschuuren, MA; Rivas, JGLight: Science and Applications, 5 (2016) e16080 DOI: 10.1038/lsa.2016.80
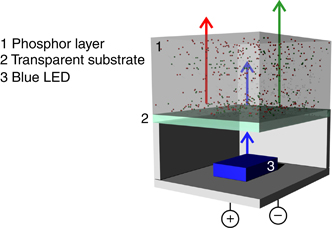
Abstract
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are driving a shift toward energy-efficient illumination. Nonetheless, modifying the emission intensities, colors and directionalities of LEDs in specific ways remains a challenge often tackled by incorporating secondary optical components. Metallic nanostructures supporting plasmonic resonances are an interesting alternative to this approach due to their strong light-matter interaction, which facilitates control over light emission without requiring external secondary optical components. This review discusses new methods that enhance the efficiencies of LEDs using nanostructured metals. This is an emerging field that incorporates physics, materials science, device technology and industry. First, we provide a general overview of state-of-the-art LED lighting, discussing the main characteristics required of both quantum wells and color converters to efficiently generate white light. Then, we discuss the main challenges in this field as well as the potential of metallic nanostructures to circumvent them. We review several of the most relevant demonstrations of LEDs in combination with metallic nanostructures, which have resulted in light-emitting devices with improved performance. We also highlight a few recent studies in applied plasmonics that, although exploratory and eminently fundamental, may lead to new solutions in illumination.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1038/lsa.2016.80
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Promoting effect of Sn on supported Ni catalyst during steam reforming of glycerol
Bobadilla, LF; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41 (2016) 9234-9244 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.04.119
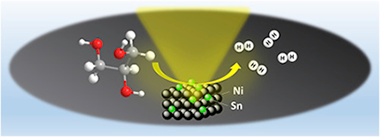
Abstract
The promoting effect of Sn on the catalytic performance of supported Ni catalyst in the reaction of glycerol steam reforming was studied. The physico-chemical properties of the prepared samples were investigated by X-ray fluorescence (XRF), BET surface area, in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD), laser Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and temperature-programmed oxidation (TPO) techniques. The characterization results of the samples after reduction treatment (in the same conditions than the activation before catalytic activity measurements) revealed the formation of NiSn alloy. The Sn-doped catalyst exhibited a high activity and it was demonstrated that the Sn addition increase the catalyst stability and durability by decreasing the coke deposition.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.04.119
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and functionalization of monodisperse near-ultraviolet and visible excitable multifunctional Eu3+, Bi3+:REVO4 nanophosphors for bioimaging and biosensing applications
Escudero, Alberto; Carrillo-Carrion, Carolina; Zyuzin, Mikhail V.; Ashraf, Sumaira; Hartmann, Raimo; Nunez, Nuria O.; Ocana, Manuel; Parak, Wolfgang J.Nanoscale, 8 (2016) 12221-12236 DOI: 10.1039/C6NR03369E
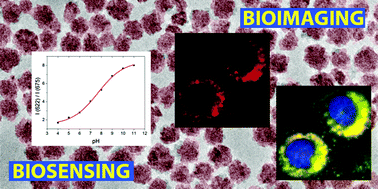
Abstract
Near-ultraviolet and visible excitable Eu- and Bi-doped NPs based on rare earth vanadates (REVO4, RE = Y, Gd) have been synthesized by a facile route from appropriate RE precursors, europium and bismuth nitrate, and sodium orthovanadate, by homogeneous precipitation in an ethylene glycol/water mixture at 120 °C. The NPs can be functionalized either by a one-pot synthesis with polyacrylic acid (PAA) or by a Layer-by-Layer approach with poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (PAH) and PAA. In the first case, the particle size can also be tuned by adjusting the amount of PAA. The Eu- Bi-doped REVO4 based nanophosphors show the typical red luminescence of Eu(III), which can be excited through an energy transfer process from the vanadate anions, resulting in a much higher luminescence intensity in comparison to the direct excitation of the europium cations. The incorporation of Bi into the REVO4 structure shifts the original absorption band of the vanadate anions towards longer wavelengths, giving rise to nanophosphors with an excitation maximum at 342 nm, which can also be excited in the visible range. The suitability of such nanophosphors for bioimaging and biosensing applications, as well as their colloidal stability in different buffer media of biological interest, their cytotoxicity, their degradability at low pH, and their uptake by HeLa cells have been evaluated. Their suitability for bioimaging and biosensing applications is also demonstrated.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/C6NR03369E
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
The role of carbon overlayers on Pt-based catalysts for H-2-cleanup by CO-PROX
Romero-Sarria, F; Garcia-Dali, S; Palma, S; Jimenez-Barrera, EM; Oliviero, L; Bazin, P; Odriozola, JASurface Science, 648 (2016) 84-91 DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2015.12.017
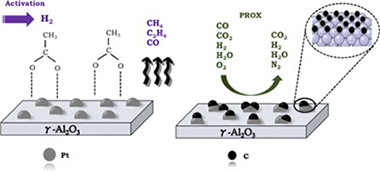
Abstract
In this work, we analyze the effect of the activation method on the catalytic activity of Pt-based catalysts supported on alumina in the PROX reaction. For this, model Pt/Al2O3 catalysts with variable amounts of acetic acid were prepared and their thermal evolution studied by FTIR spectroscopy. From the analysis of the nature of the platinum surface upon acetic acid decomposition and the gas phase evolved products, we have demonstrated the formation of partially hydrogenated carbon overlayers that tailor the activity of Pt-based catalysts in the PROX reaction.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2015.12.017
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The 16th European Conference on Applications of Surface and Interface Analysis
Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis DOI: 10.1002/sia.5937
Reactividad de Sólidos
A hybrid silver-magnetite detector based on surface enhanced Raman scattering for differentiating organic compounds
Caro, C; Sayagues, MJ; Franco, V; Conde, A; Zaderenko, P; Gamez, FSensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 228 (2016) 124-133 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.003
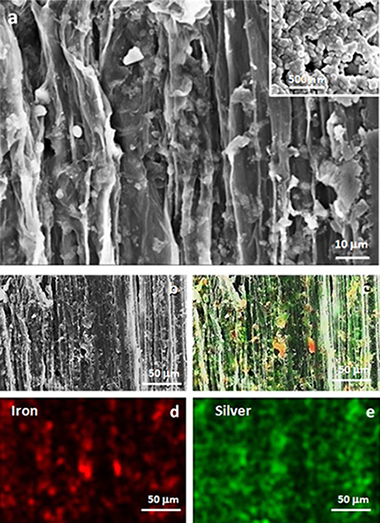
Abstract
In this work a cheap detector of organic molecules is developed. It comprises a cellulose fiber doped with a mixture of magnetite and reduced silver nanoparticles, the latter ones synthesized anew. The nanoparticles and the fiber were characterized with well-established spectroscopic, microscopic and magnetic techniques, namely infrared, UV–vis spectroscopies, vibrating sample magnetometry and electronic microscopies. The so-obtained doped-fibers were tested as surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy detector in aqueous samples with a diluted mixture of two pollutant models (rhodamine 6G and picric acid), being able to differentiate between both organic compounds. Hence, the nanoparticle-impregnated fiber is proposed as a reliable preliminary qualitative and semiquantitative test of the presence of specific organic molecules in solutions. Moreover, the magnetite nanoparticles provide the detector with a saturation magnetization value that enables the separation of the fiber from the solution with the aid of a commercial magnet.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.003
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
In-situ hydrogasification/regeneration of NiAl-hydrotalcite derived catalyst in the reaction of CO2 reforming of methane: A versatile approach to catalyst recycling
Abdelsadek, Z; Sehailia, M; Halliche, D; Gonzalez-Delacruz, VM; Holgado, JP; Bachari, K; Caballero, A; Cherifi, OJournal of CO2 Utilization, 14 (2016) 98-105 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2016.03.004
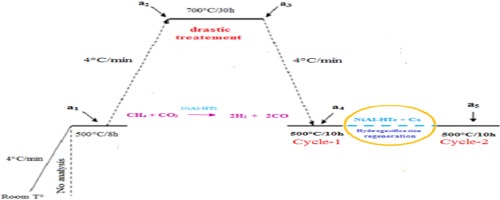
Abstract
A novel approach describing the in-situ regeneration of NiAl hydroalcite derived catalyst between two cycle reaction systems of CO2 reforming of methane, also known as dry reforming of methane (DRM) is described herein. The catalyst was initially prepared by co-precipitation method at pH = 11 and calcined at 450 degrees C for 6 h. The obtained material was characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), thermogravimetry (TG/ATD) and temperature programmed reduction (TPR-H-2) techniques. Following treatment of our catalyst under DRM conditions, the catalyst was subjected to in-situ hydrogasification conditions to promote regeneration followed by a second DRM cycle. An increase of 15.7% in the conversion of CH4 and 17.3% in the conversion of CO2 was attained, while the ratio of resulting H-2/CO augmented by 14%. The ratio of H-2 consumed over the course of two hours hydrogasification, to that generated over ten hours of DRM, was 9.6%. The small particle sizes of resulting Ni degrees species as well as their high stability were both key factors contributing to the increase in the amount of H-2/CO produced prior to and after regeneration.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2016.03.004
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A Full Vacuum Approach for the Fabrication of Hybrid White-Light-Emitting Thin Films and Wide-Range In Situ Tunable Luminescent Microcavities
Y. Oulad-Zian, J.R. Sánchez-Valencia, M. Oliva, J. Parra-Barranco, M. Alcaire, F.J. Aparicio, A. Mora-Boza, J.P. Espinós, F. Yubero, A.R. González-Elipe, A. Barranco, A. BorrasAdvanced Optical Materials, 4 (2016) 1134 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201670041
Abstract
A wide-range in situ tunable 1D Bragg microcavity including a hybrid layer as white light emitter defect is shown by J. R. Sanchez-Valencia, A. Borras, and co-workers on page 1124. White emission is obtained by Förster resonance energy transfer between blue (1,3,5-triphenyl-2-pyrazoline) and orange (rubrene) dyes homogeneously infiltrated within the host nanocolumnar SiO2film, which is formed by glancing angle deposition. Sequential physical vapor deposition at low temperatures provides the organic dyes localization within the porous nanostructure of the defect layer.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201670041
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Dye-based photonic sensing systems
Aparicio, FJ; Alcaire, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, A; Holgado, M; Casquel, R; Sanza, FJ; Griol, A; Bernier, D; Dortu, F; Caceres, S; Antelius, M; Lapisa, M; Sohlstrom, H; Niklaus, FSensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 228 (2016) 649-657 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.092
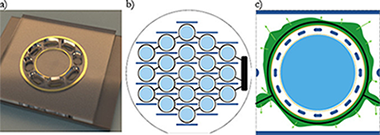
Abstract
We report on dye-based photonic sensing systems which are fabricated and packaged at wafer scale. For the first time luminescent organic nanocomposite thin-films deposited by plasma technology are integrated in photonic sensing systems as active sensing elements. The realized dye-based photonic sensors include an environmental NO2 sensor and a sunlight ultraviolet light (UV) A+B sensor. The luminescent signal from the nanocomposite thin-films responds to changes in the environment and is selectively filtered by a photonic structure consisting of a Fabry-Perot cavity. The sensors are fabricated and packaged at wafer-scale, which makes the technology viable for volume manufacturing. Prototype photonic sensor systems have been tested in real-world scenarios.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.092
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
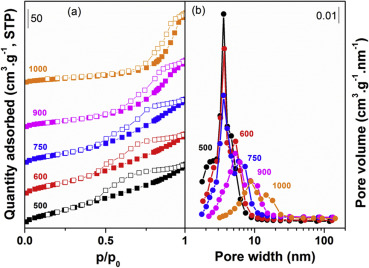
Nickel catalyst with outstanding activity in the DRM reaction prepared by high temperature calcination treatment
Smolakova, L; Kout, M; Capek, L; Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Gonzalez-Delacruz, VM; Hromadko, L; Caballero, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41 (2016) 8459-8469 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.161
Abstract
The catalytic performance of some Ni-Ce/Al2O3 catalytic systems (11 wt.% Ni and 3 wt.% Ce) were checked after being submitted to different calcination and reduction treatments. It was found that, the reduced Ni-Ce/Al2O3 catalysts were more active and stable in the dry reforming reaction of methane than thecorresponding not-reduced catalysts. This high activity was initially connected with the smaller size of pre-reduced Ni species, which at the same time leads on to the formation of filamentous carbon. The best overall performance was obtained for the reduced catalyst after being calcined at 1000 degrees C. This catalyst presents a very high stability, a low level of carbon formation, maintaining the nickel particle size constant during reaction. Surprisingly, although its reduction degree is only 12% at 750 degrees C, its catalytic activity is similar to the full reduced catalysts. So, the small number of reduced metallic particles of this catalyst shows a very high activity, much higher than the other catalysts.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.161
Reactividad de Sólidos
Use of steel slag for CO2 capture under realistic calcium-looping conditions
Miranda-Pizarro, J; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LARSC Advances, 6 (2016) 37656-37663 DOI: 10.1039/C6RA03210A

Abstract
In this study, CaO derived from steel slag pretreated with diluted acetic acid has been tested as a dry sorbent for CO2 capture under realistic Ca-Looping (CaL) conditions, which necessarily implies calcination under high CO2 partial pressure and fast transitions between carbonation and calcination stages. The multicycle capture performance of the sorbent has been investigated by varying the precalcination time, carbonation/calcination residence times and with the introduction of a recarbonation stage. Results show that the sorbent can be regenerated in very short residence times at 900 °C under high CO2 partial pressure, thus reducing the calciner temperature by about 30–50 °C when compared to limestone. Although the introduction of a recarbonation stage to reactivate the sorbent, as suggested in previous studies for limestone, results in a slightly enhanced capture capacity, the sorbent performance can be significantly improved if the main role of the solid-state diffusion-controlled carbonation is not dismissed. Thus, a notable enhancement of the capture capacity is achieved when the carbonation residence time is prolonged beyond just a few minutes, which suggests a critical effect of solids residence time in the carbonator on the CO2 capture efficiency of the CaL process when integrated into a power plant.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/C6RA03210A
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Portable IR dye laser optofluidic microresonator as a temperature and chemical sensor
Lahoz, F; Martin, IR; Gil-Rostra, J; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AROptics Express, 24 (2016) 14383-14392 DOI: 10.1364/OE.24.014383
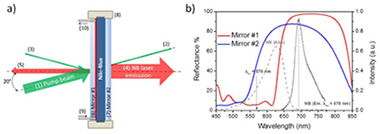
Abstract
A compact and portable optofluidic microresonator has been fabricated and characterized. It is based on a Fabry-Perot microcavity consisting essentially of two tailored dichroic Bragg mirrors prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering deposition. The microresonator has been filled with an ethanol solution of Nile-Blue dye. Infrared laser emission has been measured with a pump threshold as low as 0.12 MW/cm2 and an external energy conversion efficiency of 41%. The application of the device as a temperature and a chemical sensor is demonstrated. Small temperature variations as well as small amount of water concentrations in the liquid laser medium are detected as a shift of the resonant laser modes.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1364/OE.24.014383
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Plasmonic Nanoparticles as Light-Harvesting Enhancers in Perovskite Solar Cells: A User’s Guide
Carretero-Palacios, S.; Jiménez-Solano, A.; Míguez, H.ACS Energy Letters, 1 (2016) 323-331 DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00138
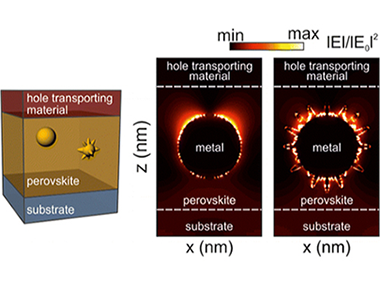
Abstract
In this Perspective we discuss the implications of employing metal particles of different shape, size, and composition as absorption enhancers in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite solar cells, with the aim of establishing some guidelines for the future development of plasmonic resonance-based photovoltaic devices. Hybrid perovskites present an extraordinarily high absorption coefficient which, as we show here, makes it difficult to extrapolate concepts and designs that are applied to other solution-processed photovoltaic materials. In addition, the variability of the optical constants attained from perovskite films of seemingly similar composition further complicates the analysis. We demonstrate that, by means of rigorous design, it is possible to provide a realistic prediction of the magnitude of the absorption enhancement that can be reached for perovskite films embedding metal particles. On the basis of this, we foresee that localized surface plasmon effects will provide a means to attain highly efficient perovskite solar cells using films that are thinner than those usually employed, hence facilitating collection of photocarriers and significantly reducing the amount of potentially toxic lead present in the device.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00138
Reactividad de Sólidos
Targeted multifunctional tannic acid nanoparticles
Aguilera, J. R.; Venegas, V.; Oliva, J. M.; Sayagues, M. J.; de Miguel, M.; Sanchez-Alcazar, J. A.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, M.; Zaderenko, A. P.RSC Advances, 6 (2016) 7279-7287 DOI: 10.1039/C5RA19405A
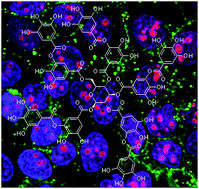
Abstract
Tannic acid (TA) has multiple effects against cancer, being especially promising in those types that overexpress the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), as TA modulates its activation and downstream signaling pathways, triggering apoptosis. Nonetheless, despite the important role of this receptor in the pathogenesis and progression of a wide variety of tumors, no TA systems targeted to this receptor have been described yet. In this work, we synthesize, characterize by physico-chemical techniques and study the cytotoxic effect and cell uptake of TA nanoparticles targeted to EGFR in both tumoral and normal human skin cells. Our nanoparticles exhibited an extremely high entrapment efficiency, and were only toxic for the tumoral cells. The uptake assay demonstrated that nanoparticles are able to enter the cells through a receptor-mediated mechanism. Furthermore, we have included fluorescent markers in these nanoparticles to combine imaging and therapeutic applications, thus building effectively a multifunctional tool for biomedicine.
June, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/C5RA19405A
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of dolomite decomposition under CO2 on its multicycle CO2 capture behaviour under calcium looping conditions
Martos, AD; Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Garcia-Garrido, C; Perez-Maqueda, LAPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18 (2016) 16325-16336 DOI: 10.1039/c6cp01149g
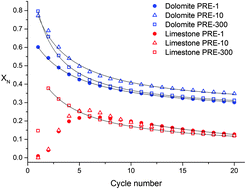
Abstract
One of the major drawbacks that hinder the industrial competitiveness of the calcium looping (CaL) process for CO2 capture is the high temperature (∼930–950 °C) needed in practice to attain full calcination of limestone in a high CO2 partial pressure environment for short residence times as required. In this work, the multicycle CO2 capture performance of dolomite and limestone is analysed under realistic CaL conditions and using a reduced calcination temperature of 900 °C, which would serve to mitigate the energy penalty caused by integration of the CaL process into fossil fuel fired power plants. The results show that the fundamental mechanism of dolomite decomposition under CO2 has a major influence on its superior performance compared to limestone. The inert MgO grains resulting from dolomite decomposition help preserve a nanocrystalline CaO structure wherein carbonation in the solid-state diffusion controlled phase is promoted. The major role played by the dolomite decomposition mechanism under CO2 is clearly demonstrated by the multicycle CaO conversion behaviour observed for samples decomposed at different preheating rates. Limestone decomposition at slow heating rates yields a highly crystalline and poorly reactive CaCO3 structure that requires long periods to fully decarbonate and shows a severely reduced capture capacity in subsequent cycles. On the other hand, the nascent CaCO3 produced after dolomite half-decomposition consists of nanosized crystals with a fast decarbonation kinetics regardless of the preheating rate, thus fully decomposing from the very first cycle at a reduced calcination temperature into a CaO skeleton with enhanced reactivity as compared to limestone derived CaO.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/c6cp01149g
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Cascade charge separation mechanism by ternary heterostructured BiPO4/TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst
Obregon, S; Zhang, YF; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Enviromental, 184 (2016) 96-103 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.11.027
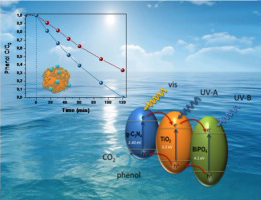
Abstract
A complex ternary BiPO4/TiO2/gC(3)N(4) heterostructure has been obtained from a simple impregnation method having good photoactivities for the degradation of phenol under solar-like irradiation. From the wide structural, surface and electronic characterization, we have stated that the formation of the ternary heterojunction notably affect photoactivity of pristine TiO2. Thus, the best result for the binary system was obtained for 70 wt%TiO2-30 wt% BiPO4 system. The incorporation of gC(3)N(4) leads to a further improvement on the photocatalytic activity when it is specifically done over TiO2. By means of photoluminescence spectroscopy and reactive oxygen species formation test, we propose that the effective charge carrier separation is taking place through a cascade-driven electronic mechanism. Therefore, by choosing the adequate band-engineering tailoring an important improved photoactivity can be achieved.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.11.027
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
O-2-assisted Water Gas Shift reaction over structured Au and Pt catalysts
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Tejada, LMM; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B: Enviromental, 185 (2016) 337-343 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.12.032

Abstract
Platinum and gold structured catalysts were compared as active phases in classical and O2-assisted Water Gas Shift (WGS) reaction. Both metals were supported on iron-doped ceria mixed oxide and then, structured on metallic micromonolithic devices. As expected the WGS activity of both micromonoliths is conditioned by the nature of the noble metals being Pt the most active metal in traditional conditions. However, the addition of oxygen to the classical water gas feed turns the balance in favor of the gold based catalysts, being the presence of gold responsible for an excessive improvement of the catalytic activity.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.12.032
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Towards the hydrogen production by photocatalysis
Colon, GApplied Catalysis A-General, 518 (2016) 48-59 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.11.042
Abstract
Nowadays, problems derived from climate change urgently demand us to focus our attention on new alternatives to fossil fuels. Within this framework, the photocatalytic production of hydrogen as a clean fuel from oxygenates arises as a necessary option that must be considered. Thus, the development of highly efficient photocatalyst is crucial in order to achieve a viable technology under the industrial point of view. For this sake, it is necessary to understand the principles of photoreforming reaction. In this brief review we will revisit the different photocatalytic materials proposed in the literature highlighting on the role of different co-catalysts.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.11.042
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biological strategy for the fabrication of highly ordered aragonite helices: the microstructure of the cavolinioidean gastropods
Checa, AG; Macias-Sanchez, E; Ramirez-Rico, JScientific Reports, 6 (2016) article number 25989 DOI: 10.1038/srep25989
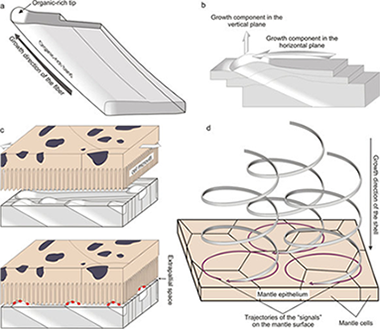
Abstract
The Cavolinioidea are planktonic gastropods which construct their shells with the so-called aragonitic helical fibrous microstructure, consisting of a highly ordered arrangement of helically coiled interlocking continuous crystalline aragonite fibres. Our study reveals that, despite the high and continuous degree of interlocking between fibres, every fibre has a differentiated organic-rich thin external band, which is never invaded by neighbouring fibres. In this way, fibres avoid extinction. These intra-fibre organic-rich bands appear on the growth surface of the shell as minuscule elevations, which have to be secreted differentially by the outer mantle cells. We propose that, as the shell thickens during mineralization, fibre secretion proceeds by a mechanism of contact recognition and displacement of the tips along circular trajectories by the cells of the outer mantle surface. Given the sizes of the tips, this mechanism has to operate at the subcellular level. Accordingly, the fabrication of the helical microstructure is under strict biological control. This mechanism of fibre-by-fibre fabrication by the mantle cells is unlike that any other shell microstructure.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1038/srep25989
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
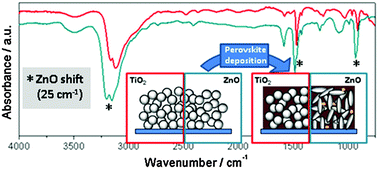
The interaction between hybrid organic-inorganic halide perovskite and selective contacts in perovskite solar cells: an infrared spectroscopy study
Idigoras, J; Todinova, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, A; Anta, JAPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18 (2016) 13583-13590 DOI: 10.1039/c6cp01265e
Abstract
The interaction of hybrid organic-inorganic halide perovskite and selective contacts is crucial to get efficient, stable and hysteresis-free perovskite-based solar cells. In this report, we analyze the vibrational properties of methylammonium lead halide perovskites deposited on different substrates by infrared absorption (IR) measurements (4000-500 cm(-1)). The materials employed as substrates are not only characterized by different chemical natures (TiO2, ZnO and Al2O3), but also by different morphologies. For all of them, we have investigated the influence of these substrate properties on perovskite formation and its degradation by humidity. The effect of selective-hole contact (Spiro-OmeTad and P3HT) layers on the degradation rate by moisture has also been studied. Our IR results reveal the existence of a strong interaction between perovskite and all ZnO materials considered, evidenced by a shift of the peaks related to the N-H vibrational modes. The interaction even induces a morphological change in ZnO nanoparticles after perovskite deposition, pointing to an acid-base reaction that takes place through the NH3+ groups of the methylammonium cation. Our IR and X-ray diffraction results also indicate that this specific interaction favors perovskite decomposition and PbI2 formation for ZnO/perovskite films subjected to humid conditions. Although no interaction is observed for TiO2, Al2O3, and the hole selective contact, the morphology and chemical nature of both contacts appear to play an important role in the rate of degradation upon exposure to moisture.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/c6cp01265e
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
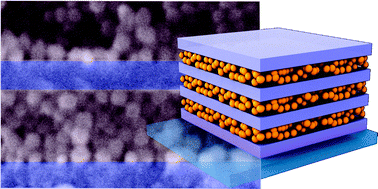
Solution processed high refractive index contrast distributed Bragg reflectors
Anaya, M; Rubino, A; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 4 (2016) 4532-4537 DOI: 10.1039/C6TC00663A
Abstract
We have developed a method to alternate porous and dense dielectric films in order to build high refractive index contrast distributed Bragg reflectors (DBRs) capable of reflecting very efficiently in a targeted spectral range employing a small number of layers in the stack. Porous layers made of SiO2 nanoparticles and compact sol–gel processed TiO2 layers are sequentially deposited. The key to the preservation of porosity of every other layer during the deposition process is the use of a sacrificial layer of polystyrene that prevents the infiltration of the interstitial voids between nanoparticles with the homogeneous solution of TiO2 precursors. Our approach allows preparing a series of DBRs operating along the whole visible spectral range. Reflectance values as high as 90% are achieved from only seven layers. The particular distribution of porosity along one direction gives rise to an interesting interplay between the optical properties of the system and the vapor pressure in the surrounding atmosphere, which we foresee could be put into practice in gas sensing devices.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/C6TC00663A
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biodegradable polyester films from renewable aleuritic acid: surface modifications induced by melt-polycondensation in air
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; de Vargas-Parody, MI; Cruz-Carrillo, MA; Morales-Florez, V; de la Rosa-Fox, N; Heredia, AJournal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 49 (2016) 175601 DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/49/17/175601
Abstract
Good water barrier properties and biocompatibility of long-chain biopolyesters like cutin and suberin have inspired the design of synthetic mimetic materials. Most of these biopolymers are made from esterified mid-chain functionalized.-long chain hydroxyacids. Aleuritic (9,10,16-trihydroxypalmitic) acid is such a polyhydroxylated fatty acid and is also the major constituent of natural lac resin, a relatively abundant and renewable resource. Insoluble and thermostable films have been prepared from aleuritic acid by melt-condensation polymerization in air without catalysts, an easy and attractive procedure for large scale production. Intended to be used as a protective coating, the barrier's performance is expected to be conditioned by physical and chemical modifications induced by oxygen on the air-exposed side. Hence, the chemical composition, texture, mechanical behavior, hydrophobicity, chemical resistance and biodegradation of the film surface have been studied by attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), atomic force microscopy (AFM), nanoindentation and water contact angle (WCA). It has been demonstrated that the occurrence of side oxidation reactions conditions the surface physical and chemical properties of these polyhydroxyester films. Additionally, the addition of palmitic acid to reduce the presence of hydrophilic free hydroxyl groups was found to have a strong influence on these parameters.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/49/17/175601
Reactividad de Sólidos
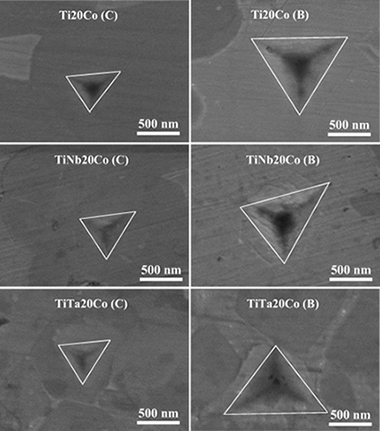
Hot-pressing of (Ti,Mt)(C,N)-Co-Mo2C (Mt = Ta,Nb) powdered cermets synthesized by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Medri, V; Guicciardi, S; Lascano, S; Cordoba, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 292 (2016) 51-61 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b00232
Abstract
A mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) has been successfully employed for manufacturing powdered cermets based on Ti, Ti–Ta and Ti–Nb carbonitrides using Co as the binder phase and Mo2C as the sintering additive. The powders were sintered by hot-pressing, and complete chemical, microstructural and mechanical characterizations were performed on the densified cermets. When elemental Ta, Nb and/or Mo2C were added to the initial raw mixture submitted to the MSR process, smaller ceramic grains were observed after sintering, which suggested that ceramic particle growth was hindered by the presence of Ta, Nb and/or Mo in the host titanium carbonitride structure. Nanoindentation measurements enabled the determination of the hardness of the ceramic and binder phases, and values in the range of 26–29 GPa and 14–16 GPa were found, respectively. The high hardness values of the binder were related to the formation of intermetallic phases.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b00232
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
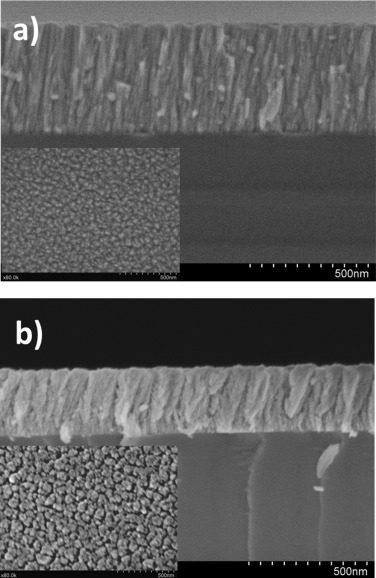
Non-enzymatic Glucose electrochemical sensor made of porous NiO thin films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Salazar, P; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochimica Acta, 201 (2016) 38-44 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.03.193
Abstract
Porous nanostructured NiO thin films have been prepared in one step by magnetron sputtering in an oblique angle configuration (MS-OAD) and used as electrodes for the non-enzymatic detection of glucose. The films have been thoroughly characterized by different complementary techniques and their performance for the analysis of glucose in basic solutions determined by electrochemical methods. These electrodes presented four times higher sensitivity that equivalent compact thin films prepared by MS in a normal configuration and were superior in terms of sensitivity than majority of nickel based electrodes prepared by other methods. Finally, a high sensitivity towards detection of glucose in blood, insensitivity to common interferences, a long term stability and high reproducibility confirmed the good performance and reliability of these electrodes for practical analytical purposes.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.03.193
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
A panchromatic modification of the light absorption spectra of metal-organic frameworks
Otal, E. H.; Kim, M. L.; Calvo, M. E.; Karvonen, L.; Fabregas, I. O.; Sierra, C. A.; Hinestroza, J. P.Chemical Communications, 52 (2016) 6665-6668 DOI: 10.1039/c6cc02319c
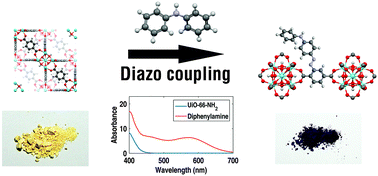
Abstract
The optical absorption of UiO-66–NH2 MOF was red-shifted using a diazo-coupling reaction. The modifications performed with naphthols and aniline yielded reddish samples, and the modifications with diphenylaniline yielded dark violet ones. The photocatalytic activity of these modified MOFs was assessed for methylene blue degradation, showing a good performance relative to traditional TiO2. The degradation performance was found to correlate with the red shift of the absorption edge. These findings suggest potential applications of these materials in photocatalysis and in dye sensitized solar cells.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/c6cc02319c
Reactividad de Sólidos
Electrical properties of reduced 3YTZP ceramics consolidated by spark plasma sintering
Poyato, R; Macias-Delgado, J; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Gonzalez-Romero, RL; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ACeramics International, 42 (2016) 6713-6719 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.01.040
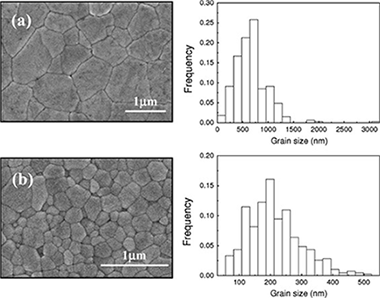
Abstract
3 mol% Yttria doped zirconia ceramics were consolidated by spark plasma sintering (SPS) at two sintering temperatures with the aim of achieving two different reduction levels. Microstructural characterization of the ceramics was performed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Electrical properties were investigated by means of impedance spectroscopy from room temperature up to 500 degrees C. The two ceramics presented a remarkably different electrical behavior. The effect of the extra electrons introduced by reduction during SPS on both the bulk and the grain boundary conductivity was analyzed and discussed.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.01.040
Reactividad de Sólidos
Obtention of Li3xLa2/3−xTiO3 ceramics from amorphous nanopowders by spark plasma sintering
Leyet, Y.; Guerrero, F.; Anglada-Rivera, J.; Martinez, I.; Amorin, H.; Romaguera-Barcelay, Y.; Poyato, R.; Gallardo-Lopez, A.Ferroelectrics, 498 (2016) 62-66 DOI: 10.1080/00150193.2016.1167538
Abstract
In this work, Li3xLa2/3-xTiO3 powder with nominal lithium content (x = 0.08) was synthesized by mechano synthesis method. Spark plasma sintering (SPS) was employed to prepare lithium lanthanum titanium oxide solid-state ceramic. The techniques of X-ray diffraction, high resolution scanning electron microscopy, and Raman spectroscopy were used to characterize the composition and microstructure of samples. The results showed that fine-grained ceramics with relative density of 95.5% were obtained by sintering the oxide powders at 1100 degrees C for only 5min.
May, 2016 · DOI: 10.1080/00150193.2016.1167538
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of temperature variations on equilibrium distances in levitating parallel dielectric plates interacting through Casimir forces
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HJournal of Applied Physics, 119 (2016) 144301 DOI: 10.1063/1.4945428
Abstract
We study at thermal equilibrium the effect of temperature deviations around room temperature on the equilibrium distance (d(eq)) at which thin films made of Teflon, silica, or polystyrene immersed in glycerol levitate over a silicon substrate due to the balance of Casimir, gravity, and buoyancy forces. We find that the equilibrium nature (stable or unstable) of d(eq) is preserved under temperature changes, and provide simple rules to predict whether the new equilibrium position will occur closer to or further from the substrate at the new temperature. These rules depend on the static permittivities of all materials comprised in the system (epsilon((m))(0)) and the equilibrium nature of d(eq). Our designed dielectric configuration is excellent for experimental observation of thermal effects on the Casimir force indirectly detected through the tunable equilibrium distances (with slab thickness and material properties) in levitation mode.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1063/1.4945428
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth Assisted by Glancing Angle Deposition: A New Technique to Fabricate Highly Porous Anisotropic Thin Films
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Longtin, R; Rossell, MD; Groning, PACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8 (2016) 8686-8693 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b00232
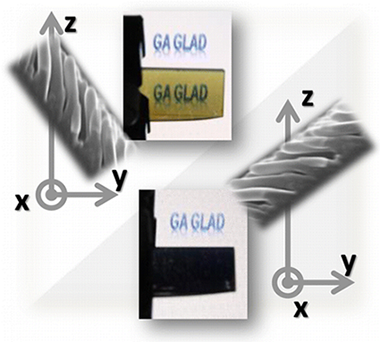
Abstract
We report a new methodology based on glancing angle deposition (GLAD) of an organic molecule in combination with perpendicular growth of a second inorganic material. The resulting thin films retain a very well-defined tilted columnar microstructure characteristic of GLAD with the inorganic material embedded inside the columns. We refer to this new methodology as growth assisted by glancing angle deposition or GAGLAD, since the material of interest (here, the inorganic) grows in the form of tilted columns, though it is deposited under a nonglancing configuration. As a “proof of concept”, we have used silver and zinc oxide as the perpendicularly deposited material since they usually form ill-defined columnar microstructures at room temperature by GLAD. By means of our GAGLAD methodology, the typical tilted columnar microstructure can be developed for materials that otherwise do not form ordered structures under conventional GLAD. This simple methodology broadens significantly the range of materials where control of the microstructure can be achieved by tuning the geometrical deposition parameters. The two examples presented here, Ag/Alq3 and ZnO/Alq3, have been deposited by physical vapor deposition (PVD) and plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), respectively: two different vacuum techniques that illustrate the generality of the proposed technique. The two type of hybrid samples present very interesting properties that demonstrate the potentiality of GAGLAD. On one hand, the Ag/Alq3 samples present highly optical anisotropic properties when they are analyzed with linearly polarized light. To our knowledge, these Ag/Alq3 samples present the highest angular selectivity reported in the visible range. On the other hand, ZnO/Alq3 samples are used to develop highly porous ZnO thin films by using Alq3 as sacrificial material. In this way, antireflective ZnO samples with very low refractive index and extinction coefficient have been obtained.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b00232
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Nanogold mesoporous iron promoted ceria catalysts for total and preferential CO oxidation reactions
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Idakiev, V; Tabakova, T; Centeno, MA; Deng, QF; Yuan, ZY; Odriozola, JAJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 414 (2016) 62-71 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2016.01.003

Abstract
Herein, a series of highly efficient gold based catalysts supported on mesoporous CeO2-Fe2O3 mixed oxides for CO elimination reactions have been developed. The materials have been fully characterized by means of XRD, Raman and UV-vis spectroscopies among other techniques. We identify the Ce-Fe synergism as a fundamental factor controlling the catalytic performance. Our data clearly reveal that the CO oxidation activity is maximized when the electronic and structural properties of the support are carefully controlled. In this situation, fairly good catalysts for environmental applications as for example H-2 streams purification for fuel cell goals or CO abatement at room temperature can be designed.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2016.01.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Pre-prosthetic use of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) membranes treated with oxygen plasma and TiO2 nanocomposite particles for guided bone regeneration processes
Castillo-Dali, G; Castillo-Oyague, R; Terriza, A; Saffar, JL; Batista-Cruzado, A; Lynch, CD; Sloan, AJ; Gutierrez-Perez, JL; Torres-Lagares, DJournal of Dentistry, 47 (2016) 71-79 DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2016.01.015
Abstract
Objectives: Guided bone regeneration (GBR) processes are frequently necessary to achieve appropriate substrates before the restoration of edentulous areas. This study aimed to evaluate the bone regeneration reliability of a new poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) membrane after treatment with oxygen plasma (PO2) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) composite nanoparticles.
Methods: Circumferential bone defects (diameter: 10 mm; depth: 3 mm) were created on the parietal bones of eight experimentation rabbits and were randomly covered with control membranes (Group 1: PLGA) or experimental membranes (Group 2: PLGA/PO2/TiO2). The animals were euthanized two months afterwards, and a morphologic study was then performed under microscope using ROI (region of interest) colour analysis. Percentage of new bone formation, length of mineralised bone formed in the grown defects, concentration of osteoclasts, and intensity of osteosynthetic activity were assessed. Comparisons among the groups and with the original bone tissue were made using the Kruskal-Wallis test. The level of significance was set in advance at a = 0.05.
Results: The experimental group recorded higher values for new bone formation, mineralised bone length, and osteoclast concentration; this group also registered the highest osteosynthetic activity. Bone layers in advanced formation stages and low proportions of immature tissue were observed in the study group.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2016.01.015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nickel-copper bilayer nanoporous electrode prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles for the non-enzymatic determination of glucose
Salazar, P; Rico, V; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 226 (2016) 436-443 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.12.003
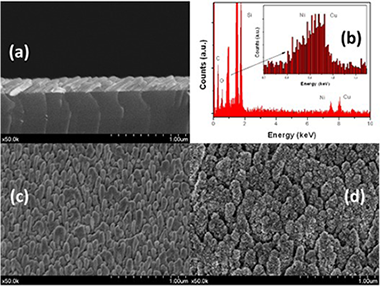
Abstract
This work presents a novel bilayer Ni/Cu porous nanostructured film electrode prepared by physical vapor deposition (PVD) in an oblique angle configuration. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) data revealed that the film, with an approximate thickness of 200 nm, is formed by tilted nanocolumns of around 50 nm of diameter and an inclination of 30° with respect to the surface normal. X ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) data confirmed a bilayer configuration with Cu and Ni located at the top and bottom parts of the film, respectively. A porosity of ca. 45–35% as determined by Rutherford back scattering (RBS) offered a large exposed area and excellent diffusion properties that, combined with a very good catalytic activity, rendered these films excellent electrodes for the quantitative determination of glucose. Under optimized working conditions of detection these electrodes presented a high sensitivity of 2.53 A M−1 cm−2 (R2: 0.999), a limit of detection of 0.23 μM and a time response of ca. 2 s. The sensors did not show any loss of response during a period of 4 months. The selectivity of the sensor was checked against various interferences, including physiological compounds, different sugars and ethanol, in all cases with excellent results. The feasibility of using of this sensor for practical applications was confirmed by successfully determining the glucose content in different commercial beverages.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.12.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Light management: porous 1-dimensional nanocolumnar structures as effective photonic crystals for perovskite solar cells
Ramos, FJ; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Nazeeruddin, MK; Graetzel, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Ahmad, SJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 4 (2016) 4962-4970 DOI: 10.1039/c5ta08743k
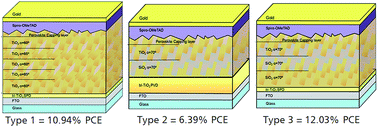
Abstract
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite solar cells are a topic of increasing interest, as in a short time span they are able to lead in the third generation photovoltaics. Organohalide perovskites possess exceptional optoelectronic and physical properties, thus making their implementation possible in many diverse configurations of photovoltaic devices. In this work, we present three different configurations of porous 1-dimensional photonic crystals (1-DPCs) based on alternated nanocolumnar layers of oxides with different refractive indices (n) that were deposited by Physical Vapor Deposition at Oblique Angle Deposition (PVD-OAD). They are then implemented as the photoanode in CH3NH3PbI3 solar cells to improve the management of light into the device. These configurations improved the performance of the photovoltaic system by designing a light interference structure capable of enhancing the absorption capability of the perovskite. A device fabricated using these photonic crystal structures presented an efficiency >12% in contrast with only 10.22% for a reference device based on non-photonic crystal TiO2 layers deposited under analogous conditions.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/c5ta08743k
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Strength and microplasticity of biocarbons prepared by carbonization in the presence of a catalyst
Shpeizman, VV; Orlova, TS; Smirnov, BI; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 58 (2016) 703-710 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783416040223
Abstract
The microdeformation has been investigated under uniaxial compression of beech-derived biocarbons partially graphitized during carbonization in the presence of a Ni- or Fe-containing catalyst. The strength and ultimate fracture strain have been determined at different temperatures of carbonization of the samples in the absence or in the presence of a catalyst. It has been shown using high-precision interferometry that the deformation of biocarbon samples under uniaxial loading occurs through jumps (in magnitude and rate of deformation) with axial displacements in the nanometer and micrometer ranges. The use of a catalyst leads to a decrease in the size of nanometer-scale jumps and in the number of micrometer-scale jumps. The standard deviations of the strain rate on loading steps from the smooth average dependence of the strain rate on the displacement have been calculated for micrometer-scale jumps. A similar characteristic for nanometer- scale jumps has been determined from the distortion of the shape of beats in the primary interferogram. It has been shown that the variation in the standard deviation of the strain rate with a change in the carbonization temperature is similar to the corresponding dependence of the ultimate fracture strain.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783416040223
Materiales Avanzados
Effect of lime on stabilization of phyllite clays
Garzon, E; Cano, M; O'Kelly, BC; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Clay Science, 123 (2016) 329-334 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.01.042
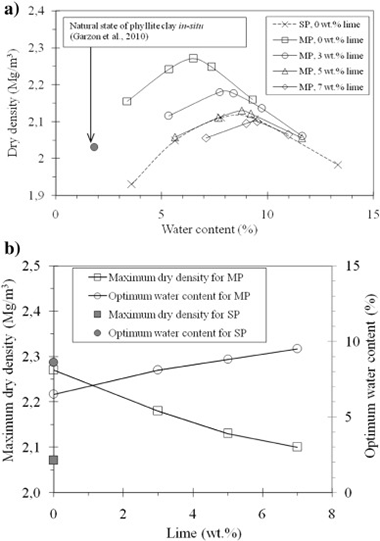
Abstract
This paper represents a new advance in the study of engineering properties and material applications of phyllite clays. Considering their potential use as construction materials for structures subjected to low stress levels, this laboratory research investigated the stabilization and improvement in engineering properties of a Spanish phyllite clay achieved by the addition of 3, 5 and 7 wt.% lime. Geotechnical properties investigated include the consistency limits, compaction, California Bearing Ratio, swelling potential and water-permeability. The phyllite clay–lime mixtures had good compaction properties and very to extremely low permeability-coefficient values, with a semi-logarithmic correlation between increasing permeability and increasing proportion of lime additive. The addition of 3 wt.% lime was sufficient to reach the index of capacity amble specified in the Sheet of Technical General Prescriptions for Works of Roads and Bridges PG–3 (Spanish Highways Agency, 2008), significantly reducing the plasticity index value, with the compacted mixture undergoing no swelling under soakage. The required pavement thicknesses for the raw phyllite–clay material and the phyllite clay–lime mixtures are compared and discussed. Potential applications for phyllite clay–lime mixtures include for pavements/road subgrade, earth construction, building materials and for impermeabilization purposes.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.01.042
The Structure and Chemical Composition of Wall Paintings From Islamic and Christian Times in the Seville Alcazar
Robador, MD; De Viguerie, L; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Rousseliere, H; Walter, P; Castaing, JArchaeometry, 58 (2016) 255-270 DOI: 10.1111/arcm.12218
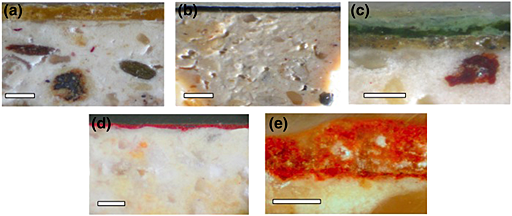
Abstract
Wall paintings from the Islamic epoch (10th to 12th centuries) and the Christian monarchy (14th to 16th centuries) have been recovered in discarded materials and on walls after reconstruction works in the Seville Alcazar. These paintings have spent centuries underground or under a plaster coat. Portable X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and combined XRF/X-ray diffraction (XRD) were employed in situ, as well as scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDX), grazing angle incidence XRD and micro-Raman spectroscopy, on cross-section samples to fully characterize the materials in the wall paintings. Using these methods, the fresco technique was demonstrated, and many kinds of pigments were identified in accordance with the various periods of the history of the Alcazar, thus assessing the authenticity of all the wall paintings studied here.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1111/arcm.12218
Materiales Coloidales
Transparent polycrystalline SrREGa3O7 melilite ceramics: potential phosphors for tuneable solid state lighting
Boyer, M; Carrion, AJF; Ory, S; Becerro, AI; Villette, S; Eliseeva, SV; Petoud, S; Aballea, P; Matzen, G; Allix, MJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 15 (2016) 3238-3247 DOI: 10.1039/C6TC00633G
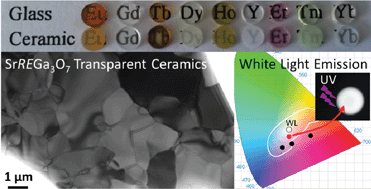
Abstract
Full and congruent crystallization from glass is applied to the SrREGa3O7 melilite family (RE = Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Y). This innovative process enables the synthesis of polycrystalline ceramics exhibiting high transparency both in the visible and near infrared regions, despite tetragonal crystal structures and micrometer scale grain sizes. Moreover, glass crystallization provides an original route to synthesize new crystalline phases which are not accessible via a classic solid state reaction, as demonstrated for SrYbGa3O7 and SrTmGa3O7. To illustrate the potential optical applications of such materials, SrGdGa3O7 transparent polycrystalline ceramics are doped with Dy3+ or Tb3+/Eu3+ in order to generate white light emission under UV excitation. It is foreseen that such transparent melilite ceramic phosphors, prepared via a cost-effective process, can be successfully used in solid state lighting devices of considerable technological interest.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1039/C6TC00633G
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Structure, electrochemical properties and functionalization of amorphous CN films deposited by femtosecond pulsed laser ablation
Maddi, C; Bourquard, F; Tite, T; Loir, AS; Donnet, C; Garrelie, F; Barnier, V; Wolski, K; Fortgang, P; Zehani, N; Braiek, M; Lagarde, F; Chaix, C; Jaffrezic-Renault, N; Rojas, TC; Sanchez-Lopez, JCDiamond and Related Materials,65 (2016) 17-25 DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2016.01.001
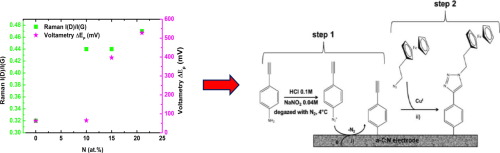
Abstract
Amorphous carbon nitride (a-C:N) material has attracted much attention in research and development Recently, it has become a more promising electrode material than conventional carbon based electrodes in electrochemical and biosensor applications. Nitrogen containing amorphous carbon (a-C:N) thin films have been synthesized by femtosecond pulsed laser deposition (fs-PLD) coupled with plasma assistance through Direct Current (DC) bias power supply. During the deposition process, various nitrogen pressures (0 to 10 Pa) and DC bias (0 to -350 V) were used in order to explore a wide range of nitrogen content into the films. The structure and chemical composition of the films have been studied by using Raman spectroscopy, electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). Increasing the nitrogen pressure or adding a DC bias induced an increase of the N content, up to 21 at%. Nitrogen content increase induces a higher sp(2) character of the film. However DC bias has been found to increase the film structural disorder, which was detrimental to the electrochemical properties. Indeed the electrochemical measurements, investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV), demonstrated that a-C:N film with moderate nitrogen content (10 at.%) exhibited the best behavior, in terms of reversibility and electron transfer kinetics. Electrochemical grafting from diazonium salts was successfully achieved on this film, with a surface coverage of covalently bonded molecules close to the dense packed monolayer of ferrocene molecules. Such a film may be a promising electrode material in electrochemical detection of electroactive pollutants on bare film, and of biopathogen molecules after surface grafting of the specific affinity receptor.
April, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2016.01.001
Reactividad de Sólidos
Fabrication and characterization of CeO2 pellets for simulation of nuclear fuel
Garcia-Ostos, C; Rodriguez-Ortiz, JA; Arevalo, C; Cobos, J; Gotor, FJ; Torres, YNuclear Engineering and Design, 298 (2016) 160-167 DOI: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2015.12.026
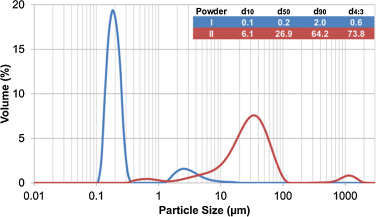
Abstract
Cerium Oxide, CeO2, has been shown as a surrogate material to understand irradiated Mixed Oxide (MOX) based matrix fuel for nuclear power plants due to its similar structure, chemical and mechanical properties. In this work, CeO2 pellets with controlled porosity have been developed through conventional powder-metallurgy process. Influence of the main processing parameters (binder content, compaction pressure, sintering temperature and sintering time) on porosity and volumetric contraction values has been studied. Microstructure and physical properties of sintered compacts have also been characterized through several techniques. Mechanical properties such as dynamic Young's modulus, hardness and fracture toughness have been determined and connected to powder-metallurgy parameters. Simulation of nuclear fuel after reactor utilization with radial gradient porosity is proposed.
March, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2015.12.026
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Nitrogen Nanobubbles in a-SiOxNy Coatings: Evaluation of Its Physical Properties and Chemical Bonding State by Spatially Resolved Electron Energy-Loss Spectroscopy
Lacroix, B.; Godinho, V.; Fernández, A.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120 (2016) 5651-5658 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b09036
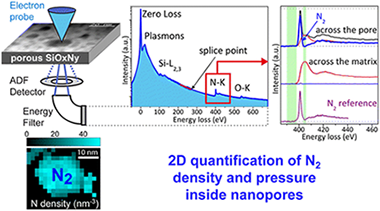
Abstract
Nanoporous silicon-based materials with closed porosity filled with the sputtering gas have been recently developed by magnetron sputtering. In this work the physical properties (density and pressure) of molecular nitrogen inside closed pores in a SiOxNy coating are investigated for the first time using spatially resolved electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) in a scanning transmission electron microscope. The paper offers a detailed methodology to record and process multiple EELS spectrum images (SIs) acquired at different energy ranges and with different dwell times. An adequate extraction and quantification of the N–K edge contribution due to the molecular nitrogen inside nanopores is demonstrated. Core-loss intensity and N chemical bond state were evaluated to retrieve 2D maps revealing the stable high density of molecular nitrogen (from 40 to 70 at./nm3) in nanopores of different size (20–11 nm). This work provides new insights into the quantification of molecular N2 trapped in porous nitride matrices that could also be applied to other systems.
March, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b09036
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Perspectives on oblique angle deposition of thin films: From fundamentals to devices
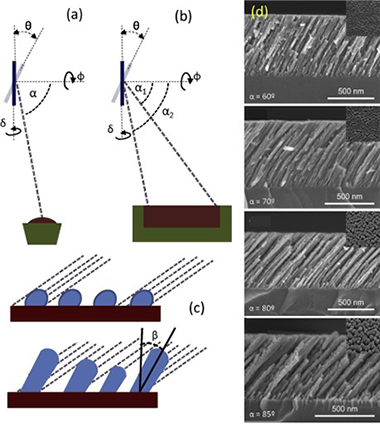
Barranco, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, AProgress in Materials Science, 78 (2016) 59-153 DOI: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.06.003
Abstract
The oblique angle configuration has emerged as an invaluable tool for the deposition of nanostructured thin films. This review develops an up to date description of its principles, including the atomistic mechanisms governing film growth and nanostructuration possibilities, as well as a comprehensive description of the applications benefiting from its incorporation in actual devices. In contrast with other reviews on the subject, the electron beam assisted evaporation technique is analyzed along with other methods operating at oblique angles, including, among others, magnetron sputtering and pulsed laser or ion beam-assisted deposition techniques. To account for the existing differences between deposition in vacuum or in the presence of a plasma, mechanistic simulations are critically revised, discussing well-established paradigms such as the tangent or cosine rules, and proposing new models that explain the growth of tilted porous nanostructures. In the second part, we present an extensive description of applications wherein oblique-angle-deposited thin films are of relevance. From there, we proceed by considering the requirements of a large number of functional devices in which these films are currently being utilized (e.g., solar cells, Li batteries, electrochromic glasses, biomaterials, sensors, etc.), and subsequently describe how and why these nanostructured materials meet with these needs.
March, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.06.003
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Comparison of supported TiO2 catalysts in the photocatalytic degradation of NOx
Rodriguez, MJH; Melian, EP; Diaz, OG; Arana, J; Macias, M; Orive, AG; Rodriguez, JMDJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 413 (2016) 56-66 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2015.12.007
Abstract
A comparison is made in this study of the effectiveness of various commercial catalysts in the oxidation of NOx by heterogeneous photocatalysis. The following catalysts were considered: Aeroxide TiO2 P25, Aeroxide TiO2 P90, Hombikat UV-100, Kronos vlp7000, CristalACTIV PC105, CristalACTIV PC500, Kemira 650 and Anatasa Aldrich. All catalysts were deposited by a dip -coating technique onto borosilicate 3.3 glass plates. Optimization of catalyst load showed no significant enhancement of photoactivity, in general, above a deposited mass of 1.16 mg cm(-2). Differences between photocatalyst activity were more apparent at longer illumination times. Photoactivity decreased in the presence of humidity and differences in the adsorbed products were detected. Photocatalyst activity was strongly influenced by specific surface area, with the best results obtained by the catalysts with the largest surface area, namely the PC500, Hombikat and Kronos. Photocatalyst stability was demonstrated in successive reuse cycles.
March, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2015.12.007
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrocatalytic System for the Simultaneous Hydrogen Production and Storage from Methanol
Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Valverde, JL; de Lucas-Consuegra, AACS Catalysis, 6 (2016) 1942-1951 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.5b02844
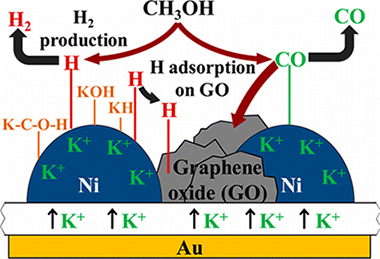
Abstract
This paper reports a groundbreaking approach for simultaneous hydrogen production and storage that entails catalysis, electrochemistry, surface science, and materials synthesis. A novel electrocatalytic system is developed based on nickel nanocolumnar films of controlled microstructure prepared on K-βAl2O3 solid electrolyte supports by oblique angle physical vapor deposition. The outstanding characteristics of this system are a hydrogen storage capacity of up to 19 g of H2 (100 g of Ni)−1, which is unparalleled in the literature and the possibility of controlling its release electrochemically, under fixed mild conditions (280 °C and normal pressure). H2 is produced in situ by methanol steam re-forming on the Ni catalyst, and it spills over onto graphene oxide aggregates formed during the catalytic process, as confirmed by SEM, FTIR, and Raman spectroscopy. The proposed storage mechanism considers a synergetic contribution of both Ni and graphene oxide, promoted by K+ ions, in enhancing the hydrogen storage capacity of the system.
March, 2016 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.5b02844
Materiales Avanzados
Ceramics from clays and by-product from biodiesel production: Processing, properties and microstructural characterization
Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Eliche-Quesada, D; Carrasco-Hurtado, B; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Angelopoulos, GNApplied Clay Science, 121 (2016) 119-126 DOI: 10.1016/j.day.2015.12.003
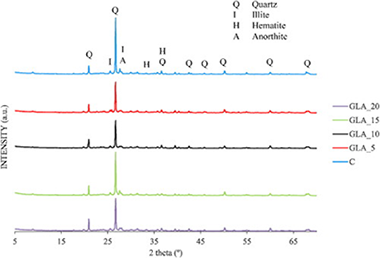
Abstract
The production of biodiesel generates a by-product called glycerine which contains glycerol that cannot be reintegrated into the same manufacturing process. The ceramic bricks are an interesting option to set in their structure a wide range of by-products and residues materials and composites, sometimes serving only as a reservoir for the inert residue, and other, having a positive effect on the ceramic material or process. In the present work, the incorporation of this waste in raw clays has been studied. The raw materials: clay and glycerine was characterized by XRD, XRF, CNHS analysis, higher heating value and thermal analysis and after, using conventional moulding and sintering processing methods to prepare clay-glycerine composites, the influence of the amount of waste added to clay has been evaluated. To do this, percentages of glycerine were added to the clay from 5% to 20% and evaluated by a series of technological properties such as compressive strength, absorption and suction of water, bulk density, the study of porosity generated by adsorption-desorption isotherms of N-2, thermal conductivity and finally by the compressive strength after freezing-thaw, it was considered as the maximum permissible rate of addition of glycerol 10-15% in weight, because higher additions have a strong effect on the properties of the obtained materials such as compression strength and bulk density which descending dramatically due to the large amount of porosity generated as reflected by high values of absorption and suction experiments. It was concluded that adding 5% glycerol to the ceramic paste generated plasticity in clay to achieve be moulded, with values of compressive strength of 84 MPa while gets to reduce the density apparent by almost.
March, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.day.2015.12.003
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
TiO2-clay based nanoarchitectures for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production
Perez-Carvajal, J; Aranda, P; Obregon, S; Colon, G; Ruiz-Hitzky, EMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 222 (2016) 120-127 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.10.007
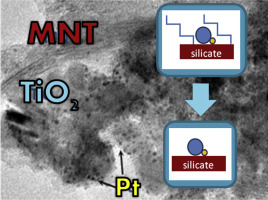
Abstract
New functional TiO2-clay nanoarchitectures based on layered and fibrous silicates and incorporating Pd and Pt noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) have been synthesized by applying a sol–gel methodology that involves the use of commercial organoclays. The incorporation of the noble metal NPs can be done using two different approaches: i) direct addition to the synthesis medium of a noble metal precursor (typically acetylacetonate) during the generation of the nanoarchitecture, and ii) selective photodeposition of the noble metal NPs in a post-treatment of the TiO2-clay nanoarchitecture. The resulting materials have been characterized by means of XRD, FTIR, Raman, 29Si-NMR, FE-SEM, TEM and N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms. The efficiency of these nanoarchitectures in the photocatalytic hydrogen production has been tested in the photoreforming of methanol. The higher rate in the hydrogen production corresponds to the nanoarchitectures containing Pt and TiO2 NPs derived from sepiolite.
March, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.10.007
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Active metal brazing of silicon nitride ceramics using a Cu-based alloy and refractory metal interlayers
Fernandez, JM; Asthana, R; Singh, M; Valera, FMCeramics International, 42 (2016) 5447-5454 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.12.087
Abstract
Silicon nitride/silicon nitride joints with refractory metal (W and Mo) interlayers were vacuum brazed using an active braze, Cu-ABA (Cu-3Si-2Al-2.25Ti, wt%), and two interlayer arrangements in a double-lap offset configuration: Si3N4/Cu-ABA/W/Cu-ABA/Mo/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 and Si3N4/Cu-ABA /Si3N4. Titanium segregated at the Si3N4/Cu-ABA and Mo/Cu-ABA interfaces, but not at the W/Cu-ABA interface. The room-temperature compression-shear strength values of Si3N4/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 and Si3N4/Cu-ABA/W/Cu-ABA/Mo/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 joints were 118 +/- 24 MPa and 22 +/- 5 MPa, respectively. Elevated-temperature compression tests showed that Si3N4/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 joints had strength of 31 +/- 6 MPa at 1023 K and 17 +/- 3 MPa at 1073 K. Likewise, Si3N4/Cu-ABA/W/Cu-ABA/Mo/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 joints had strength of 19 +/- 4 MPa at 1023 K and 13 +/- 3 MPa at 1073 K. Knoop microhardness profiles revealed hardness gradients across the joints. The effect of joint microstructure and test configuration on the mechanical behavior is discussed.
March, 2016 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.12.087
- ‹ previous
- 21 of 37
- next ›














