Scientific Papers in SCI
2014
2014
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Direct evidence of Lowenstein's rule violation in swelling high-charge micas
Pavon, E; Osuna, FJ; Alba, MD; Delevoye, LChemical Communications, 53 (2014) 6984-6986 DOI: 10.1039/C4CC01632G
Abstract
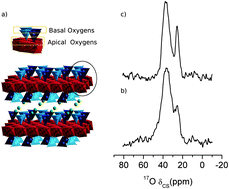
The structure of high-charged micas, Na-n-micas (n = 2 and 4), a family of synthetic silicates with a wide range of applications, was investigated through the use of 17O solid-state NMR at natural abundance in order to preserve quantitative spectral information. The use of a very high-field and highly sensitive probehead, together with 17O NMR literature data allowed for the detection of an isolated signal at 26 ppm, assigned partially to AlOAl, as evidence of the violation of Lowenstein's rule for Na-4-mica.
July, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C4CC01632G
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced oxidation resistance of Ti(C,N)-based cermets containing Ta
Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Cordoba, JMCorrosion Science, 84 (2014) 11-20 DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.03.007
Abstract
(TixTa1−x)(C0.5N0.5)–Co-based cermets with various Ta contents (x = 0, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2) were oxidized at 900 °C for 48 h in static air. A parabolic rate law, which is indicative of the formation of a protective oxide layer, was observed for all samples. The multi-layered oxide scale and the internal oxidation region that formed as the oxidation progressed toward the interior of the cermet specimens were characterized using XRD, SEM and EDS. The enhanced oxidation resistance achieved in cermets composed by a hard component with stoichiometry Ti0.95Ta0.05C0.5N0.5 may satisfy the optimal requirements for many applications in the field of cutting tools.
July, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.03.007
Reactividad de Sólidos
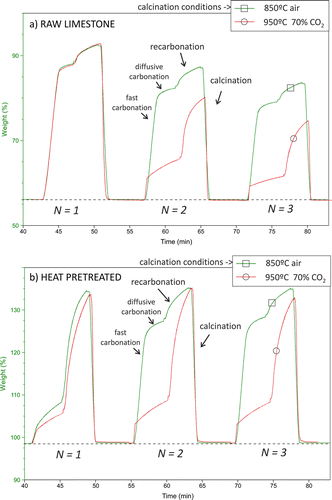
Role of crystal structure on CO2 capture by limestone derived CaO subjected to carbonation/recarbonation/calcination cycles at Ca-looping conditions
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Quintanilla, MAS; Perez-Vaquero, JApplied Energy, 125 (2014) 264-275 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.065
Abstract
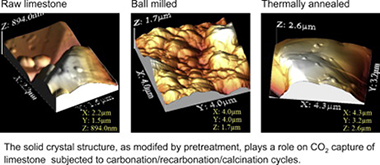
Large scale pilot plants are currently demonstrating the feasibility of the Calcium-looping (CaL) technology built on the multicyclic calcination/carbonation of natural limestone for post-combustion and precombustion CO2 capture. Yet, limestone derived CaO exhibits a drop of conversion when subjected to multiple carbonation/calcination cycles, which lessens the efficiency of the technology. In this paper we analyze a novel CaL concept recently proposed to mitigate this drawback based on the introduction of an intermediate stage wherein carbonation is intensified at high temperature and high CO2 partial pressure. It is shown that carbonation in this stage is mainly driven by solid-state diffusion, which is determined by the solid's crystal structure. Accordingly, a reduction of crystallinity by ball milling, which favors diffusion, serves to promote recarbonation. Conversely, thermal annealing, which enhances crystallinity, hinders recarbonation. An initial fast phase has been identified in the recarbonation stage along which the rate of carbonation is also a function of the crystal structure indicating a relevant role of surface diffusion. This is consistent with a recently proposed mechanism for nucleation of CaCO3 on the CaO surface in islands with a critical size determined by surface diffusion. A further issue analyzed has been the effects of pretreatment and cycling on the mechanical strength of the material, whose fragility hampers the CaL process efficiency. Particle size distribution of samples dispersed in a liquid and subjected to high energy ultrasonic irradiation indicate that milling promotes friability whereas thermal annealing enhances the resistance of the particles to fragmentation even though pretreatment effects become blurred after cycling. Our study demonstrates that recarbonation conditions and crystal-structure controlled diffusion are important parameters to be considered in order to assess the efficiency of CO2 capture in the novel CaL concept.
July, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.065
Reactividad de Sólidos
Multicyclic conversion of limestone at Ca-looping conditions: The role of solid-sate diffusion controlled carbonation
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAFuel, 127 (2014) 131-140 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.064
Abstract
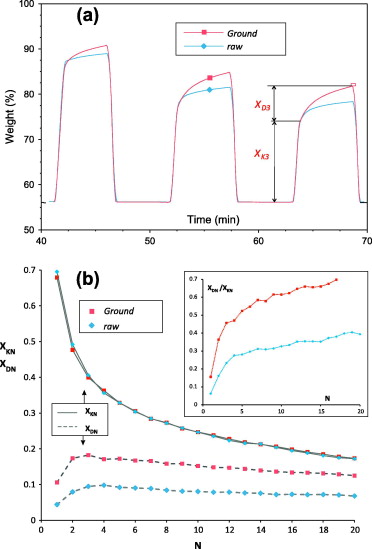
Limestone derived CaO conversion when subjected to multiple carbonation/calcination cycles is a subject of interest currently fueled by several industrial applications of the so-called Ca-looping (CaL) technology. The multicyclic CaO conversion at Ca-looping conditions exhibits two main features as demonstrated by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). On one hand, carbonation occurs by two well differentiated phases: a first kinetically-driven fast phase and a subsequent much slower solid-state diffusion controlled phase. On the other, carbonation in the fast phase usually shows a drastic decay with the cycle number along the first carbonation/calcination cycles. This trend can be reversed by means of heat pretreatment, which induces a marked loss of fast conversion in the first carbonation but enhances diffusion of CO2 in the solid. Upon decarbonation the regenerated CaO skeleton displays an increased conversion in the fast carbonation phase of the next cycle, a phenomenon which has been referred to as reactivation. Nonetheless, sorbent reactivation is hampered by looping carbonation/calcination conditions as those to be likely found in practice such as carbonation stages characterized by low CO2 concentrations and short duration and calcination stages at high temperatures in a CO2 enriched atmosphere, which causes a sintering and loss of activity of the regenerated CaO skeleton. We analyze in this work sorbent reactivation as affected by heat pretreatment and carbonation/calcination conditions. Aimed at shedding light on the role played by these conditions on reactivation we look separately at the multicyclic evolution of conversion in the kinetic and diffusive phases. Generally, the evolution of multicyclic conversion after the first cycle can be described by a balance between the surface area gain due to diffusive carbonation and the surface area loss as caused by sintering in the calcination stage. A significant gain of relative surface area after the first cycle, which is favored by harshening the heat pretreatment conditions, leads however to a marked decay of it during subsequent cycles, which precludes reactivation for an extended interval of cycles. On the other hand, sorbent grinding, if performed before heat pretreatment, leads to a less marked but more sustainable reactivation along the cycles. A novel observation reported in our work is that pretreatment of limestone in a CO2 atmosphere leads upon a subsequent quick decarbonation to a CaO skeleton with extraordinarily enhanced reactivity in the kinetically-driven carbonation phase and with a high resistance to solid-state diffusion, which can be attributed to annealing of the crystal structure as reported by independent studies.
July, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.064
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanocolumnar growth of thin films deposited at oblique angles: Beyond the tangent rule
Alvarez, R; Lopez-Santos, C; Parra-Barranco, J; Rico, V; Barranco, A; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, AJournal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 32 (2014) 041802 DOI: 10.1116/1.4882877
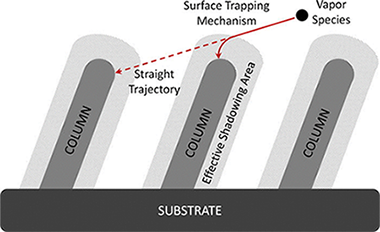
Abstract
The growth of nanostructured physical vapor deposited thin films at oblique angles is becoming a hot topic for the development of a large variety of applications. Up to now, empirical relations, such as the so-called tangent rule, have been uncritically applied to account for the development of the nanostructure of these thin films even when they do not accurately reproduce most experimental results. In the present paper, the growth of thin films at oblique angles is analyzed under the premises of a recently proposed surface trapping mechanism. The authors demonstrate that this process mediates the effective shadowing area and determines the relation between the incident angle of the deposition flux and the tilt angle of the columnar thin film nanostructures. The analysis of experimental data for a large variety of materials obtained in our laboratory and taken from the literature supports the existence of a connection between the surface trapping efficiency and the metallic character of the deposited materials. The implications of these predictive conclusions for the development of new applications based on oblique angle deposited thin films are discussed.
July, 2014 · DOI: 10.1116/1.4882877
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The Flexible Surface Revisited: Adsorbate-Induced Reconstruction, Homocoupling, and Sonogashira Cross-Coupling on the Au(100) Surface
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Feria, L; Sanz, JF; Lambert, RMJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 11677-11684 DOI: 10.1021/jp501321u
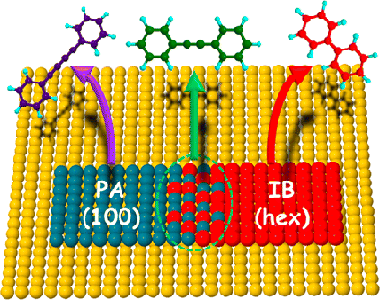
Abstract
Phenylacetylene (PA) and iodobenzene (IB) are prototypical reactants in Sonogashira cross-coupling. Their adsorption behavior and reactivity on the Au(100) surface were studied by STM, temperature-programmed desorption and reaction, and DFT calculations that included the effect of dispersion forces. The two species exhibited very different behavior. Thus, even at 200 K, PA rearranged Au surface atoms so as to lift the hex reconstruction and adsorb in 4-fold-symmetric islands on the unreconstructed 100 surface. On the other hand, IB adsorbed on the reconstructed hex surface, again as islands, forming three different coexisting close-packed structures. The DFT results are in good accord with these findings, demonstrating the strong preference of PA and IB for the (100) and hex surfaces, respectively. Moreover, the calculated adsorption energies were in satisfactory agreement with values estimated from the desorption data. Adsorbed separately, both PA and IB underwent homocoupling yielding diphenyl diacetylene and biphenyl, respectively; in the former case, reaction appeared to originate at island boundaries. On the well-annealed surface, coadsorbed PA and IB behaved independently, generating only products of homocoupling. However, on the Ar+ roughened surface, Sonogashira cross-coupling also occurred, yielding diphenyl acetylene. These findings are discussed in terms of the island-forming propensity of the reactants, amplified by the labile nature of the Au 100 surface under adsorption and the marked preference of the two reactants for different substrate structures, factors that act to inhibit the formation of a mixed adlayer and suppress reactivity. The implications for the behavior of practical Au nanoparticle catalysts are considered.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/jp501321u
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The growth of cobalt oxides on HOPG and SiO2 surfaces: A comparative study
Diaz-Fernandez, D; Mendez, J; Bomati-Miguel, O; Yubero, F; Mossanek, RJO; Abbate, M; Dominguez-Canizares, G; Gutierrez, A; Tougaard, S; Soriano, LSurface Science, 624 (2014) 145-153 DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2014.02.007
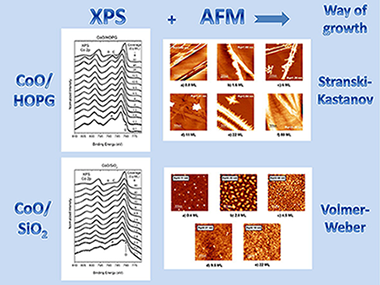
Abstract
The growth of cobalt oxides by reactive thermal evaporation of metallic cobalt on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) and SiO2 (X cut quartz surface), in an oxygen atmosphere at room temperature, has been chemically and morphologically studied by means of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. The chemical analysis, which also includes cluster calculations, reveals that for the early deposition stages on both substrates, Co2 + species are stabilized at the surface up to a coverage which depends on the substrate. Further coverages lead to the formation of the spinel oxide Co3O4. The results are discussed in terms of the dependence of the surface energy on the size of the CoO deposited moieties. On the other hand, it has been found that the initial way of growth of cobalt oxides on HOPG is of Stranski–Krastanov mode whereas on SiO2 the growth is of Volmer–Weber mode. The differences in the growth morphology have been discussed in terms of the surface diffusivity of the CoO deposits on the substrates.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2014.02.007
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Infrared and Raman spectroscopic features of plant cuticles: a review
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJ; Dominguez, E; Bayer, IS; Cingolani, R; Athanassiou, A; Heredia, AFrontiers in Plant Science, 25 (2014) DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00305
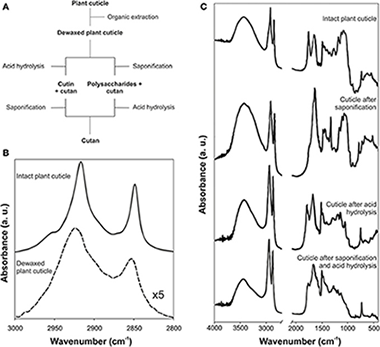
Abstract
The cuticle is one of the most important plant barriers. It is an external and continuous lipid membrane that covers the surface of epidermal cells and whose main function is to prevent the massive loss of water. The spectroscopic characterization of the plant cuticle and its components (cutin, cutan, waxes, polysaccharides and phenolics) by infrared and Raman spectroscopies has provided significant advances in the knowledge of the functional groups present in the cuticular matrix and on their structural role, interaction and macromolecular arrangement. Additionally, these spectroscopies have been used in the study of cuticle interaction with exogenous molecules, degradation, distribution of components within the cuticle matrix, changes during growth and development and characterization of fossil plants.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00305
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
A General Perspective of the Characterization and Quantification of Nanoparticles: Imaging, Spectroscopic, and Separation Techniques
Lapresta-Fernandez, A; Salinas-Castillo, A; de la Llana, SA; Costa-Fernandez, JM; Dominguez-Meister, S; Cecchini, R; Capitan-Vallvey, LF; Moreno-Bondi, MC; Marco, MP; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Anderson, ISCritical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences, 39 (2014) 423-458 DOI: 10.1080/10408436.2014.899890
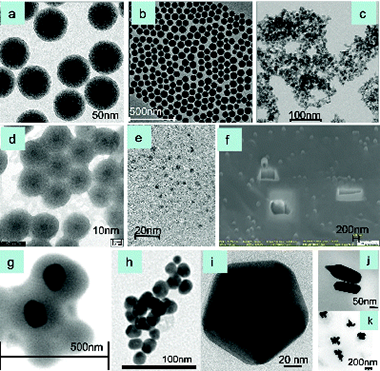
Abstract
This article gives an overview of the different techniques used to identify, characterize, and quantify engineered nanoparticles (ENPs). The state-of-the-art of the field is summarized, and the different characterization techniques have been grouped according to the information they can provide. In addition, some selected applications are highlighted for each technique. The classification of the techniques has been carried out according to the main physical and chemical properties of the nanoparticles such as morphology, size, polydispersity characteristics, structural information, and elemental composition. Microscopy techniques including optical, electron and X-ray microscopy, and separation techniques with and without hyphenated detection systems are discussed. For each of these groups, a brief description of the techniques, specific features, and concepts, as well as several examples, are described.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1080/10408436.2014.899890
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tomographic Heating Holder for In Situ TEM: Study of Pt/C and PtPd/Al2O3 Catalysts as a Function of Temperature
Gontard, LC; Dunin-Borkowski, RE; Fernandez, A; Ozkaya, D; Kasama, TMicroscoy and Microanalysis, 20 (2014) 982-990 DOI: 10.1017/S1431927614000373
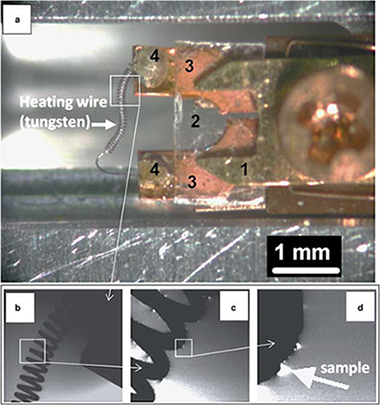
Abstract
A tomographic heating holder for transmission electron microscopy that can be used to study supported catalysts at temperatures of up to similar to 1,500 degrees C is described. The specimen is placed in direct thermal contact with a tungsten filament that is oriented perpendicular to the axis of the holder without using a support film, allowing tomographic image acquisition at high specimen tilt angles with minimum optical shadowing. We use the holder to illustrate the evolution of the active phases of Pt nanoparticles on carbon black and PtPd nanoparticles on gamma-alumina with temperature. Particle size distributions and changes in active surface area are quantified from tilt series of images acquired after subjecting the specimens to increasing temperatures. The porosity of the alumina support and the sintering mechanisms of the catalysts are shown to depend on distance from the heating filament.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1017/S1431927614000373
Materials characteristics of Roman and Arabic mortars and stuccoes from The Patio de Banderas in the Real Alcazar of Seville (SPAIN)
Garofano, I; Robador, MD; Duran, AArchaeometry, 56 (2014) 541-561 DOI: 10.1111/arcm.12041
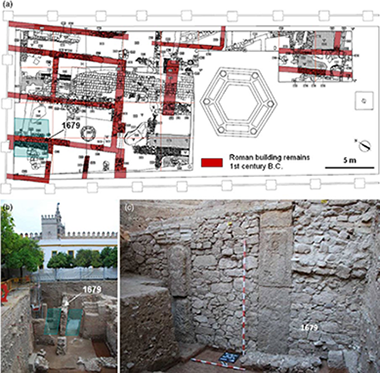
Abstract
This study discusses the materials and traditional knowledge used in the manufacture and application of lime mortars and stuccoes by Romans and Arabs in Seville (southern Iberian Peninsula). All of the samples studied contain calcite as a binder, combined with aggregates based on river sand from the filling materials of the Guadalquivir River's depression, located in the vicinity of the Real Alcazar Palace in Seville, Spain, where the artefacts were discovered. The Romans used high-quality production technology, as evidenced by the careful selection of raw materials as well as by the adequate binder-to-aggregate ratio and the elevated homogeneity of the mortars and stuccoes. The suitable distribution of aggregates resulted in higher density values for Roman fragments than for Arabic ones. Results derived from Arabic samples suggest a decline in technology manufacture over time. This work provides useful information, particularly regarding the Roman and Arabic periods in the Iberian Peninsula. The analytical techniques employed in this study were X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF)—using conventional and portable systems, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), petrographic microscopy, differential thermal analysis/thermogravimetry (DTA/TG), particle-size analysis and mercury intrusion porosimetry.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1111/arcm.12041
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Excellent photocatalytic activity of Yb3+, Er3+ co-doped BiVO4 photocatalyst
Obregon, S.; Colon, G.Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 152-153 (2014) 328-334 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.01.054
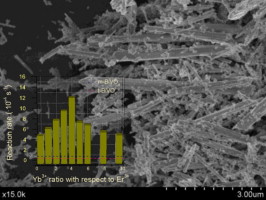
Abstract
Ytterbium-Erbium co-doped BiVO4 have been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of Methylene Blue and O2 evolution reactions. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Yb3+ and Er3+ induces the stabilization of the tetragonal phase probably due to its substitutional incorporation in the BiVO4 lattice. The occurrence of the Yb3+,Er3+ co-doped monoclinic-tetragonal BiVO4 heterostructure induces the higher photocatalytic activities. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the sample with 1:4 Er3+:Yb3+ ratio. The observed NIR photoactivity clearly denotes the occurrence of an up-conversion mechanism involved in the overall photocatalytic process.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.01.054
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
A study of the optical properties of metal-doped polyoxotitanium cages and the relationship to metal-doped titania
Lv, YK; Cheng, J; Matthews, PD; Holgado, JP; Willkomm, J; Leskes, M; Steiner, A; Fenske, D; King, TC; Wood, PT; Gan, LH; Lambert, RM; Wright, DSDalton Transactions, 43 (2014) 8679-8689 DOI: 10.1039/C4DT00555D
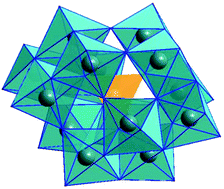
Abstract
To what extent the presence of transition metal ions can affect the optical properties of structurally well-defined, metal-doped polyoxotitanium (POT) cages is a key question in respect to how closely these species model technologically important metal-doped TiO2. This also has direct implications to the potential applications of these organically-soluble inorganic cages as photocatalytic redox systems in chemical transformations. Measurement of the band gaps of the series of closely related polyoxotitanium cages [MnTi14(OEt)28O14(OH)2] (1), [FeTi14(OEt)28O14(OH)2] (2) and [GaTi14(OEt)28O15(OH)] (3), containing interstitial Mn(II), Fe(II) and Ga(III) dopant ions, shows that transition metal doping alone does not lower the band gaps below that of TiO2 or the corresponding metal-doped TiO2. Instead, the band gaps of these cages are within the range of values found previously for transition metal-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. The low band gaps previously reported for 1 and for a recently reported related Mn-doped POT cage appear to be the result of low band gap impurities (most likely amorphous Mn-doped TiO2).
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C4DT00555D
Reactividad de Sólidos
The role of boron oxide and carbon amounts in the mechanosynthesis of ZrB2–SiC–ZrC nanocomposite via a self-sustaining reaction in the zircon/magnesium/boron oxide/graphite system
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 598 (2014) 113-119 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.02.033
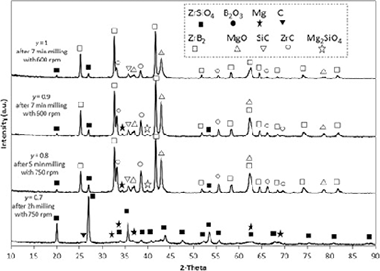
Abstract
Herein, ZrSiO4/B2O3/Mg/C system was used to synthesize a ZrB2-based composite by means of a high energy ball milling process. A mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction was achieved in this system. A nanocomposite powder of ZrB2–SiC–ZrC was prepared with an ignition time of approximately 6 min of milling. The role of the stoichiometric amounts of B2O3 and carbon was investigated to clarify the governing mechanism for the formation of the product.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.02.033
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Influence of the synthesis parameter on the interlayer and framework structure of lamellar octadecyltrimethylammonium kanemite
Corredor, JI; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Osuna, FJ; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 95 (2014) 9-17 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.02.030
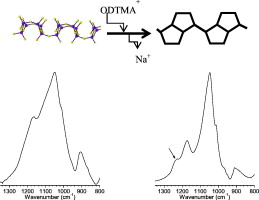
Abstract
Inorganic–organic nanostructures, used as host materials for selective adsorption of functional molecules and as mesostructured material precursors, can be constructed by the interlayer modification of inorganic layered materials with surfactants. The formation mechanism is mainly determined by the surfactant assemblies in the 2D limited space. In this paper, a detailed structural analysis of the lamellar mesophases prepared from kanemite, a lamellar silicate, and octadecyltrimethylammonium (ODTMA) under various conditions was reported. The adsorbed amount of ODTMA and the long and short range structural orders were explored by TGA, XRD, IR/FT and MAS NMR spectroscopies. The results revealed that ODTMA molecules were efficiently intercalated in the interlayer space of kanemite and, in all synthesis conditions, an ordered lamellar structure was obtained. The ODTMA adsorption in kanemite caused changes not only in the interlayer space but also in the silicate framework, where five-member rings were formed. The characteristics of the final products were influenced by the synthesis conditions, although the separation mode, filtration or centrifugation, was not relevant. Therefore, the adsorption conditions of ODTMA in kanemite will contribute to the design of novel layered materials with potential environmental and technological use.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.02.030
Reactividad de Sólidos
Processing and characterisation of cermet/hardmetal laminates with strong interfaces
Gotor, FJ; Bermejo, R; Cordoba, JM; Chicardi, E; Medri, V; Fabbriche, DD; Torres, YMaterials & Design, 58 (2014) 226-233 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.01.076
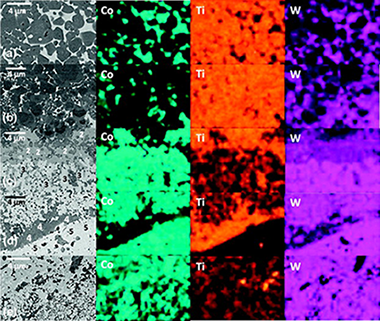
Abstract
Cemented carbides and cermets are potential materials for high speed machining tools. However, cemented carbides are not chemically stable at high temperature and cermets present poor fracture toughness. Novel cermet/hardmetal multilayer systems show a huge potential for this intended application. It would be possible to achieve the right balance of the required thermomechanical properties using cermet as temperature protective outer layers and hardmetal as reinforcement layers. In this work, preliminary results on the microstructural and mechanical characterisation of a multilayer TiCxN1−x–Co/WC–Co composite densified by hot pressing are presented, with special attention to the properties of the interface. Microstructural observations revealed the existence of strong bonding interfaces between cermet and hardmetal layers due to chemical interaction during the sintering process. As a consequence, owing to the different coefficient of thermal expansion between cermet and hardmetal, a tensile and compressive biaxial residual stress of σres,Cermet ≈ +260 ± 50 MPa and σres,WC–Co ≈ −350 ± 70 MPa was estimated in the corresponding layers. Microindentation cracks introduced in the cermet layers (the less toughness material) and propagated transversely to the layers were arrested at the interface, showing the combined effect of toughness and compressive stresses on crack shielding.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.01.076
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
On the Deposition Rates of Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films at Oblique Angles
Alvarez, R; Garcia-Martin, JM; Lopez-Santos, MC; Rico, V; Ferrer, FJ; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, APlasma Processes and Polymers, 11 (2014) 571-576 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300201
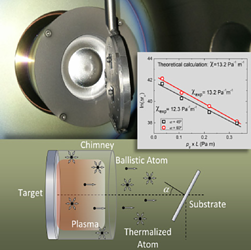
Abstract
We describe here the deposition of thin films using magnetron sputtering at oblique angles. General relations between the deposition rates of the films and experimental parameters, such as gas pressure or substrate tilt angles, are deduced and experimentally tested. The model also permits the direct determination of the thermalization mean free path of the sputtered particles in the plasma gas, a key parameter defining the balance between ballistic and diffusive flows in the deposition reactor. The good agreement between experimental and calculated results supports the validity of our description, which becomes a useful tool to explain the main features of the magnetron sputtering deposition of thin films at oblique angles.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300201
Reactividad de Sólidos - Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Phase assembly and electrical conductivity of spark plasma sintered CeO2-ZrO2 ceramics
Poyato, R; Cruz, SA; Cumbrera, FL; Moreno, B; Chinarro, E; Odriozola, JAJournal of Materials Science, 49 (2014) 6353-6362 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-014-8361-6
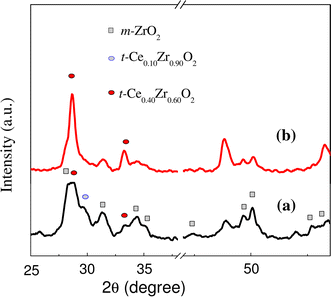
Abstract
Cex Zr1−x O2 (x = 0.10, 0.16 and 0.33) nanocrystalline powders were obtained by a two-step synthesis technique and sintered by spark plasma sintering (SPS). As consequence of the reduction of Ce4+ to Ce3+ species by carbon in the graphite environment in SPS, phase assemblies including tetragonal, monoclinic and pyrochlore phases were generated in the ceramics during the sintering process. The electrical conductivity was highly dependent on phase assembly and atmosphere (N2, H2 and O2). A significant decrease in the activation energy was noticed in the ceramics with high pyrochlore content when measuring the conductivity in H2 atmosphere, consequence of the strong reduction promoted in these ceramics during the measurement. Equal conduction behavior with similar activation energy was observed in all the ceramics when measuring in O2 atmosphere.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1007/s10853-014-8361-6
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of high SWNT content on the room temperature mechanical properties of fully dense 3YTZP/SWNT composites
Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Gutierrez-Mora, F; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 34 (2014) 1571-1579 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.12.024
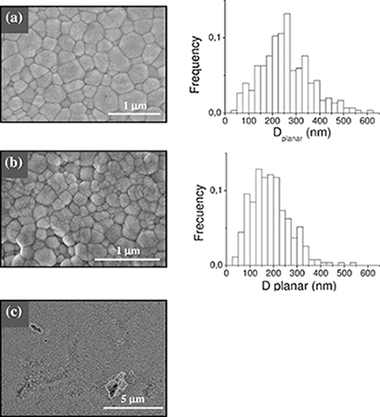
Abstract
This paper is devoted to correlate the microstructure and room temperature mechanical properties of single-wall carbon nanotube (SWNT) reinforced 3 mol% yttria stabilized tetragonal zirconia with high SWNT content (2.5, 5 and 10 vol%). Fully dense composites were prepared by using a combination of aqueous colloidal powder processing and Spark Plasma Sintering. SWNTs were located at the ceramic grain boundaries and they were not damaged during the sintering process. The weak interfacial bonding between SWNTs and ceramic grains together with the detachment of SWNTs within thick bundles have been pointed out as responsible for the decrease of hardness and fracture toughness of the composites in comparison with the monolithic 3YTZP ceramic.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.12.024
Reactividad de Sólidos
Improvement of the thermal stability of branched poly(lactic acid) obtained by reactive extrusion
Carrasco, F; Cailloux, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Maspoch, MLPolymer Degradation and Stability, 104 (2014) 40-49 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.03.026
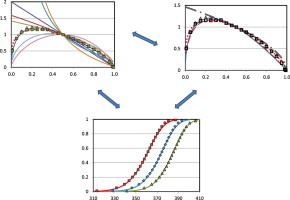
Abstract
One-step reactive extrusion-calendering process (REX-calendering) has been used in order to obtain sheets of 1 mm from poly(lactic acid) modified with a styrene-acrylic multifunctional oligomeric agent. In a preliminary internal mixer study, torque versus time has been monitored in order to ascertain chain extender ratios and reaction time. Once all the parameters were optimized, reactive extrusion experiments have been performed. An enhanced general analytical equation has been developed in order to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the thermal degradation of PLA sheets manufactured by reactive extrusion. This improvement has consisted of replacing the n-order conversion function by a modified form of the Sestak–Berggren equation f(α) = c (1 − α)nαm that led to a better adjustment of experimental data and also adequately represented the conventional mechanisms for solid-state processes. The kinetic parameters so obtained have been compared to those determined by conventional differential methods and n-order reaction kinetics. Given that the thermal degradation of PLA has been argued to be caused by random chain scission reactions of ester groups, the conversion function f(α) = 2 (α1/2 − α), corresponding to a random scission mechanism for L = 2 (as well as other functions for L values up to 8), has been tested. Once optimized the kinetic model, the thermal degradation kinetics of sheets obtained by REX-calendering process was compared to that of conventional sheets and polymer matrix.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.03.026
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Heat Pretreatment/Recarbonation in the Ca-Looping Process at Realistic Calcination Conditions
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAEnergy & Fuels, 27 (2014) 4062-4067 DOI: 10.1021/ef5007325
Abstract
Even though an increasing number of pilot-scale plants are demonstrating the potential efficiency of the Ca-looping technology to capture CO2 at a commercial level, a still standing matter of concern is the loss of carbonation reactivity of the regenerated CaO by calcination, which is expected to be particularly marked at realistic conditions necessarily implying a high CO2 partial pressure in the calciner. In this work, we address the effect of previously reported strategies for sorbent reactivation, namely heat pretreatment and the introduction of a recarbonation stage before regeneration. Both techniques, either combined or separately, are shown to favor the carbonation reactivity, albeit CaO regeneration is usually carried out at low CO2 partial pressure in lab-scale tests. Novel results reported in this paper show the opposite when the sorbent is regenerated by calcination at high CO2 concentration, which is arguably due to the diverse mechanisms that rule decarbonation depending on the CO2 concentration in the calciner atmosphere. Dynamic and reversible adsorption/desorption of CO2 is thought to govern decarbonation during calcination at high CO2 partial pressure, which would be hindered by the introduction of a recarbonation stage before carbonation. Moreover, carbonation in the fast phase is severely hampered as a result of the marked loss of reactivity of the surface of CaO regenerated under high CO2 partial pressure. On the other hand, heat pretreatment and harsh calcination conditions lead to a notable enhancement of diffusion, which would favor the process efficiency. In these conditions, diffusion controlled carbonation becomes a significant contribution to CaO conversion, which is notably increased by prolonging the carbonation stage. Heat pretreatment allows also reducing the calcination temperature at high CO2 partial pressure while still achieving full decarbonation in short residence times.
June, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/ef5007325
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
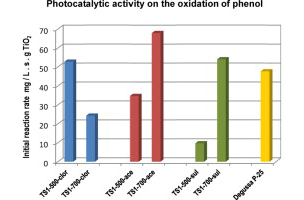
Effect of the type of acid used in the synthesis of titania–silica mixed oxides on their photocatalytic properties
Llano, B; Hidalgo, MC; Rios, LA; Navio, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 150-151 (2014) 389-395 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.12.039
Abstract
TiO2–SiO2 mixed oxides were synthesized by the sol–gel technique using three different acids, i.e., acetic, sulfuric, or chlorhydric acid. Their photocatalytic behavior was evaluated on the phenol oxidation in liquid phase and correlated with the characterization results. It was found that the kind of acid used during the preparation strongly influences the phase composition and stability of the TiO2 phases incorporated in the silica structure as well as the photocatalytic activity. In all cases, silica introduced a dispersive effect that stabilized the TiO2 crystalline phases upon calcination at 700 °C. SO42− and CH3COO− ions stabilized the anatase phase at high calcination temperatures (700 °C) leading to samples with the highest photoactivities. Cl− ions induced the formation of traces of rutile and brookite resulting in a lower photoactivity. The highest photoactivity was achieved with the catalyst synthesized with acetic acid and calcined at 700 °C (TS1-700-ace). The photocatalytic performance of this material was even better than that obtained with the commercial catalyst Degussa P-25.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.12.039
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
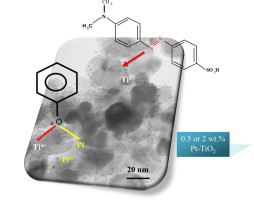
Correlation study between photo-degradation and surface adsorption properties of phenol and methyl orange on TiO2 Vs platinum-supported TiO2
Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Arana, J; Dona-Rodriguez, JMApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 150-151 (2014) 107-115 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.12.010
Abstract
Adsorption of phenol and methyl orange on the surface of TiO2 and Pt–TiO2 photocatalysts was investigated by FT-IR spectroscopy. It was found that platinum plays an important role in the adsorption properties of the studied substrates on TiO2. Platinum deposits modified the phenol-photocatalyst interaction providing new adsorption sites on TiO2 surface. On Pt–TiO2 photocatalysts, phenol mainly interacts via formation of adsorbed phenolates species. It was also found that the adsorption of methyl orange on titania and Pt–TiO2 photocatalysts occurs via interaction of the azo group with surface Ti4+. Pt photodeposition significantly increases the TiO2 photoreactivity in phenol and methyl orange photo-degradation; however, this increase depends on the properties of the Pt deposits. Moreover, it was observed that platinum content is the main factor determining the substrate-photocatalyst interaction and therefore the Pt–TiO2 photocatalytic performance.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.12.010
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
In situ XAS study of an improved natural phosphate catalyst for hydrogen production by reforming of methane
Abba, MO; Gonzalez-DelaCruz, VM; Colon, G; Sebti, S; Caballero, AApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 150-151 (2014) 459-465 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.12.031
Abstract
Some nickel catalysts supported on natural phosphate (NP) have been tested for the dry methane reforming reaction. Although the original impregnated 15%Ni/NP catalyst has no activity at all, the modification of the support by mechano-chemical and/or acid treatment strongly improved the catalytic performance, yielding a series of very active and stable catalysts. The chemical and physical characterization by X-ray diffraction (XRD), temperature programmed reduction (TPR), in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and other techniques have shown that these treatments mainly modify the interaction between the nickel phase and the support surface. The nickel ions occupy calcium position in the surface of the phosphate phase, which stabilizes and improves the dispersion of nickel species. The final reduced catalysts present a much better dispersed metallic phase interacting with the NP surface, which has been identified as responsible for the observed outstanding catalytic performances.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.12.031
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Osteoconductive Potential of Barrier NanoSiO(2) PLGA Membranes Functionalized by Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapour Deposition
Terriza, A; Vilches-Perez, JI; de la Orden, E; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Caballero, JL; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Vilches, J; Salido, MBioMed Research International, 2014 (2014) 253590 DOI: 10.1155/2014/253590
Abstract
The possibility of tailoring membrane surfaces with osteoconductive potential, in particular in biodegradable devices, to create modified biomaterials that stimulate osteoblast response should make them more suitable for clinical use, hopefully enhancing bone regeneration. Bioactive inorganic materials, such as silica, have been suggested to improve the bioactivity of synthetic biopolymers. An in vitro study on HOB human osteoblasts was performed to assess biocompatibility and bioactivity of SiO2 functionalized poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) membranes, prior to clinical use. A 15 nm SiO2 layer was deposited by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD), onto a resorbable PLGA membrane. Samples were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). HOB cells were seeded on sterilized test surfaces where cell morphology, spreading, actin cytoskeletal organization, and focal adhesion expression were assessed. As proved by the FT-IR analysis of samples, the deposition by PECVD of the SiO2 onto the PLGA membrane did not alter the composition and other characteristics of the organic membrane. A temporal and spatial reorganization of cytoskeleton and focal adhesions and morphological changes in response to SiO2 nanolayer were identified in our model. The novedous SiO2 deposition method is compatible with the standard sterilization protocols and reveals as a valuable tool to increase bioactivity of resorbable PLGA membranes.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1155/2014/253590
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biomechanical properties of the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit cuticle during development are modulated by changes in the relative amounts of its components
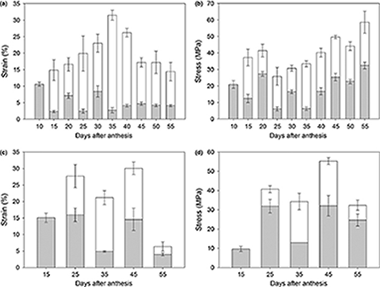
Espana, L; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Segado, P; Benitez, JJ; Heredia, A; Dominguez, ENew Phytologist, 202 (3) (2014) 790-802 DOI: 10.1111/nph.12727
Abstract
Keywords:
attenuated total reflectance–Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR);biomechanics;cuticle;cutin;flavonoids;tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit
Summary
- In this study, growth-dependent changes in the mechanical properties of the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) cuticle during fruit development were investigated in two cultivars with different patterns of cuticle growth and accumulation.
- The mechanical properties were determined in uniaxial tensile tests using strips of isolated cuticles. Changes in the functional groups of the cuticle chemical components were analysed by attenuated total reflectance–Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR).
- The early stages of fruit growth are characterized by an elastic cuticle, and viscoelastic behaviour only appeared at the beginning of cell enlargement. Changes in the cutin:polysaccharide ratio during development affected the strength required to achieve viscoelastic deformation. The increase in stiffness and decrease in extensibility during ripening, related to flavonoid accumulation, were accompanied by an increase in cutin depolymerization as a result of a reduction in the overall number of ester bonds.
- Quantitative changes in cuticle components influence the elastic/viscoelastic behaviour of the cuticle. The cutin:polysaccharide ratio modulates the stress required to permanently deform the cuticle and allow cell enlargement. Flavonoids stiffen the elastic phase and reduce permanent viscoelastic deformation. Ripening is accompanied by a chemical cleavage of cutin ester bonds. An infrared (IR) band related to phenolic accumulation can be used to monitor changes in the cutin esterification index.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1111/nph.12727
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Metallic structured catalysts: Influence of the substrate on the catalytic activity
Dominguez, MI; Perez, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 478 (2014) 45-57 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.03.028
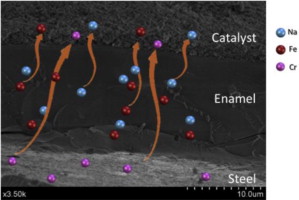
Abstract
In order to study the influence of the metallic substrate on the catalytic activity of structured micromonolithic catalysts, a CuOx/CeO2 catalyst was deposited on different oxidized or enameled metallic micromonoliths and tested in the PROX reaction under ideal and realistic conditions. The obtained results show as both activity and selectivity depend on the nature of the alloy and the nature of the interphase between the metal substrate and the catalyst layer. In oxidized micromonoliths, diffusion of Cr and Fe has been observed. For enameled micromonoliths, together with that diffusion, the interaction of the glass-ceramic interphase with the reactive gas streams resulted in the partial hydrolysis of this layer leading to diffusion toward the catalyst surface of the hydrolysis products, namely Na, Ca and Si cations. In some cases, the alteration of the surface composition favors the spreading of the copper active phase. As a result, it must be concluded that the metallic substrates are not spectators, at least in the PROX reaction, playing a fundamental role in the performances of the catalytic devices.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.03.028
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Structure determination and electronic structure of Cu3Au0.5N
Soto, G; Ponce, I; Moreno, MG; Yubero, F; De la Cruz, WJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 594 (2014) 48-51 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.01.113
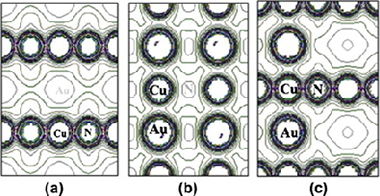
Abstract
This study investigated the formation of a Cu3Au-nitride alloy using both experimental and computational methods. The alloy was produced as thin film by sputtering a Cu3Au target in a nitrogen atmosphere. The films were characterized for structure and composition by spectroscopic and diffraction techniques. The structure was established by Rietveld and ab inito methods. The structure is cubic and of the Fm3m space group, with a composition close to Cu6AuN2. Relative to the Cu3N structure, the Cu atoms occupy the faces, Au the half corners, and N the centers. The compound is a narrow-gap semiconductor with a positive hall coefficient that could be used for infrared detection.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.01.113
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Pt vs. Au in water-gas shift reaction
Castano, MG; Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Catalysis, 314 (2014) 1-9 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.03.014
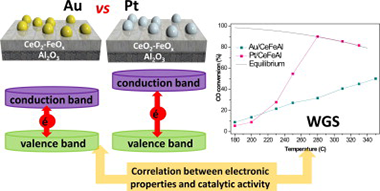
Abstract
This work presents a comparison of the gold- and platinum-based catalysts behavior in the water–gas shift (WGS) reaction. The influence of the support, e.g., its composition and electronic properties, studied in detail by means of UV–Vis spectroscopy, of the metal nature and dispersion and of the stream composition has been evaluated. The catalytic performance of the samples is directly correlated with the electronic properties modification as a function of metal and/or support. Both metals present high activity in the selected reaction although in a different operation temperature window.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.03.014
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermal conductivity at the amorphous-nanocrystalline phase transition in beech wood biocarbon
Parfen'eva, LS; Orlova, TS; Smirnov, BI; Smirnov, IA; Misiorek, H; Jezowski, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysica of the Solid State, 56 (2014) 1071-1080 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783414050229
Abstract
High-porosity samples of beech wood biocarbon (BE-C) were prepared by pyrolysis at carbonization temperatures T carb = 650, 1300, and 1600°C, and their resistivity ρ and thermal conductivity κ were studied in the 5–300 and 80–300 K temperature intervals. The experimental results obtained were evaluated by invoking X-ray diffraction data and information on the temperature dependences ρ(T) and κ(T) for BE-C samples prepared at T carb = 800, 1000, and 2400°C, which were collected by the authors earlier. An analysis of the κ(T carb) behavior led to the conclusion that the samples under study undergo an amorphous-nanocrystalline phase transition in the interval 800°C < T carb < 1000°C. Evaluation of the electronic component of the thermal conductivity revealed that the Lorentz number of the sample prepared at T carb = 2400°C exceeds by far the classical Sommerfeld value, which is characteristic of metals and highly degenerate semiconductors.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783414050229
Reactividad de Sólidos
High and stable CO2 capture capacity of natural limestone at Ca-looping conditions by heat pretreatment and recarbonation synergy
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAFuel, 123 (2014) 79-85 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.01.045
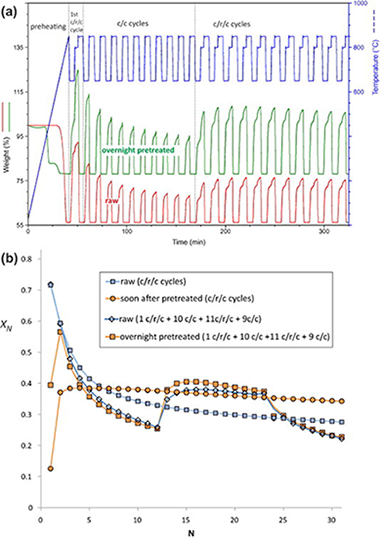
Abstract
The Ca-looping (CaL) process, based on the multicyclic carbonation/calcination of limestone derived CaO, has emerged recently as a potentially economically advantageous technology to achieve sustainable postcombustion and precombustion CO2 capture efficiencies. Yet, a drawback that hinders the efficiency of the CaL process is the drastic drop of limestone capture capacity as the number of carbonation/calcination cycles is increased. Precalcination of limestone at high temperatures for a prolonged period of time has been proposed as a potential technique to reactivate the sorbent, which is however precluded by regeneration temperatures above 850 degrees C and low CO2 concentrations in the carbonator to be found in the practical situation. Under these conditions, heat pretreatment leads to a stable yet very small CaO conversion. On the other hand, the introduction of a recarbonation stage between the ordinary carbonation and calcination stages has been shown to decelerate the rate of sorbent activity decay even though this favorable effect is not noticeable up to a number of above 10-15 cycles. The present manuscript demonstrates that the synergetic action of heat pretreatment and recarbonation yields a high and stable value for the multicyclic conversion of limestone derived CaO. It is foreseen that recarbonation of heat pretreated limestone would lead to a reduction of process costs especially in the case of precombustion applications. Even though sorbent purging will always be needed because of ash accumulation and sul-phation in postcombustion CO2 capture applications, the stable and high multicyclic CaO conversion achieved by the combination of these techniques would make it necessary to a lesser extent.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.01.045
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Could an efficient WGS catalyst be useful in the CO-PrOx reaction?
Reina, TR; Papadopoulou, E; Palma, S; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Ioannides, T; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 150-151 (2014) 554-563 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.01.001
Abstract
This work presents an evaluation of a high performance series of water gas shift (WGS) catalysts in the preferential CO oxidation reaction (PrOx) in order to examine the applicability of the same catalyst for both processes as a first step for coupling both reactions in a single process. Gold based catalysts are applied in an extensive study of the CO-PrOx reaction parameters, such as λ, WHSV, CO concentration and [H2O]/[CO2] ratio in order to obtain the best activity/selectivity balance. CO and H2 oxidation reactions were treated separately in order to establish the degree of CO/H2 oxidation competition. Additionally the catalysts behavior in the CO-PrOx parallel reactions such a WGS and RWGS have been also carried out to analyze their effect on product composition.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.01.001
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Viability of Au/CeO2-ZnO/Al2O3 Catalysts for Pure Hydrogen Production by the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Delgado, JJ; Ivanov, I; Idakiev, V; Tabakova, T; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemCatChem, 6 (2014) 1401-1409 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201300992
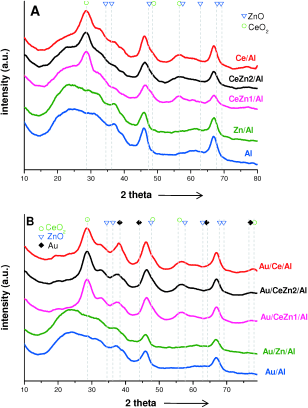
Abstract
The production of H2 pure enough for use in fuel cells requires the development of very efficient catalysts for the water–gas shift reaction. Herein, a series of gold catalysts supported on ZnO-promoted CeO2–Al2O3 are presented as interesting systems for the purification of H2 streams through the water–gas shift reaction. The addition of ZnO remarkably promotes the activity of an Au/CeO2/Al2O3 catalyst. This increase in activity is mainly associated with the enhanced oxygen storage capacity exhibited for the Zn-containing solids. High activity and good stability and resistance towards start-up–shut-down situations was found, which makes these catalysts a promising alternative for CO clean-up applications.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201300992
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Oxygen Optical Sensing in Gas and Liquids with Nanostructured ZnO Thin Films Based on Exciton Emission Detection
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Alcaire, M; Romero-Gomez, P; Macias-Montero, M; Aparicio, FJ; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 9852-9859 DOI: 10.1021/jp5026027
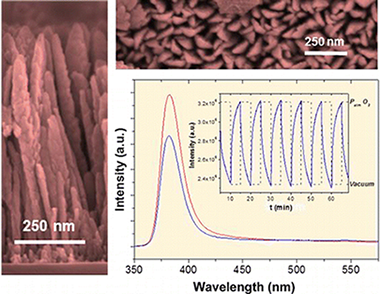
Abstract
Transparent nanocolumnar porous ZnO thin films have been prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. By controlling the H-2/O-2 ratio in the plasma gas, the deposition conditions were optimized to obtain an intense exciton emission at around 381 nm and virtually no luminescence in the visible region associated with electronic states in the gap. The intensity of the exciton band varied significantly and reversibly with the partial pressure of oxygen in the environment. This behavior and its variations with temperature and water vapor sustain the use of these thin films as photonic sensors of oxygen. Further experiments in liquid water show that fluorescence intensity also varies with the amount of dissolved oxygen even for concentrations lower than 0.02 mg/L where commercial oxygen galvanic sensors show limited sensitivity. These results and the use of ZnO as photonic sensor of oxygen are discussed by assuming a classical mechanism involving the photoactivated adsorption of oxygen when this oxide is irradiated with UV light during its fluorescence interrogation.
May, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/jp5026027
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Detecting single-electron events in TEM using low-cost electronics and a silicon strip sensor
Gontard, LC; Moldovan, G; Carmona-Galn, R; Lin, C; Kirkland, AIMicroscopy, 63(2) (2014) 119-130 DOI: 10.1093/jmicro/dft051
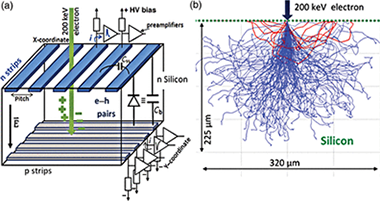
Abstract
There is great interest in developing novel position-sensitive direct detectors for transmission electron microscopy (TEM) that do not rely in the conversion of electrons into photons. Direct imaging improves contrast and efficiency and allows the operation of the microscope at lower energies and at lower doses without loss in resolution, which is especially important for studying soft materials and biological samples. We investigate the feasibility of employing a silicon strip detector as an imaging detector for TEM. This device, routinely used in high-energy particle physics, can detect small variations in electric current associated with the impact of a single charged particle. The main advantages of using this type of sensor for direct imaging in TEM are its intrinsic radiation hardness and large detection area. Here, we detail design, simulation, fabrication and tests in a TEM of the front-end electronics developed using low-cost discrete components and discuss the limitations and applications of this technology for TEM.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1093/jmicro/dft051
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Surface Oxygen Vacancies in Gold Based Catalysts for CO Oxidation
Romero-Sarria, F; Plata, JJ; Laguna, OH; Marquez, AM; Centeno, MA; Sanz, JF; Odriozola, JARSC Advances, 4 (2014) 13145-13152 DOI: 10.1039/c3ra46662k
Abstract
Experimental catalytic activity measurements, Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Spectroscopy, and Density Functional Theory calculations are used to investigate the role and dynamics of surface oxygen vacancies in the CO oxidation with O2 catalyzed by Au nanoparticles supported on a Y-doped TiO2 catalyst. Catalytic activity measurements show that the CO conversion is improved in a second cycle of reaction if the reactive flow is composed by CO and O2 (and inert) while if water is present in the flow, the catalyst shows a similar behaviour in two successive cycles. DRIFTS-MS studies indicate the occurrence of two simultaneous phenomena during the first cycle in dry conditions: the surface is dehydroxylated and a band at 2194 cm-1 increases (proportionally to the number of surface oxygen vacancies). Theoretical calculations were conducted in order to explain these observations. On one hand, the calculations show that there is a competition between gold nanoparticles and OH to occupy the surface oxygen vacancies and that the adsorption energy of gold on these sites increases as the surface is being dehydroxylated. On another hand, these results evidence that a strong electronic transfer from the surface to the O2 molecule is produced after its adsorption on the Au/TiO2 perimeter interface (activation step), leaving the gold particle in a high oxidation state. This explains the appearance of a band at a wavenumber unusually high for the CO adsorbed on oxidized gold particles (2194 cm-1) when O2 is present in the reactive flow. These simultaneous phenomena indicate that a gold redispersion on the surface occurs under reactive flow in dry conditions generating small gold particles very actives at low temperature. This fact is notably favoured by the presence of surface oxygen vacancies that improve the surface dynamics. The obtained results suggest that the reaction mechanism proceeds through the formation of a peroxo-like complex formed after the electronic transfer from the surface to the gas molecule.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/c3ra46662k
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and luminescence of uniform europium-doped bismuth fluoride and bismuth oxyfluoride particles with different morphologies
A. Escudero; E. Moretti; M. OcañaCrysEngComm, 16 (2014) 3274-3283 DOI: 10.1039/C3CE42462F
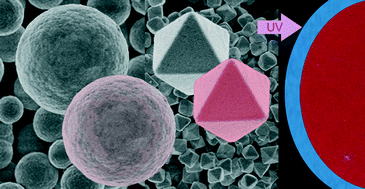
Abstract
Facile synthesis routes have been developed for the preparation of uniform cubic bismuth fluoride and bismuth oxyfluoride particles. The synthesis methods are based on homogeneous precipitation reactions at 120 °C in solutions of bismuth nitrate and sodium tetrafluoroborate precursors in polyol-based solvents. Both the nature of the solvent and the heating modes (conventional or microwave-assisted heating) have a remarkable effect on the morphology and crystallinity of the resulting particles. Thus, polycrystalline spheres of α-BiF3 with a mean diameter ranging from 1.2 to 2 μm could be obtained by heating solutions with the appropriate reagent concentrations in a mixture of ethylene glycol and glycerol (1 : 1 by volume) using a conventional oven, whereas octahedral single crystals of α-BiOyF3−2y with mean edges ranging from 250 nm to 920 nm precipitated when using a diethylene glycol–water mixture (8 : 2 in volume) as solvent and a microwave reactor for heating. To explain these different morphological and structural features, the mechanism of formation of such particles was investigated. Both kinds of particles were also doped with Eu3+, and both the morphological and luminescence properties of the resulting materials were evaluated. It was found that the luminescence intensity of the europium-doped α-BiOyF3−2y nanoparticles was higher than that of the europium-doped α-BiF3 sub-micrometric spheres, which was associated with the higher crystallinity of the former. Moreover, the presence of oxygen in the europium-doped α-BiOyF3−2y samples permits the excitation of the europium cations through an Eu–O energy transfer process, which results in a much higher luminescence intensity with respect to that corresponding to the direct excitation of the europium cations. Finally, the effect of the amount of dopant on the luminescence properties of the phosphors was also evaluated.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C3CE42462F
Reactividad de Sólidos
Chemical and electrical properties of LSM cathodes prepared by mechanosynthesis
Moriche, R.; Marrero-López, D.; Gotor, F.J.; Sayagués, M.J.Journal of Power Sources, 252 (2014) 43-50 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.11.093

Abstract
Mechanosynthesis of La1−xSrxMnO3 (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1) was carried out at room temperature from stoichiometric mixtures of La2O3, Mn2O3 and SrO, obtaining monophasic powders with the perovskite structure. Physical properties of these materials and their chemical compatibility with the electrolyte yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ), which depend strongly on the La/Sr ratio, were evaluated to corroborate availability to be implemented as cathode material in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). Electrical conductivity values in air ranged between 100 and 400 S cm−1 in the temperature range of 25–850 °C. Samples presented low reactivity with YSZ in the working temperature range (600–1000 °C) maintaining the grain size small enough to preserve the catalytic activity for oxygen reduction.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.11.093
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Tuning the transmittance and the electrochromic behavior of CoxSiyOz thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at glancing angle
Gil-Rostra, J; Garcia-Garcia, F; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSolar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 123 (2014) 130-138 DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2013.12.020
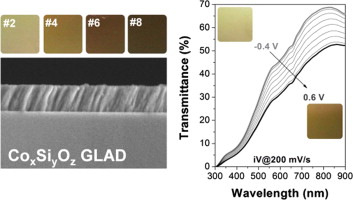
Abstract
This work reports the synthesis and the characterization of amorphous CoxSiyOz thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering from a single cathode. Porous layers with outstanding electrochromic properties are obtained at room temperature in one step by performing the deposition at a glancing angle configuration. The electrochromic behavior of these layers in a basic aqueous medium was dependent on the Co/Si ratio in the films and in all cases was characterized by a fast response, a high coloration efficiency and a complete reversibility after several hundred cycles. A characteristic feature of these electrochromic layers is that, for a similar thickness, the range of transmittance modulation can be tuned by changing the Co/Si ratio in the films and, specifically for films with a high concentration of silicon, to change their aspect from an almost transparent to a full colored state.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2013.12.020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Mechanisms of Electron Transport and Recombination in ZnO Nanostructures for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Vega-Poot, AG; Macias-Montero, M; Idigoras, J; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lizama-Tzec, FI; Oskam, G; Anta, JAChemphyschem, 15 (2014) 1088-1097 DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201301068
Abstract
ZnO is an attractive material for applications in dye-sensitized solar cells and related devices. This material has excellent electron-transport properties in the bulk but its electron diffusion coefficient is much smaller in mesoporous films. In this work the electron-transport properties of two different kinds of dye-sensitized ZnO nanostructures are investigated by small-perturbation electrochemical techniques. For nanoparticulate ZnO photoanodes prepared via a wet-chemistry technique, the diffusion coefficient is found to reproduce the typical behavior predicted by the multiple-trapping and the hopping models, with an exponential increase with respect to the applied bias. In contrast, in ZnO nanostructured thin films of controlled texture and crystallinity prepared via a plasma chemical vapor deposition method, the diffusion coefficient is found to be independent of the electrochemical bias. This observation suggests a different transport mechanism not controlled by trapping and electron accumulation. In spite of the quite different transport features, the recombination kinetics, the electron-collection efficiency and the photoconversion efficiency are very similar for both kinds of photoanodes, an observation that indicates that surface properties rather than electron transport is the main efficiency-determining factor in solar cells based on ZnO nanostructured photoanodes.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201301068
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effect of clays and metal containers in retaining Sm3+ and ZrO2+ and the process of reversibility
El Mrabet, S; Castro, MA; Hurtado, S; Orta, MM; Pazos, MC; Villa-Alfageme, M; Alba, MDAmerican Mineralogist, 99 (4) (2014) 696-703 DOI: 10.2138/am.2014.4665
Abstract
Knowledge and understanding about radionuclides retention processes on the materials composing the engineered barrier (clay mineral and metallic container waste) are required to ensure the safety and the long-term performance of radioactive waste disposal. Therefore, the present study focuses on the competitiveness of clay and the metallic container in the process of adsorption/desorption of the radionuclides simulators of Am3+ and UO22+. For this purpose, a comparative study of the interaction of samarium (chosen as chemical analog for trivalent americium) and zirconyl (as simulator of uranyl and tetravalent actinides) with both FEBEX bentonite and metallic container, under subcritical conditions, was carried out. The results revealed that the AISI-316L steel container, chemical composition detailed in Table 1, immobilized the high-radioactive waste (HRW), even during the corrosion process. The ZrO2+ was irreversibly adsorbed on the minireactor surface. In the case of samarium SEM/EDX analysis revealed the formation of an insoluble phase of samarium silicate on the container surface. There was no evidence of samarium diffusion through the metallic container. Samarium remained adsorbed by the container also after desorption experiment with water. Therefore, steel canister is actively involved in the HRW immobilization.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.2138/am.2014.4665
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Production of hydrogen by water photo-splitting over commercial and synthesised Au/TiO2 catalysts
Mendez, JAO; Lopez, CR; Melian, EP; Diaz, OG; Rodriguez, JMD; Hevia, DF; Macias, MApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 147 (2014) 439-452 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.09.029
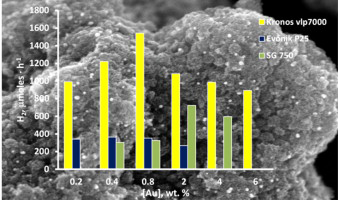
Abstract
H2 production from methanol/water photo-splitting was compared using various commercial photocatalysts (Evonik P25 (P25), Hombikat UV-100 (HB) and Kronos vlp7000 (KR)) and others synthesised with a sol–gel-hydrothermal (HT) process and a sol–gel method followed by calcination (SG400 and SG750). All photocatalysts had been surface modified with Au at different concentrations, from 0.2 to 6.0 wt.%, using the photodeposition method. A complete characterisation study of the different photocatalysts was performed (BET, XRD, TEM, SEM-EDX, FTIR, UV–vis Reflectance Diffuse Spectra and aggregate size). The experiments were conducted for 3.5 h using 1 g L−1 of photocatalyst with methanol (25 vol.%) as sacrificial agent. In addition to H2 generation, production of the main intermediates, formaldehyde and formic acid, and of CO2 was also evaluated. The commercial photocatalyst KR at 0.8 wt.% Au had the highest H2 production of all the photocatalysts studied with 1542.9 μmol h−1. Of the photocatalysts synthesised by our group, SG750 at Au loading of 2.0 wt.% gave the highest H2 production of 723.1 μmol h−1. The SG750 photocatalyst at Au loading of 2.0 wt.% also had the highest H2 production yield per unit of surface area at 45.5 μmol g h−1 m−2.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.09.029
Reactividad de Sólidos
Nanosilica supported CaO: A regenerable and mechanically hard CO2 sorbent at Ca-looping conditions
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Valverde, JMApplied Energy, 118 (2014) 92-99 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.12.024
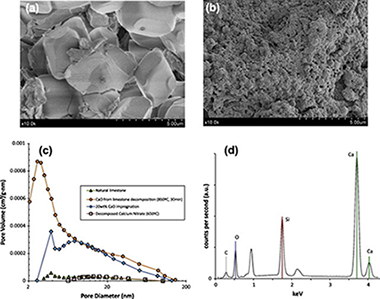
Abstract
This work presents a CO2 sorbent that may be synthesized from low-cost and widely available materials following a simple method basically consisting of impregnation of a nanostructured silica support with a saturated solution of calcium nitrate. In a first impregnation stage, the use of a stoichiometric CaO/SiO2 ratio serves to produce a calcium silicate matrix after calcination. This calcium silicate matrix acts as a thermally stable and mechanically hard support for CaO deposited on it by further impregnation. The CaO-impregnated sorbent exhibits a stable CaO conversion at Ca-looping conditions whose value depends on the CaO wt% deposited on the calcium silicate matrix, which can be increased by successive reimpregnations. A 10 wt% CaO impregnated sorbent reaches a stable conversion above 0.6 whereas the stable conversion of a 30 wt% CaO impregnated sorbent is around 0.3, which is much larger than the residual conversion of CaO derived from natural limestone (between 0.07 and 0.08). Moreover, particle size distribution measurements of samples predispersed in a liquid and subjected to high energy ultrasonic waves indicate that the CaO-impregnated sorbent has a relatively high mechanical strength as compared to limestone derived CaO.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.12.024
Reactividad de Sólidos
The effect of polymer matrices on the thermal hazard properties of RDX-based PBXs by using model-free and combined kinetic analysis
Yan, QL; Zeman, S; Jimenez, PES; Zhao, FQ; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Malek, JJournal of Hazardous Materials, 271 (2014) 185-195 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.02:019
Abstract
In this paper, the decomposition reaction models and thermal hazard properties of 1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazinane (RDX) and its PBXs bonded by Formex P1, Semtex 1A, C4, Viton A and Fluorel polymer matrices have been investigated based on isoconversional and combined kinetic analysis methods. The established kinetic triplets are used to predict the constant decomposition rate temperature profiles, the critical radius for thermal explosion and isothermal behavior at a temperature of 82 C. It has been found that the effect of the polymer matrices on the decomposition mechanism of RDX is significant resulting in very different reaction models. The Formex P1, Semtex and C4 could make decomposition process of RDX follow a phase boundary controlled reaction mechanism, whereas the Viton A and Fluorel make its reaction model shifts to a two dimensional Avrami-Erofeev nucleation and growth model. According to isothermal simulations, the threshold cook-off time until loss of functionality at 82 degrees C for RDX-C4 and RDX-FM is less than 500 days, while it is more than 700 days for the others. Unlike simulated isothermal curves, when considering the charge properties and heat of decomposition, RDX-FM and RDX-C4 are better than RDX-SE in storage safety at arbitrary surrounding temperature.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.02:019
Reactividad de Sólidos
Comparison of thermal behavior of natural and hot-washed sisal fibers based on their main components: Cellulose, xylan and lignin. TG-FTIR analysis of volatile products
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Lopez-Beceiro, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Pascual-Cosp, JThermochimica Acta, 581 (2014) 70-86 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2014.02.013
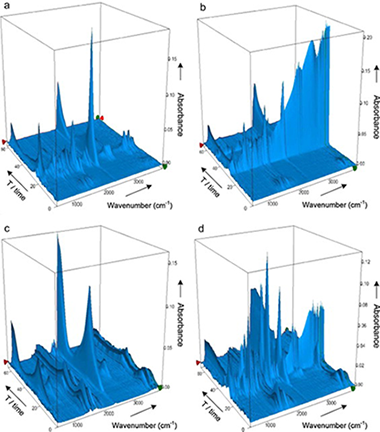
Abstract
This paper presents in a comprehensive way the thermal behavior of natural and hot-washed sisal fibers, based on the fundamental components of lignocellulosic materials: cellulose, xylan and lignin. The research highlights the influence exerted on the thermal stability of sisal fibers by other constituents such as non-cellulosic polysaccharides (NCP) and mineral matter.
Thermal changes were investigated by thermal X-ray diffraction (TXRD), analyzing the crystallinity index (%Ic) of cellulosic samples, and by simultaneous thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis coupled with Fourier-transformed infrared spectrometry (TG/DTA-FTIR), which allowed to examine the evolution of the main volatile compounds evolved during the degradation under inert and oxidizing atmospheres. The work demonstrates the potential of this technique to elucidate different steps during the thermal decomposition of sisal, providing extensible results to other lignocellulosic fibers, through the analysis of the evolution of CO2, CO, H2O, CH4, acetic acid, formic acid, methanol, formaldehyde and 2-butanone, and comparing it with the volatile products from pyrolysis of the biomass components. The hydroxyacetaldehyde detected during pyrolysis of sisal is indicative of an alternative route to that of levoglucosan, generated during cellulose pyrolysis.
Hot-washing at 75 °C mostly extracts non-cellulosic components of low decomposition temperature, and reduces the range of temperature in which sisal decomposition occurs, causing a retard in the pyrolysis stage and increasing TbNCP and TbCEL, temperatures at the maximum mass loss rate of non-cellulosic polysaccharides and cellulose decompositions, respectively. However, enriching sisal fibers in cellulose produces a decrease of TbCEL under an oxidizing atmosphere, and furthermore, a delay of the combustion process, displacing TbCOM to higher temperatures.
The results and findings of the paper would help further understanding of thermal processes where Agave fibers are involved, as the decomposition of their composites.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2014.02.013
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the acid–base properties over NiSn/MgO–Al2O3 catalysts in the hydrogen production from glycerol steam reforming
Bobadilla, LF; Penkova, A; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 39 (2014) 5704-5712 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.01.136
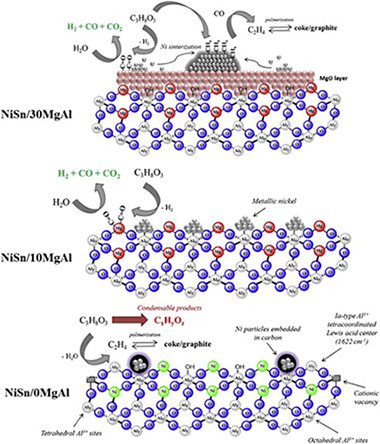
Abstract
In this work we have investigated the hydrogen production from glycerol steam reforming. The effect of the acid-base properties was evaluated using four catalysts based in an alloy Ni-Sn as active phase supported over (Upsilon)-Al2O3 with different content in MgO, varying between 0 and 30 wt.% The incorporation of MgO results in the formation of MgAl2O4 spinel, which modifies the acid-base properties of the catalyst. Addition of MgO favored the glycerol conversion into gas, and the catalyst loaded with 10 wt.% MgO exhibited better catalytic performance and higher stability. A blank test with quartz was performed indicating that pyrolysis of glycerol takes place in the quartz.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.01.136
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Understanding the Role of the Cosolvent in the Zeolite Template Function of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid
Ayala, R; Ivanova, S; Blanes, JMM; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 118 (2014) 3650–3660 DOI: 10.1021/jp410260g
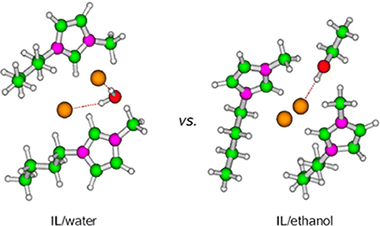
Abstract
In this work, a study for understanding the role played by [ClBmim], [BF4Bmim], [PF6Bmim], and [CH3SO3Bmim] ionic liquids (ILs) in the synthesis of zeolites is presented. The use of [ClBmim] and [CH3SO3Bmim] ILs, as reported earlier [ Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2122] led to the formation of MFI or BEA type zeolites. Contrary, [BF4Bmim] and [PF6Bmim] ILs did not succeed in organizing the Si–Al network into a zeolite structure. To try to explain these results, a series of quantum mechanical calculations considering monomers ([XBmim]) and dimers ([XBmim]2) by themselves and plus cosolvent (water or ethanol) were carried out, where X ≡ Cl–, BF4–, PF6–, or CH3SO3–. Our attention was focused on the similarities and differences among the two types of cosolvents and the relation between the structure and the multiple factors defining the interactions among the ILs and the cosolvent. Although a specific pattern based on local structures explaining the different behavior of these ILs as a zeolite structuring template was not found, the calculated interaction energies involving the Cl– and CH3SO3– anions were very close and larger than those for BF4– and PF6– species. These differences in energy can be used as an argument to describe their different behavior as structure directing agents. Moreover, the topology of the cosolvent is also an ingredient to take into account for a proper understanding of the results.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/jp410260g
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Perovskite Solar Cells Based on Nanocolumnar PlasmaDeposited ZnO Thin Films
Ramos, FJ; Lopez-Santos, MC; Guillen, E; Nazeeruddin, MK; Gratzel, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Ahmad, SChemphyschem, 15 (2014) 1148-1153 DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201301215
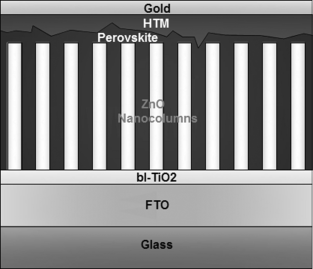
Abstract
ZnO thin films having a nanocolumnar microstructure are grown by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition at 423 K on pre-treated fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) substrates. The films consist of c-axis-oriented wurtzite ZnO nanocolumns with well-defined microstructure and crystallinity. By sensitizing CH3NH3PbI3 on these photoanodes a power conversion of 4.8 % is obtained for solid-state solar cells. Poly(triarylamine) is found to be less effective when used as the hole-transport material, compared to 2,2′,7,7′-tetrakis(N,N-di-p-methoxyphenylamine)-9,9′-spirobifluorene (spiro-OMeTAD), while the higher annealing temperature of the perovskite leads to a better infiltration in the nanocolumnar structure and an enhancement of the cell efficiency.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201301215
Reactividad de Sólidos
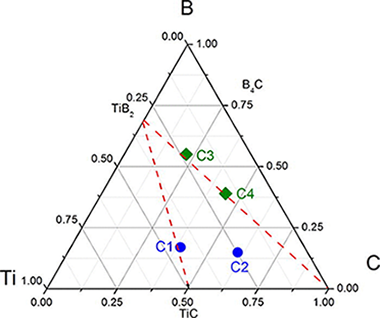
Self-propagating combustion synthesis via an MSR process: An efficient and simple method to prepare (Ti, Zr, Hf)B2–Al2O3 powder nanocomposites
Sayagues, MJ; Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Gotor, FJPowder Technology, 256 (2014) 244-250 DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.031
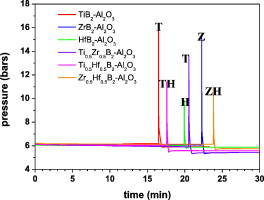
Abstract
The synthesis of (Ti1 − xZrx)B2–Al2O3, (Ti1 − xHfx)B2–Al2O3 and (Zr1 − xHfx)B2–Al2O3 (x = 0, 0.5 and 1) powder nanocomposites via a mechanochemical method using TiO2, ZrO2, HfO2, HBO2 and Al as the raw materials was investigated. The formation of the nanocomposites proceeds via a mechanically-induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process that involves several simultaneous reactions. The aluminothermic reductions of the TMO2 and HBO2 produce Al2O3 and transition metal and boron elements, which in turn react to yield the diboride phase. The ignition of the complex combustion reaction occurred after a short milling time (15–30 min), instantly transforming most of the reactants into products. The sample composition was marked by the stoichiometry of the combustion reaction, and the resulting nanocomposites were analysed using XRD, ED, SEM, TEM and EDX techniques. The X-ray results confirmed the biphasic character of the prepared composite powder (TMB2 and Al2O3 structures); minor amounts of the Zr and Hf oxides were also observed. The achieved microstructure was characterised by the agglomeration of Al2O3 nanocrystallites and diboride crystals with a diffraction domain size ranging between 100 and 300 nm.
April, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.031
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Long-term high temperature oxidation of CrAl(Y)N coatings in steam atmosphere
Mato, S; Alcala, G; Brizuela, M; Galindo, RE; Perez, FJ; Sanchez-Lopez, JCCorrosion Science, 80 (2014) 453-460 DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.11.066
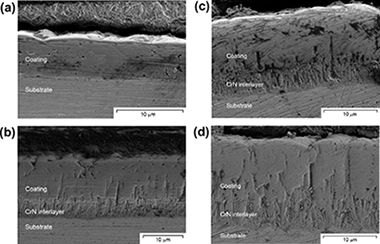
Abstract
The oxidation resistance of CrAl(Y)N coatings deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering on P92 steel substrates was tested at 650 °C in 100% steam atmosphere up to 2000 h of oxidation. Mass gain measurements and characterisation of coatings and scales after oxidation show the enhanced oxidation resistance provided by the coatings with respect to that of the substrate. The dominant influence of the film microstructure developed due to the presence of an adhesion interlayer of CrN at the coating/substrate interface over Y additions is evidenced. The best performance is achieved by a CrAlN dense coating of around 6 μm without adhesion interlayer.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.11.066
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Mechanical and phase stability of TiBC coatings up to 1000 degrees C
Abad, MD; Veldhuis, SC; Endrino, JL; Beake, BD; Garcia-Luis, A; Brizuela, M; Sanchez-Lopez, JCJournal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 32 (2014) 021508 DOI: 10.1116/1.4861365
Abstract
TiBC coatings with different phase compositions (nanocrystalline TiBxCy or TiB2 phases mixed or not with amorphous carbon, a-C) were prepared by magnetron sputtering. These coatings were comparatively studied in terms of phase stability after thermal annealing at 250, 500, 750, and 1000 °C in argon using Raman and x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy techniques. The main differences were observed at temperatures above 500 °C when oxidation processes occur and the mechanical properties deteriorate. At 1000 °C, the samples were fully oxidized forming a-C, TiO2, and B2O3 as final products. Higher hardness and reduced indentation modulus values and better tribological properties were observed at 750 °C for nanocomposite structures including amorphous carbon and ternary TiBxCy phases. This behavior is attributed to a protective effect associated with the a-C phase which is achieved by the encapsulation of the nanocrystals in the coating and the better hard/lubricant phase ratio associated with this type of coating.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1116/1.4861365
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Osteoblasts Interaction with PLGA Membranes Functionalized with Titanium Film Nanolayer by PECVD. In vitro Assessment of Surface Influence on Cell Adhesion during Initial Cell to Material Interaction
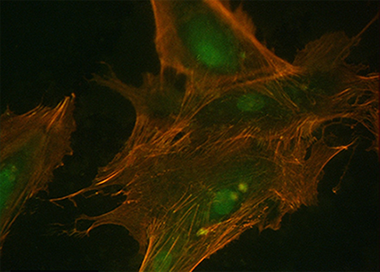
Terriza, A; Vilches-Perez, JI; Gonzalez-Caballero, JL; de la Orden, E; Yubero, F; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Vilches, J; Salido, MMaterials, 7(3) (2014) 1687-1708 DOI: 10.3390/ma7031687
Abstract
New biomaterials for Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR), both resorbable and non-resorbable, are being developed to stimulate bone tissue formation. Thus, the in vitro study of cell behavior towards material surface properties turns a prerequisite to assess both biocompatibility and bioactivity of any material intended to be used for clinical purposes. For this purpose, we have developed in vitro studies on normal human osteoblasts (HOB®) HOB® osteoblasts grown on a resorbable Poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) membrane foil functionalized by a very thin film (around 15 nm) of TiO2 (i.e., TiO2/PLGA membranes), designed to be used as barrier membrane. To avoid any alteration of the membranes, the titanium films were deposited at room temperature in one step by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition. Characterization of the functionalized membranes proved that the thin titanium layer completely covers the PLGA foils that remains practically unmodified in their interior after the deposition process and stands the standard sterilization protocols. Both morphological changes and cytoskeletal reorganization, together with the focal adhesion development observed in HOB osteoblasts, significantly related to TiO2 treated PLGA in which the Ti deposition method described has revealed to be a valuable tool to increase bioactivity of PLGA membranes, by combining cell nanotopography cues with the incorporation of bioactive factors.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.3390/ma7031687
Reactividad de Sólidos
Analysis on the mechanical strength of WC-Co cemented carbides under uniaxial and biaxial bending
Torres, Y; Bermejo, R; Gotor, FJ; Chicardi, E; Llanes, LMaterials & Design, 55 (2014) 851-856 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.10.051
Abstract
The mechanical strength of three WC-Co grades was determined and compared under uniaxial and biaxial bending. Uniaxial four-point bending was conducted on bar-shaped specimens; biaxial testing was performed on discs using the ball-on-three-balls (B3B) method. Strength results were analysed within the frame of the Weibull theory. Differences in characteristic strength between uniaxial and biaxial bending were explained as an effect of the effective surface tested in each case. A higher Weibull modulus was obtained in one grade, independent of the testing method, which was related to its higher fracture toughness. The use and validity of the B3B biaxial test to determine the strength distribution of cemented carbides is discussed.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.10.051
Reactividad de Sólidos
An investigation on the formation mechanism of nano ZrB2 powder by a magnesiothermic reaction
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 588 (2014) 36-41 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.050
Abstract
Nanocrystalline zirconium diboride (ZrB2) powder was produced by mechanochemistry from the magnesiothermic reduction in the Mg/ZrO2/B2O3 system. The use of high-energy milling conditions was essential to induce a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) and significantly reduce the milling time required for complete conversion. Under these conditions, it was found that the ignition time for ZrB2 formation was only about a few minutes. In this study, the mechanism for the formation of ZrB2 in this system was determined by studying the relevant sub-reactions, the effect of stoichiometry, and the thermal behavior of the system.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.050
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced general analytical equation for the kinetics of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid)/montmorillonite nanocomposites driven by random scission
Carrasco, F; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Santana, OO; Maspoch, MLPolymer Degradation and Stability, 101 (2014) 52-59 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.01.014
Abstract
An enhanced general analytical equation has been developed in order to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the thermal degradation of nanocomposites, composed of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and organo-modified montmorillonite (OMMT) nanoparticles. This improvement has consisted of replacing the n-order conversion function by a modified form of the Sestak–Berggren equation f(α) = c (1 − α)nαm that led to a better adjustment of experimental data and also adequately represented the conventional mechanisms for solid-state processes. The kinetic parameters so obtained have been compared to those determined by conventional differential and isoconversional methods. Given that the thermal degradation of PLA has been argued to be caused by random chain scission reactions of ester groups, the conversion function f(α) = L (L − 1)x(1 − x)L−1, corresponding to a random scission mechanism, has been tested. Once optimized the kinetic model, the thermal degradation kinetics of nanocomposites (0.5 and 2.5% of OMMT) was compared to that of the polymer matrix. Moreover, the thermal stability of nanocomposites was tested and compared to that of the polymer matrix.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.01.014
Mineralogical Characterization of the Polychrome in Cultural Heritage Artifacts (Antiquity to Date) from Southern Spain Using Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Complementary Techniques
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Duran, ASpectroscopy Letters: An International Journal for Rapid Communication, 47 (2014) 223-237 DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2013.791857
Abstract
This work reports on the use of micro-Raman spectroscopy for the characterization of materials used for producing the polychrome in cultural heritage artifacts from southern Spain. The micro-Raman technique was applied for the characterization of several types of artworks or for cross-sections from these works, which were produced along different historical epochs. This technique was demonstrated to be valuable for the characterization of compounds, which were all detected within the artworks studied. The identification of all of these compounds by micro-Raman was confirmed by other complementary techniques, such as micro-X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2013.791857
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Additive-free superhard B4C with ultrafine-grained dense microstructures
Moshtaghioun, BM; Cumbrera, FL; Ortiz, AL; Castillo-Rodriguez, M; Gomez-Garcia, DJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 34 (2014) 841-848 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.10.006

Abstract
A unique combination of high-energy ball-milling, annealing, and spark-plasma sintering has been used to process superhard B4C ceramics with ultrafine-grained, dense microstructures from commercially available powders, without sintering additives. It was found that the ultrafine powder prepared by high-energy ball-milling is hardly at all sinterable, but that B2O3 removal by gentle annealing in Ar provides the desired sinterability. A parametric study was also conducted to elucidate the role of the temperature (1600–1800 °C), time (1–9 min), and heating ramp (100 or 200 °C/min) in the densification and grain growth, and thus to identify optimal spark-plasma sintering conditions (i.e., 1700 °C for 3 min with 100 °C/min) to densify completely (>98.5%) the B4C ceramics with retention of ultrafine grains (∼370 nm). Super-high hardness of ∼38 GPa without relevant loss of toughness (∼3 MPa m1/2) was thus achieved, attributable to the smaller grain size and to the transgranular fracture mode of the B4C ceramics.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.10.006
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
A new route of synthesis of Na-Mica-4 from sodalite
Naranjo, M; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 188 (2014) 176-180 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.12.004
Abstract
Synthesis of Na-Mica-4 has been achieved by a “mix and calcine” method using sodalite and magnesium fluoride as the only precursors. Previous research found sodalite as a key intermediate reaction product in the formation of Na-Mica-4 when the NaCl melt method was employed. Similarities in structure, chemical composition and cation distribution in products using the proposed method and the NaCl melt method are described and suggest that Na-Mica-4 is a very stable product. The use of sodalite as precursor provokes microporous formation in the final mica. The absence of excess Na leads to a lower particle size and to the presence of less impurity in the calcined product. Different sodalites could be used in the synthesis of different Na-Mica-4 with presumably different physicochemical properties.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.12.004
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effect of carbonization temperature on the microplasticity of wood-derived biocarbon
Shpeizman, VV; Orlova, TS; Kardashev, BK; Smirnov, BI; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 56 (2014) 538-545 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783414030305
Abstract
The uniaxial compression strength under stepped loading and the 325-nm-stepped deformation rate of biocarbon samples obtained by carbonization of beech wood at different temperatures in the 600–1600°C range have been measured using high-precision interferometry. It has been shown that the strength depends on the content of nanocrystalline phase in biocarbon. The magnitude of deformation jumps at micro- and nanometer levels and their variation with a change in the structure of the material and loading time have been determined. For micro- and nanometer-scale jumps, standard deviations of the differences between the experimentally measured deformation rate at loading steps and its magnitude at the smoothed fitting curve have been calculated, and the correlation of the error with the deformation prior to destruction has been shown. The results obtained have been compared with the previously published data on measurements of the elastic properties and internal friction of these materials.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783414030305
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
c- C4F8 Plasmas for the Deposition of Fluorinated Carbon Films
Terriza, A; Macias-Montero, M; Lopez-Santos, MC; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 11 (2014) 289-299 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300129
Abstract
Highly fluorinated polymeric (CFX), fluorine containing diamond-like carbon (F-DLC) and, for comparison, diamond-like carbon (DLC) films have been plasma deposited in a RF parallel plate reactor by using c-C4F8 as fluorine precursor and different mixtures of argon, C2H2, and H2. Plasmas have been characterized by optical emission spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and Langmuir probe measurements. Differences in the film composition and structure have been related with the type of species formed in the plasma and with the self-bias potential developed at the deposition electrode. Additional experiments using CF4 have confirmed that the formation in the plasmas of neutral or ionized CxFy species with x > 2 is a critical factor for the synthesis of fluorine rich films.
March, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300129
- ‹ previous
- 25 of 37
- next ›














