Scientific Papers in SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Direct mechanosynthesis of pure BiFeO3 perovskite nanoparticles: reaction mechanism
Perejon, A; Murafa, N; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Subrt, J; Dianez, MJ; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 1 (2013) 3551-3562 DOI: 10.1039/C3TC30446A
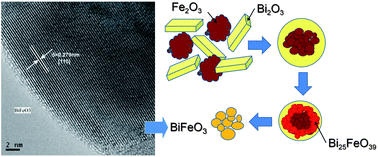
Abstract
In this work, a mechanochemical procedure is proposed as a simple and fast method to synthesize the pure BiFeO3 perovskite phase as a nanostructured material without the need for purification treatments, while the mechanochemical reaction mechanism has been investigated and correlated with that of the conventional solid-state reaction. Thus, different milling conditions have been used as a tool for tailoring the crystallite size of the resulting BiFeO3 nanoparticles. The materials prepared by the mechanochemical reaction could be annealed or sintered without the formation of undesirable phases. Both the ferroelectric and ferromagnetic transitions were observed by DSC. Finally, the dielectric constants of the prepared material at different frequencies as a function of the temperature have been measured, showing that the material is clearly an isolator below 200 °C, characteristic of a high quality BiFeO3 material.
June, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3TC30446A
Materiales Avanzados
Estudio in-situ de la transformación térmica de limonita utilizada como pigmento procedente de Perú
Romero-Gomez, P; Gonzalez, JC; Bustamante, A; Ruiz-Conde, A; Sanchez-Soto, PJBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 52 (2013) 127-131 DOI: 10.3989/cyv.162013
Abstract
Se ha realizado un estudio cinético de la transformación térmica de limonita [FeO(OH).nH2O] mediante análisis térmico gravimétrico (TGA), termodifracción de rayos X (DRX) y espectroscopía μ-Raman. La muestra estudiada fue extraída de un yacimiento en el distrito de Taraco, provincia de Huancané, Región de Puno (Perú). La técnica DRX en polvo identificó la fase goetita como el principal componente mineralógico, además de cuarzo. La muestra se sometió a un tratamiento térmico
in-situ en un intervalo de temperaturas de 100 a 500 °C en atmósfera de aire e inerte (nitrógeno) y se estudió por DRX. Los resultados han mostrado que la fase goetita permanece estable desde la temperatura ambiente hasta 200 °C. A partir de los 250 °C se produce una transformación de fase α-FeO(OH)→α-Fe2O3
con un cambio cromático, es decir, el paso de la fase
hidroxilada goetita (amarillo) a la fase oxidada hematites (rojo) con una pérdida de peso de un 8 %, teniendo como evidencia la evolución de los perfiles de difracción y los resultados de ATG. Los espectros μ-Raman del tratamiento térmico in-situ corroboran que se produce también una transición de fase a la temperatura de 290 °C a través de la transformación de las bandas Raman características de la fase goetita hacia la fase hematites en el rango de frecuencias de 200 a 1800cm-1.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.3989/cyv.162013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Solution Properties of the System ZrSiO4–HfSiO4: A Computational and Experimental Study
Cota, Agustin; Burton, Benjamin P.; Chain, Pablo; Pavon, Esperanza; Alba, Maria D.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 10013-10019 DOI: 10.1021/jp401539g

Abstract
ZrSiO4 and HfSiO4 are of considerable interest because of their low thermal expansions, thermal conductivities, and the optical properties of HfSiO4. In addition, silicate phases of both are studied as model radioactive waste disposal materials. Previous first principles calculations reported near ideal mixing in the Zr1–xHfxSiO4 system, with a very weak propensity for phase separation. Density functional theory (DFT)/cluster-expansion first principles calculations presented in this work indicate near ideal mixing with a very weak propensity for ordering. Zr1–xHfxSiO4 samples (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.0) were synthesized from intimate stoichiometric mixtures of constituent-oxides and annealing at 1823 K for 20 days in a platinum crucible. Samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD; Rietveld analysis) and 29Si MAS NMR. The XRD data exhibited a pronounced negative deviation from Vegard’s law in the excess volume of mixing, and the 29Si MAS NMR spectra also suggest nonideal mixing. Given the very weak energetics that favor cation ordering, it is clear that there must be some other cause(s) for the observed deviations from ideal mixing behavior.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/jp401539g
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Resonant Photocurrent Generation in Dye-Sensitized Periodically Nanostructured Photoconductors by Optical Field Confinement Effects
Anaya, M; Calvo, ME; Luque-Raigon, JM; Miguez, HJournal of the American Chemical Society, 135 (2013) 7803-7806 DOI: 10.1021/ja401096k
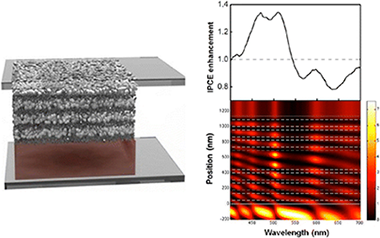
Abstract
Herein we show experimental evidence of resonant photocurrent generation in dye-sensitized periodically nanostructured photoconductors, which is achieved by spectral matching of the sensitizer absorption band to different types of localized photon modes present in either periodic or broken symmetry structures. Results are explained in terms of the calculated spatial distribution of the electric field intensity within the configurations under analysis.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/ja401096k
Materiales Coloidales
Energy transfer efficiency in YF3 nanocrystals: Quantifying the Yb3+ to Tm3+ infrared dynamics
Quintanilla, M; Nuñez, NO; Cantelar, E; Ocaña, M; Cussó, FJournal of Applied Physics, 113 (2013) 174308 (6 pages) DOI: 10.1063/1.4803540
Abstract
In this work, we report on the determination of the infrared Yb3+ → Tm3+ energy transfer efficiency in YF3:Yb3+/Tm3+ nanocrystals through the study of Yb3+ dynamics. The obtained results are compared to those previously reported in macrocrystals to analyze possible changes related to size reduction. Luminescence lifetimes are much shorter in the nanoparticles than in bulk samples, a behavior that can be related to Yb3+ → Yb3+ migration and the enhanced surface/volume ratio of the nanoparticles. On the other hand, Yb3+ → Tm3+ energy transfer macroparameter remains unaltered, demonstrating that spectroscopic intrinsic parameters such as radiative and non-radiative probabilities are not affected by size reduction. Finally, a formula that describes Yb3+ lifetime dependence with Yb3+ and Tm3+ concentration is proposed, considering both the effects produced by migration between Yb3+ ions and energy transfer from Yb3+ to Tm3+ ions.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1063/1.4803540
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Combined reactive magnetron sputtering and plasma decomposition of non-volatile precursors to grow luminescent thin films
Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Ferrer, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSurface and Coatings Technology, 222 (2013) 144-150 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.02.016
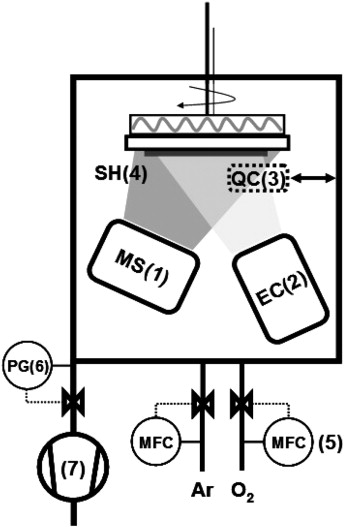
Abstract
This paper reports a new procedure of the preparation of mixed oxide thin films that combines the traditional reactive magnetron sputtering deposition with the plasma activated decomposition of non-volatile precursors sublimated by means of an effusion cell. The possibilities of this new experimental procedure are illustrated with the preparation of luminescent thin films consisting of rare earth (RE) cations (Tb3 +, Eu3 +) incorporated in an oxide matrix (TiO2 and SiO2). The oxide matrix component was supplied by reactive magnetron sputtering from metallic Ti or Si targets, while the RE cation was dosed by sublimation of acetylacetonate compounds of the selected elements. The obtained mixed oxide thin films have been fully characterized by different methods and their luminescent properties studied as a function of the matrix type and concentration of the RE element present in the film. The advantages of the synthesis procedure are highlighted with regard to its versatility and the possibility of tailoring the properties of complex luminescent materials.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.02.016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis and characterization of kanemite from fluoride-containing media: Influence of the alkali cation
Corredor, JI; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Alba, MDAmerican Mineralogist, 98 (2013) 1000-1007 DOI: 10.2138/am.2013.4372
Abstract
Kanemite belongs to the group of naturally occurring sodium silicate minerals that was first found in Kanem, at the edge of the Lake Chad, and has been synthesized in different ways from NaOH-SiO2 mixtures and used as precursor for the design of microporous and mesoporous materials. The fluoride route to the synthesis of microporous materials is based on the substitution of OH− anions by fluoride anions, which may subsequently also play a mineralizing role, and gives rise to materials with higher hydrophobicity and thermal and hydrothermal stability. Moreover, F− plays an important role in the incorporation of framework heteroatoms, thereby affecting the activity of the final material. The aim of this study was to synthesize fluorokanemite using different synthetic routes and different F− source. The final product was characterized by a combination of methods that provided information regarding the incorporation of fluorine into the framework and the short- and long-range structural order of the fluorosilicate. Kanemite with water content close to ideal was obtained in all cases. The washing process was found to have no effect in the long- or short-range structural order of the layer framework, although it did affect the structure of the cation in the interlayer space of kanemite. The mineralizing agent therefore appears to be the key to the synthesis. Furthermore, it governs the resulting kanemite structure by controlling the formation of hydrogen bonds in the framework, and therefore the degree of lamellar structure condensation.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.2138/am.2013.4372
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of sintering time on the microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets
Chicardi, E; Torres, Y; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Rodriguez, JA; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 38 (2013) 73-80 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.01.001
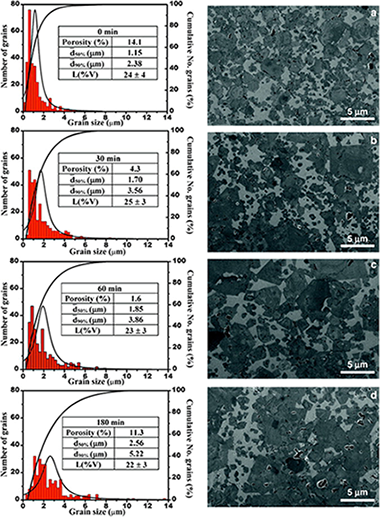
Abstract
Complete solid-solution cermets based on titanium–tantalum carbonitride using a starting nominal composition with 80 wt.% of (Ti0.8Ta0.2)(C0.5N0.5) and 20 wt.% of Co were performed by pressure-less sintering at 1550 °C for different times (from 0 to 180 min) in an inert atmosphere. Chemical and phase analyses were conducted using X-ray diffraction (XRD), elemental analysis and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX). The binder mean free path and the contiguity of the carbonitride particles were used to rationalise the microstructural effects of the mechanical behaviour. Mechanical characterisation included determining the Vickers hardness, the fracture toughness (conventional indentation microfractures, IM), the dynamic Young's modulus (ultrasonic technique), the biaxial strength (ball on three ball) and a detailed fractographic examination. Finally, the experimental findings were combined with a theoretical fracture mechanics analysis to estimate the critical processing flaw sizes. Binder-less carbonitride clusters, pores and coarse carbonitride grains were the main defects observed and were responsible for the fractures.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.01.001
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Steam reforming of methanol over supported Ni and Ni–Sn nanoparticles
Bobadilla, LF; Palma, S; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38 (2013) 6646-6656 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.03.143

Abstract
The influence of the synthesis method and Sn addition on Ni/CeO2–MgO–Al2O3 catalyst is correlated to its catalytic behavior in the reaction of methanol steam reforming. The catalysts prepared by impregnation method are compared to samples obtained by deposition of previously obtained nanoparticles by the polyol method. X-ray diffraction (XRD), specific surface area measurements and H2-temperature programmed reduction (TPR) were used to characterize the catalysts. The differences of the structure, phase transformation and reduction behavior are discussed and related to the catalytic performance of the samples as well as the nature of the carbonaceous deposits formed during the reaction.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.03.143
Reactividad de Sólidos
Liquid-phase sintering of Ti(C,N)-based cermets. The effects of binder nature and content on the solubility and wettability of hard ceramic phases
Cordoba, JM; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 559 (2013) 34-38 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.046
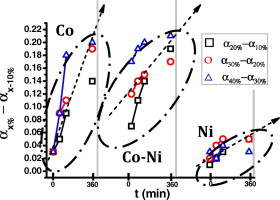
Abstract
Different commercial TiC–TiN/Co/Ni mixtures were used as raw materials for Ti(C,N) cermets, and the effects of the sintering parameters (binder content, binder nature, sintering time and additives) on the final hard ceramic phase were studied at the sintering temperature of 1400 °C. When Co is used as the binder medium, it is possible to completely convert the starting commercial TiC–TiN mixture into TiCxN1−x. When Ni is used, which exhibits lower solubilising capacity than Co, the total conversion can never be reached and the metallurgical reactions between TiC and TiN during the liquid-phase sintering are more dependent on the sintering time than on the binder content. However, the use of Co–Ni mixtures, showing a synergic effect between the wettability capacity of Ni and the solubilising capacity of Co, enhances the metallurgical reactions at short sintering times.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.046
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Structure and tribological properties of MoCN-Ag coatings in the temperature range of 25–700 °C
Shtansky, DV; Bondarev, AV; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, PV; Rojas, TC; Godinho, V; Fernandez, AApplied Surface Science, 273 (2013) 408-414 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.02.055
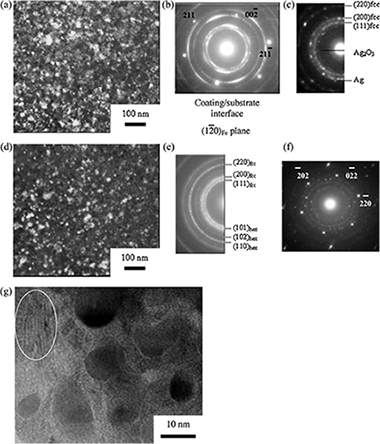
Abstract
The preparation of hard coatings with low friction coefficient over a wide temperature range is still a challenge for the tribological community. The development of new nanocomposite materials consisting of different metal-ceramic phases, each of which exhibiting self-lubricating characteristics at different temperatures, may help to solve this problem. We report on the structure and tribological properties of MoCN-Ag coatings deposited by magnetron co-sputtering of Mo and C (graphite) targets and simultaneous sputtering of an Ag target either in pure nitrogen or in a gaseous mixture of Ar + N2. The structure and elemental composition of the coatings were studied by means of X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy. The tribological properties of the coatings against an Al2O3 ball were investigated first at discrete temperatures of 25, 500, and 700 °C, and then during continuous heating in the temperature range of 25–700 °C. The coating structure and their respective wear tracks were also examined to elucidate their phase transformations during heat treatments. The lowest friction coefficients (<0.4) were observed in the temperature ranges of 25–100 °C and 400–700 °C and can be explained by the presence of a free amorphous carbon phase, which served as a lubricant at low temperatures, and by a positive role of silver and two phases forming at elevated temperatures, molybdenum oxide and silver molybdate, which provided lubrication above 400 °C. In the temperature range between 100 and 400 °C, the friction coefficient was relatively high. This problem is to be addressed in future works.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.02.055
Reactividad de Sólidos
Limitations of model-fitting methods for kinetic analysis: Polystyrene thermal degradation
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMResources, Conservation and Recycling, 74 (2013) 75-81 DOI: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.02.014
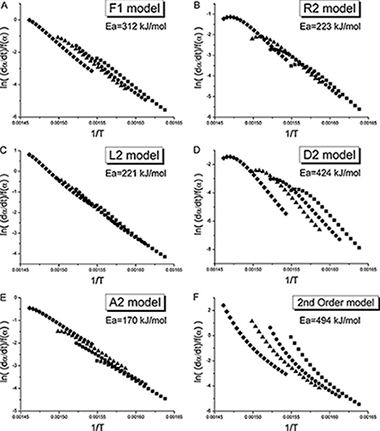
Abstract
In this paper, some clarifications regarding the use of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis are provided in response to the lack of plot linearity and dispersion in the activation energy values for the thermal degradation of polystyrene found in the literature and some results proposing an nth order model as the most suitable one. In the present work, two model-fitting methods based on the differential and integral forms of the general kinetic equation are evaluated using both simulated and experimental data, showing that the differential method is recommended due to its higher discrimination power. Moreover, the intrinsic limitations of model-fitting methods are highlighted: the use of a limited set of kinetic models to fit experimental data and the ideal nature of such models. Finally, it is concluded that a chain scission model is more appropriate than first order.
May, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.02.014
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Light induced hydrophilicity and osteoblast adhesion promotion on amorphous TiO2
Terriza, A; Diaz-Cuenca, A; Yubero, F; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Caballero, JLG; Vilches, J; Salido, MJournal of Biomedical Materials Research A, 101A (2013) 1026-1035 DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.34405
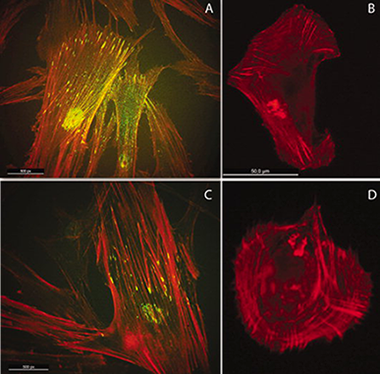
Abstract
We have studied the effect of the UV induced superhydrophilic wetting of TiO2 thin films on the osteoblasts cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization on its surface. To assess any effect of the photo-catalytic removal of adventitious carbon as a factor for the enhancement of the osteoblast development, 100 nm amorphous TiO2 thin layers were deposited on polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a substrate well known for its poor adhesion and limited wettability and biocompatibility. The TiO2/PET materials were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy and their wetting behavior under light illumination studied by the sessile drop method. The amorphous TiO2 thin films showed a very poor photo-catalytic activity even if becoming superhydrophilic after illumination. The illuminated samples recovered partially its initial hydrophobic state only after their storage in the dark for more than 20 days. Osteoblasts (HOB) were seeded both on bare PET and on TiO2/PET samples immediately after illumination and also after four weeks storage in darkness. Cell attachment was much more efficient on the immediately illuminated TiO2/PET samples, with development of focal adhesions and cell traction forces. Although we cannot completely discard some photo-catalytic carbon removal as a factor contributing to this cell enhanced attachment, our photodegradation experiments on amorphous TiO2 are conclusive to dismiss this effect as the major cause for this behavior. © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Biomed Mater Res Part A, 2013.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.34405
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effects of thermal and mechanical treatments on montmorillonite homoionized with mono- and polyvalent cations: Insight into the surface and structural changes
Fernandez, M; Alba, MD; Sanchez, RMTColloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 423 (2013) 1-10 DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.01.040
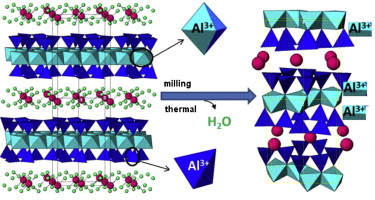
Abstract
Smectite is a family of clay minerals that have important applications. In the majority of these clay minerals, the hydrated interlayer cations play a crucial role on the properties of the clay. Moreover, many studies have revealed that both thermal and grinding treatments affect the MMT structure and that interlayer cations play an important role in the degradation of the structure, primarily after mechanical treatment. In this study, the effects of these treatments on MMTs homoionized with mono (Na+, Li+ or K+) or polyvalent (Ca2+ or Al3+) cations were analyzed by the combination of a set of techniques that can reveal the difference of bulk phenomena from those produced on the surface of the particles. The thermal and mechanical (in an oscillating mill) treatments affected the framework composition and structure of the MMT, and the thermal treatment caused less drastic changes that the mechanical one. The effect of the interlayer cations is primarily due to the oxidation state and, to the size of the cations, which also influenced the disappearance of aluminum in the MMT tetrahedral sheet. These treatments caused a decrease in the surface area and an increase in the particle agglomeration and the isoelectric point. Both treatments caused the leaching of the framework aluminum. Furthermore, the mechanical treatment induced structural defects, such as the breakup of the particles, which favored the dehydroxylation and the increase of the isoelectric points of the montmorillonites.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.01.040
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Angular response of photonic crystal based dye sensitized solar cells
López López, C.; Colodrero, S.; Calvo, M.E. and Míguez, H.Energy & Environmental Science, 6 (2013) 1260-1266 DOI: 10.1039/C3EE23609A
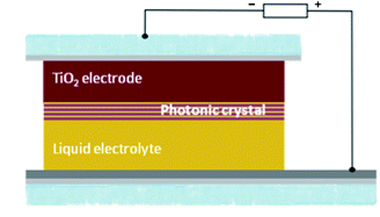
Abstract
Herein we report an experimental analysis of the performance of photonic crystal based dye solar cells (PC-DSCs) as the incident light angle moves away from the normal with respect to the cell surface. Nanoparticle multilayers operating at different wavelength ranges were coupled to the working electrode of a dye solar cell for this study. The interplay between optical and photovoltaic properties with the incident light angle is discussed. We demonstrate that an efficiency enhancement is attained for PC-DSCs at all angles measured, and that rational design of the photonic crystal back mirror leads to a reduction of the photocurrent losses related to the tilt angle of the cell, usually labeled as cosine losses. Angular variations of the cell transparency are also reported and discussed. These angular properties are relevant to the application of these solar devices in building integrated photovoltaics as potential window modules.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3EE23609A
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Tuning Dichroic Plasmon Resonance Modes of Gold Nanoparticles in Optical Thin Films
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Ferrer, J; Garcia-Gutierrez, MC; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Functional Materials, 23 (2013) 1655-1663 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201201900
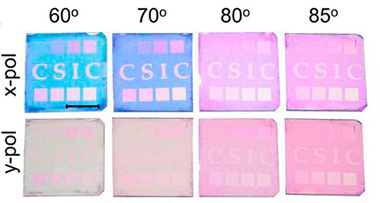
Abstract
A simple method is presented to tune the gold surface plasmon resonance (SPR) modes by growing anisotropic nanoparticles into transparent SiO2 thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition. In this type of composite film, the anisotropy of the gold nanoparticles, proved by gracing incidence small angle X-ray scattering, is determined by the tilted nanocolumnar structure of the SiO2 host and yields a strong film dichroism evidenced by a change from an intense colored to a nearly transparent aspect depending on light polarization and/or sample orientation. The formation in these films of lithographic non-dichroic SPR patterns by nanosecond laser writing demonstrates the potentialities of this procedure to develop novel optical encryption or anti-counterfeiting structures either at micrometer- or macroscales.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201201900
Characterization and repair measures of the medieval building materials of a Hispanic–Islamic construction
Pineda, P; Robador, MD; Perez-Rodriguez, JLConstruction and Building Materials, 41 (2013) 612-633 DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.12.034
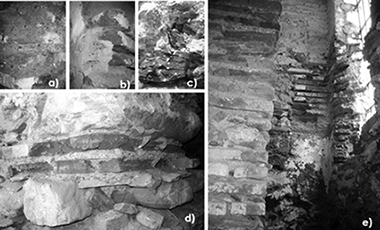
Abstract
This paper focuses on the physical–chemical and mechanical characterization of the building materials of a precious damaged structure, the Salares tower, a Hispanic–Islamic medieval construction located in the South of Spain, an active seismic area. An exhaustive description of the materials has been obtained, enriching the knowledge on historical construction materials. Sophisticated laboratory tests (XRD, SEM, EDX, FTIR, Micro-Raman spectroscopy, DTA and TG) have provided crucial complementary data to use together with traditional laboratory procedures, especially when the damage processes are the main concern. The experimental investigation has allowed a better understanding of the remote origin and of the failure mechanisms of this damaged structure. On the basis of these results, the most adequate repair materials are selected.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.12.034
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Differences in n-type doping efficiency between Al- and Ga-ZnO films
Gabas, M; Landa-Canovas, A; Costa-Kramer, JL; Agullo-Rueda, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Diaz-Carrasco, P; Hernandez-Moro, J; Lorite, I; Herrero, P; Castillero, P; Barranco, A; Ramos-Barrado, JRJournal of Applied Physics, 113 (2013) 163709 (9 pages) DOI: 10.1063/1.4803063
Abstract
A careful and wide comparison between Al and Ga as substitutional dopants in the ZnO wurtzite structure is presented. Both cations behave as n-type dopants and their inclusion improves the optical and electrical properties of the ZnO matrix, making it more transparent in the visible range and rising up its electrical conductivity. However, the same dopant/Zn ratio leads to a very different doping efficiency when comparing Al and Ga, being the Ga cation a more effective dopant of the ZnO film. The measured differences between Al- and Ga-doped films are explained with the hypothesis that different quantities of these dopant cations are able to enter substitutionally in the ZnO matrix. Ga cations seem to behave as perfect substitutional dopants, while Al cation might occupy either substitutional or interstitial sites. Moreover, the subsequent charge balance after doping appear to be related with the formation of different intrinsic defects that depends on the dopant cation. The knowledge of the doped-ZnO films microstructure is a crucial step to optimize the deposition of transparent conducting electrodes for solar cells, displays, and other photoelectronic devices.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1063/1.4803063
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Segregation to the grain boundaries in YSZ bicrystals: A Molecular Dynamics study
Gonzalez-Romero, RL; Melendez, JJ; Gomez-Garcia, D; Cumbrera, FL; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ASolid State Ionics, 237 (2013) 8-15 DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2013.02.002
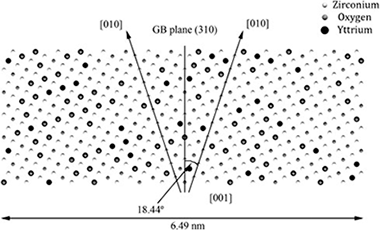
Abstract
A Molecular Dynamics study about the segregation of yttrium at 1500 K to a Σ5 grain boundary in 8 mol% YSZ has been performed. Segregation has been induced by explicitly taking into account the excess energy associated to the elastic misfit effect for yttrium cations located nearby the grain boundary planes. After an initial transient, a steady regime is reached, in which the number of yttrium cations does not increase with time. Accumulation of yttrium cations is accompanied by that of zirconium ones and oxygen vacancies at some distance of the grain boundary planes. The changes in the radial distribution functions for different ionic pairs are discussed, as also the effect of segregation on oxygen diffusion along the grain boundaries and in volume. Finally, the possibility that segregated yttrium located at available free sites at the grain boundaries is pointed out.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2013.02.002
Reactividad de Sólidos
Electrical Properties of Stoichiometric BiFeO3 Prepared by Mechanosynthesis with Either Conventional or Spark Plasma Sintering
Perejon, A; Maso, N; West, AR; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Poyato, R; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 96 (2013) 1220-1227 DOI: 10.1111/jace.12186
Abstract
Phase-pure powders of stoichiometric BiFeO3 have been prepared by mechanosynthesis. Ceramics sintered by either conventional heating in air or spark plasma sintering (SPS) followed by oxidative anneal in air are highly insulating at room temperature with resistivity, extrapolated from the Arrhenius plots, of ~1016 Ωcm and activation energy 1.15(2) eV, comparable with those of a good-quality BiFeO3 single crystal. By contrast, the as-prepared SPS sample without the postsinter anneal shows lower resistivity, e.g., ~1010 Ωcm at 25°C and activation energy 0.67(3) eV, indicating some reduction in the sample by the SPS process. The reason for the high conductivity reported for some ceramic samples in the literature remains unclear at present.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.12186
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Au/TiO2 supported on ferritic stainless steel monoliths as CO oxidation catalysts
Milt, VG; Ivanova, S; Sanz, O; Dominguez, MI; Corrales, A; Odriozola, JA; Centeno, MAApplied Surface Science, 270 (2013) 169-177 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.159
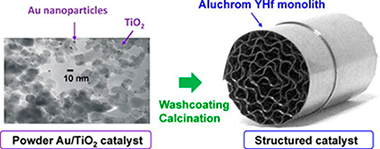
Abstract
Metallic supported structured catalysts were obtained by washcoating AluchromYHf monoliths with an Au/TiO2 catalyst. The powder catalyst was synthesized by DAE (direct anionic exchange) method. Using this catalyst, a stable slurry was prepared and used to washcoat the monoliths. TEM and SEM studies revealed that gold nanoparticles in the Au/TiO2 powder catalyst had an average diameter of 3–4 nm, but during the preparation of the structured catalyst, aggregate Au particles of the slurry reached diameters of 9 nm. Before coating, Aluchrom YHf monoliths were thermally treated to generate a homogeneous and well-adhered oxide rough surface layer, mainly composed of α-Al2O3 whiskers, which favored the anchoring of the catalyst. The catalytic layer deposited was well attached and contained not only the Au/TiO2 catalyst but also metallic oxides formed from stainless steel components that diffused through the oxide scale. The structural characterization was performed by XRD, XRF, TEM, SEM, GD-OES and SBET.
The catalytic activity of the powder and structured catalysts was tested in the oxidation of the CO reaction. Catalysts demonstrated to be active at room temperature. After a first activation run, and in spite of their larger gold particle size, the catalytic activities of the structured catalysts overcame those of the powder catalyst. This improvement is probably due to the segregation of the transition metal oxides toward the surface oxide scale.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.159
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
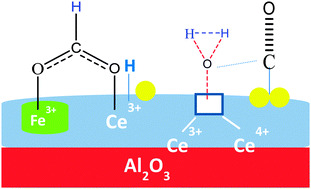
In situ characterization of iron-promoted ceria–alumina gold catalysts during the water-gas shift reaction
Reina, TR; Xu, WQ; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Hanson, J; Rodriguez, JA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 205 (2013) 41-48 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.08.004
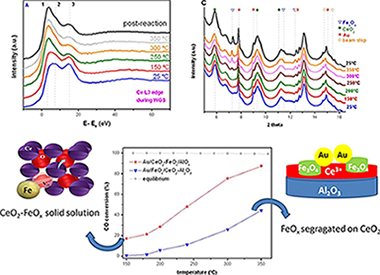
Abstract
In this work an in situ XRD and XANES study of two gold catalysts supported on iron-promoted ceria–alumina carriers was carried out during the water-gas shift reaction (WGS). The first catalyst, Au/CeO2–FeOx/Al2O3, was prepared using a commercial alumina support in order to obtain a Ce–Fe oxide solid solution and in the second one, Au/FeOx/CeO2–Al2O3, an iron oxide monolayer was deposited onto a ceria–alumina commercial support to promote its redox properties. Catalytic activities in the WGS were remarkably different for both systems. The catalytic activity of the Au/CeO2–FeOx/Al2O3 catalyst was higher than the one shown by the Au/FeOx/CeO2–Al2O3 catalyst that resulted active at much higher temperatures. In situ XRD demonstrates the formation of magnetite (Fe3O4) during the WGS reaction and the presence of big gold particles, ca. 21 nm in diameter, in the low-activity system. This in contrast to the high-activity system that shows undetectable gold nanoparticles and the absence of diffraction peaks corresponding to magnetite during the WGS. The data obtained using in situ XANES states that Ce4+ species undergo reduction to Ce3+during the WGS for both catalysts, and also confirms that in the high-activity catalyst iron is just present as Fe3+ species while in the low-activity catalyst Fe3+ and Fe2+ coexist, resulting in iron spinel observed by XRD. These results allow us conclude that the Au/CeO2–Fe2O3/Al2O3 catalyst is a suitable catalyst for WGS when avoiding the formation of magnetite, in such a case Fe3+ species favors reduction and water splitting increasing the catalytic activity in the WGS reaction.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.08.004
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth of SiO2 and TiO2 thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering and PECVD by the incorporation of non-directional deposition fluxes
Alvarez, R; Romero-Gomez, P; Gil-Rostra, J; Cotrino, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, APhysica Status Solidi (a), 210 (2013) 796-801 DOI: 10.1002/pssa.201228656
Abstract
We have deposited TiO2 and SiO2 thin films by techniques as different as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) and reactive magnetron sputtering under experimental conditions where highly directional deposition fluxes are avoided. The results indicate that whatever the deposition technique employed or even the precursor gas in the PECVD technique, films share common microstructural features: a mounded surface topography and a columnar arrangement in the bulk, with the column width growing linearly with film thickness. With the help of a Monte Carlo model of the deposition, we conclude that these common aspects are explained by solely taking into consideration the incorporation of a low-energy, isotropically directed, deposition flux onto a substrate at low temperature and under a weak plasma/surface interaction environment.
April, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/pssa.201228656
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Hydration properties of synthetic high-charge micas saturated with different cations: An experimental approach
Pavon, E; Castro, MA; Naranjo, M; Orta, MM; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDAmerican Mineralogist, 98 (2013) 394-400 DOI: 10.2138/am.2013.4217
Abstract
An understanding of the interaction mechanisms between exchangeable cations and layered silicates is of interest from both a basic and an applied point of view. Among 2:1 phyllosilicates, a new family of swelling high-charge synthetic micas has been shown to be potentially useful as decontaminant. However, the location of the interlayer cations, their acidity and the water structure in the interlayer space of these silicates are still unknown. The aim of this paper was therefore to study the hydration state of the interlayer cations in the interlayer space of high-charge expandable micas and to evaluate the effect that this hydration has on the swelling and acidity behavior of these new materials. To achieve these objectives, three synthetic micas with different charge density total layer charges (ranging between 2 and 4 per unit cell) and with five interlayer cations (Na+, Li+, K+, Mg2+, and Al3+) were synthesized and their hydration state, interlayer space, and acidity analyzed by DTA/TG, XRD, and 1H MAS NMR spectroscopy. The results showed that the hydration state depends on both the layer charge and the nature of the interlayer cation. A high participation of the inner-sphere complexes in the highly charged confined space has been inferred and proposed to induce Brønsted acidity in the solid.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.2138/am.2013.4217
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Competing Misfit Relaxation Mechanisms in Epitaxial Correlated Oxides
Sandiumenge, F; Santiso, J; Balcells, L; Konstantinovic, Z; Roqueta, J; Pomar, A; Espinos, JP; Martinez, BPhysical Review Letters, 110 (2013) 107206 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.107206
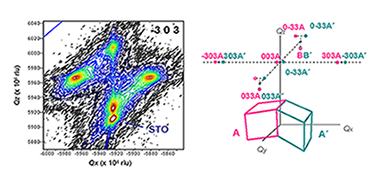
Abstract
Strain engineering of functional properties in epitaxial thin films of strongly correlated oxides exhibiting octahedral-framework structures is hindered by the lack of adequate misfit relaxation models. Here we present unreported experimental evidence of a four-stage hierarchical development of octahedral-framework perturbations resulting from a progressive imbalance between electronic, elastic, and octahedral tilting energies in La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 epitaxial thin films grown on SrTiO3 substrates. Electronic softening of the Mn-O bonds near the substrate leads to the formation of an interfacial layer clamped to the substrate with strongly degraded magnetotransport properties, i.e., the so-called dead layer, while rigid octahedral tilts become relevant at advanced growth stages without significant effects on charge transport and magnetic ordering.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.107206
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
High-performance Er3+–TiO2 system: Dual up-conversion and electronic role of the lanthanide
Obregon, S; Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Colon, GJournal of Catalysis, 299 (2013) 298-306 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2012.12.021
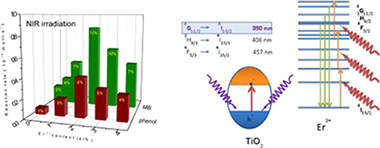
Abstract
Erbium-doped TiO2 materials are synthesized by means of a surfactant-free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities for the liquid-phase degradation of phenol and MB and the gas phase of toluene. From the structural and morphological characterization, it has been stated that the presence of Er3+ induces a progressive anatase cell expansion due to its incorporation in the TiO2 lattice. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with 2 at% of Er3+ irrespective of the chemical degradation reaction essayed. From activity and optical studies under different irradiation excitation conditions, a dual-type mechanism is proposed to be at the origin of the photocatalytic activity enhancement. On one hand, the improvement observed under UV irradiation occurs by the effective charge separation promoted by Er3+ species which would act as electron scavenger. Besides, the up-conversion luminescence process of Er3+ allows profiting the NIR range of the lamp and transferring energy in the UV range to the TiO2. The dual action of Er ions located at anatase networks will open up a wide roadway for the developing of an integral solar active photocatalyst.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2012.12.021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Colored and Transparent Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering: The Glass Blower Approach
Gil-Rostra, J; Chaboy, J; Yubero, F; Vilajoana, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5 (2013) 1967-1976 DOI: 10.1021/am302778h

Abstract
This work describes the reactive magnetron sputtering processing at room temperature of several mixed oxide MxSiyOz thin films (M: Fe, Ni, Co, Mo, W, Cu) intended for optical, coloring, and aesthetic applications. Specific colors can be selected by adjusting the plasma gas composition and the Si–M ratio in the magnetron target. The microstructure and chemistry of the films are characterized by a large variety of techniques including X-ray photoemission spectroscopy, X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and infrared spectroscopy, while their optical properties are characterized by UV–vis transmission and reflection analysis. Particularly, XAS analysis of the M cations in the amorphous thin films has provided valuable information about their chemical state and local structure. It is concluded that the M cations are randomly distributed within the SiO2 matrix and that both the M concentration and its chemical state are the key parameters to control the final color of the films.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/am302778h
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the O2/CO ratio and the presence of H2O and CO2 in the feed-stream during the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX) over a CuOx/CeO2-coated microchannel reactor
Laguna, OH; Dominguez, MI; Oraa, S; Navajas, A; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LM; Centeno, MA; Montes, M; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 203 (2013) 182-187 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.04.021
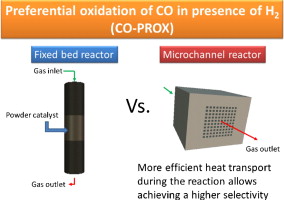
Abstract
The catalytic performance of a CuOx/CeO2 powder catalyst and that of a microchannel reactor or microreactor (MR) coated with the same solid was determined and compared. The catalytic activity measurements were carried out with varying O2/CO molar ratios in the feed-stream. In addition, the influence of the presence of CO2 and H2O in the reaction mixture was studied. Some discrepancies were observed between the performances of the powder catalyst and the MR depending on the O2/CO ratio. The MR presented a very good performance with a superior selectivity for CO conversion. This behaviour was due to a more efficient heat removal in the case of the MR that inhibited the H2 oxidation reaction and the r-WGS. The isothermicity of the microreactor during the process was demonstrated through the monitoring of the MR inlet and outlet temperatures.
Concerning the presence of CO2 or H2O in the feed-stream, both compounds gave rise to a decrease of the CO conversion. The negative effect on the catalytic performance was more marked when both compounds were fed together, although the principal inhibitor effect was associated to the CO2. This seems to be related with the formation of stable carbonates at the catalyst surface.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.04.021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Cystine-capped CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites: mechanochemical synthesis, properties, and the role of capping agent
Balaz, M; Balaz, P; Tjuliev, G; Zubrik, A; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Kostova, NJournal of Materials Science, 48 (2013) 2424-2432 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-012-7029-3
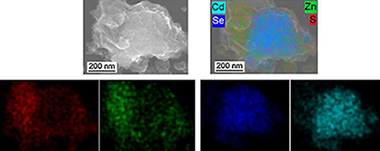
Abstract
Cystine-capped CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites were synthesized mechanochemically with the aim to prepare a material which could be used in medicine for biosensing applications. Although synthesized CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites were capped with l-cysteine, cystine was formed from l-cysteine during the milling process. It was proven that water plays the key role in this oxidative transformation. The novel material was characterized by the complex of physico-chemical methods (FTIR, XPS, SEM, EDX, surface area measurements) and CHNS analysis. The leakage of Cd2+ and Zn2+ ions into physiological solution was also studied.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1007/s10853-012-7029-3
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Behaviour of Au-citrate nanoparticles in seawater and accumulation in bivalves at environmentally relevant concentrations
Garcia-Negrete, C. A.; Blasco, J.; Volland, M.; Rojas, T. C.; Hampel, M.; Lapresta-Fernandez, A.; Jimenez de Haro, M. C.; Soto, M.; Fernandez, A.Environmental Pollution, 174 (2013) 134-141 DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.014
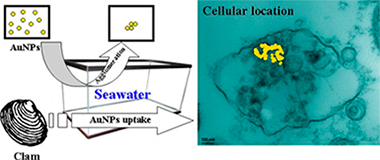
Abstract
The degree of aggregation and/or coalescence of Au-citrate nanoparticles (AuNPs, mean size 21.5 ± 2.9 nm), after delivery in simulated seawater, are shown to be concentration-dependent. At low concentrations no coalescence and only limited aggregation of primary particles were found. Experiments were performed in which the marine bivalve (Ruditapes philippinarum) was exposed to AuNPs or dissolved Au and subsequently, bivalve tissues were studied by Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy and chemical analyses. We show that the bivalve accumulates gold in both cases within either the digestive gland or gill tissues, in different concentrations (including values of predicted environmental relevance). After 28 days of exposure, electron-dense deposits (corresponding to AuNPs, as proven by X-ray microanalysis) were observed in the heterolysosomes of the digestive gland cells. Although non-measurable solubility of AuNPs in seawater was found, evidence is presented of the toxicity produced by Au3+ dissolved species (chloroauric acid solutions) and its relevance is discussed.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.014
Materiales Coloidales
Solvent-Controlled Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Uniform Eu:YVO4 Nanophosphors with Different Morphologies
Nunez, N; Sabek, J; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cantelar, E; Escudero, A; Ocañaa, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 8 (2013) 1301-1309 DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201201016
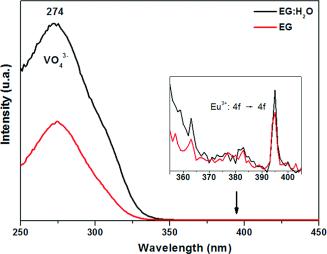
Abstract
A facile solvothermal route has been developed for the preparation of tetragonal europium-doped yttrium orthovanadate nanoparticles (Eu:YVO4) and is based on a homogeneous precipitation reaction at 120 °C from solutions of rare earth precursors (yttrium acetylacetonate and europium nitrate) and sodium orthovanadate in ethylene glycol or ethylene glycol/water mixtures. The nature of the solvent has a dramatic effect on the morphology and crystallinity of the resulting nanoparticles. Polycrystalline nanoellipsoids (130 × 60 nm) were obtained in pure ethylene glycol, whereas quasispherical nanoparticles (100 nm) with monocrystalline character precipitated in ethylene glycol/water (7:3 by volume) mixtures. To explain these different morphological and structural features, the mechanism of particles formation was investigated. The effects of the doping level on the luminescence properties (emission spectra and luminescence lifetime) were also evaluated to find the optimum nanophosphors. Finally, it is shown that the luminescent efficiency of the quasispherical nanoparticles was higher than that of the nanoellipsoids; this can be related to differences in crystallinity and in impurity content.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201201016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Joining and interface characterization of in situ reinforced silicon nitride
Asthana, R; Singh, M; Martinez-Fernandez, JJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 552 (2013) 137-145 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.09.104
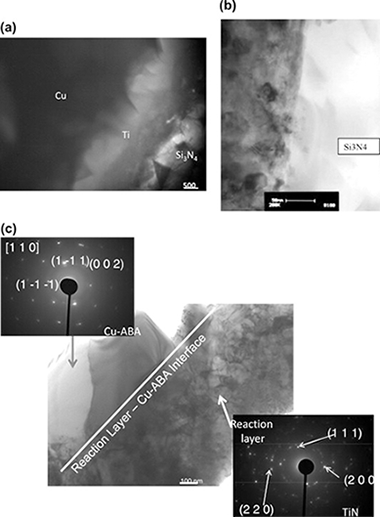
Abstract
Copper-base active metal interlayers were used to bond in situ reinforced silicon nitride (Honeywell AS800) at 1317 K for 5 and 30 min in vacuum. The joints were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), electron back scattered diffraction (EBSD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). A Ti-rich interaction zone (∼3.0–3.5 μm thick) formed at the Si3N4/braze interface. This reaction layer grew toward the inner part of the joint with a featureless microstructure, creating a strong bond. Regions of a Ti-rich phase were frequently found next to the reaction layer but surrounded by the Cu alloy. Extensive Ti and Si enrichments were noted at the interface but there was no evidence of interfacial segregation of Y, La, and Sr (from Y2O3, La2O3 and SrO, added as sintering aids). The reaction layer thickness and composition did not change when brazing time increased from 5 min to 30 min suggesting rapid growth kinetics in the early stages of reaction. The joints were crack-free and showed features associated with plastic deformation, which indicated that the metal interlayer accommodated strain associated with CTE mismatch. The inner part of the joint consisted of highly textured large grains of the braze alloy.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.09.104
Materiales Coloidales
Ionic Liquid Mediated Synthesis and Surface Modification of Multifunctional Mesoporous Eu:GdF3 Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications
Rodriguez-Liviano, S; Nunez, NO; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MLangmuir, 29 (2013) 3411-3418 DOI: 10.1021/la4001076
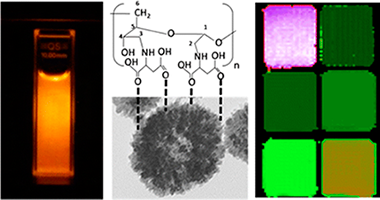
Abstract
A procedure for the synthesis of multifunctional europium(III)-doped gadolinium(III) fluoride (Eu:GdF3) nanoparticles (85 nm) with quasispherical shape by precipitation at 120 °C from diethylene glycol solutions containing lanthanide chlorides and an ionic liquid (1-Butyl, 2-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate) as fluoride source has been developed. These nanoparticles were polycrystalline and crystallized into a hexagonal structure, which is unusual for GdF3. They were also mesoporous (pore size = 3.5 Å), having a rather high BET surface area (75 m2 g–1). The luminescent and magnetic (relaxivity) properties of the Eu:GdF3 nanoparticles have been also evaluated in order to assess their potentiality as “in vitro” optical biolabels and contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. Finally, a procedure for their functionalization with aspartic-dextran polymers is also reported. The functionalized Eu:GdF3 nanoparticles presented negligible toxicity for Vero cells, which make them suitable for biotecnological applications.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/la4001076
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The distribution of elements in sequentially prepared MgB2 on SiC buffered Si substrate and possible pinning mechanisms
S. Chromik; A. Nishida; V. Strbik; M. Gregor; J.P. Espinós; J. Liday; R. DurnyApplied Surface Science, 269 (2013) 29-32 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.10.019
Abstract
MgB2 thin films are prepared by sequential evaporation of boron and magnesium bilayers on SiC buffered Si substrates followed by an in situ annealing. Precursor Mg–B bilayers are deposited by electron beam evaporation at room temperature. The amount of B is varied so as to result in different thickness (15 nm and 50 nm) of stoichiometric MgB2 final film after an in situ reaction with the excess Mg top layer in the vacuum. We show the distribution of the elements through the film.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses have shown that carbon is not free in the films (except the surface of the film) and silicon is in the compound form, too. In the case of the 15 nm thick films we see a strong interdiffusion of the elements (C, B) and we observe a suppression of TC of the film to 20 K. We register different slope of the HC2(T)HC2(T) dependence – the lowest temperature value of HC2HC2 for the 15 nm thick film exceeds the one for the 50 nm thick film in spite of lower TC. We suppose that δl pinning mechanism is dominant for the 15 nm thick film.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.10.019
Materiales Coloidales
LaPO4:Er microspheres with high NIR luminescent quantum yield
Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cantelar, E; Justo, A; Ocana, M; Cusso, FMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 138 (2013) 666-671 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.12.036

Abstract
Er-doped LaPO4 microspheres have been synthesized by spray pyrolysis and the near infrared (NIR) properties have been characterized. It has been found that, following an adequate post-annealing treatment, the emission properties are remarkably improved. The NIR luminescence intensity is highly enhanced and its decay time increases to a value almost coincident with the reported radiative lifetime, which implies that the quantum yield approaches η ≈ 100%. This improvement in luminescence characteristics is probably related to the suppression of residual OH− radicals, that otherwise act as NIR luminescence quenchers, and to the increase in material's crystallinity.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.12.036
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Impact of Ce–Fe synergism on the catalytic behaviour of Au/CeO2–FeOx/Al2O3 for pure H2 production
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Idakiev, V; Delgado, JJ; Ivanov, I; Tabakova, T; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Science & Technology, 3 (2013) 779-787 DOI: 10.1039/C2CY20537H
Abstract
In this work the development of a series of gold catalysts, essentially based on γ-alumina promoted with a small superficial fraction of Ce–Fe mixed oxides, is reported. The catalytic behaviour is evaluated in the water gas shift reaction. The formation of a Ce–Fe solid solution is evidenced by XRD and related to the catalytic activity where the importance of the Ce–Fe interaction is demonstrated. The best catalyst reached CO conversions very close to the equilibrium limit. A long-term stability test is performed and the loss of activity is observed and attributed to reaction intermediates. Almost complete recovery of the initial conversion is achieved after oxidation treatment, suggesting that the problem of stability could be overcome by a suitable change in the reaction parameters thus leading to a highly efficient catalyst for future applications in H2 production and clean-up.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C2CY20537H
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
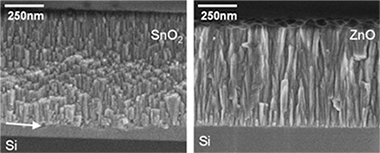
Growth of silver on ZnO and SnO2 thin films intended for low emissivity applications
Alvarez, R; Gonzalez, JC; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Cueva, A; Villuendas, FApplied Surface Science, 268 (2013) 507-515 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.156
Abstract
In the present work we have investigated the relationships existing between the optical properties and the growth mechanism, microstructure and surface roughness of SnO2 and ZnO oxide films prepared by magnetron sputtering under conditions resembling those utilized in industry. Thin films of these oxides with different thicknesses were characterized by atomic force microscopy, glancing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD), X-ray reflectometry and spectroscopic ellipsometry. The roughness evolution of the film properties (density, surface roughness and refraction index) as a function of their thickness has been evaluated within the concepts of the Dynamic Scaling Theory of thin film growth. Zinc oxide films were rougher than tin oxide films of similar thickness, indicating a different growing mechanism for the two materials. Silver was evaporated onto the surface of the two oxide thin films and its earlier stages of nucleation studied by background analysis of the X-ray photoemission spectra. A different nucleation mechanism was found depending on the nature of the oxide acting as substrate. The superior performance of the zinc oxide based low emissive coatings is related with a better wetting of silver on the surface of this oxide despite the comparatively lower roughness of the tin oxide layers.
March, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.156
Materiales Coloidales
A Novel 3D Architecture of GdPO4 Nanophosphors: Multicolored and White Light Emission
Becerro, AI; Rodriguez-Liviano, S; Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Ocaña, MCrystal Growth & Design, 55 (2013) 454-460 DOI: 10.1021/cg301023k
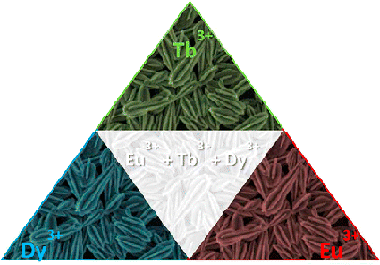
Abstract
Homogeneous monoclinic GdPO4 particles composed of three intersecting lance-shaped crystals forming a penetration twin have been synthesized following a very restrictive, simple, and fast (10 min) method consisting of the hydrothermal reaction of gadolinium acetylacetonate with H3PO4 in a mixture of ethylene glycol and water at 180 °C. Slightly increasing the amount of water in the solvent mixture leads to hexagonal rodlike GdPO4·0.5H2O nanoparticles, whereas the variation of the Gd source, PO4 source, aging temperature, and polyol type gave rise to heterogeneous particles. The synthesis procedure is also suitable for the preparation of Eu3+-, Tb3+-, and Dy3+-doped GdPO4 particles with the same morphology and crystalline structure as the undoped materials. The effect of the doping level on the luminescent properties of the twinlike nanophosphors was evaluated, finding optimum doping levels of 5, 5, and 1% for the Eu3+-, Tb3+-, and Dy3+-doped materials, respectively. The twinlike GdPO4 nanophosphors were found to be more efficient than the rodlike GdPO4 ones in terms of emission intensity. Finally, a solid-state single-phase white-light-emitting nanophosphor has been fabricated for the first time in this system by triply doping the GdPO4 twined particles with appropriate concentrations of Eu3+, Tb3+, and Dy3+ and exciting through the Gd–Ln energy-transfer band at 273 nm. In addition to this energy transfer band, other energy charge transfer processes among the three dopants (Eu3+, Tb3+, and Dy3+) have been observed in the triply doped material.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/cg301023k
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Improved photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4/TiO2 composites prepared by a simple impregnation method
Miranda, C; Mansilla, H; Yanez, J; Obregon, S; Colon, GJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 253 (2013) 16-21 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.12.014
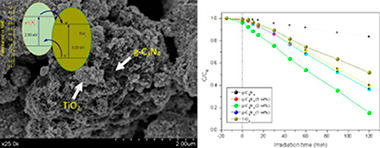
Abstract
g-C3N4 and TiO2 hybrid structures are synthesized by means of a simple impregnation method having good photoactivities for the degradation of phenol under UV irradiation. From the wide structural and surface characterization we have stated that the presence of g-C3N4 notably affect the surface feature of TiO2 (surface area and pore size distribution). Enhanced photoactivities have been obtained for composites systems. The best result was obtained for 2 wt% loading of g-C3N4 leading to a 70% of improvement with respect to bare TiO2 in the reaction rate. The effective charge carrier separation was proposed as the responsible of such improved photoactivity.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.12.014
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser induced enhancement of dichroism in supported silver nanoparticles deposited by evaporation at glancing angles
Filippin, AN; Borras, A; Rico, VJ; Frutos, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARNanotechnology, 24 (2013) 045301 DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/4/045301
Abstract
Silver nanoparticles (NPs) depicting well defined surface plasmon resonance (SPR) absorption were deposited on flat substrates by physical vapor deposition in a glancing angle configuration. The particles were characterized by scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy and their optical properties examined by UV–vis absorption spectroscopy using linearly polarized light. It was found that, depending on the amount of deposited silver and the evaporation angle, part of the 'as-prepared' samples present NPs characterized by an anisotropic shape and a polarization dependent SPR absorption and different colors when using polarized white light at 0° and 90°. Low-power irradiation of these materials with an infrared Nd-YAG nanosecond laser in ambient conditions produced an enhancement in such dichroism. At higher powers, the dichroism was lost and the SPR bands shifted to lower wavelengths as a result of the reshaping of the silver NPs in the form of spheres. The possible factors contributing to the observed changes in dichroism are discussed.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/4/045301
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetic approach to partially overlapped thermal decomposition processes
Koga, N; Goshi, Y; Yamada, S; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 111 (2013) 1463-1474 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-012-2500-6
Abstract
Practical usefulness of the kinetic deconvolution for partially overlapped thermal decomposition processes of solids was examined by applying to the co-precipitated basic zinc carbonate and zinc carbonate. Comparing with the experimental deconvolutions by thermoanalytical techniques and mathematical deconvolutions using different statistical fitting functions, performance of the kinetic deconvolution based on an accumulative kinetic equation for the independent processes overlapped partially was evaluated in views of the peak deconvolution and kinetic evaluation. Two-independent kinetic processes of thermal decompositions of basic zinc carbonate and zinc carbonate were successfully deconvoluted by means of the thermoanalytical measurements in flowing CO2 and by applying sample controlled thermal analysis (SCTA). The deconvolutions by the mathematical curve fittings using different fitting functions and subsequent formal kinetic analysis provide acceptable values of the mass-loss fractions and apparent activation energies of the respective reaction processes, but the estimated kinetic model function changes depending on the fitting functions employed for the peak deconvolution. The mass-loss fractions and apparent kinetic parameters of the respective reaction processes can be optimized simultaneously by the kinetic deconvolution based on the kinetic equation through nonlinear least square analysis, where all the parameters indicated acceptable correspondences to those estimated through the experimental and mathematical deconvolutions. As long as the reaction processes overlapped are independent kinetically, the simple and rapid procedure of kinetic deconvolution is useful as a tool for characterizing the partially overlapped kinetic processes of the thermal decomposition of solids.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-012-2500-6
Preferential oxidation of CO in excess H2 over CuO/CeO2 catalysts: Characterization and performance as a function of the exposed face present in the CeO2 support
Gamarra, D; Camara, AL; Monte, M; Rasmussen, SB; Chinchilla, LE; Hungria, AB; Munuera, G; Gyorffy, N; Schay, Z; Corberan, VC; Conesa, JC; Martinez-Arias, AApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 130-131 (2013) 224-238 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.11.008
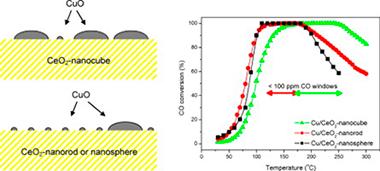
Abstract
A series of oxidised copper-cerium nanostructured catalysts prepared by impregnation of copper over ceria supports synthesized by different methods (hydrothermal with varying preparation parameters, microemulsion/precipitation), in order to achieve different specific morphologies (nanocubes, nanorods and nanospheres), have been examined with respect to their catalytic properties for preferential oxidation of CO in excess H2 (CO-PROX). The catalysts have been characterized in detail by XRD, Raman, SBET measurement, HREM, XPS, TPR and EPR, which allows establishing a model of structural characteristics of the catalysts. The characterization results have been correlated with analysis of CO-PROX catalytic properties by means of catalytic activity measurements complemented by operando-DRIFTS. Structural dependence of the CO oxidation reaction on the dispersed copper oxide entities as a function of the exposed face present at the surface of the different ceria supports is revealed. An important overall enhancement of the CO-PROX performance is detected for the sample supported on ceria nanocubes which is proposed to be a consequence of the interaction between copper oxide and (1 0 0) faces of the ceria support.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.11.008
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Valence band electronic structure characterization of the rutile TiO2 (110)-(1 x 2) reconstructed surface
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Garnier, MG; Aebi, P; Blanco-Rey, M; de Andres, PL; Martin-Gago, JA; Lopez, MFSurface Science, 608 (2013) 92-96 DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.09.019
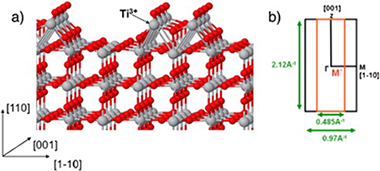
Abstract
The electronic structure of the TiO2 (110)-(1 × 2) surface has been studied by means of angular resolved ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (ARUPS). The valence band dispersion along the high symmetry surface directions, [001] and [1–10], has been recorded. The experimental data show no dispersion of the band-gap Ti 3d states. However, the existence of dispersive bands along the [001] direction located at about 7 eV below the Fermi level is reported. The existence of two different contributions in the emission from the defects-related state located in the gap of the surface is univocally shown for the first time.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.09.019
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Biocompatible Europium-Doped Calcium Hydroxyapatite and Fluoroapatite Luminescent Nanospindles Functionalized with Poly(acrylic acid)
Escudero, A; Calvo, ME; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MLangmuir, 29 (2013) DOI: 10.1021/la304534f
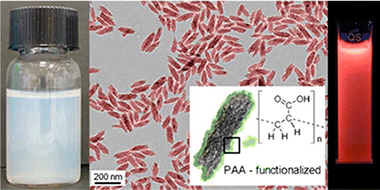
Abstract
Europium-doped calcium hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite nanophosphors functionalized with poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) have been synthesized through a one-pot microwave-assisted hydrothermal method from aqueous basic solutions containing calcium nitrate, sodium phosphate monobasic, and PAA, as well as sodium fluoride in the case of the fluoroapatite particles. In both cases a spindlelike morphology was obtained, resulting from an aggregation process of smaller subunits which also gave rise to high specific surface area. The size of the nanospindles was 191 (32) × 40 (5) nm for calcium hydroxyapatite and 152 (24) × 38 (6) nm for calcium fluoroapatite. The luminescent nanoparticles showed the typical red luminescence of Eu3+, which was more efficient for the fluoroapatite particles than for the hydroxyapatite. This is attributed to the presence of OH– quenchers in the latter. The nanophosphors showed negligible toxicity for Vero cells. Both PAA-functionalized nanophosphors showed a very high (up to at least 1 week) colloidal stability in 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES) at pH 6.5, which is a commonly used buffer for physiological pH. All these features make both kinds of apatite-based nanoparticles promising tools for biomedical applications, such as luminescent biolabels and tracking devices in drug delivery systems.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/la304534f
Allochthonous red pigments used in burial practices at the Copper Age site of Valencina de la Concepción (Sevilla, Spain): characterisation and social dimension
Rogerio-Candelera, MA; Herrera, LK; Miller, AZ; Sanjuan, LG; Molina, CM; Wheatley, DW; Justo, A; Saiz-Jimenez, CJournal of Archaeological Science, 40 (2013) 279-290 DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2012.08.004

Abstract
The use of red pigments linked to burial practices is widely documented in the Iberian prehistoric record and very often it has been traditionally interpreted as a ritual practice entailing the utilisation of local raw materials (iron oxides). Some research works, nevertheless, have also detected the use of red pigments which can only be interpreted as allochthonous. The red pigments spread over a single inhumation in a monumental Megalithic tomb surrounding Valencina de la Concepción Copper Age settlement was studied by means of X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray microfluorescence, micro-Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopies. This approach allowed characterising the red pigments as cinnabar, mixed with tiny amounts of iron oxides. The presence of cinnabar, a product that was necessarily imported, in a context of an exceptional set of grave goods, suggests that the use of cinnabar was linked not only to ritual but also to practices related to the display of social status.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2012.08.004
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Efficient and affordable hydrogen production by water photo-splitting using TiO2-based photocatalysts
Melian, EP; Diaz, OG; Mendez, AO; Lopez, CR; Suarez, MN; Rodriguez, JMD; Navio, JA; Hevia, DF; Pena, JPInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38 (2013) 2144-2155 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.005
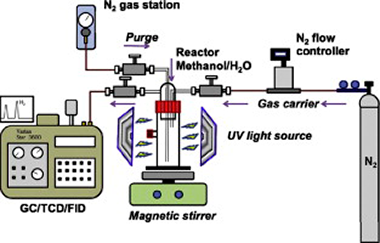
Abstract
TiO2-based photocatalyst materials were synthesized through a sol–gel method, followed either by: (1) hydrothermal treatment (150 °C/24 h), or (2) heat treatment (calcination) in a temperature range between 400 and 900 °C. The resulting materials were characterized through BET, XRD, TEM, FTIR, RAMAN, laser diffraction and UV–Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy. Photoactivity of the various materials was checked against photocatalytic water-splitting for hydrogen production and a relationship between TiO2 structure and hydrogen production capacity was identified. Optimum results were obtained for anatase-rutile mixtures in a ratio of 87:13. The activity of the home-made photocatalysts was also compared (under the same conditions) with the best commercially available materials which have been widely described in the literature: Hombikat UV100, Millenium PC100, Kronos vlp7000,Degussa P25and Kemira 625.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.005
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Effects of plasma surface treatments of diamond-like carbon and polymeric substrata on the cellular behavior of human fibroblasts
Lopez-Santos, C; Fernandez-Gutierrez, M; Yubero, F; Vazquez-Lasa, B; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, A; San Roman, JJournal of Biomaterials Applications, 27 (2013) 669-683 DOI: 10.1177/0885328211422832
Abstract
Surface properties play an important role in the functioning of a biomaterial in the biological environment. This work describes the influence of the changes that occurred on diamond-like carbon (DLC) and polymeric substrata by different nitrogen and ammonia plasmas treatments and its effects on the cell proliferation on these materials. All substrata were additionally subjected to the effect of neutral beams of nitrogen atoms and NH species for comparison purposes. Results about the proliferation, viability, and morphology of fibroblasts were correlated with surface chemical composition, surface tension, and topography. It was found that the presence of amine groups on the surface and the surface tension are beneficial factors for the cell growth. Surface roughness in DLC also plays a positive role in favoring cell adhesion and proliferation, but it can be detrimental for some of the treated polymers because of the accumulation of low molecular weight fragments formed as a result of the plasma treatments. Analysis of the overall results for each type of material allowed to define a unique parameter called ‘factor of merit’ accounting for the influence of the different surface characteristics on the cell deployment, which can be used to predict qualitatively the efficiency for cell growth.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1177/0885328211422832
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Multiple Zeolite Structures from One Ionic Liquid Template
Blanes, JMM; Szyja, BM; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Hensen, EJM; Odriozola, JA; Ivanova, SChemistry-A European Journal, 19 (2013) 2122-2130 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201202556
Abstract
This study reports the use of 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium methanesulfonate ionic liquid as a template in the synthesis of zeolites. It is found that the silicon source determines the formation of beta (BEA), mordenite framework inverted (MFI), or analcime (ANA) zeolites. Depending on this source, different preorganized complexes are obtained that drive the formation of the different zeolite structures. In the presence of ethanol, the ionic liquid form preorganized complexes that drive the formation of MFI. In its absence, BEA is obtained. Whereas, the large amount of sodium present when using sodium metasilicate leads to ANA formation. A molecular simulation study of the relative stability of the template-framework system and location of the template provides further insight into the mechanism of synthesis.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/chem.201202556
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Heat capacity of Bio-SiC and SiC/Si ecoceramics prepared from white eucalyptus, beech, and sapele tree wood
Smirnov, IA; Smirnov, BI; Orlova, TS; Wlosewicz, D; Hackemer, A; Misiorek, H; Mucha, J; Jezowski, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Martinez-Fernandez, JPhysics of the Solid State, 55 (2013) 454-460 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783413020285
Abstract
This paper reports on measurement of the heat capacity at constant pressure C p of silicon bio-carbide prepared within the 5–300 K temperature interval from beech tree wood (bio-SiC(BE)), and within 80–300 K, from tree wood of sapele (bio-SiC(SA)), as well as SiC/Si ecoceramics of beech, sapele, and white eucalyptus wood. It has been shown that in bio-SiC(BE) the measured heat capacity contains a significant contribution of surface heat capacity, whose magnitude decreases with increasing temperature. Of the ecoceramics, only SiC/Si(SA) characterized by a high enough porosity has revealed a small contribution to the heat capacity coming from its surface component. The experimental results obtained are discussed.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783413020285
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth regimes of porous gold thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique incidence: from compact to columnar microstructures
Alvarez, R; Garcia-Martin, JM; Macias-Montero, M; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Gonzalez, JC; Rico, V; Perlich, J; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ANanotechnology, 24 (2013) 045604 DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/4/045604
Abstract
Growth regimes of gold thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles and low temperatures are studied from both theoretical and experimental points of view. Thin films were deposited in a broad range of experimental conditions by varying the substrate tilt angle and background pressure, and were analyzed by field emission scanning electron microscopy and grazing-incidence small-angle x-ray scattering techniques. Results indicate that the morphological features of the films strongly depend on the experimental conditions, but can be categorized within four generic microstructures, each of them defined by a different bulk geometrical pattern, pore percolation depth and connectivity. With the help of a growth model, a microstructure phase diagram has been constructed where the main features of the films are depicted as a function of experimentally controllable quantities, finding a good agreement with the experimental results in all the studied cases.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/4/045604
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermopower of Bio-SiC and SiC/Si ecoceramics prepared from sapele tree wood
Smirnov, IA; Smirnov, BI; Orlova, TS; Sulkovski, C; Misiorek, H; Muha, J; Jezowski, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Martinez-Fernandez, JPhysics of the Solid State, 55 (2013) 54-59 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783413010307
Abstract
The thermopower coefficients of bio-SiC and SiC/Si ecoceramics prepared from sapele tree wood have been measured in the temperature interval 5–300 K. The measurements have been performed both along and perpendicular to empty (bio-SiC), as well as empty and partially silicon-filled (SiC/Si) channels in the samples. In bio-SiC, a contribution to thermopower associated with electron drag by phonons has been shown to exist within the temperature interval 5–200 (250) K. No such effect is realized in SiC/Si. This is assumed to derive from the presence in this material of heavily doped silicon embedded in SiC channels and the dominant part it plays in the behavior of the thermopower of this ceramics. The results obtained for the thermopower are compared with the available data for bio-SiC prepared from white eucalyptus tree wood and heavily doped bismuth.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783413010307
Reactividad de Sólidos
Comments on “Thermal decomposition of pyridoxine: an evolved gas analysis-ion attachment mass spectrometry study”. About the application of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis to single non-isothermal curves
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMRapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 27 (2013) 500-502 DOI: 10.1002/rcm.6472
Reactividad de Sólidos
Clarifications regarding the use of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis for determining the activation energy from a single non-isothermal curve
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMChemistry Central Journal, 7 (2013) 25 DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-25
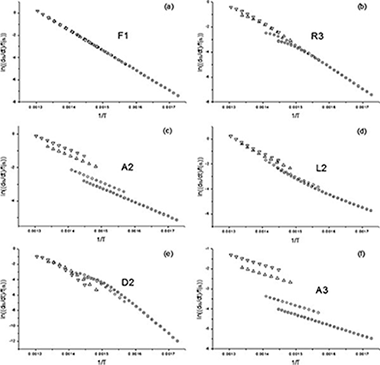
Abstract
Background
This paper provides some clarifications regarding the use of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis for estimating the activation energy of a process, in response to some results recently published in Chemistry Central journal.
Findings
The model fitting methods of Arrhenius and Savata are used to determine the activation energy of a single simulated curve. It is shown that most kinetic models correctly fit the data, each providing a different value for the activation energy. Therefore it is not really possible to determine the correct activation energy from a single non-isothermal curve. On the other hand, when a set of curves are recorded under different heating schedules are used, the correct kinetic parameters can be clearly discerned.
Conclusions
Here, it is shown that the activation energy and the kinetic model cannot be unambiguously determined from a single experimental curve recorded under non isothermal conditions. Thus, the use of a set of curves recorded under different heating schedules is mandatory if model-fitting methods are employed.
February, 2013 · DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-25
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Strong quantum confinement effects in SnS nanocrystals produced by ultrasound-assisted method
Azizian-Kalandaragh, Y; Khodayari, A; Zeng, ZP; Garoufalis, CS; Baskoutas, S; Gontard, LCJournal of Nanoparticle Research, 15 (2013) 1388 DOI: 10.1007/s11051-012-1388-1
Abstract
Nanocrystalline SnS powder has been prepared using tin chloride (SnCl2) as a tin ion source and sodium sulfide (Na2S) as a sulfur ion source with the help of ultrasound irradiation at room temperature. The as-synthesized SnS nanoparticles were quantitatively analyzed and characterized in terms of their morphological, structural, and optical properties. The detailed structural and optical properties confirmed the orthorhombic SnS structure and a strongly blue shifted direct band gap (1.74 eV), for synthesized nanoparticles. The measured band gap energy of SnS nanoparticles is in a fairly good agreement with the results of theoretical calculations of exciton energy based on the potential morphing method in the Hartree–Fock approximation.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1007/s11051-012-1388-1
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrochromism in WOx and WxSiyOz Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering at Glancing Angles
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARNanoscience and Nanotechnology Letters, 5 (2013) 89-93 DOI: 10.1166/nnl.2013.1449
Abstract
This work reports the electrochromic evaluation of WxSiyOz and WOx glad thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering at glancing angle. Their electrochemical properties were assessed by the analysis of cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry measurements in 0.1 M HClO4, whereas their optical properties were determined by studying their transmission and absorption spectra under operation conditions. Both types of thin films presented outstanding electrochromic properties characterized by a fast response, a high coloration and a complete reversibility after more than one thousand cycles.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1166/nnl.2013.1449
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribological properties of surface-modified Pd nanoparticles for electrical contacts
Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JCWear, 297 (2013) 943-951 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2012.11.009
Abstract
A fully comprehensive study of the tribological behavior of palladium nanoparticles (Pd NPs) capped by tetrabutylammonium chains using a ball-on-disk tribometer under different conditions of applied load, concentration, tribometer motion, linear speed and nature of the counterface is revised. A low concentration of NPs (2 wt%) in tetrabutylammonium acetate was found sufficient to improve the tribological properties due to the formation of a protective transfer film (TF) comprised of metallic Pd. The increase of the applied load (up to 20 N, 1.82 GPa of contact pressure) confirmed the excellent extreme-pressure behavior avoiding the counterfaces from severe wear. After a running-in period whose duration depends on the operating conditions, the TF build-up allows to maintain a low contact electrical resistance through the contact (<0.1 kΩ) during the entire test. When the Pd NPs are used with ceramic counterfaces, the nanoparticles increase the load-bearing capabilities and performance of the base without forming TF, likely by mixed or boundary lubrication and healing effects. Finally, the Pd NPs are demonstrated to be useful as a thin solid lubricant film in reciprocating motion yielding a comparable tribological behavior. Hence, the presented surface Pd NPs can be very helpful to extend life of sliding components due to their high strength resistance providing a gateway to electrical conduction as well.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2012.11.009
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Reverse osmosis membranes oxidation by hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide: spectroscopic techniques vs. Fujiwara test
Sandin, R; Ferrero, E; Repolles, C; Navea, S; Bacardit, J; Espinos, JP; Malfeito, JJDesalination and water treatment, 51 (2013) 318-327 DOI: 10.1080/19443994.2012.700010
Abstract
The aim of this work was the study of degradation of a commercial polyamide membrane by two commonly employed oxidants for disinfection in seawater desalination, hypochlorite, and chlorine dioxide. A conventional reverse osmosis (RO) membrane is a thin film composite membrane composed of three different layers, a polyester support web, a microporous polysulfone interlayer, and a thin cross-linked polyamide barrier layer on the top surface, which is the active layer of the RO membrane. The degree of membrane degradation in seawater was evaluated in terms of decline in membrane performance calculated from permeability and salt rejection. In order to establish a relationship between the hydraulic properties and spectroscopic data, infrared and X-ray photoemission techniques (ATR-FTIR and XPS) were employed. The obtained results were compared with the Fujiwara test which is usually performed in membrane autopsies to check the degradation of polyamides with halogens. The chemical degradation of the surface active layer was analyzed using infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) by monitoring the changes in the characteristic infrared bands of the polyamide. It is possible to calculate the transmittance bands ratio between peak at 1540 cm(-1) (due to amide II) and peak at 1585 cm(-1) (due to the polysulfone layer) in order to get the comparison of the degraded membranes with a virgin membrane. The amide II band was selected to evaluate the degradation process, because it is the first band that reduces its transmittance value when the degradation process begins. Once the ratio is obtained for the degraded membrane and considering the value obtained from the virgin membrane as the reference point, a new index is calculated named as degradation index. The higher the parameter is, the greater the chemical attacks the polyamide layer. X-ray spectroscopy (XPS) measures the elemental composition and the chemical state of the elements that exist in the surface of a solid. Evaluation of the binding energy is possible to determine if the halogens are attached to the polyamide structure. It was concluded in this work that both spectroscopic techniques ATR-FTIR and XPS could detect the membrane degradation process earlier than Fujiwara test.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1080/19443994.2012.700010
Colour and ultrasound propagation speed changes by different ageing of freezing/thawing and cooling/heating in granitic materials
Inigo, AC; Garcia-Talegon, J; Vicente-Tavera, S; Martin-Gonzalez, S; Casado-Marin, S; Vargas-Munoz, M; Perez-Rodriguez, JLCold Regions Science and Technology, 85 (2013) 71-78 DOI: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2012.08.004
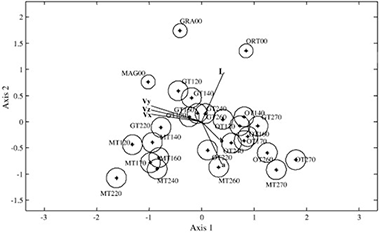
Abstract
In the present work we determined the chromatic coordinates (L*, a*, b*) and ultrasound propagation speeds on the three spatial planes (Vx, Vy, Vz) of three ornamental granites (Aqueduct of Segovia, Spain) before, during, and after being subjected to 70 cycles of two types of accelerated ageing (typical of cold regions): a) freezing/thawing and cooling/heating (T1), and b) freezing/thawing and cooling/heating + salt crystallization (T2). A multivariate technique (Canonical Biplot) was applied to the data obtained, with the observation of significant variations between the two types of accelerated artificial ageing as compared with those obtained in quarry rock in the three chromatic coordinates (L*, a*, b*). With regard to the ultrasound propagation speed, we only detected differences in the results of the T2 artificial ageing treatment with respect to those of quarry rock. This fact is confirmed by the estimated data of resistance to compression.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2012.08.004
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of Sb2S3 and Bi2S3 nanoparticles
Dutkova, E; Takacs, L; Sayagues, MJ; Balaz, P; Kovac, J; Satka, AChemical Engineering Science, 85 (2013) 25-29 DOI: 10.1016/j.ces.2012.02.028
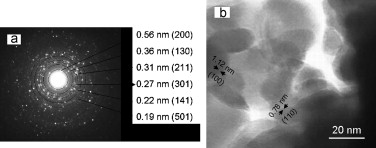
Abstract
The mechanochemical synthesis of Sb2S3 and Bi2S3 nanoparticles has been studied, starting from the corresponding metals and sulfur and using high-energy mechanochemical processing in a planetary laboratory mill. XRD, specific surface area measurement, SEM and TEM (HRTEM) with ED were used for the characterization of the nanoparticles. The XRD patterns confirmed the production of Sb2S3 (JCPDS 42–1393, orthorhombic) and Bi2S3 (JCPDS 17–320, orthorhombic) nanopowders. The transformation is about three times faster in the Bi–S than in the Sb–S system. The kinetics of the reaction has been determined from XRD line intensities. The grain size is about 30 nm for Sb2S3 and 24 nm for Bi2S3. The particles are highly agglomerated due to their nanometer size consequent large specific surface area. Unlike more conventional methods, mechanochemical synthesis is a simple and fast alternative for the preparation of these nanopowders that can be carried out at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ces.2012.02.028
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the milling parameters on the mechanical work intensity in planetary mills
Gotor, FJ; Achimovicova, M; Real, C; Balaz, PPowder Technology, 233 (2013) 1-7 DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.08.031
Abstract
The formation of ZnSe via a mechanically-induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) from a Zn/Se mixture showed that only size reduction and mixing of the reactants without product formation occurred during the induction period prior to ignition. Therefore, all mechanical energy supplied by the planetary mill during this time, called the ignition time (tig), was used exclusively in the activation of the reactants. This system was chosen to study the dependence of tig on the main parameters characterising the milling intensity of planetary mills. The variation of the ignition time with the process conditions reflected changes in the mechanical dose rate of the planetary mill. A direct relationship between the inverse of the ignition time and the power of the planetary mill was established, which allows the validation of theoretical models proposed in the literature for the energy transfer in milling devices and the comparison of milling equipment efficiencies.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.08.031
- ‹ previous
- 28 of 37
- next ›














