Scientific Papers in SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the milling parameters on the mechanical work intensity in planetary mills
Gotor, FJ; Achimovicova, M; Real, C; Balaz, PPowder Technology, 233 (2013) 1-7 DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.08.031
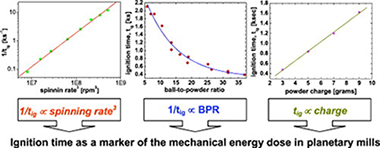
Abstract
The formation of ZnSe via a mechanically-induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) from a Zn/Se mixture showed that only size reduction and mixing of the reactants without product formation occurred during the induction period prior to ignition. Therefore, all mechanical energy supplied by the planetary mill during this time, called the ignition time (tig), was used exclusively in the activation of the reactants. This system was chosen to study the dependence of tig on the main parameters characterising the milling intensity of planetary mills. The variation of the ignition time with the process conditions reflected changes in the mechanical dose rate of the planetary mill. A direct relationship between the inverse of the ignition time and the power of the planetary mill was established, which allows the validation of theoretical models proposed in the literature for the energy transfer in milling devices and the comparison of milling equipment efficiencies.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.08.031
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Small Pt nanoparticles on the TiO2 (110)–(1 × 2) surface
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Martin-Gago, JA; Lopez, MFSurface Science, 607 (2013) 159-163 DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.08.028
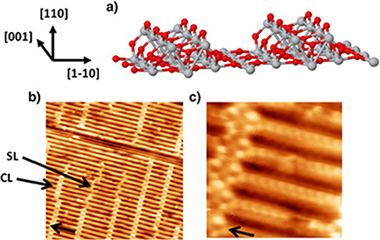
Abstract
Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) has been used to study the initial stages of Pt deposition on the TiO2 (110)–(1 × 2) surface. Experimental STM images recorded for Pt coverage of 0.1 and 0.4 ML, suggest a Volmer-Weber growth. For low coverage and RT deposition, small clusters homogeneously distributed on the surface terraces are observed. However, after annealing at 825 K, material agglomeration, with nucleation mainly at the cross-links, is observed as a consequence of Pt diffusion on the surface. Finally, the structure of small clusters has been determined, in good agreement with previous theoretical calculations.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.08.028
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Gas-phase Photocatalytic Partial Oxidation of Cyclohexane to Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone on Au/TiO2 Photocatalysts
Sannino, D; Vaiano, V; Ciambelli, P; Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JAJournal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 16 (2013) 71-82 DOI: 10.1515/jaots-2013-0107
Abstract
The heterogeneous photocatalytic partial oxidation of cyclohexane in gas-phase as an alternative green process for fine chemicals synthesis was successfully achieved on Au/TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by photodeposition technique. Different gold loadings ranging between 0.5 and 2 wt.% of photodeposited Au on TiO2 synthesized by sol-gel method were obtained by changing the concentration of gold precursor at fixed illumination intensity and time. The cyclohexane partial photoxidation was conducted in a gas-solid photocatalytic fluidized bed reactor at high illumination efficiency. Main observed reaction products were cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone and CO2. The resulting selectivity was dramatically influenced by the gold content. The reaction temperature was a critical parameter to reach the photocatalysts stability, avoiding deactivation phenomena while the tuning of Au content of the photocatalysts, resulted in the promotion of the formation of cyclohexanol or cyclohexanone with high selectivity. In particular, by increasing Au content, the process selectivity is completely reversed, passing from high cyclohexanol selectivity (75%) to high selectivity to cyclohexanone (80%). These promising results evidenced that Au/TiO2 catalysts in the selected operating conditions, are effective materials for the synthesis of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol in gas-phase by photocatalysis, at very low reaction temperatures and without the additional step of catalyst recovering needed in the liquid partial oxidation of cyclohexane.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1515/jaots-2013-0107
Reactividad de Sólidos
Generalized master plots as a straightforward approach for determining the kinetic model: The case of cellulose pyrolysis
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMThermochimica Acta, 552 (2013) 54-59 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2012.11.003
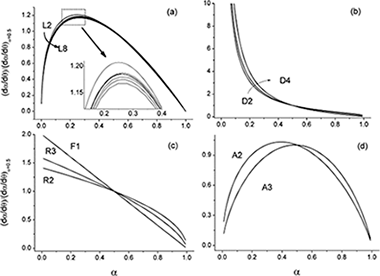
Abstract
The thermal degradation of cellulose is a complex reaction and, despite the large amount of work by many investigators during the last decades, the actual understanding of the thermal decomposition kinetics is still very limited. Thus, while several mechanisms have been proposed to describe the process, the real model has not yet been clearly identified. In this paper, a set of experimental curves recorded under different heating schedules, i.e., linear heating rate, isothermal and constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA), has been analyzed using isoconversional and master plots methodology to discriminate the kinetic model followed by the reaction.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2012.11.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and functionalization of biocompatible Tb:CePO4 nanophosphors with spindle-like shape
Rodriguez-Liviano, S; Aparicio, FJ; Becerro, AI; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cantelar, E; Rivera, S; Hernandez, Y; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MJournal of Nanoparticle Research 15 (2013) 15:1402 DOI: 10.1007/s11051-012-1402-7
Abstract
Monoclinic Tb:CePO4 nanophosphors with a spindle-like morphology and tailored size (in the nanometer and micrometer range) have been prepared through a very simple procedure, which consists of aging, at low temperature (120 °C), ethylene glycol solutions containing only cerium and terbium acetylacetonates and phosphoric acid, not requiring the addition of surfactants or capping agents. The influence of the heating mode (conventional convection oven or microwave oven) and the Tb doping level on the luminescent, structural and morphological features of the precipitated nanoparticles have also been analyzed. This study showed that microwave-assisted heating resulted in an important beneficial effect on the luminescent properties of these nanophosphors. Finally, a procedure for the functionalization of the Tb:CePO4 nanoparticles with aspartic-dextran is also reported. The functionalized nanospindles presented negligible toxicity for Verocells, which along with theirs excellent luminescent properties, make them suitable for biomedical applications.
January, 2013 · DOI: 10.1007/s11051-012-1402-7
2012
2012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Chemical–physical characterization of isolated plant cuticles subjected to low-dose γ-irradiation
Heredia-Guerrero, Jose A; de Lara, Rocio; Dominguez, Eva; Heredia, Antonio; Benavente, Juana; Benitez, Jose JChemistry and physics of lipids, 165 (2012) 803-808 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2012.10.003
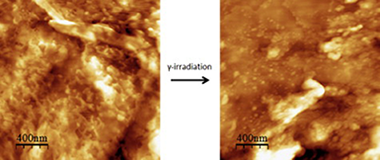
Abstract
Isolated tomato fruit cuticles were subjected to low dose (80 Gy) γ-irradiation, as a potential methodology to prevent harvested fruit and vegetables spoilage. Both irradiated and non-irradiated samples have been morphologically and chemically characterized by scanning electron (SEM), atomic force (AFM), attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) and X-ray photoelectron (XPS) spectroscopies. Additionally, electrochemical measurements comprising membrane potential and diffusive permeability were carried out to detect modifications in transport properties of the cuticle as the fruit primary protective membrane. It has been found that low dose γ-irradiation causes some textural changes on the surface but no significant chemical modification. Texture modification is found to be due to a partial removal of outermost (epicuticular) waxes which is accompanied by mild changes of electrochemical parameters such as the membrane fixed charge, cation transport number and salt permeability. The modification of such parameters indicates a slight reduction of the barrier properties of the cuticle upon low dose γ-irradiation.
December, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2012.10.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
XPS and AES analyses of cerium conversion coatings generated on AA5083 by thermal activation
Sanchez-Amaya, JM; Blanco, G; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Bethencourt, M; Botana, FJSurface and Coatings Technology, 213 (2012) 105-116 DOI:
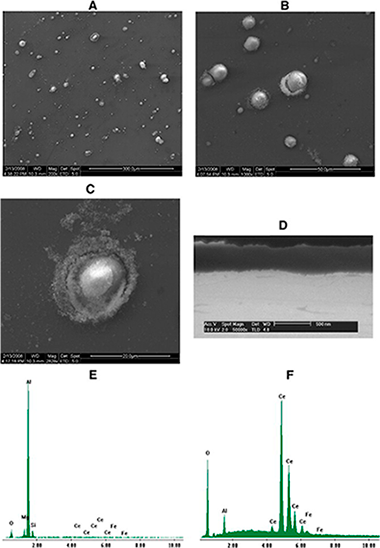
Abstract
This paper describes the deep analysis of cerium conversion coatings developed with thermal activation on AA5083 under optimum processing conditions. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), electron dispersive spectroscopy (EDX), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) were employed to study these layers. Ar+ sputtering was also employed to analyse the coatings' core. Although conversion coatings based on Ce salts have been widely characterised in the literature for different aluminium alloys, the coatings developed with thermal activation on Al–Mg alloys have not been previously investigated with these techniques. SEM/EDX studies have demonstrated the existence of a heterogeneous layer formed by a film of aluminium oxide/hydroxide on the matrix as well as a series of dispersed islands of cerium deposited on the cathodic intermetallics. These results have been further confirmed by means of XPS. The XPS and AES results revealed that the outer layer comprises a mixture coating of Ce3 + (70%) and Ce4 + (30%) compounds. Although only Ce3 + compounds were detected at the inner part of the coating, possible reduction of Ce(IV) to Ce(III) due to the Ar+ beam could not be discarded. Obtained results allowed authors to confirm that the cerium conversion coatings developed have a similar structure to those previously reported for other aluminium alloys.
December, 2012 · DOI:
Reactividad de Sólidos
Bulk TiCxN1−x–15%Co cermets obtained by direct spark plasma sintering of mechanochemical synthesized powders
Borrell, A; Salvador, MD; Rocha, VG; Fernandez, A; Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJMaterials Research Bulletin, 47 (2012) 4487-4490 DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.09.066
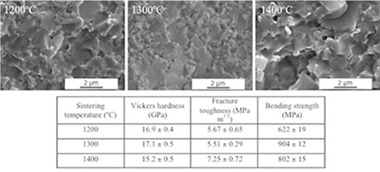
Abstract
TiCxN1−x–15 wt.%Co cermets were obtained by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) and sintered by spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique at different temperatures (1200–1400 °C) for 1 min in vacuum under a uniaxial load of 80 MPa. The evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties was investigated. SPS allowed high densification with limited grain growth at a relatively low temperature. Material sintered at 1300 °C showed a good combination of mechanical properties with Vickers hardness of 17.1 ± 0.5 GPa, fracture toughness of 5.51 ± 0.29 MPa m1/2 and bending strength of 904 ± 12 MPa. Lower sintering temperature resulted in a decrease in bending strength due to poor cohesion between the ceramic and binder phases. An increase in sintering temperature would allow tailoring the cermet microstructure and, therefore, adjusting the Vickers hardness/fracture toughness relation.
December, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.09.066
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Nanoporous silica microparticle interaction with toll-like receptor agonists in macrophages
Cejudo-Guillen, M; Ramiro-Gutierrez, M L; Labrador-Garrido, A; Diaz-Cuenca, A; Pozo, DActa Biomaterialia, 8 (2012) 4295-4303 DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.07.026
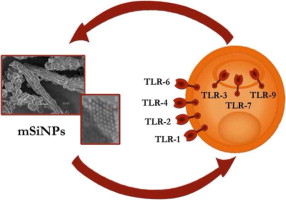
Abstract
Nanoporous silica microparticles (NSiO2-MP) are considered to be potential drug delivery systems and scaffolding platforms in tissue engineering. However, few biocompatibility studies regarding NSiO2-MP interaction with the immune system have been reported. Toll-like receptors (TLR) are involved in host defence as well as autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. The results show that NSiO2-MP up to 100 μg ml−1 do not affect macrophage cell viability after 24 h cell culture. Moreover, NSiO2-MP do not compromise the cell viability of TLR-activated Raw 264.7 cells, for either cell surface TLR (TLR1/TLR2/TLR4/TLR6) or endocytic compartment TLR (TLR3/TLR7/TLR9). Furthermore, Raw 264.7 cells do not respond to NSiO2-MP exposure in terms of IL-6 or IL-10 secretion. NSiO2-MP co-treatment in the presence of TLR ligands does not impair or enhance the secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 or the regulatory cytokine IL-10. Thus, NSiO2-MP do not affect macrophage polarization towards a pro-inflammatory or immunosuppressive status, representing added value in terms of biocompatibility compared with other SiO2-based micro- and nanoparticles.
December, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.07.026
Reactividad de Sólidos
Quantum-Mechanical Study on the Aquaions and Hydrolyzed Species of Po(IV), Te(IV), and Bi(III) in Water
Ayala, Regla; Manuel Martinez, Jose; Pappalardo, Rafael R.; Sanchez Marcos, EnriqueJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 116 (2012) 14903-14914 DOI: 10.1021/jp309439f
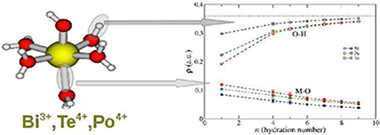
Abstract
A systematic study of [M(H2O)n(OH)m]q+ complexes of Te(IV) and Bi(III) in solution has been undertaken by means of quantum mechanical calculations. The results have been compared with previous information obtained for the same type of Po(IV) complexes ( J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 487) to get insight into the similarities and differences among them from a theoretical view. The evolution of the coordination number (n + m) with the degree of hydrolysis (m) for the stable species shows a systematic decrease regardless the ion. A general behavior on the M–O distances when passing from the gas phase to solution, represented by the polarizable continuum model (PCM), is also observed: RM–O values corresponding to water molecules decrease, while those of the hydroxyl groups slightly increase. The hydration numbers of aquaions are between 8 and 9 for the three cations, whereas hydrolyzed species behave differently for Te(IV) and Po(IV) than for Bi(III), which shows a stronger trend to dehydrate with the hydrolysis. On the basis of the semicontinuum solvation model, the hydration Gibbs energies are −800 (exptl −834 kcal/mol), −1580 and −1490 kcal/mol for Bi(III), Te(IV), and Po(IV), respectively. Wave function analysis of M–O and O–H bonds along the complexes has been carried out by means of quantum theory of atoms in molecule (QTAIM). Values of electron density and its Laplacian at bond critical points show different behaviors among the cations in aquaions. An interesting conclusion of the QTAIM analysis is that the prospection of the water O–H bond is more sensitive than the M–O bond to the ion interaction. A global comparison of cation properties in solution supplies a picture where the Po(IV) behavior is between those of Te(IV) and Bi(III), but closer to the first one.
December, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp309439f
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Hydrogenation of 2,2,2-trifluoroacetophenone: Molecular insight into the role of solvent in enantioselection
Rosa Pereñiguez; Gianluca Santarossa; Tamas Mallat; Alfons BaikerJournal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 365 (2012) 39-49 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2012.08.006
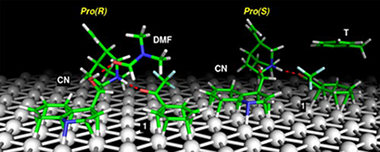
Abstract
The unique solvent effect in the enantioselective hydrogenation of α-fluorinated ketones has been investigated in ten different solvents using the hydrogenation of 2,2,2-trifluoroacetophenone (1) on cinchonine (CN)-modified Pt/Al2O3 as a model reaction. Application of strongly basic solvents – but also increasing hydrogen pressure or conversion – inverted the sense of enantiodifferentiation from (S)-alcohol (expected enantiomer based on the stereochemistry of CN) to (R)-alcohol. The known formation of hemiketals was the origin of the inversion in alcohols. Considering only the non-reacting solvents and low conversions at low pressures, the best correlation was established between the enantiomeric excess and the solvent basicity represented by the H-bond acceptor ability (β). In contrast to former proposals, solvent acidity (α) did not play a significant role. The experimental results are validated by theoretical calculations. The docking of 1 to CN has been investigated in the absence of solvent and also in the presence of toluene and dimethyl formamide. Several competing docking complexes have been isolated that can coexist on the metal surface. Detailed analyses of these complexes show that their stabilities depend on the formation of enantiospecific local interactions between 1, CN, and the platinum surface. The presence of solvent interferes with these interactions, affecting the relative stability of the docking complexes. A correlation between the solvent-induced interactions at molecular level and changes in enantioselectivity is suggested.
December, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2012.08.006
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
New insights into the synergistic effect in bimetallic-boron catalysts for hydrogen generation: The Co–Ru–B system as a case study
Arzac, G. M.; Rojas, T. C.; Fernandez, A.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 128 (2012) 39-47 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.013
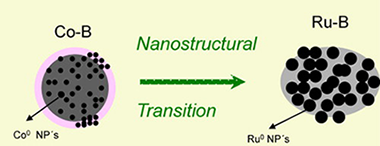
Abstract
Catalysed sodium borohydride hydrolysis is a high-potential method to produce hydrogen for portable applications. Co–B catalysts are the most chosen because they are easily prepared, cheap and efficient. The addition of small amounts of Ru produces a significant enhancement in catalytic activity.
In the present work a series of Co–Ru–B catalysts with variable Ru content was prepared, isolated and characterized. The comprehension of the synergistic effect was achieved trough the incorporation of the nanostructural dimension to the study of surface and bulk chemical states of the involved atoms along the series. It was found that up to 70% (of total metal) atomic content of Ru the catalysts can be considered isostructural to the single Co–B catalyst in the nanoscale. A structural transition occurs in the case of the pure Ru–B material to produce a boron deficient material with higher nanoparticle size. This structural transition together with Co segregation and Ru dispersion play a key role when explaining a [OH−] dependent effect.
The inexistence of borate layers in Ru rich catalysts is suggestive in the research for non deactivating catalysts.
November, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.013
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Preparation of nanostructured nickel aluminate spinel powder from spent NiO/Al2O3 catalyst by mechano-chemical synthesis
Nazemi, M. K.; Sheibani, S.; Rashchi, F.; Gonzalez-DelaCruz, V. M.; Caballero, A.Advanced Powder Technology, 23 (2012) 833-838 DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2011.11.004
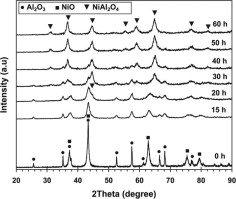
Abstract
In this paper, the possibility of mechano-chemical synthesis, as a single step process for preparation of nanostructured nickel aluminate spinel powder from NiO/Al2O3 spent catalyst was investigated. Powder samples were characterized in terms of composition, morphology, structure, particle size and surface area using complementary techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), differential thermal analysis (DTA) and volumetric adsorption of nitrogen. It was found that formation of spinel was possible after 60 h of milling with no heat treatment. Additionally, influence of mechanical activation on the heat treatment temperature was discussed. It was observed that heat treatment of 15 h milled sample at 1100 °C is enough to produce nickel aluminate spinel. A product of direct mechanical milling showed higher value of surface area (42.3 m2/g) and smaller crystallite size (12 nm) as compared to the heat treated product.
November, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2011.11.004
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Ethanol partial photoxidation on Pt/TiO2 catalysts as green route for acetaldehyde synthesis
Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Vaiano, V; Ciambelli, P; Sannino, DCatalysis Today, 196 (2012) 101-109 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.02.033
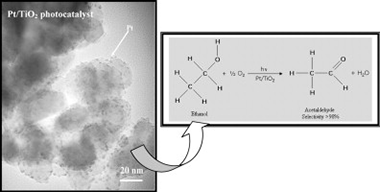
Abstract
Heterogeneous photocatalytic partial oxidation of ethanol was studied over different Pt/TiO2 as an alternative green process for acetaldehyde production.
The catalysts were synthesized through the photodeposition of Pt over sol–gel TiO2 with platinum loads of 0.5 and 1 wt.%. The effect of some experimental conditions during photodeposition, such as deposition time and Pt loading, was investigated. A short deposition time at 0.5 wt.% Pt nominal loading led to small average particle size of platinum (2–3 nm) homogeneously distributed all over the TiO2 surface.
Ethanol partial oxidation was tested in a gas–solid photocatalytic fluidized bed reactor at high illumination efficiency, using different reaction temperatures. Activity results have been correlated with characterization results of the different samples. Platinized samples prepared with short deposition times showed high conversion levels and high selectivity to acetaldehyde. Materials prepared at longer times, 120 min, showed selectivities >98%, although with lower ethanol conversion.
Sample with 1 wt.% Pt loading prepared with 15 min deposition time combined a good compromise between a relevant ethanol conversion and a very high selectivity to acetaldehyde at a selected reaction temperature of 80 °C, with an acetaldehyde yield higher than 80%, which make of this catalyst a good candidate for acetaldehyde production by photocatalysis.
November, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.02.033
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Selective photooxidation of alcohols as test reaction for photocatalytic activity
Lopez-Tenllado, F. J.; Marinas, A.; Urbano, F. J.; Colmenares, J. C.; Hidalgo, M. C.; Marinas, J. M.; Moreno, J. M.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 128 (2012) 150-158 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.015
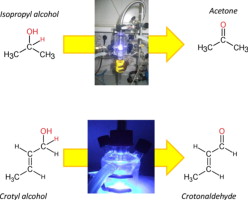
Abstract
Twenty-four different titania-based systems synthesized through the sol–gel process varying the precursor (titanium isopropoxide or tetrachloride) and/or the ageing conditions (magnetic stirring, ultrasounds, microwave or reflux) were tested for liquid-phase selective photooxidation of 2-butenol (crotyl alcohol) to 2-butenal (crotonaldehyde) and gas-phase selective photooxidation of 2-propanol to acetone. To the best of our knowledge, the former process is suggested for the first time as test reaction for photocatalytic activity. Interestingly, both test reactions (despite having very different reactant/catalyst ratio and contact times) showed quite similar results in terms of influence of the precursor (titanium isopropoxide leading to better results than titanium tetrachloride) and the metals (the presence of iron, palladium or zinc being detrimental to activity whereas zirconium and especially gold improved the results as compared to pure titania). To our mind, these results give validity to both processes as test reactions for a fast screening of catalysts for photocatalytic tranformations. Finally, some gold-containing solids even improved photocatalytic activity of Degussa P25.
November, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.015
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effect of ytterbium doping on the microstructure and plastic deformation of BaCeO3 perovskite oxide
Jimenez-Melendo, M; Vaquero-Aguilar, C; Huaman-Mamani, FAFuel Processing Technology, 103 (2012) 146-150 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.10.005
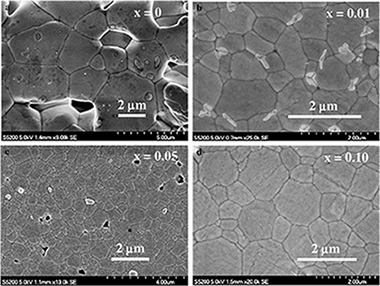
Abstract
Trivalent cation-doped barium cerate perovskites are attractive materials for clean-energy applications, in particular solid oxide fuel cells, due to their singular proton conductivity in wet environments. Furthermore, these devices operate at high temperatures, where creep and other deformation processes determine the lifetime and overall performance. In this work, the structural and microstructural characteristics of undoped and ytterbium-doped (1 to 10 at.%) BaCeO 3 polycrystals produced by solid state reaction have been investigated. A single orthorhombic perovskite phase was found after sintering in air at 1500 °C for 10 h. The microstructure shows a complex evolution with doping: the average grain size firstly decreases with increasing Yb content up to 5 at.%, and then increases with further Yb additions. The high-temperature mechanical properties have been studied in compression between 1100 and 1250 °C in air at constant initial strain rate. The creep strength increases with increasing Yb content. Extended steady states of deformation were attained at lower strain rates and higher temperatures when increasing doping amount.
November, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.10.005
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold supported on pillared clays for CO oxidation reaction: Effect of the clay aggregate size
Alvarez, A; Moreno, S; Molina, R; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Clay Science, 69 (2012) 22-29 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2012.07.008
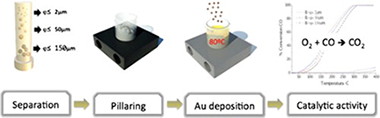
Abstract
A series of 1% m/m gold particles supported on Fe, Ce and Al pillared bentonite (from Valle del Cauca, Colombia) and clay “M64” (from Tolima, Colombia) using three different fractions of aggregate sizes (≤ 2 μm, ≤ 50 μm, and ≤ 150 μm) were characterized by particle size measurements, X-ray diffraction, transmission electronic microscopy (TEM), SBET and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) techniques. The materials tested with CO oxidation. The separation yield for each fraction depended on the type of clay. Whatever the clay or the aggregate size, the pillaring process was successfully carried out, introducing Fe, Ce and Al pillars and increasing the microporosity and the specific surface area of the material. Gold particles presented a homogenous distribution of 2–3 nm on the pillared bentonite, and of about 10 nm on the pillared clay M64. The aggregate size slightly influenced the amount of deposited gold particles and their size. All gold catalysts were active in CO oxidation, the activity depending on the nature of the clay as well as the gold loading and average gold particle size but not on the aggregate size.
November, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2012.07.008
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of PVP in magnetic properties of NiSn nanoparticles prepared by polyol method
Bobadilla, LF; Garcia, C; Delgado, JJ; Sanz, O; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 324 (2012) 4011-4018 DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.07.005

Abstract
The influence of PVP on the magnetic properties of NiSn nanoparticles prepared by polyol method has been studied. NiSn nanoparticles exhibit superparamagnetic behavior although there is a ferromagnetic contribution due to particles agglomerated below the blocking temperature. The particle size is controlled by the addiction of PVP in varying amounts. The addition of PVP also favours the particles isolation, narrow the particle size distribution and decrease the interparticle interaction strength increasing the superparamagnetic contribution.
November, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.07.005
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructural and high-temperature mechanical characteristics of nickel oxide/zirconia composites for solid oxide fuel cells
Oliva-Ramirez, M.; Huaman-Mamani, F. A.; Jimenez-Melendo, M.Fuel Processing Technology, 103 (2012) 45-50 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.09.013

Abstract
NiO/8YSZ (8 mol% Y 2O 3-stabilized ZrO 2) composites with different NiO contents (10, 20 and 40 mol%) have been fabricated by a conventional route of mechanical mixing of NiO and 8YSZ powders and sintering at 1500 °C for 10 h in air. The resulting microstructures have been characterized by electron microscopy. In 10 and 20 mol% NiO/8YSZ, the composite is formed by isolated NiO particles surrounded by zirconia matrix grains; this phase is interconnected in the 40 mol% NiO/8YSZ composite. Mechanical tests at constant strain rate and at constant load were conducted on these materials at temperatures of up to 1350 °C. Different behaviors were found depending on the percolation of the NiO phase. Microstructural observations after deformation are essential to understand the overall mechanical behavior of the composites.
November, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.09.013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity of SiC/Si ecoceramics prepared from sapele wood biocarbon
Parfen'eva, LS; Orlova, TS; Smirnov, BI; Smirnov, IA; Misiorek, H; Mucha, J; Jezowski, A; Pardo, AG; Rico, JRPhysics of the Solid State, 54 (2012) 2132-2141 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783412100289
Abstract
Samples of β-SiC/Si ecoceramics with a silicon concentration of ∼21 vol % have been prepared using a series of consecutive procedures (carbonization of sapele wood biocarbon, synthesis of high-porosity biocarbon with channel-type pores, infiltration of molten silicon into empty channels of the biocarbon, formation of β-SiC, and retention of residual silicon in channels of β-SiC). The electrical resistivity ρ and thermal conductivity κ of the β-SiC/Si ecoceramic samples have been measured in the temperature range 5–300 K. The values of ρ Si chan(T) and κ Si chan(T) have been determined for silicon Sichan located in β-SiC channels of the synthesized β-SiC/Si ecoceramics. Based on the performed analysis of the obtained results, the concentration of charge carriers (holes) in Sichan has been estimated as p ∼ 1019 cm−3. The factors that can be responsible for such a high value of p have been discussed. The prospects for practical application of β-SiC/Si ecoceramics have been considered.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783412100289
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Creep strength of nickel oxide/zirconia composites under different environmental atmospheres
M. Jiménez-Melendo; F.A. Huamán-MamaniSolid State Ionics, 225 (2012) 471-475 DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2012.02.011
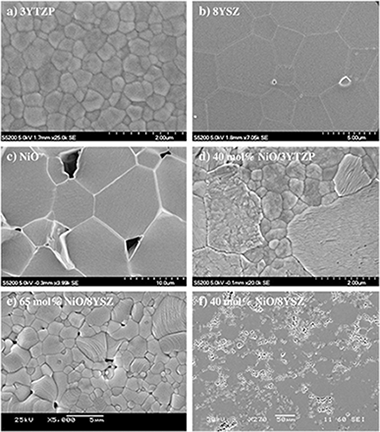
Abstract
NiO/8YSZ (8 mol% Y2O3-stabilized cubic ZrO2) and NiO/3YTZP (3 mol% Y2O3-stabilized tetragonal ZrO2) composites with different NiO contents have been fabricated by a conventional route of mechanical mixing of NiO and zirconia powders and sintering at 1500 °C for 10 h in air. The resulting microstructures have been characterized by electron microscopy. The composites show a duplex microstructure formed by equiaxed grains of NiO and ZrO2, without any intermediate phase. Compressive mechanical tests at constant strain rate were carried out at temperatures between 1150 and 1350 °C under different environments: air, inert (Ar) and reducing (5% H2/95% Ar) atmospheres. The overall creep behavior of the composites is essentially controlled by the zirconia matrix, due to the softness of the NiO phase in the experimental conditions used in this study. The creep strength is not affected by oxygen partial pressure. However, a large decrease in creep resistance under reducing conditions was observed in samples submitted to in situ redox cycling.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2012.02.011
Materiales Coloidales
Revealing Structural Detail in the High Temperature La2Si2O7–Y2Si2O7 Phase Diagram by Synchrotron Powder Diffraction and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Allix, M; Florian, P; Suchomel, MR; Becerro, AIJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 21523-21535 DOI: 10.1021/jp305777m
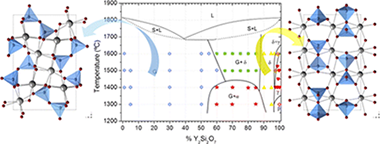
Abstract
High resolution synchrotron powder XRD, 89Y CPMG NMR, and 139La MAS NMR spectroscopy have been applied to eventually draw the phase diagram of the La2Si2O7–Y2Si2O7 system. The diagram presents a solid solubility region of G-(La,Y)2Si2O7, which extends to the La0.9Y1.1Si2O7 composition at any temperature of this study. Compositions richer in Y show two-phase domains, with G + α at T < 1450 °C and G + δ at T > 1450 °C. The Y-rich extreme is more complex, showing two solid solution regions of δ- and γ-(La,Y)2Si2O7 polymorphs which appear with increasing Y content, respectively. It is interesting to note that the La for Y substitution mechanism in the G-(La,Y)2Si2O7 polymorph is not homogeneous, but a preferential occupation of Y for the RE2 site is observed. Finally, the 89Y and 139La isotropic chemical shift values in G-(La,Y)2Si2O7 have been described here for the first time and assigned to the different RE crystallographic sites of the unit cell.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp305777m
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
High-temperature plastic deformation mechanisms of ytterbium-doped barium cerate proton conductor
M. Jiménez-MelendoSolid State Ionics, 225 (2012) 286-290 DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2012.03.031
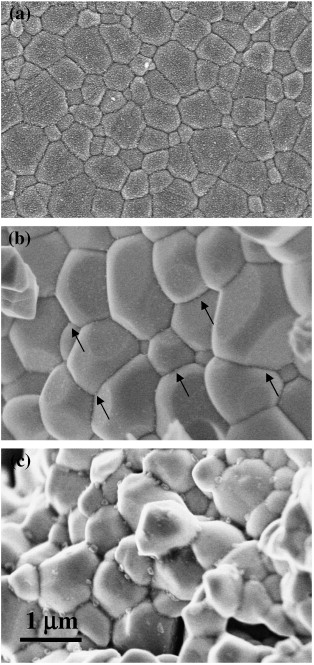
Abstract
The enhanced proton conductivity exhibited by trivalent cation-doped barium cerate perovskites makes these materials excellent candidates for electrochemical applications, in particular as electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells. These devices operate at elevated temperatures, where creep and other deformation processes influence the overall efficiency and lifetime. In this work, the high-temperature plastic deformation mechanisms of fine-grained 5 at.% Yb-doped BaCeO3 polycrystals produced by conventional solid-state reaction has been investigated by means of compressive tests at constant load between 1150 and 1250 °C in air. The creep curves show an unusual sigmoidal behavior, followed by extended steady states of deformation. Grain boundary sliding is the main deformation mechanism, characterized by a stress exponent n of 2, as found in other fine-grained superplastic ceramics and metals.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2012.03.031
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Deactivation, reactivation and memory effect on Co–B catalyst for sodium borohydride hydrolysis operating in high conversion conditions
Arzac, GM; Hufschmidt, D; De Haro, MCJ; Fernandez, A; Sarmiento, B; Jimenez, MA; Jimenez, MMInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 37 (2012) 14373-14381 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.06.117
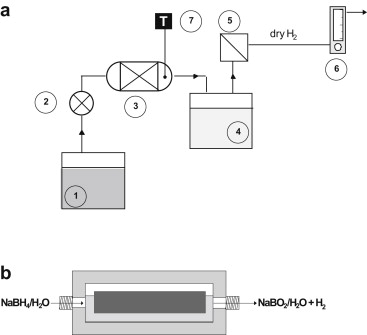
Abstract
A system with a continuous reactor to produce hydrogen by sodium borohydride hydrolysis was designed and built. The purpose was to test a supported Co–B catalyst durability upon cycling and long life experiments in high conversion conditions. A Stainless Steel monolith was built and calcined to improve adherence. For comparison a Ru–B catalyst was tested upon cycling. Both Co–B and Ru–B catalysts are durable during 6 cycles and then deactivate. A known reactivation procedure has proven to be more effective for the Co–B than for the Ru–B catalyst. This is related to stronger adsorption of B–O based compounds on the Co–B catalyst which is reversible upon acid washing. For the Ru–B catalyst deactivation may be more related to particle agglomeration than to the adsorption of B–O based species. The continuous system enlarges the catalysts durability because of the continuous borate elimination at elevated temperatures.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.06.117
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Characterization of Mesoporous Thin Films by Specular Reflectance Porosimetry
Hidalgo, N; Lopez-Lopez, C; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HLangmuir, 28 (2012) 13777-13782 DOI: 10.1021/la3025793
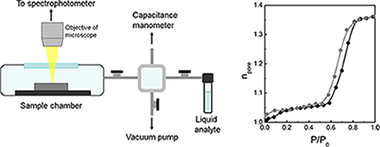
Abstract
The pore size distribution of mesoporous thin films is herein investigated through a reliable and versatile technique coined specular reflectance porosimetry. This method is based on the analysis of the gradual shift of the optical response of a porous slab measured in quasi-normal reflection mode that occurs as the vapor pressure of a volatile liquid varies in a closed chamber. The fitting of the spectra collected at each vapor pressure is employed to calculate the volume of solvent contained in the interstitial sites and thus to obtain adsorption–desorption isotherms from which the pore size distribution and internal and external specific surface areas are extracted. This technique requires only a microscope operating in the visible range attached to a spectrophotometre. Its suitability to analyze films deposited onto arbitrary substrates, one of the main limitations of currently employed ellipsometric porosimetry and quartz balance techniques, is demonstrated. Two standard mesoporous materials, supramolecularly templated mesostructured films and packed nanoparticle layers, are employed to prove the concept proposed herein.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/la3025793
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Chemical and microstructural characterization of (Y or Zr)-doped CrAlN coatings
Rojas, T. C.; El Mrabet, S.; Dominguez-Meister, S.; Brizuela, M.; Garcia-Luis, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, J. C.Surface and Coatings Technology, 211 (2012) 104-110 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.07.071
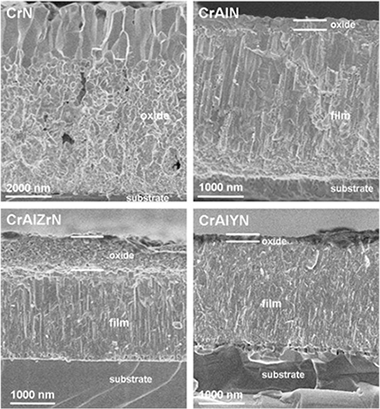
Abstract
Magnetron sputtered chromium aluminium nitride films are excellent candidates for advanced machining and protection for high temperature applications. In this work CrAlN-based coatings including Y or Zr as dopants (≈ 2 at.%) are deposited by d.c. reactive magnetron sputtering on silicon substrates using metallic targets and Ar/N2 mixtures. The hardness properties are found in the range of 22–33 GPa with H/E ratios close to 0.1. The influence of the dopant element in terms of oxidation resistance after heating in air at 1000 °C is studied by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy (X-SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX). The microstructure and chemical bonding are investigated using a transmission electron microscope (TEM) and electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) respectively. The improvement in oxidation resistance as compared to pure CrN coating is manifested in the formation of a Al-rich outer layer that protects the underneath coating from oxygen diffusion. The best performance obtained with the CrAlYN film is investigated by in situ annealing of this sample inside the TEM in order to gain knowledge about the structural and chemical transformations induced during heating.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.07.071
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
DLC coatings for UHMWPE: Relationship between bacterial adherence and surface properties
Del Prado, G; Terriza, A; Ortiz-Perez, A; Molina-Manso, D; Mahillo, I; Yubero, F; Puertolas, JA; Manrubia-Cobo, M; Barrena, EG; Esteban, JJournal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 100A (2012) 2813-2820 DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.34220
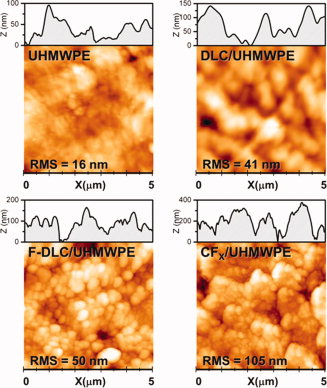
Abstract
Development of intrinsically antibacterial surfaces is of key importance in the context of prostheses used in orthopedic surgery. This work presents a thorough study of several plasma-based coatings that may be used with this functionality: diamond-like carbon (DLC), fluorine-doped DLC (F-DLC), and a high-fluorine-content-carbon-fluor polymer (CFX). The coatings were obtained by a radio-frequency plasma-assisted deposition on ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) samples and physicochemical properties of the coated surfaces were correlated with their antibacterial performance against collection and clinical Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis strains. The fluorine content and the relative amount of CC and CF bonds were controlled by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and hydrophobicity and surface tension by contact angle measurements. Surface roughness was studied by Atomic Force Microscopy. Additional nanoidentation studies were performed for DLC and F-DLC coatings. Unpaired t test and regression linear models evaluated the adherence of S. aureus and S. epidermidis on raw and coated UHMWPE samples. Comparing with UHMWPE, DLC/UHMWPE was the least adherent surface with independence of the bacterial species, finding significant reductions (p ≤ 0.001) for nine staphylococci strains. Bacterial adherence was also significantly reduced in F-DLC/ UHMWPE and CFx/UHMWPE for six strains. © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 100A:2813–2820, 2012.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.34220
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Effect of deposition of silver on structural characteristics and photoactivity of TiO2-based photocatalysts
Melian, EP; Diaz, OG; Rodriguez, JMD; Colon, G; Navio, JA; Macias, M; Pena, JPApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 127 (2012) 112-120 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.08.007
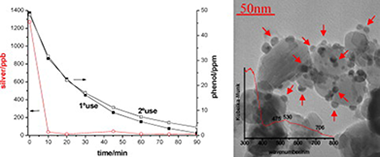
Abstract
The homemade bare TiO2 photocatalyst obtained in a previous work was modified with nanosized silver particles by liquid impregnation and photodeposition methods to obtain different noble metal loadings (0.3–1 at.%). Characterization of the synthesized photocatalysts was carried out by the BET method, XPS, TEM, SEM-EDX, XRD and diffuse reflectance measurements. Photocatalytic activity of these silver-deposited TiO2 nanoparticles was tested by photocatalytic degradation of phenol as a reference model representing phenolic pollutants. The noble metal content on the TiO2 surface affected the efficiency of the photocatalytic process, and the photocatalytic activity of noble metal-modified TiO2 was considerably better than that of bare TiO2. Phenol decomposition rate was higher with TiO2 modified by the liquid impregnation method than with TiO2 modified by the photodeposition method.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.08.007
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline BiSe, Bi 2Se 3 semiconductors
Achimovicova, M; Gotor, FJ; Real, C; Daneu, NJournal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 23 (2012) 1844-1850 DOI: 10.1007/s10854-012-0672-2
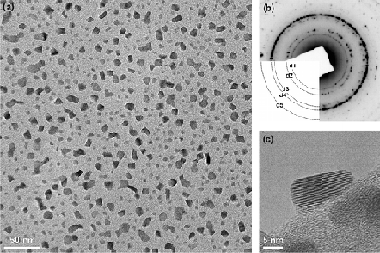
Abstract
Mechanochemical synthesis of bismuth selenides (BiSe, Bi 2Se 3) was performed by high-energy milling of bismuth and selenium powders in a planetary ball mill. The particle size distribution and the specific surface area of Bi/Se and 2Bi/3Se powder mixtures were analysed at increasing milling time. The products were characterized by X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry and transmission electron microscopy. The presence of bismuth selenide phases was observed after only 1 min of milling and full conversion into hexagonal BiSe phase (nevskite) and rhombohedral Bi 2Se 3 phase (paraguanajuatite) was reached after 10 min of milling. The nanocrystalline nature of both mechanochemically synthesised bismuth selenides was confirmed and their optical band gap energies were obtained on the basis of the recorded absorption spectra in UV-Vis spectral region.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1007/s10854-012-0672-2
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Selective Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds by Spectral Imaging of Porphyrin Derivatives Bound to TiO2 Porous Films
Roales, J; Pedrosa, JM; Castillero, P; Cano, M; Richardson, TH; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4 (2012) 5147-5154 DOI: 10.1021/am301069
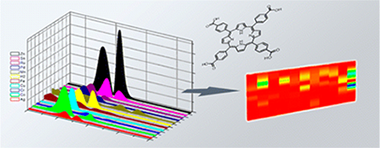
Abstract
In this work, the carboxylic acid derivatives of a free-base porphyrin, 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)-21H,23H-porphyrin, and 10 of its metal derivatives (TCPPs) have been used for optical gas sensing. For this purpose, microstructured columnar TiO2 thin films prepared by GAPVD (glancing angle physical vapor deposition) have been used as host materials for the porphyrins as they are non–dispersive and porous, allowing their use for UV–visible spectroscopy and gas sensing. The chemical binding between the dye molecules and the TiO2 has been studied through infrared spectroscopy, and the obtained spectral changes have been found to be compatible with chelating and/or bidentate binding modes of the carboxylate groups on the TiO2 surface. When hosted in the film, the UV–visible spectra of the porphyrins featured a blue shift and broadening of the Soret band with respect to the solution, which has been attributed to the formation of π–π aggregates between porphyrin molecules. The composite porphyrin/TiO2 films obtained from each of the 11 porphyrins have been exposed to 12 different volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and their respective gas–sensitive properties have been analyzed as a function of the spectral changes in their Soret band region in the presence of the analytes. The set of composite films has shown high selectivity to the analyzed volatile compounds. For each analyte, an innovative way of showing the different responses has been developed. By means of this procedure, an imagelike recognition pattern has been obtained, which allows an easy identification of every compound. The kinetics of the exposure to several analytes showed a fast, reversible and reproducible response, with response times of a few seconds, which has been attributed to both the sensitivity of the porphyrins and the high porosity of the TiO2 films. Also, increasing concentrations of the analytes resulted in an increase in the magnitude of the response, indicating that the sensor behavior is also concentration-dependent.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/am301069
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microcalorimetric study of the annealing hardening mechanism of a Cu–2.8Ni–1.4Si (at%) alloy
Donoso, E; Espinoza, R; Dianez, MJ; Criado, JMMaterials Science and Engineering: A, 556 (2012) 612-616 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.07.035
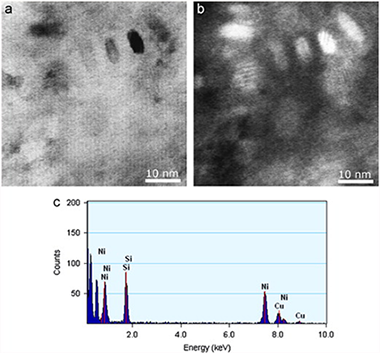
Abstract
The precipitation processes in a Cu–2.8 at% Ni–1.4 at% Si alloy were studied using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and microhardeness measurements. The analysis of the calorimetric curves from room temperature to 900 K shows the presence of one exothermic reaction attributed to the formation of δ-Ni2Si particles in the copper matrix that was confirmed by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and EDS microanalysis. The activation energies calculated for the precipitation of δ-Ni2Si was lower than the ones corresponding to diffusion of nickel and silicon in copper. A correlation between of microhardness of the alloy and the formation of δ-Ni2Si particles has been found.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.07.035
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Following the Wetting of One-Dimensional Photoactive Surfaces
Macias-Montero, M; Borras, A; Alvarez, R; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARLangmuir, 28 (2012) 15047-15055 DOI: 10.1021/la3028918
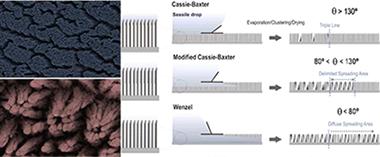
Abstract
This article aims toward a full description of the wetting conversion from superhydrophobicity to superhydrophilicity under illumination with UV light of high-density ZnO nanorods surfaces by (i) following the evolution of the clusters and superstructures formed by the nanocarpet effect as a function of the water contact angle (WCA); (ii) characterization of the superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic states with an environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM); and (iii) using the nanocarpet effect as a footprint of both local and apparent water contact angles. Thus, the main objective of the article is to provide a general vision of the wettability of 1D photoactive surfaces. In parallel, the nanocarpet (NC) formation by clustering of vertically aligned ZnO nanorods (NR) when water is dripped on their surface and then dried is studied for the first time by taking advantage of the possibility of tuning the surface water contact angle of the ZnO NR structure under UV preillumination. As a result, we demonstrate the feasibility of controlling the size and other morphological characteristics of the NCs. Moreover, a strong anisotropic wetting behavior, characterized by a Δθ = θ – θ = 30°, is shown on an asymmetrically aligned NC surface resulting from arrays of tilted NRs. The study of the condensation/evaporation of water on/from an as-prepared (superhydrophobic) or a preilluminated (superhydrophilic) NR surface examined by an environmental scanning electron microscope has evidenced the formation of supported water droplets with polygonal shapes in the first case and the complete filling of the inter-NR space in the latter. The long-term stability of the NC clusters has been utilized as a footprint to track the penetration depth of water within the inter-NR space in the three borderline regions of water droplets. This analysis has shown that for moderately hydrophobic surfaces (i.e., water contact angles lower than 130°) water droplets do not present a well-defined borderline trace but a spreading region where water penetrates differently with the NR interspace. The transition from a Cassie–Baxter to a modified Cassie–Baxter to finish in a Wenzel wetting state is found on these surfaces depending on the UV preillumination time and is explained with a model where water interaction with the NR units is the critical factor determining the macroscopic wetting behavior of these surfaces.
October, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/la3028918
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructure and high-temperature mechanical behavior of melt-growth Al2O3/Er3Al5O12/ZrO2 ternary eutectic composites
Huaman-Mamani, FA; Jimenez-Melendo, M; Mesa, MC; Oliete, PBJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 536 (2012) S527-S531 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.01.105
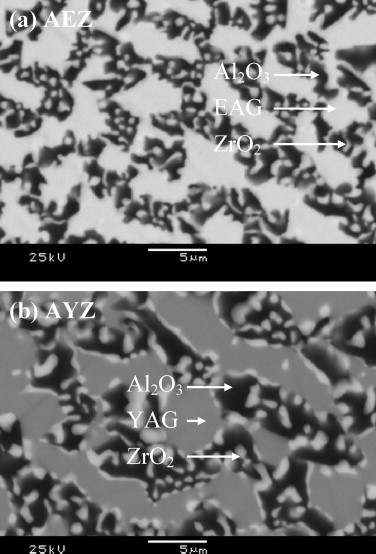
Abstract
The microstructural and high-temperature mechanical characteristics of directionally solidified rods of Al2O3–Er3Al5O12–ZrO2 ternary eutectic oxides processed by the laser-heated floating zone method at different growth rates have been investigated. The eutectic microstructure displayed an entangled three-dimensional network of Al2O3 and Er3Al5O12 phases of similar sizes, elongated along the growth direction; the minority zirconia phase formed small fibers into the alumina phase. The interphase spacing is reduced with increasing solidification rate, changing about 2 μm down to 200 nm. These microstructural features are essentially the same exhibited by Al2O3–Y3Al5O12–ZrO2 composites processed by the same technique. Compressive deformation tests performed at 1400 °C at constant strain rate showed that the creep resistance decreased when increasing the growth rate due to the refinement of the microstructure.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.01.105
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
High-temperature mechanical characteristics of NiO/3YTZP composites
Jimenez-Melendo, M; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Huaman-Mamani, FAJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 536 (2012) S472-S476 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.11.040
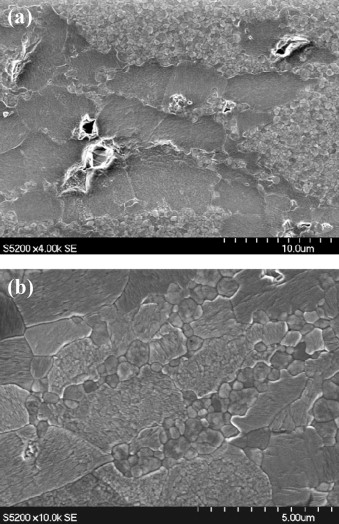
Abstract
NiO/3YTZP (3 mol% Y2O3-stabilized tetragonal ZrO2) composites with 40 mol% NiO (26 vol% NiO) have been fabricated by mechanical mixing of NiO and 3YTZP powders and sintering at 1500 °C for 10 h in air. The resulting microstructures have been characterized by electron microscopy. Compressive mechanical tests at constant strain rate were conducted on these materials at temperatures between 1150 and 1350 °C in air. The σ–ɛ curves display extended secondary creep regimes without signals of macroscopic failure. The composite creep behavior is characterized by a stress exponent n = 2 and an activation energy for flow Q = 490 kJ/mol. The overall creep behavior of the composites is essentially controlled by the zirconia matrix, due to the softness of the NiO phase in the experimental conditions used in this study.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.11.040
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Making Photo-selective TiO2 Materials by Cation–Anion Codoping: From Structure and Electronic Properties to Photoactivity
Marquez, AM; Plata, JJ; Ortega, Y; Sanz, JF; Colon, G; Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, MJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 18759-18767 DOI: 10.1021/jp3045143
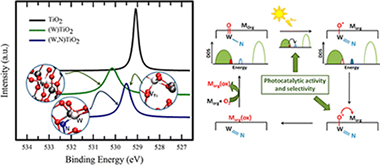
Abstract
Photoselective oxidation yielding high-added value chemicals appears as a green novel process with potential to be explored. In this study we combine spectroscopic XPS (N 1s and O 1s) and multiwavelength Raman data with density functional theory calculations to explore the structural and electronic properties of W,N-codoped TiO2 anatase surfaces and interpret the outstanding photocatalytic properties of such a system in partial oxidation reactions. Theoretical calculations allow us to examine several substitutional and N-interstitial configurations at different concentrations of the W,N dopants (similar to those experimentally found), as well as their interaction with structural point defects: Ti cation vacant sites and surface wolframyl species that are required to compensate the extra charge of the W6+ and N-containing anions. The joint use of theoretical and experimental XPS and Raman tools renders key structural information of W,N-codoped microcrystalline TiO2 solids. The incorporation of N at substitutional positions of anatase with the concomitant presence of W═O species introduces localized states in the band gap, a result that is critical in interpreting the chemical behavior of the solids. The combination of the electronic and geometric structural information leads to a simple mechanism that rationalizes the experimentally observed photoactivity and selectivity in partial oxidation reactions.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp3045143
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Characterization of highly crosslinked polyethylenes by colorimetry
Martinez-Morlanes, MJ; Terriza, A; Yubero, F; Puertolas, JAPolymer Testing, 31 (2012) 841-847 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.06.005
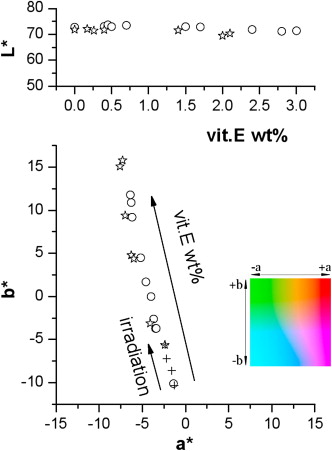
Abstract
Colour analysis appears to be a robust technique for characterizing vitamin E doping and gamma irradiation of medical grade polyethylene samples. The analysis procedure described in this paper is of great interest because it can easily distinguish between polyethylene samples with differences in vitamin E (α-tocopherol) doping of about 0.1 wt% and gamma irradiation doses of 30 kGy. It is found that the colour differences (with respect to untreated samples) induced by gamma irradiation and/or vitamin E doping add-up linearly. This method for detecting the presence of vitamin E is fast, simple and non-destructive.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.06.005
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Phase composition and tribomechanical properties of Ti-B-C nanocomposite coatings prepared by magnetron sputtering
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Abad, MD; Justo, A; Gago, R; Endrino, JL; Garcia-Luis, A; Brizuela, MJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 45 (2012) 375401 DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/45/37/375401
Abstract
Protective nanocomposite coatings based on hard ceramic phases (TiC, TiB2) combined with amorphous carbon (a-C) are of interest because of their adequate balance between mechanical and tribological performances. In this work, Ti–B–C nanocomposite coatings were prepared by co-sputtering of graphite and TiB2 targets. Varying the discharge power ratio applied to the graphite and TiB2 targets from 0 to 2, the a-C content in the coatings could be tuned from 0 to 60%, as observed by means of Raman and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The microstructural characterization demonstrated a progressive decrease in crystallinity from an initial nanocrystalline (nc) TiB2-like structure to a distorted TiBxCy ternary compound with increasing C concentration. X-ray absorption near-edge structure measurements on the B K-edge helped to determine a hexagonal arrangement around the B atoms in the ternary TiBxCy phase. A fitting analysis of the C 1s XPS peak allowed us to evaluate the relative amount of a-C and TiBxCy components. A drastic change in hardness (from 52 to 13 GPa) and friction coefficient values (from 0.8 to 0.2) is noticed when moving from nc-TiB2 to TiBC/a-C nanocomposites. The fraction of a-C necessary to decrease the friction below 0.2 was found to be 45%. Raman observation of the wear tracks determined the presence of disordered sp2-bonded carbon phase associated with the diminution of the friction level.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/45/37/375401
Reactividad de Sólidos - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Obituary: Prof. Andrés Ortega
Luque, JMC; Martinez, FJG; Azana, MM; Perez, CRThermochimica Acta, 543 (2012) 318-319 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2012.06.001

Abstract
Prof. Andrés Ortega passed away on last January after a painful and long illness. He was Professor of Inorganic Chemistry at the University of Seville (Spain) and was an outstanding researcher in the field of solid state reaction kinetics, an area to which he devoted his entire career since 1983, when he submitted his PhD thesis entitled ‘Critical study of non-isothermal methods for the kinetic analysis of solid-state reactions’. During his post doc stage and collaboration with Prof. Jean Rouquerol, his interest was raised by the Sample Controlled Thermal Analysis (SCTA) technique and its application to the kinetic study of solid state reactions, this latter one developed in Seville along with Prof. José Manuel Criado. A paper from this period should be highlighted: ‘Correlation between the shape of controlled-rate thermal analysis curves and the kinetics of solid-state reactions’ [Thermochimica Acta 157 (1990) 171], the most cited one in his research career. Most of his scientific production was published in Thermochimica Acta and in the Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. A tireless professional, he remained active until a few weeks before dying. Being seriously ill he developed a method for the kinetic analysis of reactions with variable activation energies that notably simplifies the previous one proposed by Vyazovkin. The results were published in Thermochimica Acta under the title ‘A simple and precise linear integral method for isoconversional data’ [Thermochim. Acta 474 (2008) 81]. The high number of citations of this article – according to the ISI WEB of Knowledge – in spite of the short time elapsed since it was published reveals its impact within the scientific community.
He was also very much involved in teaching duties, developing new subjects and applying new teaching methodologies. He chaired two important academic positions at the University of Seville related to his works on teaching and educational sciences, as Director of the Institute of Educational Science and as Chairman of the Committee on Education of the University.
Though he sometimes appeared to be reserved, Andrés was a kind man, always ready to help in any problem that was presented to him. With a critical attitude and many cultural interests, he had a vast knowledge and a great ability to interpret the most diverse questions, frequently presenting a reasoning alternative to those commonly established. This was a continuous source of enrichment for both his friends and colleagues, who never will forget him.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2012.06.001
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Wall slip phenomena in concentrated ionic liquid-based magnetorheological fluids
Gomez-Ramirez, A; Lopez-Lopez, MT; Gonzalez-Caballero, F; Duran, JDGRheologica Acta, 51 (2012) 793-803 DOI: 10.1007/s00397-012-0639-5
Abstract
Ionic liquids (ILs) have been recently proposed as carrier for magnetorheological (MR) fluids. Their special properties, such as very low vapor pressure and high thermal stability, make ILs highly suitable dispersion media to increase the broad range of technological applications that magnetorheological fluids already have. It has been just reported that using ILs as carriers in MR fluids an improvement in the colloidal stability and suspension redispersibility is obtained. In this work, the magnetorheological behavior of highly concentrated suspensions in ILs is studied. Two kinds of suspensions were analyzed: using an ionic liquid of low conductivity and a mineral oil as carriers. In both cases, silica-coated iron microparticles were used as solid phase, being the solid volume concentration of 50% vol. A complete magnetorheological analysis focused on the wall slip phenomenon was performed. Steady-state and oscillatory experiments were carried out. In order to study wall slip effects, all experiments were performed with a plate-plate system, using both smooth and rough measuring surfaces. A significant effect of wall slip was observed when the experiments were performed using smooth surfaces. The novelty of this paper is mainly based on (1) the use of an ionic liquid as carrier to prepare magnetic suspensions, and (2) the analysis of wall slip phenomena in MR fluids with a particle content close to the maximum packing fraction.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1007/s00397-012-0639-5
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effects of the presence of Fe(0) on the sorption of lanthanum and lutetium mixtures in smectites
Galunin, E; Alba, MD; Santos, MJ; Vidal, MApplied Clay Science, 65-66 (2012) 162-172 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2012.06.011
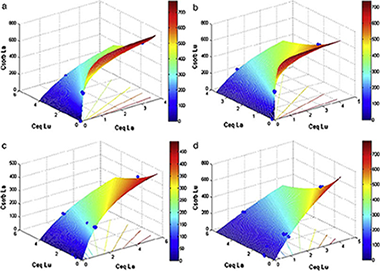
Abstract
The sorption of La and Lu mixtures was examined in two bentonites after incubation for three months at 20 and 80 °C with Fe(0), as a laboratory approach to evaluate the effects of waste canister corrosion in a deep repository on the performance of clay engineered barriers. The sorption/desorption parameters were determined from batch tests in two ionic media: deionized water and, to consider the additional effect of cement leachates, 0.02 mol L− 1 Ca.
Results from XRD analyses showed the formation of crystalline FeO(OH), goethite, in a few samples and the degradation of the bentonites due to Fe(0) oxidation during incubation. Moreover, the EDX spectra showed that the lanthanides were sorbed primarily at smectite sites, although sorption onto goethite was also observed, whereas Fe(0) particles did not contribute to lanthanide sorption. The formation of goethite could explain the high Kd values measured in a few scenarios (e.g., those with single solutions or mixtures with the lowest initial concentration of the competitive lanthanide in which high affinity sites governed sorption), with up to 3-fold increases over the values obtained without Fe incubation. However, at higher lanthanide concentration, Kd values decreased or remained constant compared to the samples without Fe incubation, which could be explained by bentonite degradation. In the Ca medium, as much as 5 times lower Kd values were obtained, because of the competitive effect of the Ca ions, especially for Lu in the MX80 bentonite. This indicated that the small number of high affinity sites had been diminished.
The sorption data were satisfactorily fitted to a two-solute Langmuir model. In addition, Kd values correlated well with desorption data, which showed that the larger the decrease in Kd, the larger the increase in sorption reversibility. It is suggested that corrosion products from the metal canister might compromise the long-term radionuclide retention of the clay-engineered barriers.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2012.06.011
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
A CFD study on the effect of the characteristic dimension of catalytic wall microreactors
Arzamendi, G; Uriz, I; Navajas, A; Dieguez, PM; Gandia, LM; Montes, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAAlChE Journal, 58 (2012) 2785-2797 DOI: 10.1002/aic.12790
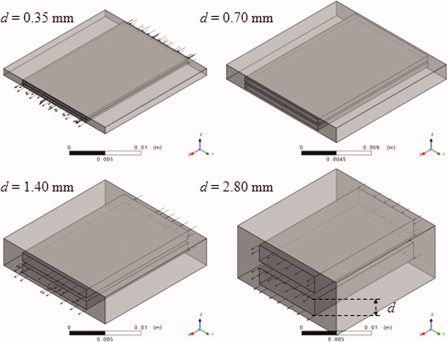
Abstract
A three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics study of the steam methane reforming (SMR) in microreactors is presented. Emphasis has been made on investigating the effects of the characteristic dimension (d: 0.35, 0.70, 1.40, and 2.80 mm) on the performance of two microreactor geometries: square microchannels and microslits. Results have shown that for both geometries the SMR conversion decreases markedly as d increases. Conversely, the microchannels provide a methane conversion slightly higher than that of the microslits. The different performance of the microreactors is only partially due to the different surface-to-volume ratio. Pronounced transverse temperature and concentration gradients develop as the characteristic dimension increases especially for microslits in the first half of the reactor. Therefore, external transport limitations can affect the performance of microreactors for SMR, although the characteristic dimensions are of the order of very few millimeters.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1002/aic.12790
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical interference for the matching of the external and internal quantum efficiencies in organic photovoltaic cells
Betancur, R; Martinez-Otero, A; Elias, X; Romero-Gomez, P; Colodrero, S; Miguez, H; Martorell, JSolar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 104 (2012) 87-91 DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2012.04.047
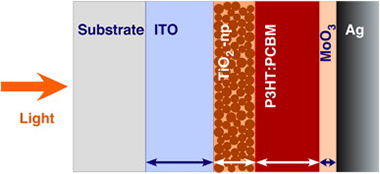
Abstract
We demonstrate experimentally that an appropriate combination of the layer thicknesses in an inverted P3HT:PCBM cell leads to an optical interference such that the EQE amounts to 91% of IQE. We observe that reflectivity between layers is minimized in a wavelength range of more than 100 nm. In that range the EQE closely matches the IQE. The role played by the optical interference in improving the performance of the fabricated solar cells is confirmed by EQE calculated numerically using a model based on the transfer matrix method. Additionally, we observed that a similar cell with an active material 1.7 times thicker exhibited a lower PCE. The poor photon harvesting in the later cell configuration is attributed to an EQE that amounts only to 72% of the IQE.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2012.04.047
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Insights towards the influence of Pt features on the photocatalytic activity improvement of TiO2 by platinisation
Murcia, JJ; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 126 (2012) 76-85 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.07.013
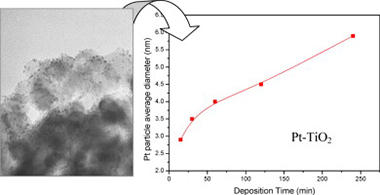
Abstract
The influence of Pt features, such as particle size, dispersion, oxidation state and amount of metal, on the improvement of the photoactivity of TiO2 for phenol and methyl orange degradation was studied.
The size of Pt deposits was precisely controlled by changing deposition time under medium light intensity during the photodeposition, with sizes ranging from 3 to 6 nm. Pt oxidation state was also strongly dependent on the photodeposition time.
Photocatalytic activity results showed that the fraction of metallic platinum (Pt0) was the crucial factor for the improvement of the activity. When the fraction of Pt0 was similar, metal deposit size became the dominant parameter influencing the activity.
The influence of the substrate to be degraded (phenol or methyl orange) was also studied.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.07.013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Critical thickness and nanoporosity of TiO2 optical thin films
Borras, A; Alvarez, R; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Ferrer, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMicroscopy and Microanalysis, 18 (2012) 1-9 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.04.035
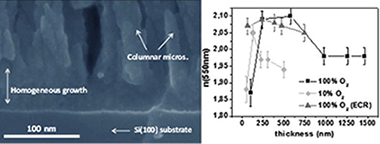
Abstract
This work reports on the porosity and refraction index of TiO2 thin films as a function of the film thickness. Samples were fabricated by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) in a microwave electron cyclotron resonance (MW-ECR) reactor at room temperature using titanium tetra-isopropoxide (MP) as precursor. Experimental parameters such as plasma gas composition (pure oxygen and argon/oxygen mixtures) and pressure (either ECR conditions or "normal" pressure, i.e. 10(-4) or 10(-3) torrs correspondently) were varied. The evolution of the thin film microstructure, porosity and optical properties is critically studied by AFM, SEM, water adsorption isotherms, ellipsometry and UV-Vis transmittance and the existence of a certain critical thickness (t(c)) demonstrated. The porosity of the films with thicknesses ranging from several tens of nanometers up to half a micrometer is evaluated by QCM-isotherms at room temperature. The dependency of this critical thickness with the plasma conditions is evaluated experimental and theoretically. Thus, the microstructure change at t(c) is attributed to a transition from a surface diffused dominated growth mechanism for t < t(c) to another where shadowing is predominant. Dynamic scaling analysis of the two regimes and their Monte Carlo simulation complete the reported study.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.04.035
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Microstructural characterization of hydrophobic Ti1−xAlxN coatings with moth-eye-like surface morphology
Godinho, V; Lopez-Santos, C; Rojas, TC; Philippon, D; de Haro, MCJ; Lucas, S; Fernandez, AJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 536 (2012) S398-S406 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.02.178
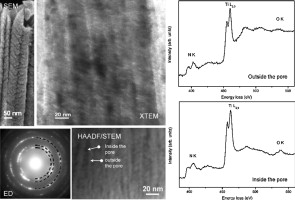
Abstract
Ti1−xAlxN thin films with different Al content were deposited by magnetron sputtering. The combination of electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) was used to evaluate the composition of the coatings. The effect of Al content on the morphology and properties of the coatings was investigated. High resolution electron microscopy and related techniques revealed the formation of a pillared moth-eye-like nanostructure with variable size and distribution of meso- and nano-columns and different degree of open porosity that depends on the Al content on the coating. For low Al content (x ≤ 0.21) c-(Ti,Al)N highly porous columns ending in a sharp pyramidal shape present low reflectivity and high hydrophobicity. While the precipitation of h-AlN phase at the column boundaries for x = 0.71 suppresses the c-(Ti,Al)N columnar growth and produces a smother surface, with higher reflectivity and less hydrophobic character.
September, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.02.178
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructural Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications
A. P. Zaderenkoa1, P. M. Castillo, M. de la Mata, M.J. Sayagués and J. A. SánchezMicroscopy and Microanalysis, 18 (2012) 55-56 DOI: 10.1017/S1431927612012937
Abstract
There is a growing interest in nanoparticles as carriers of chemotherapeutic agents in order to improve their administration and minimize their side effects. Despite the fact that silver nanoparticles can be conjugated to therapeutic agents, offering additionally advantages due their unique and tunable optical properties, few examples have been described yet.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1017/S1431927612012937
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructural Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles for Bioimaging Applications
Zaderenko, AP; Caro, C; de la Mata, M; Sanchez, JA; Sayagues, MJMicroscopy and Microanalysis, 18 (2012) 53-54 DOI: 10.1017/S1431927612012925
Abstract
Silver nanoparticles are emerging as a powerful tool in bioimaging applications owing to their unique plasmonic properties i.e., extremely high molar extinction coefficients, resonant Rayleigh scattering and enhanced local electromagnetic fields. Through the optimization of these properties, by controlling composition, size, shape, and interparticle spacing of nanoparticles and their assemblies, highly enhanced local electromagnetic fields in the vicinity of nanoparticles are achievable giving rise to IR, Raman and fluorescence surface enhanced spectroscopies (SEIRS, SERS and MEF, respectively).
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1017/S1431927612012925
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Charge collection properties of dye-sensitized solar cells based on 1-dimensional TiO2 porous nanostructures and ionic-liquid electrolytes
Gonzalez-Garcia, Lola; Idigoras, Jesus; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Barranco, Angel; Anta, Juan A.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A-Chemistry, 241 (2012) 58-66 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.05.015
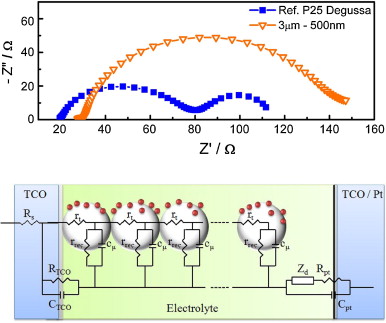
Abstract
Dye solar cells consisting of mesoporous TiO 2 nanocolumnar films sensitized with a highly absorptive indoline dye were studied to estimate the charge collection efficiency provided by porous 1-dimensional (1-D) nanostructures in combination with viscous, fast-recombining electrolytes. The TiO 2 mesoporous nanostructured films were prepared by physical vapor deposition at glancing incidence (GLAD-PVD). Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) in the dark was utilized to extract the transport and recombination properties of the fabricated devices. Due to their high porosity, the TiO 2 nanocolumnar electrodes incorporated a dye amount similar to that admitted by nanoparticulated electrodes with higher thickness. This fact, together with the longer lifetimes of electrons obtained for the GLAD-PVD electrodes, lead to an overall improvement of the charge collection and photovoltaic properties with respect to randomly packed electrodes. Measured diffusion lengths were improved by a factor between 2 and 3 with respect to the disordered nanostructure. The present results demonstrate the capability of partially ordered nanostructures to improve charge collection in devices constructed with fast-recombining electrolytes.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.05.015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Software package to calculate the effects of the core hole and surface excitations on XPS and AES
Tougaard, S; Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis, 44 (2012) 1114-1118 DOI: 10.1002/sia.4855
Abstract
We report on a new software package that allows to calculate the energy loss processes in a photo- and Auger electron spectrum. The calculations are performed within our previously published semiclassical dielectric response model. The model takes into account energy loss, which takes place because of the sudden creation of the static core hole and as the photoelectron travels in the bulk, passes the surface region and continues in the vacuum where it interacts with its image charge before it ends up in the electron spectrometer. It is a one-step model, which includes interference effects between these excitations. The only input in the calculations is the dielectric function of the material. We discuss the capabilities of the software and illustrate some examples of its practical application, including comparison with experimental spectra. We hope the software will be useful for the investigations of fundamental excitation mechanisms in XPS and AES. The software is free for noncommercial use.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1002/sia.4855
Materiales Coloidales
Structural and kinetic study of phase transitions in LaYSi2O7
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Escudero, A; Suchomel, MR; Becerro, AIJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 32 (2012) 2477-2486 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.03.009
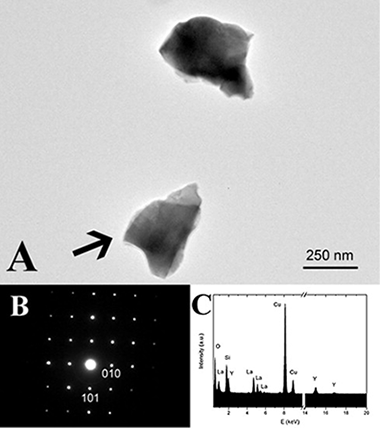
Abstract
Phase transitions in LaYSi 2O 7 have been investigated as a function of temperature using XRD, NMR and TEM. Previously described empirical crystal structure guidelines based on average cation radius in rare-earth RE 2Si 2O 7-type disilicates predict a stable tetragonal A-LaYSi 2O 7 polymorph at temperatures below 1500°C. This study demonstrates that A-LaYSi 2O 7 is not thermodynamically stable at these temperatures and suggests that guidelines based on average cation size do not accurately describe the equilibrium behaviour of this silicate system. The A to G-type polymorph transition is extremely sluggish; complete transformation requires ~250h at 1200°C, and more than 3 weeks of calcination at 1100°C. This observation is important when this type of material is used as environmental barrier coating (EBC) of advanced ceramics. Analysis of XRD and TEM data reveal complete substitution of Y and La on the rare-earth cation sites in both LaYSi 2O 7 polymorphs, but indicate preferential site occupancies in the G-type polymorph.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.03.009
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Introducing structural colour in DSCs by using photonic crystals: interplay between conversion efficiency and optical properties
Colonna, D; Colodrero, S; Lindstrom, H; Di Carlo, A; Miguez, HEnergy & Environmental Science, 5 (2012) 8238-8243 DOI: 10.1039/c2ee02658a
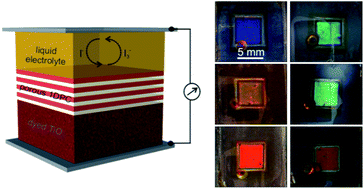
Abstract
Herein we analyze experimentally the effect that introducing highly reflecting photonic crystals, operating at different spectral ranges, has on the conversion efficiency of dye sensitized solar cells. The interplay between structural colour and cell performance is discussed on the basis of the modified spectral response of the photogenerated current observed and the optical characterization of the cells. We demonstrate that, with the approach herein discussed, it is possible to achieve relatively high efficiencies using thin electrodes while preserving transparency. At the same time, the appearance of the device can be controllably modified, which is of relevance for their potential application in building integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) as window modules.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1039/c2ee02658a
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Evidence of upconversion luminescence contribution to the improved photoactivity of erbium doped TiO2 systems
Obregon, S; Colon, GChemical Communications, 48 (2012) 7865-7867 DOI: 10.1039/C2CC33391K
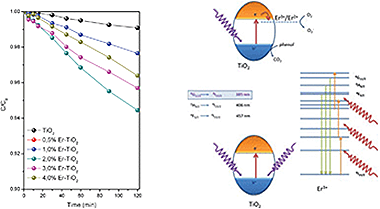
Abstract
Er3+–TiO2 synthesized by a surfactant free hydrothermal method exhibits good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of phenol. The presence of Er3+ does not affect the structural and morphological features of the TiO2 significantly. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with 2 wt% of Er. Different photocatalytic runs indicated that the incorporation of the Er3+ cation would be responsible for the enhanced photocatalytic activity, which participates in different mechanisms under UV and NIR excitation.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1039/C2CC33391K
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermal conductivity of high-porosity heavily doped biomorphic silicon carbide prepared from sapele wood biocarbon
Parfen'eva, LS; Orlova, TS; Smirnov, BI; Smirnov, IA; Misiorek, H; Mucha, J; Jezowski, A; Cabezas-Rodriguez, R; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 54 (2012) 1732-1739 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783412080240
Abstract
The electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity of high-porosity (~52 vol %, channel-type pores) bio-SiC samples prepared from sapele wood biocarbon templates have been measured in the temperature range 5-300 K. An analysis has been made of the obtained results in comparison with the data for bio-SiC samples based on beech and eucalyptus, as well as for polycrystalline β-SiC. The conclusion has been drawn that the electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity of bio-SiC samples based on natural wood are typical of heavily doped polycrystalline β-SiC.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783412080240
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of the active metals on the selective H-2 production in glycerol steam reforming
Araque, M; Martinez, LM; Vargas, JC; Centeno, MA; Roger, ACApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 125 (2012) 556-566 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.06.028
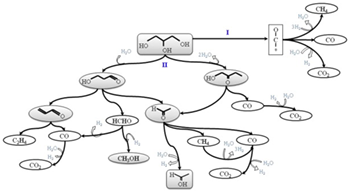
Abstract
The production of hydrogen by glycerol steam reforming was studied using CeZr(Co, CoRh) catalysts. The effect of Co and Rh presence on the properties of the mixed oxides and the effect on the catalytic behavior were considered. The catalysts were characterized before and after testing by XRD, Raman, TPR, H 2-TPD, TPD-TPO and HRTEM. It was observed that the presence of Co allowed the selective H 2 production related with the presence of a metallic phase at the beginning of the reaction. The presence of Rh favored even more the H 2 production and also increased the stability of the catalyst. For CeZrCoRh, the presence of both metals enhanced the catalyst reduction capacity, a characteristic that significantly improved the catalytic behavior for glycerol steam reforming. The selective H 2 production was related to the capacity of the catalyst to activate H 2O under the reaction conditions. The progressive loss of this capacity decreases the production of H 2, and glycerol decomposition is actually favored over glycerol steam reforming. According to the initial distribution of products, and its evolution with time on stream, two main reaction pathways were proposed.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.06.028
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biomimetic mineralization of calcium phosphate on a functionalized porous silicon carbide biomaterial
Dey, A; van den Hoogen, CJ; Rosso, M; Lousberg, N; Hendrix, MMRM; Friedrich, H; Ramirez-Rico, J; Zuilhof, H; de With, G; Sommerdijk, NAJMChemPlusChem, 77 (2012) 694-699 DOI: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cplu.201200118/full
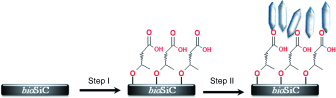
Abstract
Porous biomorphic silicon carbide (bioSiC) is a structurally realistic, high-strength, and biocompatible material which is promising for application in load-bearing implants. The deposition of an osteoconductive coating is essential for further improvement of its integration with the surrounding tissue. A new strategy towards biomimetic calcium phosphate coatings on bioSiC is described. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis shows that using 10-undecenoic acid methyl ester a covalently bound monolayer can be synthesized on the surface of the bioSiC. After hydrolysis it exposes carboxylic acid groups that promote the selective nucleation and growth of a very well-defined crystalline layer of calcium phosphate. The resulting calcium phosphate coating is characterized by X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy techniques. Further, ion beam imaging is employed to quantify the mineral deposition meanwhile, three-dimensional dual-beam imaging (FIB/SEM) is used to visualize the bioSiC/mineral interface. The monolayer is show to actively induce the nucleation of a well-defined and highly crystalline mixed octacalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite (OCP/HAP) coating on implantable bioSiC substrates with complex geometry. The mild biomimetic procedure, in principle, allows for the inclusion of bioactive compounds that aid in tissue regeneration. Moreover, the mixed OCP/HAP phase will have a higher solubility compared to HAP, which, in combination with its porous structure, is expected to render the coating more reabsorbable than standard HAP coatings.
August, 2012 · DOI: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cplu.201200118/full
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of a TiCN–SiC polyhedron and elongated crystals nanopowder at low nitrogen concentration
Engstrom, A; Mouzon, J; Cordoba, JM; Tegman, R; Antti, MLMaterials Letters, 81 (2012) 148-150 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2012.04.071
Abstract
At room temperature diluted TiCl4 and CCl4 were reduced by sodium particles and mixed with a polycarbomethylsilane (PCS) solution to yield a precursor. It was dried and subsequently annealed at 1300 °C, 1400 °C and 1450 °C in a tube furnace using argon with 10 ppm N2. After the 1450 °C annealing a nanocrystalline powder of TiC0.5N0.5–SiC polyhedron and elongated crystals was obtained. At the low nitrogen concentration during annealing a gradual nitration is proposed. It is promoted by carbon gaseous species, precursor oxidation, a sufficient temperature and a summarised nitrogen surplus compared to the titanium and carbon amount.
August, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2012.04.071
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The effect of nickel on alloy microstructure and electrochemical behaviour of AA1050 aluminium alloy in acid and alkaline solutions
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Skeldon, P; Thompson, GE; Smith, GCElectrochimica Acta, 75 (2012) 229-238 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.106
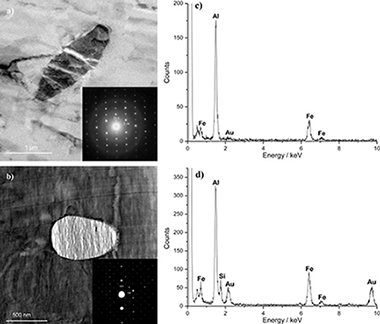
Abstract
The study investigates the influence of nickel and magnesium additions to AA1050 aluminium alloy on the alloy electrochemical behaviour in sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric solutions under conditions relevant to industries that use alkaline etching as a standard surface treatment procedure and to the lithographic and electronic industries where surface convolution is assisted by pitting in hydrochloric acid. Scanning and transmission electron microscopes were used to characterize the intermetallic particles, and scanning Kelvin probe microscopy was utilised in monitoring the surface potential. Nickel is shown to be incorporated into second phase particles, which mostly consisted of Al3Fe and α-(AlFeSi) phases, resulting in enhanced cathodic activity on the aluminium surface. Consequently, the dissolution rates of the superpure aluminium, alloys without nickel addition and alloy with nickel addition are increased respectively in sodium hydroxide, and increased pitting is respectively promoted in hydrochloric acid. In contrast, the addition of magnesium to the alloy had negligible influence on the etching and pitting behaviour.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.106
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical Synthesis and Characterization of II-VI Nanocrystals: Challenge for Cytotoxicity Issues
Balaz, P; Jardin, R; Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Balaz, M; Mojzisova, G; Mojzis, J; Turianicova, E; Fabian, MActa Physica Polonica A, 122 (2012) 224-229 DOI: ---
Abstract
CdSe@ZnS nanocrystals have been prepared by a two-step solid state mechanochemical synthesis. CdSe prepared from elements in the first step is mixed with ZnS synthesized from zinc acetate and sodium sulfide in the second step. The crystallite size of the new type CdSe@ZnS nanocrystals determined by X-ray diffraction Rietveld refined method was 35 nra and 10 Jam for CdSe and ZnS, respectively. Energy dispersive/transmission electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy methods show good crystallinity of the nanoparticles and scanning electron microscopy elemental mapping illustrate consistent distribution of Cd, Se, Zn and S elements in the bulk of samples. UV-VIS spectra show an onset at 320 urn with calculated bandgap 3.85 eV. This absorption arises from the vibration modes of Zn-S bonds. The nanocrystals show the blue shift from the bandgap of bulk ZnS (3.66 eV). The synthesized CdSe@ZnS nanocrystals have been tested for dissolution, cytotoxicity and L-cysteine conjugation. The dissolution of Cd was less than 0.05 mu g mL(-1) (in comparison with 0.8 mu g mL(-1) which was evidenced for CdSe alone). The very low cytotoxic activity for selected cancer cell lines has been evidenced. CdSe@ZnS nanocrystals coated with L-cysteine are water-soluble and have a great potential in biomedical engineering as fluorescent labels.
July, 2012 · DOI: ---
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of nanostructured electrode architecture and semiconductor deposition strategy on the photovoltaic performance of quantum dot sensitized solar cells
Samadpour, M; Gimenez, S; Boix, PP; Shen, Q; Calvo, ME; Taghavinia, N; Zad, AI; Toyoda, T; Miguez, H; Mora-Sero, IElectrochimica Acta, 75 (2012) 139-147 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.087
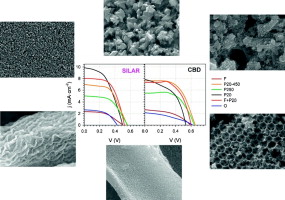
Abstract
Here we analyze the effect of two relevant aspects related to cell preparation on quantum dot sensitized solar cells (QDSCs) performance: the architecture of the TiO 2 nanostructured electrode and the growth method of quantum dots (QD). Particular attention is given to the effect on the photovoltage, V oc, since this parameter conveys the main current limitation of QDSCs. We have analyzed electrodes directly sensitized with CdSe QDs grown by chemical bath deposition (CBD) and successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR). We have carried out a systematic study comprising structural, optical, photophysical and photoelectrochemical characterization in order to correlate the material properties of the photoanodes with the functional performance of the manufactured QDSCs. The results show that the correspondence between photovoltaic conversion efficiency and the surface area of TiO 2 depends on the QDs deposition method. Higher V oc values are systematically obtained for TiO 2 morphologies with decreasing surface area and for cells using CBD growth method. This is systematically correlated to a higher recombination resistance of CBD sensitized electrodes. Electron injection kinetics from QDs into TiO 2 also depends on both the TiO 2 structure and the QDs deposition method, being systematically faster for CBD. Only for electrodes prepared with small TiO 2 nanoparticles SILAR method presents better performance than CBD, indicating that the small pore size disturb the CBD growth method. These results have important implications for the optimization of QDSCs.Elect
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.087
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Novel approaches to flexible visible transparent hybrid films for ultraviolet protection
Calvo, ME; Smirnov, JRC; Miguez, HJournal of Polymer Science Part B-Polymer Physics, 50 (2012) 945-956 DOI: 10.1002/polb.23087
Abstract
Herein, we present an overview of the most recent achievements and innovations regarding the development of flexible visible transparent films for selective ultraviolet (UV) shielding, with focus on those based on hybrid inorganic-organic materials. The main synthetic paths used nowadays to ensure a high degree of protection are reviewed. Polymers containing organic UV absorbing molecules, hybrid mixtures of polymers and nanoparticles, and the recently introduced series of structures displaying structural color, are identified as the three main types of materials used for this purpose. The use of biocompatible and flexible films to achieve spectrally selective UV protection can find applications in a wide diversity of fields such as photo-treatment of skin diseases, food and beverage packing, and storage of cosmetics. © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys, 2012 In this review, the different approaches taken to obtain flexible and transparent films that block ultraviolet radiation based on the use of hybrid materials are covered. The synthetic pathways that lead to films that can shield against UV radiation either by absorption or by interference are described.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1002/polb.23087
- ‹ previous
- 29 of 37
- next ›














