Scientific Papers in SCI
2012
2012
Materiales Coloidales
Aluminum solubility in TiO2 rutile at high pressure and experimental evidence for a CaCl2-structured polymorph
Escudero, A; Langenhorst, F; Muller, WFAmerican Mineralogist, 97 (2012) 1075-1082 DOI: 10.2138/am.2012.4049
Abstract
Aluminum incorporation into TiO 2 has been studied in the TiO 2-Al 2O 3 system as a function of pressure at temperatures of 900 and 1300 °C using commercial Al 2TiO 5 nanopowder as starting material. A new orthorhombic TiO 2 polymorph with the CaCl 2 structure has been observed in the recovered samples synthesized from 4.5 to 7 GPa and 900 °C and from 2.5 to 7 GPa at 1300 °C. The phase transition to the α-PbO 2 type TiO 2 phase takes place between 7 and 10 GPa at both temperatures. Two mechanisms of Al incorporation in TiO 2 rutile have been observed in the recovered samples. The substitution of Ti 4+ by Al 3+ on normal octahedral sites is dominant at lower pressures. High pressure induces the incorporation of Al 3+ into octahedral interstices of the rutile structure, which is responsible for an orthorhombic distortion of the TiO 2 rutile structure and gives rise to a (110) twinned CaCl 2 type structure. This phase is probably a result of temperature quench at high pressure. Aluminum solubility in TiO 2 increases with increasing pressure. TiO 2 is able to accommodate up to 9.8 wt% Al 2O 3 at 7 GPa and 1300 °C. Temperature has a large effect on the aluminum incorporation in TiO 2, especially at higher pressures. High pressure has a strong effect on both the chemistry and the microstructure of Al-doped TiO 2. Enhanced aluminum concentration in TiO 2 rutile as well as TiO 2 grains with a microstructure consisting of twins are a clear indication of high-pressure conditions.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.2138/am.2012.4049
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Ethanol over Au/TiO2 Photocatalysts
Sannino, Diana; Vaiano, Vincenzo; Ciambelli, Paolo; Carmen Hidalgo, M.; Murcia, Julie J.; Antonio Navio, J.Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 15 (2012) 284-293 DOI: ---
Abstract
Au/TiO2 photocatalysts were used in ethanol oxidative dehydrogenation. Catalysts at gold loading ranging between 0.5-2 wt.% were synthesized by photodeposition (using different deposition times: 15 and 120 min) over an own-prepared TiO2 by sol-gel method. For reference purposes, a commercial 1 wt.% Au/TiO2 catalyst (AUROlite (TM), Strem Chemicals) was also tested. Photocatalytic reactions were carried out in a gas-solid photocatalytic fluidized bed reactor. Catalytic activity depends strongly both on Au loading and on the material properties, such as particle size and distribution of metal on titania surface. Acetaldehyde was the main reaction product, with ethylene, crotonaldehyde and CO2 as by-products. An important improvement of TiO2 photoactivity was achieved for the catalyst with 0.5 wt.% gold prepared with 120 min deposition time. For an ethanol inlet concentration of 0.2 vol% at 60 degrees C, the maximum conversion and acetaldehyde selectivity were 82% and 95%, respectively. These values are considerably higher than those obtained over pristine TiO2 and over the commercial catalyst.
July, 2012 · DOI: ---
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
LaNiO3 as a precursor of Ni/La2O3 for CO2 reforming of CH4: Effect of the presence of an amorphous NiO phase
Rosa Pereñiguez , Victor M. Gonzalez-delaCruz, Alfonso Caballero, Juan P. Holgado,Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 123-124 (2012) 324-32 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.044
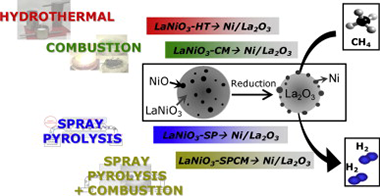
Abstract
The objective of the present work has been the study of the physico-chemical and catalytic properties of Ni/La2O3 catalysts obtained by reduction of four LaNiO3 samples prepared by different methods. The LaNiO3 precursors as well as the resulting Ni/La2O3 catalysts, were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), temperature programmed reduction and oxidation (TPR, TPO). The catalytic performances of these systems for dry reforming of methane (DRM) were also tested. These samples show different physico-chemical properties resulting from the synthesis method used. The XAS and TPR measurements show that in all four LaNiO3 samples there is, in addition of the crystalline LaNiO3 rhombohedrical phase, a significant amount of an amorphous NiO phase, not detectable by XRD but evidenced by XAS. The amount of this NiO amorphous phase seems to play, together with some other microstructural parameters, an important role in the performance of the Ni/La2O3 samples for the DRM reaction.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.044
Reactividad de Sólidos - Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Processing of Swnt-Reinforced Yttria Stabilized Zirconia by Spark Plasma Sintering and Microstructure Characterization
S. de Bernardi-Martín, R. Poyato, Diego Gómez García, Arturo Domínguez-RodríguezJournal of Nano Research, 18-19 (2012) 317-323 DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/JNanoR.18-19.317
Abstract
Single wall carbon nanotube reinforced yttria stabilized zirconia ceramic materials have been obtained by means of spark plasma sintering technique. Single wall carbon nanotubes were treated in an acid solution before mixing with zirconia powders to obtain a uniform distribution of both powders. This method allows obtaining ceramic materials with a grain size between 200 nanometers and 1 micron and with a grain size distribution which depends on processing conditions. This new route opens a new perspective for new ceramic composites tailoring with enhanced mechanical properties as structural materials
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/JNanoR.18-19.317
Reactividad de Sólidos
In Situ Synthesis of Ceramic Composite Materials in the Ti-B-C-N System by a Mechanically Induced Self-Sustaining Reaction
Aviles, MA; Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 95 (2012) 2133-2139 DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05174.x

Abstract
The synthesis of multicomponent ceramic materials in the titanium-diboride-carbide-nitride-carbonitride system by the mechanochemical process known as the mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) was investigated. Ceramic composite powders containing TiB 2and TiC, TiN or TiC xN 1-xwere prepared from a blended mixture of the elements by exploiting the highly exothermic nature of the formation reactions. The synthesis of the composite materials was made possible by the ability of the MSR to simultaneously induce independent self-sustaining reactions, generating a mixture of ceramic phases. The composition of the ceramic composites was designed using the initial atomic ratio of the reactants, and the achieved microstructure was characterized by TiB 2particles in the micrometric range, surrounded by submicrometric and nanometric TiC, TiN, or TiC xN 1-xcrystals.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05174.x
Reactividad de Sólidos
Rapid carbothermic synthesis of silicon carbide nano powders by using microwave heating
Moshtaghioun, BM; Poyato, R; Cumbrera, FL; de Bernardi-Martin, S; Monshi, A; Abbasi, MH; Karimzadeh, F; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 32 (2012) 1787-1794 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.12.021
Abstract
This paper reports an improved procedure for synthesis of silicon carbide nanopowders from silica by carbothermic reduction under fast microwave-induced heating. The powders have been prepared by direct solid-state reaction in a 2.45 GHz microwave field in nitrogen atmosphere after 40 h milling. For the first time, the formation of silicon carbide (beta-SiC) as a major phase can be achieved at 1200 degrees C in 5 min of microwave exposure, resulting in nano sized particles ranging from 10 to 40 nm under optimized synthesis condition. The Rietveld quantitative phase-composition analysis confirmed that the major SiC polytype is cubic SiC (beta-SiC) with 98.5(4) weight fraction and the remained is minor hexagonal SiC polytypic (alpha-SiC) phases. Therefore this method is the most efficient one for SiC powder synthesis in terms of energy and time saving as well as preparation of SiC nano powders.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.12.021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Sub-ambient CO oxidation over mesoporous Co3O4: Effect of morphology on its reduction behavior and catalytic performance
Alvarez, A; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 431 (2012) 9-17 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.04.006
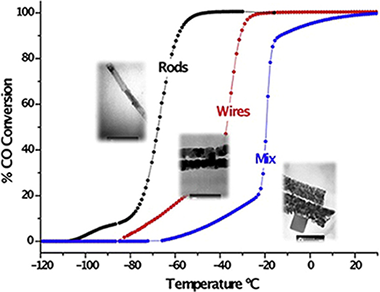
Abstract
The influence of the Co 3O 4 morphology on its redox behavior and catalytic performance in the CO oxidation reaction is studied. Three different Co 3O 4 morphologies were synthesized by precipitation and hydrothermal methods. TEM and SEM observations clearly show the different obtained morphologies: rods, wires and a mixture of plates and cubes. The textural properties depend on the morphology and the redox ones on the particle size. XRD analysis reveals a spinel structure in all solids with a preferential exposition of the [1 1 0] plane in the Co 3O 4 rods sample. This preferential exposition, along with its higher specific surface area provides the rods with more efficient oxygen storage capacity resulting in an excellent catalytic performance compared to the other two morphologies.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.04.006
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the shape of Ni catalysts in the glycerol steam reforming
Bobadilla, L. F.; Alvarez, A.; Dominguez, M. I.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Centeno, M. A.; Montes, M.; Odriozola, J. A.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 123-124 (2012) 379-390 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.05.004
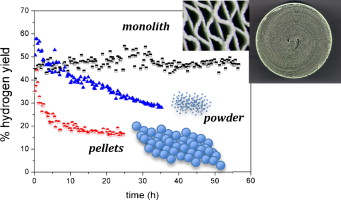
Abstract
Biomass is an alternative to replace the use of fossil fuels. Glycerol, a byproduct in the biodiesel production, can be used for obtaining hydrogen. The most efficient method for obtaining hydrogen from glycerol is the steam reforming (SR). So far all the published papers report the use of conventional catalyst. In this paper, a structured catalyst has been prepared and compared with the conventional ones (powder and spherical pellets). Results show that the structured catalyst (monolith) is more stable as formation of coke was not observed.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.05.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Cu-modified cryptomelane oxide as active catalyst for CO oxidation reactions
Hernandez, Willinton Y.; Centeno, Miguel A.; Ivanova, Svetlana; Eloy, Pierre; Gaigneaux, Eric M.; Odriozola, Jose A.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 123-124 (2012) 27-35 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.024
Abstract
Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves (cryptomelane structure) were synthesized by a solvent-free method and tested in the total oxidation of CO (TOX), and preferential oxidation of CO in presence of hydrogen (PROX). The influence of Cu in the cryptomelane structure was evaluated by several characterization techniques such as: X-ray fluorescence (XRF), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), hydrogen temperature programmed reduction (TPR-H2) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The Cu-modified manganese oxide material (OMS-Cu) showed very high catalytic activity for CO oxidation in comparison to the bare manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve (OMS). The improved catalytic activity observed in OMS-Cu catalyst was associated to a high lattice oxygen mobility and availability due to the formation of Cusingle bondMnsingle bondO bridges. In addition, under PROX reaction conditions the catalytic activity considerably decreases in the presence of 10% (v/v) CO2 in the feed while the same amount of water provokes an improvement in the CO conversion and O2 selectivity.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.024
Reactividad de Sólidos
Absence of the core-rim microstructure in TixTa1-xCyN1-y-based cermets developed from a pre-sintered carbonitride master alloy
Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 33 (2012) 38-43 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2012.02.005
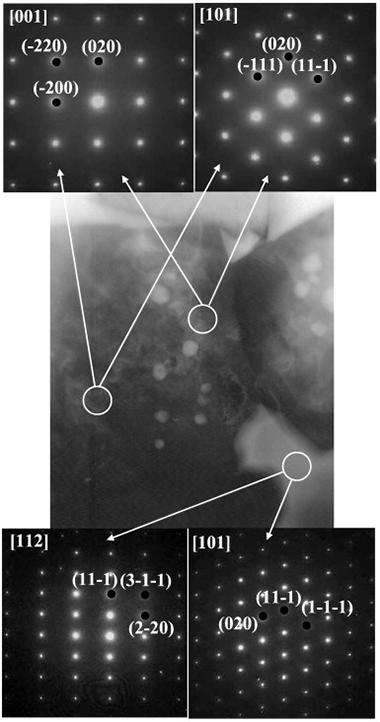
Abstract
(Ti,Ta)(C,N) solid solution-based cermets with cobalt as the binder phase were synthesised by a two-step milling process. The titanium-tantalum carbonitride solid solution (the ceramic phase) was obtained via a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process from stoichiometric elemental Ti, Ta, and graphite powder blends in a nitrogen atmosphere. Elemental Co (the binder phase) was added to the ceramic phase, and the mixture was homogenised by mechanical milling (MM). The powdered cermet was then sintered in a tubular furnace at temperatures ranging from 1400°C to 1600°C in an inert atmosphere. The chemical composition and microstructure of the sintered cermets were characterised as ceramic particles grown via a coalescence process and embedded in a complex (Ti,Ta)-Co intermetallic matrix. The absence of the typical core-rim microstructure was confirmed.
July, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2012.02.005
Materiales Coloidales
Chromium incorporation into TiO2 at high pressure
Escudero, A; Langenhorst, FJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 190 (2012) 61-67 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2012.01.041

Abstract
Chromium incorporation into TiO 2 up to 3 GPa at 1300 °C and 900 °C has been studied by XRD as well as TEM. A CaCl 2 type TiO 2 polymorph has been observed in the quenched samples from high pressure. Two different mechanisms of solubility occur in the recovered samples. Chromium replaces titanium on normal octahedral sites but it also occupies interstitial octahedral sites, especially in the samples recovered from higher pressures. Interstitial chromium is responsible for an orthorhombic distortion of the TiO 2 rutile structure in the quenched samples and gives rise to a (1 1 0) twinned CaCl 2-structured polymorph. This phase is very likely the result of temperature quench at high pressure. The formation of this phase is directly related to the chromium content of the TiO 2 grains. Chromium solubility in TiO 2 increases with increasing the synthesis pressure. TiO 2 is able to accommodate up to 15.3 wt% Cr 2O 3 at 3 GPa and 1300 °C, compared to 5.7 wt% at atmospheric pressure at the same temperature.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2012.01.041
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Integration of Gold Nanoparticles in Optical Resonators
Jimenez-Solano, A; Lopez-Lopez, C; Sanchez-Sobrado, O; Luque, JM; Calvo, ME; Fernandez-Lopez, C; Sanchez-Iglesias, A; Liz-Marzan, LM; Miguez, HLangmuir, 28 (2012) 9161-9167 DOI: 10.1021/la300429k
Abstract
The optical absorption of one-dimensional photonic crystal based resonators containing different types of gold nanoparticles is controllably modified by means of the interplay between planar optical cavity modes and localized surface plasmons. Spin-casting of metal oxide nanoparticle suspensions was used to build multilayered photonic structures that host (silica-coated) gold nanorods and spheres. Strong reinforcement and depletion of the absorptance was observed at designed wavelength ranges, thus proving that our method provides a reliable means to modify the optical absorption originated at plasmonic resonances of particles of arbitrary shape and within a wide range of sizes. These observations are discussed on the basis of calculations of the spatial and spectral dependence of the optical field intensity within the multilayers.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/la300429k
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Vertical and tilted Ag-NPs@ZnO nanorods by plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition
Macias-Montero, M; Borras, A; Saghi, Z; Espinos, JP; Barranco, A; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARNanotechnology, 23 (2012) 255303 DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/25/255303
Abstract
Supported ZnO nanorods have been prepared at 405 K by plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD) using diethylzinc as precursor, oxygen plasma and silver as the promotion layer. The nanorods are characterized by a hollow and porous microstructure where partially percolated silver nanoparticles are located. By changing different deposition parameters like the thickness of the silver layer, the type of oxidation pretreatment or the geometry of the deposition set-up, the length, the width and the tilting angle of the nanorods with respect to the substrate can be modified. Other nanostructures like nanobushes, zigzag linear structures and stacked bilayers with nanocolumns of TiO 2 can also be prepared by adjusting the deposition conditions. A phenomenological model relying on the assessment of the diverse nanostructure morphologies and the evidence provided by an in situ x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) experiment has been proposed to describe their formation mechanism. From this analysis it is deduced that the effect of the electrical field of the plasma sheath, the high mobility of silver and silver oxide, and the diffusion of the precursor molecules are some of the critical factors that must converge by the formation of the nanorods.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/25/255303
Weakly Interacting Molecular Layer of Spinning C60 Molecules on TiO2 (110) Surfaces
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Lanzilotto, V; Gonzalez, C; Verdini, A; de Andres, PL; Floreano, L; Lopez, MF; Martin-Gago, JAChemistry-A European Journal, 18 (2012) 7382-7387 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201200627
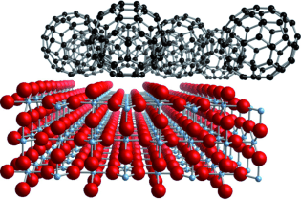
Abstract
The adsorption of C60, a typical acceptor organic molecule, on a TiO2 (110) surface has been investigated by a multitechnique combination, including van der Waals density functional calculations. It is shown that the adsorbed molecules form a weakly interacting molecular layer, which sits on the fivefold-coordinated Ti that is confined between the prominent bridging oxygen rows (see figure).
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1002/chem.201200627
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Investigation of the growth mechanisms of a-CH x coatings deposited by pulsed reactive magnetron sputtering
Lopez-Santos, C; Colaux, JL; Gonzalez, JC; Lucas, SJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 12017-12026 DOI: 10.1021/jp300697s
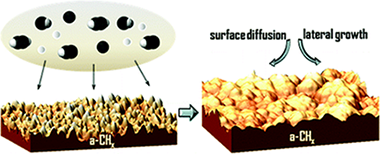
Abstract
The study of the growth mechanisms of amorphous hydrogenated carbon coatings (a-CH x) deposited by reactive pulsed magnetron discharge in Ar + C 2H 2, Ar + H 2, and Ar + C 2H 2 + H 2 low-pressure atmospheres is presented in this work. Hydrogen-containing species of the reactant gas affect the microstructure and surface properties of the a-CH x thin films. The dynamic scaling theory has been used to relate the main reactive species involved in the deposition process to the growth mechanisms of the thin film by means of the analysis of the roughness evolution. Anomalous scaling effects have been observed in smooth a-CH x coatings. Dynamic scaling exponents α, β, and z indicate a general growth controlled by surface diffusion mechanisms. Hydrogen species have an influence on the lateral growth of the a-CH x coatings and are involved in the development of a polymeric-like structure. Meanwhile, hydrocarbon species promote the generation of higher aggregates, which increases the roughness of a more sp 2 clustering structure of the a-CH x coating.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp300697s
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Three-dimensional fabrication and characterisation of core-shell nano-columns using electron beam patterning of Ge-doped SiO2
Gontard, LC; Jinschek, JR; Ou, HY; Verbeeck, J; Dunin-Borkowski, REApplied Physics Letters, 100 (2012) 263113 DOI: 10.1063/1.4731765
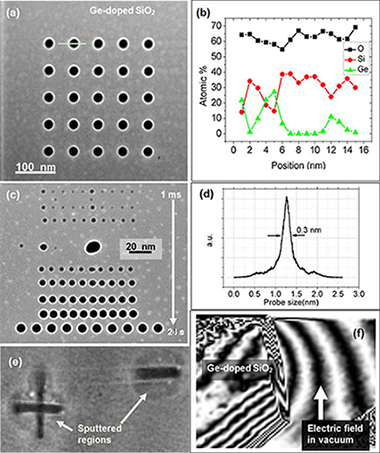
Abstract
A focused electron beam in a scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) is used to create arrays of core-shell structures in a specimen of amorphous SiO2 doped with Ge. The same electron microscope is then used to measure the changes that occurred in the specimen in three dimensions using electron tomography. The results show that transformations in insulators that have been subjected to intense irradiation using charged particles can be studied directly in three dimensions. The fabricated structures include core-shell nano-columns, sputtered regions, voids, and clusters.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1063/1.4731765
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Roughness assessment and wetting behavior of fluorocarbon surfaces
Terriza, A; Alvarez, R; Borras, A; Cotrino, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 376 (2012) 274-282 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2012.03.010
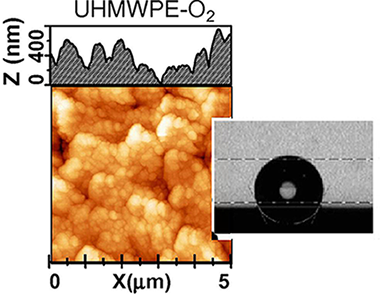
Abstract
The wetting behavior of fluorocarbon materials has been studied with the aim of assessing the influence of the surface chemical composition and surface roughness on the water advancing and receding contact angles. Diamond like carbon and two fluorocarbon materials with different fluorine content have been prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition and characterized by X-ray photoemission, Raman and FT-IR spectroscopies. Very rough surfaces have been obtained by deposition of thin films of these materials on polymer substrates previously subjected to plasma etching to increase their roughness. A direct correlation has been found between roughness and water contact angles while a superhydrophobic behavior (i.e., water contact angles higher than 150° and relatively low adhesion energy) was found for the films with the highest fluorine content deposited on very rough substrates. A critical evaluation of the methods currently used to assess the roughness of these surfaces by atomic force microscopy (AFM) has evidenced that calculated RMS roughness values and actual surface areas are quite dependent on both the scale of observation and image resolution. A critical discussion is carried out about the application of the Wenzel model to account for the wetting behavior of this type of surfaces.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2012.03.010
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Microstructural and chemical characterization of nanostructured Tialsin coatings with nanoscale resolution
Godinho, V; Rojas, TC; Trasobares, S; Ferrer, FJ; Delplancke-Ogletree, MP; Fernandez, AMicroscopy and Microanalysis, 18 (2012) 568-581 DOI: 10.1017/S1431927612000384
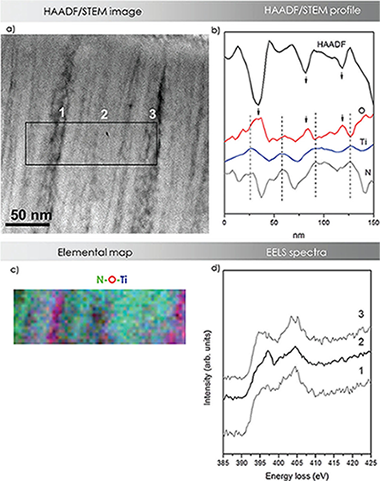
Abstract
Nanoscale resolution electron microscopy analysis combined with ion beam assisted techniques are presented here, to give answers to full characterization of morphology, growth mode, phase formation, and compositional distribution in nanocomposite TiAlSiN coatings deposited under different energetic conditions. Samples were prepared by magnetron sputtering, and the effects of substrate temperature and bias were investigated. The nanocomposite microstructure was demonstrated by the formation of a face-centered cubic (Ti,Al)N phase, obtained by substitution of Al in the cubic titanium nitride (c-TiN) phase, and an amorphous matrix at the column boundary regions mainly composed of Si, N (and O for the samples with higher oxygen contents). Oxygen impurities, predicted as the principal responsible for the degradation of properties, were identified, particularly in nonbiased samples and confirmed to occupy preferentially nitrogen positions at the column boundaries, being mainly associated to silicon forming oxynitride phases. It has been found that the columnar growth mode is not the most adequate to improve mechanical properties. Only the combination of moderate bias and additional substrate heating was able to reduce the oxygen content and eliminate the columnar microstructure leading to the nanocomposite structure with higher hardness (>30 GPa).
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1017/S1431927612000384
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhancement of Fast CO2 Capture by a Nano-SiO2/CaO Composite at Ca-Looping Conditions
Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAEnvironmental Science and Technology, 46 (2012) 6401-6408 DOI: 10.1021/es3002426
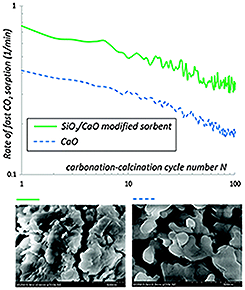
Abstract
In this paper we show the performance of a new CO 2 sorbent consisting of a dry physical mixture of a Ca-based sorbent and a SiO 2 nanostructured powder. Thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA) performed at conditions close to the Ca-looping process demonstrate that the rate of CO 2 capture by the mixture is enhanced during the fast carbonation stage of practical interest in applications. Moreover, the residual capture capacity of the mixture is increased. SEM/EDX, physisorption, and XRD analyses indicate that there is a relevant interaction between the nanostructured SiO 2 skeleton and CaO at high temperatures, which serves to improve the efficiency of the transfer of CO 2 to small reactive pores as well as the stability of the sorbent pore structure.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/es3002426
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of multicomponent-multiphase materials based on (Ti,Ta,Nb)CxN1-x carbonitride solid solutions
Cordoba, JM; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJChemical Engineering Journal, 192 (2012) 58-66 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.046
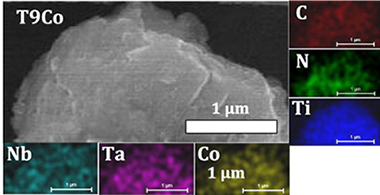
Abstract
A set of powdered cermets based on (Ti,Ta,Nb)C xN 1-x carbonitride solid solutions were synthesized from mixtures of elemental powders by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) method and subsequently sintered using a pressureless method. Differing nominal compositions of the hard phase were used, and the nature of the metallic-binder phase (Co, Ni, or Co-Ni) was varied. For comparative purposes, the design of the material was performed using two different synthesis pathways. The composition and microstructure of the ceramic and binder phases before and after sintering were analyzed and related to the microhardness of the material, which was found to increase with increasing contiguity of the hard phase and with decreasing particle size.The samples synthesized in one step (SERIES 2) showed higher microhardness and a more homogeneous microstructure with smaller particle size of the hard phase due to the presence of Ti, Ta, and Nb in the molten binder that hindered ceramic growth during liquid phase sintering.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.046
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Investigation of the Growth Mechanisms of a-CHx Coatings Deposited by Pulsed Reactive Magnetron Sputtering
López-Santos, C; Colaux, JL; González, JC; Lucas, SJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 12017-12026 DOI: 10.1021/jp300697s
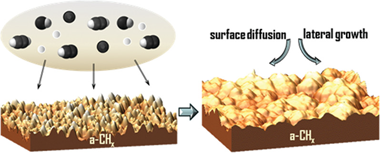
Abstract
The study of the growth mechanisms of amorphous hydrogenated carbon coatings (a-CHx) deposited by reactive pulsed magnetron discharge in Ar + C2H2, Ar + H-2, and Ar + C2H2 + H-2 low-pressure atmospheres is presented in this work. Hydrogen-containing species of the reactant gas affect the microstructure and surface properties of the a-CHx thin films. The dynamic scaling theory has been used to relate the main reactive species involved in the deposition process to the growth mechanisms of the thin film by means of the analysis of the roughness evolution. Anomalous scaling effects have been observed in smooth a-CHx coatings. Dynamic scaling exponents alpha, beta, and z indicate a general growth controlled by surface diffusion mechanisms. Hydrogen species have an influence on the lateral growth of the a-CHx coatings and are involved in the development of a polymeric-like structure. Meanwhile, hydrocarbon species promote the generation of higher aggregates, which increases the roughness of a more sp(2) clustering structure of the a-CHx coating.
June, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp300697s
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Tuning liver stiffness against tumours: An in vitro study using entrapped cells in tumour-like microcapsules
Leal-Egana, A; Fritsch, A; Heidebrecht, F; Diaz-Cuenca, A; Nowicki, M; Bader, A; Kas, JJournal of the mechanical behavior of biomedical materials, 9 (2012) 113-121 DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.01.013
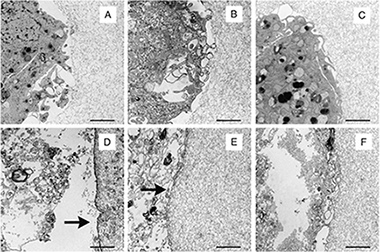
Abstract
Liver fibrosis is a reversible pathology characterized by the up-regulated secretion and deposition of ECM proteins and inhibitors of metalloproteinases, which increase the stiffness and viscosity of this organ. Since recent studies have shown that fibrosis preceded the generation of hepatocellular carcinomas, we hypothesize that liver fibrosis could play a role as a mechanism for restricting uncontrolled cell proliferation, inducing the mortality of cancer cells and subsequent development of primary tumours.
With this purpose, in this work we analysed in vitro how the modulation of stiffness can influence proliferation, viability and aggregation of hepatocarcinoma cells (HepG(2)) embedded in 3D micromilieus mimicking values of elasticity of fibrotic liver tissues.
Experiments were performed by immobilizing up to 10 HepG(2) cells within microcapsules made of 0.8%, 1.0% and 1.4% w/v alginate which, besides having values of elasticity from the lower-healthy to the upper-fibrotic range liver tissues, lacked domains for proteases, mimicking the micromilieu existing in hepatic primary tumours.
Our results show that entrapped cells exhibited a short duplication phase followed by an irreversible decay stage, in which cell mortality could be mediated by two mechanisms: mechanical stress, in the case of cells entrapped in a stiffer micromilieu; and mass transfer limitations produced by pore coarsening at the interface cell-matrix, in softer micromilieus.
According to the authors' knowledge, this work represents the first attempt to elucidate the role of liver fibrosis during Hepatocarcinoma pathologies, suggesting that the generation of a non-biodegradable and mechanically unfavourable environment surrounding cancer cells could control the proliferation, migration of metastatic cells and the subsequent development of primary tumours.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.01.013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Remediation of metal-contaminated soils with the addition of materials - Part II: Leaching tests to evaluate the efficiency of materials in the remediation of contaminated soils
Gonzalez-Nunez, R; Alba, MD; Orta, MM; Vidal, M; Rigol, AChemosphere, 87 (2012) 829-837 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.015
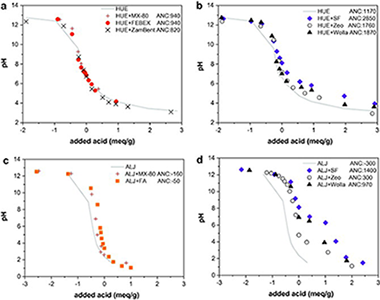
Abstract
The effect of the addition of materials on the leaching pattern of As and metals (Cu, Zn, Ni, Pb, and Cd) in two contaminated soils was investigated. The examined materials included bentonites, silicates and industrial wastes, such as sugar foam, fly ashes and a material originated from the zeolitization of fly ash. Soil + material mixtures were prepared at 10% doses. Changes in the acid neutralization capacity, crystalline phases and contaminant leaching over a wide range of pHs were examined by using pHstat leaching tests. Sugar foam, the zeolitic material and MX-80 bentonite produced the greatest decrease in the leaching of pollutants due to an increase in the pH and/or the sorption capacity in the resulting mixture. This finding suggests that soil remediation may be a feasible option for the reuse of non-hazardous wastes.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.015
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Hydrothermal synthesis of BiVO4: Structural and morphological influence on the photocatalytic activity
Obregon, S; Caballero, A; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 117 (2012) 59-66 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.12.037
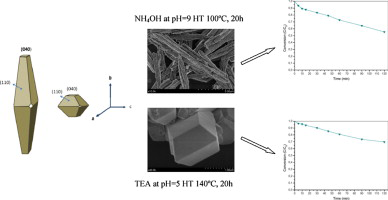
Abstract
BiVO 4 hierarchical heterostructures are synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities for the degradation of methylene blue under UV-vis irradiation. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that BiVO 4 present the monoclinic crystalline phase with different morphologies depending on the pH value, type of precipitating agent and hydrothermal temperature and treatment time. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with needle-like morphology.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.12.037
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of diffuse light scattering designs on the efficiency of dye solar cells: An integral optical and electrical description
Galvez, FE; Kemppainen, E; Miguez, H; Halme, JJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 11426-11433 DOI: 10.1021/jp2092708
Abstract
Herein, we present an integral optical and electrical theoretical analysis of the effect of different diffuse light scattering designs on the performance of dye solar cells. Light harvesting efficiencies and electron generation functions extracted from optical numerical calculations based on a Monte Carlo approach are introduced in a standard electron diffusion model to obtain the steady-state characteristics of the different configurations considered. We demonstrate that there is a strong dependence of the incident photon to current conversion efficiency, and thus of the overall conversion efficiency, on the interplay between the value of the electron diffusion length considered and the type of light scattering design employed, which determines the spatial dependence of the electron generation function. Other effects, like the influence of increased photoelectron generation on the photovoltage, are also discussed. Optimized scattering designs for different combinations of electrode thickness and electron diffusion length are proposed.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp2092708
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic activity of single and mixed nanosheet-like Bi2WO6 and TiO2 for Rhodamine B degradation under sunlike and visible illumination
Murcia-Lopez, S; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 423-424 (2012) 34-41 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.016
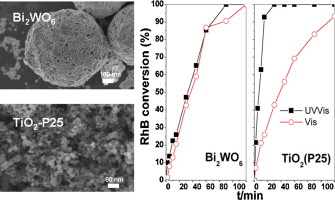
Abstract
The photocatalytic activity, under sunlike illumination, for Rhodamine B (RhB) degradation using Bi2WO6-TiO2 samples, is reported. Two different kinds of Bi2WO6-TiO2 samples were studied, obtained by distinct methods: first, a mechanical mixing, by adding to synthesized nanosheet-like Bi2WO6 powder the corresponding amount of TiO2 nanoparticles (P25) in order to obtain physical mixtures of both catalysts with different percentages of TiO2 (5, 10 and 50 wt%); second, a single Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructure was prepared by adding commercial TiO2-P25 to the Bi2WO6 precursors (50 wt%) prior to the hydrothermal treatment, thus obtaining a sample with "in situ" TiO2 incorporation. Comparisons between the photocatalytic behaviour of these samples and those exhibited by the single materials Bi2WO6 and TiO2 (P25) were carried out, in order to establish the effect not only of the TiO2 addition but also of the way in which TiO2 (P25) is incorporated. The role of each single photocatalyst in the mixtures in the RhB degradation and mineralization under sunlike and just visible illumination was also studied.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Spark plasma sintering of Ti yNb 1-yC xN 1-x monolithic ceramics obtained by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Borrell, A; Salvador, MD; Garcia-Rocha, V; Fernandez, A; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJMaterials Science and Engineering A, 543 (2012) 173-179 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.071
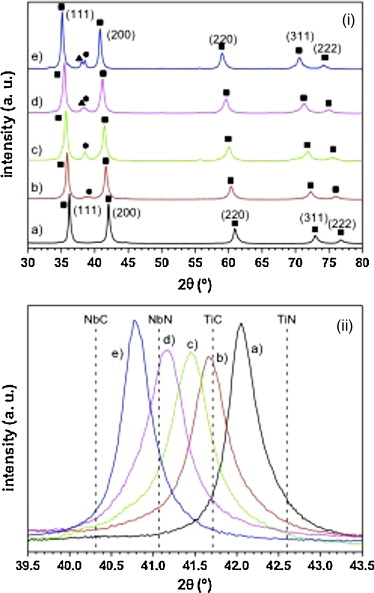
Abstract
Nanometer-sized titanium-niobium carbonitride powders (Ti yNb 1-yC xN 1-x) with different Ti/Nb atomic ratios were obtained by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction, and sintered by spark plasma sintering technique at 1500°C for 1min in a vacuum atmosphere. Mechanical properties such as hardness and Young's modulus were determined by nanoindentation technique and friction and wear coefficients assessed by ball-on-disk testing using alumina ball in dry sliding conditions. The fracture surface and wear tracks of samples were examined by scanning electron microscopy. Results showed that it is possible to obtain dense monolithic ceramics from the solid solution (Ti yNb 1-yC xN 1-x) with good mechanical properties and excellent wear resistance. The optimum values of nanomechanical properties were found for the Ti 0.3Nb 0.7C 0.5N 0.5 ceramic composition, which exhibited a high hardness over 26.0GPa and Young's modulus around 400GPa.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.071
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Interfacial characterization of silicon nitride/silicon nitride joints brazed using Cu-base active metal interlayers
Singh, M; Fernandez, JM; Asthana, R; Rico, JRCeramics Intenational, 38 (2012) 2793-2802 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.11.050
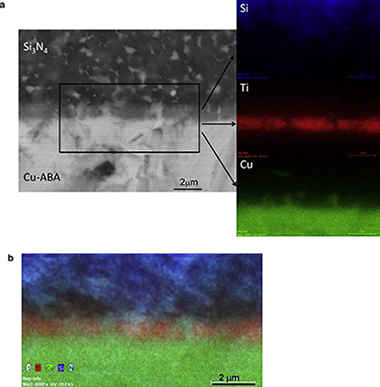
Abstract
Silicon nitride/silicon nitride joints were vacuum brazed at 1317 K for 5 min and 30 min using ductile Cu-base active metal interlayers. The joints were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), electron back scattered diffraction (EBSD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). An inhomogeneous Ti-rich reaction layer (similar to 2-3 mu m thick) formed in 5 min at the Si3N4/braze interface. The inhomogeneity disappeared after brazing for 30 min and was replaced with a compact and featureless reaction zone. TEM studies revealed fine grains in the reaction layer, and larger grains in the inner part of the joint interfaces. The joints were crack-free and presented features associated with plastic deformation, which indicated accommodation of strain associated with CTE mismatch. Electron Backscatter diffraction (EBSD) revealed a highly textured braze alloy interlayer and its crystallographic orientation was determined. The formation of additional phases at the joint interface during brazing is discussed.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.11.050
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthetic high-charge organomica: Effect of the layer charge and alkyl chain length on the structure of the adsorbed surfactants
Pazos, MC; Castro, MA; Orta, MM; Pavon, E; Rios, JSV; Alba, MDLangmuir, 28 (2012) 7325-7332 DOI: 10.1021/la300153e
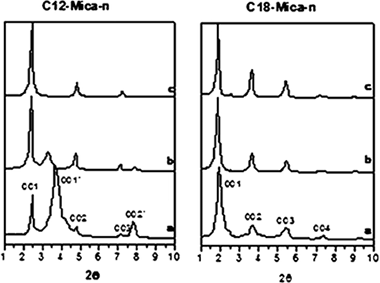
Abstract
A family of organomicas was synthesized using synthetic swelling micas with high layer charge (NanSi8-nAlnMg6F4O20 center dot XH2O, where n = 2, 3, and 4) exchanged with dodecylammonium and octadecylammonium cations. The molecular arrangement of the surfactant was elucidated on the basis on XRD patterns and DTA. The ordering conformation of the surfactant molecules into the interlayer space of micas was investigated by C-13, Al-27, and Si-29 MAS NMR The arrangement of alkylammonium ions in these high-charge synthetic micas depends on the combined effects of the layer charge of the mica and the chain length of the cation. In the organomicas with dodecylammonium, a transition from a parallel layer to a bilayer-paraffin arrangement is observed when the layer charge of the mica increases. However, when octadecylammonium is the interlayer cation, the molecular arrangement of the surfactant was found to follow the bilayer-paraffin model for all values of layer charge. The amount of ordered conformation all-trans is directly proportional of layer charge.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/la300153e
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Attenuation lengths of high energy photoelectrons in compact and mesoporous SiO2 films
Ferrer, FJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Rubio-Zuazo, J; Romero-Gomez, P; Lopez-Santos, MC; Yubero, FSurface Science, 606 (2012) 820-824 DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.01.017
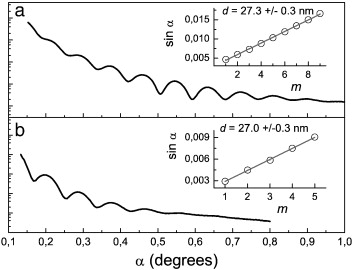
Abstract
We have experimentally evaluated attenuation lengths (AL) of photoelectrons traveling in compact and micro and mesoporous (∼ 45% voids) SiO 2 thin films with high (8.2-13.2 keV) kinetic energies. The films were grown on polished Si(100) wafers. ALs were deduced from the intensity ratio of the Si 1s signal from the SiO 2 film and Si substrate using the two-peaks overlayer method. We obtain ALs of 15-22 nm and 23-32 nm for the compact and porous SiO 2 films for the range of kinetic energies considered. The observed AL values follow a power law dependence on the kinetic energy of the electrons where the exponent takes the values 0.81 ± 0.13 and 0.72 ± 0.12 for compact and porous materials, respectively.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.01.017
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Correlation lengths, porosity and water adsorption in TiO2 thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Garcia-Gutierrez, MC; Hernandez, JJ; Rueda, DR; Ezquerra, TANanotechnology, 23 (2012) 205701 DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/20/205701
Abstract
This paper reports a thorough microstructural characterization of glancing angle deposited (GLAD) TiO 2 thin films. Atomic force microscopy (afm), grazing-incidence small-angle x-ray scattering (GISAXS) and water adsorption isotherms have been used to determine the evolution of porosity and the existence of some correlation distances between the nanocolumns constituting the basic elements of the films nanostructure. It is found that the deposition angle and, to a lesser extent, the film thickness are the most important parameters controlling properties of the thin film. The importance of porosity and some critical dimensions encountered in the investigated GLAD thin films is highlighted in relation to the analysis of their optical properties when utilized as antireflective coatings or as hosts and templates for the development of new composite materials.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/20/205701
Reactividad de Sólidos
Nanoclay Nucleation Effect in the Thermal Stabilization of a Polymer Nanocomposite: A Kinetic Mechanism Change
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 11797-11807 DOI: 10.1021/jp302466p
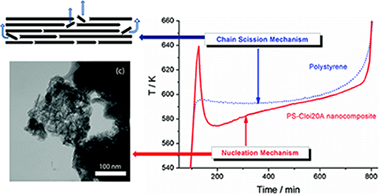
Abstract
The enhanced thermal stability of polymer-clay nanocomposites over the original polymers is one of their most interesting features, and it has been profusely studied within the last decades. Here, a thorough kinetic analysis of polystyrene and a montmorillonite-polystyrene nanocomposite has been performed making use of state-of-the-art kinetic procedures. It has been found that the degradation mechanism changes from a chain scission process for the polymer to a complex two-step nucleation-driven reaction for the nanocomposite. This mechanism change can explain the delayed onset of degradation found in the nanocomposite. Moreover, observation by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) has shown that the clay platelets within the composite could act as nucleation centers for the decomposition.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp302466p
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold supported cryptomelane-type manganese dioxide OMS-2 nanomaterials deposited on AISI 304 stainless steels monoliths for CO oxidation
Martinez, LM; Romero-Sarria, F; Hernandez, WY; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 423 (2012) 137-145 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.026

Abstract
Gold supported on cryptomelane-type OMS-2 catalysts deposited on AISI 304 stainless steels monoliths have been prepared for the first time, characterised and tested in the CO oxidation reaction. An easy and non-conventional method of incorporation of gold to the cryptomelane solid is used. This method allows the preparation of the monolithic catalysts without altering the structural and textural characteristics of the parent OMS-2 material. Although these catalysts do not show an optimal performance for the oxidation of CO, the presence of small gold particles enhances the catalytic performances of the cryptomelane producing promissory CO oxidation catalysts. The non-conventional gold deposition favours a partial loss of K + into the channels, resulting in an increment of the average oxidation state of manganese which favours the catalytic behaviour of these kinds of materials. This study can be taken as a starting point to obtain very active gold catalysts supported on OMS-2 materials through the optimisation of the gold-support interaction and the decrease in the gold particle size.
May, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.026
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Self-assembly at room temperature of thermally stable discrete and extended oligomers of polycyclic aromatics on Ag(100): induced dipoles and cooperative effects
Papageorgiou, AC; Alavi, A; Lambert, RMChemical Communications, 48 (2012) 3394-3396 DOI: 10.1039/c2cc17728e
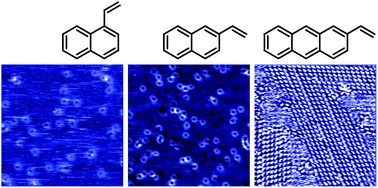
Abstract
Thermally stable nanoarchitectures are realized on the Ag(100) surface by self-assembly of asymmetrically substituted arenes. The process is instigated by adsorption-induced molecule → surface charge transfer that gives rise to in-plane dipole moments. Observation and calculation indicate that cooperative interactions further enhance the stability of these polarizable systems.
April, 2012 · DOI: 10.1039/c2cc17728e
Materiales Coloidales
Incorporation of Si into TiO2 phases at high pressure
Escudero, A; Langenhorst, FAmerican Mineralogist, 97 (2012) 524-531 DOI: 10.2138/am.2012.3941
Abstract
Silicon incorporation in TiO 2 phases at increasing pressures until 20 GPa at 1300 °C has been studied by XRD and TEM. Rutile is the stable Si-doped TiO 2 phase until at least 7 GPa, transforming into α-PbO 2 structured TiO2 between 7 and 10 GPa. The further transformation to the TiO 2 polymorph with the baddeleyite structure, akaogiite, has not been observed on the quenched samples. XRD and TEM-EDX data suggest that the Si-doped TiO 2 akaogiite polymorph is non-quenchable and reverts to a-PbO2 structured TiO 2 when releasing the pressure. This transformation gives rise to α-PbO 2 structured TiO 2 grains decorated with p fringes stacking faults. Silicon solubility in TiO 2 phases increases with increasing the synthesis pressure until 16 GPa, implying the substitutional solid solution to be the mechanism of solubility. The influence of the dopants on the stability of the rutile and the α-PbO2 structured TiO 2 has also been analyzed.
April, 2012 · DOI: 10.2138/am.2012.3941
Reactividad de Sólidos
Room temperature mechanosynthesis of the La 1-xSr xMnO 3±δ (0≤x≤1) system and microstructural study
Sayagues, MJ; Cordoba, JM; Gotor, FJJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 188 (2012) 11-16 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2012.01.018
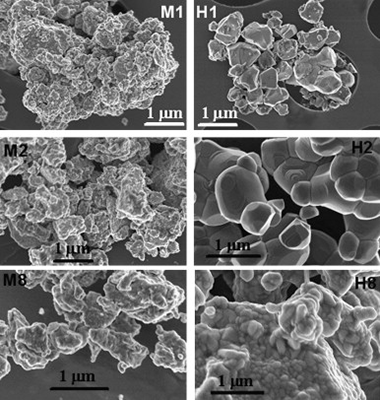
Abstract
Monophase nanocrystalline powders belonging to the La1−xSrxMnO3±δ system (0≤x≤1) with a perovskite structure have been obtained by mechanochemistry synthesis using a planetary ball milling equipment from La2O3, SrO, and Mn2O3 mixtures. The solid state reaction was complete after one hour of milling treatment. For all the compositional range, the diffraction domain was very small and the structure appeared as a pseudo cubic perovskite. After annealing at 1100 °C under static air, the symmetry evolution due to the La substitution by Sr was analyzed by X-ray and electron diffraction. Samples with x=0, 0.25, 0.5, and 0.75 were assigned to R-3c space group (1 6 7) in the rhombohedral system and perovskite structure. However, the symmetry of the last term of the system (x=1), SrMnO3±δ sample, changed to P63/mmc space group (1 9 4) in the hexagonal system. The terms with x=0.8, 0.85, and 0.9 presented mainly rhombohedral symmetry.
April, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2012.01.018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of Vanadium or Cobalt Oxides on the CO Oxidation Behavior of Au/MOx/CeO2-Al2O3 Systems
Reina, TR; Moreno, AA; Ivanova, S; Odriozola, JA; Centeno, MAChemcatchem, 4 (2012) 512-520 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201100373
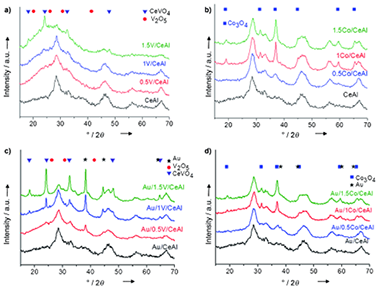
Abstract
A series of V2O5- and Co3O4-modified ceria/alumina supports and their corresponding gold catalysts were synthesized and their catalytic activities evaluated in the CO oxidation reaction. V2O5-doped solids demonstrated a poor capacity to abate CO, even lower than that of the original ceria/alumina support, owing to the formation of CeVO4. XRD, Raman spectroscopy, and H2-temperature programmed reduction studies confirmed the presence of this stoichiometric compound, in which cerium was present as Ce3+ and its redox properties were avoided. Co3O4-doped supports showed a high activity in CO oxidation at subambient temperatures. The vanadium oxide-doped gold catalysts were not efficient because of gold particle agglomeration and CeVO4 formation. However, the gold–cobalt oxide–ceria/alumina catalysts demonstrated a high capacity to abate CO at and below room temperature. Total conversion was achieved at −70 °C. The calculated apparent activation energy values revealed a theoretical optimum loading of a half-monolayer.
April, 2012 · DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201100373
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
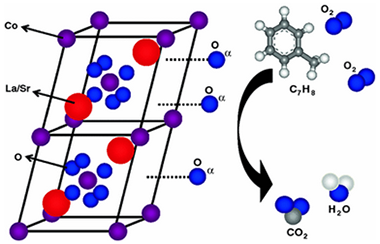
Study of Oxygen Reactivity in La1-x Sr (x) CoO3-delta Perovskites for Total Oxidation of Toluene
Pereniguez, R; Hueso, JL; Gaillard, F; Holgado, JP; Caballero, ACatalysis Letters, 142 (2012) 408-416 DOI: 10.1007/s10562-012-0799-z
Abstract
The total oxidation of toluene is studied over catalytic systems based on perovskite with general formula AA′CoO 3-δ (A = La, A′ = Sr). The systematic and progressive substitution of La 3+ by Sr 2+ cations in the series (La 1-xSr xCoO 3-δ system) of the perovskites have been studied to determine their influence in the final properties of these mixed oxides and their corresponding reactivity performance for the total oxidation of toluene as a model volatile organic compound with detrimental effects for health and environment. The structure and morphology of the samples before and after reaction have been characterized by XRD, BET and FE-SEM techniques. Additional experiments of temperature programmed desorption of O 2 in vacuum and reduction in H 2 were also performed to identify the main surface oxygen species and the reducibility of the different perovskites. It is remarkable that the La 1-xSr xCoO 3-δ series presents better catalytic performance for the oxidation of toluene, with lower values for the T 50 (temperature of 50 % toluene conversion) than the previously studied LaNi 1-yCoyO 3 series.
April, 2012 · DOI: 10.1007/s10562-012-0799-z
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Residual stresses in Al2O3-ZrO 2 (3mol.% Y2O3) directionally solidified eutectic ceramics as a function of temperature
Ramirez-Rico, J; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Pena, JI; Singh, D; Routbort, JMaterials Science and Engineering A, 541 (2012) 61-66 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.001
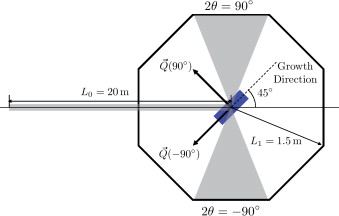
Abstract
Directionally solidified eutectics are in situ composites grown from the melt. Due to the differences in the thermoelastic properties of the different phases present in the material, these composites often exhibit residual stresses that can affect their mechanical properties. In this work we use neutron diffraction to investigate residual stresses in Al 2O 3-ZrO 2 eutectic composites as a function of temperature, for samples processed at two different growth rates, 10mm/h and 750mm/h. Our results show that the stress-free temperature is in the range of 1200±200°C. We explain the experimental observations based on the thermoelastic properties of the phases in the material and confirm our measurements using a simple, self-consistent model.
April, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.001
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma deposition of perylene-adamantane nanocomposite thin films for NO 2 room-temperature optical sensing
Aparicio, FJ; Blaszczyk-Lezak, I; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Alcaire, M; Gonzalez, JC; Serra, C; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 8731-8740 DOI: 10.1021/jp209272s
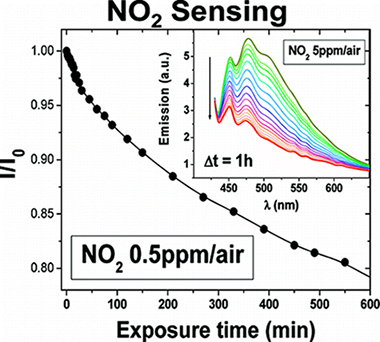
Abstract
This work reports the preparation, by a new remote assisted plasma deposition process, of luminescent nanocomposite thin films consisting of an insoluble organic matrix where photonically active perylene molecules are embedded. The films are obtained by the remote plasma deposition of adamantane and perylene precursor molecules. The results show that the adamantane precursor is very effective to improve the perylene–adamantane nanocomposite transparency in comparison with plasma deposited perylene films. The plasma deposited adamantane films have been characterized by secondary-ion mass spectrometry and FT-IR spectroscopy. These techniques and atomic force microscopy (AFM) have been also used for the characterization of the nanocomposite films. Their optical properties (UV–vis absorption, fluorescence, and refractive index) have been also determined and their sensing properties toward NO2 studied. It is found that samples with the perylene molecules embedded within the transparent plasma deposited matrix are highly sensitive toward this gas and that the sensitivity of the films can be adjusted by modifying the aggregation state of the perylene molecules, as determined by the analysis of their fluorescence spectra. By monitoring the fluorescence emission of these films, it has been possible to detect a NO2 concentration as low as 0.5 ppm in air at room temperature. Because of their chemical stability and transparency in the UV region, the remote plasma deposited adamantane thin films have revealed as an optimum host matrix for the development of photonically active composites for sensing applications.
April, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp209272s
Sonication induced reduction of the Ojen (Andalucia, Spain) vermiculite under air and under nitrogen
Poyato, J; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Lerf, A; Wagner, FEUltrasonics Sonochemistry, 19 (2012) 373-375 DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2011.07.004
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and Structure Resolution of RbLaF4
Rollet, AL; Allix, M; Veron, E; Deschamps, M; Montouillout, V; Suchomel, MR; Suard, E; Barre, M; Ocana, M; Sadoc, A; Boucher, F; Bessada, C; Massiot, D; Fayon, FInorganic Chemistry, 51 (2012) 2272-2282 DOI: 10.1021/ic202301e
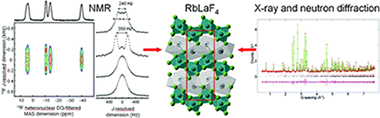
Abstract
The synthesis and structure resolution of RbLaF4 are described. RbLaF4 is synthesized by solid-state reaction between RbF and LaF3 at 425 degrees C under a nonoxidizing atmosphere. Its crystal structure has been resolved by combining neutron and synchrotron powder diffraction data refinements (Pnma, a = 6.46281(2) angstrom, b = 3.86498(1) angstrom, c = 16.176:29(4) angstrom, Z = 4). One-dimensional Rb-87, La-139, and F-19 MAS NMR spectra have been recorded and are in agreement with the proposed structural model. Assignment of the F-19 resonances is performed on the basis of both F-19-La-139 J-coupling multiplet patterns observed in a heteronudear DQ-filtered J-resolved spectrum and F-19-Rb-87 HMQC MAS experiments. DFT calculations of both the F-19 isotropic chemical shieldings and the Rb-87, La-139 electric field gradient tensors using the GIPAW and PAW methods implemented in the CASTEP code are in good agreement with the experimental values and support the proposed structural model. Finally, the conductivity of RbLaF4 and luminescence properties of Eu-doped LaRbF4 are investigated.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/ic202301e
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Advanced nanoarchitectures for solar photocatalytic applications
Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Colon, GChemical Reviews, 112 (2012) 1555-1614 DOI: 10.1021/cr100454n
Abstract
Advanced nanostructured materials that demonstrate useful activity under solar excitation in fields concerned with the elimination of pollutants, partial oxidation and the valorization of chemical compounds, water splitting and CO 2 reduction processes, are discussed. Point defects present in nanoparticulated anatase present both 5-fold- and 6-fold-coordinated titanium atoms, as well as 2-fold- and 3-fold-coordinated oxygens. The requirement of using sunlight as the excitation source for the degradation reaction demands, as a principal requirement, the modification of the electronic characteristics of a UV absorber system such as anatase-TiO 2. Some reports also indicate the need for large doping concentrations for N-doping in specific cases where notable changes in the valence band onset are subsequently observed. The effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) on the crystallization is reported by Yin et al. They showed that the presence of CTAB induces the appearance of BiOBr during the synthesis at 80°C using an aqueous method.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/cr100454n
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quantification of low levels of fluorine content in thin films
Ferrer, FJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Terriza, A; Rey, G; Jimenez, C; Garcia-Lopez, J; Yubero, FNuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B-Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 274 (2012) 65-69 DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2011.11.042
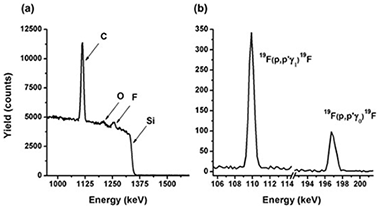
Abstract
Fluorine quantification in thin film samples containing different amounts of fluorine atoms was accomplished by combining proton-Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (p-RBS) and proton induced gamma-ray emission (PIGE) using proton beams of 1550 and 2330 keV for p-RBS and PIGE measurements, respectively. The capabilities of the proposed quantification method are illustrated with examples of the analysis of a series of samples of fluorine-doped tin oxides, fluorinated silica, and fluorinated diamond-like carbon films. It is shown that this procedure allows the quantification of F contents as low as 1 at.% in thin films with thicknesses in the 100-400 nm range.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2011.11.042
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Efficient Transparent Thin Dye Solar Cells Based on Highly Porous 1D Photonic Crystals
Colodrero, S; Forneli, A; Lopez-Lopez, C; Pelleja, L; Miguez, H; Palomares, EAdvanced Functional Materials, 22 (2012) 1303-1310 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201102159
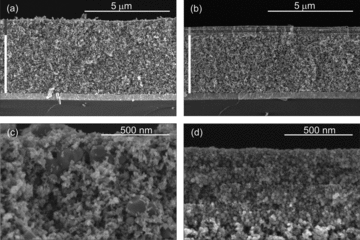
Abstract
A working electrode design based on a highly porous 1D photonic crystal structure that opens the path towards high photocurrents in thin, transparent, dye-sensitized solar cells is presented. By enlarging the average pore size with respect to previous photonic crystal designs, the new working electrode not only increases the device photocurrent, as predicted by theoretical models, but also allows the observation of an unprecedented boost of the cell photovoltage, which can be attributed to structural modifications caused during the integration of the photonic crystal. These synergic effects yield conversion efficiencies of around 3.5% by using just 2 mu m thick electrodes, with enhancements between 100% and 150% with respect to reference cells of the same thickness.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201102159
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Electrostatic Induced Molecular Tilting in Self-Assembled Monolayers of n-Octadecylamine on Mica
Oviedo, J; San-Miguel, MA; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 7099-7105 DOI: 10.1021/jp300829g
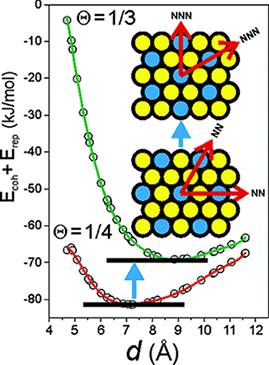
Abstract
Self-assembled monolayers of n-octadecylamine on mica (ODA/mica SAMs) have been investigated by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and by attenuated total reflectance infrared (ATR-FTIR) and X-ray photoelectron (XPS) spectroscopies. Topographic data characterizes a stable configuration with the alkyl skeleton tilted approximate to 46 degrees from the surface normal that is rationalized according to a well established structural alkyl chain packing model. Extended contact with air increases molecular tilting up to approximate to 58 degrees. ATR-FTIR and XPS reveal the presence of protonated amino groups within the monolayer and its increment upon exposure to air. The transition between both tilted states is explained assuming the protonation reaction as the driving force and introducing a model to evaluate an electrostatic repulsions term in the overall cohesive energy balance of the system. ODA molecules in the self-assembled monolayer respond to their spontaneous protonation by atmospheric water by tilting as a mechanism to relax the repulsions between -NH3+ heads.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp300829g
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Influence of plasma-generated negative oxygen ion impingement on magnetron sputtered amorphous SiO2 thin films during growth at low temperatures
Macias-Montero, M; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Alvarez, R; Gil-Rostra, J; Gonzalez, JC; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, AJournal of Applied Physics, 111 (2012) 054312 (6 pages) DOI: 10.1063/1.3691950
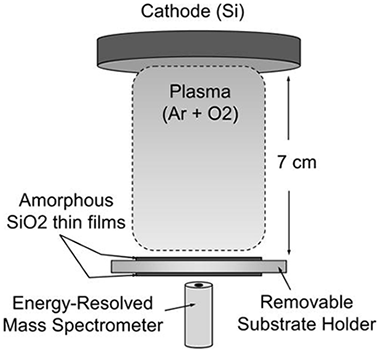
Abstract
Growth of amorphous SiO2 thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering at low temperatures has been studied under different oxygen partial pressure conditions. Film microstructures varied from coalescent vertical column-like to homogeneous compact microstructures, possessing all similar refractive indexes. A discussion on the process responsible for the different microstructures is carried out focusing on the influence of (i) the surface shadowing mechanism, (ii) the positive ion impingement on the film, and (iii) the negative ion impingement. We conclude that only the trend followed by the latter and, in particular, the impingement of O- ions with kinetic energies between 20 and 200 eV, agrees with the resulting microstructural changes. Overall, it is also demonstrated that there are two main microstructuring regimes in the growth of amorphous SiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering at low temperatures, controlled by the amount of O2 in the deposition reactor, which stem from the competition between surface shadowing and ion-induced adatom surface mobility.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1063/1.3691950
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO-Induced Morphology Changes in Zn-Modified Ceria: A FTIR Spectroscopic Study
Penkova, A; Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 5747-5756 DOI: 10.1021/jp210996b
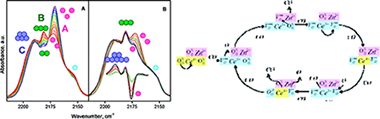
Abstract
A FTIR study of the CO adsorption on a Zn-modified ceria is presented. The results indicate that at lower activation temperatures only Ce 4+ carbonyls were detected, which were reduced with the increase of the activation temperature. At higher activation temperatures, up to three Zn 2+ carbonyls were also identified according to the arrangement of the Zn 2+ cations. The consecutive CO adsorptions demonstrated an irreversible modification of the surface, resulting in an agglomeration of the zinc cations. A stepwise conversion of the isolated Zn 2+ carbonyls into carbonyls of the closely situated zinc cations followed by formation of bigger zinc oxide clusters was observed. The carbon monoxide coordinated on the isolated Zn 2+ cations at the interface with ceria reacts with the lattice oxygen leading to formation of oxygen vacancies. An insight into the origin of the activation during the CO oxidation process is proposed.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp210996b
Reactividad de Sólidos
Inverse core-rim microstructure in (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets developed by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 31 (2012) 39-46 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.09.003
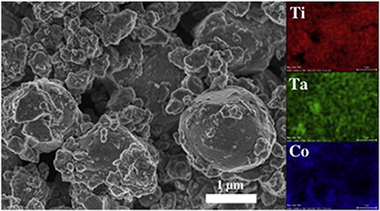
Abstract
Cermets with a nominal composition (Tia(0.8)Ta(0.2)C(0.5)N(0.5)-20 wt.% Co) were synthesised by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process from stoichiometric elemental powder blends. The MSR allowed the production of a complex (Ti,Ta)(C,N) solid solution, which was the raw material used for the sintering process. The pressureless sintering process was performed at temperatures between 1400 degrees C and 1600 degrees C in an inert atmosphere. The microstructural characterisation showed a complex microstructure composed of a ceramic phase with an unusual inverse core-rim structure and a Ti-Ta-Co intermetallic phase that acted as the binder.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.09.003
Reactividad de Sólidos - Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Nanostructured Spark Plasma Sintered Ce-TZP Ceramics
Cruz, SA; Poyato, R; Cumbrera, FL; Odriozola, JAJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 95 (2012) 901-906 DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2011.04978.x
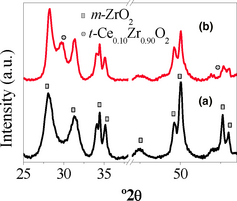
Abstract
In this work, spark plasma sintering (SPS) of 10 mol% CeO 2-doped ZrO 2 nanocrystalline powders, obtained by a two-step synthesis procedure, allows the preparation of fully densified nanostructured ceramics. The CeO 2-ZrO 2 powders with particle size below 100 nm are obtained after CeO 2 deposition on hydrothermally synthesized ZrO 2 particles by the impregnation method. Tetragonal CeO 2-ZrO 2 ceramics are obtained when sintering at 1200°C without holding time. A graded material containing tetragonal, monoclinic, and pyrochlore phases are obtained when sintering at 1200°C and for 5 min holding time. This is explained in terms of the gradual reduction of Ce 4+ to Ce 3+ species by carbon in the graphite environment during SPS. With the successful combination of the stabilizer coating technique and SPS, we achieve not only the stabilization of the tetragonal phase in the ceramics, but also good control of the grain size, by producing nanostructured ceramics with 40-70 nm grain sizes.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2011.04978.x
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
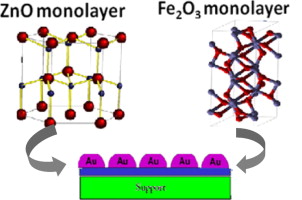
Sub-ambient CO oxidation over Au/MOx/CeO2-Al2O3 (M = Zn or Fe)
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 419-420 (2012) 58-66 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.01.012
Abstract
A series of ZnO and Fe 2O 3 modified ceria/alumina supports and their corresponding gold catalyst were prepared and studied in the CO oxidation reaction. ZnO-doped solids show a superior catalytic activity compared to the bare CeO 2-Al 2O 3, which is attributed to the intimate contact of the ZnO and CeO 2 phases, since an exchange of the lattice oxygen occurs at the interface. In a similar way, Fe 2O 3-modified supports increase the ability of the CeO 2-Al 2O 3 solids to eliminate CO caused by both the existence of Ce-Fe contact surface and the Fe 2O 3 intrinsic activity. All of the gold catalysts were very efficient in oxidising CO irrespective of the doping metal oxide or loading, with the ZnO containing systems better than the others. The majority of the systems reached total CO conversion below room temperature with the ZnO and Fe 2O 3 monolayer loaded systems the most efficient within the series.
March, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.01.012
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Public concern over ecotoxicology risks from nanomaterials: Pressing need for research-based information
Lapresta-Fernandez, A; Fernandez, A; Blasco, JEnvironment International, 39 (2012) 148-149 DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.10.012
Abstract
[No abstract available]
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.10.012
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Enhanced diffusion through porous nanoparticle optical multilayers
Lopez-Lopez, C; Colodrero, S; Raga, SR; Lindstrom, H; Fabregat-Santiago, F; Bisquert, J; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry, 22 (2012) 1751-1757 DOI: 10.1039/c1jm15202e
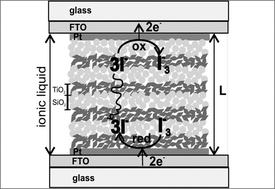
Abstract
Herein we demonstrate improved mass transport through nano-particle one-dimensional photonic crystals of enhanced porosity. Analysis is made by impedance spectroscopy using iodine and ionic liquid based electrolytes and shows that newly created large pores and increased porosity improve the diffusion of species through the photonic crystal. This achievement is based on the use of a polymeric porogen (polyethylene glycol), which is mixed with the precursor suspensions used for the deposition of nanoparticle TiO2 and SiO2 layers and then eliminated to generate a more open interconnected void network, as confirmed by specular reflectance porosimetry. A compromise between pore size and optical quality of these periodic structures is found.
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1039/c1jm15202e
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermal behaviour of ground and unground acid leached vermiculite
Perez-Maqueda, LA; Maqueda, C; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Subrt, J; Cerny, Z; Balek, VJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 107 (2012) 431-438 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-011-1480-2
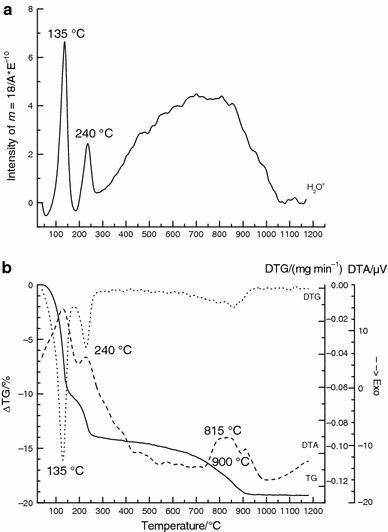
Abstract
Acid leaching of vermiculite is an interesting procedure to prepare high surface area porous silica. Thermal behaviour of unground and ground vermiculite leached with HCl solutions has been studied by TG, DTA, ETA and high temperature XRD. Important differences have been observed in the thermal behaviour of unground and ground vermiculite after the acid treatments. Thus, for the acid-treated unground vermiculite, dehydrated vermiculite, enstatite and cristobalite were formed during the heating, while for the acid-treated ground vermiculite only iron oxides and cristobalite phases were observed. Structural modifications due to acid treatment were responsible for changes in the transport properties determined by ETA for the vermiculite samples.
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-011-1480-2
Operando DRIFTS study of the redox and catalytic properties of CuO/Ce1−xTbxO2−δ (x = 0–0.5) catalysts: evidence of an induction step during CO oxidation
Martinez-Arias, A.; Hungria, A. B.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.; Iglesias-Juez, A.; Soria, J.; Conesa, J. C.; Anderson, J. A.; Munuera, G.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 14 (2012) 2144-2151 DOI: 10.1039/C1CP23298C
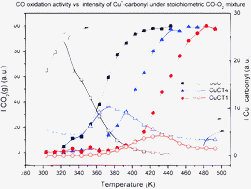
Abstract
Catalysts of 1 wt% copper oxide supported on cerium oxide or cerium–terbium mixed oxides are comparatively examined with respect to their redox and catalytic properties for CO oxidation. Characterization of the catalysts had shown that they contain highly dispersed CuO-type entities on the corresponding nanostructured fluorite supports with copper dispersion increasing with increasing amounts of terbium in the support. In contrast, the CO oxidation catalytic activity decreases with increasing amounts of terbium in the support. On the basis of operando-DRIFTS experiments, one of the factors that could explain such behaviour is related to the greater difficulty in generating reduced copper sites active for the reaction in the presence of terbium, which in turn is evidenced to constitute an induction stage. Analysis of the redox properties is complemented by XPS which confirms the greater resistance to copper reduction in the presence of terbium.
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1039/C1CP23298C
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
An international round-robin calibration protocol for nanoindentation measurements
Cabibbo, M; Ricci, P; Cecchini, R; Rymuza, Z; Sullivan, J; Dub, S; Cohen, SMicron, 43 (2012) 215-222 DOI: 10.1016/j.micron.2011.07.016
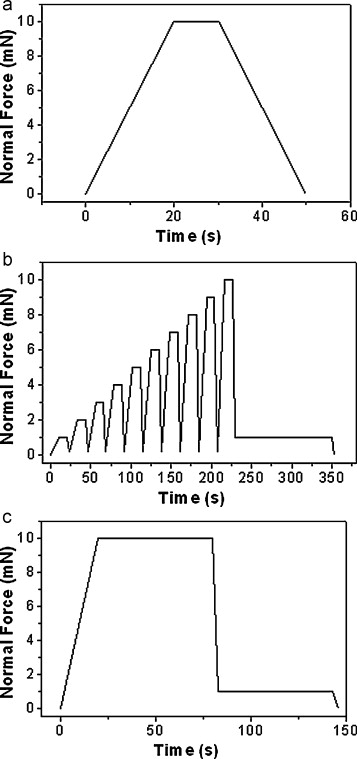
Abstract
Nanoindentation has become a common technique for measuring the hardness and elastic–plastic properties of materials, including coatings and thin films. In recent years, different nanoindenter instruments have been commercialised and used for this purpose. Each instrument is equipped with its own analysis software for the derivation of the hardness and reduced Young's modulus from the raw data. These data are mostly analysed through the Oliver and Pharr method. In all cases, the calibration of compliance and area function is mandatory. The present work illustrates and describes a calibration procedure and an approach to raw data analysis carried out for six different nanoindentation instruments through several round-robin experiments. Three different indenters were used, Berkovich, cube corner, spherical, and three standardised reference samples were chosen, hard fused quartz, soft polycarbonate, and sapphire. It was clearly shown that the use of these common procedures consistently limited the hardness and reduced the Young's modulus data spread compared to the same measurements performed using instrument-specific procedures. The following recommendations for nanoindentation calibration must be followed: (a) use only sharp indenters, (b) set an upper cut-off value for the penetration depth below which measurements must be considered unreliable, (c) perform nanoindentation measurements with limited thermal drift, (d) ensure that the load–displacement curves are as smooth as possible, (e) perform stiffness measurements specific to each instrument/indenter couple, (f) use Fq and Sa as calibration reference samples for stiffness and area function determination, (g) use a function, rather than a single value, for the stiffness and (h) adopt a unique protocol and software for raw data analysis in order to limit the data spread related to the instruments (i.e. the level of drift or noise, defects of a given probe) and to make the H and Er data intercomparable.
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micron.2011.07.016
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of one-dimensional silver–H2Ti3O7 nanotubes
Rodriguez-Gonzalez, V; Obregon-Alfaro, S; Lozano-Sanchez, LM; Lee, SWJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 353 (2012) 163-170 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2011.11.020

Abstract
The formation of silver hydrogen trititanate nanotubes, based on the controllable microwave-assisted hydrothermal nanocrystalline TiO2 transition, was investigated by means of XRD, UV–vis–DRS, Raman, FESEM and HRTEM. The results show that the rapid formation of H-trititanate nanotubes is achieved by self-assemblage of silver nanoparticles in which the lamellar intermediates react with NaOH in hydrothermal conditions. The presence of Ag° nanoparticles in the precursor promotes rapid and more complete formation of layered H2Ti3O7 nanotubes. After reacting for 4 h without subsequent thermal treatment, the inner diameters of the cylinder-like nanotubes are in the range of 3.6–4.0 nm, while their outer diameters are in the range of 7.6–8 nm. In addition, some straight nanotubes form bundles which are hundreds of nanometers in length. As-synthesized ultrathin nanotubes and crystalline precursors were evaluated by methyl orange dye (MOD) UV photo-oxidation. The complete degradation of MOD is achieved after 3.5 h of UV irradiation in the presence of silver–TiO2 nanocomposites, resulting in 50% of dye mineralization.
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2011.11.020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrochromic Behavior of WxSiyOz Thin Films Prepared by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering at Normal and Glancing Angles
Gil-Rostra, J; Cano, M; Pedrosa, JM; Ferrer, FJ; Garcia-Garcia, F; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4 (2012) 628-638 DOI: 10.1021/am2014629
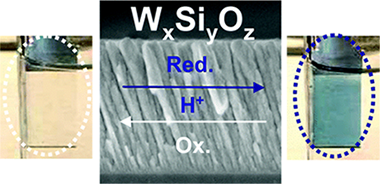
Abstract
This work reports the synthesis at room temperature of transparent and colored WxSiyOz thin films by magnetron sputtering (MS) from a single cathode. The films were characterized by a large set of techniques including X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), and Raman spectroscopies. Their optical properties were determined by the analysis of the transmission and reflection spectra. It was found that both the relative amount of tungsten in the W–Si MS target and the ratio O2/Ar in the plasma gas were critical parameters to control the blue coloration of the films. The long-term stability of the color, attributed to the formation of a high concentration of W5+ and W4+ species, has been related with the formation of W–O–Si bond linkages in an amorphous network. At normal geometry (i.e., substrate surface parallel to the target) the films were rather compact, whereas they were very porous and had less tungsten content when deposited in a glancing angle configuration. In this case, they presented outstanding electrochromic properties characterized by a fast response, a high coloration, a complete reversibility after more than one thousand cycles and a relatively very low refractive index in the bleached state.
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/am2014629
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Nanoecotoxicity effects of engineered silver and gold nanoparticles in aquatic organisms
Lapresta-Fernandez, A; Fernandez, A; Blasco, JTrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 32 (2012) 40-59 DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2011.09.007
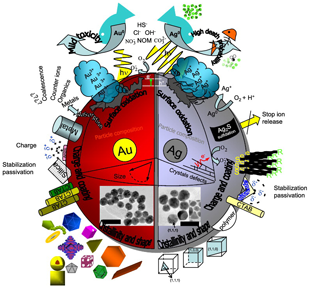
Abstract
Engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) are increasingly being incorporated into commercial products. A better understanding is required of their environmental impacts in aquatic ecosystems.
This review deals with the ecotoxicity effects of silver and gold ENPs (AgNPs and AuNPs) in aquatic organisms, and considers the means by which these ENPs enter aquatic environments, their aggregation status and their toxicity. Since ENPs are transported horizontally and vertically in the water column, we discuss certain factors (e.g., salinity and the presence of natural organic materials), as they cause variations in the degree of aggregation, size range and ENP toxicity. We pay special attention to oxidative stress induced in organisms by ENPs.
We describe some of the main analytical methods used to determine reactive oxygen species, antioxidant enzyme activity, DNA damage, protein modifications, lipid peroxidation and relevant metabolic activities. We offer an overview of the mechanisms of action of AgNPs and AuNPs and the ways that relevant environmental factors can affect their speciation, agglomeration or aggregation, and ultimately their bio-availability to aquatic organisms.
Finally, we discuss similarities and differences in the adverse effects of ENPs in freshwater and salt-water systems.
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2011.09.007
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
In Situ XAS Study of Synergic Effects on Ni-Co/ZrO2 Methane Reforming Catalysts
Gonzalez-delaCruz, VM; Pereniguez, R; Ternero, F; Holgado, JP; Caballero, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 2919-2926 DOI: 10.1021/jp2092048
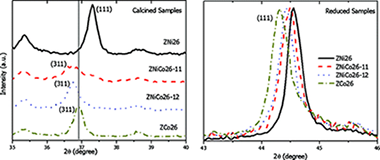
Abstract
Four different mono and bimetallic Ni–Co/ZrO2 catalysts have been studied by means of in situ XAS, X-ray diffraction, TPR, and measurements of the catalytic activity in the dry reforming reaction of methane (DRM). Even though the cobalt monometallic system has no activity for the methane reforming reaction, both bimetallic catalysts (with 1:1 and 1:2 Ni/Co ratio, respectively), showed a better activity and stability than the nickel monometallic system. The XRD data indicate that a mixed cobalt–nickel spinel is formed by calcination of the precursor solids, leading to the formation of an alloy of both metals after reduction in hydrogen. In situ XAS experiments showed a much better resistance of metals in the bimetallic systems to be oxidized under reaction conditions at temperatures until 750 °C. After these results, we proposed the formation in the bimetallic systems of a more reducible nickel–cobalt alloy phase, which remains completely metallic in contact with the CO2/CH4 reaction mixture at any temperature. The presence of adjacent nickel and cobalt sites seems to avoid the deactivation of cobalt in the DRM reaction. In the case of cobalt sites, the presence of adjacent nickel atoms seems to prevent the deposition of carbon over the cobalt sites, now showing its higher activity in the dry reforming reaction. Simultaneously, this higher activity of the cobalt sites in the bimetallic system produces more hydrogen as a product, maintaining the nickel atoms completely reduced under reaction conditions. This synergic effect accounts for the better performance of the bimetallic systems and points at both, the oxidation state of nickel particles under reaction conditions and the carbon deposition processes, as important factors responsible for differences in catalytic activities and stabilities in this hydrocarbon reaction.
February, 2012 · DOI: 10.1021/jp2092048
- ‹ previous
- 30 of 37
- next ›














