Scientific Papers in SCI
2011
2011
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of the strong metal support interaction effect (SMSI) of Pt/TiO(2) and Pd/TiO(2) systems in the photocatalytic biohydrogen production from glucose solution
Colmenares, JC; Magdziarz, A; Aramendia, MA; Marinas, A; Marinas, JM; Urbano, FJ; Navio, JACatalysis Communications, 16 (2011) 1-6 DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2011.09.003
Abstract
Two different catalysts consisting of Pt/TiO2 and Pd/TiO 2 were submitted to diverse oxidative and reductive calcination treatments and tested for photocatalytic reforming of glucose water solution (as a model of biomass component) in H2 production. Oxidation and reduction at 850°C resulted in better photocatalysts for hydrogen production than Degussa P-25 and the ones prepared at 500°C, despite the fact that the former consisted in very low surface area (6-8 m2/g) rutile titania specimens. The platinum-containing systems prepared at 850°C give the most effective catalysts. XPS characterization of the systems showed that thermal treatment at 850°C resulted in electron transfer from titania to metal particles through the so-called strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) effect. Furthermore, the greater the SMSI effect, the better the catalytic performance. Improvement in photocatalytic behavior is explained in terms of avoidance of electron-hole recombination through the electron transfer from titania to metal particles.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2011.09.003
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Application of the solid state NMR to the study of the alcohol/alkane mixtures adsorption onto graphite
María D. Alba, Miguel A. Castro, Stuart M. Clarke, Santiago Medina, Loic Messe, Carmen MillánSolid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 40 (2011) 138-143 DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2011.11.002
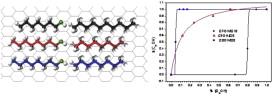
Abstract
The mixing of molecules adsorbed from solution to different interfaces has both industrial and academic relevance and the mixing behaviour at the interface is a key to understanding for example, that the surface tension of a mixture of two surfactants is lower than either of the two pure materials and many other effects. In this paper, we report, for the first time, the application of Solid State NMR to the study of alkane/alcohol mixtures, in a range of relative size ratio between 0 and 0.35, adsorbed onto graphite at high, multilayer coverage. Moreover, this paper evaluated, for the first time, the utility of the combined used of 1H and 2H NMR for: (i) determining the surface composition and (ii) making a theoretical approach to the sorption isotherm. A variety of preferential adsorption behaviour is reported. Preferential adsorption of the longer molecule (decane vs. heptanol) from a mixture has been observed. However, if both components are of similar length, the alcohol is preferentially adsorbed (heptanol vs. octane and octanol vs. octane). Finally, a linear relation between the relative size ratio and the amount of alcohol at monolayer coverage is observed.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2011.11.002
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structure, Electrical Resistivity, and Thermal Conductivity of Beech Wood Biocarbon Produced at Carbonization Temperatures below 1000 degrees C
Parfen'eva, LS; Orlova, TS; Kartenko, NF; Smirnov, BI; Smirnov, IA; Misiorek, H; Jezowski, A; Muha, J; Vera, MCPhysics of the Solid State, 53 (2011) 2398-2407 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783411110230
Abstract
This paper reports on measurements of the thermal conductivity. and the electrical resistivity. in the temperature range 5-300 K, and, at 300 K, on X-ray diffraction studies of high-porosity (with a channel pore volume fraction of similar to 47 vol %) of the beech wood biocarbon prepared by pyrolysis (carbonization) of tree wood in an argon flow at the carbonization temperature T(carb) = 800 degrees C. It has been shown that the biocarbon template of the samples studied represents essentially a nanocomposite made up of amorphous carbon and nanocrystallites-"graphite fragments" and graphene layers. The sizes of the nanocrystallites forming these nanocomposites have been determined. The dependences rho(T) and kappa(T) have been measured for the samples cut along and perpendicular to the tree growth direction, thus permitting determination of the magnitude of the anisotropy of these parameters. The dependences rho(T) and kappa(T), which have been obtained for beech biocarbon samples prepared at T(carb) = 800 degrees C, are compared with the data amassed by us earlier for samples fabricated at T(carb) = 1000 and 2400 degrees C. The magnitude and temperature dependence of the phonon thermal conductivity of the nanocomposite making up the beech biocarbon template at T(carb) = 800 degrees C have been found.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783411110230
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Structural and catalytic properties of lanthanide (La, Eu, Gd) doped ceria
Hernandez, WY; Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 184 (2011) 3014-3020 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2011.09.018
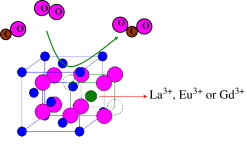
Abstract
Ce0.9M0.1O2-δ mixed oxides (M=La, Eu and Gd) were synthesized by coprecipitation. Independent of the dopant cation, the obtained solids maintain the F-type crystalline structure, characteristic of CeO2 (fluorite structure) without phase segregation. The ceria lattice expands depending on the ionic radii of the dopant cation, as indicated by X-ray diffraction studies. This effect also agrees with the observed shift of the F2g Raman vibrational mode. The presence of the dopant cations in the ceria lattice increases the concentration of structural oxygen vacancies and the reducibility of the redox pair Ce4/Ce3. All synthesized materials show higher catalytic activity for the CO oxidation reaction than that of bare CeO2, being Eu-doped solid the one with the best catalytic performances despite of its lower surface area.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2011.09.018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of Al2O3 reinforcement on precipitation kinetic of Cu–Cr nanocomposite
S. Sheibani, A. Ataie, S. Heshmati-Manesh, A. Caballero, J.M. CriadoThermochimica Acta, 526 (2011) 222-228 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2011.09.024
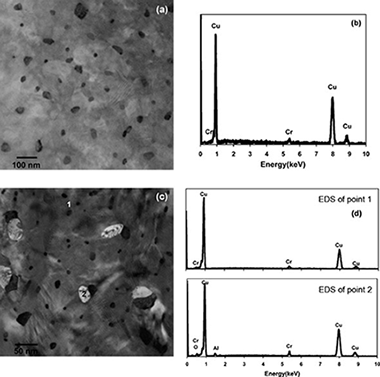
Abstract
In this paper, the kinetic of precipitation process in mechanically alloyed Cu-1 wt.% Cr and Cu-1 wt.% Cr/3 wt.% Al2O3 solid solution was compared using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ageing kinetics in Cu–Cr and Cu–Cr/Al2O3 can be described using Johnson–Mehl–Avrami (JMA) and Sestak–Berggren (SB) models, respectively. These different behaviors have been discussed in details. It was found that in presence of Al2O3 reinforcement, the ageing activation energy is decreased and the overall ageing process is accelerated. This behavior is probably due to higher dislocation density previously obtained during ball milling and Al2O3–Cu interface. TEM observations confirm that Al2O3–Cu interface and structural defects act as a primary and secondary nucleation sites, respectively.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2011.09.024
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Remediation of metal-contaminated soils with the addition of materials – Part I: Characterization and viability studies for the selection of non-hazardous waste materials and silicates
R. González-Núñez, M.D. Alba, M.M. Orta, M. Vidal, A. RigolChemosphere, 85 (2011) 1511-1517 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.09.042
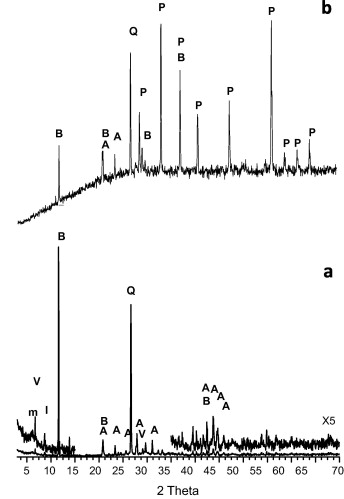
Abstract
Contamination episodes in soils require interventions to attenuate their impact. These actions are often based on the addition of materials to increase contaminant retention in the soil and to dilute the contaminant concentration. Here, non-hazardous wastes (such as sugar foam, fly ash and a material produced by the zeolitization of fly ash) and silicates (including bentonites) were tested and fully characterized in the laboratory to select suitable materials for remediating metal-contaminated soils. Data from X-ray fluorescence (XRF), N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy/energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM–EDX) analyses revealed the chemical composition, specific surface area and the phases appearing in the materials. A pH titration test allowed the calculation of their acid neutralization capacity (ANC). The metal sorption and desorption capacities of the waste materials and silicates were also estimated. Sugar foam, fly ash and the zeolitic material were the best candidate materials. Sugar foam was selected because of its high ANC (17 000 meq kg−1), and the others were selected because of their larger distribution coefficients and lower sorption reversibilities than those predicted in the contaminated soils.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.09.042
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Comments on "an essay on contact angle measurements": Determination of surface roughness and modeling of the wetting behavior
Terriza, A; Alvarez, R; Yubero, F; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 8 (2011) 998-1002 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201100081
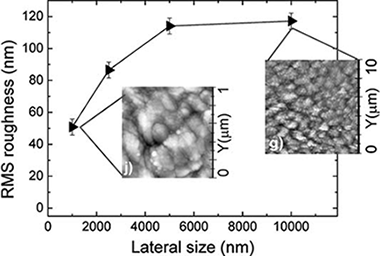
Abstract
This commentary addresses the problem of determining surface roughness values and their use to assess the wetting behavior of surfaces. For very rough surfaces it is shown that depending on the observation scale by atomic force microscopy (AFM) quite different RMS roughness values can be obtained and that only the values taken at saturation can be used for properly describing the roughness of the examined materials. This effect has clear consequences when trying to apply wetting models to account for the influence of roughness on contact angles. These ideas are discussed with examples taken from rough polymer surfaces subjected to plasma etching. Debate - Discussion: To account for the wetting behavior of real surfaces within the Wenzel and similar models only surface roughness values determined at saturation can be used. This implies to check different observation areas by AFM and to choose the RMS roughness values once a maximum value of this parameter has been reached.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201100081
Reactividad de Sólidos
Formation of the complete range of Ti5Si3-xGex solid solutions via mechanically induced self-sustained reactions
José M. Córdoba, Ernesto Chicardi, Miguel A. Avilés, Francisco J. GotorIntermetallics, 19 (2011) 1688-1692 DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2011.07.005
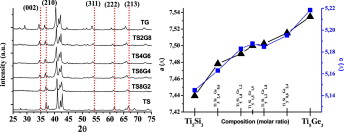
Abstract
The complete range of Ti5Si3–Ti5Ge3 solid solutions was synthesised from elemental mixtures of Ti, Si, and Ge under an inert atmosphere via mechanically induced self-sustaining reactions (MSR). The stoichiometry of Ti5Si3−xGex solid solutions was controlled by adjusting the Si/Ge ratio of the initial mixture. The chemical composition and lattice parameters of the materials confirmed that Ti5Si3–Ti5Ge3 solid solutions with good chemical homogeneity could be produced via MSR.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2011.07.005
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Soft plasma processing of organic nanowires: a route for the fabrication of 1D organic heterostructures and the template synthesis of inorganic 1D nanostructures
Maria Alcaire, Juan R. Sanchez-Valencia, Francisco J. Aparicio, Zineb Saghi, Juan C. Gonzalez-Gonzalez, Angel Barranco, Youssef Oulad Zian, Agustin R. Gonzalez-Elipe, Paul Midgley, Juan P. Espinos, Pierangelo Groening and Ana BorrasNanoscale, 3 (2011) 4554-4559 DOI: 10.1039/C1NR11001B
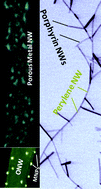
Abstract
Hierarchical (branched) and hybrid metal-NPs/organic supported NWs are fabricated through controlled plasma processing of metalloporphyrin, metallophthalocyanine and perylene nanowires. The procedure is also applied for the development of a general template route for the synthesis of supported metal and metal oxide nanowires.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1039/C1NR11001B
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Well-defined negatively charged gold carbonyls on Au/SiO2
Chakarova, K., Mihaylov, M., Ivanova, S., Centeno, M.A., Hadjiivanov, K.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115 (2011) 21273-21282 DOI: 10.1021/jp2070562
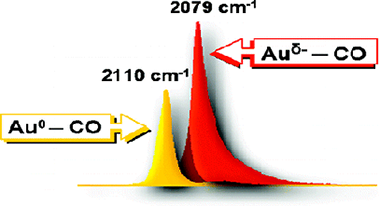
Abstract
A Au/SiO2 sample was prepared by ammonia-assisted grafting using HAuCl4 as a gold precursor. Gold on the sample evacuated at 673 K is essentially in metallic form: adsorption of CO at 100 K results in formation of Au0-CO species (IR band at 2122 cm-1 shifting to 2103 cm-1 at high coverage). Coadsorption of CO and O2 even at ambient temperature leads to creation of Auδ+ sites and oxidation of CO. On the contrary, increase of the contact time between CO and the sample leads to a gradual reduction of Au0 to Au δ- species. The process is slightly favored by the presence of water and strongly enhanced in the presence of hydrogen. Back oxidation of Auδ- to Au0 and to Auδ+ occurs in the presence of oxygen. The Auδ- sites strongly adsorb CO and form different interconverting carbonyls observed in the 2080-2050 cm -1 region. On the basis of adsorption of CO-13CO and CO-13C18O isotopic mixtures, it is concluded that all Auδ--CO species are linear, and probably ordered structures are formed. Intensity transfer phenomena are nicely monitored during adsorption of CO isotopic mixtures. The eventual role of negatively charged gold in catalysis is discussed.
November, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/jp2070562
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Evolution of Phases and Al–Si Distribution during Na-4-Mica Synthesis
María D. Alba, Miguel A. Castro, Moisés Naranjo, M. Mar Orta, Esperanza Pavón, and M. Carolina PazosJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115 (41), pp 20084–20090 DOI: 10.1021/jp207408h
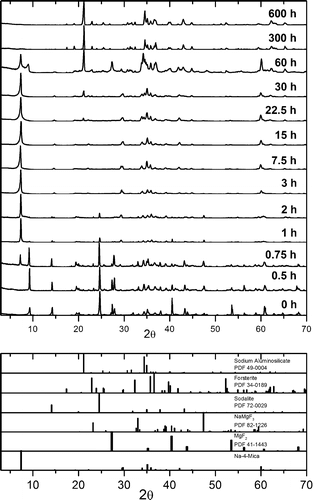
Abstract
Na-4-mica, a highly charged fluorophlogopite, has recently attracted much attention because of its unique combination of high charge (four charges per unit cell) and its swelling and cation-exchange properties. The ability to improve the properties of this mica depends on gaining knowledge about its phase evolution during the calcination process. For the synthesis, the stoichiometric powder mixture (4SiO 2/2Al 2O 3/6MgF 2/8NaCl) was heated to 900 °C for 0-600 h. The obtained solids were characterized by X-ray fluorescence (XRF); X-ray diffraction (XRD); scanning electron microscopy/energy-dispersive X-ray (SEM/EDX) analysis; 29Si, 27Al, and 23Na magic-angle-spinning MAS NMR spectroscopy; and thermogravimetric/differential thermal analysis (TG/DTA). The results showed that the precursors are rapidly (t < 3 h) transformed into sodalite, Al 6Na 8(SiO 4) 6Cl 2, and a 2:1 phyllosilicate. For t = 7.5 h, the amount of 2:1 phyllosilicate increased as a result of the decomposition of sodalite, with a progressive incorporation of aluminum in the 2:1 phyllosilicate being observed. For t = 7.5 h, synthesis of Na-4-mica was considered to be complete, as the material remained essentially unaltered for the next 15 h. For t = 30 h, the mica started to decompose, and for very long reaction times (t ≥ 300 h), only forsterite and a carnegierite phase were present.
October, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/jp207408h
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Magnetic and fluorescent core-shell nanoparticles for ratiometric pH sensing
Lapresta-Fernández, A., Doussineau, T., Dutz, S., Steiniger, F., Moro, A.J., Mohr, G.J.Nanotechnology, 22 (2011), Article number 415501 DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/22/41/415501
Abstract
This paper describes the preparation of nanoparticles composed of a magnetic core surrounded by two successive silica shells embedding two fluorophores, showing uniform nanoparticle size (50-60nm in diameter) and shape, which allow ratiometric pH measurements in the pH range 5-8. Uncoated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (∼10nm in diameter) were formed by the coprecipitation reaction of ferrous and ferric salts. Then, they were added to a water-in-oil microemulsion where the hydrophilic silica shells were obtained through hydrolysis and condensation of tetraethoxyorthosilicate together with the corresponding silylated dye derivatives - a sulforhodamine was embedded in the inner silica shell and used as the reference dye while a pH-sensitive fluorescein was incorporated in the outer shell as the pH indicator. The magnetic nanoparticles were characterized using vibrating sample magnetometry, dynamic light scattering, transmission electron microscopy, x-ray diffraction and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The relationship between the analytical parameter, that is, the ratio of fluorescence between the sensing and reference dyes versus the pH was adjusted to a sigmoidal fit using a Boltzmann type equation giving an apparent pKa value of 6.8. The fluorescence intensity of the reference dye did not change significantly (∼3.0%) on modifying the pH of the nanoparticle dispersion. Finally, the proposed method was statistically validated against a reference procedure using samples of water and physiological buffer with 2% of horse serum, indicating that there are no significant statistical differences at a 95% confidence level.
October, 2011 · DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/22/41/415501
Old and modern pigments identification from a 14th century sculpture by Micro-Raman
M. L. Franquelo, A. Duran, D. Arquillo & J. L. Perez-RodriguezSpectroscopy Letters, 44 (2011) 464-468 DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2011.610401
Abstract
The chromatic characterization of the external part of the sculpture showed homogeneity values in the majority of the colored zones. The optical microscopy study showed different layers in the painting cross-sections. The complex polychromy was attributed to several restoration processes carried out along the time. The composition of the different layers of painting cross-sections was studied using the micro-Raman technique. The micro-Raman technique was very useful in characterizing some pigments that are difficult to determine by other experimental techniques. The study showed the presence of several pigments that had been applied in ancient and recent times.
October, 2011 · DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2011.610401
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structure and Chemical State of Octadecylamine Self-Assembled Monolayers on Mica
Benitez, JJ; San-Miguel, MA; Dominguez-Meister, S; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Salmeron, MJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 115 (40) (2011) 19716-19723 DOI: 10.1021/jp203871g
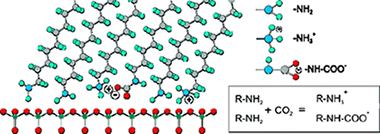
Abstract
Structural and chemical data on n-octadecylamine self-assembled monolayers on mica (ODA/mica SAMs) have been obtained from ATR-FTIR and XPS spectroscopies. The analysis of the methylene modes concludes that alkylamine molecules are arranged in a rigid and well-ordered packing. Besides, the magnitude of the splitting of the methylene scissoring deflection is consistent with a molecular tilted configuration within the self-assembled layer, as already reported from topographic AFM data. Molecular dynamics simulations have supported this conclusion. XPS has revealed the presence of an important fraction of protonated amino groups (-NH3+) even in freshly prepared ODA/mica SAMs in air at RT. Two sources of protonation are proposed: (i) the acid-base reaction of (-NH2) end groups with the water adlayer on the surface of hydrophilic mica and (ii) the formation of an alkylamonium alkylcarbamate by a fast reaction with the atmospheric CO2 dissolved in such water adlayer. Though the water induced amino protonation is hypothetical, the presence of carbamate is univocally confirmed by ATR-FTIR. Upon extended contact with air (ripening) the conformational ordering in ODA/mica SAMs is slightly improved. Besides, further amino group protonation takes place with no additional carbamate formation. The process is described by a tentative mechanism in which protons are transferred from water molecules at the edges of SAMs islands to the inside. On the other side, carbamation is hindered by the steric effect of CO2 molecules trying to penetrate the close packed structure of octadecylamine molecules.
October, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/jp203871g
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
The effect of polymorphic structure on the structural and chemical stability of yttrium disilicates
Evgeny Galunin, Miquel Vidal and María D. AlbaAmerican Mineralogist, 96 (2011) 1512-1520 DOI: 10.2138/am.2011.3659
Abstract
Under pressure and temperature conditions like those found in deep geological repositories (DGRs), rare-earth cations may react with silicates to form rare-earth disilicates. This study establishes the stability range of yttrium disilicates in response to changes in pH. The α, β, γ, and δ polymorphs of Y2Si2O7 were synthesized by the sol-gel process at temperatures between 1100 and 1650 °C and subjected to pHstat leaching tests. By measuring the Y and Si leaching rates and monitoring the transformation of the crystalline and amorphous phases, we showed that yttrium disilicates were stable at pH > 5. At pH < 5, the pH stability sequence was consistent with the temperature-dependent stabilities of Y2Si2O7 phases, with the δ polymorph showing the lowest leaching rates. Because rare-earth compounds can be used as a proxy for analogous actinide hosts, the results of this study can be used to predict the performance of engineered barriers in DGR.
October, 2011 · DOI: 10.2138/am.2011.3659
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhanced gas sensing performance of TiO2 functionalized magneto-optical SPR sensors
M.G. Manera, G. Montagna, E. Ferreiro-Vila, L. González-García, J.R. Sánchez-Valencia, A.R. González-Elipe, A.Cebollada, J.M. Garcia-Martin, A. Garcia-Martin, G. Armelles and R. RellaJournal of Materials Chemistry, 21 (2011) 16049-16056 DOI: 10.1039/c1jm11937k
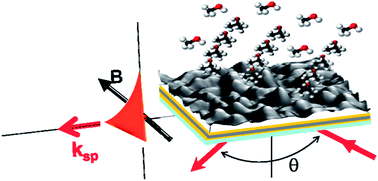
Abstract
Porous TiO2 thin films deposited by glancing angle deposition are used as sensing layers to monitor their sensing capabilities towards Volatile Organic Compounds both in a standard Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) sensor and in Magneto-Optical Surface Plasmon Resonance (MO-SPR) configuration in order to compare their sensing performances. Here our results on the enhanced sensing capability of these TiO2 functionalized MO-SPR sensors with Au/Co/Au transducers with respect to traditional SPR gas sensors are presented.
October, 2011 · DOI: 10.1039/c1jm11937k
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Colored semi-transparent Cu-Si oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering
Gil-Rosta, J; Yubero, F; Fernandez, R; Vilajoana, T; Artus, P; Dursteler, JC; Cotrino, J; Ortega, I; Gonzalez-Elipe, AROptical Material Express, 1 (2011) 1100-1112 DOI: 10.1364/OME.1.001100

Abstract
Colored semi-transparent Cu-Si oxide thin films have been prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering from a single cathode of copper-silicon composition. Thin films of different composition and optical response were obtained by changing process parameters like the relative amount of copper in the target and the O2/Ar mixture of the reactive plasma gas. The film characteristics were analyzed by several techniques. Their optical properties (refractive index, absorption coefficient, color) have been correlated with the process parameters used in the film preparation as well as with the film stoichiometry and chemistry.
September, 2011 · DOI: 10.1364/OME.1.001100
Analytical study of Roman and Arabic wall paintings in the Patio De Banderas of Reales Alcazares' Palace using non-destructive XRD/XRF and complementary techniques
Duran, A., Perez-Rodriguez, J.L., Jimenez de Haro, M.C., Franquelo, M.L., Robador, M.D.Journal of Archaeological Science, 38 (2011) 2366-2377 DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2011.04.021
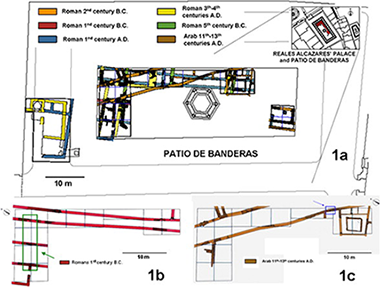
Abstract
A portable XRD/XRF system and complementary laboratory techniques were employed to improve the knowledge of the procedures used to create Roman and Arabic wall paintings. Integrated physico-chemical investigations were conducted on fragments of artworks collected from the archaeological excavation of the Patio de Banderas in the Reales Alcazares' Palace of Seville (Spain), and a comparative study on the pigments from both historical periods was performed. As a result, pigments such as vermilion, red ochre, yellow ochre, green earth, Egyptian blue, carbon and phosphor-based black pigments were detected in Roman samples; however, in the Arabic fragments, only haematite was observed. In addition, the size and shape of the particles of the wall paintings were studied with an XRD 2-dimensional detector and SEM-EDX.
September, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2011.04.021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO oxidation at low temperature on Au/CePO4: Mechanistic aspects
Romero-Sarria, F., Domínguez, M.I., Centeno, M.A., Odriozola, J.A.Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 107 (2011), 268-273 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.07.022
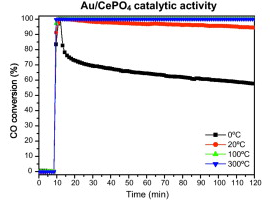
Abstract
This work reports the synthesis and characterization of a cerium phosphate supported gold catalyst as well as its catalytic activity for the oxidation of CO. A precipitation method in the presence of an organic modifier followed by a hydrothermal treatment was used for the support synthesis, resulting in high surface area nanometric particles. Gold/cerium phosphate catalyst with a 1% (w/w) nominal gold content was characterized using XRF, XRD, N2 adsorption-desorption measurements, TEM and DRIFTS-MS. The catalyst shows good catalytic activity at low temperature. The activity is related to the generation of oxygen vacancies in the support caused by the elimination of structural oxygen. In situ studies revealed that the reaction of the oxygen vacancies with gaseous oxygen resulted in the formation of peroxo species. These species are responsible for the activity detected at room temperature in both the catalyst and the support. Moreover, the presence of carbonate and hydrogen carbonate acting as reaction intermediates have been observed.
September, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.07.022
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Aligned TiO(2) nanocolumnar layers prepared by PVD-GLAD for transparent dye sensitized solar cells
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Gonzalez-Valls, I; Lira-Cantu, M; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AREnergy and Environmental Science, 4 (2011) 3426-3435 DOI: 10.1039/C0EE00489H
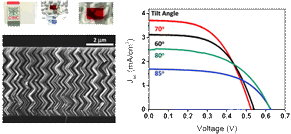
Abstract
Transparent thin film electrodes made of vertically aligned nanocolumns of TiO2 with well-controlled oblique angles were grown by physical vapor deposition at glancing incidence (PVD-GLAD). For an electrode thickness of 500 nm, we report a 40% variation on solar cell efficiency (from 0.6% to 1.04%) when the deposition angle was modified between 60° and 85°. Transparent thicker films with higher surface area deposited at the optimal angle of 70° were grown with a zigzag morphology which confers high mechanical strength to the thin films. Using this topology, the application of an electrode thickness of 3 m in a DSC resulted in a power conversion efficiency of 2.78% maintaining electrode transparency.
September, 2011 · DOI: 10.1039/C0EE00489H
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of Bi-doped TiO2 photocatalysts under simulated solar irradiation
Murcia-López, S., Hidalgo, M.C., Navío, J.A.Applied Catalysis A: General, 404 (2011) 59-67 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.07.008
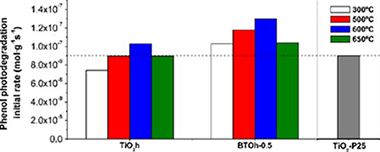
Abstract
A series of Bi3+-doped TiO2 catalysts with a doping concentration up to 2 wt% were prepared by a sol-gel hydrothermal method. The prepared photocatalysts were characterized by different techniques to determine their structure, morphology and light absorption properties. The activities were evaluated in the photocatalytic oxidation of phenol in aqueous solution under UV-vis illumination. The experimental results indicate that the presence of Bi3+ in TiO2 catalysts enhances the photocatalytic reaction of phenol degradation, although the efficiency of the process markedly depends on the nominal content of the Bi3+ and on the calcination temperature. It was found that the optimal dosage of 0.5 wt% Bi3+ in TiO2 and calcinations at 600 °C 4 h achieved the fastest reaction of phenol degradation under the experimental conditions. From the comparison of the initial rates of the photocatalytic degradation of phenol between home prepared undoped and Bi3+-doped TiO2 with commercial TiO2 Degussa P25, it can be inferred that home prepared TiO 2 calcined at temperatures above 500 °C clearly exceed the photocatalytic performance of P25. When bismuth is incorporated, the reaction rate values are even higher, especially at 600 °C. Even when Bi 3+-doped TiO2 (0.5 wt% Bi3+) calcined at 600 °C has almost the same BET surface than P25, its activity is better. In particular, the reaction rate for the sample with a 0.5% mass content of Bi 3+ calcined at 600 °C not only present higher value with respect to the other series but also a degree of mineralization close to 100%.
September, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.07.008
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Theoretical and experimental characterization of TiO2 thin films deposited at oblique angles
Álvarez, R., González-García, L., Romero-Gómez, P., Rico, V., Cotrino, J., Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R., Palmero, A.Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 44 (2011) Article number 385302 DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/44/38/385302
Abstract
The microstructural features of amorphous TiO2 thin films grown by the electron beam physical vapour deposition technique at oblique angles have been experimentally and theoretically studied. The microstructural features of the deposited films were characterized by considering both the column tilt angle and the increase in the column thickness with height. A Monte Carlo model of film growth has been developed that takes into account surface shadowing, short-range interaction between the deposition species and the film surface, as well as the angular broadening of the deposition flux when arriving at the substrate. The good match between simulations and experimental results indicates the importance of these factors in the growth and microstructural development of thin films deposited at oblique angles.
September, 2011 · DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/44/38/385302
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Oxidation of CO over gold supported on Zn-modified ceria catalysts
Laguna, O.H., Centeno, M.A., Romero-Sarria, F., Odriozola, J.A.Catalysis Today, 172 (2011) 118-123 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.02.015

Abstract
A series of Zn-modified ceria solids were prepared by thermal decomposition of the corresponding metal propionates. The formation of segregated ZnO particles on the ceria surface is evidenced for these solids using X-ray diffraction; in addition to this the characterization data may allow discarding the formation of a ZnO-CeO2 solid solution. On modifying with Zn, the reducibility of the ceria support is enhanced, being the highest reducibility the one obtained for the ZnO-CeO2 solid having a 1:9 Zn:Ce atomic ratio (CeZn10). The activity of this solid in the CO oxidation reaction was the highest among the tested Zn-modified ceria solids. Therefore, catalysts containing 1 wt.% gold, supported on pure ceria and CeZn solids, were prepared, characterized and their catalytic activities tested. The Zn-modified gold catalyst is more active than the un-modified Au/CeO2 catalyst in the oxidation of CO; this behavior is related to the higher metallic dispersion of gold on the CeZn support surface. However, the number of oxygen vacancies acting as nucleation sites for gold, is hardly modified in the Zn-modified ceria support and, therefore, the higher gold dispersion must be related to high electron density sites on the catalyst surface as a result of Au-Ce-Zn interaction, this improved gold dispersion results in higher activities for CO oxidation.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.02.015
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Angular emission properties of a layer of rare-earth based nanophosphors embedded in one-dimensional photonic crystal coatings
Sánchez-Sobrado, O., Yacomotti, A.M., Calvo, M.E., Martínez, O.E., Ocaña, M., Núñez, N., Levenson, J.A., Míguez, H.Applied Physics Letters, 99 (2011) Article number 051111 DOI: 10.1063/1.3619814
Abstract
The angular properties of light emitted from rare-earth based nanophosphors embedded in optical resonators built in one-dimensional photonic crystal coatings are herein investigated. Strong directional dependence of the photoluminescence spectra is found. Abrupt angular variations of the enhancement caused by the photonic structure and the extraction power are observed, in good agreement with calculated polar emission patterns. Our results confirm that the optical cavity favors the extraction of different wavelengths at different angles and that integration of nanophosphors within photonic crystals provides control over the directional emission properties that could be put into practice in phosphorescent displays.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1063/1.3619814
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structural elucidation of Β-(Y,Sc)2Si2O 7: Combined use of 89Y MAS NMR and powder diffraction
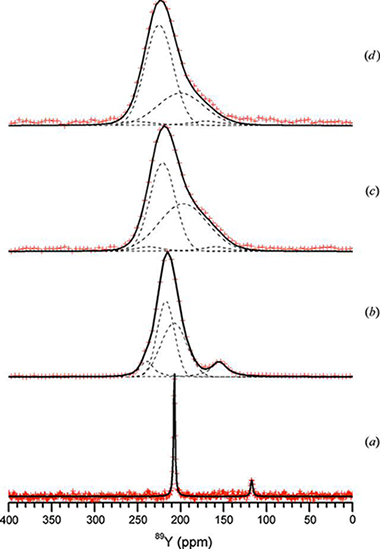
Allix, M., Alba, M.D., Florian, P., Fernandez-Carrion, A.J., Suchomel, M.R., Escudero, A., Suard, E., Becerro, A.I.Journal of Applied Crystallography, 44 (2011) 846-852 DOI: 10.1107/S0021889811021303
Abstract
Although the structures of pure Sc2Si2O7 and Β-Y2Si 2O7 have been described in the literature using the C2/m space group, 29Si magic angle spinning (MAS) NMR measurements of the intermediate members of the Sc2Si2O7-Β- Y2Si2O7 system indicate a lowering of the symmetry to the C2 space group. Indeed, these compositions exhibit a unique Si crystallographic site and an Si-O-Si angle lower than 180°, incompatible with the C2/m space group. C2 is the only possible alternative. Space group Cm can be discarded with regard to its two different Si sites per unit cell. Moreover, 89Y MAS NMR data have revealed the existence of two different Y sites in the structure of the intermediate members of the Sc 2Si2O7-Β-Y2Si2O 7 system, confirming the lowering of the symmetry to the C2 space group. The viability of the C2 model has therefore been tested and confirmed by refinement of synchrotron and neutron powder diffraction data for the different members of the system. The structural evolutions across the Sc 2Si2O7-Β-Y2Si2O 7 system are discussed.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1107/S0021889811021303
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Aspects of heterogeneous enantioselective catalysis by metals
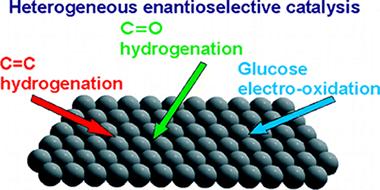
Kyriakou, G., Beaumont, S.K., Lambert, R.M.Langmuir, 27 (2011) 9687-9695 DOI: 10.1021/la200009w
Abstract
Some aspects of metal-catalyzed heterogeneous enantioselective reactions are reviewed with specific reference to four different systems where the phenomena that control enantioselection appear to be very different. In the case of glucose electro-oxidation, it is clear that any intrinsic chirality present at the metal surface plays a vital role. With α-keto hydrogenation, achiral surfaces modified by the adsorption of chiral agents become effective enantioselective catalysts and the formation of extended arrays of chiral species appears not to be of importance: instead a 1:1 docking interaction controlled by hydrogen bonding between the adsorbed chiral modifier and the prochiral reactant determines the outcome. Hydrogen bonding also plays a central role in β-ketoester hydrogenation, but here fundamental studies indicate that the formation of ordered arrays involving the reactant and chiral ligand is of importance. Asymmetric C=C hydrogenation, though relatively little studied, has the potential for major impact in synthetic organic chemistry both on the laboratory scale and in the manufacture of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals. The structural attributes that determine whether a given chiral ligand is effective have been identified; the ability to form strong covalent bonds with the metal surface while also resisting hydrogenation and displacement by the strongly adsorbing reactant under reaction conditions is an essential necessary condition. Beyond this, ligand rigidity in the vicinity of the chirality center coupled with resistance to SAM formation is a critically important factor whose absence results in racemic chemistry.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/la200009w
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Formation of organo-highly charged mica
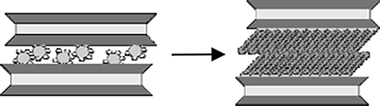
Alba, M.D. , Castro, M.A., Orta, M.M., Pavón, E., Pazos, M.C., Valencia Rios, J.S.Langmuir, 16 (2011) 9711-9718 DOI: 10.1021/la200942u
Abstract
The interlayer space of the highly charged synthetic Na-Mica-4 can be modified by ion-exchange reactions involving the exchange of inorganic Na + cations by surfactant molecules, which results in the formation of an organophilic interlayer space. The swelling and structural properties of this highly charged mica upon intercalation with n-alkylammonium (RNH 3) + cations with varying alkyl chain lengths (R = C12, C14, C16, and C18) have been reported. The stability, fine structure, and evolution of gaseous species from alkylammonium Mica-4 are investigated in detail by conventional thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD), and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS NMR) techniques. The results clearly show the total adsorption of n-alkylammonium cations in the interlayer space which expands as needed to accommodate intercalated surfactants. The surfactant packing is quite ordered at room temperature, mainly involving a paraffin-type bilayer with an all-trans conformation, in agreement with the high density of the organic compounds in the interlayer space. At temperatures above 160 °C, the surfactant molecules undergo a transformation that leads to a liquid-like conformation, which results in a more disordered phase and expansion of the interlayer space.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/la200942u
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Boron Compounds as Stabilizers of a Complex Microstructure in a Co-B-based Catalyst for NaBH4 Hydrolysis
Arzac, G.M., Rojas, T.C., Fernández, A.ChemCatChem, 3 (2011) 1305-1313 DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201100101
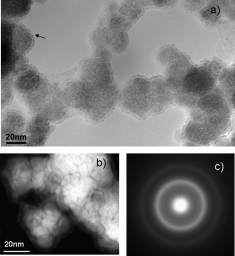
Abstract
Co-B-based materials are widely used as catalysts for hydrogen generation through sodium borohydride self-decomposition. In the mid 1990s, the aqueous and organic chemistry involved in Co-B synthesis and handling was studied. Nevertheless, the exact microstructure of these catalysts has remained unsolved. Herein we present an exhaustive study which shows a new and complete microstructural view of a Co-B-based material together with the chemistry of the cobalt and boron involved. By using nanoscale-resolution microscopy and spectroscopy techniques, we have elucidated the role of boron compounds as stabilizers in a complex microstructure, which also explains its high catalytic performance and long-term stability. The catalyst is proposed to be made up of 1-3nm hcp Co0 nanoparticles embedded in amorphous CoxB (x=1, 2, 3), CoxOy, Co(BO2)2, and B2O3 phases alternatively or all together. All of these amorphous phases protect the nanocrystalline metallic core from growth and oxidation.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201100101
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Fe-doped ceria solids synthesized by the microemulsion method for CO oxidation reactions
O.H. Laguna, M.A. Centeno, M. Boutonnet, J.A. OdriozolaApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 106 (2011) 621-629 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.06.025
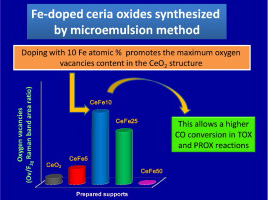
Abstract
A series of Ce-Fe mixed oxides as well as the pure oxides were synthesized by the microemulsions method. The solid solution formation was established for all the Fe-doped systems and only a hardly noticeable segregation of α-Fe2O3 was appreciated for the solid with the maximum iron content (50at.% Fe). The oxygen exchange is improved for all the Fe-doped systems; however the 10at.% Fe appears as the optimal iron content for achieving the maximum oxygen vacancies concentration and the higher reducibility efficiency. The CO oxidation (TOX, PROX) is especially achieved for the solids with the lower iron contents but with a superior oxygen vacancies proportion. These Ce-Fe systems prepared from microemulsions are very attractive to be considered as supports for depositing active phases capable of enhancing oxygen exchange ability of the whole system, allowing higher CO oxidation abilities.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.06.025
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Ionic liquid protected heteropoly acids for methanol dehydration
Ivanova, S., Nitsch, X., Romero-Sarria, F., Louis, B., Centeno, M.A., Roger, A.C., Odriozola, J.A.Catalysis Today, 171 (2011) 236-241 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.077
Abstract
We report herein the synthesis of an organic-inorganic hybrid composed by the ionic liquid protected Keggin structure, as a precursor for acid catalyst and its subsequent application in the methanol dehydration reaction. Special attention was paid to the thermal stability of the resulted hybrids as a function of the Keggin anion. The catalytic behaviour of these new materials are also studied and compared to the metal salt Cs2HPW 12O40. The prepared hybrids are less thermally stable than the metal salt, but their partial decomposition results in very active and selective catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.077
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of Ti1−xZrxB2 and Ti1−xHfxB2 solid solutions
M.A. Avilés, J.M. Córdoba, M.J. Sayagués and F.J. GotorCeramics International, 37 (2011) 1895-1904 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.02.004
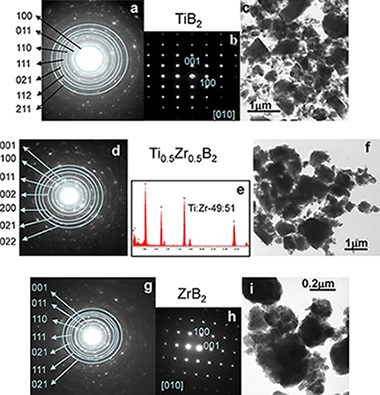
Abstract
Solid solutions of TiB2-ZrB2 and TiB 2-HfB2 were obtained under an inert atmosphere by high-energy ball-milling mixtures of Ti/Zr/B and Ti/Hf/B, respectively. Milling promoted mechanically induced self-sustaining reactions (MSR), and the ignition time was dependent on the initial composition of the mixture. The stoichiometry of Ti1-xZrxB2 and Ti1-xHf xB2 solid solutions was controlled by adjusting the atomic ratio of the reactants. The solid solutions were characterised by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, electron diffraction, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The results revealed that TiB2- ZrB2 possessed a nanometric microstructure and good chemical homogeneity. However, in the TiB2-HfB2 system, an inhomogeneous solid solution was obtained when a Ti-rich mixture was employed. The solid solutions showed good thermal stability; thus, can be used as raw materials for the development of technological materials for structural applications.
August, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.02.004
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Bacterial adherence on UHMWPE with vitamin E: an in vitro study
E. Gómez-Barrena, J. Esteban, D. Molina-Manso, H. Adames, M.J. Martínez-Morlanes, A. Terriza, F. Yubero and J. A. PuértolasJournal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 22 (2011) 1701-1706 DOI: 10.1007/s10856-011-4340-5
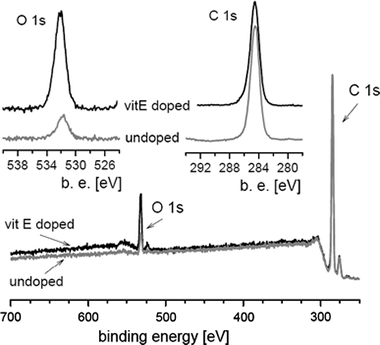
Abstract
Orthopaedic materials may improve its capacity to resist bacterial adherence, and subsequent infection. Our aim was to test the bacterial adherence to alpha-tocopherol (frequently named vitamin E, VE) doped or blended UHMWPE with S. aureus and S. epidermidis, compared to virgin material. Collection strains and clinical strains isolated from patients with orthopaedic infections were used, with the biofilm-developing ability as a covariable. While collection strains showed significantly less adherence to VE-UHMWPE, some clinical strains failed to confirm this effect, leading to the conclusion that VE doped or blended UHMWPE affects the adherence of some S. epidermidis and S. aureus strains, independently of the concentration in use, but the results showed important intraspecies differences and cannot be generalized.
July, 2011 · DOI: 10.1007/s10856-011-4340-5
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Microstructure and chemical bonding of DLC films deposited on ACM rubber by PACVD
Martinez-Martinez, D., Schenkel, M., Pei, Y.T., Sánchez-López, J.C., De Hosson, J.T.H.M.Surface and Coatings Technology, 205 (2011) S75-S78 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.02.067
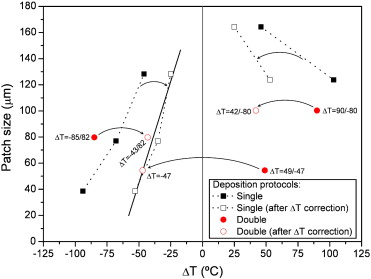
Abstract
The microstructure and chemical bonding of DLC films prepared by plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition on acrylic rubber (ACM) are studied in this paper. The temperature variation produced by the ion impingement during plasma cleaning and subsequent film deposition was used to modify the film microstructure by controlling the different degrees of strain applied to the substrate. The film microstructure is studied by top view and cross sectional SEM. The observed patch sizes are correlated with the variation of temperature that occurred during deposition. Finally, the chemical bonding of the samples is studied by Raman spectroscopy. All the samples show similar spectra regardless the bias voltage used.
July, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.02.067
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Porous supramolecularly templated optical resonators built in 1D photonic crystals
Hidalgo, N., Calvo, M.E., Bellino, M.G., Soler-Illia, G.J.A.A., Míguez, H.Advanced Functional Materials, 21 (2011) 2534-2540 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201002486
Abstract
A synthetic route to attain photonic multilayers that presents controlled porosity only at the middle-layer level is shown. The spectral resonance associated with this porous layer shows strong sensitivity to the presence of vapors adsorbed or condensed within the void network, providing a potentially relevant material for gas detection. The importance of the interplay between pore and probe-molecule diameters is studied and its implications in size-selective detection are discussed. Controlled porosity: Photonic multilayers that presents controlled porosity only at the middle-layer level are herein introduced. The optical response of the ensemble shows strong sensitivity to the presence of vapors adsorbed or condensed within the void network, providing a potentially relevant material for gas detection.
July, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201002486
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Mechanical, microstructural and oxidation properties of reactively sputtered thin Cr-N coatings on steel
Cecchini, R., Fabrizi, A., Cabibbo, M., Paternoster, C., Mavrin, B.N., Denisov, V.N., Novikova, N.N., Haïdopoulo, M.Thin Solid Films, 519 (2011) 6515-6521 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.04.115
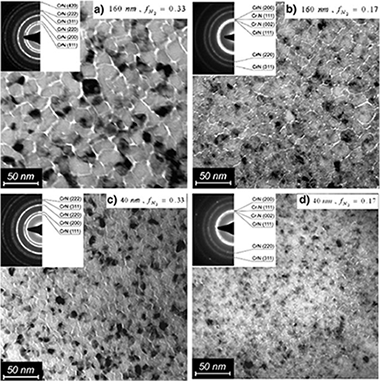
Abstract
Thin (40 nm and 160 nm) CrN coatings were deposited on steel by reactive magnetron sputtering deposition, varying the N2 flow. The coatings were characterized in the as-deposited condition and after annealing in air at 500 °C for 1 h, by X-Ray Diffraction, Transmission Electron Microscopy, Raman and Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopies. Hardness was measured by nanoindentation. Coatings have a nanocrystalline microstructure with the phase shifting from Cr2N to CrN, increasing grain size, thermal stability and resistance to oxidation with increasing N2. Also intrinsic coating hardness is influenced by both N2 flow during deposition and film thickness, as a result of changes in phase composition and microstructural properties.
July, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.04.115
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
High-stable mesoporous Ni-Ce/clay catalysts for syngas production
Daza, C.E., Gamba, O.A., Hernández, Y., Centeno, M.A., Mondragón, F., Moreno, S., Molina, R.Catalysis Letters, 141 (2011) 1037-1046 DOI: 10.1007/s10562-011-0579-1
Abstract
A mesoporous-type catalytic support was synthesized through the modification of a smectite with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and microwaves. Texture and micro-morphology of the support was determined. Several techniques were employed in order to describe the chemical environment of active species on the surface. Ni0 particle sizes were dependent on the structural site of reducible species. High stable Ni-Ce catalysts (calcined at 800 °C) were evaluated in the CO2 reforming of methane reaction at 700 °C (WHSV = 96 L g-1 h-1, without dilution gas and pre-reduction). The catalysts have presented CH4 conversions between 40 and 65%, CO2 conversion between 35 and 65% and H2/CO ratios between 0.2 and 0.4.
July, 2011 · DOI: 10.1007/s10562-011-0579-1
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
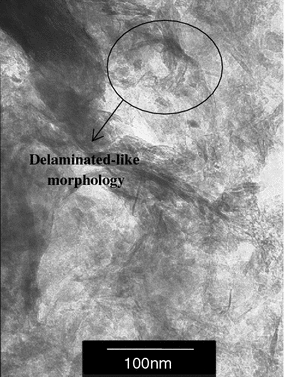
Solid solubility of Yb2Si2O7 in β-, γ- And δ-Y2Si2O7
Fernández-Carrión, A.J., Alba, M.D., Escudero, A., Becerro, A.I.Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 184 (2011) 1882-1889 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2011.05.034
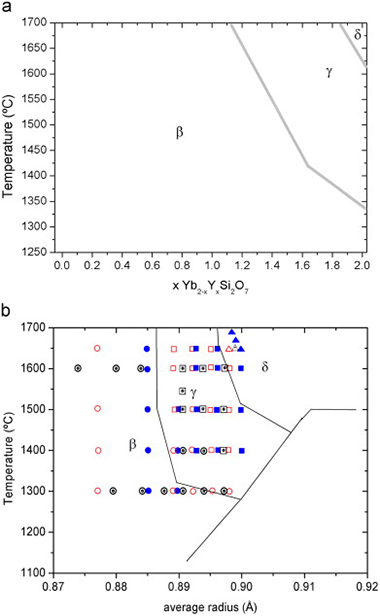
Abstract
This paper examines the structural changes with temperature and composition in the Yb2Si2O7–Y2Si2O7 system; members of this system are expected to form in the intergranular region of Si3N4 and SiC structural ceramics when sintered with the aid of Yb2O3 and Y2O3 mixtures. A set of different compositions have been synthesised using the sol–gel method to obtain a xerogel, which has been calcined at temperatures between 1300 and 1650 °C during different times. Isotherms at 1300 and 1600 °C have been analysed in detail to evaluate the solid solubility of Yb2Si2O7 in β-Y2Si2O7 and γ-Y2Si2O7. Although Yb2Si2O7 shows a unique stable polymorph (β), Yb3+ is able to replace Y3+ in γ-Y2Si2O7 and δ-Y2Si2O7 at high temperatures and low Yb contents. IR results confirm the total solid solubility in the system and suggest a constant SiOSi angle of 180° in the Si2O7 unit across the system. The temperature–composition diagram of the system, obtained from powder XRD data, is dominated by the β-RE2Si2O7 polymorph, with γ-RE2Si2O7 and δ-RE2Si2O7 showing reduced stability fields. The diagram is in accordance with Felsche's diagram if average ionic radii are assumed for the members of the solid solution at any temperature, as long as the β–γ phase boundary is slightly shifted towards higher radii.
July, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2011.05.034
Characterization of materials and conservation process of the collection of Arabic manuscript documents of granada archive histórico-provincial
T. Espejo Arias, I. Lazarova Stoytcheva, D. Campillo García, A. Durán Benito, A. Jiménez de HaroAl-Qantara, 32 (2011) 519-532 DOI:

Abstract
This paper presents the main conclusions of our study of the Arabic documents preserved in the Archivo Histórico Provincial of Granada. The analysis of the contents of each document, the materials and inks used in their support, and also the similarities of the page layout reveals the use of identical production protocols. Furthermore, this research also enables us to establish important similarities between the paper production processes in the latter stages of the Islamic rule in the Iberian Peninsula and the earlier stages of its incorporation in the Crown of Castilla - in particular in relation to how the archival documents were issued, both externally and internally.
July, 2011 · DOI:
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Identification of Ternary Phases in TiBC/a-C Nanocomposite Thin Films: Influence on the Electrical and Optical Properties
Manuel David Abad, Rosendo Sanjinés, Jose Luis Endrino, Raúl Gago, Joakim Andersson, Juan Carlos Sánchez-LópezPlasma Processes and Polymers, 8 (2011) 579-588 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201000182
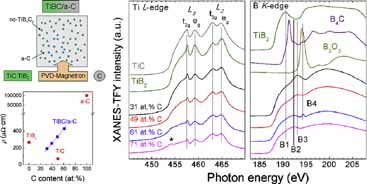
Abstract
The local structure of TiBC and amorphous carbon (a-C) nanocomposite films (TiBC/a-C) was correlated with their optical and electrical properties. TiBC/a-C films with increasing C content were deposited by magnetron co-sputtering from TiC:TiB2 (60:40) and graphite targets. Chemical composition is determined by electron energy-loss spectroscopy. Grazing incidence X-ray diffraction reveals that the microstructure of the films is amorphous with small nanocrystallites emerging by increasing the C content that could be attributed to the formation of ternary (TiBxCy) or mixed binary (TiB2 and TiC) phases. Further information was then obtained by studying the chemical bonding by measuring the near-edge fine structure (NES) by electron energy-loss (B K-, C K-, and Ti L-edges) and X-ray absorption (B K- and Ti L-edges) spectroscopies. The NES analysis indicates the formation of a nanocrystalline ternary TiBxCy compound concomitant with the segregation of an a-C phase as the carbon content is increased. The optical properties were studied by spectroscopic ellipsometry and the electrical resistivity was measured by the Van der Pauw method between 20 and 300 K. The films continuously lose their metallic character in terms of optical constants and resistivity with increasing carbon content. Theoretical fitting of the electrical properties using the grain-boundary scattering model supported the formation of a nanocomposite structure based on a ternary TiBxCy phase embedded in a matrix of a-C. The electron transport properties are mainly limited by the high density of point defects, grain size, and transmission probability.
July, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201000182
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermal study of unaltered and altered dolomitic rock samples from ancient monuments - The case of Villarcayo de Merindad de Castilla la Vieja (Burgos, Spain)
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Duran, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 104 (2011) 467-474 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-011-1348-5
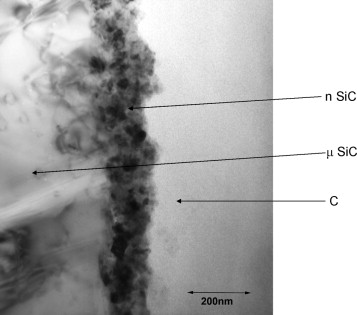
Abstract
In this study, the decomposition behaviour of unaltered and altered dolomitic rock samples used in Cultural Heritage buildings was studied by simultaneous TG-DTA experiments at different atmospheres, X-ray diffraction in a high-temperature chamber, and evolved gas analysis. The components of dolomite rock samples and hydrated calcium oxalate formed during the alteration processes of the rocks were characterized, and the decomposition mechanisms of these components were determined. The TG-DTA experiments carried out at CO2 atmosphere were used to determine the carbonate compounds in the rock samples. The TG-DTA study characterized the presence of organic compounds formed during the biological degradation of the rock samples, possibly responsible of the hydrated calcium oxalate formation.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-011-1348-5
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Comparative investigation of Al- and Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings
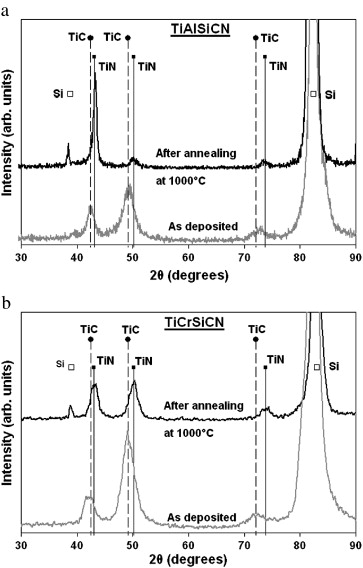
D.V. Shtansky, K.A. Kuptsov, Ph.V. Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, A.N. Sheveiko, A. Fernandez and M.I. PetrzhikSurface and Coatings Technology, 205 (2011) 4640-4648 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.04.012
Abstract
The aim of this work was a comparative investigation of the structure and properties of Al- and Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering of composite TiAlSiCN and TiCrSiCN targets produced by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method. Based on X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy data, the Al- and Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings possessed nanocomposite structures (Ti,Al)(C,N)/a-(Si,C) and (Ti,Cr)(C,N)/a-SiCxNy/a-C with cubic crystallites embedded in an amorphous matrix. To evaluate the thermal stability and oxidation resistance, the coatings were annealed either in vacuum at 1000, 1100, 1200, and 1300°C or in air at 1000°C for 1h. The results obtained show that the hardness of the Al-doped TiSiCN coatings increased from 41 to 46GPa, reaching maximum at 1000°C, and then slightly decreased to 38GPa at 1300°C. The Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings demonstrated high thermal stability up to 1100°C with hardness above 34GPa. Although both Al- and Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings possessed improved oxidation resistance up to 1000°C, the TiAlSiCN coatings were more oxidation resistant than their TiCrSiCN counterparts. The TiCrSiCN coatings showed better tribological characteristics both at 25 and 700°C and superior cutting performance compared with the TiAlSiCN coatings.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.04.012
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Surface-functionalized fluorescent silica nanoparticles for the detection of ATP
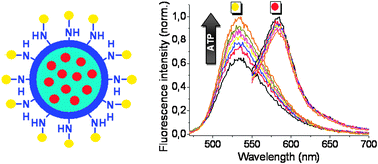
Moro, AJ; Schmidt, J; Doussineau, T; Lapresta-Fernandez, A; Wegener, J; Mohr, GJChemical Communications, 47 (2011) 6066-6068 DOI: 10.1039/C1CC10419E
Abstract
The design of two-dyed fluorescent silica nanoparticles for ATP detection is presented. The indicator dye possesses a dipicolyl-amine (DPA) unit complexed with Zn(ii) as a receptor function for ATP while a rhodamine derivative is used as the reference dye. The nanoparticles were fully characterized regarding analytical performance, morphology and cytocompatibility.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1039/C1CC10419E
Natural earth pigments from Roman and Arabic wall paintings revealed by spectroscopic techniques
Garofano, I., Duran, A., Perez-Rodriguez, J.L., Robador, M.D.Spectroscopy Letters, 44 (2011) 560-565 DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2011.610655
Abstract
Full identification of pigments used in wall paintings by Romans and Arabs that were recently discovered was achieved by the combined application of several spectroscopy methods. Identification of pigments was provided by the use of micro-Raman and FT-IR spectroscopy, while UV-Visible spectroscopy and chromatic studies permitted the authors to identify slight variations of hue attributed to mixtures of pigments. Natural earths and minerals were detected as the main pigments employed by both civilizations, although some differences were found between them. Red ochre, vermilion, yellow ochre, Egyptian blue, green earth, calcite, carbon, and possibly ivory blacks were identified in the Roman paintings. Only hematite and calcite were observed in the Arabic fragments.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2011.610655
Reactividad de Sólidos
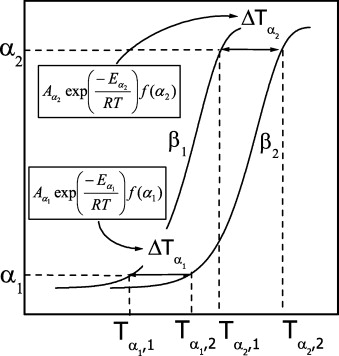
ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data
Vyazovkin, S., Burnham, A.K., Criado, J.M., Pérez-Maqueda, L.A., Popescu, C., Sbirrazzuoli, N.Thermochimica Acta, 520 (2011) 1-19 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2011.03.034
Abstract
The present recommendations have been developed by the Kinetics Committee of the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC). The recommendations offer guidance for reliable evaluation of kinetic parameters (the activation energy, the pre-exponential factor, and the reaction model) from the data obtained by means of thermal analysis methods such as thermogravimetry (TGA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and differential thermal analysis (DTA). The recommendations cover the most common kinetic methods, model-free (isoconversional) as well as model-fitting. The focus is on the problems faced by various kinetic methods and on the ways how these problems can be resolved. Recommendations on making reliable kinetic predictions are also provided. The objective of these recommendations is to help a non-expert with efficiently performing analysis and interpreting its results.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2011.03.034
Reactividad de Sólidos - Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
High-temperature mechanical behavior of polycrystalline yttrium-doped barium cerate perovskite
Vaquero-Aguilar, C; Lopez-Robledo, MJ; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Real, C; Jimenez-Melendo, MJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 1333-1338 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.05.023

Abstract
The high-temperature mechanical properties of the mixed ionic-electronic conductor perovskite BaCe0.95Y0.05O3−δ with average grain size of 0.40 μm have been studied in compression between 1100 and 1300 °C in air at different initial strain rates. The true stress–true strain curves display an initial stress drop, followed by an extended steady-state stage. As the temperature decreases and/or the strain rate increases, there is a transition to a damage-tolerant strain-softening stage and eventually to catastrophic failure. Analysis of mechanical and microstructural data revealed that grain boundary sliding is the primary deformation mechanism. The strength drop has been correlated with the growth of ultrafine grains during deformation, already present at grain boundaries and triple grain junctions in the as-fabricated material.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.05.023
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Surface-modified Pd and Au nanoparticles for anti-wear applications
J.C. Sánchez-López, M.D. Abad, L. Kolodziejczyk, E. Guerrero and A. FernándezTribology International, 44 (2011) 720-726 DOI: 10.1016/j.triboint.2009.12.013
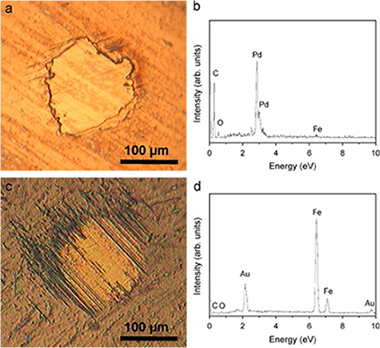
Abstract
This work reports the employment of metallic nanoparticles (palladium and gold) with a mean particle size of 2.2 nm surface-protected with tetraalkylammonium and alkanethiolate chains, respectively, as lubricant additives. Dispersions of both types of nanoparticles (5 wt%) are prepared using tetrabutylammonium acetate (TBA) and paraffin as base oils, respectively. The tribological properties are then evaluated by a ball-on-disc tribometer at two different loads (7 and 15 N) with excellent results: friction (<0.1), wear rate (not, vert, similar10−10 mm3/Nm). The excellent anti-wear response is explained by the formation of a metal-containing transfer film and their action as counterface spacers avoiding direct contact.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.triboint.2009.12.013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructural and mechanical evaluation of a Cu-based active braze alloy to join silicon nitride ceramics
Singh, M; Asthana, R; Varela, FM; Martinez-Fernandez, JJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 1309-1316 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.07.022
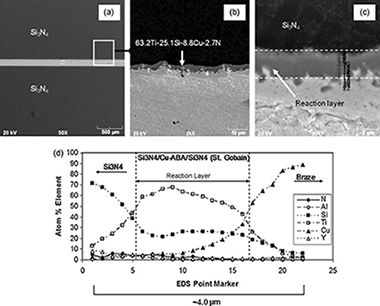
Abstract
Self-joining of St. Gobain Si3N4 (NT-154) using a ductile Cu–Al–Si–Ti active braze (Cu-ABA) was demonstrated. A reaction zone (∼2.5–3.5 μm thick) developed at the interface after 30 min brazing at 1317 K. The interface was enriched in Ti and Si. The room temperature compressive shear strengths of Si3N4/Si3N4 and Inconel/Inconel joints (the latter created to access baseline data for use with the proposed Si3N4/Inconel joints) were 140 ± 49 MPa and 207 ± 12 MPa, respectively. High-temperature shear tests were performed at 1023 K and 1073 K, and the strength of the Si3N4/Si3N4 and Inconel/Inconel joints were determined. The joints were metallurgically well-bonded for temperatures above 2/3 of the braze solidus. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy studies revealed a fine grain microstructure in the reaction layer, and large grains in the inner part of the joint with interfaces being crack-free. The observed formation of Ti5Si3 and AlN at the joint interface during brazing is discussed.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.07.022
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Photocatalytic coatings of silver–TiO2 nanocomposites on foamed waste-glass prepared by sonochemical process
Lee, S.W., Obregón-Alfaro, S., Rodríguez-González, V.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 221 (2011) 71-76 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2011.04.026
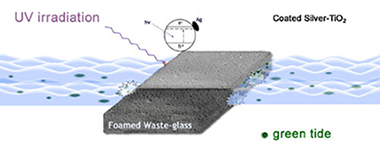
Abstract
Silver-TiO2 nanocomposite was prepared by photodeposition of silver nanoparticles on the surface of titanium dioxide. The sonochemical method was used for the deposition of silver-TiO2 powder on commercial foamed waste-glass strips (FWGS). The silver-TiO2 and the coated FWGS was characterized by XRD, DRS, SEM, TEM and nitrogen adsorption. In order to enhance silver-TiO2 deposition, different parameters were evaluated such as the solvent effect and use of stabilizing agents. The best deposition was obtained with an aqueous solution of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and an ultrasound irradiation source of 23.3 kHz. The photocatalytic activity of the silver-TiO2 coated FWGS was evaluated in the UV photo-assisted destruction of the noxious microalgae, Tetraselmis suecica. It was found that after the photocatalytic irradiation, for 180 min, the algae cells were deformed, fragmented and annihilated, thereby avoiding its regeneration.2
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2011.04.026
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructural and mechanical evaluation of porous biomorphic silicon carbide for high temperature filtering applications
Bautista, MA; Cancapa, JQ; Fernandez, JM; Rodriguez, MA; Singh, MJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 1325-1332 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.06.014
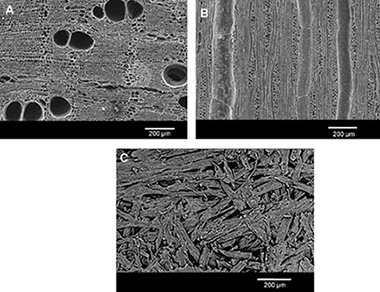
Abstract
Biomorphic SiC (bioSiC) is a low cost SiC/Si composite obtained by melt infiltration of carbon preforms obtained from the pyrolysis of cellulose precursors. The porosity and pore size distribution of bioSiC can be tailored for specific applications by adequate selection of the wood precursor. Natural and artificial industrial woods were explored as possible bioSiC precursors. Silicon was removed by chemical etching. Relevant microstructural parameters such as pore size distribution, total porosity, and permeability were characterized. Since the filtration process involves large pressure gradients along the material at high temperatures, mechanical properties of porous bioSiC from the different precursors were evaluated at room temperature and 800 °C. The feasibility of porous bioSiC as a filtration material for high temperature gasification processes is discussed in terms of these properties. MDF-bioSiC is shown to be a promising material for such applications because of its good mechanical properties, interconnected porosity, pore sizes, and permeability.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.06.014
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Compressive strength degradation in ZrB2-based ultra-high temperature ceramic composites
Ramirez-Rico, J; Bautista, MA; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, MJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 1345-1352 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.05.020
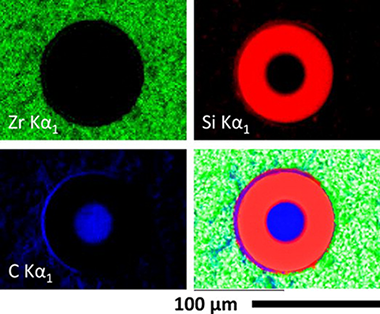
Abstract
The high temperature compressive strength behavior of zirconium diboride (ZrB2)-silicon carbide (SiC) particulate composites containing either carbon powder or SCS-9a silicon carbide fibers was evaluated in air. Constant strain rate compression tests have been performed on these materials at room temperature, 1400, and 1550°C. The degradation of the mechanical properties as a result of atmospheric air exposure at high temperatures has also been studied as a function of exposure time. The ZrB2-SiC material shows excellent strength of 3.1±0.2GPa at room temperature and 0.9±0.1GPa at 1400°C when external defects are eliminated by surface finishing. The presence of C is detrimental to the compressive strength of the ZrB2-SiC-C material, as carbon burns out at high temperatures in air. As-fabricated SCS-9a SiC fiber reinforced ZrB2-SiC composites contain significant matrix microcracking due to residual thermal stresses, and show poor mechanical properties and oxidation resistance. After exposure to air at high temperatures an external SiO2 layer is formed, beneath which ZrB2 oxidizes to ZrO2. A significant reduction in room temperature strength occurs after 16-24h of exposure to air at 1400°C for the ZrB2-SiC material, while for the ZrB2-SiC-C composition this reduction is observed after less than 16h. The thickness of the oxide layer was measured as a function of exposure time and temperatures and the details of oxidation process has been discussed.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.05.020
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Electrical properties of biomorphic SiC ceramics and SiC/Si composites fabricated from medium density fiberboard
T.S. Orlova, V.V. Popov, J. Quispe Cancapa, D. Hernández Maldonado, E. Enrique Magarino, F.M. Varela Feria, A. Ramírez de Arellano, J. Martínez FernándezJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 1317-1323 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.06.015

Abstract
A study has been made of the dependences of the electrical resistivity and the Hall coefficient on the temperature in the range 1.8–1300 K and on magnetic fields of up to 28 kOe for the biomorphic SiC/Si (MDF-SiC/Si) composite and biomorphic porous SiC (MDF-SiC) based upon artificial cellulosic precursor (MDF – medium density fiberboards). It has been shown that electric transport in MDF-SiC is effected by carriers of n-type with a high concentration of ∼1020 cm−3 and a low mobility of ∼0.4 cm2 V−1 s−1. The specific features in the conductivity of MDF-SiC are explained by quantum effects arising in disordered systems and requiring quantum corrections to conductivity. The TEM studies confirmed the presence of disordering structural features (nanocrystalline regions) in MDF-SiC. The conductivity of MDF-SiC/Si composite originates primarily from Si component in the temperature range 1.8–500 K and since ∼500 to 600 K the contribution of MDF-SiC matrix becomes dominant.
June, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.06.015
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Determination of Pore Size Distribution at the Cell-Hydrogel Interface
Leal-Egana, A., Dietrich-Braumann, U., Diaz-Cuenca, A., Nowicki, M., Bader, A.Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 9 (2011) Page 24 DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-24
Abstract
Analyses of the pore size distribution in 3D matrices such as the cell-hydrogel interface are very useful when studying changes and modifications produced as a result of cellular growth and proliferation within the matrix, as pore size distribution plays an important role in the signaling and microenvironment stimuli imparted to the cells. However, the majority of the methods for the assessment of the porosity in biomaterials are not suitable to give quantitative information about the textural properties of these nano-interfaces.
May, 2011 · DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-24
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Interplay of Resonant Cavity Modes with Localized Surface Plasmons: Optical Absorption Properties of Bragg Stacks Integrating Gold Nanoparticles
Olalla Sánchez-Sobrado, Gabriel Lozano, Mauricio E. Calvo, Ana Sánchez-Iglesias, Luis M. Liz-Marzán, Hernán MíguezAdvanced Materials, 23 (2011) 2108-2112 DOI: 10.1002/adma.201004401
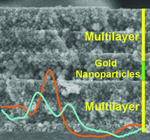
Abstract
A procedure to prepare porous photonic crystal resonators containing gold nanoparticles is reported. The optical absorption of the ensemble, resulting from the excitation of the localized surface plasmon of the metallic beads, is finely tuned by a gradual shift of the cavity mode. This is achieved by infiltration of the void network with different guest compounds.
May, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/adma.201004401
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Stability of Rare-Earth Disilicates: Ionic Radius Effect
Galunin, E; Alba, MD; Vidal, MJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 94 (2011) 1568–1574 DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04272.x
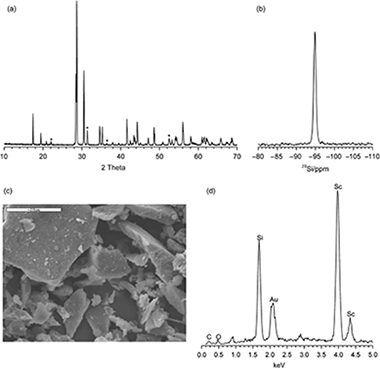
Abstract
Rare-earth (RE) disilicates, of general formula RE2Si 2O7, are one of the products of the chemical reaction between RE (elements), which are actinide simulators, and the silicates used in the engineered barrier systems of deep geological repositories (DGPs). The aim of this paper is to establish the stability range of the disilicate phase as function of the nature of the RE (RE=Sc, Lu, or Y) and examine whether this phase would permit RE leaching under experimental conditions simulating those of the DGP. The β-polymorphs of the RE disilicates were synthesized by the sol-gel method and subsequently submitted to a pHstat leaching test. The rates of RE and Si leaching were measured and the transformation of the crystalline and amorphous phases was examined by X-ray powder diffraction and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. The results indicate that the disilicate phases were stable within a wide range of pH, their stability being related to the hydrated ratio of the RE. Disilicate stability increased with the ionic radius of the RE. As a result, the Sc disilicate was stable throughout the pH range tested, whereas Y and Lu disilicate leaching was only observed at pH<4. Thus, it was confirmed that the formation of the disilicate phases could contribute to the confinement of radioactive wastes in engineered barriers.
May, 2011 · DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04272.x
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structure and support induced structure disruption of soft nanoparticles obtained from hydroxylated fatty acids
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; San-Miguel, MA; Luna, M; Dominguez, E; Heredia, A; Benitez, JJSoft Matter, 7 (2011) 4357-4363 DOI: 10.1039/c0sm01545h
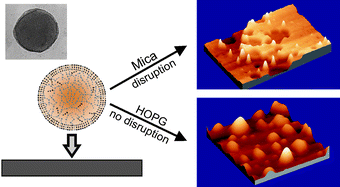
Abstract
Soft and spherical nanoparticles, named as cutinsomes, have been prepared from concentrated 9(10),16-dihydroxypalmitic acid (diHPA) in aqueous solution. After isolation, cutinsomes have been chemically and structurally characterized by ATR-FTIR, TEM and dynamic atomic force microscopy (dynamic AFM). The nanoparticle can be described as a lipidic, liquid-like and mostly esterified core surrounded by a polar shell of carboxylate/carboxylic acid molecules. Molecular dynamic (MD) simulations have been used to support this model. The structural stability of soft cutinsomes has been tested by deposition on both non-polar (HOPG) and polar (mica) flat substrates. It has been found that the magnitude of the interaction between the polar shell of cutinsomes and the support determines their structure conservation or its spreading or rupture and spill out of the liquid-like content. The structural consistence of these nanoparticles as a function of the polarity of substrate is of interest in elucidating the formation mechanism of cutin, the most abundant biopolyester in nature and a very interesting biomaterial to be mimetized.
May, 2011 · DOI: 10.1039/c0sm01545h
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Hydroxyapatite Synthesis on Mesoporous Silica: A High Resolution Electron Microscopy Study
D.R. Acosta, A. Díaz-Cuenca, A.Acta Microscopica, 20 (2011) 29-35 DOI:
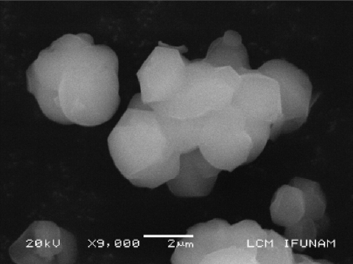
Abstract
En este trabajo se presentan resultados de la síntesis de hidroxiapatita (HA) en sílice mesoporosa SBA-15. Se ha hecho un estudio de la síntesis de ambos materiales y un seguimiento del efecto del doble tratamiento térmico posterior a la síntesis. Las muestras se sometieron a distintas temperaturas de tratamiento hidrotermal entre 353 y 393 K con incrementos de 10 K durante 24 horas. En cada caso y una vez filtrado y seco el material se volvió a tratar con una calcinación a 773 K durante 10 hs. Se presentan los resultados del estudio del material compuesto SBA-15-HA por microscopia electrónica de transmisión convencional y avanzada ( STEM, Contraste Z, HREM) . El crecimiento de HA en los túneles de la matriz de sílice mesoporosa y el nivel de ocupación de los mismos aumenta con la temperatura del primer tratamiento hidrotermal y también del segundo tratamiento que favorece el sinterizado dentro de los túneles.
May, 2011 · DOI:
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Interaction of Eu-isotopes with saponite as a component of the engineered barrier
María D. Alba, Miguel A. Castro, P. Chaín, Santiago Hurtado, M. Mar Orta, M. Carolina Pazos and María VillaApplied Clay Science, 52 (2011) 253-257 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2011.02.027

Abstract
Bentonite is accepted as the best clay material in the engineered barrier of deep geological repositories (DGRs) for radioactive waste disposal. In recent years, the interactions between a wide range of rare-earth (REE) cations and smectites have been studied. A combined study of stable europium and radioactive isotopes is reported here. Saponite was subjected to hydrothermal reactions with stable and radioactive (152Eu) europium ions under subcritical conditions. The structural changes of saponite were evaluated by XRD and SEM. The effect of temperature and reaction time on the changes was quantified by measuring 152Eu through gamma spectrometry. The reaction between europium and saponite was a first-order reaction. The presence of Eu in the precipitate in an amount much higher than the cation exchange capacity of saponite confirmed participation of chemical reactions or surface adsorption in the europium immobilization, even at temperatures as low as 150 °C. The reaction rate constant indicated that an 8- to 9-month period was needed for the completion, without significant changes, of the europium/saponite chemical reaction under the subcritical conditions of 200 °C and 350 °C.
May, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2011.02.027
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Supported plasma-made 1D heterostructures: Perspectives and applications
Borras, A; Macias-Montero, M; Romero-Gomez, P; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 44 (2011) 174016 DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/44/17/174016
Abstract
Plasma-related methods have been widely used in the fabrication of carbon nanotubes and nanofibres (NFs) and semiconducting inorganic nanowires (NWs). A natural progression of the research in the field of 1D nanostructures is the synthesis of multicomponent NWs and NFs. In this paper we review the state of the art of the fabrication by plasma methods of 1D heterostructures including applications and perspectives. Furthermore, recent developments on the use of metal seeds (Ag, Au, Pt) to obtain metal@oxide nanostructures are also extensively described. Results are shown for various metal substrates, either metal foils or supported nanoparticles/thin films of the metal where the effects of the size, surface coverage, percolation degree and thickness of the metal seeds have been systematically evaluated. The possibilities of the process are illustrated by the preparation of nanostructured films and supported NFs of different metal@oxides (Ag, Au and SiO2, TiO2, ZnO). Particularly, in the case of silver, the application of an oxygen plasma treatment prior to the deposition of the oxide was critical for efficiently controlling the growth of the 1D heterostructures. A phenomenological model is proposed to account for the thin-film nanostructuring and fibre formation by considering basic phenomena such as stress relaxation, inhomogeneities in the plasma sheath electrical field and the local disturbance of the oxide growth.
May, 2011 · DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/44/17/174016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Constant rate thermal analysis for thermal stability studies of polymers
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMPolymer Degradation and Stability, 96 (2011) 974-981 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.01.027
Abstract
This paper explores the relationship between the shapes of temperature-time curves obtained from experimental data recorded by means of constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA) and the kinetic model followed by the thermal degradation reaction. A detailed shape analysis of CRTA curves has been performed as a function of the most common kinetic models. The analysis has been validated with simulated data, and with experimental data recorded from the thermal degradation of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), poly(1,4-butylene terephthalate) (PBT), polyethylene (PE) and poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC). The resulting temperature-time profiles indicate that the studied polymers decompose through phase boundary, random scission, diffusion and nucleation mechanisms respectively. The results here presented demonstrate that the strong dependence of the temperature-time profile on the reaction mechanism would allow the real kinetic model obeyed by a reaction to be discerned from a single CRTA curve.
May, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.01.027
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structural, chemical surface and transport modifications of regenerated cellulose dense membranes due to low-dose γ-radiation
Vazquez, MI; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Galan, P; Benitez, JJ; Benavente, JMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 126 (2011) 734-740 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.12.051
Abstract
Modifications caused in commercial dense regenerated cellulose (RC) flat membranes by low-dose γ-irradiation (average photons energy of 1.23 MeV) are studied. Slight structural, chemical and morphological surface changes due to irradiation in three films with different RC content were determined by ATR-FTIR, XRD, XPS and AFM. Also, the alteration of their mechanical elasticity has been studied. Modification of membrane performance was determined from solute diffusion coefficient and effective membrane fixed charge concentration obtained from NaCl diffusion measurements. Induced structural changes defining new and effective fracture propagation directions are considered to be responsible for the increase of fragility of irradiated RC membranes. The same structural changes are proposed to explain the reduction of the membrane ion permeability through a mechanism involving either ion pathways elongation and/or blocking.
April, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.12.051
- ‹ previous
- 31 of 37
- next ›














