Scientific Papers in SCI
2011
2011
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structural, chemical surface and transport modifications of regenerated cellulose dense membranes due to low-dose γ-radiation
Vazquez, MI; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Galan, P; Benitez, JJ; Benavente, JMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 126 (2011) 734-740 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.12.051
Abstract
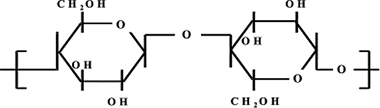
Modifications caused in commercial dense regenerated cellulose (RC) flat membranes by low-dose γ-irradiation (average photons energy of 1.23 MeV) are studied. Slight structural, chemical and morphological surface changes due to irradiation in three films with different RC content were determined by ATR-FTIR, XRD, XPS and AFM. Also, the alteration of their mechanical elasticity has been studied. Modification of membrane performance was determined from solute diffusion coefficient and effective membrane fixed charge concentration obtained from NaCl diffusion measurements. Induced structural changes defining new and effective fracture propagation directions are considered to be responsible for the increase of fragility of irradiated RC membranes. The same structural changes are proposed to explain the reduction of the membrane ion permeability through a mechanism involving either ion pathways elongation and/or blocking.
April, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.12.051
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bulk and Adsorbed Monolayer Phase Behavior of Binary Mixtures of Undecanoic Acid and Undecylamine: Catanionic Monolayers
Sun, C; Bojdys, MJ; Clarke, SM; Harper, LD; Jefferson, A; Castro, MA; Medina, SLangmuir, 27 (2011) 3626-3637 DOI: 10.1021/la1048198
Abstract
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray powder diffraction (PXRD) have been used to determine the phase behavior of the binary mixtures of undecanoic acid (A) and undecylamine (B) in the bulk. In addition, we report DSC data that indicates very similar behavior for the solid monolayers of these materials adsorbed on the surface of graphite. The two species are found to form a series of stoichiometric complexes of the type AB, A2B, and A 3B on the acid rich side of the phase diagram. Interestingly, no similar series of complexes is evident on the amine rich side. As a result of this complexation, the solid monolayers of the binary mixtures exhibit a very pronounced enhancement in stability relative to the pure adsorbates.
April, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/la1048198
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Novel guests for porous columnar thin films: The switchable perchlorinated trityl radical derivatives
Oliveros, M; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Mugnaini, V; Yubero, F; Roques, N; Veciana, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Rovira, CLangmuir, 27 (2011) 5098-5106 DOI: 10.1021/la200470f
Abstract
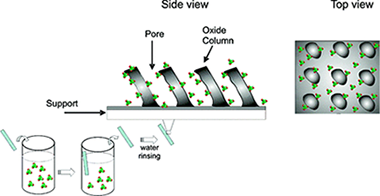
TiO2 and SiO2 porous thin films consisting of tilted nanocolumns prepared by glancing angle evaporation (GLAD) have been infiltrated with guest derivatives belonging to the family of perchlorinated trityl radicals, novel guest molecules presenting an open-shell electronic configuration associated with paramagnetism, fluorescence, and electroactivity. The main driving forces for infiltration from aqueous solutions of the carboxylate-substituted radical derivatives are the electrostatic interactions between their negative charge and the net positive charges induced on the film pores. Positive charges on the internal surface of the films were induced by either adjusting the radical solution pH at values lower than the point of zero charge (PZC) of the oxide or passivating the nanocolumns oxide surface with a positively charged aminosilane. The infiltrated composite thin films are robust and easy to handle thanks to the physical protection exerted by the film columns. They also keep the multifunctionality of the used guests, as confirmed by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), UV-vis spectroscopy, and fluorescence spectroscopy. To prove the electroactivity of the infiltrated porous films, a porous TiO2 host layer was supported onto conductive indium tin oxide (ITO). By application of an appropriate redox potential, the guest radical molecules have been reversibly switched from their open-shell electronic configuration to their diamagnetic state and hence changed their optical properties. On the basis of these results, it is herein proposed that the appropriate surface functionalization of the pore internal surface of GLAD thin films can be used to prepare novel radical-oxide composite thin films usable for the development of robust switchable electrically driven photonic and magnetic devices.
April, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/la200470f
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photodeposition of gold on titanium dioxide for photocatalytic phenol oxidation
Hidalgo, MC; Murcia, JJ; Navio, JA; Colon, GApplied Catalysis A-General, 397 (2011) 112-120 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.02.030
Abstract
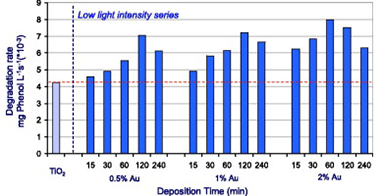
The influence of experimental conditions during the photodeposition in the preparation of supported Au on TiO2 has been studied. Besides preparation pH, light intensity and deposition time showed to have a high influence on the final properties of gold deposits. Photodeposition using illumination with a high light intensity UV-vis lamp (140 W/m2 UVA range) resulted to be an ineffective method for obtaining nanoparticles of gold on the titania, producing very large and poorly distributed gold deposits. Thus obtained materials did not show any important improvement of their photocatalytic activity tested for phenol oxidation. By contrast, photodeposition using a low light intensity of illumination (0.15 W/m 2 UVA range), produced materials with notably improved photocatalytic activity. The illumination with such a low light intensity allowed the control of the amount, aggregation and oxidation state of gold by changing deposition time, enabling a feasible method of tailoring Au-TiO2 with the appropriate properties for a high photocatalytic activity. Best photocatalytic behaviour for phenol photodegradation was obtained for Au-TiO2 samples prepared by photodeposition at low light intensity with 120 min photodeposition time for catalysts with a 0.5% and 1% nominal content of gold and with 60 min photodeposition time for catalyst with a 2% nominal content of gold.
April, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.02.030
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Rhodamine 6G and 800 J-heteroaggregates with enhanced acceptor luminescence (HEAL) adsorbed in transparent SiO2 GLAD thin films
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Aparicio, FJ; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, APhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 13 (2011) 7071-7082 DOI: 10.1039/c0cp02421j
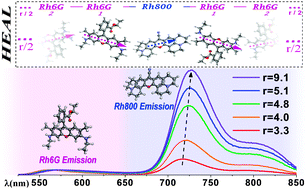
Abstract
An enhanced fluorescent emission in the near infrared is observed when the Rhodamine 800 (Rh800) and 6G (Rh6G) dyes are coadsorbed in porous SiO 2 optical thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition (GLAD). This unusual behavior is not observed in solution and it has been ascribed to the formation of a new type of J-heteroaggregates with enhanced acceptor luminescence (HEAL). This article describes in detail and explains the main features of this new phenomenology previously referred in a short communication [J. R. Sánchez-Valencia, J. Toudert, L. González-García, A. R. González-Elipe and A. Barranco, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 4372-4374]. It is found that the efficiency and characteristics of the energy transfer process are dependent on the Rh6G/Rh800 concentration ratio which can be easily controlled by varying the pH of the solutions used for the infiltration of the molecules or by thermal treatments. A simple model has been proposed to account for the observed enhanced acceptor luminescence in which the heteroaggregates order themselves according to a "head to tail" configuration due to the geometrical constrains imposed by the SiO2 porous matrix thin film. The thermal stability of the dye molecules within the films and basic optical (absorption and fluorescence) principles of the HEAL process are also described.
April, 2011 · DOI: 10.1039/c0cp02421j
Materiales Coloidales
Tuning from blue to magenta the up-converted emissions of YF3:Tm3+/Yb3+ nanocrystals
Quintanilla, M; Nunez, NO; Cantelar, E; Ocana, M; Cusso, FNanoscale, 3 (2011) 1046-1052 DOI: 10.1039/c0nr00676a
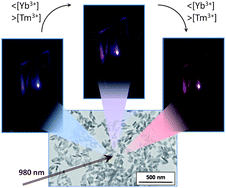
Abstract
Monodisperse YF3:Tm3+/Yb3+ nanocrystals have been synthesized to explore the visible up-converting properties under near infrared (975 nm) excitation. It has been found that the nanoparticles exhibit intense red up-converted emissions, in addition to the characteristic UV and blue Tm3+-bands. It is demonstrated that, by carefully selecting Tm3+ and Yb3+ contents, the relative intensity of the different emissions can be changed producing an overall emission colour that can be tuned from blue to magenta.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1039/c0nr00676a
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of visible light sensitive titanium dioxide photocatalyst
Šubrt, J., Criado, J.M., Szatmáry, L., Diánez-Millán, M.J., Murafa, N., Pérez-Maqueda, L.A., Brezová, V.International Journal of Photoenergy, 2011 (2011) Article number 156941 DOI: 10.1155/2011/156941

Abstract
Phase transition of anatase nanoparticles into the phases TiO2-II and rutile under grinding was studied. The addition of ammonium carbamate to the reaction mixture inhibits the phase conversion and the cold welding of particles. The UV-visible absorption spectrum showed narrowing the band gap width after grinding with an ammonium carbamate additive resulting in shift of the light absorption of the ground sample towards the visible region. By EPR, intensive formation of OH• radical at irradiation of the sample with both UV (λ > 300 nm) and visible (λ > 435 nm) light was observed. High photocatalytic activity of the ground sample in visible light region was demonstrated also by measurement of kinetics of the photocatalytic decomposition of 4-chlorophenol.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1155/2011/156941
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold nanoparticles on yttrium modified titania: Support properties and catalytic activity
Plata, JJ; Marquez, AM; Sanz, JF; Avellaneda, RS; Romero-Sarria, F; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JATopics in Catalysis, 54 (2011) 219-228 DOI: 10.1007/s11244-011-9639-4
Abstract
A series of titanium oxide catalysts modified with yttrium has been prepared by sol-gel method and their structural properties have been studied. The incorporation of yttrium in the titania lattice favors the formation of oxygen vacancies while at low Y loadings the anatase structure is preserved. The catalytic activity of these solids for CO oxidation is found to be significantly dependent on their physical properties. In particular the amount of dopant controls the number of surface oxygen vacancies created as well as the gold particle size, which directly affects the catalytic activity. Also, a linear relationship between the catalytic activity and the band gap values, which depend on the Y loading, is observed. Density functional theory based calculations show that Y atoms are incorporated at the TiO2 surface at substitutional positions only, while the preferred oxygen vacancies arise by removing the bridge surface oxygen atoms. These O-vacancies are the preferential adsorption sites for Au atoms and nanoparticles, acting as nucleation centers that favor the dispersion of the catalyst active phase over the support surface. In agreement with experiment, Y doping is found to decrease the band gap of the support due to a destabilization of the valence band of the oxide. © 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1007/s11244-011-9639-4
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
A comparative study of the role of additive in the MgH2 vs. the LiBH4–MgH2 hydrogen storage system
A. Fernández, E. Deprez, O. FriedrichsInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 36 (2011) 3932-3940 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.12.112
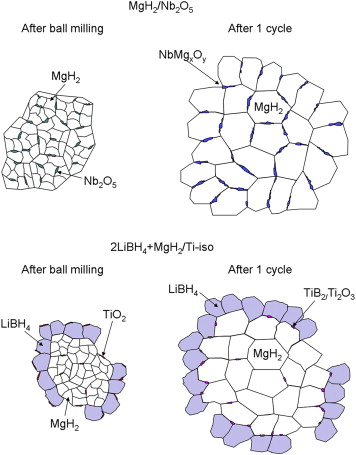
Abstract
The objective of the present work is the comparative study of the behaviour of the Nb- and Ti-based additives in the MgH2 single hydride and the MgH2 + 2LiBH4 reactive hydride composite. The selected additives have been previously demonstrated to significantly improve the sorption reaction kinetics in the corresponding materials. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS), X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Electron Microscopy (TEM) analysis were carried out for the milled and cycled samples in absence or presence of the additives. It has been shown that although the evolution of the oxidation state for both Nb- and Ti-species are similar in both systems, the Nb additive is performing its activity at the surface while the Ti active species migrate to the bulk. The Nb-based additive is forming pathways that facilitate the diffusion of hydrogen through the diffusion barriers both in desorption and absorption. For the Ti-based additive in the reactive hydride composite, the active species are working in the bulk, enhancing the heterogeneous nucleation of MgB2 phases during desorption and producing a distinct grain refinement that favours both sorption kinetics. The results are discussed in regards to possible kinetic models for both systems.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.12.112
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Selective CO removal over Au/CeFe and CeCu catalysts in microreactors studied through kinetic analysis and CFD simulations
Arzamendi, G; Uriz, I; Dieguez, PM; Laguna, OH; Hernandez, WV; Alvarez, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Montes, M; Gandia, LMChemical Engineering Journal, 167 (2011) 588-596 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.083
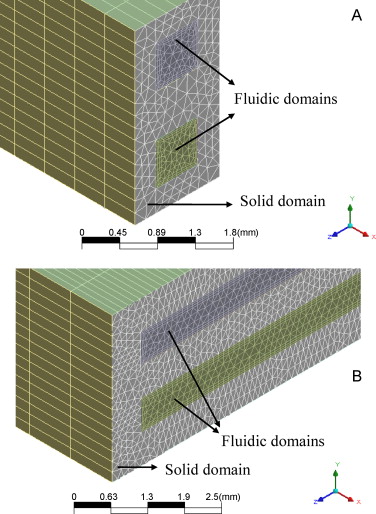
Abstract
A kinetic study of the preferential oxidation of CO in H2 rich streams (CO-PrOx) over a cerium-copper oxide (CeCu) and a gold catalyst supported on cerium-iron oxide (Au/CeFe) is presented. The gold catalyst is very active but the CeCu oxide is more selective. A kinetic model describing the CO-PrOx system with CO2 and H2O in the feed has been formulated considering the oxidation of CO and H2 and the reverse water-gas shift reaction. The rate equations have been implemented in computational fluid dynamics codes to study the influence of the operating variables on the CO-PrOx in microchannels and microslits. The CeCu catalyst is the only one capable of achieving final CO contents below 10-100ppmv. Due to the opposite effect of temperature on activity and selectivity there is an optimal temperature at which the CO content is minimal over CeCu. This temperature varies between 170 and 200°C as the GHSV increases from 10,000 to 50,000h-1. Simulations have evidenced the very good heat transfer performance of the microdevices showing that the CO-PrOx temperature can be controlled using air as cooling fluid although the inlet temperature and flow rate should be carefully controlled to avoid reaction extinction. Both microchannels and microslits behaved similarly. The fact that the microslits are much easier to fabricate may be an interesting advantage in favour of that geometry in this case. © 2010 Elsevier B.V.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.083
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in microchannels
Almeida, LC; Echave, FJ; Sanz, O; Centeno, MA; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LM; Sousa-Aguiar, EF; Odriozola, JA; Montes, MChemical Engineering Journal, 167 (2011) 536-544 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.091
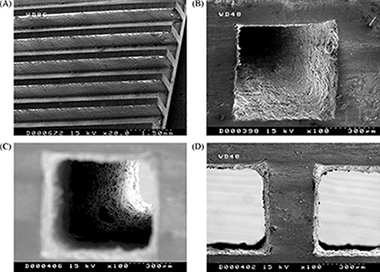
Abstract
Different metallic supports (aluminum foams of 40ppi, honeycomb monolith and micromonolith of 350 and 1180cpsi, respectively) have been loaded with a 20%Co-0.5%Re/γ-Al2O3 catalyst by the washcoating method. Layers of different thicknesses have been deposited onto the metallic supports. The catalytic coatings were characterized measuring their textural properties, adhesion and morphology. These structured catalysts have been tested in the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis (FTS) and compared with a microchannel block presenting perpendicular channels for reaction and cooling. The selectivity depends on the type of support used and mainly on the thickness of the layer deposited. In general, the C5+ selectivity decreased at increasing CO conversion for all of the systems (powder, monoliths, foams and microchannels block). On the other hand, the selectivity to methane increased with the thickness of the catalytic layer due to the higher effective H2/CO ratio over the active sites resulting from the higher diffusivity of H2 compared with CO in the liquid products filling the pores. The C5+ selectivity of the microchannels reactor is higher than that of the structured supports and the powder catalyst. © 2010 Elsevier B.V.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.091
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Monolayer structures of alkyl aldehydes: Odd-membered homologues
Phillips, TK; Clarke, SM; Bhinde, T; Castro, MA; Millan, C; Medina, SThin Solid Films, 519 (2011) 3123-3127 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.12.084
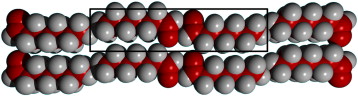
Abstract
Crystalline monolayers of three aldehydes with an odd number of carbon atoms in the alkyl chain (C7, C9 and C11) at low coverages are observed by a combination of X-ray and neutron diffraction. Analysis of the diffraction data is discussed and possible monolayer crystal structures are proposed; although unique structures could not be ascertained for all molecules. We conclude that the structures are flat on the surface, with the molecules lying in the plane of the layer. The C11 homologue is determined to have a plane group of either p2, pgb or pgg, and for the C7 homologue the p2 plane group is preferred.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.12.084
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
The biophysical design of plant cuticles: an overview
Dominguez, E; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Heredia, ANew Phytologist, 189 (2011) 938-949 DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03553.x
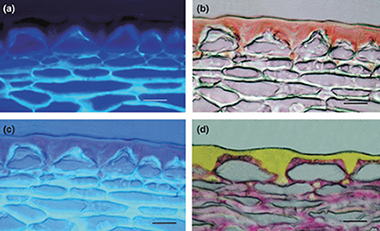
Abstract
The outer surfaces of epidermal cell walls are impregnated with an extracellular matrix called the cuticle. This composite matrix provides several functions at the interface level that enable plants to thrive in different habitats and withstand adverse environmental conditions. The lipid polymer cutin, which is the main constituent of the plant cuticle, has some unique biophysical properties resulting from its composition and structure. This review summarizes the progress made towards understanding the biophysical significance of this biopolymer with special focus on its structural, thermal, biomechanical, and hydric properties and relationships. The physiological relevance of such biophysical properties is discussed in light of existing knowledge on the plant cuticle.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03553.x
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nitridation of nanocrystalline TiO2 thin films by treatment with ammonia
Romero-Gomez, P; Rico, V; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palgrave, RG; Egdell, RGThin Solid Films, 519 (2011) 3587-3595 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.01.267
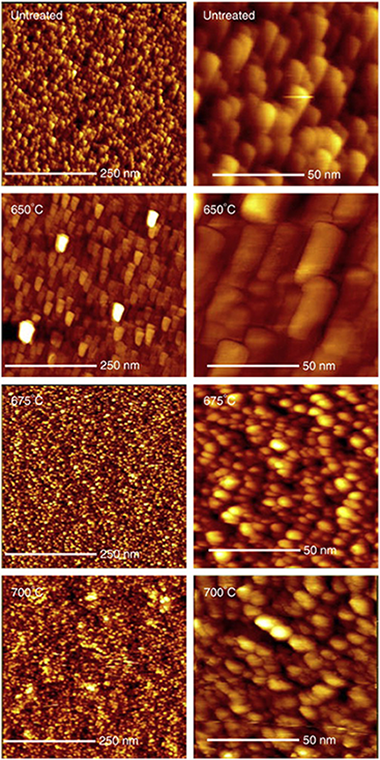
Abstract
Nanocrystalline anatase (TiO2) thin films prepared by a physical vapour deposition method were nitrided by annealing in flowing NH3 at temperatures ranging between 650 °C and 700 °C. It was established that there was a narrow window of temperatures which allowed both incorporation of interstitial nitrogen into the films with retention of the anatase phase without chemical reduction and preservation of the characteristic nanocrystalline morphology. These optimally modified films responded to visible light in photowetting tests and showed the ability to degrade an organic dye under visible light irradiation.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.01.267
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Blocking of grain reorientation in self-doped alumina materials
Suarez, M; Fernandez, A; Menendez, JL; Ramirez-Rico, J; Torrecillas, RScripta Materialia, 64 (2011) 517-520 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.11.031
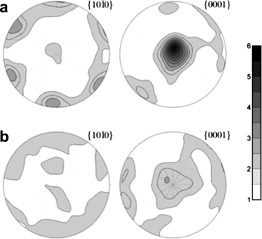
Abstract
Alumina nanoparticles 10-20 nm in diameter were nucleated on alumina particles, 150 nm average diameter, by a colloidal route followed by calcination. It is shown that after sintering, the final grain size is up to 20% smaller due to the addition of the alumina nanoparticles. Electron backscattered diffraction analysis shows that whereas a correlation in the relative crystalline orientations between neighbouring grains exists in the pure materials, the addition of alumina nanoparticles results in a random crystalline orientation.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.11.031
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Creep behavior of TiCxN1-x-CoTi cermets synthesized by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Cordoba, JM; Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 299-302 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.10.007
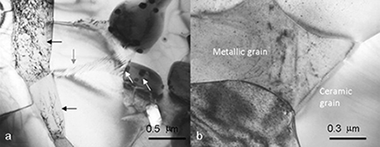
Abstract
The plastic flow of TiCxN1-x-CoTi cermets has been investigated by uniaxial compression tests carried out in argon atmosphere at temperatures between 1100 and 1200°C. Two different cermets, with 5wt.% W or WC content as sintering additives, have been explored to assess the influence of the sintering additives on creep. The microstructural observations of deformed samples and the mechanical results indicate that the hard phase (ceramic grains) controls the plastic deformation. The stress exponent changes from 1 to 2 with increasing strain rate, suggesting a transition in the deformation mechanism from diffusional creep to grain boundary sliding; both with similar activation energy values of about 400kJ/mol. This value of activation energy agrees with C diffusion in the carbonitride grains as the strain rate controlling mechanism.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.10.007
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Endurance of TiAlSiN coatings: Effect of Si and bias on wear and adhesion
Philippon, D; Godinho, V; Nagy, PM; Delplancke-Ogletree, MP; Fernandez, AWear, 270 (2011) 541-549 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2011.01.009
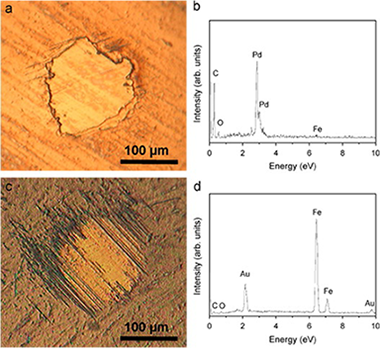
Abstract
In this work, the endurance of TiAlSiN nanocomposite thin films subjected to tribological solicitation is studied. These coating were deposited on M2 steel substrate by magnetron sputtering. Dry sliding experiments were conducted at ambient temperature against WC-Co ball. Coefficients of friction, wear rates and endurances were correlated with the composition, microstructure, mechanical properties, residual stress and adhesion of the coatings. The hardness and elastic modulus were found dependent not only on the composition but also on the residual stress induced by the deposition process. Friction coefficient was found to be independent on Si content while the wear rate is strongly reduced for higher Si contents. The formation of a nanocomposite microstructure, the amount of amorphous Si-based phase and both, wear resistance and adhesion are shown as the critical factors to determine the endurance of the coating.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2011.01.009
Reactividad de Sólidos - Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Design and testing of a microchannel reactor for the PROX reaction
Cruz, S; Sanz, O; Poyato, R; Laguna, OH; Echave, FJ; Almeida, LC; Centeno, MA; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LM; Souza-Aguiar, EF; Montes, M; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 167 (2011) 634-642 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.088
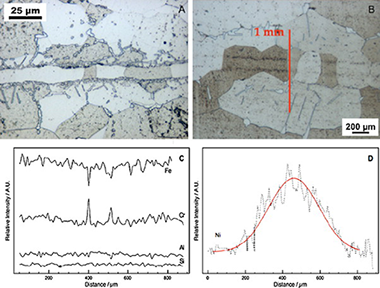
Abstract
The different steps for manufacturing a microchannel reactor for the PROX reaction are discussed. Transient Liquid Phase bonding (TLP) using a Ni-B-Si amorphous melt spun is used for joining micromilled Al-alloyed ferritic stainless steel plates followed by recrystallization at 1200°C for 5h. A CuOx-CeO2 catalyst synthesized by the coprecipitation method was washcoated on the microchannel block resulting in a homogenous 20-30μm thick layer. The catalytic activity for CO-PROX reaction is similar in both the powder catalyst and the microchannel coated reactor but the selectivity is higher in the microchannel reactor. © 2010 Elsevier B.V.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.088
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetic Analysis of Complex Solid-State Reactions. A New Deconvolution Procedure
Antonio Perejón, Pedro E. Sánchez-Jiménez, José M. Criado, and Luis A. Pérez-MaquedaJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115 (8), pp 1780–1791 DOI: 10.1021/jp110895z
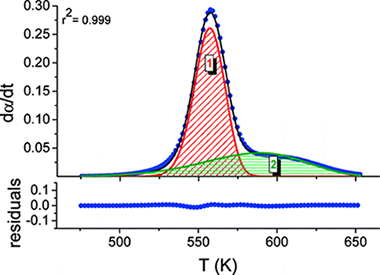
Abstract
The kinetic analysis of complex solid-state reactions that involve simultaneous overlapping processes is challenging. A method that involves the deconvolution of the individual processes from the overall differential kinetic curves obtained under linear heating rate conditions, followed by the kinetic analysis of the discrete processes using combined kinetic analysis, is proposed. Different conventional mathematical fitting functions have been tested for deconvolution, paying special attention to the shape analysis of the kinetic curves. It has been shown that many conventional mathematical curves such as the Gaussian and Lorentzian ones fit kinetic curves inaccurately and the subsequent kinetic analysis yields incorrect kinetic parameters. Alternatively, other fitting functions such as the Fraser-Suzuki one properly fit the kinetic curves independently of the kinetic model followed by the reaction and their kinetic parameters, and moreover, the subsequent kinetic analysis yields the correct kinetic parameters. The method has been tested with the kinetic analysis of complex processes, both simulated and experimental.
March, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/jp110895z
Study of ground and unground leached vermiculite II. Thermal behaviour of ground acid-treated vermiculite
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Maqueda, C; Murafa, N; Subrt, J; Balek, V; Pulisova, P; Lancok, AApplied Clay Science, 51 (2011) 274-282 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.11.031
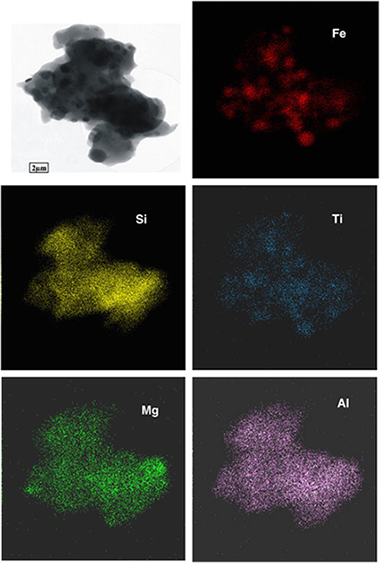
Abstract
In this study, we examined the annealing effect on the material obtained after acid treatment of ground vermiculite which constituted amorphous silica and β-FeOOH. The XRD patterns of the starting sample measured at temperatures from 30 to 1200°C showed that the crystalline phase was present until ~300°C; whereas the sample heated between 300 and 800°C was practically amorphous. This is in agreement with previous observations that β-FeOOH decomposes to amorphous or poorly crystalline phase, β-Fe2O3, and transforms only slowly to crystalline α-Fe2O3. At 850°C the sample showed the first signs of a crystalline phase which was fully developed at 1050°C. The XRD, HRTEM and Mössbauer spectroscopy showed, after heating at 1050°C, the presence of crystalline phase, consisting of quartz, cristobalite, α-Fe2O3 and ε-Fe2O3. This effect showed in fact that well crystallized iron oxide nanoparticles embedded into the silica matrix are usually formed at relative high temperatures (~1000°C), which is in contrast to silica-free material. Element mapping of one particle of the composite obtained by annealing the sample at the highest temperature showed well-separated Fe2O3 and SiO2 particles in a composite material. Impurities of Al and Mg (from the original vermiculite) accompanied the silica components and TiO2 associated with Fe2O3 grains was also detected.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.11.031
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Influence of OH− concentration on the illitization of kaolinite at high pressure
M. Mantovani, A. Escudero, A.I. Becerro,Applied Clay Science, 51 (2011) 220-225 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.11.021
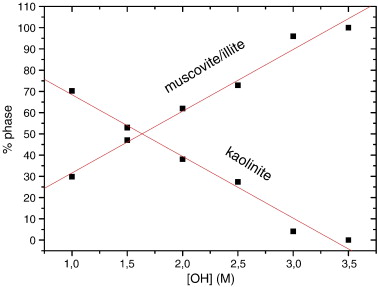
Abstract
The products of hydrothermal reactions of kaolinite at 300 °C and 1000 bars were studied in KOH solutions covering an OH− concentration, [OH−], of 1 M to 3.5 M. XRD patterns indicated a notable influence of the [OH−] on the reaction. At [OH] ≥ 3 M, the only stable phase was muscovite/illite. The content of muscovite/illite was calculated from the analysis of the diagnostic 060 reflections of kaolinite and muscovite/illite. The results showed a linear dependence of kaolinite and muscovite/illite contents with [OH−]. 27Al MAS NMR spectroscopy revealed the formation of small nuclei of K-F zeolite at high [OH−]. Finally, modelling of the 29Si MAS NMR spectra indicated that the Si/Al ratio of the muscovite/illite formed was very close to that of muscovite, at least in the mineral formed at low [OH−]. In good agreement with the XRD data, the quantification of the reaction products by 29Si MAS NMR indicated a linear decrease of the kaolinite content with increasing OH− concentration.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.11.021
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Effect of thermal treatments on the catalytic behaviour in the CO preferential oxidation of a CuO-CeO2-ZrO2 catalyst with a flower-like morphology
Moretti, E; Storaro, L; Talon, A; Lenarda, M; Riello, P; Frattini, R; de Yuso, MDM; Jimenez-Lopez, A; Rodriguez-Castellon, E; Ternero, F; Caballero, A; Holgado, JPApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 102 (2011) 627-637 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.01.004

Abstract
A Ce–Zr–Cu oxide system with a flower-like morphology was prepared by a slow co-precipitation method in the absence of any structure directing agent. Four portions of the oxide were thermally treated at four different temperatures (350 °C, 450 °C, 550 °C, 650 °C). The resulting materials samples were characterized by quantitative XRD, adsorption–desorption of N2 at-196 °C, SEM and TEM microscopy, –H2-TPR, XPS and Operando-XANES. All samples were tested in the preferential CO oxidation (CO-PROX) in the 40–190 °C temperature range. Thermal treatments were found to induce slight structural changes without altering the starting morphology of the samples. The samples treated at higher temperature 550–650 °C showed a quite interesting CO-PROX activity and selectivity in a temperature range suitable for a practical use within the FEMFC technology.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.01.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Aluminum anodization in oxalic acid: Controlling the Texture of Al 2O3/Al monoliths for catalytic aplications
Sanz, O; Echave, FJ; Odriozola, JA; Montes, MIndustrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 50 (2011) 2117-2125 DOI: 10.1021/ie102122x
Abstract
The anodization and postanodization processes of aluminum in order to prepare monoliths for catalytic applications have been studied in this work using oxalic acid as electrolyte. The effect of anodization variables (anodization time, current density, temperature, and electrolyte concentration) and postanodization processes on the surface morphology and textural properties of AAO (anodic aluminum oxide) films is analyzed. The anodization variables affect the two main processes taking part in the Al2O3 layer formation: alumina generation and its dissolution that are controlled by temperature, electrolyte concentration and time. The proper combination of both processes, as a result of the anodization variables choice, produces adherent alumina layers with tailored porosity and surface morphology that show excellent properties to be used as catalyst structured support. Larger pore sizes and the complete absence of sulfur that may poison reduced metal-supported active phases are main differences with the classical, most often used, sulfuric acid anodization process. © 2011 American Chemical Society.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/ie102122x
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
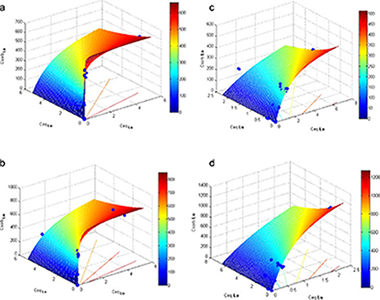
Examination of competitive lanthanide sorption onto smectites and its significance in the management of radioactive waste
Galunin, E; Alba, MD; Santos, MJ; Abrao, T; Vidal, MJournal of Hazardous Materials, 186 (2011) 1930-1941 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.098
Abstract
The competitive effect of La and Lu (analogues of radionuclides appearing in radioactive waste) in the sorption in four smectites was examined. Sorption and desorption distribution coefficients (Kd; Kd,des), and desorption rates (Rdes) were determined from batch tests in two media: deionized water and, to consider the influence of cement leachates, 0.02molL-1 Ca. The competitive effect was lower when high-affinity sites were available, as in the water medium at the lowest range of initial lanthanide concentration, with high Kd for La and for Lu (5-63×104Lkg-1). Lower Kd was measured at higher initial concentrations and in the Ca medium, where Lu showed a stronger competitive effect. This was confirmed by fitting the sorption data to a two-solute Langmuir isotherm. The desorption data indicated that sorption was virtually irreversible for the scenarios with high sorption, with an excellent correlation between Kd and Kd,des (R2 around 0.9 for the two lanthanides). Assuming that radioactive waste is a mixture of radionuclides, and that Ca ions will be provided by the cement leachates, this would reduce the retention capacity of clay engineered barriers.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.098
Intercalation and dynamics of hydrated Fe2+ in the vermiculites from Santa Olalla and Ojén
Anton Lerf, Friedrich E. Wagner, Juan Poyato and José Luis Pérez-RodríguezJournal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 15 (2011) 223-229 DOI: 10.1007/s10008-010-1171-0
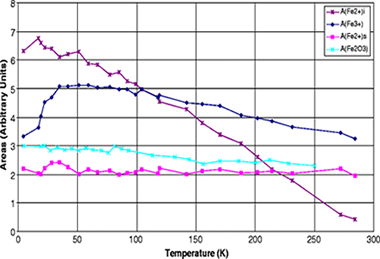
Abstract
Although the intercalation of Fe3+ into layered phyllosicilicates-especially into smectites-attracted much attention in the past two decades, the information about Fe2+ loaded phyllosilicates is sparse. Here we present an investigation of the Fe2+ exchanged vermiculites from Santa Olalla and Ojén (Andalusia, Spain) by means of Mössbauer spectroscopy. The room temperature Mössbauer spectra are very similar to those of the starting compounds (Na forms) except for a decrease of the contribution of structural Fe3+ and a concomitant increase of the contribution of Fe2+ sites, indicating an internal redox process. The extent of this redox reaction is different for the two vermiculites. Thus, the intercalated Fe2+ acts as an electron mediator from the external medium to the structural Fe3+ ions. A new component attributable to intercalated Fe2+ is practically invisible in the room temperature Mössbauer spectra, but increases strongly and continuously during cooling to 4.2 K, where it is the dominant feature of the Mössbauer patterns. At 4.2 K, its quadruple splitting amounts to 3.31 mm/s, which is in excellent agreement with the quadrupole slitting of Fe2+ coordinated to six water molecules in a highly symmetric octahedral arrangement. The strong decrease of the Mössbauer-Lamb factor of this component with increasing temperature indicates a weak bonding of the Fe 2+ in the interlayer space.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1007/s10008-010-1171-0
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Lateral and in-depth distribution of functional groups on diamond-like carbon after oxygen plasma treatments
Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARDiamond and Related Materials, 20 (2011) 49-56 DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2010.11.024
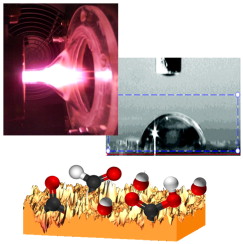
Abstract
A diamond like carbon material has been exposed to a low pressure microwave and atmospheric pressure plasma of oxygen to enhance its hydrophilicity and surface energy. For comparison, data are also reported after activation with a beam of neutral atoms of oxygen. The surface incorporation of oxygenated functional groups and the determination of the in-depth distribution of this element have been analysed by means of the X ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS). Atomic force microscopy (AFM) has been used to get information of the surface topography and, by recording friction maps of the surface, the lateral distribution of oxygenated functional groups formed after the different activation treatments. Differences in surface composition, topography and in-depth and lateral distribution of oxygen have been correlated with the intrinsic characteristics of the activation plasma processes.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2010.11.024
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Transparent Nanometric Organic Luminescent Films as UV-Active Components in Photonic Structures
Aparicio, FJ; Holgado, M; Borras, A; Blaszczyk-Lezak, I; Griol, A; Barrios, CA; Casquel, R; Sanza, FJ; Sohlstrom, H; Antelius, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, AAdvanced Materials, 23 (2011) 761-765 DOI: 10.1002/adma.201003088
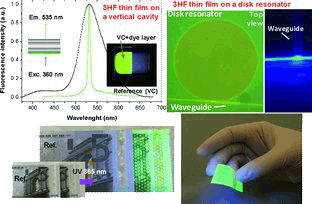
Abstract
A new kind of visible-blind organic thin-film material, consisting of a polymeric matrix with a high concentration of embedded 3-hydroxyflavone (3HF) dye molecules, that absorbs UV light and emits green light is presented. The thin films can be grown on sensitive substrates, including flexible polymers and paper. Their suitability as photonic active components photonic devices is demonstrated.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/adma.201003088
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Modifying the Size of Nickel Metallic Particles by H2/CO Treatment in Ni/ZrO2 Methane Dry Reforming Catalysts
Gonzalez-Delacruz, VM; Pereñiguez, R; Ternero, F; Holgado, JP; Caballero, AACS Catalysis, 1 (2011) 82-88 DOI: 10.1021/cs100116m
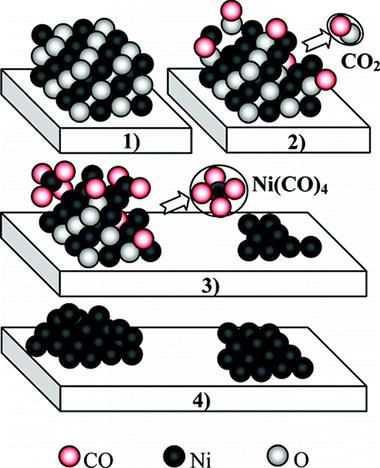
Abstract
The effect of a reduction process with CO or H-2 on the Size of nickel particles in Ni/ZrO2 dry methane reforming catalysts have been studied by means of in situ X-ray Spectroscopy (XAS) and Diffuse Reflectance FTIR Spectroscopy (DRIFTS). Our results clearly indicate that a high temperature treatment with CO increases the dispersion of the nickel metallic phase. XAS results have shown a lower coordination number of Ni in the sample treated with CO than that reduced with H-2. From the DRIFTS results, it can he established that, under the CO treatment, the formation of Ni(CO)(4) complexes corrodes the nickel particles, decreasing their size. The formation of these gas molecules occurs without measurable losses of nickel from the catalyst which maintains the same nickel content after the hydrogen or the CO treatment at high temperature:Therefore, this airborne nickel compound, by colliding with the zirconia surface, must deposit the nickel metal metal atoms around onto the support. This behavior is evidence of an important interaction b etween nickel and zirconia surface as unlike other supports there is no losses of nickel during the dispersion process on zirconia. Although different effects of CO on nickel catalysts have been previously described, we have found for the first time several experimental evidences demonstrating the whole redispersion phenomenon.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1021/cs100116m
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Selective Dichroic Patterning by Nanosecond Laser Treatment of Ag Nanostripes
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Toudert, J; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Lahoz, R; de la Fuente, GF; Frutos, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Materials, 23 (2011) 848-853 DOI: 10.1002/adma.201003933
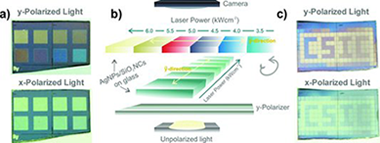
Abstract
A simple route for the fabrication of dichroic optical structures based on Ag nanoparticles deposited onto SiO2 nanocolumns is presented. The strict control of the optical response is achieved after infrared laser treatment of the supported nanoparticles with a commercial nanosecond pulsed laser. Preliminary examples of the utilization of the laser-treated AgNPs/SiO2 nanocolumn system for optical recoding and encryption are shown.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/adma.201003933
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nitrogen plasma functionalization of low density polyethylene
Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSurface and Coatings Technology, 205 (2011) 3356-3365 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.11.038
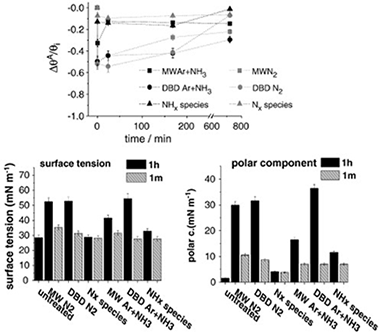
Abstract
Low density polyethylene (LDPE) films have been treated with different nitrogen containing plasmas with the purpose of incorporating nitrogen functional groups on its surface and analyzing the changes experienced in their surface tension. Effects of a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) at atmospheric pressure and a microwave discharge (MW) at reduced pressure are compared with those obtained by using an atom source supplied with N2 and mixtures Ar+NH3 as plasma gas. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis has provided information about the chemical surface changes whereas the surface topography of the treated samples has been examined by atomic force microscopy (AFM). Non-destructive depth profiles of oxygen and carbon have been obtained for the treated and one month aged samples by means of the non-destructive Tougaard's method of XPS background analysis. Generally, an oxygen enrichment of the deeper region of treated LDPE surfaces has been observed. Chemical derivatization of the treated samples has shown that a DBD plasma with a mixture of Ar+NH3 was the most efficient treatment for nitrogen and amine group functionalization. It is argued that the high concentration of NH* species in this plasma is the most important factor in enhancing the nitrogen functionalization of this polymer. It has been also found that the observed increase in hydrophilicity and surface tension cannot be attributed to the anchored nitrogen functional groups formed on plasma treated LDPE. Differences in the plasma activation behaviour of LDPE and that of other polymers subjected to similar treatments are stressed.
February, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.11.038
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Thermal analysis of monument patina containing hydrated calcium oxalates
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Duran, A; Centeno, MA; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Robador, MDThermochimica Acta, 512 (2011) 5-12 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2010.08.015
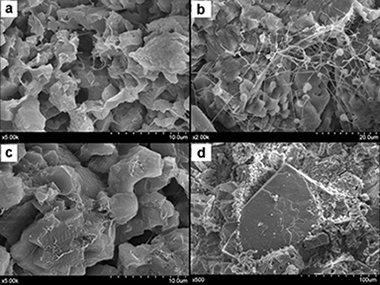
Abstract
This work describes the thermal transformation of patina samples formed on the surface of dolomitic rocks used to build the Romanesque Torme's Church (Burgos, Spain). Analyses were performed using a combination of high-temperature XRD, simultaneous TG/DTA and gas mass spectrometry. The XRD analysis revealed the presence of hydrated calcium oxalates. The following three steps were proposed for the thermal transformation of the raw material: dehydration of weddellite/whewellite to form calcium oxalate, transformation of calcium oxalate to calcium carbonate, and formation of calcium oxide produced via decomposition of the calcite. DTA/TG and mass spectrometry analyses confirmed this mechanism. In addition, a high proportion of organic compounds was detected and was possibly formed via degradation of products applied for the building's conservation by the action of microorganisms attack. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed CO (and CO2) gas evolved during the transformation of CaC2O4 to CaCO3. The CO2 gas also appears at 765 °C due to the decomposition of calcium carbonate, and it appears over a large range of temperatures due to the decomposition of organic compounds. The TG analyses performed in a CO2 atmosphere were used to determine the percentages of Ca and Mg contained in dolomite, and the calcium carbonate formed by oxalate decomposition. DRIFTS and mass spectrometry results revealed the presence of several aliphatic and/or aromatic compounds containing CO groups.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2010.08.015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhanced photoactivity in bilayer films with buried rutile-anatase heterojunctions
Romero-Gomez, P; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARChemPhysChem, 12 (2011) 191-196 DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201000734
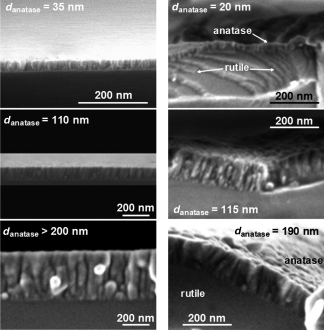
Abstract
Herein, we study the photoactivity of anatase–rutile bilayer thin films consisting of an anatase overlayer of variable thickness from some tenths to some hundred nanometers deposited onto a rutile thin film. As references single anatase layers of equivalent thickness were deposited onto silicon. All the films were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Raman spectroscopy. The photoactivity of the samples was assessed by following the evolution with the UV illumination time of both the wetting angle on the thin film surface and the decoloration of a dye in a water solution. While a similar efficiency is found for the first type of experiments irrespective of the anatase thickness, in the second type a maximum in the photoactivity is found for a thickness of the anatase layer of about 130 nm. This enhanced photoactivity in bilayer systems with a buried anatase–rutile heterojunction is related to the formation of different Schottky potential barriers in the anatase layer, depending on its thickness and the substrate (i.e. rutile or SiO2) where it is deposited.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201000734
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Comparative study of the photodeposition of Pt, Au and Pd on pre-sulphated TiO2 for the photocatalytic decomposition of phenol
Maicu, M; Hidalgo, MC; Colon, G; Navio, JAJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 217 (2011) 275-283 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2010.10.020
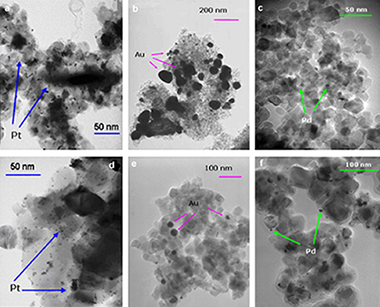
Abstract
A comparative study of the photodeposition of Pt, Au and Pd under the same experimental conditions onto pre-sulphated and non-sulphated TiO2 was performed. Morphological and surface characterisation of the samples as well as photocatalytic activity for phenol photooxidation was studied. The influence of sulphate pre-treatment on the deposits size and dispersion onto the TiO2 surface, and photodeposition yields with the different metals were also analysed. The photocatalytic activity of the doped materials was then investigated, observing that catalytic behaviour can be correlated to physical characteristics of the samples determined by (XRD) X-ray diffraction, (XPS) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, (XRF) X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and (TEM) transmission electron microscopy. Sulphate pre-treatment was found to influence both the level of dispersion and the size of metal clusters on the TiO2 surface. Sulphation and metallisation of samples was found to produce a synergistic enhancement in photoactivity for the degradation of phenol. The photoactivity of the catalysts with respect to the doped metal species was ordered Pt > Pd > Au.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2010.10.020
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Combined x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy studies of the LiBH4-MgH2 reactive hydride composite with and without a Ti-based additive
Deprez, E; Munoz-Marquez, MA; de Haro, MCJ; Palomares, FJ; Soria, F; Dornheim, M; Bormann, R; Fernandez, AJournal of Applied Physics, 109 (2011) 014913 (10 pages) DOI: 10.1063/1.3525803
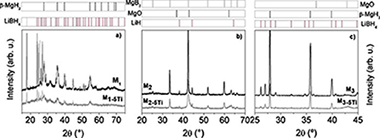
Abstract
A detailed electronic and microstructural characterization is reported for the LiBH4-MgH2 reactive hydride composite system with and without titanium isopropoxide as additive. Surface characterization by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy combined to a morphological study by scanning electron microscopy as well as elemental map composition analysis by energy dispersive x-ray emission are presented in this paper for the first time for all sorption steps. Although sorption reactions are not complete at the surface due to the unavoidable superficial oxidation, it has been shown that the presence of the additive is favoring the heterogeneous nucleation of the MgB2 phase. Ti-based phases appear in all the samples for the three sorption steps well dispersed and uniformly distributed in the material. Li-based phases are highly dispersed at the surface while the Mg-based ones appear, either partially covered by the Li-based phases, or forming bigger grains. Ball milling is promoting mixing of phases and a good dispersion of the additive what favors grain refinement and heterogeneous reactions at the interfaces.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.1063/1.3525803
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Forgery detection on an Arabic illuminated manuscript by micro-Raman and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy
Duran, A; Franquelo, ML; Centeno, MA; Espejo, T; Perez-Rodriguez, JLJournal of Raman Spectroscopy, 42 (2011) 48-55 DOI: 10.1002/jrs.2644

Abstract
An Arabic manuscript, supposed to be from the 14th century, was investigated and its components (pigments and dyestuffs) characterised using micro-Raman and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy, the latter employing a portable XRF/X-ray diffraction (XRD) system. The presence of anatase, rutile, calcite, barite, zinc oxide, carbon black, vermilion, hematite, goethite, β-naphthol, copper phthalocyanine, pigmosol green and a brass-based pigment was detected in the different zones of the illuminated manuscript. The detection of titanium oxides, barite and organic synthetic colourants such as β-naphthol and copper phthalocyanine and derived compounds provides indisputable indication of forging, repainting or retouching after the 19th century in the image of the manuscript.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.1002/jrs.2644
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Novel Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructures for Rhodamine B degradation under sunlike irradiation
Lopez, SM; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Colon, GJournal of Hazardous Materials, 185 (2011) 1425-1434 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.065
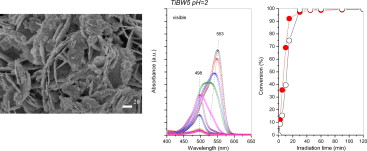
Abstract
Highly efficient Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructure is synthesized by means of a hydrothermal method having highly photoactivity for the degradation of Rhodamine B under sunlike irradiation. From the structural characterization it has been demonstrated that TiO2 is incorporated on the Aurivillius structure. Interesting synergetic effect between TiO2 and Bi2WO6 leads to an improved charge carrier separation mechanism, causing the excellent photocatalytic performance under sunlike irradiation. The photocatalytic performance of Bi2WO6 and Bi2WO6-TiO2 was compared under different irradiation conditions and using increasing Rhodamine B concentration up to 25ppm. After the photocatalytic analysis of both systems, the mineralization efficiency of the heterostructure appears significantly higher with respect to Bi2WO6.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.065
Materiales Coloidales
A facile single-step procedure for the synthesis of luminescent Ln 3+:YVO4 (Ln = Eu or Er + Yb)-silica nanocomposites
Ocana, M; Cantelar, E; Cusso, FMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 125 (2011) 224-230 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.09.011
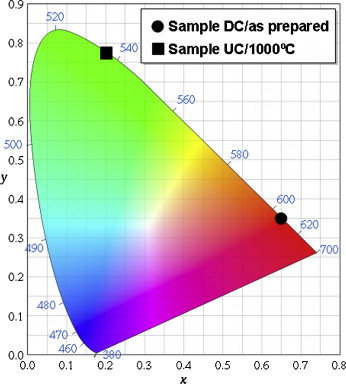
Abstract
A simple and single-step method for the production of Ln-doped YVO 4 nanocrystals and their simultaneous encapsulation in a silica network based on the pyrolysis of liquid aerosols at 800 °C is reported. The procedure is illustrated for Yb,Er:YVO4-silica nanocomposites consisting of spherical particles, which present up-converted green luminescence after IR excitation whose efficiency increased on annealing up to 1000 °C due to the release of impurities (adsorbed water, and residual anions). XPS spectroscopy and TEM observations revealed that the surface of the composite particles was enriched in silica, which would facilitate their functionalisation required to use them in biological applications. The procedure can also be used to prepare other rare earth doped systems as illustrated for the case of Eu-doped YVO4/silica having down-converted red luminescence.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.09.011
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis and characterization of titanium-vanadium ternary nitride (Tix V1-x N)
Roldan, MA; Alcala, MD; Ortega, A; Real, CBoletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 50 (2011) 31-40 DOI: 10.3989/cyv.052011
Abstract
Titanium-Vanadium nitride (TiVN) has been prepared from carbothermal reduction of corresponding oxides and also by direct nitridation of a mix of two metals employing the ATVC method. The characterization of the final product by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, electron energy loss (EELS), and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is presented. The synthesis of the ternary nitride has been possible in all range of composition and the final product is obtained with nanometric particle size and a high microhardness after sintering.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.3989/cyv.052011
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming on NiSn/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts: The role of MgO addition
Penkova, A; Bobadilla, L; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Roger, AC; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General,392 (2011) 184-191 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2010.11.016
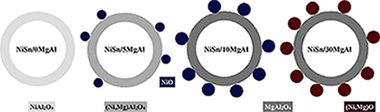
Abstract
The effect of the magnesia loading on the surface structure and catalytic properties of NiSn/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts for hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming has been investigated. The catalysts have been obtained by impregnation of γ-Al2O3 by the incipient wetness method, with variation of the MgO content. X-ray diffraction (XRD), BET surface area and H2-temperature programmed reduction (TPR) have been used to characterise the prepared catalysts. From this, it has been concluded that the incorporation of MgO results in the formation of MgAl2O4 spinel, which modifies the acid-base properties of the catalysts. The formation of Ni-Sn alloys after the reductive pre-treatment has also been evidenced. The influence of the temperature of reaction and of the MgO loading on the hydrogen production by reforming of methanol has been established. Moreover, tests of catalytic stability have been carried out for more than 20 h. The carbonaceous deposits have been examined by temperature-programmed oxidation (TPO). The analysis of the catalysts after reaction has confirmed the low level of carbon formation on these catalysts. In no case, carbon nanotubes have been detected on the solids.
January, 2011 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2010.11.016
2010
2010
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Effect of process parameters on mechanical and tribological performance of pulsed-DC sputtered TiC/a-C:H nanocomposite films
Shaha, KP; Pei, YT; Martinez-Martinez, D; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; De Hosson, JTMSurface and Coatings Technology, 205 (2010) 2633-2642 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.10.020
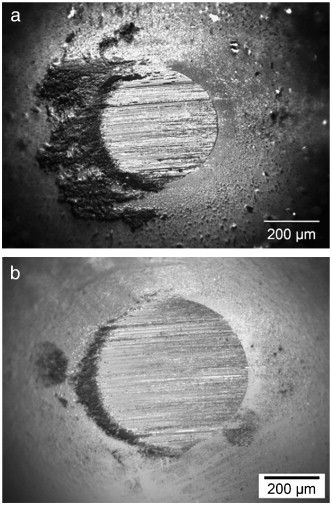
Abstract
Mechanical, structural, chemical bonding (sp(3)/sp(2)). and tribological properties of films deposited by pulsed-DC sputtering of Ti targets in Ar/C2H2 plasma were studied as a function of the substrate bias voltage, Ti-target current, C2H2 flow rate and pulse frequency by nanoindentation, Raman spectroscopy and ball-on-disc tribometry. The new findings in this study comprise: dense, column-free, smooth, and ultra-low friction TiC/a-C:H films are obtained at a lower substrate bias voltage by pulsed-DC sputtering at 200 and 350 kHz frequency. The change in chemical and phase composition influences the tribological performance where the TiC/a-C:H films perform better than the pure a-C:H films. In the case of TiC/a-C:H nanocomposite films, a higher sp(2) content and the presence of TiC nanocrystallites at the sliding surface promote formation of a transfer layer and yield lower friction. In the case of a-C:H films, a higher sp(3) content and higher stress promote formation of hard wear debris during sliding, which cause abrasive wear of the ball counterpart and yield higher friction.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.10.020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Physicochemical Characterization and Use of Wastes from Stainless Steel Mill
Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAEnvironmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 29 (2010) 471-480 DOI: 10.1002/ep.10435
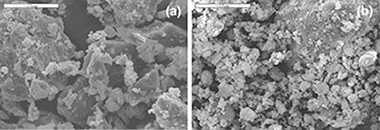
Abstract
Several types of wastes are produced during the manufacture of stainless steel (slags, refractory bricks, and dust). Most of these wastes are not recycled but stored in security deposits or landfills depending on their environmental danger This article reports the study of the physicochemical and mineralogical properties of stainless steel wastes. Their possible uses are also discussed.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1002/ep.10435
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Study of the stabilization of zinc phthalocyanine in sol-gel TiO2 for photodynamic therapy applications
Lopez, T; Ortiz, E; Alvarez, M; Navarrete, J; Odriozola, JA; Martinez-Ortega, F; Paez-Mozo, EA; Escobar, P; Espinoza, KA; Rivero, IANanomedicine-Nanotechnology Biology and Medicine, 6 (2010) 777-785 DOI: 10.1016/j.nano.2010.04.007
Abstract
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has emerged as an alternative and promising noninvasive treatment for cancer. It is a two-step procedure that uses a combination of molecular oxygen, visible light, and photosensitizer (PS) agents; phthalocyanine (Pc) was supported over titanium oxide but has not yet been used for cell inactivation. Zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc) molecules were incorporated into the porous network of titanium dioxide (TiO2) using the sol-gel method. It was prepared from stock solutions of ZnPc and TiO2. ZnPc-TiO2 was tested with four cancer cell lines. The characterization of supported ZnPc showed that phthalocyanine is linked by the N-pyrrole to the support and is stable up to 250 degrees C, leading to testing for PDT. The preferential localization in target organelles such as mitochondria or lysosomes could determine the cell death mechanism after PDT. The results suggest that nanoparticulated TiO2 sensitized with ZnPc is an excellent candidate as sensitizer in PDT against cancer and infectious diseases. From the Clinical Editor: Photodynamic therapy is a two-step procedure that uses a combination of molecular oxygen, visible light and photosensitizer agents as an alternative and promising non-invasive treatment for cancer. The results of this study suggest that nanoparticulated TiO2 sensitized with ZnPc is an excellent photosensitizer candidate against cancer and infectious diseases.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nano.2010.04.007
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold supported on metal-doped ceria catalysts (M = Zr, Zn and Fe) for the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX)
Laguna, OH; Sarria, FR; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Catalysis, 276 (2010) 360-370 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2010.09.027
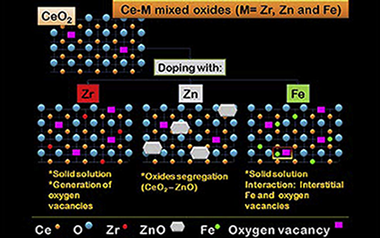
Abstract
A series of ceria oxides doped with 10 mol % of Zr Zn and Fe have been prepared by a pseudo sol-gel method throughout the thermal decomposition of the corresponding metallic propionates With these supports 1 wt % gold catalysts were prepared by the deposition-precipitation method All the solids were characterized by means of XRF N-2 adsorption XRD Raman spectroscopy and SEM techniques and their catalytic activity toward preferential oxidation of CO (PROX) reaction tested The results showed solid solution when doping with Zr and Fe and ZnO surface segregation in the case of Zn We demonstrate that gold dispersion depends on not only the oxygen vacancy concentration but also the nature of the doping agent Finally the catalytic activity was highly promoted by gold in all cases being the doped gold catalysts more active than Au/CeO2 at low temperature.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2010.09.027
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
A first study of the high-temperature plasticity of ceria-doped zirconia polycrystals
de Bernardi-Martin, S; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; de Portu, GJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 30 (2010) 3357-3362 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.07.043
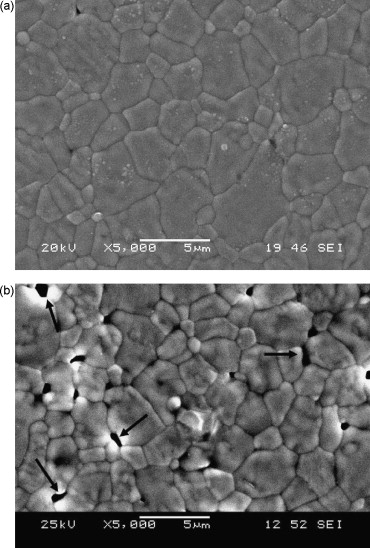
Abstract
Ceria zirconia ceramic alloys were sintered by high-temperature annealing, considering several synthesis temperatures to obtain a full-dense ceria zirconia ceramic material using a temperature as low as possible. It was found that fully density is achieved at temperatures of 1450 degrees C. Monolithic specimens were crept under compression at high temperatures. The creep results fitted an empirical constitutive equation consistent with a classical Ratchinger mechanism for grain switching. This result was confirmed through microstructural characterization of as-received and post-mortem specimens. Since the conventional Ashby-Verrall model is contrary to the mechanism controlling creep in other zirconia alloys, the results are considered in the framework of a new grain boundary sliding model, with particular discussion of the validity of that model for the ceria zirconia case.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.07.043
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Band Gap Narrowing versus Formation of Electronic States in the Gap in N-TiO2 Thin Films
Romero-Gomez, P; Hamad, S; Gonzalez, JC; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 22546-22557 DOI: 10.1021/jp104634j
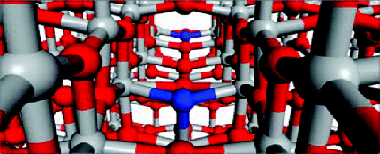
Abstract
N-containing TiO2 thin films with different amounts of nitrogen have been prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) by using different titanium precursors without (titanium isopropoxide, TTIP) and with (tetrakis diethylamino titanium, TDEAT and tetrakis dimethylamino titanium, TDMAT) nitrogen in their structures and different N-2/O-2 ratios as plasma gas. For low/high content of nitrogen, Ti-NO- and/or Ti-N-like species have been detected in the films by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Their optical behavior is characterized by a red shift of their absorption edge when Ti-N species are a majority, and by an unmodified edge with localized absorption states in the gap when only Ti-NO-like species are present in the film. The experimental results have been interpreted by calculating the density of states of model systems consisting of a 2 x 2 x 3 repetition of the anatase unit cell. This basic structure incorporates nitrogen defects in either substitutional or interstitial lattice positions that are considered equivalent to the Ti-N- and Ti-NO-like species detected by XPS. To simulate the effect of, respectively, a low or a high concentration of nitrogen, calculations have been carried out by placing two nitrogen defects either in separated or in nearby positions of the anatase structure. The computational analysis reveals that the defects have different stabilization energies and confirm that an edge shift of the valence band is induced by the substitutional nitrogen centers, as observed when a high concentration of Ti-N species becomes incorporated into the films. In agreement with the experimental results, when only Ti-NO-like species are detected by XPS, no band gap narrowing is obtained by the calculations that predict the appearance of localized electronic states in the gap. The fact that only these latter films present water wetting angle photoactivity when irradiated with visible light supports that the presence of Ti-NO-like species is a required condition for visible light photoactivity.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1021/jp104634j
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bioactivation of biomorphous silicon carbide bone implants
Will J, Hoppe A, Muller FA, Raya CT, Fernandez JM, Greil PActa Biomaterialia, 6 (2010) 448-4494 DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.06.036

Abstract
Wood-derived silicon carbide (SiC) offers a specific biomorphous microstructure similar to the cellular pore microstructure of bone. Compared with bioactive ceramics such as calcium phosphate, however, silicon carbide is considered not to induce spontaneous interface bonding to living bone. Bioactivation by chemical treatment of biomorphous silicon carbide was investigated in order to accelerate osseointegration and improve bone bonding ability. Biomorphous SiC was processed from sipo (Entrandrophragma utile) wood by heating in an inert atmosphere and infiltrating the resulting carbon replica with liquid silicon melt at 1450 °C. After removing excess silicon by leaching in HF/HNO3 the biomorphous preform consisted of β-SiC with a small amount (approximately 6 wt.%) of unreacted carbon. The preform was again leached in HCl/HNO3 and finally exposed to CaCl2 solution. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared analyses proved that oxidation of the residual carbon at the surface induced formation of carboxyl [COO-] groups, which triggered adsorption of Ca2+, as confirmed by XPS and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy measurements. A local increase in Ca2+ concentration stimulated in vitro precipitation of Ca5(PO 4)3OH (HAP) on the silicon carbide preform surface during exposure to simulated body fluid, which indicates a significantly increased bone bonding activity compared with SiC.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.06.036
Variscite source and source analysis: testing assumptions at Pico Centeno (Encinasola, Spain)
Odriozola, CP; Linares-Catela, JA; Hurtado-Perez, VJournal of Archaeological Science, 37 (2010) 3146-3157 DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2010.07.016
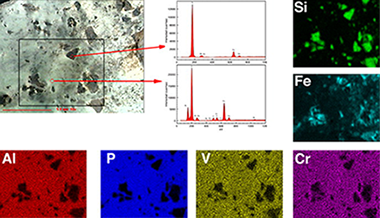
Abstract
The analysis of trade and their implications for understanding social interaction is a major research question of prehistoric research in Europe. Variscite is a rare mineral that offers an excellent opportunity to study trade and exchange patterns in prehistoric Europe through proveniencing of source material. In this paper we discuss the exploitation and exchange of variscite at Pico Centeno mining district during the Copper Age. XRF, XRD, and FTIR analyses of the mineral recovered at Pico Centeno mining district during archaeological survey provides a baseline mineral signature for the source and sub-sources, which were then compared to other Iberian sources and to 44 green beads from 8 megalithic tombs from two different regions, in order to test ‘provenance postulate’ and distribution models. Mineral sampled during survey at Pico Centeno mining district turned out to be pure variscite phases, while extremely varied for the studied green beads: variscite, muscovite, talc or chlorite. On testing ‘provenance postulate’ we have focused on compositional comparison of Pico Centeno’s variscite with reference from various geological sources of Western Europe. We found that the concentrations of trace elements do not allow us to establish the origin of the beads, as traditionally claimed, due to the strong natural variability on minor and trace elements of the sources. Instead we found after FTIR analysis, that different proportions of phosphate species, which results in P/Al ratios higher than 1, arose during the genesis of the variscite deposits and resulted from the associated pH and nature of the host-rocks, modifying the concentrations of PO43−, H2PO4− and HPO42−. Thus, the P/Al atomic ratio should be an indication of provenance as it is established during mineral genesis. This issue has not been addressed in any of the other studied sources where this ratio seems to be ≈1.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2010.07.016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Illization of kaolinite: The effect of pressure on the reaction rate
Mantovani, M; Becerro, AIClays and Clay Minerals, 58 (2010) 766-771 DOI: 10.1346/CCMN.2010.0580604
Abstract
Studies of the paragenesis of authigenic illite in arkosic sandstonesof various regions and ages have revealed that the illitizationof kaolinite is an important reaction accounting for the formationof authigenic illite in sandstones during burial diagenesis.The illitization of kaolinite takes place at an intermediateburial depth of 3–4 km, where pressure can reach valuesof 100 MPa ( 1000 bars). The purpose of the present study wasto analyze the effect of pressure on the rate of kaolinite illitizationin alkaline conditions. Hydrothermal reactions were conductedon KGa-1b kaolinite in KOH solution at 300°C and under pressuresof 500, 1000, and 3000 bars for 1 to 24 h. The visual examinationof the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns indicated a notableinfluence of pressure on the reaction rate. Molar percentagesof muscovite/illite formed at each time interval were calculatedfrom the analysis of two diagnostic XRD peaks, representingthe 060 reflections of kaolinite and muscovite/illite. The datawere modeled to obtain the initial rate of conversion at eachpressure. The results indicated that the initial rate of kaoliniteto muscovite/illite conversion is one order of magnitude greaterat 3000 bars than at 500 or 1000 bars. Comparison of these datawith those in the literature show a faster conversion rate (severalorders of magnitude) in an initially high-alkaline solutionthan in a near-neutral solution.
1000 bars). The purpose of the present study wasto analyze the effect of pressure on the rate of kaolinite illitizationin alkaline conditions. Hydrothermal reactions were conductedon KGa-1b kaolinite in KOH solution at 300°C and under pressuresof 500, 1000, and 3000 bars for 1 to 24 h. The visual examinationof the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns indicated a notableinfluence of pressure on the reaction rate. Molar percentagesof muscovite/illite formed at each time interval were calculatedfrom the analysis of two diagnostic XRD peaks, representingthe 060 reflections of kaolinite and muscovite/illite. The datawere modeled to obtain the initial rate of conversion at eachpressure. The results indicated that the initial rate of kaoliniteto muscovite/illite conversion is one order of magnitude greaterat 3000 bars than at 500 or 1000 bars. Comparison of these datawith those in the literature show a faster conversion rate (severalorders of magnitude) in an initially high-alkaline solutionthan in a near-neutral solution.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1346/CCMN.2010.0580604
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Study of nanoporous catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx
Rico, MJO; Moreno-Tost, R; Jimenez-Lopez, A; Rodriguez-Castellon, E; Pereniguez, R; Caballero, A; Holgado, JPCatalysis Today, 158 (2010) 78-88 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.04.016
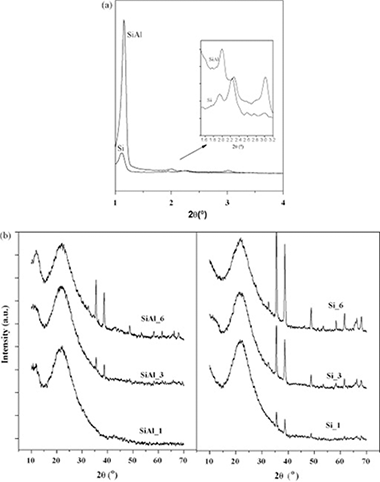
Abstract
Two SBA-15 type materials were synthesized using a low-cost route, a pure silica SBA-15 and an Al containing SBA-15 (with a Si/Al ratio of 10), where Al was added by a post-synthesis modification. The later solid was achieved without any significant loss in the textural properties of SBA-15, besides improving its properties as support of catalysts. Copper impregnated catalysts were prepared through the incipient wetness impregnation of the two supports. With both supports, the copper weight loading were 1, 3 and 6 wt%. The copper incorporation kept the support mesoporous structures, obtaining a better dispersion of the active phase in the containing aluminium support. All the catalysts showed a moderated catalytic activity in the SCR of NO with propane in presence of an excess of oxygen in the whole studied interval of temperatures and a much better performance was observed when using NH3 instead of propane. The changes of the active phases were studied by operando XAS spectroscopy. Factor analysis of in operando XANES results with sample SiAl_6 indicate that no Cu-0 was detected, but only Cu1+ and Cu2+. The temperature where the Cu1+/Cu2+ ratio is maximum occurs at the reaction temperature where the observed catalytic NO conversion is also maximum.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.04.016
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Tunable Nanostructure and Photoluminescence of Columnar ZnO Films Grown by Plasma Deposition
Romero-Gomez, P; Toudert, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 20932-20940 DOI: 10.1021/jp103902u
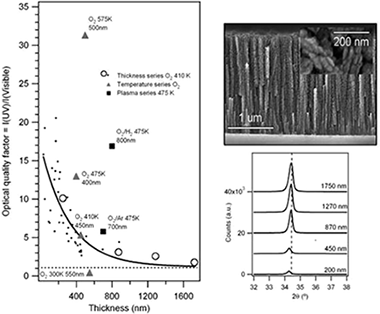
Abstract
Nanoporous ZnO thin films presenting a tunable nanostructure and photoluminescence (PL) were grown by plasma enhanced vapor deposition on surface oxidized Si substrates. These films consist of c-axis oriented wurtzite ZnO nanocolumns whose topology, crystallinity, and PL can be tuned through the substrate temperature (varied in the 300-573 K range) and the nature of the plasma assistance (pure O-2, O-2/Ar, O-2/H-2, or O-2/N-2 mixture). In particular, these processing parameters influence the intensity of the UV and visible PL bands of the films, related to excitonic and defective radiative transitions, respectively. Increasing the substrate temperature enhances the UV PL and rubs out the visible PL due to the increase of grain size and the removal of interstitial defects. Additional tuning of the intensity ratio between the UV and visible bands can be done by controlling the film thickness. A decrease of the UV PL is observed when the films go thicker, an effect that is likely to be linked to the microstructure of the films rather than to their crystallinity that is improved upon increasing of the film thickness, as seen from PL spectroscopy and XRD measurements. Indeed, a gradient of stress, decreasing from the substrate to the surface, is evidenced and related to a concentration gradient of interstitial defects. The drawbacks of the thickness effect, which prohibits growing thick films with a high optical quality, can be bypassed by growing the films in a O-2/H-2 plasma.
December, 2010 · DOI: 10.1021/jp103902u
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Segregation-induced grain boundary electrical potential in ionic oxide materials: A first principles model
D. Gómez-García, Juan J. Meléndez, Robert L. González-Romero, A. Domínguez-RodríguezActa Materialia, 58 (2010) 6404-6410 DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.08.002
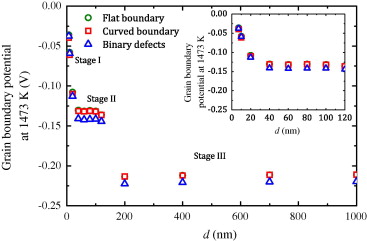
Abstract
A first principles continuum analytical model for cationic segregation to the grain boundaries in complex ceramic oxides is presented. The model permits one to determine the electric charge density and the segregation-induced electric potential profiles through the grain and can be extrapolated to the range of nanostructured grain sizes. The theoretical predictions are compared with existing data for yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals. The implications for physical properties (mainly high temperature plasticity and hardening behaviour) are then discussed.
November, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.08.002
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Iron-modified ceria and Au/ceria catalysts for Total and Preferential Oxidation of CO (TOX and PROX)
Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LM; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 157 (2010) 155-159 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.04.011
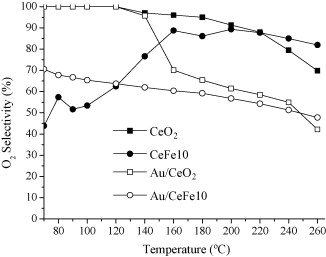
Abstract
Iron-modified ceria supports containing different molar percentages of Fe (0% 10% 25% and 50%) were synthesized by thermal decomposition of the metal propionates The formation of a Ce-Fe oxide solid solution is evidenced through XRF XRD BET and Raman spectroscopy For Iron contents above 25% the formation of alpha-Fe2O3 was detected pointing out the formation of the isolated oxides The catalytic activity of the Fe-modified catalysts in the Total Oxidation of CO reaction (TOX) is higher than for the bare CeO2 material The synergy between Ce and Fe shows a maximum for 10% Fe content (CeFe10) catalyst that shows the highest CO conversion per atom of Fe incorporated Gold catalyst was also prepared on CeFe10 and its catalytic activity compared with Au/CeO2 catalyst The addition of iron to the gold catalyst resulted in an enhancement of the catalytic activity for CO oxidation especially at low temperature This Au/CeFe10 catalyst was also active and selective with excellent stability in the Preferential Oxidation of CO (PROX) showing a higher CO conversion than the Au/CeO2 catalyst at temperatures below 150 C being hardly affected by the presence of CO2 and H2O in the gas stream.
November, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.04.011
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effect of pressure on kaolinite illitization
Mantovani, M; Escudero, A; Becerro, AIApplied Clay Science, 50 (2010) 342-347 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.08.024
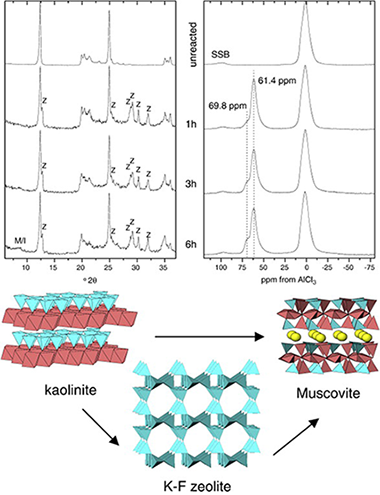
Abstract
The illitization of kaolinite at increasing pressures was followed by hydrothermal experiments of kaolinite in KOH solution at 300 degrees C for 12 h and pressures between 500 and 3000 bar XRD indicated a direct transformation of kaolinite into muscovite/illite with increasing pressure However the (27)AI MAS NMR spectra showed in addition to the muscovite/illite resonances the presence of a signal at 61 ppm that should correspond to a secondary phase not detected by XRD A second series of experiments at 300 degrees C and 1000 bar for 1 3 and 6 h was carried out to show direct evidence of such phase The XRD patterns of the products clearly showed the crystallization of K-F zeolite while the (27)AI MAS NMR spectra of these samples displayed a signal at 61 ppm that must correspond therefore to Al in the K-F zeolite structure In conclusion kaolinite transformed into muscovite/illite when submitted to hydrothermal reaction in KOH solution with increasing pressure with the formation of a secondary metastable phase called K-F zeolite whose coherent diffraction domains were too small as to be detected by XRD.Effect of pressure on kaolinite illitization
November, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.08.024
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Improved Non-Covalent Biofunctionalization of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Using Carbohydrate Amphiphiles with a Butterfly-Like Polyaromatic Tail
Assali, M; Leal, MP; Fernandez, I; Romero-Gomez, P; Baati, R; Khiar, NNano Research, 3 (2010) 764-778 DOI: 10.1007/s12274-010-0044-2
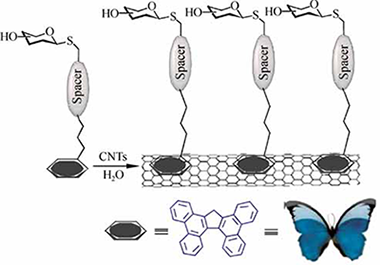
Abstract
We have developed an efficient strategy for the non-covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) which allows a biomimetic presentation of carbohydrates on their surface by pi-pi stacking interactions. The strategy is based on the use of sugar-based amphiphiles functionalized with tetrabenzo[a,c,g,i] fluorene (Tbf), a polyaromatic compound with a topology that resembles a butterfly with open wings. The new carbohydrate-tethered Tbf amphiphiles have been synthesized in a straightforward manner using click chemistry. The reported method has been developed in order to improve the rather low ability of pyrene-based systems to exfoliate MWCNTs in water. By means of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), and fluorescence spectroscopies the interaction between MWCNTs and the Tbf group has been found to be stronger than those involving pyrene-based amphiphilic carbohydrates. The resulting aggregates with a multivalent sugar exposition on their surface are able to engage in specific ligand-lectin interactions similar to glycoconjugates on a cell membrane.
November, 2010 · DOI: 10.1007/s12274-010-0044-2
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Modified cryptomelane-type manganese dioxide nanomaterials for preferential oxidation of CO in the presence of hydrogen
Hernandez, WY; Centeno, MA; Romero-Sarria, F; Ivanova, S; Montes, M; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 157 (2010) 160-165 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.03.010
Abstract
Transition metal (Cu Co Ni and Zn)-modified cryptomelane-type manganese dioxide nanomaterials were synthesized by the milling method The obtained solids have been characterized by means of Xray diffraction (XRD) scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM) N-2 adsorption-desorption measurements at 77 K Raman spectroscopy and temperature programmed reduction (TPR-H-2) showing similar structural and textural properties All the solids were active in the preferential oxidation of CO in the presence of hydrogen (PROX) being the modified with copper the most active The catalytic activity correlates fairly well with the TPR results finding higher CO conversion for the material with higher reducibility (OMS-Cu) The O-2 selectivity measured as ([CO](in)-[CO](out)/2[O-2](in)-[O-2](out)) x 100 is very similar for all synthesized materials.
November, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.03.010
Reactividad de Sólidos
Quantitative Characterization of Multicomponent Polymers by Sample-Controlled Thermal Analysis
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Crespo-Amoros, JE; Lopez, J; Perejon, A; Criado, JMAnalytical Chemistry, 82 (2010) 8875-8880 DOI: 10.1021/ac101651g
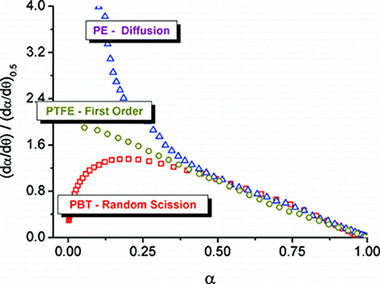
Abstract
This paper explores the potential of sample-controlled thermal analysis (SCTA) in order to perform compositional analysis of multicomponent polymeric materials by means of thermogravimetric experiments. In SCTA experiments, the response of the sample to the temperature determines the evolution of the temperature by means of a feedback system; thus, what is controlled is not the temperature time profile, as in conventional analysis, but rather the evolution of the reaction rate with time. The higher resolving power provided by the technique has been used for determining the composition of polymer blends composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and different commercial plasticizers, a system where the individual components have very similar thermal stabilities, thereby rendering useless thermogravimetric experiments run under conventional conditions. Different SCTA procedures, such as constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA), which has received special attention, and high-resolution and stepwise isothermal analysis have been tested, and the results obtained have been compared with linear heating rate technique. It has been proven that CRTA can be used to effectively determine the exact composition of the blend.
November, 2010 · DOI: 10.1021/ac101651g
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Characterisation and photocatalytic properties of titania-silica mixed oxides doped with Ag and Pt
Llano, B; Restrepo, G; Marin, JM; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCApplied Catalysis A-General, 387 (2010) 135-140 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2010.08.021
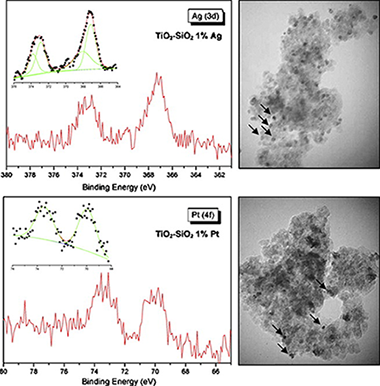
Abstract
TiO2-SiO2 mixed oxides have been synthesised and modified by Ag and Pt deposition. Due to the effect of the silica on the mixed oxide, the prepared materials presented high surface areas and stabilised anatase as the only crystalline phase after calcination at 700 degrees C. Even using the same photodeposition experimental conditions, the yield for metal deposition depended highly on the metal considered, being much lower for Ag deposition. XPS studies permitted to estimate metal dispersion and oxidation state of the different samples, being both factors of high importance regarding photocatalytic improvement by metal deposition.
October, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2010.08.021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Wetting Properties of Polycrystalline TiO2 Surfaces: A Scaling Approach to the Roughness Factors
Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARLangmuir, 26 (2010) 15875-15882 DOI: 10.1021/la101975e
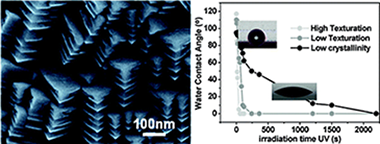
Abstract
This work presents a thorough study on the wettability of polycrystalline anatase TiO2 thin films prepared at 250 degrees C in a microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (MW-PECVD) reactor with Ar/O-2 plasmas. Anatase polycrystalline thin films with different microstructures, textures, and surface roughness were obtained as a function of their thickness. The water contact angle of the samples was analyzed within the assumptions of the Wenzel, Cassie, and Miwa models to ascertain the effect of roughness and other surface heterogeneities on their characteristic parameters. The roughness factors defined in the different models were calculated from the atomic force microscopy (AFM) images of the films for two different observation scales within the premises of the dynamic scaling theories. The obtained results indicate that the wetting angle of an equivalent flat anatase surface with a value of 82 degrees can only be properly estimated for observation scales of 5 x 5 mu m(2) and using the Miwa model. The analysis of the UV induced hydrophilization of the surface state of the anatase films and the posterior recovery of the partially hydrophobic character of these surfaces in the absence of UV photons suggest a clear dependence of the light induced wettability on their texture and size of crystalline domains.
October, 2010 · DOI: 10.1021/la101975e
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Versatility and multifunctionality of highly reflecting Bragg mirrors based on nanoparticle multilayers
Olalla Sánchez-Sobrado, Mauricio E. Calvo and Hernán MíguezJournal of Materials Chemistry, 20 (2010) 8240-8246 DOI: 10.1039/c0jm01508c
Abstract
The use of both supported and flexible self-standing nanoparticle-based one dimensional photonic crystal films as effective frequency selective filters in the UV-vis-NIR is herein evaluated. The requirements to achieve a flat spectral response at the desired frequency range are analyzed and a synthetic route to realize materials with such properties presented. Strict control over the structural parameters yields multilayers in which the opening or closing of higher order photonic band gaps can be devised, thus leading to films capable of blocking the UV and NIR ranges simultaneously. Furthermore, the physico-chemical properties of the mirror can be modified to yield either moisture-repelling or, on the contrary, environmentally responsive optical filters. These materials present a great potential to be used as versatile and multifunctional optical elements.
October, 2010 · DOI: 10.1039/c0jm01508c
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Microstructural study of the LiBH4-MgH2 reactive hydride composite with and without Ti-isopropoxide additive
Deprez, E; Justo, A; Rojas, TC; Lopez-Cartes, C; Minella, CB; Bosenberg, U; Dornheim, M; Borrnann, R; Fernandez, AActa Materialia, 58 (2010) 5683-5694 DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.06.043

Abstract
An exhaustive microstructural characterization is reported for the LiBH4-MgH2 reactive hydride composite (RHC) system with and without titanium isopropoxide additive. X-ray diffraction with Rietveld analysis, transmission electron microscopy coupled to energy dispersive X-ray analysis, selected-area electron diffraction and electron energy loss spectroscopy are presented in this paper for the first time for this system for all sorption steps. New data are reported regarding average crystallite and grain size, microstrain, phase formation and morphology; these results contribute to the understanding of the reaction mechanism and the influence of the additives on the kinetics. Microstructural effects, related to the high dispersion of titanium-based additives, result in a distinct grain refinement of MgB2 and an increase in the number of reaction sites, causing acceleration of desorption and absorption reactions. Considerations on the stability of phases under electron beam irradiation have also been reported.
October, 2010 · DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.06.043
- ‹ previous
- 32 of 37
- next ›














