Scientific Papers in SCI
2023
2023
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Coal Chemistry Industry: From Production of Liquid Fuels to Fine Chemicals to Carbon Materials
Zhang, YY; Li, HT; Reina, TR; Liu, JEnergy & Fuels, (2023) DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c02661
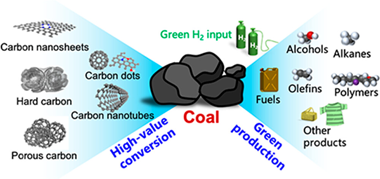
Abstract
Coal resources are one of the key energy sources and essential for modern economic development. Despite the traditional coal industries having made considerable contributions to chemical production and energy storage, the accompanying environmental pollution and high energy consumption have also arisen that cause significant influence of the ecological balance. Hence, there is an urgent need to exploit feasible approaches to the sustainable utilization of coal resources. This review begins with a comprehensive summary of the representative coal chemistry technologies with critical discussions. Subsequently, a novel strategy coupled with green hydrogen is discussed for sustainable conversion of coal and highly efficient manufacture of downstream products. Moreover, the unique role of coal in terms of high-value-added carbon material production is highlighted as a low-cost resource for distinct applications. Finally, we propose several future directions for advanced coal chemistry development.
November, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c02661
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Guaiacol hydrotreatment in an integrated APR-HDO process: Exploring the promoting effect of platinum on Ni-Pt catalysts and assessing methanol and glycerol as hydrogen sources
Jin, W; Gandara-Loe, J; Pastor-Perez, L; Villora-Pico, JJ; Sepulveda-Escribano, A; Rinaldi, R; Reina, TRRenewable Energy, 215 (2023) 118907 DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2023.118907
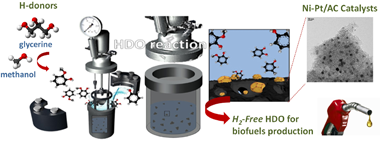
Abstract
This study presents an integrated approach combining aqueous phase reforming (APR) and hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) for the hydrotreatment of guaiacol, a model compound representing lignin-derived phenols in pyrolysis bio-oils. The APR process enables in-situ H2 generation, eliminating the need for an external hydrogen source. We examine the interplay between metal species, the Pt-promoting effect on Ni-Pt catalyst supported on activated carbon (AC), and the choice of hydrogen source (methanol or glycerol). Amongst the monometallic catalysts, a 1% Pt/AC catalyst notably achieved over 96% guaiacol conversion at 300 degrees C with either hydrogen source. Interestingly, when 0.5-1% of the Ni loading is replaced with Pt, the resulting bimetallic Ni-Pt/AC catalysts demonstrate a significant improvement in guaiacol conversion, reaching 70% when methanol is employed as the hydrogen source. Surprisingly, no comparable enhancement in guaiacol conversion is observed when employing glycerol as the hydrogen source. This observation underlines one of the pivotal effects of the hydrogen source on catalyst performance. X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) pinpointed strong Ni-Pt interactions in the catalyst. It also revealed distinctive electronic features of Ni-Pt/AC, which are favourable for steering selectivity towards cyclohexanol rather than phenol when Pt loading is increased from 0.5 to 1%. Moreover, Pt enhanced catalyst stability by inhibiting the oxidation of Ni sites and mitigating Ni-Pt phase sintering. Overall, our findings offer important insights into integrating APR and HDO processes, the promotion effect of Pt, and the importance of hydrogen source selection in terms of guaiacol conversion and catalyst stability.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2023.118907
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of Long-Term CaO Storage Conditions on the Calcium Looping Thermochemical Reactivity
Amghar, N; Perejón, A; Ortiz, C; Maqueda, LAP; Sánchez-Jiménez, PEEnergy & Fuels, 37 (2023) 16904-16914 DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c02652
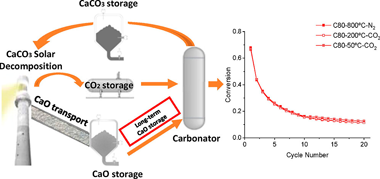
Abstract
Long-term storage capability is often claimed as one of the distinct advantages of the calcium looping process as a potential thermochemical energy storage system for integration into solar power plants. However, the influence of storage conditions on the looping performance has seldom been evaluated experimentally. The storage conditions must be carefully considered as any potential carbonation at the CaO storage tank would reduce the energy released during the subsequent carbonation, thereby penalizing the round-trip efficiency. From lab-scale to conceptual process engineering, this work considers the effects of storing solids at low temperatures (50–200 °C) in a CO2 atmosphere or at high temperatures (800 °C) in N2. Experimental results show that carbonation at temperatures below 200 °C is limited; thus, the solids could be stored during long times even in CO2. It is also demonstrated at the lab scale that the multicycle performance is not substantially altered by storing the solids at low temperatures (under CO2) or high temperatures (N2 atmosphere). From an overall process perspective, keeping solids at high temperatures leads to easier heat integration, a better plant efficiency (+2–4%), and a significantly higher energy density (+40–62%) than considering low-temperature storage. The smooth difference in the overall plant efficiency with the temperature suggests a proper long-term energy storage performance if adequate energy integration is carried out.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c02652
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Sol–Gel Technologies to Obtain Advanced Bioceramics for Dental Therapeutics
X. Song; J.J. Segura-Egea; A.Díaz-CuencaMolecules, 28 (2023) 6967 DOI: 10.3390/molecules28196967
Abstract
The aim of this work is to review the application of bioceramic materials in the context of current regenerative dentistry therapies, focusing on the latest advances in the synthesis of advanced materials using the sol–gel methodology. Chemical synthesis, processing and therapeutic possibilities are discussed in a structured way, according to the three main types of ceramic materials used in regenerative dentistry: bioactive glasses and glass ceramics, calcium phosphates and calcium silicates. The morphology and chemical composition of these bioceramics play a crucial role in their biological properties and effectiveness in dental therapeutics. The goal is to understand their chemical, surface, mechanical and biological properties better and develop strategies to control their pore structure, shape, size and compositions. Over the past decades, bioceramic materials have provided excellent results in a wide variety of clinical applications related to hard tissue repair and regeneration. Characteristics, such as their similarity to the chemical composition of the mineral phase of bones and teeth, as well as the possibilities offered by the advances in nanotechnology, are driving the development of new biomimetic materials that are required in regenerative dentistry. The sol–gel technique is a method for producing synthetic bioceramics with high purity and homogeneity at the molecular scale and to control the surfaces, interfaces and porosity at the nanometric scale. The intrinsic nanoporosity of materials produced by the sol–gel technique correlates with the high specific surface area, reactivity and bioactivity of advanced bioceramics.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/molecules28196967
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones - Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Mechanistic aspects of the reduction of rutile titanium dioxide and its Re-oxidation. Development and destruction of crystallographic shear structures
Bickley, RI; Garside, GR; González-Carreño, T; González-Elipe, AR; Navío, JAJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 326 (2023) 124174 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2023.124174
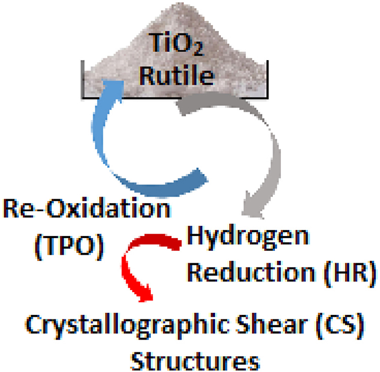
Abstract
A model is presented giving the mean dimensions of acicular octadecahedral microcrystallites of a rutile titanium dioxide powder. Reduction at 823 K, in conjunction with ESR, electrical conductivity and controlled re-oxidation has enabled the model to be applied to reduced microcrystallites. At 300 K they contain <0.1% of paramagnetic [Ti3+↑ VO: ↑Ti3+] reduced edge sites and >99.9% of reduced spin-paired [Ti3+↑↓ Ti3+ VO:] sites. These sites are situated on the external crystal faces and on polygonal bulk crystallographic shear (CS) structures inclined to the microcrystal four-fold symmetry axis. CS structures are quantum-sized [Ti4O7VO:] environments which broaden the paramagnetic signals at 78 K. Temperature programmed reduction in H2(g) reveals atomic hydrogen as a precursor to CS structure formation via a lattice template formed on microcrystallite faces. Shear structures are oxidised on their polygonal perimeters at differing rates on the respective microcrystallite faces by anionic vacancy transfer from sub-surface regions.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2023.124174
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Understanding the Problem of Hydrogen Storage Using a Demonstration: Coupling a Hydrogen Generator Based on the Hydrolysis of Sodium Borohydride to a Fuel-Cell Kit
Arzac, GM; Calvo, ME; Fernández, AJournal of Chemical Education. 100 (2023) 4554-4558 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00590
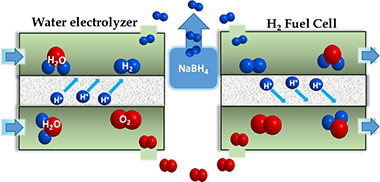
Abstract
In the context of a green global energy paradigm, hydrogen (H-2) is a very promising energy carrier. In fuel cells, hydrogen can be used to generate electricity to drive an electric motor, producing water as its only byproduct. However, to implement hydrogen as an energy vector, developing methods for its production, storage, distribution, and use is essential. Sodium borohydride is a potential hydrogen source capable of releasing H-2 through catalytic hydrolysis. Herein, we present a demonstration that couples a hydrogen generator based on the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride to a commercial fuel-cell kit. The commercial fuel-cell kit operates using the hydrogen generated by an electrolyzer and includes a small fan to prove the successful generation of electricity. The performance of the fuel cell coupled with the borohydride-based reactor is compared to the performance achieved using the hydrogen produced by the electrolyzer. The borohydride-based reactor is designed to power the fan for 300 s and demonstrates efficient and safe hydrogen storage within a small volume of sodium borohydride. This study showcases the hydrogen cycle, the hydrogen storage problem, and the potential of sodium borohydride as a hydrogen storage material in a simple and useful way, contributing to science education and dissemination in the field of energy sustainability.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00590
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Sustainable Integration of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Enhancing Properties of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Electrospun Nanofibers and Cast Films
Abdullah, JAA; Benítez, JJ; Guerrero, A; Romero, ACoatings, 13 (2023) 1665 DOI: 10.3390/coatings13101665
Abstract
This study investigated the impact of adding zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) to electrospun membranes and cast films made of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL). The physicochemical, mechanical, and morphological properties of the samples were analyzed. Physicochemical parameters included water contact angle (WCA), water vapor transmission rate (WVTR), permeance, water vapor permeability (WVP), light transmission (T-600), and transparency (T). Mechanical properties, such as maximum stress (6(max)), elongation (epsilon(max)), and Young's modulus (MPa), were also evaluated. Morphological properties were analyzed in terms of thickness, dispersion, and surface roughness (measured by the arithmetic (Ra) and quadratic (Rq) averages). The crystallinity and melting point, as well as the functional DPPH center dot scavenging percentage (SP%), were also studied. The results showed that adding 1 wt% ZnO-NPs improved the water barrier properties of PCL membranes and films, increasing WCA by 1%-6% and decreasing WVTR by 11%-19%, permeance by 34%-20%, and WVP by 4%-11%, respectively. The T-600 values of PCL/ZnO-NPs membranes and films were 2-3 times lower than those of neat PCL samples, indicating improved optical properties. The mechanical properties of the composite membranes and films also improved, with 6(max) increasing by 56%-32% and Young's modulus increasing by 91%-95%, while epsilon(max) decreased by 79%-57%. The incorporation of ZnO-NPs also increased the thickness and surface roughness of the samples. The SP% of PCL/ZnO-NPs increased by almost 69%, demonstrating the beneficial effects of ZnO-NPs on the system. These findings suggest that incorporating ZnO-NPs into PCL membranes and films can enhance their properties, making them well suited for various applications, such as those within the realm of materials science and nanotechnology.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/coatings13101665
Reactividad de Sólidos
Metal- based eggshell particles prepared via successive incipient wetness impregnation method as a promoted sorbent for CO2 capturing in the calcium looping process
Imani, M; Tahmasebpoor, M; Sanchez-Jimenez, PEJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11 (2023) 110584 DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.110584
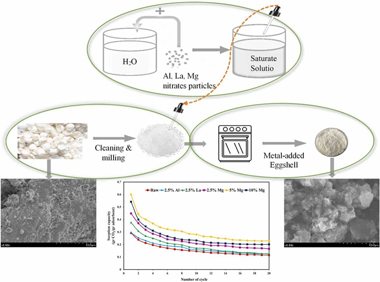
Abstract
Cyclic adsorption by using of bio-waste eggshell particles as a cheap, accessible and environmentally friendly CaCO3 source has been considered as one of the important methods to decrease or remove CO2 from the flue gas. However, deactivation of eggshell particles and CO2 capture capacity decaying with increasing the cycle's number remained as an important challenge. Using metal nitrates as one of the modification methods has been proposed by the researchers to overcome this problem. Current study investigates the influence of three metal nitrates of Al, La and Mg added to the eggshell particles via successive incipient wetness impregnation (SIWI) method to improve their adsorption performance. The TGA results at the end of the 20th carbonation/calcination cycle revealed a meaningful relationship between CaO molar conversion of eggshell modified with metal nitrates and their crystallite size as well as the surface area of the sorbents, so that the smaller the crystal size and the larger the surface area, the higher the molar conversion of CaO could be achieved. Due to the highest conversion obtained for Mg-containing sample, the effect of different weight percentages of this additive was also investigated. Results showed that 5 wt% MgO contained eggshell particles could be reported as the most outstanding sample for its improved molar conversion, capture capacity at the end of 20th carbonation/calcination cycle and BET surface area, which were 30.18%, 0.23 gr CO2/gr adsorbent and 3.5 m2/g while the corresponding amounts for raw eggshell were 17.26%, 0.11 gr CO2/gr adsorbent and 1.63 m2/g, respectively.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.110584
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biodegradability Assessment of Prickly Pear Waste-Polymer Fibers under Soil Composting
Correa-Pacheco, ZN; Bautista-Baños, S; Benítez-Jiménez, JJ; Ortega-Gudiño, P; Cisneros-López, EO; Hernández-López, MPolymers, 15 (2023) 4164 DOI: 10.3390/polym15204164
Abstract
Nowadays, solving the problems associated with environmental pollution is of special interest. Therefore, in this work, the morphology and thermal and mechanical properties of extruded fibers based on polylactic acid (PLA) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) added to prickly pear flour (PPF) under composting for 3 and 6 months were evaluated. The highest weight loss percentage (92 +/- 7%) was obtained after 6-month degradation of the PLA/PBAT/PPF/CO/AA blend, in which PPF, canola oil (CO), and adipic acid (AA) were added. Optical and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed structural changes in the fibers as composting time increased. The main changes in the absorption bands observed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) were related to the decrease in -C=O (1740 cm-1) and -C-O (1100 cm-1) groups and at 1269 cm-1, associated with hemicellulose in the blends with PPF. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showed an increase in the cold crystallization and melting point with degradation time, being more evident in the fibers with PPF, as well as a decrease in the mechanical properties, especially Young's modulus. The obtained results suggest that PPF residues could promote the biodegradability of PLA/PBAT-based fiber composites.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/polym15204164
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Catalytic conversion of syngas to light hydrocarbons via simulated intermediates CO/CO2/DME/N2/H2 over the regulated acidity of SAPO-34
Meng, FH; Wang, LA; Nawaz, MA; Wang, Q; Gong, ZY; Li, ZChemical Engineering Journal, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145895

Abstract
Direct conversion of syngas to light hydrocarbons has been intensively studied in recent years; however, the high selectivity of light hydrocarbons is still a challenging task to achieve a high CO conversion. Here, a bifunctional catalyst consisting of a methanol synthesis catalyst (CZA) and a methanol to dimethyl ether (DME) catalyst (Al2O3) was employed with a hydrocarbon synthesis catalyst (SAPO-34), for syngas conversion to light hydrocarbons in a dual fixed-bed reactor. The conversion of simulated intermediates CO/CO2/DME/N2/H2 with a molar ratio of 9/6/4/5/76, obtained from syngas conversion to DME over CZA and Al2O3, was studied over SAPO-34 zeolites. It was found that SP34-0.1 with Si/Al ratio of 0.1, exhibited low amount of strong acid (0.60 mmol/g) and high selectivity to light olefins (74.1%), while SP34-0.4 with Si/Al ratio of 0.4 exhibited high amount of strong acid (1.00 mmol/g) leading to high selectivity of light paraffins (88.4%). The in-situ DRIFTS analysis illustrated that DME can be rapidly adsorbed on the hydroxyl site of SAPO-34 and decomposed into the surface methyl species, where SP34-0.4 could produce more dimethylcyclopentenyl cationic species than SP340.1. It was suggested that the overall reaction route led to a high selectivity to light olefins (84.2%) with a CO conversion of 61.2% on (CZA + Al2O3) catalyst combined with SP34-0.1, while a high selectivity to light paraffins (76.3%) could be achieved by combining with SP34-0.4 at 70.3% CO conversion. Since, the current study interprets that the selectivity of hydrocarbons can be adjusted by regulating the acidity of SAPO-34 to achieve a high CO conversion in the dual fixed-bed reactor scheme.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145895
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Impact of topology framework of microporous solids on methanol carbonylation: An operando DRIFTS-MS study
Luque-Alvarez, LA; Serrano-Cruz, M; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Bobadilla, LF; Odriozola, JAMicroporous and mesoporous materials, 360 (2023) 112725 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2023.112725
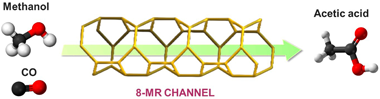
Abstract
Methanol carbonylation was evaluated over heterogeneous catalysts based on Cu-exchanged zeolitic materials with different topology: Cu@MOR, Cu@FER, and Cu@ZSM-5. Despite the similar Si/Al ratios, it is crucial to acknowledge that the acid strength is influenced by the framework topology, as supported by the NH3-TPD results. This, along with other characterization techniques allowed us to estimate the impact of pore size and pore distribution in these microporous materials on catalytic performance. The channel structure influenced catalytic parameters such as conversion and selectivity. The higher methanol conversion achieved on Cu@FER shows the importance of Bronsted acid sites and redox centres location regarding the topology of the material. Concerning the selectivity, the production of acetic acid was endorsed by the 12-MR (MOR) channels, methyl acetate's production by the 10-MR (FER) channels. Finally, the presence of 6-MR (ZSM-5) channels led to a complete selectivity towards DME production. The reaction mechanism was elucidated via operando DRIFTS-MS and results revealed a bifunctional mechanism in which methanol adsorbs and dehydrates on acidic Bronsted sites and CO is activated over Cu+ species.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2023.112725
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Water-assisted HDO of biomass model compounds enabled by Ru-based catalysts
Carrasco-Ruiz, S; Parrilla-Lahoz, S; Santos, JL; Penkova, A; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TR; Pastor-Pérez, LFuel Processing Technology, 249 (2023) 107860 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2023.107860
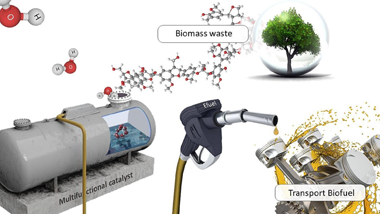
Abstract
Biofuels upgrading gathering momentum in view of the gradual depletion of fossil fuels and the pursuit of renewable energy sources to mitigate global warming. Hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) is a key reaction in the upgrading of bio-oil to produce hydrocarbon fuels or high-value chemicals. Oxygen removal in bio-oil increases its calorific value, improve thermal and chemical stability, reduce corrosiveness, etc., making the upgraded biooil suitable as a fuel or blending fuel. However, the dependence on high-pressure hydrogen is a serious disadvantage, as it is an expensive resource whose use also poses safety concerns. In this scenario, we propose a pioneering route for model biomass compounds upgrading via H2-free HDO. Herein we have developed multifunctional catalysts based on Ru and ceria supported on carbon able conduct the hydrodeoxygenation reaction using water as hydrogen source. We found that cerium oxide improves ruthenium metallic dispersion and the overall redox properties of the multicomponent system leading to enhanced catalytic performance. Along with the successful catalytic formulation we identify 300 degrees C as an optimal temperature validating the H2-free HDO route for bio-compounds upgrading.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2023.107860
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Enroute to the Carbon-Neutrality Goals via the Targeted Development of Ammonia as a Potential Nitrogen-Based Energy Carrier
Nawaz, MA; Blay-Roger, R; Saif, M; Meng, FH; González-Arias, J; Miao, BJ; Bobadilla, LF; Ramírez-Reina, T; Odriozola, J.A.ACS Catalysis, 13 (2023) 14415-14453 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.3c02410

Abstract
The reliance of a future carbon-free horizon is strongly aligned with the long-term energy storage avenues which are completely derived from renewable energy resources. Ammonia with its high energy content and density can perform as a decent candidate for buffering the short-term storage options. However, the current NH3 production majorly feeding the current huge desire for ammonia is dominated by the conventional nonrenewable Haber–Bosch (H–B) process route, thus continuously damaging the target of carbon neutrality goals. High-purity hydrogen (H2) gas is an essential precursor for the H–B process; however, it is a significant energy consumer (about 2% of the global energy supply) and contributes over 420 million tons of CO2/annum. Therefore, the research on the renewable synthesis of nitrogen-based energy carriers (such as ammonia) from the direct electrochemical, photocatalytic, or plasma catalytic processes; its conversion; and utilization to the potential derivatives has been a hot topic in the past few decades. A prospective analysis of the highly appealing processes has been summarized in this study, which could facilitate the adaption of renewable alternatives as an effective approach for zero carbon emission, paving the excellent pathways along the road to the development of nitrogen-based energy technologies, especially the targeted development of ammonia. Further, this Review covers the current and future impacts of the H–B process, the development of aspiring ammonia synthesis routes (via electro, photo, bio, chemical loop, or plasma catalysis), and its conversion and utilization to the renewable derivatives in terms of fabrication of model catalysts, advanced characterization technology, and efficient device design.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.3c02410
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Mechanical treatments on design powder ceramic materials: Insight into the textural and structural changes
Osuna, FJ; Fernández, M; Pavón, E; Sánchez, RMT; Alba, MDAdvanced Powder Technology, 34 (2023) 104189 DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2023.104189
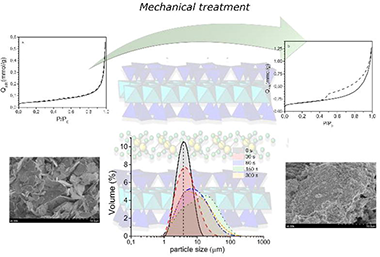
Abstract
Mechanical treatment of porous ceramics, such as porous clay minerals, is a crucial step in ceramic processing. Among clay minerals, design swelling brittle micas have shown exceptional properties for further applications, although they exhibit low surface area and porosity. But, their mechanical activation could improve their textural properties and deserves to be investigated. Thus, the aim of this work was to evaluate the effects of gradual grinding in their surface and framework. At short grinding times, the surface area increases and mesoporous and microporous are generated. Long grinding time provokes particle agglomeration with the consequent change in their colloidal stability. At bulk level, framework defects are observed in both tetrahedral and octahedral sheets and increase with the total layer charge.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2023.104189
Reactividad de Sólidos
Negative emissions power plant based on flexible calcium-looping process integrated with renewables and methane production
Ortiz, C; García-Luna, S; Carro, A; Chacartegui, R; Pérez-Maqueda, LRenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 185 (2023) 113614 DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113614
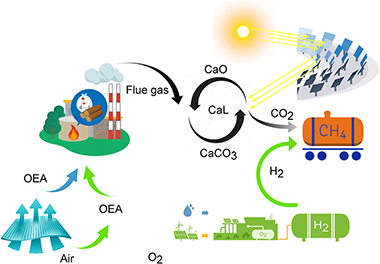
Abstract
This paper provides a review of negative carbon capture technologies. Based on these technologies, here it is proposed an innovative negative emissions power plant combining the generation and storage of energy from biomass, photovoltaic, and concentrated solar power, capturing and recovering CO2 by producing H2 or CH4 as green energy carriers. The main features of the system are i) large-scale energy production system with negative CO2 emissions; ii) 100% renewable system based on biomass and solar energy with the possibility of integrating other renewables; iii) synergistic integration of processes and systems; iv) recovery of O2 generated by photovoltaic-driven electrolysis within the process of partial biomass oxycombustion and v) solar-driven limestone calcination. A detailed model of the entire plant is developed to evaluate the integration of the process. The model performance is assessed on an hourly basis throughout the whole year. The base case results show an energy consumption from 1 to 2.1 MJ/kg CO2 to capture 60–77% of CO2 emitted from the biomass plant and green methane production of more than 7500 tons/year. The negative emissions associated with the process are -612 kg CO2/MWh. It justifies the interest in the proposed negative emissions power plant.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113614
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Low-temperature reverse water gas-shift reaction over highly efficient Cu-hydrotalcites: Mechanistic insights on the role of malachite phase
Alvarez-Hernandez, D; Marin-Sanchez, M; Lobo-Andrades, L; Azancot, L; Bobadilla, LF; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MACatalysis Today, 422 (2023) 114235 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2023.114235
Abstract
Carbon dioxide (CO2) transformation into valuable fuels and chemicals is in most cases a challenge far from readiness nowadays. One possible route for its conversion is the reverse water gas shift reaction (rWGS), crucial for syngas generation and required for the chemical conversion of CO2 to fuels and platform chemicals. In this paper, well organized Cu/Zn/Al structures were proposed as efficient catalysts for rWGS reaction at low tem-peratures. The results of in situ XRD revealed the formation of layered structures such malachite and hydro-talcite. The operando DRIFTS-MS studies of those structure suggests a participation of Cu2+/Cu+ pair in the reaction, promoting the redox mechanism and enhancing the activity at lower temperature. This work also provides a new strategy to design Cu-based rWGS catalysts able to prevent the sintering of active phase.
October, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2023.114235
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma assisted dry reforming of methane: Syngas and hydrocarbons formation mechanisms
Navascues, P; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AFuel Processing Technology, 248 (2023) 107827 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2023.107827
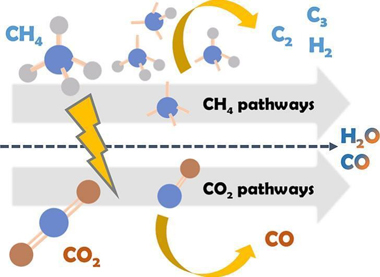
Abstract
Plasma reactions of CO2 + CH4 mixtures have been proposed as a suitable process for the dry reforming of methane. Without specific catalysts, most studies report the formation of CO and H2 as main reaction products and arise the question whether CHx radicals coming from CH4 may interact with intermediate species formed by electron impact dissociation of CO2, a critical step for the formation of high added value oxygenated compounds. We have addressed this question studying the CO2 + CH4 plasma reaction in a ferroelectric-moderated packed -bed reactor varying the reactants ratio. Analysis of the reaction products by mass spectrometry and the plasma reaction intermediates by optical emission spectroscopy suggest that few direct cross-link interactions exist between intermediate plasma species issued from CH4 or CO2. This preliminary evidence is corroborated by experiments using 13CO2 instead 12CO2 as reactant. The isotope labeling procedure has proved that plasma re-action mechanisms of CO2 and CH4 molecules proceed almost independently, with the formation of small amounts of water and the removal of carbon deposits resulting CH4 plasma decomposition as sole evidences of cross reactions. These results highlight the need of using catalysts to promote specific surface reactions for a better control of the selectivity of the process.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2023.107827
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Process design and utilisation strategy for CO2 capture in flue gases. Technical assessment and preliminary economic approach for steel mills
Navarro, JC; Baena-Moreno, FM; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Almagro, JF; Odriozola, JARenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 184 (2023) 113537 DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113537
Abstract
The steel industry is the most relevant sector in emerging economies due to its application in numerous fields. However, steel manufacturing involves large energy investment and produces significant greenhouse gas emissions. The current world economic and environmental scenario therefore necessitates that improvements in the footprint of the steel industry be made without affecting its viability. Considering the present challenge, we report two possible processes for Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU). The first process is the competitive capture of CO2-SO2, followed by CO2 valorisation to methane. However, the CO2 capture capacity and lifetime for the adsorbent after multiple cycles could be improved through preliminary desulphurization of the gas current. The improved system demonstrates net profitability in a typical stainless steel plant. Therefore, it can be implemented in an industrial setting without profitability loss to steelmaking operations, fulfilling bot the goal of reducing CO2 emissions while protecting the mainstay of the plant.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113537
Materiales Semiconductores para la Sostenibilidad
Understanding ice and water film formation on soil particles by combining density functional theory and Casimir-Lifshitz forces
Bostrom, M; Kuthe, S; Carretero-Palacios, S; Esteso, V; Li, Y; Brevik, I; Gopidi, HR; Malyi, OI; Glaser, B; Persson, CPhysical Review B, 108 (2023) 125434 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.108.125434
Abstract
Thin films of ice and water on soil particles play crucial roles in environmental and technological processes. Understanding the fundamental physical mechanisms underlying their formation is essential for advancing scientific knowledge and engineering practices. Herein, we focus on the role of the Casimir-Lifshitz force, also referred to as dispersion force, in the formation and behavior of thin films of ice and water on soil particles at 273.16 K, arising from quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field and depending on the dielectric properties of interacting materials. We employ the first-principles density functional theory (DFT) to compute the dielectric functions for two model materials, CaCO3 and Al2O3, essential constituents in various soils. These dielectric functions are used with the Kramers-Kronig relationship and different extrapolations to calculate the frequency-dependent quantities required for determining forces and free energies. Moreover, we assess the accuracy of the optical data based on the DFT to model dispersion forces effectively, such as those between soil particles. Our findings reveal that moisture can accumulate into almost micron-sized water layers on the surface of calcite (soil) particles, significantly impacting the average dielectric properties of soil particles. This research highlights the relevance of DFT-based data for understanding thin film formation in soil particles and offers valuable insights for environmental and engineering applications.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.108.125434
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Paper-based ZnO self-powered sensors and nanogenerators by plasma technology
Garcia-Casas, X; Aparicio, FJ; Budagosky, J; Ghaffarinejad, A; Orozco-Corrales, N; Ostrikov, K; Sánchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, ANano Energy, 114 (2023) 108686 DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108686
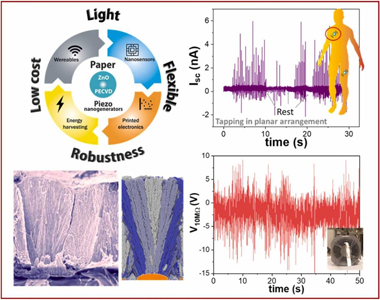
Abstract
Nanogenerators and self-powered nanosensors have shown the potential to power low-consumption electronics and human-machine interfaces, but their practical implementation requires reliable, environmentally friendly and scalable processes for manufacturing and processing. Furthermore, the emerging flexible and wearable electronics technology demands direct fabrication onto innovative substrates such as paper and plastics typically incompatible with high process temperatures. This article presents a plasma synthesis approach for the fabri-cation of piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) and self-powered sensors on paper substrates. Polycrystalline ZnO nanocolumnar thin films are deposited by plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition on common paper supports using a microwave electron cyclotron resonance reactor working at room temperature yielding high growth rates and low structural and interfacial stresses. Applying Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation, we elucidate the basic shadowing mechanism behind the characteristic microstructure and porosity of the ZnO thin films, relating them to an enhanced piezoelectric response to periodic and random inputs. The piezoelectric devices are assembled by embedding the ZnO films in polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and using Au thin layers as elec-trodes in two different configurations, namely laterally and vertically contacted devices. We present the response of the laterally connected devices as a force sensor for low-frequency events with different answers to the applied force depending on the impedance circuit, i.e. load values range, a behaviour that is theoretically analyzed. The characterization of the vertical devices in cantilever-like mode reaches instantaneous power densities of 80 nW/ cm2 with a mean power output of 20 nW/cm2. Besides, we analyze their actual-scenario performance by acti-vation with a fan and handwriting. Overall, this work demonstrates the advantages of implementing plasma deposition for piezoelectric films to develop robust, flexible, stretchable, and enhanced-performance nano-generators and self-powered piezoelectric sensors compatible with inexpensive and recyclable supports.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108686
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Exalted dual-scale surface roughening in laser ablated aluminum capped with a transparent thin film: Wetting and anti-icing behavior
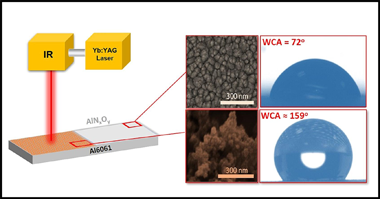
Ghemras, I; Montes, L; Lopez-Santos, C; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Rico, VApplied Surface Science, 630 (2023) 157357 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157357
Abstract
Near infrared laser ablation of metals, specifically aluminum, has been systematically applied to generate surface roughness. Very high laser fluences may even lead to a so called "explosive" ablation regime where roughness becomes dramatically enhanced. In the present work we have developed an alternative methodology that, uti-lizing milder laser irradiation conditions (i.e. laser fluences from 0.37 to 0.72 J/cm2), renders aluminum surfaces with a dual-scale roughness character and Sp parameter values twice or even trice the value found in reference samples. This has been possible for aluminum substrates coated with a highly transparent aluminum oxynitride capping layer. The resulting surfaces, consisting of very rough partially oxidized aluminum with negligible amounts of nitrogen species, resulted highly hydrophobic and depicted long icing delay times as required for anti-icing applications. A correlation has been found between the wetting and anti-icing behaviors, the use of a capping layer and the laser irradiation conditions. To account for this exalted roughening phenomenon, we propose that the transparent capping layer confines the laser energy within the aluminum shallow zones, delays the formation of the plasma plume and produces an enhancement in the aluminum ablation, even at relatively low laser fluences.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157357
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of the effective refractive index on the radiative decay rate in nanoparticle thin films
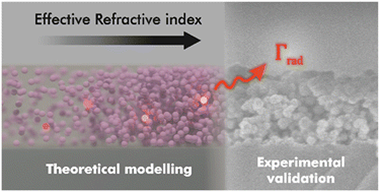
Romero, M; Sánchez-Valencia, JR; Lozano, G; Míguez, HNanoscale, 15 (2023) 15279-15287 DOI: 10.1039/d3nr03348a
Abstract
In this work, we theoretically and experimentally study the influence of the optical environment on the radiative decay rate of rare-earth transitions in luminescent nanoparticles forming a thin film. We use electric dipole sources in finite-difference time-domain simulations to analyze the effect of modifying the effective refractive index of transparent layers made of phosphor nanocrystals doped with rare earth cations, and propose a correction to previously reported analytical models for calculating the radiative decay rate. Our predictions are tested against an experimental realization of such luminescent films, in which we manage to vary the effective refractive index in a gradual and controllable manner. Our model accurately accounts for the measurements attained, allows us to discriminate the radiative and non-radiative contributions to the time-resolved photoluminescence, and provides a way to rationally tune the spontaneous decay rate and hence the photoluminescence quantum yield in an ensemble of luminescent nanoparticles.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/d3nr03348a
Materiales Coloidales
Lanthanide vanadate-based trimodal probes for near-infrared luminescent bioimaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography
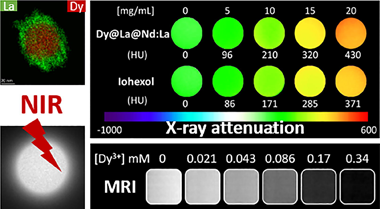
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Nunez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Becerro, AI; Ocaña, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 646 (2023) 721-731 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.05.078
Abstract
We have developed a trimodal bioimaging probe for near-infrared luminescent imaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography using Dy3+ as the paramagnetic component and Nd3+ as the luminescent cation, both of them incorporated in a vanadate matrix. Among different essayed architectures (single phase and core-shell nanoparticles) the one showing the best luminescent properties is that consisting of uniform DyVO4 nanoparticles coated with a first uniform layer of LaVO4 and a second layer of Nd3+-doped LaVO4. The magnetic relaxivity (r2) at high field (9.4 T) of these nanoparticles was among the highest values ever reported for this kind of probes and their X-ray attenuation properties, due to the presence of lanthanide cations, were also better than those of a commercial contrast agent (iohexol) commonly used for X-ray computed to-mography. In addition, they were chemically stable in a physiological medium in which they could be easily dispersed owing to their one-pot functionalization with polyacrylic acid, and, finally, they were non-toxic for human fibroblast cells. Such a probe is, therefore, an excellent multimodal contrast agent for near-infrared luminescent imaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.05.078
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones - Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Alkaline Salts on Pyrolyzed Solid Wastes in Used Edible Oils: An Attenuated Total Reflectance Analysis of Surface Compounds as a Function of the Temperature
Romero-Sarria, F; Real, C; Córdoba, JM; Hidalgo, C; Alcalá, MDSpectroscopy Journal, 1 (2023) 98-110 DOI: 10.3390/spectroscj1020009
Abstract
Biochars obtained via the pyrolysis of biomass are very attractive materials from the point of view of their applications and play key roles in the current energy context. The characterization of these carbonaceous materials is crucial to determine their field of application. In this work, the pyrolysis of a non-conventional biomass (solid wastes in used edible oils) was investigated. The obtained biochars were characterized using conventional techniques (TG, XRD, and SEM-EDX), and a deep analysis via ATR-FTIR was performed. This spectroscopic technique, which is a rapid and powerful tool that is well adapted to study carbon-based materials, was employed to determine the effect of temperature on the nature of functional groups on the surface. Moreover, the water washing of the raw sample (containing important quantities of inorganic salts) before pyrolysis evidenced that the inorganic salts act as catalysts in the biomass degradation and influence the degree of condensation (DOC) of PAH. Moreover, it was observed that these salts contribute to the retention of oxygenated compounds on the surface of the solid.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/spectroscj1020009
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Preparation, characterization and activation of Pd catalysts supported on CNx foam for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid
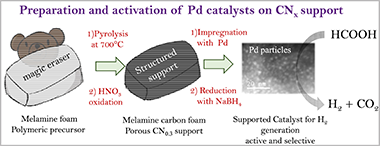
Arzac, GM; Rojas, TC; Real, C; Fernández, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48 (2023) 31899-31613 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.04.244
Abstract
In this work, we have prepared a series of Pd catalysts on a CNx support for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid. The structured CNx support was obtained through thermal pyrolysis of melamine foam and the pyrolysis conditions were optimized to achieve high surface area. The resulting support contains high amount of nitrogen with a contribution of pyridinic component. Several Pd catalysts were prepared and under optimized condi-tions, we were able to obtain small (2.7 +/- 0.9) nm Pd particles by using the oxidized support in powdery form. The activity of the optimized catalyst was studied under different con-ditions in the fresh and the used form. The fresh catalyst did not show significant activity. However, we found that the catalyst activated after use. Activation was understood in terms of the variation of surface Pd oxidation states under the effect of formic acid/sodium formate solutions. We found that the best activity is achieved under an optimal proportion of Pd0/PdII surface states according to previous reports. Under the best conditions, the activity of the best catalyst (8.6Pd/CN0.3) was as high as 9245 h-1, attributable to the small particle size, the Pd0/PdII ratio, the amount of pyridinic nitrogen, and the testing conditions, which included the preadsorption of sodium formate
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.04.244
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Cobalt Stabilization through Mesopore Confinement on TiO2 Support for Fischer-Tropsch Reaction
Platero, F; Todorova, S; Aoudjera, L; Michelin, L; Lebeau, B; Blin, JL; Holgado, JP; Caballero, A; Colón, GACS Applied Energy Materials, 6 (2023) 9475-9486 DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c01432
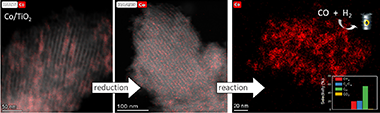
Abstract
Cobalt supported on mesostructured TiO2 catalysts has been prepared by a wet-impregnation method. The Co/TiO2 catalytic system showed better catalytic performance after support calcination at 380 °C. Co nanoparticles appeared well distributed along the mesopore channels of TiO2. After reduction pretreatment and reaction, a drastic structural change leads to mesopore structure collapse and the dispersion of the Co nanoparticles on the external surface. Along this complex process, Co species first form discrete nanoparticles inside the pore and then diffuse out as the pore collapses. Through this confinement, a strong metal–support interaction effect is hindered, and highly stable metal active sites lead to better performance for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis reaction toward C5+ products.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c01432
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Germination and First Stages of Growth in Drought, Salinity, and Cold Stress Conditions of Plasma-Treated Barley Seeds
Perea-Brenes, A; Garcia, JL; Cantos, M; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, A; López-Santos, CACS Agricultural Science & Technology, 3 (2023) 760-770 DOI: 10.1021/acsagscitech.3c00121

Abstract
Numerous works have demonstrated that cold plasma treatments constitute an effective procedure to accelerate seed germination under nonstress conditions. Evidence also exists about a positive effect of plasmas for germination under environmental stress conditions. For barley seeds, this work studies the influence of cold plasma treatments on the germination rate and initial stages of plant growth in common stress environments, such as drought, salinity, and low-temperature conditions. As a general result, it has been found that the germination rate was higher for plasma-treated than for untreated seeds. Plasma also induced favorable changes in plant and radicle dimensions, which depended on the environment. The obtained results demonstrate that plasma affects the biochemical metabolic chains of seeds and plants, resulting in changes in the concentration of biochemical growing factors, a faster germination, and an initially more robust plant growth, even under stress conditions. These changes in phenotype are accompanied by differences in the concentration of biomarkers such as photosynthetic pigments (chlorophylls a and b and carotenoids), reactive oxygen species, and, particularly, the amino acid proline in the leaves of young plants, with changes that depend on environmental conditions and the application of a plasma treatment. This supports the idea that, rather than an increase in seed water imbibition capacity, there are clear beneficial effects on seedling of plasma treatments.
September, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acsagscitech.3c00121
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
H2-rich syngas production from biogas reforming: Overcoming coking and sintering using bimetallic Ni-based catalysts
Carrasco-Ruiz, S; Zhang, Q; Gándara-Loe, J; Pastor-Pérez, L; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TR; Bobadilla, LFInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48 (2023) 72 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.03.301
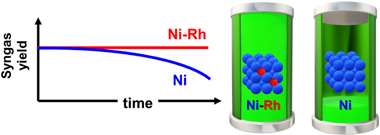
Abstract
Dry reforming of methane is a very appealing catalytic route biogas (mainly composed by greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide and methane) conversion into added value syngas, which could be further upgraded to produce liquid fuels and added value chemicals. However, the major culprits of this reaction are coking and active phase sintering that result in catalysts deactivation. Herein we have developed a highly stable bimetallic Ni–Rh catalyst supported on mixed CeO2–Al2O3 oxide using low-noble metal loadings. The addition of small amounts of rhodium to nickel catalysts prevents coke formation and improves sintering resistance, achieving high conversions over extended reaction times hence resulting in promising catalysts for biogas upgrading.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.03.301
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Measurement principles for quantum spectroscopy of molecular materials with entangled photons
Moretti, L; Rojas-Gatjens, E; Uboldi, L; Tiede, DO; Kumar, EJ; Trovatello, C; Preda, F; Perri, A; Manzoni, C; Cerullo, G; Kandada, ARSJournal of Chemical Physics, 159 (2023) 084201 DOI: 10.1063/5.0156598
Abstract
Nonlinear spectroscopy with quantum entangled photons is an emerging field of research that holds the promise to achieve superior signal-to-noise ratio and effectively isolate many-body interactions. Photon sources used for this purpose, however, lack the frequency tunability and spectral bandwidth demanded by contemporary molecular materials. Here, we present design strategies for efficient spontaneous parametric downconversion to generate biphoton states with adequate spectral bandwidth and at visible wavelengths. Importantly, we demonstrate, by suitable design of the nonlinear optical interaction, the scope to engineer the degree of spectral correlations between the photons of the pair. We also present an experimental methodology to effectively characterize such spectral correlations. Importantly, we believe that such a characterization tool can be effectively adapted as a spectroscopy platform to optically probe system-bath interactions in materials.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1063/5.0156598
Reactividad de Sólidos
Touch-free reactive flash sintering of dense strontium hexaferrite permanent magnet
Jalali, SIA; Manchon-Gordon, AF; Chacartegui, R; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Blazquez, JS; Perejon, A; Raj, R; Pérez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society (2023) DOI: 10.1111/jace.19389
Abstract
This work presents an extension of the touch-free flash sintering technique. In the proposed technique, chemical reaction and sintering occur in a single step, without the use of electrodes, in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. We show that a dense, single-phase strontium hexaferrite magnet can be produced from a mixture of commercial carbonate and oxide powders in a single step in a little more than a minute. This new technique implies significant reduction in energy and time consumption (primarily because of ultrafast processing) relative to conventional sintering.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.19389
Ruthenium nanoparticles stabilized by 1,2,3-triazolylidene ligands in the hydrogen isotope exchange of E-H bonds (E = B, Si, Ge, Sn) using deuterium gas
Molinillo, P; Puyo, M; Vattier, F; Lacroix, B; Rendon, N; Lara, P; Suarez, ANanoscale DOI: 10.1039/d3nr02637j
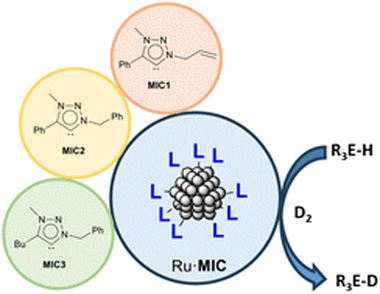
Abstract
A series of ruthenium nanoparticles (Ru & BULL;MIC) stabilized with different mesoionic 1,2,3-triazolylidene (MIC) ligands were prepared by decomposition of the Ru(COD)(COT) (COD = 1,5-cyclooctadiene; COT = 1,3,5-cyclooctatriene) precursor with H-2 (3 bar) in the presence of substoichiometric amounts of the stabilizer (0.1-0.2 equiv.). Small and monodisperse nanoparticles exhibiting mean sizes between 1.1 and 1.2 nm were obtained, whose characterization was carried out by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM), including high resolution TEM (HRTEM), inductively coupled plasma (ICP) analysis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). In particular, XPS measurements confirmed the presence of MIC ligands on the surfaces of the nanoparticles. The Ru & BULL;MIC nanoparticles were used in the isotopic H/D exchange of different hydrosilanes, hydroboranes, hydrogermananes and hydrostannanes using deuterium gas under mild conditions (1.0 mol% Ru, 1 bar D-2, 55 & DEG;C). Selective labelling of the E-H (E = B, Si, Ge, Sn) bond in these derivatives, with high levels of deuterium incorporation, was observed.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/d3nr02637j
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Plasmas and acoustic waves to pattern the nanostructure and chemistry of thin films
Rico, V; Regodon, GF; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alcaide, AM; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rojas, TC; Alvarez, R; Palomares, FJ; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARActa Materialia, 255 (2023) 119058 DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2023.119058
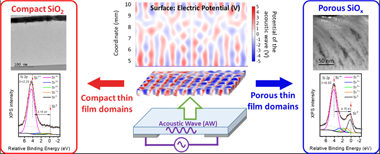
Abstract
In this work, piezoelectric AWs and plasmas have been brought together during the growth of a thin film as a novel methodology of plasma-assisted thin film structuration. The ensuing effects have been investigated on a model system where SiO2 and SiOx (x<2) thin films have been deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles (MS-OAD) on an electro-acoustically excited LiNbO3 piezoelectric substrate under resonant conditions. The microstructure of the resulting films was 2D patterned and depicted submillimeter size intermingled zones with different optical characteristics, compositions (SiO2 and SiOx) and porosity, from highly porous to dense and compact regions. The 2D nanostructural pattern mimics the AW distribution and has been accounted for by means of a specific simulation model. It is concluded that the morphological and chemical film pattern replicates the distribution of polarization potential on the surface of the AW activated substrate immersed in the plasma. Moreover, we show that the main mechanism responsible for the appearance of domains with different morphology and chemical composition is the focused impingement of Ar+plasma ions on certain regions of the substrate. The general character of this patterning process, the underlying physics and its possibilities to tailor the composition and microstructure of dielectric thin film materials are discussed.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2023.119058
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Charting a path to catalytic upcycling of plastic micro/nano fiber pollution from textiles to produce carbon nanomaterials and turquoise hydrogen
Silvia Parrilla-Lahoz; Marielis C. Zambrano; Vlad Stolojan; Rachida Bance-Soualhi; Joel J. Pawlak; Richard A. Venditti; Tomas Ramirez Reina; Melis S. DuyarRSC Sustainability, 1 (2023) 1177-1183 DOI: 10.1039/D3SU00095H

Abstract
Washing synthetic textile fibers releases micro/nano plastics, endangering the environment. As new filters and associated regulations are developed to prevent fiber release from washing machines, there emerges a need to manage the collected waste, for which the only current options are combustion or landfill. Herein we show for the first time the application of a catalytic pyrolysis approach to upcycle textile derived fibrous micro/nano plastics waste, with the aim of keeping carbon in the solid phase and preventing its release as a greenhouse gas. Herein, we demonstrate the co-production of hydrogen and carbon nanomaterials from the two most prevalent global textile microfiber wastes: cotton and polyester. Our results pave a way forward to a realistic process design for upcycling mixed micro/nano fiber waste collected from laundering, drying, vacuuming, and environmental cleanup.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/D3SU00095H
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Ti6Al4V coatings on titanium samples by sputtering techniques: Microstructural and mechanical characterization
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Rodriguez-Albelo, M; Sanchez-Perez, M; Godinho, V; Lopez-Santos, C; Torres, YJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 952 (2023) 170018 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170018

Abstract
Although titanium is widely used as biomaterial, the control of the interface properties between its surface and the surrounding physiological environment (like bone, other tissues or biofluids) results crucial to achieve a successful osseointegration and good biomechanical and functional performance. In this work, commercially pure titanium (Grade IV) discs obtained by conventional powder metallurgy were coated with 1-3 mu m of Ti6Al4V (Grade V) alloy using DC-pulsed or high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) technique with the aim of improving their biomedical performance. SEM, confocal microscopy, X-ray dif-fraction, nanoindentation and wetting measurements are used to evaluate the bio-interface role of the titanium-coated implants. Conformal Ti6Al4V coatings with controlled nano-roughness can be deposited with enhanced mechanical (H = 5-8 GPa; E = 140-160 GPa) and hydrophobic properties thanks to a dense columnar structure. The increased Ti-O bonding at the interface helps to prevent the corrosion due to the formation of a surface passivation layer. Particularly in the case of the HiPIMS process, the surface mod-ification of titanium implants (chemistry, morphology and structure) appears as an effective strategy for satisfying the biomedical requirements and functionality, with enhanced mechanical properties and na-nostructuration for prevention of bacteria colonization.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170018
Threads of memory: Reviving the ornament of a dead child at the Neolithic village of Ba`ja (Jordan)
Alarashi, H et al. [Aviles, MA]Plos One, 18 (2023) DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288075
Abstract
In 2018, a well-constructed cist-type grave was discovered at Ba`ja, a Neolithic village (7,400-6,800 BCE) in Southern Jordan. Underneath multiple grave layers, an 8-year-old child was buried in a fetal position. Over 2,500 beads were found on the chest and neck, along with a double perforated stone pendant and a delicately engraved mother-of-pearl ring discovered among the concentration of beads. The first was found behind the neck, and the second on the chest. The meticulous documentation of the bead distribution indicated that the assemblage was a composite ornament that had gradually collapsed, partly due to the burying position. Our aim was to challenge time degradation and to reimagine the initial composition in order to best explore the significance of this symbolic category of material culture, not as mere group of beads, but as an ornamental creation with further aesthetic, artisanal and socioeconomic implications. The reconstruction results exceeded our expectations as it revealed an imposing multi-row necklace of complex structure and attractive design. Through multiple lines of evidence, we suggest that the necklace was created at Ba`ja, although significant parts of beads were made from exotic shells and stones, including fossil amber, an unprecedented material never attested before for this period. The retrieval of such an ornament from life and its attribution to a young dead child highlights the significant social status of this individual. Beyond the symbolic functions related to identity, the necklace is believed to have played a key role in performing the inhumation rituals, understood as a public event gathering families, relatives, and people from other villages. In this sense, the necklace is not seen as belonging completely to the realm of death but rather to the world of the living, materializing a collective memory and shared moments of emotions and social cohesion.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288075
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrogen production by catalytic aqueous-phase reforming of waste biomass: a review
González-Arias, J; Zhang, Z; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAEnvironmental Chemistry Letters, 21 (2023) 3089-3104 DOI: 10.1007/s10311-023-01643-w
Abstract
The rising adverse effects of climate change call for a rapid shift to low-carbon energy and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. For that, biorefineries appear as promising alternatives to produce energy, chemicals, and fuels using biomass and waste as raw materials. Here, we review catalytic aqueous-phase reforming to convert biomass and organic waste carbohydrates into renewable hydrogen, with focus on reforming basics; catalyst design; reforming of model compounds, wastewater and biomass; economics and life cycle assessment. We found that platinum and palladium are technically highly effective, yet their high price may limit upscaling. Alternatively, addition of tin to nickel gives acceptable results and improves hydrogen selectivity from 35 to 90%. We observed that hydrogen production decreases from 14% for crude glycerol to 2% for pure glycerol, thus highlighting the need to do experiments with real wastewater. The rare experiments on real wastewater from brewery, juice, tuna, and cheese industries have given hydrogen production rates of up to 149.7 mg/L. Aqueous-phase reforming could be shortly competitive with prices around 3-6 USD per kg of hydrogen, which are nearing the current market prices of 2-3 USD per kg.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1007/s10311-023-01643-w
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Inkjet-Printed and Nanopatterned Photonic Phosphor Motifs with Strongly Polarized and Directional Light-Emission
Cabello-Olmo, E; Romero, M; Kainz, M; Bernroitner, A; Kopp, S; Muhlberger, M; Lozano, G; Miguez, HAdvanced Functional Materials, (2023) 2305907 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202305907
Abstract
Herein a versatile and scalable method to prepare periodically corrugated nanophosphor surface patterns displaying strongly polarized and directional visible light emission is demonstrated. A combination of inkjet printing and soft lithography techniques is employed to obtain arbitrarily shaped light emitting motifs. Such predesigned luminescent drawings, in which the polarization and angular properties of the emitted light are determined and finely tuned through the surface relief, can be used as anti-counterfeiting labels, as these two specific optical features provide additional means to identify any unauthorized or forged copy of the protected item. The potential of this approach is exemplified by processing a self-standing photoluminescent quick response code whose emission is both polarized and directionally beamed. Physical insight of the mechanism behind the directional out-coupled photoluminescence observed is provided by finite-difference time-domain calculations.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202305907
Materiales Semiconductores para la Sostenibilidad
Surfactant-Dependent Bulk Scale Mechanochemical Synthesis of CsPbBr3 Nanocrystals for Plastic Scintillator-Based X-ray Imaging
Ghosh, J; O'Neill, J; Masteghin, MG; Braddock, I; Crean, C; Dorey, R; Salway, H; Anaya, M; Reiss, J; Wolfe, D; Sellin, PACS Applied Nano Materials, DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.3c02531
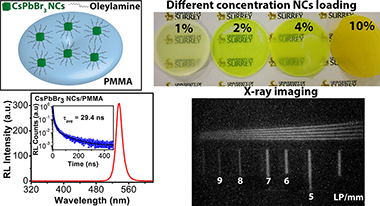
Abstract
We report a facile, solvent-free surfactant-dependentmechanochemicalsynthesis of highly luminescent CsPbBr3 nanocrystals (NCs)and study their scintillation properties. A small amount of surfactantoleylamine (OAM) plays an important role in the two-step ball millingmethod to control the size and emission properties of the NCs. Thesolid-state synthesized perovskite NCs exhibit a high photoluminescencequantum yield (PLQY) of up to 88% with excellent stability. CsPbBr3 NCs capped with different amounts of surfactant were dispersedin toluene and mixed with polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) polymer andcast into scintillator discs. With increasing concentration of OAMduring synthesis, the PL yield of CsPbBr3/PMMA nanocompositewas increased, which is attributed to reduced NC aggregation and PLquenching. We also varied the perovskite loading concentration inthe nanocomposite and studied the resulting emission properties. Themost intense PL emission was observed from the 2% perovskite-loadeddisc, while the 10% loaded disc exhibited the highest radioluminescence(RL) emission from 50 kV X-rays. The strong RL yield may be attributedto the deep penetration of X-rays into the composite, combined withthe large interaction cross-section of the X-rays with the high-Zatoms within the NCs. The nanocomposite disc shows an intense RL emissionpeak centered at 536 nm and a fast RL decay time of 29.4 ns. Further,we have demonstrated the X-ray imaging performance of a 10% CsPbBr3 NC-loaded nanocomposite disc.
August, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.3c02531
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Ultrapure Green High Photoluminescence Quantum Yield from FAPbBr3 Nanocrystals Embedded in Transparent Porous Films
Romero-Pérez, C; Delgado, NF; Herrera-Collado, M; Calvo, ME; Míguez, H (MigChemistry of Materials, 35 (2023) 5541-5549 DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c00934
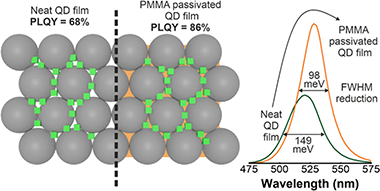
Abstract
Achieving highly transparent and emissive films based on perovskite quantum dots (PQDs) is a challenging task since their photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) typically drops abruptly when they are used as building blocks to make a solid. In this work, we obtain highly transparent films containing FAPbBr(3) quantum dots that display a narrow green emission (lambda = 530 nm, full width at half-maximum (FWHM) = 23 nm) with a PLQY as high as 86%. The method employed makes use of porous matrices that act as arrays of nanoreactors to synthesize the targeted quantum dots within their void space, providing both a means to keep them dispersed and a protective environment. Further infiltration with poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) increases the mechanical and chemical stability of the ensemble and serves to passivate surface defects, boosting the emission of the embedded PQD and significantly reducing the width of the emission peak, which fulfills the requirements established by the Commission Internationale de l'E ' clairage (CIE) to be considered an ultrapure green emitter. The versatility of this approach is demonstrated by fabricating a color-converting layer that can be easily transferred onto a light-emitting device surface to modify the spectral properties of the outgoing radiation.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c00934
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of noble metal addition over active Ru/TiO2 catalyst for CO selective methanation from H2 rich- streams
Bobadilla, LF; Muñoz-Murillo, A; Gandara-Loe, J; Perez, A; Laguna, OH; Martinez, TLM; Penkova, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48 (2023) 25065-25074 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.07.072
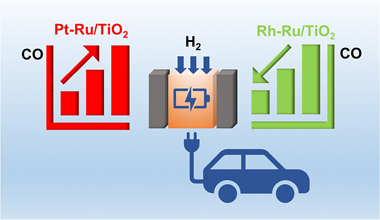
Abstract
Selective CO methanation from H2-rich stream has been regarded as a promising route for deep removal of low CO concentration and catalytic hydrogen purification processes. This work is focused on the development of more efficient catalysts applied in practical conditions. For this purpose, we prepared a series of catalysts based on Ru supported over titania and promoted with small amounts of Rh and Pt. Characterization details revealed that Rh and Pt modify the electronic properties of Ru. The results of catalytic activity showed that Pt has a negative effect since it promotes the reverse water gas shift reaction decreasing the selectivity of methanation but Rh increases remarkably the activity and selectivity of CO methanation. The obtained results suggest that RuRh-based catalyst could become important for the treatment of industrial-volume streams.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.07.072
Reactividad de Sólidos
R-curve evaluation of 3YTZP/graphene composites by indirect compliance method
Lopez-Pernia, C; Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Prada-Rodrigo, J; Moreno, P; Reveron, H; Chevalier, J; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 43 (2022) 3486-3497 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2023.02.002
Abstract
This work addresses the crack growth resistance of 3 mol% Yttria-doped Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystalline (3YTZP) spark-plasma sintered (SPS) composites containing two types of graphene-based nanomaterials (GBN): exfoliated graphene nanoplatelets (e-GNP) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO). The crack growth resistance of the composites is assessed by means of their R-Curve behavior determined by three-point bending tests on single edge "V" notched beams (SEVNB), in two different orientations of the samples: with the crack path perpendicular or parallel to the pressure axis during the SPS sintering. The sharp edge notches were machined by ultrashort laser pulsed ablation (UPLA). The compliance and optical-based methods for evaluating the crack length are compared on the basis of the experimental R-Curve results in composites with 2.5 vol% rGO tested in the perpendicular orientation. Moreover, the activation of reinforcement mechanisms is evaluated by both the fracture surface inspection by Scanning Electron Microscopy and a compliance analysis. It is shown that the indirect compliance method is relevant and reliable for calculating the R-Curve of 3YTZP/GBN composites. The effect of the type and content of GBN on the crack growth resistance of the composites is also discussed.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2023.02.002
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
ZnO/TiO2 and ZnO/Nb2O5 as effective systems for the treatment of enteric bacteria and commercial dyes
Hernandez, JS; Murcia, JJ; Rojas, H; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JARevista Facultad de Ingeniería-Universidad de Antioquia, 108 (2023) 9-17 DOI: 10.17533/udea.redin.20220785
Abstract
In this study, ZnO/TiO2 and ZnO/Nb2O5 photocatalysts were evaluated in the river pollution remediation and wastewater treatment from textile factories, thus, the target pollutants selected for this study were enteropathogenic bacteria and commercial dyes. The mixed oxide systems were extensively analyzed in order to explore their physicochemical properties. From this analysis, it was found that the coupling of two oxides did not modify the crystallinity of the pristine semiconductors. As a result, XRD Wurtzite phase, hexagonal phase, and anatase phases were identified for ZnO, Nb2O5, and TiO2 photocatalyst, respectively. Using UV-Vis DRS, a higher absorption for mixed oxides in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum was observed, along with a decrease in the band gap value in these materials. The results of the photocatalytic activity evaluation showed that the coupling of ZnO with Nb2O5 and TiO2 increased the effectiveness of the total organic carbon (TOC) and E. Coli elimination. 83% of TOC and elimination of 64% of E. coli were achieved using ZnO/Nb2O5 photocatalyst for the treatment of water samples from the polluted river.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.17533/udea.redin.20220785
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Dielectric multilayers for broadband optical rotation enhancement
Pellegrini, G; Mogni, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Fossati, S; Dostálek, J; Vázquez, RM; Osellame, R; Celebrano, M; Finazzi, M; Biagioni, PNuovo Cimento C-Colloquia and Communications in Physics, 46 (2023) 111 DOI: 10.1393/ncc/i2023-23111-1
Abstract
We design a simple dielectric multilayer capable of sustaining broadband superchiral surface waves. We show that the platform can produce large optical chirality enhancements in a wavelength range of hundreds of nanometers. We finally demonstrate that these properties result in the enhancement of the optical rotation signal well above two orders of magnitude, thus extending surface-enhanced chiral spectroscopies beyond the traditionally addressed circular dichroism signals.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1393/ncc/i2023-23111-1
Reactividad de Sólidos
An overview of polymeric composite scaffolds with piezoelectric properties for improved bone regeneration
Donate, R; Paz, R; Moriche, R; Sayagués, MJ; Alemán-Domínguez, ME; Monzón, MMaterials & Design, 231 (2023) 112085 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112085
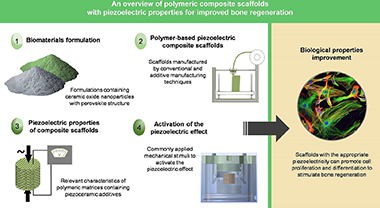
Abstract
Despite the dramatic change that Tissue Engineering or stem cell therapies have brought to current therapeutic strategies, there is a lack of functionalities in the available biomaterials for manufacturing scaffolds to treat several highly prevalent osseous diseases (osteochondral defects, osteoporosis, etc.). One promising approach to fill this gap involves the development of innovative piezoelectric scaffolds for improved bone regeneration. Scaffolds with the appropriate piezoelectricity can positively influence the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to regenerate bone tissue, since surface electrical charges play a key role in the mechanotransduction process. In this work, polymeric-based composite scaffolds with piezoelectric properties intended for bone tissue engineering are reviewed. Special attention is paid to biocompatible, piezoelectric polymers that show suitable properties to be pro-cessed by additive manufacturing techniques. Previous works on composite scaffolds based of these poly-meric matrices and containing piezoceramic additives are summarized. The use of piezoelectric nanostructured composite formulations containing lead-free ceramic oxide nanoparticles with per-ovskite structure is highlighted. Also, different commonly applied mechanical stimuli to activate the piezoelectric effect of the developed materials are presented. Finally, other applications of such scaffolds are mentioned, including their capabilities for real-time monitoring
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112085
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Biochar production from cellulose under reductant atmosphere: influence of the total pyrolysis time
Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JARSC Advances, 13 (2023) 21071-21079 DOI: 10.1039/d3ra03093h

Abstract
Today's rising energy costs, coupled with increasing energy demand, make it necessary to search for more efficient energy processes. In recent years, there have been increasing efforts to develop efficient catalysts based on waste-derived char, by a single step where the carbon precursor and the metallic active phase one undergo a single common thermal process under a reductant atmosphere at high temperature. The use of a reductant atmosphere drives the formation of carbonaceous materials with different characteristics than those obtained under the standard nitrogen-inert one. Our work evaluates the influence of the residence time and the heating rate on the physicochemical properties of the biochar obtained. Relatively long residence times and slow heating rates, improve the yield to the resulting biochar, without increasing production cost, making the subsequent char-based metallic catalyst synthesis more efficient. The heating rate was shown to be key in improving the properties of the char in a smoother and more controlled way, unlocking a new working pathway for the efficient design and production of char-based catalysts in a one-pot synthesis.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/d3ra03093h
Materiales Avanzados
Influence of firing temperature on the ceramic properties of illite-chlorite-calcitic clays
Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Vilarejo, L; Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJCeramics International, 49 (2023) 24541-24557 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.11.077
Abstract
The influence of firing temperature on the ceramic properties of illite-chlorite-calcitic clays has been investigated. Three samples of the same clay deposit have been selected. Weight loss, dimensional changes, water absorption, bulk density, open porosity, flexural and compressive strengths, initial capillary water absorption rate and thermal conductivity have been determined as a function of firing temperature in the range 900-1200 degrees C with 1 h of soaking time. The microstructures of the fired samples have been examined by SEM and the phase evolution studied by XRD. The water absorption capacity decreased from similar to 22% at 900 degrees C/1 h to a maximum of 12% at 1200 degrees C/1 h with a maximum linear shrinkage of similar to 2.7%. The open porosities decreased from similar to 22% at 900 degrees C/1 h up to similar to 20% at 1200 degrees C/1 h as an effect of progressive sintering with higher densification degree of the ceramic bodies. The flexural strength reached a maximum value of similar to 34 MPa at 1200 degrees C/1 h. In contrast, the compressive strengths increased by firing up to a maximum of similar to 114 MPa at 1200 degrees C/1 h. The thermal conductivity increased slightly as increasing firing temperature with a maximum value of 0.582 W/m.K in samples fired at 1200 degrees C/1 h. The Ryshkevitch-Duckworth equation was applied and the results indicated that compressive strength is related linearly with open porosity. A linear correlation was found between thermal conductivity and open porosity. The microstructural evolution by SEM indicated that there is a change of the fired samples at 1100 degrees C as compared to SEM observations at 900 and 1000 degrees C. There is an increase of contacts between particles and layered structures associated to dehydroxylated clay minerals (illite and chlorite), quartz particles and pores developed by firing. At 1200 degrees C/1 h, the microstructures have changed associated to the higher degree of vitrification in the fired sample, with consolidation of the material, interparticle and neck contacts with formation of vitrified bridges. The formation of closed and large open pores of several sizes has been achieved by firing. Small particles were observed as a fine precipitation of crystals in the vitrified structures associated to anorthite, hematite and quartz relicts. This change in microstructure allowed deduce that the compressive strength increased upon firing, with maximum values of this ceramic property at 1200 degrees C. The ceramic bodies were more sintered by firing and the open porosity decreased progressively. Brickmaking is the main application of these fired illite-chlorite calcitic clays. These clays fired at 900-1100 degrees C, with 1 h of soaking time, could be applied in the fabrication of clay roofing tiles, tiles and even porous ceramic supports with small variations on shrinkage and porosity, good flexural strengths and high compressive strengths. Samples fired at higher temperatures, 1100 degrees C/1 h, could be applied as ceramic bricks showing a medium porosity (similar to 20%). They show almost the same bulk density when they are fired at lower temperatures (900 degrees C). Samples fired at higher temperatures (1150-1200 degrees C/1 h) could be applied as dark ceramic products. This investigation was interesting because a better knowledge of illite-chlorite-calcitic clays applied as ceramic raw materials has been achieved.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.11.077
Reactividad de Sólidos
Seville history insight through their construction mortars
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Franquelo, ML; Duran, AJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, (2023) DOI: 10.1007/s10973-023-12313-y
Abstract
Seville is intimately linked to its historic role and extensive cultural heritage. The city has been occupied by Romans, Arabs and Christians, who built important historical buildings. Roman (first-second centuries) and Arabic (eleventh century) buildings, medieval Shipyard (thirteenth century), San Isidoro and Santa Maria de las Cuevas monasteries (fifteenth century), Santa Maria de las Cuevas (fifteenth century modified in eighteenth century), El Salvador Church (eighteenth century), the Royal Ordnance building (eighteenth century) and Santa Angela de la Cruz convent (twentieth century) performed with lining mortars, and mortars used in building stones (City Hall and Marchena Gate), all of them located in Seville (Spain), have been studied. Ninety-four mortar samples (employed as structural, plaster, coating) originally used or applied in restoration processes have been collected to perform an archaeometry study. The ratio of CO2 mass loss to hydraulic water (H2O) mass loss, and the mineralogical characterization by X-ray diffraction has been used to compare the mortars used in the different historical periods. Mainly hydraulic mortars were widely used in all these studied monuments as most mortars showed CO2/H2O ratios within the 4-10 range. Moreover, the thermal analysis curves also showed a broad temperature range for the thermal decomposition of the carbonate fraction of the mortars.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-023-12313-y
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
New 3D Printing Strategy for Structured Carbon Devices Fabrication
Delgado-Martin, G; Rodriguez, N; Dominguez, MI; Agamez-Pertuz, YY; Tejada, MM; Ruiz-Lopez, E; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MACatalysts, 13 (2023) 1039 DOI: 10.3390/catal13071039
Abstract
This work shows a new method for the preparation of 100% carbon-structured devices. The method is based on resorcinol-formaldehyde polymerization, using starch as a binder with the addition of a certain amount of external carbon source before polymerization. Molds obtained by 3D printing are used to shape the structured devices in the desired shape, and the ultimate pyrolysis step consolidates and produces the carbonaceous devices. The proposed method allows obtaining supports with different textural and surface properties varying the carbonaceous source, the solvent, or the pyrolysis conditions, among other factors. The as-obtained devices have demonstrated their usefulness as palladium supports for the gas-phase formic acid dehydrogenation reaction. The monolith shows a high conversion of formic acid (81% according to H-2 production) and a high selectivity towards hydrogen production at mild temperatures (80% at 423 K).
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/catal13071039
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermochemical energy storage using calcium magnesium acetates under low CO2 pressure conditions
Amghar, N; Jimenez, PES; Maqueda, LAP; Perejon, AJournal of Energy Storage, 63 (2023) 106958 DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2023.106958
Abstract
The calcium looping multicycle performance of CaO-based materials, derived from calcium magnesium acetates with different Mg content were tested under experimental conditions compatible with thermochemical energy storage. In order to reduce the sintering-induced decay in performance, calcination at an absolute CO2 pressure of 0.1 bar and 0.01 bar is implemented. CaO carbonation is performed at standard 1 bar CO2 conditions. The samples can be fully calcined in short residence times. Samples with MgO present high cycling stability, even when the MgO content is as low as 5 mol%. The effective conversion values lie within the range 0.88-0.84 over ten calcination/carbonation cycles, which provides an accumulated energy storage density of 90.9 GJ/m3. This outstanding reactivity is related with the microstructure of the sample after calcination composed of CaO nanoparticles that are highly reactive for carbonation.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2023.106958
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Setting a comprehensive strategy to face the runback icing phenomena
Mora, J et al.Surface & Coatings Technology, 465 (2023) 129585 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2023.129585
Abstract
The development of anti-icing robust surfaces is a hot topic nowadays and particularly crucial in the aeronautics or wind energy sectors as ice accretion can compromise safety and power generation efficiency. However, the current performance of most anti-icing strategies has been proven insufficient for such demanding applications, particularly in large unprotected zones, which located downstream from thermally protected areas, may undergo secondary icing. Herein, a new testing methodology is proposed to evaluate accretion mechanisms and secondary icing phenomena through, respectively, direct impact and running-wet processes and systematically applied to anti-icing materials including commercial solutions and the latest trends in the state-of-the-art. Five categories of materials (hard, elastomeric, polymeric matrix, SLIPS and superhydrophobic) with up to fifteen formulations have been tested. This Round-Robin approach provides a deeper understanding of anti-icing mechanisms revealing the strengths and weaknesses of each material. The conclusion is that there is no single passive solution for anti-ice protection. Thus, to effectively protect a given real component, different tailored materials fitted for each particular zone of the system are required. For this selection, shape analysis of such a component and the impact characteristics of water droplets under real conditions are needed as schematically illustrated for aeronautic turbines.
July, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2023.129585
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of thermal treatments below devitrification temperature on the magnetic and magnetocaloric properties in mechanically alloyed Fe70Zr30 powders
Manchon-Gordon, AF; Blazquez, JS; Kowalczyk, M; Ipus, JJ; Kulik, T; Conde, CFJournal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 609 (2023) 122267 DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2023.122267
Abstract
In this work, the relaxation of the amorphous structure of mechanically alloyed Fe70Zr30 powders has been analyzed through interrupted heating ramps below the devitrification temperature. As a result of such thermal treatment, Curie temperature and temperature at maximum magnetic entropy change curves shift to higher temperatures as the temperature of heating treatment increases. This effect can be attributed to both the release of the stress accumulated in the amorphous powder during the milling process and to the initiation of nucleation of alpha-Fe crystallites, as it has been shown by Mo center dot ssbauer spectroscopy.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2023.122267
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Microstructural characterization and thermal stability of He charged amorphous silicon films prepared by magnetron sputtering in helium
Fernández, A; Sauvage, T; Diallo, B; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Montes, O; Martínez-Blanes, JM; Caballero, J; Godinho, V; Ferrer, FJ; Ibrahim, S; Brault, P; Thomann, ALMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 301 (2023) 127674 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127674
Abstract
Sputtering of silicon in a Helium magnetron discharge has been reported as a bottom-up procedure to obtain amorphous Si films containing high amounts of gas-filled nanopores. Here we compare the microstructure and composition of Si-He nanocomposite films deposited by magnetron sputtering (MS) with 4He in DC or RF and 3He in RF operation modes. Electron microscopy (SEM and TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and ion beam analysis (IBA) have been used to analyze the films and to investigate the in-situ and ex-situ thermal evolution. Depending on deposition conditions different in depth compositions, nanopore size and shape distributions, porosity and He content could be obtained. The presence of impurities (i.e. oxygen) has shown to promote He diffusivity reducing He accumulation. The start temperature of He-release varied in the range 473-723 K without films crystallization. Films grown in RF mode reached contents of 32 and 29 at% of 4He and 3He and were respectively stable up to 573 and 723 K both in vacuum and under inert gas flow. In-situ p-EBS (proton Elastic Back Scattering) allowed monitoring the He release accompanied by blistering/delamination effects visualized by SEM. These results show the potentiality of annealing to hold nano-porous structures after liberation of trapped gas.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127674
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Low temperature nucleation of thermochromic VO2 crystal domains in nanocolumnar porous thin films
Alcaide, AM; Regodon, G; Ferrer, FJ; Rico, V; Alvarez, R; Rojas, TC; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ANanotechnology, 34 (2023) 255702 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/acc664
Abstract
The low temperature formation of monoclinic VO2 crystal domains in nanocolumnar vanadium/oxygen thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles is analyzed. The synthesis procedure involved the deposition of amorphous nanocolumnar VO1.9 thin films at room temperature and its subsequent annealing at temperatures between 250 °C and 330 °C in an oxygen atmosphere. The thermochromic transition of these films was found at a temperature of 47 °C when the annealing temperature was 270 °C and 58 °C when the annealing temperature was 280 °C and 290 °C, presenting a clear drop of the optical transmittance in the infrared region of the spectrum. The significant downshift in the temperature window to obtain VO2 in comparison with compact films and other strategies in literature is explained by the particular morphology of the nanocolumnar structures, which contains numerous defects along with open and embedded porosity.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/acc664
Reactividad de Sólidos
A practical analysis for decelerated growth processes to get physically meaningful kinetic parameters from classical nucleation and growth theory despite of overgrowth
Blazquez, JS; Caballero-Flores, R; Manchon-Gordon, AF; Borrego, JM; Conde, CFJournal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 610 (2023) 122305 DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2023.122305
Abstract
We have analyzed the overgrowth problem arising in decelerated growth processes of spherical crystals in the frame of classical nucleation and growth theory developed by Kolmogorov, Johnson and Mehl, and Avrami (KJMA). To do that, simulations of decelerated growth transformations with a constant nucleation rate have been performed, changing the linear growth rate of spherically shaped nuclei from null (instantaneous growth rate) to constant (characteristic of interface controlled growth processes). We propose the determination of the actual kinetic parameters through the analysis of the inflection point of time evolution of transformed fraction. The correlations found between the effective kinetic parameters from direct KJMA analysis and the actual ones make it possible obtaining physically meaningful parameters. The proposed analysis has been applied to the nano-crystallization of amorphous FINEMET-type compositions.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2023.122305
Reactividad de Sólidos
Reversibility and thermal dependence of the martensitic transformation in a melt-spun Ni55Fe17Ga26Co2 Heusler alloy
Manchon-Gordon, AF; Vidal-Crespo, A; Blazquez, JS; Kowalczyk, M; Ipus, JJ; Kulik, T; Conde, CFJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 946 (2023) 169484 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169484
Abstract
An almost single phase 14 M modulated martensite is obtained in melt spun ribbon of Ni55Fe17Ga26Co2 Heusler alloy. The effect of thermal treatments on the stability of the reverse martensitic transformation from 14 M modulated martensite to austenite phase in this system has been investigated by both non -isothermal and isothermal treatments. Heating above martensitic transformation promotes a continuous reduction of the martensitic transformation temperature, which stabilizes the austenite phase at room temperature and induces the precipitation of the gamma phase. However, thermal treatments at tem-peratures between the austenite start and finish temperatures induce the decoupling of the austenite formation in a subsequent heating. The two successive reverse martensitic transformations could be as-cribed to the untransformed martensite in the previous interrupted heating and to the new martensite formed during cooling.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169484
Reactividad de Sólidos
Partial oxycombustion-calcium looping hybridisation for CO2 capture in waste-to-energy power plants
Ortiz, C; García-Luna, S; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Pérez-Maqueda, LJournal of Cleaner Production, 403 (2023) 136776 DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136776
Abstract
Integrating bioenergy and carbon capture and storage (BECCS) presents a great opportunity for power produc-tion with negative global CO2 emissions. This work explores a novel synergetic system that integrates mem-branes, partial biomass oxycombustion and the calcium looping (CaL) process. Polymeric membranes generate oxygen-enriched air (OEA) with an O2 concentration of 39%v/v, which is used for partial oxycombustion of biomass waste. The CO2-enriched flue gas evolves from the waste-to-energy plant to the CaL unit, where CO2 concentration is increased up to 90-95%v/v, ready for purification and sequestration. Compared to only oxy-combustion systems, the proposed concept presents fewer technological challenges in retrofitting boilers to waste-to-energy plants. Moreover, this new approach is highly efficient as integrating membranes to produce OEA instead of cryogenic distillation systems significantly reduces energy consumption. A novel integration concept is modelled to evaluate the whole process efficiency and the effect of key parameters on the system performance, such as the temperature of the reactors, the membrane surface area, and the partial oxy-combustion degree. The results show that the so-called mOxy-CaL system has an energy consumption associ-ated with CO2 capture below 4 MJ/kg CO2 (a 31% lower than that for a conventional CaL process), with a higher CO2 capture efficiency than oxycombustion and the CaL process separately. On the other hand, the economic analysis shows a higher CO2 capture cost for the novel configuration than for the typical CaL configuration due to the additional investment cost of the membrane system. Improvements in membrane performance by increasing its permeance and diminishing the required surface area would significantly reduce the economic cost of this novel integration. Using membranes with permeance over 400 GPU would boost the system's competitiveness.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136776
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Are Ni/ and Ni5Fe1/biochar catalysts suitable for synthetic natural gas production? A comparison with g-Al2O3 supported catalysts
González-Castaño, M; Morales, C; de Miguel, JCN; Boelte, JH; Klepel, O; Flege, JI; Arellano-Garcia, HGreen Energy & Environment, 8 (2023) 744-756 DOI: 10.1016/j.gee.2021.05.007
Abstract
Among challenges implicit in the transition to the post-fossil fuel energetic model, the finite amount of resources available for the technological implementation of CO2 revalorizing processes arises as a central issue. The development of fully renewable catalytic systems with easier metal recovery strategies would promote the viability and sustainability of synthetic natural gas production circular routes. Taking Ni and NiFe catalysts supported over g-Al2O3 oxide as reference materials, this work evaluates the potentiality of Ni and NiFe supported biochar catalysts for CO2 methanation. The development of competitive biochar catalysts was found dependent on the creation of basic sites on the catalyst surface. Displaying lower Turn Over Frequencies than Ni/Al catalyst, the absence of basic sites achieved over Ni/C catalyst was related to the depleted catalyst performances. For NiFe catalysts, analogous Ni5Fe1 alloys were constituted over both alumina and biochar supports. The highest specific activity of the catalyst series, exhibited by the NiFe/C catalyst, was related to the development of surface basic sites along with weaker NiFe-C interactions, which resulted in increased Ni0:NiO surface populations under reaction conditions. In summary, the present work establishes biochar supports as a competitive material to consider within the future low-carbon energetic panorama.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.gee.2021.05.007
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrothermal carbonization vs. anaerobic digestion to valorize fruit and vegetable waste: A comparative technical and energy assessment
Metyouy, K; Gonzalez, R; Gomez, X; Gonzalez-Arias, J; Martinez, EJ; Chafik, T; Sanchez, ME; Cara-Jiménez, JJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11 (2023) 109925 DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.109925
Abstract
Herein, the valorization of vegetable and fruit waste was assessed via hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) and anaerobic digestion (AD) in terms of product characterization and energy requirements. HTC was conducted at reaction temperatures between 150 & DEG;C and 190 & DEG;C, and residence times between 20 min and 40 min. The increase in the process severity resulted in hydrochars with higher carbon contents and higher energy densification ratios. AD was performed in two different ways. i.e., batch and semi-continuous reactions. From the batch experiments a methane yield of 300 L CH4/kg VS was obtained, while for the semi-continuous, the average specific methane production estimated (for HRTs from 75 to 50 days) was 213 & PLUSMN; 32 L CH4/kg VS. To estimate the energy re-quirements, mass and energy balances were performed considering the basic stages of each process to obtain a suitable biofuel material. In this sense, it was concluded that for this specific waste, AD was a more suitable process with a positive energy net balance. On the contrary, HTC presented a negative energy net balance being required 1.29 MJ/kg of fresh food waste. A combined HTC-AD treatment may be an efficient method to take advantage of both technologies leading to higher energy efficiencies and other valuable products.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.109925
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Review and Perspectives of CO2 Absorption by Water- and Amine-Based Nanofluids
Yuan, CT; Wang, Y; Baena-Moreno, FM; Pan, Z; Zhang, R; Zhou, H; Zhang, ZEnergy & Fuels, 37 (2023) 8883-8901 DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c00874
Abstract
The emission of greenhouse gases, especially CO2, hasbecome a major cause of environmental degradation, and carbon capture,utilization, and storage (CCUS) is a proposed solution to mitigateits impact. Nanofluids, a relatively new method for CO2 absorption, have gained attention in recent years. This review focuseson conventional methods for preparing nanofluids along with techniquesto improve their stability and enhance the CO2 absorptionand desorption mechanisms. Additionally, the influences of factors,i.e., nanoparticle and base solution types as well as nanoparticleconcentration, on the CO2 absorption process are summarized.Furthermore, models that can predict the absorption of CO2 accurately are outlined. It is found that the types of both baseliquids and nanoparticles have an important impact on the absorptionby nanofluids. In-depth studies on the predictive capabilities ofartificial intelligence (AI) models hold immense potential in thisregard. This review also puts forth effective strategies to addressprevailing challenges. This will provide a solid theoretical basisfor this field and underscore the promising potential of nanofluidsas CO2 solvents. There are still many unexplored aspectsto be considered, such as the economic viability and energy consumptionof this technology.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c00874
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Toluene combustion on MnOx, CeO2, and Mn-Ce-O solids prepared via citrate complexation, and citrate and urea combustion methods
Rahou, S; Benadda-Kordjani, A; Ivanova, S; Odriozola, JA; Chebout, R; Mahzoul, H; Zouaoui, NJournal of Nanoparticle Research, 25 (2023) 114 DOI: 10.1007/s11051-023-05759-6
Abstract
MnOx, CeO2, and MnCe-O (Mn/Ce = 1) solids have been prepared via the citrate complexation and combustion method using citrate and urea precursors. The solids have been characterized by XRD, SEM-EDX, N-2-adsorption-desorption, UV-Vis spectroscopy, TPR, O-2-TPD, and XPS techniques. The catalytic reactivity of the manganese oxides was not affected by the preparation protocol. In the case of ceria and mixed oxides, the synthesis method greatly affected the structural and chemical properties, ultimately altering their reactivity. The citrate complexation method produced the most homogeneous and active mixed oxide, whereas the urea combustion method resulted in less active solids. The mixed oxide prepared via urea combustion was less active than the manganese single oxide; the decrease in activity was attributed to phase separation and the formation of Mn3O4 domains on the surface of ceria. In contrast, citrate complexation resulted in solids with the lowest particle size (similar to 3 nm), the highest oxidation state for manganese, and the highest proportion of oxygen vacancies, which promote the oxidation reaction.
June, 2023 · DOI: 10.1007/s11051-023-05759-6
- ‹ previous
- 4 of 37
- next ›














