Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
New Insights on the Conversion Reaction Mechanism in Metal Oxide Electrodes for Sodium-Ion Batteries
Mosa, J; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Aparicio, MNanomaterials, 11 (2021) 966
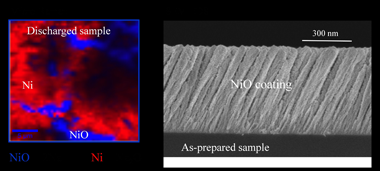
Due to the abundance and low cost of exchanged metal, sodium-ion batteries have attracted increasing research attention for the massive energy storage associated with renewable energy sources. Nickel oxide (NiO) thin films have been prepared by magnetron sputtering (MS) deposition under an oblique angle configuration (OAD) and used as electrodes for Na-ion batteries. A systematic chemical, structural and electrochemical analysis of this electrode has been carried out. The electrochemical characterization by galvanostatic charge-discharge cycling and cyclic voltammetry has revealed a certain loss of performance after the initial cycling of the battery. The conversion reaction of NiO with sodium ions during the discharge process to generate sodium oxide and Ni metal has been confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) and micro-Raman analysis. Likewise, it has been determined that the charging process is not totally reversible, causing a reduction in battery capacity.
April, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/nano11040966
Reactividad de Sólidos
EGFR-targeting antitumor therapy: Neuregulins or antibodies?
de Lavera, I; Merkling, PJ; Oliva, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Cotan, D; Sanchez-Alcazar, JA; Infante, JJ; Zaderenko, A.P.European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 158 (2021) 105678
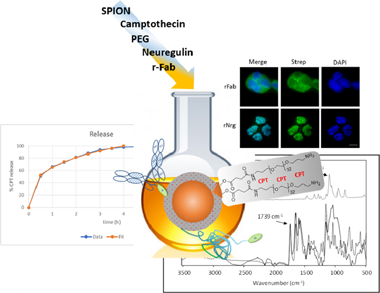
Malignancies such as lung, breast and pancreatic carcinomas are associated with increased expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR, and its role in the pathogenesis and progression of tumors has made this receptor a prime target in the development of antitumor therapies. In therapies targeting EGFR, the development of resistance owing to mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms, and the expression of the receptor ligands themselves are very serious issues. In this work, both the ligand neuregulin and a bispecific antibody fragment to EGFR are conjugated separately or together to the same drug-delivery system to find the most promising candidate. Camptothecin is used as a model chemotherapeutic drug and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a delivery system. Results show that the lowest LD50 is achieved by formulations conjugated to both the antibody and the ligand, demonstrating a synergy. Additionally, the ligand location in the nucleus favors the antitumor activity of Camptothecin. The high loading capacity and efficiency convert these systems into a good alternative for administering Camptothecin, a drug whose use is otherwise severely limited by its chemical instability and poor solubility. Our choice of targeting agents allows treating tumors that express ErbB2 (Her2+ tumors) as well as Her2- tumors expressing EGFR.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105678
Reactividad de Sólidos
A first insight into the microstructure and crack propagation in novel boron nitride nanosheet/3YTZP composites
Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 60 (2021) 128-136
In this work, novel 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycristalline (3YTZP) ceramic composites with boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) are investigated for the first time. Highly densified composites with 1 and 4 vol% BNNS were obtained by spark plasma sintering (SPS) after BNNS synthesis using a solution exfoliation method and BNNS dispersion into the ceramic powder by ultrasonication. The BNNS presented homogeneous distribution throughout the ceramic matrix and preferential alignment in the plane perpendicular to the pressing axis during SPS. The BNNS incorporation had practically no effect on the Vickers hardness of the material nor on the Young's modulus. Anisotropy in crack development was found in the composite with 4% vol BNNS, together with a mechanism of extensive microcracking. Several energy-absorbing mechanisms during crack propagation, such as crack deflection, crack bridging, crack branching, BNNS pull-out and BNNS debonding, were identified in the composites by a close observation of the indentation-induced fracture paths.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2020.02.003
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Cation-driven electrical conductivity in Ta-doped orthorhombic zirconia ceramics
Moshtaghioun, BM; Laguna-Bercero, MA; Pena, JI; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ACeramics International, 47 (2021) 7248-7522
This paper is devoted to the study of the electrical conductivity of tantalum-doped zirconia ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. In this study, the temperature dependence of conductivity in as-prepared specimens and in those previously annealed in air is determined and compared. A semi-empirical model, which is based on the oxidation states of the cations, has been developed and successfully assessed. According to this, the conductivity is basically controlled by the diffusion of tetravalent zirconium cations in both cases, although the concentration of these species varies drastically with the amount of induced oxygen vacancies. This is a quite unexpected fact, since conductivity is normally controlled by anionic diffusion in zirconia ceramics. This option is forbidden here due to the presence of substitutional pentavalent cations. Therefore, conductivity values are much lower than those reported in trivalent or divalent substitutional cation doped zirconia ceramics.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.227
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Nanofibrous Gelatin-Based Biomaterial with Improved Biomimicry Using D-Periodic Self-Assembled Atelocollagen
Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Dalby, MJ; Diaz-Cuenca, ABiomimetics, 6 (2001) 20
Design of bioinspired materials that mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM) at the nanoscale is a challenge in tissue engineering. While nanofibrillar gelatin materials mimic chemical composition and nano-architecture of natural ECM collagen components, it lacks the characteristic D-staggered array (D-periodicity) of 67 nm, which is an important cue in terms of cell recognition and adhesion properties. In this study, a nanofibrous gelatin matrix with improved biomimicry is achieved using a formulation including a minimal content of D-periodic self-assembled atelocollagen. We suggest a processing route approach consisting of the thermally induced phase separation of the gelatin based biopolymeric mixture precursor followed by chemical-free material cross-linking. The matrix nanostructure is characterized using field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), wide angle X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The cell culture assays indicate that incorporation of 2.6 wt.% content of D-periodic atelocollagen to the gelatin material, produces a significant increase of MC3T3-E1 mouse preosteoblast cells attachment and human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) proliferation, in comparison with related bare gelatin matrices. The presented results demonstrate the achievement of an efficient route to produce a cost-effective, compositionally defined and low immunogenic “collagen-like” instructive biomaterial, based on gelatin.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics6010020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrical and reaction performances of packed-bed plasma reactors moderated with ferroelectric or dielectric materials
Gomez-Ramirez, A; Alvarez, R; Navascues, P; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Palmero, A; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, (2021) e2000193
The operational behavior of packed-bed plasma reactors depends on the dimension, shape, and chemical properties of the pellets used as moderators, but little information exists about the influence of their specific dielectric properties. Herein, we comparatively study the electrical behavior of a packed-bed reactor filled with pellets of either dielectric (Al2O3 and glass) or ferroelectric (BaTiO3 and lead zirconate titanate) materials. We found that plasma current was higher for ferroelectrics and presented a nonlineal dependence on voltage. Moreover, for BaTiO3, we found a drastic decrease at around its relatively low Curie temperature. Differences in electrical behavior have a direct effect on the reactor performance, as illustrated for the ammonia synthesis, demonstrating the importance of moderator material dielectric properties and their dependence on temperature.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000193
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synergizing carbon capture and utilization in a biogas upgrading plant based on calcium chloride: Scaling-up and profitability analysis
Baena-Moreno, FM; Reina, TR; Rodriguez-Galan, M; Navarrete, B; Vilches, LFScience of The Total Environment, 758 (2021) 143645
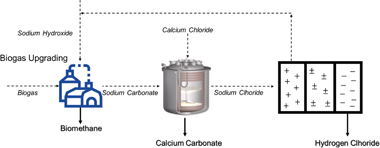
Herein we analyze the profitability of a novel regenerative process to synergize biogas upgrading and carbon dioxide utilization. Our proposal is a promising alternative which allows to obtain calcium carbonate as added value product while going beyond traditional biogas upgrading methods with high thermal energy consumption. Recently we have demonstrated the experimental viability of this route. In this work, both the scale-up and the profitability of the process are presented. Furthermore, we analyze three representative scenarios to undertake a techno-economic study of the proposed circular economy process. The scale-up results demonstrate the technical viability of our proposal. The precipitation efficiency and the product quality are still remarkable with the increase of the reactor size. The techno-economic analysis reveals that the implementation of this circular economy strategy is unprofitable without subsidies. Nonetheless, the results are somehow encouraging as the subsides needed to reach profitability are lower than in other biogas upgrading and carbon dioxide utilization proposals. Indeed, for the best-case scenario, a feed-in tariff incentive of 4.3 (sic)/MWh makes the approach profitable. A sensitivity study through tornado analysis is also presented, revealing the importance of reducing bipolar membrane electrodialysis energy consumption. Overall our study envisages the big challenge that the EU faces during the forthcoming years. The evolution towards bio-based and circular economies requires the availability of economic resources and progress on engineering technologies.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143645
Materiales Avanzados
Mining Wastes of an Albite Deposit as Raw Materials for Vitrified Mullite Ceramics
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Garzon, E; Perez-Villarejo, L; Angelopoulos, GN; Eliche-Quesada, DMinerals, 11 (2021) 232
In this work, an examination of mining wastes of an albite deposit in south Spain was carried out using X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), particle size analysis, thermodilatometry and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Thermogravimetric (TG) analysis, followed by the determination of the main ceramic properties. The albite content in two selected samples was high (65-40 wt. %), accompanied by quartz (25-40 wt. %) and other minor minerals identified by XRD, mainly kaolinite, in agreement with the high content of silica and alumina determined by XRF. The content of Na2O was in the range 5.44-3.09 wt. %, being associated with albite. The iron content was very low (<0.75 wt. %). The kaolinite content in the waste was estimated from similar to 8 to 32 wt. %. The particle size analysis indicated values of 11-31 wt. % of particles <63 mu m. The ceramic properties of fired samples (1000-1350 degrees C) showed progressive shrinkage by the thermal effect, with water absorption and open porosity almost at zero at 1200-1250 degrees C. At 1200 ffiC, the bulk density reached a maximum value of 2.38 g/cm(3). An abrupt change in the phase evolution by XRD was found from 1150 to 1200 degrees C, with the disappearance of albite by melting in accordance with the predictions of the phase diagram SiO2-Al2O3-Na2O and the system albite-quartz. These fired materials contained as main crystalline phases quartz and mullite. Quartz was present in the raw samples and mullite was formed by decomposition of kaolinite. The observation of mullite forming needle-shape crystals was revealed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The formation of fully densified and vitrified mullite materials by firing treatments was demonstrated.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/min11030232
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Zr and Fe on Pt/CeO2-MOx/Al2O3 catalysts for WGS reaction
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Ioanides, T; Arellano-Garcia, H; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, (2021)
By evaluating the functional modifications induced by Zr and Fe as dopants in Pt/CeO2‐MOx/Al2O3 catalysts (M = Fe and Zr), the key features for improving water gas shift (WGS) performance for these systems have been addressed. Pt/ceria intrinsic WGS activity is often related to improved H2 surface dynamics, H2O absorption, retentions and dissociation capacities which are influenced greatly by the support nature. Two metals, iron and zirconia, were chosen as ceria dopants in this work, either in separate manner or combined. Iron incorporation resulted in CO‐redox properties and oxygen storage capacities (OSC) improvement but the formation of Ce‐Fe solid solutions did not offer any catalytic benefit, while the Zr incorporation influenced in a great manner surface electron densities and shows higher catalytic activity. When combined both metals showed an important synergy evidenced by 30% higher CO conversions and attributed to greater surface electron densities population and therefore absorption and activity. This work demonstrates that for Pt/ceria catalysts OSC enhancement does not necessarily imply a catalytic promotion.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1002/er.6646
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Facile synthesis and characterization of a novel 1,2,4,5-benzene tetracarboxylic acid doped polyaniline@zinc phosphate nanocomposite for highly efficient removal of hazardous hexavalent chromium ions from water
Abdelghani Hsini, Yassine Naciri, Mohamed Benafqir, Zeeshan Ajmal, Nouh Aarab, Mohamed Laabd, J.A. Navío, F. Puga, Rabah Boukherroub, Bahcine Bakiz, Abdallah AlbourineJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 585 (2021) 560-573
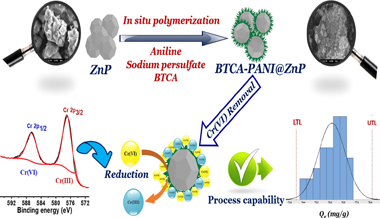
The present study describes the preparation of a novel 1,2,4,5-benzene tetracarboxylic acid doped polyaniline@zinc phosphate (BTCA-PANI@ZnP) nanocomposite via a facile two-step procedure. Thereafter, the as-prepared composite material adsorption characteristics for Cr(VI) ions removal were evaluated under batch adsorption. Kinetic approach studies for Cr(VI) removal, clearly demonstrated that the results of the adsorption process followed the pseudo second order and Langmuir models. The thermodynamic study indicated a spontaneous and endothermic process. Furthermore, higher monolayer adsorption was determined to be 933.88 mg g1 . In addition, the capability study regarding Cr(VI) ions adsorption over BTCA-PANI@ZnP nanocomposite clearly revealed that our method is suitable for large scale application. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis confirmed Cr(VI) adsorption on the BTCA-PANI@ZnP surface, followed by its subsequent reduction to Cr(III). Thus, the occurrence of external mass transfer, electrostatic attraction and reduction phenomenon were considered as main mechanistic pathways of Cr(VI) ions removal. The superior adsorption performance of the material, the multidimensional characteristics of the surface and the involvement of multiple removal mechanisms clearly demonstrated the potential applicability of the BTCA-PANI@ZnP material as an effective alternative for the removal of Cr(VI) ions from wastewater.
March, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.036
- ‹ previous
- 50 of 214
- next ›














