Scientific Papers in SCI
2019
2019
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Surface nickel particles generated by exsolution from a perovskite structure
Aguero, FN; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, MA; Cadus, LEJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 273 (2019) 75-80

LaAl1-xNixO3 (with x = 0.05 and 0.2) perovskite oxides were successfully synthesized and its behavior under reduction atmosphere was studied. HRTEM and STEM studies, coupled to HAADF and EDX detection, allowed to evidence the Ni exsolution process to the surface of the solid and to build nano-catalytic centers. The size of these centers is independent of the reduction conditions in the range studied. The high specific surface of the raw material, its porosity and the structure defects could be responsible of the low temperature at which the exsolution process starts. The content of Ni dopants allows the control of Ni centers size on the surface and the synthesis method provides Ni-nanoparticles strongly anchored to the resultant support.
May, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2019.02.036
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Differences in the Catalytic Behavior of Au-Metalized TiO2 Systems During Phenol Photo-Degradation and CO Oxidation
Oscar H. Laguna; Julie J. Murcia; Hugo Rojas; Cesar Jaramillo-Paez; Jose A. Navío; Maria C. HidalgoCatalysts, 9 (2019) 331
For this present work, a series of Au-metallized TiO2 catalysts were synthesized and characterized in order to compare their performance in two different catalytic environments: the phenol degradation that occurs during the liquid phase and in the CO oxidation phase, which proceeds the gas phase. The obtained materials were analyzed by different techniques such as XRF, SBET, XRD, TEM, XPS, and UV-Vis DRS. Although the metallization was not totally efficient in all cases, the amount of noble metal loaded depended strongly on the deposition time. Furthermore, the differences in the amount of loaded gold were important factors influencing the physicochemical properties of the catalysts, and consequently, their performances in the studied reactors. The addition of gold represented a considerable increase in the phenol conversion when compared with that of the TiO2, despite the small amount of noble metal loaded. However, this was not the case in the CO oxidation reaction. Beyond the differences in the phase where the reaction occurred, the loss of catalytic activity during the CO oxidation reaction was directly related to the sintering of the gold nanoparticles.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/catal9040331
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
UV and visible-light driven photocatalytic removal of caffeine using ZnO modified with different noble metals (Pt, Ag and Au)
Vaiano, V.; Jaramillo-Paez, C.A.; Matarangolo, M.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Materials Research Bulletin, 112 (2019) 251-260

In this work, ZnO photocatalyst was modified with different noble metals (Pt, Ag and Au) through photodeposition method and then characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, BET, UV–vis DRS, FESEM, and XPS). The addition of noble metals produces important changes in the light absorption properties with a significant absorbance in the visible region due to the existence of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) observed at about 450 nm and 550 nm for ZnO modified with Ag and Au, respectively. The morphology of the samples was studied by TEM and the size ranges of the different metals were estimated. Noble metal nanoparticles were in every case heterogeneously deposited on the larger ZnO particles. All the prepared photocatalysts were tested in the photocatalytic removal of caffeine (toxic and persistent emerging compound) under UV and visible light irradiation. It was observed an enhancement of photocatalytic caffeine removal from aqueous solutions under UV light irradiation with the increase of metal content (from 0.5 to 1 wt %) for ZnO modified with Ag and Au (Ag/ZnO and Au/ZnO). In particular, Ag/ZnO and Au/ZnO with higher Ag and Au content (1 wt %) allowed to achieve the almost complete caffeine degradation after only 30 min and a TOC removal higher than 90% after 4 h of UV light irradiation. These two photocatalysts were investigated also under visible light irradiation and it was found that their photocatalytic performances were strongly enhanced in presence of visible light compared to unmodified ZnO. In particular, Ag/ZnO photocatalyst was able to reach the complete caffeine degradation and a TOC removal of about 70% after 4 h of visible light irradiation.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.12.034
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of heat treatment on apatite coatings deposited on pre-calcified titanium substrates
Beltran, AM; Martin-Santana, Y; Gonzalez, JE; Montealegre-Melendez, I; Gonzalez, E; Peon-Aves, E; Gotor, FJ; Torres, YInternational Journal of Materials Research, 110 (2019) 351-358
Titanium and its alloys are considered interesting materials for endosseous implants. However, they still present drawbacks related to their in-vivo behavior that can be overcome by coatings, such as apatite. This work focuses on the deposition of apatite coatings on commercially pure titanium (grade II) substrates previously pre-calcified. The influence of the temperature used in the thermal treatment on the microstructure and tribo-mechanical surface properties was analyzed. The coatings were structurally and chemically characterized and their tribo-mechanical behavior was evaluated. The nano-apatite coatings were only formed on surfaces with successive treatments in NaOH and CaCl2 solutions. In addition, scratch tests showed that after the heat treatment the nanoapatite coatings had high bond strength to the substrate.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.3139/146.111746
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser-induced coloration of ceramic tiles covered with magnetron sputtered precursor layers
Rico, VJ; Lahoz, R; Rey-Garcia, F; de Francisco, I; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; de la Fuente, GF; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1589-1598

This paper reports a new methodology for the coloring of glazed ceramic tiles consisting of the near infrared pulsed laser processing of copper containing oxide coatings prepared by magnetron sputtering. As a second approach, the employ for the same purpose of a novel laser furnace technique is also described. Changing the laser parameters and using the laser furnace to treat the tiles at high temperature during irradiation has resulted in a wide color palette. The optical characterization of the modified tiles by UV-Vis spectroscopy has been complemented with their microstructural and compositional analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), and Time Of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (TOF-SIMS). The chemical composition of the surface was obtained by X-ray Photoemission Spectroscopy (XPS) and its structure determined by X?ray diffraction (XRD). The chemical resistance was characterized by several tests following the norm ISO 10545-13. Color changes have been attributed to surface microstructural and chemical transformations that have been accounted for by simple models involving different ablation, melting, diffusion, and segregation/agglomeration phenomena depending on the laser treatments employed.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.1111/jace.16022
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
3D core-multishell piezoelectric nanogenerators
A. Nicolas Filippin; Juan R.Sanchez-Valencia; Xabier Garcia-Casas; Victor Lopez-Flores; Manuel Macias-Montero; Fabian Frutos; Angel Barranco; Ana BorrasNano Energy, 58 (2019) 476-483
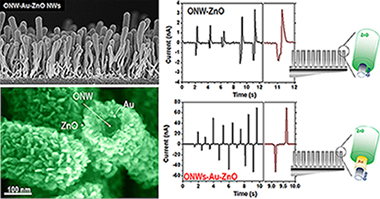
The thin film configuration presents obvious practical advantages over the 1D implementation in energy harvesting systems such as easily manufacturing and processing, and long-lasting and stable devices. However, ZnO-based piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) generally rely on the exploitation of single-crystalline nanowires because of their self-orientation in the c-axis direction and ability to accommodate long deformations resulting in high piezoelectric performance. Herein, we show an innovative approach to produce PENGs by combining polycrystalline ZnO layers fabricated at room temperature by plasma-assisted deposition with supported small-molecule organic nanowires (ONWs) acting as 1D scaffolds. Such hybrid nanostructures present convoluted core-shell morphology, formed by a single-crystalline organic nanowire conformally surrounded by a poly-crystalline ZnO shell and combine the organic core mechanical properties with the ZnO layer piezoelectric response. In a step forward towards the integration of multiple functions within a single wire, we have also developed ONW-Au-ZnO nanoarchitectures including a gold shell acting as inner electrode achieving output piezo-voltages up to 170 mV. The synergistic combination of functionalities in the ONW-Au-ZnO devices promotes an enhanced performance generating piezo-currents one order of magnitude larger than the ONW-ZnO nanowires and superior to the thin film nanogenerators for equivalent and higher thicknesses.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.047
Reactividad de Sólidos
Tribological behavior of graphene nanoplatelet reinforced 3YTZP composites
Gutierrez-Mora, F; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 39 (2019) 1381-1388

The tribological behavior of graphene nanoplatelet (GNP) reinforced 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (3YTZP) composites with different GNP content (2.5, 5 and 10 vol%) was analyzed and discussed. Their dry sliding behavior was studied using a ball-on-disk geometry with zirconia balls as counterparts, using loads between 2 and 20 N at ambient conditions and compared to the behavior of a monolithic 3YTZP ceramic used as a reference material. The composites showed lower friction coefficients and higher wear resistance than the monolithic 3YTZP. An outstanding performance was achieved at 10 N, where the friction coefficient decreased from 0.6 to 0.3 and the wear rates decreased 3 orders of magnitude in comparison with the monolithic ceramic. A layer adhered to the worn surface was found for all the composites, but it did not acted as a lubricating film. The composites with the lowest GNP content showed an overall improved tribological behavior.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.11.005
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Effect of support oxygen storage capacity on the catalytic performance of Rh nanoparticles for CO2 reforming of methane
Yentekakis, IV; Goula, G; Hatzisymeon, M; Betsi-Argyropoulou, I; Botzolaki, G; Kousi, K; Kondarides, DI; Taylor, MJ; Parlett, CMA; Osatiashtiani, A; Kyriakou, G; Holgado, JP; Lambert, RMApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 243 (2019) 490-501
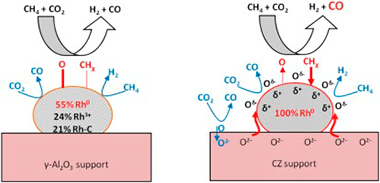
The effects of the metal oxide support on the activity, selectivity, resistance to carbon deposition and high temperature oxidative aging on the Rh-catalyzed dry reforming of methane (DRM) were investigated. Three Rh catalysts supported on oxides characterized by very different oxygen storage capacities and labilities (gamma-Al2O3, alumina-ceria-zirconia (ACZ) and ceria-zirconia (CZ)) were studied in the temperature interval 400-750 degrees C under both integral and differential reaction conditions. ACZ and CZ promoted CO2 conversion, yielding CO enriched synthesis gas. Detailed characterization of these materials, including state of the art XPS measurements obtained via sample transfer between reaction cell and spectrometer chamber, provided clear insight into the factors that determine catalytic performance. The principal Rh species detected by post reaction XPS was Rh, its relative content decreasing in the order Rh/CZ(100%) > Rh/ACZ(72%) > Fth/gamma Al2O3(55%). The catalytic activity followed the same order, demonstrating unambiguously that Rh is indeed the key active site. Moreover, the presence of CZ in the support served to maintain Rh in the metallic state and minimize carbon deposition under reaction conditions. Carbon deposition, low in all cases, increased in the order Rh/CZ < Rh/ACZ < Rh/gamma-Al2O3 consistent with a bi-functional reaction mechanism whereby backspillover of labile lattice O2- contributes to carbon oxidation, stabilization of Rh and modification of its surface chemistry; the resulting O vacancies in the support providing centers for dissociative adsorption of CO2. The lower apparent activation energy observed with CZ-containing samples suggests that CZ is a promising support component for use in low temperature DRM.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.048
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Low molecular weight epsilon-caprolactone-p-coumaric acid copolymers as potential biomaterials for skin regeneration applications
Contardi, M; Alfaro-Pulido, A; Picone, P; Guzman-Puyol, S; Goldoni, L; Benitez, J; Heredia, A; Barthel, MJ; Ceseracciu, L; Cusimano, G; Brancato, OR; Di Carlo, M; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAPLoS One, 14 (2019) e0214956
epsilon-caprolactone-p-coumaric acid copolymers at different mole ratios (epsilon-caprolactone: p-coumaric acid 1:0, 10:1, 8:1, 6:1, 4:1, and 2:1) were synthesized by melt-polycondensation and using 4-dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid as catalyst. Chemical analysis by NMR and GPC showed that copolyesters were formed with decreasing molecular weight as p-coumaric acid content was increased. Physical characteristics, such as thermal and mechanical properties, as well as water uptake and water permeability, depended on the mole fraction of p-coumaric acid. The p-coumarate repetitive units increased the antioxidant capacity of the copolymers, showing antibacterial activity against the common pathogen Escherichia coli. In addition, all the synthesized copolyesters, except the one with the highest concentration of the phenolic acid, were cytocompatible and hemocompatible, thus becoming potentially useful for skin regeneration applications.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214956
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Powder and Nanotubes Titania Modified by Dye Sensitization as Photocatalysts for the Organic Pollutants Elimination
Murcia, JJ; Avila-Martinez, EG; Rojas, H; Cubillos, J; Ivanova, S; Penkova, A; Laguna, OHNanomaterials, 9 (2019) 517
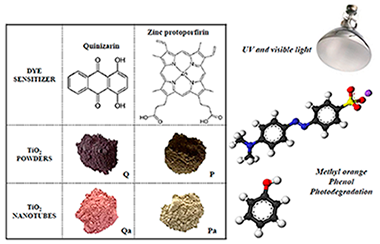
In this study, titanium dioxide powder obtained by the sol-gel method and TiO2 nanotubes, were prepared. In order to increase the TiO2 photoactivity, the powders and nanotubes obtained were modified by dye sensitization treatment during the oxide synthesis. The sensitizers applied were Quinizarin (Q) and Zinc protoporphyrin (P). The materials synthesized were extensively characterized and it was found that the dye sensitization treatment leads to modify the optical and surface properties of Titania. It was also found that the effectiveness of the dye-sensitized catalysts in the phenol and methyl orange (MO) photodegradation strongly depends on the dye sensitizer employed. Thus, the highest degradation rate for MO was obtained over the conventional Q-TiO2 photocatalyst. In the case of the nanotubes series, the most effective photocatalyst in the MO degradation was based on TiO2-nanotubes sensitized with the dye protoporfirin (ZnP). Selected catalysts were also tested in the phenol and MO photodegradation under visible light and it was observed that these samples are also active under this radiation.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/nano9040517
- ‹ previous
- 72 of 214
- next ›














