Scientific Papers in SCI
2019
2019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Powder and Nanotubes Titania Modified by Dye Sensitization as Photocatalysts for the Organic Pollutants Elimination
Murcia, JJ; Avila-Martinez, EG; Rojas, H; Cubillos, J; Ivanova, S; Penkova, A; Laguna, OHNanomaterials, 9 (2019) 517
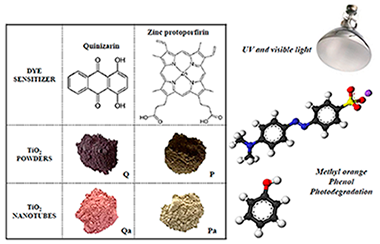
In this study, titanium dioxide powder obtained by the sol-gel method and TiO2 nanotubes, were prepared. In order to increase the TiO2 photoactivity, the powders and nanotubes obtained were modified by dye sensitization treatment during the oxide synthesis. The sensitizers applied were Quinizarin (Q) and Zinc protoporphyrin (P). The materials synthesized were extensively characterized and it was found that the dye sensitization treatment leads to modify the optical and surface properties of Titania. It was also found that the effectiveness of the dye-sensitized catalysts in the phenol and methyl orange (MO) photodegradation strongly depends on the dye sensitizer employed. Thus, the highest degradation rate for MO was obtained over the conventional Q-TiO2 photocatalyst. In the case of the nanotubes series, the most effective photocatalyst in the MO degradation was based on TiO2-nanotubes sensitized with the dye protoporfirin (ZnP). Selected catalysts were also tested in the phenol and MO photodegradation under visible light and it was observed that these samples are also active under this radiation.
April, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/nano9040517
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Transparent and Robust All-Cellulose Nanocomposite Packaging Materials Prepared in a Mixture of Trifluoroacetic Acid and Trifluoroacetic Anhydride
Guzman-Puyol, S; Ceseracciu, L; Tedeschi, G; Marras, S; Scarpellini, A; Benitez, JJ; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JANanomaterials, 9 (2019) 368
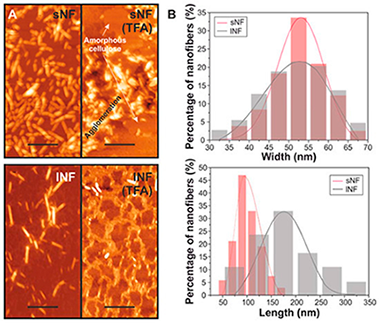
All-cellulose composites with a potential application as food packaging films were prepared by dissolving microcrystalline cellulose in a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic anhydride, adding cellulose nanofibers, and evaporating the solvents. First, the effect of the solvents on the morphology, structure, and thermal properties of the nanofibers was evaluated by atomic force microscopy (AFM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), respectively. An important reduction in the crystallinity was observed. Then, the optical, morphological, mechanical, and water barrier properties of the nanocomposites were determined. In general, the final properties of the composites depended on the nanocellulose content. Thus, although the transparency decreased with the amount of cellulose nanofibers due to increased light scattering, normalized transmittance values were higher than 80% in all the cases. On the other hand, the best mechanical properties were achieved for concentrations of nanofibers between 5 and 9 wt.%. At higher concentrations, the cellulose nanofibers aggregated and/or folded, decreasing the mechanical parameters as confirmed analytically by modeling of the composite Young's modulus. Finally, regarding the water barrier properties, water uptake was not affected by the presence of cellulose nanofibers while water permeability was reduced because of the higher tortuosity induced by the nanocelluloses. In view of such properties, these materials are suggested as food packaging films.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/nano9030368
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
The impact of photocatalytic Ag/TiO2 and Ag/N-TiO2 nanoparticles on human keratinocytes and epithelial lung cells
Rebleanu, D; Gaidau, C; Voicu, G; Constantinescu, CA; Sanchez, CM; Rojas, TC; Carvalho, S; Calin, MToxicology, 416 (2019) 30-43
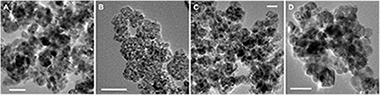
The potential human health risks following the exposure to inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) is a very important issue for their application in leather finishing industry. The aim of our study was to investigate the cytotoxic effect of silver (Ag)/titanium dioxide (TiO2) NPs on human cells. Photocatalytic NPs were prepared by electrochemical deposition of Ag on the surface of TiO2 and nitrogen (N)-TiO2 NPs and, subsequently, physicochemical characterized. Then, a set of experiments have been performed to study the cytotoxicity and cell death mechanisms involved, the changes in cell morphology and the production of ROS induced in human keratinocytes (HaCaT) and human lung epithelial cells (A549) by exposure to NPs. Moreover, the changes in major signaling pathways and the inflammatory response induced by Ag/N-TiO2 NPs in A549 cells were investigated. The data showed that cell death by late apoptosis/necrosis is induced in cells as function of the dose and the type of NPs and is characterized by morphological changes and cytoskeletal disorganization and an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. The exposure of A549 cells to Ag/N-TiO2 NPs determine the activation of ERK1/2 MAP-kinase pathway and the release of pro-inflammatory mediators CXCL1, GM-CSF and MIF, known to be involved in the recruitment of circulating neutrophils and monocytes.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2019.01.013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Controlled thermolysis of MIL-101(Fe, Cr) for synthesis of FexOy/porous carbon as negative electrode and Cr2O3/porous carbon as positive electrode of supercapacitor
Farisabadi, A; Moradi, M; Hajati, S; Kiani, MA; Espinos, JPApplied Surface Science, 469 (2019) 192-203
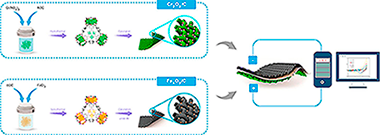
In the present study, two kinds of metal oxide/carbon nanocomposite were prepared through calcination of MIL-101(Fe, Cr). The morphological and structural properties of the specimens were investigated using X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller analysis, energy dispersive Xray spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The electrode materials were also electrochemically investigated using cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge-discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy techniques in 6 M KOH electrolyte. Because of synergistic effect of metal oxides and carbon, the obtained samples showed excellent performance; in a way that Cr2O3/C and Fe Oy/C showed high specific capacitance of 420 F g(-1) and 114 F g(-1) at current density of 2 A g(-1), respectively. The Cr2O3/C electrode also displayed high rate capability even at scan rate of 1500 mV s(-1). Moreover, we successfully developed an asymmetric supercapacitor in which Cr2O3/C served as positive electrode and Fe Oy/C served as negative electrode. The asymmetric device can deliver an energy density of 9.6 W h kg(-1) and power density of 8000 W kg(-1), with 93% capacitance retention after 3000 charge-discharge cycles. These outcomes show that the MOF-derived metal oxide/carbon composite can be regarded as a promising development for advanced electrode materials for applying in supercapacitors.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.053
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
XPS primary excitation spectra of Zn 2p, Fe 2p, and Ce 3d from ZnO, α‐Fe2O3, and CeO2
Pauly, N.; Yubero, F.; Espinós, J.P.; Tougaard, S.Surface and Interface Analysis, 51 (2019) 353-360

Metal oxides are important for current development in nanotechnology. X‐ray photoelectron spectroscopy(XPS) is a widely used technique to study the oxidation states of metals, and a basic understanding of the photoexcitation process is important to obtain the full information from XPS. We have studied core level excitations of Zn 2p, Fe 2p, and Ce 3d photoelectron emissions from ZnO, α‐Fe2O3, and CeO2. Using an effective energy‐differential XPS inelastic‐scattering cross section evaluated within the semiclassical dielectric response model for XPS, we analysed the experimental spectra to determine the corresponding primary excitation spectra, ie, the initial excitation processes. We find that simple emission (Zn 2p) as well as complex multiplet photoemission spectra (Fe 2p and Ce 3d) can be quantitatively analysed with our procedure. Moreover, for α‐Fe2O3, it is possible to use the software package CTM4XAS (Charge Transfer Multiplet program for X‐ray Absorption Spectroscopy) to calculate its primary excitation spectrum within a quantum mechanical model, and it was found to be in good agreement with the spectrum determined by analysis of the experiment.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.6587
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Comparative studies on electrochemical energy storage of NiFe-S nanoflake and NiFe-OH towards aqueous supercapacitor
Naseri, M; Moradi, M; Hajati, S; Espinos, JP; Kiani, MAJournal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 30 (2019) 4499-4510

In this study, electrochemical energy storage performances of an efficient Ni-Fe sulfide and hydroxide supported on porous nickel foam are compared. X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-rayphotoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) results confirmed the formation of Ni-Fe-S and Ni-Fe-OH electrodes. In addition, Brunauer-Emmett Teller (BET) was used to determine the specific surface area of the prepared materials. Moreover, the morphologies were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The brilliant characteristics of Ni-Fe-S could be attributed to transport acceleration in electrolyte ions and electrons, occurrence of redox reactions as well as the higher conductivity of the sample. From stand point of comparison, the capacitance of Ni-Fe-S is more than that of Ni-Fe-OH. Therefore, the exchange of O2- with S2- in Ni-Fe-OH lattice obviously improves the electrochemical performance. The as-fabricated Ni-Fe sulfide electrode exhibits a tremendous specific capacitance of 884.9Fg(-1) at 1A g(-1). Furthermore, an assembled asymmetric supercapacitor device using the activated carbon as negative electrode and this smart configuration (Ni-Fe-S) as positive electrode also provided a maximum specific power and specific energy of 8000Wkg(-1), 37.9 Whkg(-1), respectively. Also, it shows cycling stability with 88.8% capacitance retention after 1700 cycles in aqueous electrolyte, demonstrating its potential application in the next-generation high-performance supercapacitors used for energy storage.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.1007/s10854-019-00738-x
Reactividad de Sólidos - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Microstructure, interfaces and properties of 3YTZP ceramic composites with 10 and 20 vol% different graphene-based nanostructures as fillers
Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Rojas, TC; Jimenez-Pique, E; Lopez-Pernia, C; Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, AJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 777 (2019) 213-224
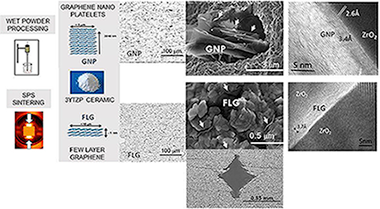
The graphene family comprises not only single layer graphene but also graphene-based nanomaterials (GBN), with remarkably different number of layers, lateral dimension and price. In this work, two of these GBN, namely graphene nanoplatelets (GNP) with n similar to 15-30 layers and few-layer graphene (FLG) with n < 3 layers have been evaluated as fillers in 3 mol% yttria stabilized tetragonal zirconia (3YTZP) ceramic composites. Composites with 10 and 20 vol% GNP or FLG have been fabricated by wet powder processing and spark plasma sintering (SPS) and the influence of the content and number of layers of the graphene-based filler has been assessed. For both graphene-based fillers, an intermediate zirconia oxycarbide has been detected in the grain boundaries. The lower stacking degree and much more homogeneous distribution of the FLG, revealed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), can improve load transfer between the GBNs and the ceramic matrix. However, high FLG contents lower densification of the composites, due partly to the larger FLG interplanar spacing also estimated by TEM. The hardness (both Vickers and nanoindentation) and the elastic modulus decrease with increased GBN content and with improved graphene dispersion. The FLG greatly inhibit the crack propagation that occur perpendicular to their preferential orientation plane. The composites with thinner FLG have higher electrical conductivity than those with GNP. The highest electrical conductivity is achieved by composites with 20 vol% FLG in the direction perpendicular to the compression axis during sintering, sigma(perpendicular to) = 3400 +/- 500 Sm-1.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.336
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Sustainable polycondensation of multifunctional fatty acids from tomato pomace agro-waste catalyzed by tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate
J.A. Heredia-Guerrero, G. Caputo, S. Guzmán-Puyol, G. Tedeschi, A. Heredia, L. Ceseracciu, J.J. Benítez, A. AthanassiouMaterials Today Sustainability, 3-4 (2019) 100004
Bioplastics were prepared from the fatty fraction (i.e., unsaturated and polyhydroxylated fatty acids) of tomato pomace agro-wastes. Aliphatic polyesters were synthesized at different temperatures (125, 150, and 175 °C), reaction times (0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 3, 5, and 7 h), and amounts of tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate (0, 0.02, 0.05, and 0.10 mmol) used as a catalyst. The rate constants and activation energies were calculated from infrared spectra. The right combination of reaction temperature and amount of catalyst improved the reaction kinetics (apparent k from ∼1 to ∼8.5 h−1), whereas the activation energy was reduced from ∼39 without catalyst to ∼28 kJ/mol when tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate was present. Glass transitions between ca. −25 and ∼0 °C were measured by differential scanning calorimetry, strictly depending on the degree of polymerization. The amorphous character of the samples was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. Young's modulus and hardness were calculated from indentation tests and were typical of soft materials, although increased as the polycondensation reaction progressed. High water-contact angles (maximum value ∼109°) and low water uptakes (minimum value ∼2.1%) were determined. Physical properties were compared with those of common man-made plastics and polymers, finding that these tomato pomace bioplastics could be their realistic alternatives.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2018.12.001
Degradation processes of historic metal threads used in some Spanish and Portuguese ornamentation pieces
Duran, A; Perez-Maqueda, R; Perez-Rodriguez, JLJournal of Cultural Heritage, 36 (2019) 135-142
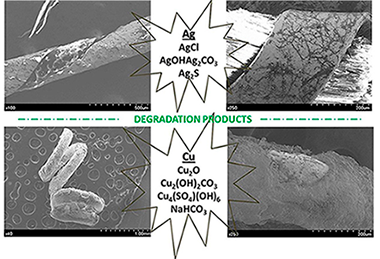
The degradation processes that occurred on metal threads applied in the embroidery used for clothing and in the ornamentation of sculptures, the Sevillian Holy Week processions, and Portuguese and Spanish palace and museum are thoroughly analyzed. Some threads from the 14th and 18–19th centuries were considered. In the metal threads, sulphur- and chlorine-based compounds were detected either individually or together, depending on the degradation process. Basic silver carbonate, sodium bicarbonate and copper-based compounds were also observed. The different degradation processes were attributed to different factors, such as environmental contamination, degradation of the fibrous cores, and inadequate cleaning and/or mechanical treatments.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2018.09.006
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Synthesis of sol-gel pyrophyllite/TiO2 heterostructures: Effect of calcination temperature and methanol washing on photocatalytic activity
El Gaidoumi, A.; Doña Rodríguez, J.M.; Pulido Melián, E.; González-Díaz, O.M.; Navío Santos, J.M.; El Bali, B.; Kherbeche, A.Surfaces and Interfaces, 14 (2019) 19-25
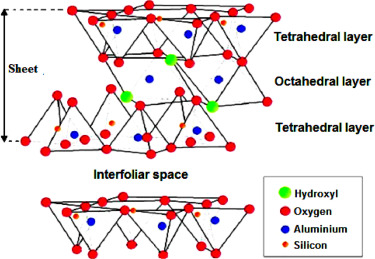
We successfully synthesized an efficient photoactive pyrophyllite/TiO2 heterostructures using a sol-gel route at ambient temperature. The samples were prepared by exfoliation of a pyrophyllite layered-type clay by TiO2. The prepared samples exhibited strong photocatalytic activity for the degradation of phenol. The heterostructure PTi750 (SBET = 16.58 m2/g) calcined at 750 °C, in which the mixed phases of anatase and rutile exist (52.2% anatase/10.7% rutile), showed the highest photocatalytic activity against commercial TiO2Aeroxide P25. The methanol washed PTi750 was 5 times faster than the corresponding unwashed sample; phenol was totally degraded with a TOC reduction of 89.2%. The materials have been characterized by: X-ray diffraction (XRD), Diffuse reflectance UV–vis spectrophotometry (UV–Vis DRS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and BET specific surface area.
March, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfin.2018.10.003
- ‹ previous
- 73 of 214
- next ›














