Artículos SCI
2020
2020
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Advances in the implementation of PVD-based techniques for the preparation of metal catalysts for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride
Arzac, GM; Fernandez, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 58 (2020) 33288-33309
Show abstract ▽
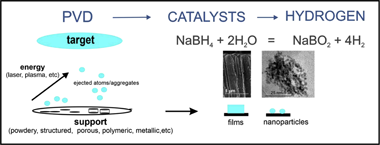
Sodium borohydride constitutes a safe alternative for the storage of hydrogen with a high gravimetric content. Catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride permits on-demand hydrogen generation for multiple applications. In this field, the rational design of efficient metal catalysts deposited on structured supports is highly desirable. For most reactions, chemical methods are the most commonly used methods for the preparation of supported metal catalysts. Physical vapour deposition techniques are emerging as an alternative for the preparation of catalytic materials because of their multiple advantages. They permit the one-step deposition of catalysts on structured supports with controlled microstructure and composition, avoiding the multi-step procedures and the generation of hazardous by-products associated with chemical routes.
In this short review, we will describe the available literature on the application of physical vapour deposition techniques for the preparation of supported metal catalysts for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. The effects of the deposition parameters on the properties of the catalytic materials will be discussed, and strategies for further improvement will be proposed. Here, we also present our new results on the study of nanoporous Pt catalysts that are prepared through the chemical dealloying of magnetron sputtered Pt-Cu thin films for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. We discuss the capabilities of the technique to tune the microstructure from columnar to closed porous microstructures, which, coupled with dealloying, produces more active supported catalysts with lower noble metal loading. At the end, we briefly mention the application of PVD for the preparation of supported catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane, another hydrogen generating reaction of high interest nowadays.
Noviembre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.09.041
Reactividad de Sólidos
Graphene-coated Ti-Nb-Ta-Mn foams: A promising approach towards a suitable biomaterial for bone replacement
Lascano, S; Chavez-Vasconez, R; Munoz-Rojas, D; Aristizabal, J; Arce, B; Parra, C; Acevedo, C; Orellana, N; Reyes-Valenzuela, M; Gotor, FJ; Arevalo, C; Torres, YSurface & Coatings Technology, 401 (2020) 126250
Show abstract ▽
The design of bone implants with proper biological and mechanical properties remains a challenge in medical implantology. The use of bioactive coatings has been shown to improve the biocompatibility of the implant surface. In this study, a new approach including porous scaffolds, beta-Ti alloys and nanocoatings to design new bone implants is presented. Porous Ti-Nb-Ta-xMn alloys (x: 2, 4, and 6 wt%) substrates were obtained by powder metallurgy and the effect of the porosity and Mn content on mechanical properties was studied. CVD single-layer graphene was transferred onto the porous substrates that presented the best mechanical response (x: 4 wt%) for further evaluation of in vitro cell behavior (biocompatibility and cell adhesion). Cytotoxicity and biocompatibility tests confirmed that cell adhesion and proliferation were successfully achieved on graphene-coated porous substrates, confirming these systems are potential candidates for using in partial bone tissue replacement.
Noviembre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126250
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Microstructure and thermal conductivity of Si-Al-C-O fiber bonded ceramics joined to refractory metals
Vera, MC; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, M; Casalegno, V; Balagna, C; Ramirez-Rico, JMaterials Letters, 276 (2020) 128203
Show abstract ▽
We explore joining Si-Al-C-O fiber-bonded ceramics to Cu-clad-Mo using an Ag-Ti-Cu brazing alloy. A temperature of 900 degrees C and times in the range of 10-20 min are required to obtain sound joints irrespectively of the fiber orientation. The reaction layer is 1-2 mu m thick and free of pores and defects. The thermal conductivity of the joined samples is well described considering that the metal and the ceramic are in series for thermal resistance. This implies that the joint is highly conductive and forms an almost perfect
Octubre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128203
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Unraveling Discharge and Surface Mechanisms in Plasma-Assisted Ammonia Reactions
Navascues, P; Obrero-Perez, JM; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8 (2020) 14855-14866
Show abstract ▽
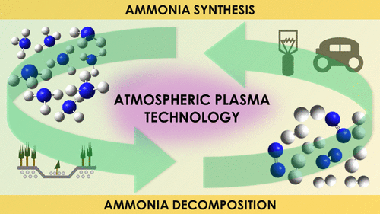
Current studies on ammonia synthesis by means of atmospheric pressure plasmas respond to the urgent need of developing less environmentally aggressive processes than the conventional Haber-Bosch catalytic reaction. Herein, we systematically study the plasma synthesis of ammonia and the much less investigated reverse reaction (decomposition of ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen). Besides analyzing the efficiency of both processes in a packed-bed plasma reactor, we apply an isotope-exchange approach (using D-2 instead of H-2) to study the reaction mechanisms. Isotope labeling has been rarely applied to investigate atmospheric plasma reactions, and we demonstrate that this methodology may provide unique information about intermediate reactions that, consuming energy and diminishing the process efficiency, do not effectively contribute to the overall synthesis/decomposition of ammonia. In addition, the same methodology has demonstrated the active participation of the interelectrode material surface in the plasma-activated synthesis/decomposition of ammonia. These results about the involvement of surface reactions in packed-bed plasma processes, complemented with data obtained by optical emission spectroscopy analysis of the plasma phase, have evidenced the occurrence of inefficient intermediate reaction mechanisms that limit the efficiency and shown that the rate-limiting step for the ammonia synthesis and decomposition reactions are the formation of NH* species in the plasma phase and the electron impact dissociation of the molecule, respectively.
Octubre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c04461
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Multiple pollutants removal by functionalized heterostructures based on Na-2-Mica
Pazos, MC; Bravo, LR; Ramos, SE; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 196 (2020) 105749
Show abstract ▽
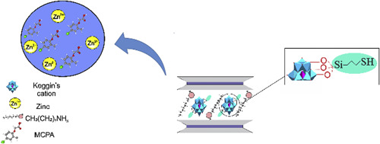
Organomica, C8-2-Mica, was obtained from a high charged synthetic mica, Na-2-Mica, by cation exchange reaction with octylammonium cations and these were used to host other bulky guest species such as polyhydroxy aluminium cations, Al(13)20. The hydrolization of 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTMS) allowed the covalent attachment with hydroxyl groups of the oligomeric cation, providing thiol groups that create specific adsorption sites, Al(13)20/SH. The structure of the adsorbents was analysed by XRD and Infrared spectroscopy and these were tested as an adsorbent for the removal of zinc and herbicide MCPA from aqueous solutions. C8-2-Mica was the best adsorbent for MCPA and thiol groups favoured the adsorption of Zn2+. Moreover, Al(13)20/SH showed excellent adsorptive properties for the simultaneous adsorption of MCPA and Zn2+.
Octubre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105749
- ‹ anterior
- 101 of 420
- siguiente ›














