Artículos SCI
2020
2020
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Internal quantum efficiency and time signals from intensity-modulated photocurrent spectra of perovskite solar cells
Riquelme, A; Galvez, FE; Contreras-Bernal, L; Miguez, H; Anta, JAJournal of Applied Physics, 128 (2020) 133103
Show abstract ▽
Intensity Modulated Photocurrent Spectroscopy (IMPS) is a small-perturbation optoelectronic technique that measures the quantum efficiency of a photoelectrochemical device as a function of optical excitation frequency. Metal Halide Perovskites (MHPs) are mixed electronic-ionic semiconductors with an extraordinary complex optoelectronic behavior and a record efficiency surpassing 25%. In this paper, we propose a simplified procedure to analyze IMPS data in MHPs based on the analysis of the internal quantum efficiency and the time signals featuring in the frequency spectra. In this procedure, we look at the change of each signal when optical excitation wavelength, photon flux, and temperature are varied for an archetypical methyl ammonium lead iodide solar cell. We use drift-diffusion modeling and comparison with relatively simpler dye-sensitized solar cells (DSC) with viscous and non-viscous electrolytes to help us to understand the origin of the three signals appearing in MHP cells and the measurement of the internal quantum efficiency.
Octubre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1063/5.0013317
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Upgrading the PtCu intermetallic compounds: The role of Pt and Cu in the alloy
Castillo, R; Garcia, ED; Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Sarria, FR; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 356 (2020) 390-398
Show abstract ▽
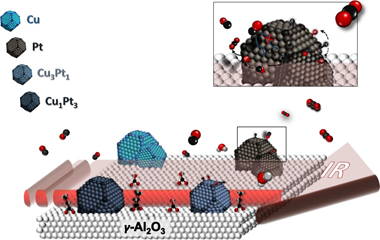
This work is devoted to the study of the role of both metals in the intermetallic PtxCuy/ γ Al2O3 catalysts commonly employed in CO-PROX reaction. Therefore, monometallic Pt and Cu based catalysts and PtCu intermetallic compound with different molar ratios (Pt3Cu1 and Pt1Cu3) supported catalysts were carefully synthesized and deeply characterized. Room temperature CO adsorptions by FTIR spectroscopy were carried out on the mono- and intermetallic catalysts being the monometallic catalyst determinant for the study. From the analysis of the nature of the platinum surface in Pt/ γ Al2O3, we have demonstrated that the role of Pt sites is based in the CO dissociation for the CO2 formation and also how the platinum surface is partially blocked by leftovers from the synthesis. Moreover, the study of the Cu/ γ Al2O3 and the bimetallic catalysts PtxCuy/ γ Al2O3 allowed elucidating the effect of the copper in the metallic site and support interphase as well as the role of copper in the hydrocarbon oxidation.
Octubre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.11.026
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tribological performance of Nb-C thin films prepared by DC and HiPIMS
Sala, N; Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Cruz, M; Caro, J; Colominas, CMaterials Letters, 277 (2020) 12834
Show abstract ▽
Nanostructured NbC thin films with variable contents of Nb and C were prepared by direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering, and for the first time, via high power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) searching for an improvement in the tribological properties. X-ray diffraction shows that increasing the carbon incorporation, the crystalline composition evolves from Nb2C to NbC phase. Further carbon enrichment leads to a nanocomposite structure formed by small NbC crystals (8-14 nm) dispersed in a-C matrix. The friction coefficient varied from high friction (0.8) to low friction (0.25) and the hardness values between 20 and 11 GPa depending on the film composition. A densification of the coatings by changing the methodology from DC to HiPIMS was not observed.
Octubre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128334
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Free-Carbon Surface for PtCu Nanoparticles: An In Situ Near Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study
Castillo, R; Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; Centeno, MA; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 19046-19056
Show abstract ▽

Usually, nanoparticle synthesis methodologies require the use of organic molecules (capping agent, solvent molecules, etc.), which results in carbon deposits on the nanoparticle surface. These residues modify the surface properties mainly affecting the catalytic behavior. In this work, unsupported poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP)-stabilized PtCu (1:3 molar ratio) bimetallic alloy nanoparticles were synthetized and characterized. An alternative surface cleaning method has been designed, which successfully removes the presence of organic fragments. To address this key issue, we have combined a first nanoparticle washing step with a near ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (NAPXPS) study in order to obtain a clean active site and the total understanding of the carbon elimination mechanism. The dynamic evolution of the surface organic species composition under different gas mixtures at 750 mTorr and 350 degrees C has been studied, and only under CO2 exposure, NAPXPS analysis revealed a total availability of the active site by the removal of the organic nanoparticle coating.
Septiembre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04713
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The wrinkling concept applied to plasma-deposited polymer-like thin films: A promising method for the fabrication of flexible electrodes
Thiry, Damien; Vinx, Nathan; Damman, Pascal; Aparicio, Francisco F.J.; Tessier, Pierre-Yves; Moerman, David; Leclere, Philippe; Godfroid, Thomas; Deprez, Sylvain; Snyders, RonyPlasma Processes and Polymers, 17 (2020) e2000119
Show abstract ▽
In this communication, we report on an innovative solvent-free method that allows for the design of nano-/micropatterns with tuneable dimensions. Our approach is based on the spontaneous wrinkling phenomenon taking place in a bilayer system formed by a mechanically responsive bottom plasma polymer layer and a top aluminum thin film. The dimensions of the wrinkles can be adjusted in a wide range (i.e., from nanometer to micrometer range) by modulating the cross-linking density as well as the thickness of the plasma polymer layer. Finally, it is demonstrated that these wrinkled surfaces could efficiently be used as flexible electrodes. The whole set of our data unambiguously reveals the attractiveness of our method for the fabrication of the micro-/nanopattern with dimensions on demand.
Septiembre, 2020 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000119
- ‹ anterior
- 102 of 420
- siguiente ›














