Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Noble Metal Supported on Activated Carbon for "Hydrogen Free" HDO Reactions: Exploring Economically Advantageous Routes for Biomass Valorisation
Jin, W; Santos, JL; Pastor-Perez, L; Gu, S; Centeno, MA; Reina, TRChemcatchem (2019) 4434-4441
Show abstract ▽

An innovative route for bio‐compounds upgrading via “hydrogen‐free” hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) is proposed and evaluated using guaiacol as a model compound in a high‐pressure batch reactor. Experimental results showed that noble metal supported on activated carbon catalysts are able to conduct tandem multiple steps including water splitting and subsequent HDO. The activity of Ru/C catalyst is superior to other studied catalysts (i. e. Au/C, Pd/C and Rh/C) in our water‐only HDO reaction system. The greater dispersion and smaller metal particle size confirmed by the TEM micrographs accounts for the better performance of Ru/C. This material also presents excellent levels of stability as demonstrated in multiple recyclability runs. Overall, the proposed novel approach confirmed the viability of oxygenated bio‐compounds upgrading in a water‐only reaction system suppressing the need of external H2 supply and can be rendered as a fundamental finding for the economical biomass valorisation to produce added value bio‐fuels.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900841
Structural and compositional analysis of Co-based coatings after catalytic tests for the sodium borohydride hydrolysis
Beltran, AMMaterials Research Express, 6 (2019) art. 085511
Show abstract ▽
The use of Co-based catalysts for the sodium borohydride hydrolysis for hydrogen production is a well-known process as a source of clean energy, although its mechanisms are still under discussion. With the aim of acquiring a deeper knowledge about this catalytic process, three different catalysts (Co, CoC and CoB) were deposited as a thin film layer by magnetron sputtering onto a polymeric membrane, used as a substrate and analyzed by advance transmission and scanning-transmission electron microscopy techniques (STEM). Structural and compositional characterizations, by electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), have been performed on the coatings before and after their use as catalysts on the sodium borohydride reaction for 90 min, to check the production of hydrogen. Results have shown the formation of CoxB nanoflakes and other Co-based compounds over the catalysts and related to their catalytic activity. Knowing the changes in the structure and composition of the catalysts is key to understanding their catalytic behavior, activity and durability. Among the analyzed catalysts, the Co-C presents better activity during the first cycles, which is related to a larger formation of CoxB.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab1e27
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
MTA HP Repair stimulates in vitro an homogeneous calcium phosphate phase coating deposition
Jiménez-Sánchez, M.D.C.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Díaz-Cuenca, A.Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, 11 (2019) e322-e326
Show abstract ▽

Background: To study the mineralization capacity in vitro of the bioceramic endodontic material MTA HP Repair. Material and Methods: Bioactivity evaluation in vitro was carried out, by soaking processed cement disk in simulated body fluid (SBF) during 168 h. The cement surface was studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX). Release to the SBF media of ionic degradation products was monitored using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Results: FT-IR showed increasing formation of phosphate phase bands at 1097, 960, 607 and 570 cm -1 with prolonged SBF soaking. FEG-SEM analysis reveals that HP produces a effectively surface covering consisting in homogeneous spherical phosphate phase aggregates with an average diameter of 0.5 -1 .0 μm. EDX analysis comparing un-treated (hydrated), 24 h and 72 h SBF treated surfaces of MTA HP Repair revealed phosphate deposition after 24 h, with high phosphorous/silicon element ratio signal measured after 24 h, indicating a very high phosphate phase deposition for this material. Conclusions: The study shows that MTA HP Repair produces a quick and effective bioactive response in vitro in terms of crystalline calcium phosphate surface coating formation. The high bioactive response of MTA HP Repair makes it an interesting candidate for endodontic use as repair cement.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.4317/jced.55661
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Physicochemical parameters - hydration performance relationship of the new endodontic cement MTA Repair HP
Jiménez-Sánchez, M.D.C.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Díaz-Cuenca, A.Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, 11 (2019) e739-e744
Show abstract ▽

Background: To characterize the chemical composition and textural parameters of the MTA Repair HP precursor powder and their influence to hydration performance. Material and Methods: Un-hydrated precursor material was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), laser diffraction (LD), N2 physisorption and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM). Setting time was assessed according to ASTM specification C 266. Hydrated material was analysed by XRD, FT-IR, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis and FEG-SEM. Results: Ca3SiO5 and Ca2SiO4, in addition to CaWO4 as radiopacifier are the main compositional phases. Other measured parameters indicate high specific surface area of 4.8 m2 g-1, high aluminium content of 1.7 wt.% and low initial and final setting times of 12 and 199 min, respectively. Singular microstructural features consisting of high aspect ratio nanoparticles are main constituents of un-hydrated precursor. Besides, FEM-SEM observation shows notably growth of hexagonal shaped plate-like morphologies homogeneously distributed along the sample during hydration process. Conclusions: The short setting time measured for HP Repair, is correlated with high surface area of precursor powder, high Al content and the absence of compositional sulphate phases.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.4317/jced.56013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bio-based composite fibers from pine essential oil and PLA/PBAT polymer blend. Morphological, physicochemical, thermal and mechanical characterization
Hernandez-Lopez, M; Correa-Pacheco, ZN; Bautista-Banos, S; Zavaleta-Avejar, L; Benitez-Jimenez, JJ; Sabino-Gutierrez, MA; Ortega-Gudino, PMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 234 (2019) 345-353
Show abstract ▽
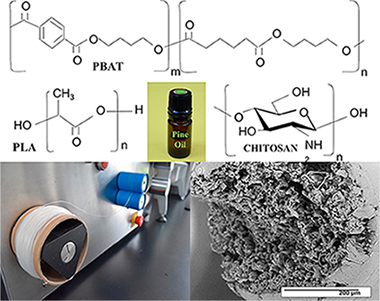
Biodegradable aliphatic polyesters are an alternative to reduce the use of synthetic plastic materials that cause severe damage to the environment. Formulations based on poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), were mixed in a 60:40 ratio, adding different concentrations of pine essential oil through the use of extrusion technology to obtain biodegradable polymer fibers. Some formulations were coated with chitosan. All the elaborated fibers were characterized by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy-Attenuated Total Reflection (FTIR-ATR), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and mechanical properties. The SEM studies showed that the PBAT improves the tenacity and provides greater elasticity promoting the interaction between the blends phases with fibril formation. In the FTIR-ATR analysis, compatibility between the blends was observed due to a possible interaction of the carbonyl group of PBAT with PLA. The DSC and the mechanical properties showed partial miscibility of the blends, indicating, that the plasticizing action of the essential oil gave greater mobility, flexibility, less rigidity and crystallization in the blends. A lower Young's modulus and greater elongation at break was also observed.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.01.034
- ‹ anterior
- 129 of 420
- siguiente ›














