Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Multifunctional antimicrobial chlorhexidine polymers by remote plasma assisted vacuum deposition
Mora-Boza, A; Aparicio, FJ; Alcaire, M; Lopez-Santos, C; Espinos, JP; Torres-Lagares, D; Borras, A; Barranco, AFrontiers of chemical science and engineering, 13 (2019) 330-339
Show abstract ▽

Novel antibacterial materials for implants and medical instruments are essential to develop practical strategies to stop the spread of healthcare associated infections. This study presents the synthesis of multifunctional antibacterial nanocoatings on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) by remote plasma assisted deposition of sublimated chlorhexidine powders at low pressure and room temperature. The obtained materials present effective antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli K12, either by contact killing and antibacterial adhesion or by biocide agents release depending on the synthetic parameters. In addition, these multifunctional coatings allow the endure hydrophilization of the hydrophobic PDMS surface, thereby improving their biocompatibility. Importantly, cell-viability tests conducted on these materials also prove their non-cytotoxicity, opening a way for the integration of this type of functional plasma films in biomedical devices.
Junio, 2019 | DOI: 10.1007/s11705-019-1803-6
Reactividad de Sólidos
Manufacturing optimisation of an original nanostructured (beta plus gamma)-TiNbTa material
Garcia-Garrido, C; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, C; Torrecillas, R; Perez-Pozo, L; Salvo, C; Chicardi, EJournal of Materials Research and Technology-JMR&T, 8 (2019) 2573-2585
Show abstract ▽
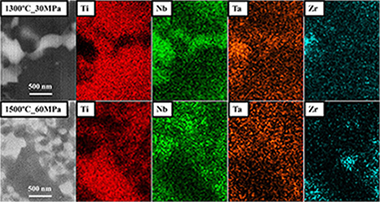
An original (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material was manufactured by an optimised powder metallurgy treatment, based on a mechanical alloying (MA) synthesis, carried out at low energy, and a subsequently field assisted consolidation technique, the pulsed electric current sintering (PECS). The successful development of this (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material was possible by the optimisation of the milling time (60 h) for the MA synthesis and the load and sintering temperature for the PECS (30 MPa and 1500 degrees C), as key parameters. Furthermore, the selected heating and cooling rates were 500 degrees C min(-1) and free cooling, respectively, to help maintain the lowest particle size and to avoid the formation of a detrimental high stiffness, hexagonal (alpha)-Ti alloy. All these optimised experimental conditions enabled the production of a full densified (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa material, with partially nanostructured areas and two TiNbTa alloys, with a body centred cubic (beta) and a novel face-centred cubic (gamma) structures. The interesting microstructural characteristics gives the material high hardness and mechanical strength that, together with the known low elastic modulus for the beta-Ti alloys, makes them suitable for their use as potential biomaterials for bone replacement implants.
Mayo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.03.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Phosphate-type supports for the design of WGS catalysts
Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 244 (2019) 853-862
Show abstract ▽
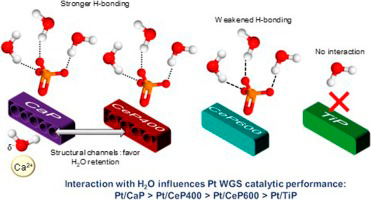
The importance of water availability during the WGS reaction has been extensively reported. Thus, the search of new supports able to interact with the water molecule is of great importance. In this work, a series of phosphate type supports containing Ce, Ca and Ti have been studied, demonstrating that water interaction with the support is closely related to the textural properties, surface composition and crystal structure of the solids. Additionally, DRIFTS results showed that different interaction mechanisms with the water molecule occur depending on the support. The system containing Ca dissociates the water molecule and interacts with it via the phosphate and Ca2+ ions. However, the Ce systems retain water in its molecular form, which interacts with the solids via hydrogen bonding with the phosphate groups. On the other hand, the Ti system experiences a loss of phosphorous, presenting a low degree of interaction with the water molecule. Additionally, the behavior of the supports with water has been successfully related to the WGS catalytic activity of the corresponding phosphate supported Pt catalysts.
Mayo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.022
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Coupling of WO3 with anatase TiO2 sample with high {001} facet exposition: Effect on the photocatalytic properties
Lara, M.A.; Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Navío, J.A.; Sánchez-Cid, P.; Hidalgo, M.C.Catalysis Today, 328 (2019) 142-148
Show abstract ▽
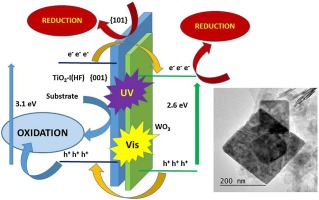
A highly faceted {001} TiO2 catalyst was hydrothermally synthesized by using Ti(IV)-isopropoxide precursor with aqueous HF addition. WO3 was synthesized by following a reported method. Coupled TiO2-WO3 samples were synthesized by adding the corresponding amount of WO3 to fluorinated TiO2 gel followed by a hydrothermal treatment. Additionally the synthesized systems were characterized by using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) and N2-adsorption (BET) for specific surface area determination. The photocatalytic activity of the single and coupled oxides was measured by means of three model reactions: the photo-oxidation of phenol (as a colourless substrate) and methyl orange (as a dye) and the photoreduction of Cr(VI) as K2Cr2O7. The coupling of WO3 with a highly faceted {001} TiO2 makes it possible to optimize the photocatalytic properties of the faceted material. In fact, {001} faceted TiO2 by itself presents a substantial improvement with respect to commercial TiO2(P25), as it can implement its photoactivity after the incorporation of WO3 with promising results, which can reduce the limitations of TiO2 in terms of its photoactivity, taking advantage of a higher percentage of solar radiation.
Mayo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Liquid switchable radial polarization converters made of sculptured thin films
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rico, VJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Arteaga, O; Bertran, E; Serna, R; Gonzalez-Elip, AR; Yubero, FApplied Surface Science, 475 (2019) 230-236
Show abstract ▽
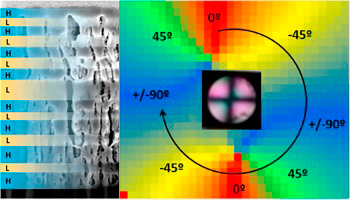
A radial polarization converter is a super-structured optical retarder that converts a conventional linearly polarized light beam into a structured beam with radial or azimuthal polarization. We present a new type of these sophisticated optical elements, which is made of porous nanostructured sculptured single thin films or multilayers prepared by physical vapor deposition at an oblique angle. They are bestowed with an axisymmetric retardation activity (with the fast axis in a radial configuration). In particular, a Bragg microcavity multilayer that exhibits a tunable transmission peak in the visible range with a retardance of up to 0.35 rad has been fabricated using this methodology. Owing to the highly porous structure of this type of thin films and multilayers, their retardance could be switched off by liquid infiltration. These results prove the possibility of developing wavelength dependent (through multilayer optical design) and switchable (through vapor condensation or liquid infiltration within the pore structure) radial polarization converters by means of oblique angle physical vapor deposition.
Mayo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.200
- ‹ anterior
- 133 of 420
- siguiente ›














