Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Coupling of WO3 with anatase TiO2 sample with high {001} facet exposition: Effect on the photocatalytic properties
Lara, M.A.; Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Navío, J.A.; Sánchez-Cid, P.; Hidalgo, M.C.Catalysis Today, 328 (2019) 142-148
Show abstract ▽
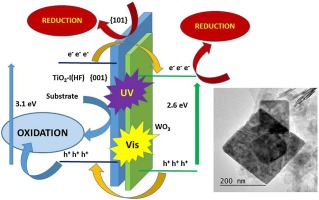
A highly faceted {001} TiO2 catalyst was hydrothermally synthesized by using Ti(IV)-isopropoxide precursor with aqueous HF addition. WO3 was synthesized by following a reported method. Coupled TiO2-WO3 samples were synthesized by adding the corresponding amount of WO3 to fluorinated TiO2 gel followed by a hydrothermal treatment. Additionally the synthesized systems were characterized by using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) and N2-adsorption (BET) for specific surface area determination. The photocatalytic activity of the single and coupled oxides was measured by means of three model reactions: the photo-oxidation of phenol (as a colourless substrate) and methyl orange (as a dye) and the photoreduction of Cr(VI) as K2Cr2O7. The coupling of WO3 with a highly faceted {001} TiO2 makes it possible to optimize the photocatalytic properties of the faceted material. In fact, {001} faceted TiO2 by itself presents a substantial improvement with respect to commercial TiO2(P25), as it can implement its photoactivity after the incorporation of WO3 with promising results, which can reduce the limitations of TiO2 in terms of its photoactivity, taking advantage of a higher percentage of solar radiation.
Mayo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Liquid switchable radial polarization converters made of sculptured thin films
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rico, VJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Arteaga, O; Bertran, E; Serna, R; Gonzalez-Elip, AR; Yubero, FApplied Surface Science, 475 (2019) 230-236
Show abstract ▽
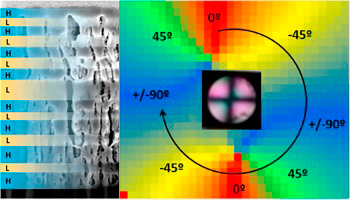
A radial polarization converter is a super-structured optical retarder that converts a conventional linearly polarized light beam into a structured beam with radial or azimuthal polarization. We present a new type of these sophisticated optical elements, which is made of porous nanostructured sculptured single thin films or multilayers prepared by physical vapor deposition at an oblique angle. They are bestowed with an axisymmetric retardation activity (with the fast axis in a radial configuration). In particular, a Bragg microcavity multilayer that exhibits a tunable transmission peak in the visible range with a retardance of up to 0.35 rad has been fabricated using this methodology. Owing to the highly porous structure of this type of thin films and multilayers, their retardance could be switched off by liquid infiltration. These results prove the possibility of developing wavelength dependent (through multilayer optical design) and switchable (through vapor condensation or liquid infiltration within the pore structure) radial polarization converters by means of oblique angle physical vapor deposition.
Mayo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.200
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Hydrophobicity, Freezing Delay, and Morphology of Laser-Treated Aluminum Surfaces
Rico, VJ; Lopez-Santos, C; Villagra, M; Espinos, JP; de la Fuente, GF; Angurel, LA; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARLangmuir, 35 (2019) 6483-6491
Show abstract ▽
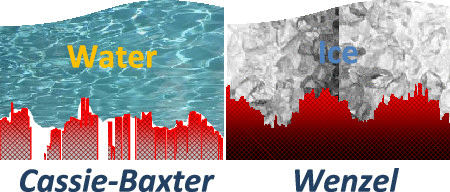
Until recently, superhydrophobicity was considered as a hint to predict surface icephobicity, an association of concepts that is by no means universal and that has been proven to depend on different experimental factors and material properties, including the actual morphology and chemical state of surfaces. This work presents a systematic study of the wetting and freezing properties of aluminum Al6061, a common material widely used in aviation, after being subjected to nanosecond pulsed IR laser treatments to modify its surface roughness and morphology. All treated samples, independent of their surface finishing state, presented initially an unstable hydrophilic wetting behavior that naturally evolved with time to reach hydrophobicity or even superhydrophobicity. To stabilize the surface state and to bestow the samples with a permanent and stable hydrophobic character, laser-treated surfaces were covered with a thin layer of CFx prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. A systematic comparison between freezing delay (FD) and wetting properties of water droplets onto these plasma-/polymer-modified laser-treated surfaces that, under conditions where a heterogeneous nucleation mechanism prevails, surface morphology rather than the actual value of the surface roughness parameter the key feature for long FD times. In particular, it is found that surface morphologies rendering a Cassie-Baxter wetting regime longer FDs than those characterized by a Wenzel-like wetting state. It is that laser treatment, with or without additional coverage with thin CFx coatings, affects wetting and ice formation behaviors and might be an efficient procedure to mitigate icing problems on metal surfaces.
Mayo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00457
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
BixTiyOz-Fe multiphase systems with excellent photocatalytic performance in the visible
Zambrano, P.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Catalysis Today, 328 (2019) 136-141
Show abstract ▽
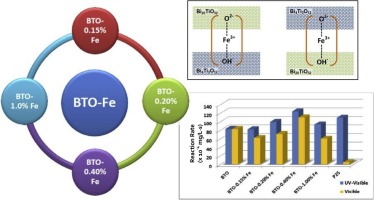
New photocatalysts based on bismuth titanates doped with iron with outstanding visible photocatalytic activity were prepared by a facile hydrothermal method followed by incipient wetness impregnation. The starting material was composed by three phases; majority of Bi20TiO32 closely interconnected to Bi4Ti3O12 and amorphous TiO2. Fe doping increased the already very high visible activity of the original material. The high visible activity showed by these materials could be ascribed to a combination of several features; i.e. low band gap energy value (as low as 1.78 eV), a structure allowing a good separation path for visible photogenerated electron-holes pairs and a relatively high surface area. Fe doping could be acting as bonding paths for the bismuth titanates phases, and the amount of Fe on the surface was found to be a crucial parameter on the photocatalytic activity of the materials. Visible activity of the best photocatalyst was superior to UV-Activity of commercial TiO2 P25 used as reference in same experimental conditions.
Mayo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.032
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Operando Spectroscopic Evidence of the Induced Effect of Residual Species in the Reaction Intermediates during CO2 Hydrogenation over Ruthenium Nanoparticles
Navarro-Jaen, S; Szego, A; Bobadilla, LF; Laguna, OH; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemcatchem, 11 (2019) 2063-2068
Show abstract ▽
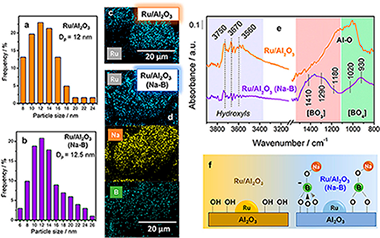
In this work, we present a highly active catalyst based on Ru nanoparticles dispersed on alumina, which showed an unexpected activity for CO2 methanation. This exceptional catalytic behavior was attributed to the presence of residual species that remained on the surface after synthesis. Furthermore, through Operando DRIFTS (diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy) measurements it was demonstrated that these remaining species provoked an induced effect on the nature of the surface intermediates spectroscopically observed, and consequently on their mechanistic role during the pathway of the CO2 hydrogenation to methane.
Abril, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900101
- ‹ anterior
- 134 of 420
- siguiente ›














