Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Reactividad de Sólidos
Tribological behavior of graphene nanoplatelet reinforced 3YTZP composites
Gutierrez-Mora, F; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 39 (2019) 1381-1388
Show abstract ▽

The tribological behavior of graphene nanoplatelet (GNP) reinforced 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (3YTZP) composites with different GNP content (2.5, 5 and 10 vol%) was analyzed and discussed. Their dry sliding behavior was studied using a ball-on-disk geometry with zirconia balls as counterparts, using loads between 2 and 20 N at ambient conditions and compared to the behavior of a monolithic 3YTZP ceramic used as a reference material. The composites showed lower friction coefficients and higher wear resistance than the monolithic 3YTZP. An outstanding performance was achieved at 10 N, where the friction coefficient decreased from 0.6 to 0.3 and the wear rates decreased 3 orders of magnitude in comparison with the monolithic ceramic. A layer adhered to the worn surface was found for all the composites, but it did not acted as a lubricating film. The composites with the lowest GNP content showed an overall improved tribological behavior.
Abril, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.11.005
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Low molecular weight epsilon-caprolactone-p-coumaric acid copolymers as potential biomaterials for skin regeneration applications
Contardi, M; Alfaro-Pulido, A; Picone, P; Guzman-Puyol, S; Goldoni, L; Benitez, J; Heredia, A; Barthel, MJ; Ceseracciu, L; Cusimano, G; Brancato, OR; Di Carlo, M; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAPLoS One, 14 (2019) e0214956
Show abstract ▽
epsilon-caprolactone-p-coumaric acid copolymers at different mole ratios (epsilon-caprolactone: p-coumaric acid 1:0, 10:1, 8:1, 6:1, 4:1, and 2:1) were synthesized by melt-polycondensation and using 4-dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid as catalyst. Chemical analysis by NMR and GPC showed that copolyesters were formed with decreasing molecular weight as p-coumaric acid content was increased. Physical characteristics, such as thermal and mechanical properties, as well as water uptake and water permeability, depended on the mole fraction of p-coumaric acid. The p-coumarate repetitive units increased the antioxidant capacity of the copolymers, showing antibacterial activity against the common pathogen Escherichia coli. In addition, all the synthesized copolyesters, except the one with the highest concentration of the phenolic acid, were cytocompatible and hemocompatible, thus becoming potentially useful for skin regeneration applications.
Abril, 2019 | DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214956
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Effect of support oxygen storage capacity on the catalytic performance of Rh nanoparticles for CO2 reforming of methane
Yentekakis, IV; Goula, G; Hatzisymeon, M; Betsi-Argyropoulou, I; Botzolaki, G; Kousi, K; Kondarides, DI; Taylor, MJ; Parlett, CMA; Osatiashtiani, A; Kyriakou, G; Holgado, JP; Lambert, RMApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 243 (2019) 490-501
Show abstract ▽
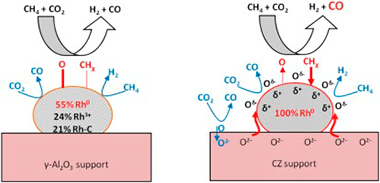
The effects of the metal oxide support on the activity, selectivity, resistance to carbon deposition and high temperature oxidative aging on the Rh-catalyzed dry reforming of methane (DRM) were investigated. Three Rh catalysts supported on oxides characterized by very different oxygen storage capacities and labilities (gamma-Al2O3, alumina-ceria-zirconia (ACZ) and ceria-zirconia (CZ)) were studied in the temperature interval 400-750 degrees C under both integral and differential reaction conditions. ACZ and CZ promoted CO2 conversion, yielding CO enriched synthesis gas. Detailed characterization of these materials, including state of the art XPS measurements obtained via sample transfer between reaction cell and spectrometer chamber, provided clear insight into the factors that determine catalytic performance. The principal Rh species detected by post reaction XPS was Rh, its relative content decreasing in the order Rh/CZ(100%) > Rh/ACZ(72%) > Fth/gamma Al2O3(55%). The catalytic activity followed the same order, demonstrating unambiguously that Rh is indeed the key active site. Moreover, the presence of CZ in the support served to maintain Rh in the metallic state and minimize carbon deposition under reaction conditions. Carbon deposition, low in all cases, increased in the order Rh/CZ < Rh/ACZ < Rh/gamma-Al2O3 consistent with a bi-functional reaction mechanism whereby backspillover of labile lattice O2- contributes to carbon oxidation, stabilization of Rh and modification of its surface chemistry; the resulting O vacancies in the support providing centers for dissociative adsorption of CO2. The lower apparent activation energy observed with CZ-containing samples suggests that CZ is a promising support component for use in low temperature DRM.
Abril, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.048
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Powder and Nanotubes Titania Modified by Dye Sensitization as Photocatalysts for the Organic Pollutants Elimination
Murcia, JJ; Avila-Martinez, EG; Rojas, H; Cubillos, J; Ivanova, S; Penkova, A; Laguna, OHNanomaterials, 9 (2019) 517
Show abstract ▽
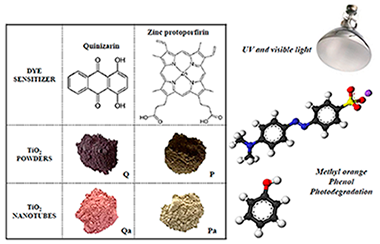
In this study, titanium dioxide powder obtained by the sol-gel method and TiO2 nanotubes, were prepared. In order to increase the TiO2 photoactivity, the powders and nanotubes obtained were modified by dye sensitization treatment during the oxide synthesis. The sensitizers applied were Quinizarin (Q) and Zinc protoporphyrin (P). The materials synthesized were extensively characterized and it was found that the dye sensitization treatment leads to modify the optical and surface properties of Titania. It was also found that the effectiveness of the dye-sensitized catalysts in the phenol and methyl orange (MO) photodegradation strongly depends on the dye sensitizer employed. Thus, the highest degradation rate for MO was obtained over the conventional Q-TiO2 photocatalyst. In the case of the nanotubes series, the most effective photocatalyst in the MO degradation was based on TiO2-nanotubes sensitized with the dye protoporfirin (ZnP). Selected catalysts were also tested in the phenol and MO photodegradation under visible light and it was observed that these samples are also active under this radiation.
Abril, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/nano9040517
Technological evolution of ceramic glazes in the renaissance: In situ analysis of tiles in the Alcazar (Seville, Spain)
de Viguerie, Laurence; Robador, Maria D.; Castaing, Jacques; Perez-Rodriguez, Jose L.; Walter, Philippe; Bouquillon, AnneJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1402-1413
Show abstract ▽
The Alcazar Palace (Seville, Spain) is famous for its ceramic decorations; 16th century wall tiles of different typologies have been analyzed in order to relate the manufacturing process of their colored glazes to the evolving technologies of the Renaissance. Chemical and mineralogical compositions have been determined in situ by nondestructive X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction on arista ceramics in the Cenador de Carlos Quinto, and majolica ceramics in the Palacio Gotico and the Royal oratory. The arista style belongs to the local Hispano-Moresque ceramic tradition. Majolica tiles have the complex microstructures of glazes from Italy. The two types are clearly differentiated by their typology, morphology (curved vs flat surface), and also microstructure (single vs multi-layers), glaze chemistry, and use of different coloring agents. Moreover, we found different glaze chemistries in the investigated majolicas, which correspond to different artists and/or practices.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1111/jace.15955
- ‹ anterior
- 136 of 420
- siguiente ›














