Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Tamm Plasmons Directionally Enhance Rare-Earth Nanophosphor Emission
Geng, DL; Cabello-Olmo, E; Lozano, G; Miguez, HACS Photonics, 6 (2019) 634-641
Show abstract ▽
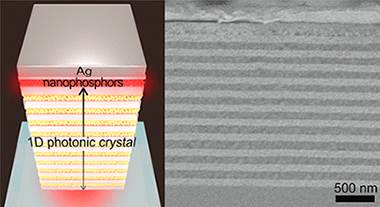
Rare-earth-based phosphors are the materials on which current solid-state lighting technology is built. However, their large crystal size impedes the tuning, optimization, or manipulation of emitted light that can be achieved by their integration in nanophotonic architectures. Herein we demonstrate a hybrid plasmonic-photonic architecture capable of both channeling in a specific direction and enhancing by eight times the emission radiated by a macroscopically wide layer of nanophosphors. In order to do so, a slab of rare-earth-based nanocrystals is inserted between a dielectric multilayer and a metal film, following a rational design that optimizes the coupling of nanophosphor emission to collective modes sustained by the metal-dielectric system. Our approach is advantageous for the optimization of solid-state lighting systems.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acsphotonics.8b01407
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Test of a He-3 target for transfer reactions in inverse kinematics
Carozzi, G; Valiente-Dobon, JJ; Gadea, A; Siciliano, M; Mengoni, D; Fernandez, A; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; Di Nitto, ANuovo cimento c-colloquia and communications in physics, 42 (2019) 94
Show abstract ▽
With the aim of studying exotic nuclei close to the proton dripline, an innovative He-3 target was produced and tested in a collaboration between the Materials Science Institute of Seville (Spain) and the Legnaro National Laboratories (Italy). The target was manufactured with a new technique that aims to reduce the costs while providing high quality targets. The target was tested at the Legnaro National Laboratories. The results of this test are presented in this contribution.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1393/ncc/i2019-19094-9
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Trapping of Gas Bubbles in Water at a Finite Distance below a Water-Solid Interface
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Thiyam, P; Miguez, H; Parsons, DF; Brevik, I; Bostrom, MLangmuir, 35 (2019) 4218-4223
Show abstract ▽
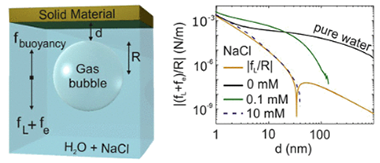
Gas bubbles in a water-filled cavity move upward because of buoyancy. Near the roof, additional forces come into play, such as Lifshitz, double layer, and hydrodynamic forces. Below uncharged metallic surfaces, repulsive Lifshitz forces combined with buoyancy forces provide a way to trap micrometer-sized bubbles. We demonstrate how bubbles of this size can be stably trapped at experimentally accessible distances, the distances being tunable with the surface material. By contrast, large bubbles (>= 100 mu m) are usually pushed toward the roof by buoyancy forces and adhere to the surface. Gas bubbles with radii ranging from 1 to 10 mu m can be trapped at equilibrium distances from 190 to 35 nm. As a model for rock, sand grains, and biosurfaces, we consider dielectric materials such as silica and polystyrene, whereas aluminium, gold, and silver are the examples of metal surfaces. Finally, we demonstrate that the presence of surface charges further strengthens the trapping by inducing ion adsorption forces.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b04176
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Promoting effect of CeO2, ZrO2 and Ce/Zr mixed oxides on Co/gamma-Al2O3 catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
Garcilaso, V; Barrientos, J; Bobadilla, LF; Laguna, OH; Boutonnet, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JARenewable Energy, 132 (2019) 1141-1150
Show abstract ▽
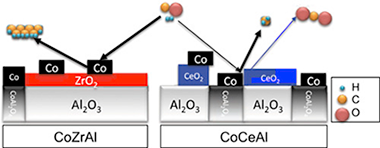
A series of cobalt-based catalysts have been synthesized using as support gamma-Al2O3 promoted by ceria/zirconia mixed oxides with a variable Ce/Zr molar ratio. The obtained catalysts demonstrated oxide promotion results in the protection of the major textural properties, especially for Zr-rich solids. Reducibility of cobalt species was enhanced by the presence of mixed oxides. The chemical composition of the oxide promoter influenced not only physicochemical properties of final catalysts but also determined their performance during the reaction. In this sense, Zr-rich systems presented a superior catalytic performance both in total conversion and in selectivity towards long chain hydrocarbons. The observed Zr-promotion effect could be explained by two significant contributions: firstly, the partial inhibition of Co-Al spinel compound formation by the presence of Zr-rich phases which enhances the availability of Co actives site and secondly, Zr-associate acidic sites promote higher hydrocarbons selectivity.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.080
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
CuxCo3-xO4 ultra-thin film as efficient anodic catalysts for anion exchange membrane water electrolysers
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, F; de Lucas-Consuegra, AJournal of Power Sources, 415 (2019) 136-144
Show abstract ▽
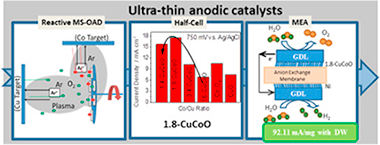
CuxCo3-xO4 ultra-thin films, deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles have been used as anodic catalysts in anion exchange membrane water electrolysers. It has been demonstrated that the used deposition procedure provides porous and amorphous samples with a strict control of the total catalyst load and Co/Cu ratio. Electrocatalytic tests showed a maximum performance for the oxygen evolution reaction at Co/Cu atomic ratio around 1.8. The optimized anodic catalyst presented a long-term stability confirmed by accelerated lifetime tests together with the chemical surface analysis of the used samples. The effect of the crystallization of a single layer CuxCo3-xO4 and a multilayer (CuO/Co3O4)(n) anodic catalyst samples was also investigated. The observed loss of catalytic performance found in both cases may prove that a particular local chemical environment around the Co and Cu sites acts as an efficient catalytic site for the oxygen evolution reaction. A catalyst film with the optimum Co/Cu atomic ratio was incorporated into a Membrane Electrode Assembly, using a sputtered Ni film as cathode. Current density values up to 100 mA cm(-2) at 2.0 V were obtained in 1.0 M KOH electrolyte. Upon normalization by the amount of catalyst, this performance is one of the highest reported in literature.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.01.056
- ‹ anterior
- 137 of 420
- siguiente ›














