Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Sustainable polycondensation of multifunctional fatty acids from tomato pomace agro-waste catalyzed by tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate
J.A. Heredia-Guerrero, G. Caputo, S. Guzmán-Puyol, G. Tedeschi, A. Heredia, L. Ceseracciu, J.J. Benítez, A. AthanassiouMaterials Today Sustainability, 3-4 (2019) 100004
Show abstract ▽
Bioplastics were prepared from the fatty fraction (i.e., unsaturated and polyhydroxylated fatty acids) of tomato pomace agro-wastes. Aliphatic polyesters were synthesized at different temperatures (125, 150, and 175 °C), reaction times (0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 3, 5, and 7 h), and amounts of tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate (0, 0.02, 0.05, and 0.10 mmol) used as a catalyst. The rate constants and activation energies were calculated from infrared spectra. The right combination of reaction temperature and amount of catalyst improved the reaction kinetics (apparent k from ∼1 to ∼8.5 h−1), whereas the activation energy was reduced from ∼39 without catalyst to ∼28 kJ/mol when tin (II) 2-ethylhexanoate was present. Glass transitions between ca. −25 and ∼0 °C were measured by differential scanning calorimetry, strictly depending on the degree of polymerization. The amorphous character of the samples was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. Young's modulus and hardness were calculated from indentation tests and were typical of soft materials, although increased as the polycondensation reaction progressed. High water-contact angles (maximum value ∼109°) and low water uptakes (minimum value ∼2.1%) were determined. Physical properties were compared with those of common man-made plastics and polymers, finding that these tomato pomace bioplastics could be their realistic alternatives.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2018.12.001
Degradation processes of historic metal threads used in some Spanish and Portuguese ornamentation pieces
Duran, A; Perez-Maqueda, R; Perez-Rodriguez, JLJournal of Cultural Heritage, 36 (2019) 135-142
Show abstract ▽
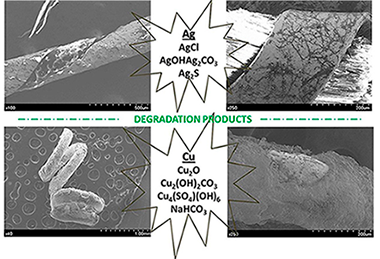
The degradation processes that occurred on metal threads applied in the embroidery used for clothing and in the ornamentation of sculptures, the Sevillian Holy Week processions, and Portuguese and Spanish palace and museum are thoroughly analyzed. Some threads from the 14th and 18–19th centuries were considered. In the metal threads, sulphur- and chlorine-based compounds were detected either individually or together, depending on the degradation process. Basic silver carbonate, sodium bicarbonate and copper-based compounds were also observed. The different degradation processes were attributed to different factors, such as environmental contamination, degradation of the fibrous cores, and inadequate cleaning and/or mechanical treatments.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2018.09.006
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Synthesis of sol-gel pyrophyllite/TiO2 heterostructures: Effect of calcination temperature and methanol washing on photocatalytic activity
El Gaidoumi, A.; Doña Rodríguez, J.M.; Pulido Melián, E.; González-Díaz, O.M.; Navío Santos, J.M.; El Bali, B.; Kherbeche, A.Surfaces and Interfaces, 14 (2019) 19-25
Show abstract ▽
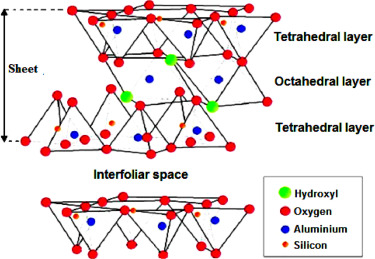
We successfully synthesized an efficient photoactive pyrophyllite/TiO2 heterostructures using a sol-gel route at ambient temperature. The samples were prepared by exfoliation of a pyrophyllite layered-type clay by TiO2. The prepared samples exhibited strong photocatalytic activity for the degradation of phenol. The heterostructure PTi750 (SBET = 16.58 m2/g) calcined at 750 °C, in which the mixed phases of anatase and rutile exist (52.2% anatase/10.7% rutile), showed the highest photocatalytic activity against commercial TiO2Aeroxide P25. The methanol washed PTi750 was 5 times faster than the corresponding unwashed sample; phenol was totally degraded with a TOC reduction of 89.2%. The materials have been characterized by: X-ray diffraction (XRD), Diffuse reflectance UV–vis spectrophotometry (UV–Vis DRS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and BET specific surface area.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfin.2018.10.003
Reactividad de Sólidos
Sample-Controlled analysis under high pressure for accelerated process studies
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Soria-Hoyo, C; Valverde, JM; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1338-1346
Show abstract ▽
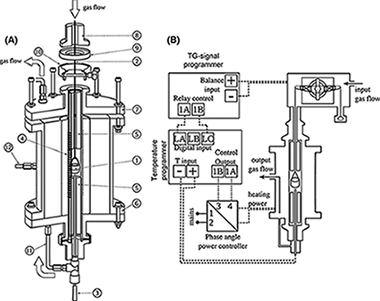
The potential of controlled rate thermal analysis (CRTA) for studying high-pressure gas-solid processes has been evaluated. CRTA is a type of smart temperature program based on a feedback system that uses any experimental signal related to the process evolution for commanding the temperature evolution. In this work, an instrument that uses the gravimetric signal for CRTA control has been designed and used for the study of two high-pressure gas-solid reactions: the highly exothermic thermal oxidation of TiC under high pressure of oxygen and the reduction in Fe2O3 under high pressure of hydrogen. Advantages of CRTA for discriminating overlapping processes and appraising kinetic reaction mechanisms are shown.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1111/jace.15960
Reactividad de Sólidos
Anisotropic lattice expansion determined during flash sintering of BiFeO3 by in-situ energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction
Wassel, MAB; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Charalambous, H; Perejon, A; Jha, SK; Okasinski, J; Tsakalakos, TScripta Materialia, 162 (2019) 286-291
Show abstract ▽
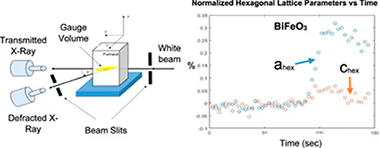
BiFeO3 has a Curie temperature (T-c) of 825 degrees C, making it difficult to sinter using conventional methods while maintaining the purity of the material, as unavoidably secondary phases appear at temperatures above T-c Flash sintering is a relatively new technique that saves time and energy compared to other sintering methods. BiFeO3 was flash sintered at 500 degrees C to achieve 90% densification. In-situ energy dispersive X-ray diffraction (EDXRD) revealed that the material did not undergo any phase transformation, having been sintered well below the Tc. Interestingly, anisotropic lattice expansion in the material was observed when the sample was exposed to the electric field.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.11.028
- ‹ anterior
- 138 of 420
- siguiente ›














