Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Mechanism of Photoluminescence Intermittency in Organic-Inorganic Perovskite Nanocrystals
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Calvo, ME; Rojas, TC; Miguez, HACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 11 (4) (2019) 6344-6349 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b17122
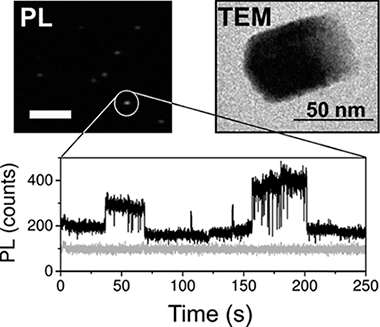
Abstract
Lead halide perovskite nanocrystals have demonstrated their potential as active materials for optoelectronic applications over the past few years. Nevertheless, one issue that hampers their applicability has to do with the observation of photoluminescence intermittency, commonly referred to as "blinking", as in their inorganic counterparts. Such behavior, reported for structures well above the quantum confinement regime, has been discussed to be strongly related to the presence of charge carrier traps. In this work, we analyze the characteristics of this intermittency and explore the dependence on the surrounding atmosphere, showing evidence for the critical role played by the presence of oxygen. We discuss a possible mechanism in which a constant creation/annihilation of halide-related carrier traps takes place under light irradiation, with the dominant rate being determined by the atmosphere.
Febrero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b17122
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
An innovative approach for micro/nano structuring plasma polymer films
Thiry, D; Vinx, N; Aparicio, FJ; Moerman, D; Lazzaroni, R; Cossement, D; Snyders, RThin Solid Films, 672 (2019) 26-32 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2018.12.050
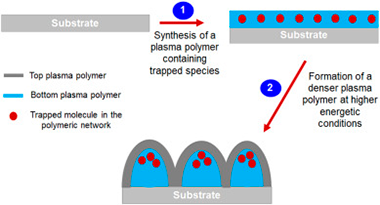
Abstract
This work aims at presenting an innovative method for tailoring the morphology of functionalized plasma polymer films (PPF). The approach is based on the formation of a plasma polymer bilayer system in which the two layers differ by their chemical composition and cross-linking degree. As a case study, propanethiol-based plasma polymer films have been investigated. As revealed by a much higher S/C ratio than in the propanethiol precursor (i.e. 0.83 vs 0.33), it has been demonstrated that the bottom layer contains a large fraction of trapped sulfur-based molecules (e.g. H2S). When further covered by a denser PPF formed at higher energetic conditions, a three-dimensional morphological reorganization takes place giving rise to the micro/nano structuration of the organic material. The shape, the dimensions as well as the density of the generated structures are found to depend on the thickness of both coatings involved in the bilayer structure, offering a great flexibility for surface engineering. Annealing experiments unambiguously confirm the major role played by the sulfur-based trapped molecules for inducing the reshaping process. The whole set of data clearly paves the way for the development of an innovative approach for finely tailoring the morphology of functionalized PPF at the micro/nano scale.
Febrero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2018.12.050
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Highly Efficient Transparent Nanophosphor Films for Tunable White-Light-Emitting Layered Coatings
Geng, DL; Lozano, G; Miguez, HACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 11 (4) (2019) 4219-4225 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b17368
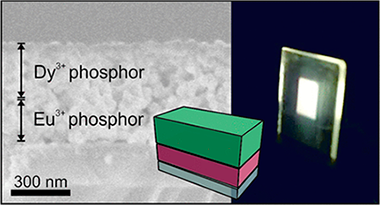
Abstract
Bright luminescence in rare-earth (RE) nanocrystals, the so-called nanophosphors, is generally achieved by choosing a host that enables an effective excitation of the RE activator through charge or energy transfer. Although tungstate, molybdate, or vanadate compounds provide the aforementioned transfer, a comparative analysis of the efficiency of such emitters remains elusive. Herein, we perform a combined structural and optical analysis, which reveals that the tetragonal GdVO4 matrix gives rise to the highest efficiency among the different transparent nanophosphor films compared. Then, we demonstrate that by a sequential stacking of optical quality layers made of Eu3+- and Dy3+-doped nanocrystals, it is possible to attain highly transparent white-light-emitting coatings of tunable shade with photoluminescence quantum yields above 35%. Layering provides a precise dynamic tuning of the chromaticity based on the photoexcitation wavelength dependence of the emission of the nanophosphor ensemble without altering the chemical composition of the emitters or degrading their efficiency. The total extinction of the incoming radiation along with the high quantum yields achieved makes these thin-layered phosphors one of the most efficient transparent white converter coatings ever developed.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b17368
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Influence of Al and Y content on the oxidation resistance of CrAlYN protective coatings for high temperature applications: New insights about the Y role
Rojas, TC; Dominguez-Meister, S; Brizuela, M; Sanchez-Lopez, JCJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 777 (2019) 1172-1181 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.280
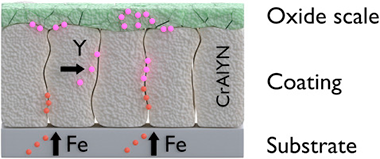
Abstract
CrAlYN hard coatings with two different average Al contents: similar to 16 at.% and similar to 25 at.%, and Y concentration varying between 1.2 and 5.7 at.% were deposited by direct current reactive magnetron co-sputtering of mixed Cr-Al and Y targets on commercial M2 steel substrates. The samples were heated to 1000 degrees C in air during 2 h to study their oxidation resistance and thermal stability. The Y content is critical and the coatings present different behaviour depending on the Al content. The best oxidation resistance and thermal stability are obtained for the coating with similar to 16 at.% Al and 3.4 at.% Y. The initial film microstructure and the cubic phase (fcc-CrAlN) were retained, and a thin (Cr,Al)(2)O-3 oxide protective scale was formed. At lower Y content (1.2 at.%) iron, from the substrate crosses the coating, while a higher content (4.6 at.%) avoided the iron diffusion at the expense of a thicker oxide scale with new oxide phases. The coatings with higher Al content (similar to 25 at. %) were not thermally stable at 1000 degrees C. A good oxidation resistance was obtained for 2.6 at.% of Y although new phases (hcp-AlN and Cr-Fe) were formed. Higher amount of yttrium (similar to 5.7 at. %) led to the complete oxidation of the coating.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.280
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Coupling of Ag2CO3 to an optimized ZnO photocatalyst: Advantages vs. disadvantages
P. Sánchez-Cid; C. Jaramillo-Páez; J.A. Navío; A.N. Martín-Gómez; M.C. HidalgoJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 369 (2019) 119-132 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.10.024

Abstract
With the aim of improving the photocatalytic properties of a previously optimized zinc oxide photocatalyst, the effect of the incorporation of different amounts of Ag2CO3 on the aforementioned ZnO has been studied. For this purpose we report the synthesis, by means of simple precipitation procedures, of bare ZnO and Ag2CO3 samples as well as the coupled materials ZnO/Ag2CO3 (X) (where X = 1%, 2%, 4% and 5% in molar percentages). Both, single and coupled materials have been characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, N2-absorption, SEM, TEM, UV–vis/DRS and XPS). To assess the advantages or disadvantages that Ag2CO3 addition could have over the optimized ZnO, the photocatalytic properties have been established by following the photo-degradation of selected toxic molecules, both in the UV and in the visible, as well as using complementary techniques of liquid medium analyses (TOC and Atomic Emission Spectrometry with plasma ICP). Three selected substrates were chosen: Rhodamine B (RhB) as a dye, and phenol and caffeine as colourless recalcitrant toxic molecules.
Our results suggest that although the use of Ag2CO3 could be beneficial to implement the optical absorption towards the visible region, however, other effects have to be bore in mind, such as the photo-corrosion of Ag2CO3 and the chemical structure of the chosen substrate, to elucidate whether the addition of Ag2CO3 has beneficial or detrimental effects on the photocatalytic properties of the coupled ZnO/Ag2CO3 materials.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.10.024
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
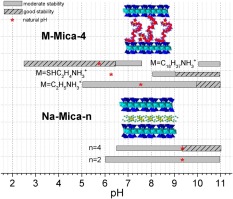
Influence of framework and interlayer on the colloidal stability of design swelling high-charged micas
Osuna, FJ; Cota, A; Fernandez, MA; Pavon, E; Sanchez, RMT; Alba, MDColloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 561 (2019) 32-38 DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.09.086
Abstract
Stability of colloidal clay minerals dispersion of fundamental in many industrial processes. Therefore, surface charge of the synthetic swelling high-charged mica family, Na-Mica-n (n = 2 or 4, n is the total layer charge) were investigated to study its colloidal dispersion stability as a function of the framework and interlayer space composition. Na-Mica-n (n = 2 or 4) micas were synthesized and functionalized with ethylammonium, mercaptoethylammonium or octadecylammonium. Their zeta-potential evolutions as a function of solution pH were correlated with their structural, compositional and morphological characteristics. The results have shown that the total charge of swelling high charged micas, Mica-n, didn´t affect significantly their colloidal dispersion stability, the interlayer composition and interlayer cation arrangement were the main factors of colloidal behaviour. The synthesis and functionalization of those synthetic micas can be tuned for their optimal use.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.09.086
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO-ZrO2 Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic Degradation and Mineralization of Phenol
Lopez, MCU; Lemus, MAA; Hidalgo, MC; Gonzalez, RL; Owen, PQ; Oros-Ruiz, S; Lopez, SAU; Acosta, JJournal of Nanomaterials (2019) art. 1015876, 12 pages DOI: 10.1155/2019/1015876
Abstract
ZnO-ZrO2 nanocomposites using zinc (II) acetylacetonate and different ZnO contents (13, 25, 50, and 75% mol) were synthesized through sol-gel method. The synthesis process was strongly related to nanocomposite properties especially on their structural composition. The obtained ZnO-ZrO2 nanomaterials presented tetragonal crystalline structure for zirconia whereas hexagonal one was formed in ZnO. Raman spectroscopy and XRD patterns confirmed the formation of tetragonal zirconia whereas inhibition of monoclinic structure was observed. Addition of ZnO affected the pore size distribution of the composite, and the measured specific surface areas were from 10 m2/g (for pure ZnO) to 46 m2/g (pristine ZrO2). Eg values of ZrO2 were modified by ZnO addition, since calculated values using Kubelka-Munk’s function varied from 4.73 to 3.76 eV. The morphology and size of the nanomaterials investigated by electron microscopy showed formation of nanorods for ZnO with sizes ranging from 50 nm to 300 nm while zirconia was formed by smaller particles (less than 50 nm). The main advantage of using the nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of phenol was the mineralization degree, since 75ZnO-ZrO2 nanocomposite surpassed mineralization reached by pure ZnO and also inhibited formation of undesirable intermediates.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1155/2019/1015876
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Flexible nanophosphor films doped with Mie resonators for enhanced out-coupling of the emission
Miranda-Munoz, JM; Geng, DL; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 7 (2019) 267-274 DOI:
Abstract
Herein, we present a general method to prepare self-standing flexible photoluminescent coatings of controlled opacity for integration into light-emitting diodes (LEDs) employing cost-effective solution-processing methods. From colloidal suspensions of nano-sized phosphors, we fabricate light-emitting transparent films that can be doped with spherical scatterers, which act as Mie resonators that trigger a controlled photoluminescence enhancement, evidenced by the reduction of the guided light along the layer. This results in an enhanced emission compared to that extracted from a bare phosphor layer. We show not only that emission is visible under ultraviolet-LED illumination for both rigid and flexible versions of the coatings, but we also prove the feasibility of the integration of these flexible conversion layers into such devices. We believe these results can contribute to develop more efficient and cost-effective illumination sources by providing efficient and easy-to-handle conversion layers susceptible to excitation by LEDs emitting at wavelengths in the near UV region.
Enero, 2019 · DOI:
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Isotope Labelling for Reaction Mechanism Analysis in DBD Plasma Processes
Navascues, P; Obrero-Perez, JM; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, ACatalysts, 9(1) (2019) 45 DOI: 10.3390/catal9010045
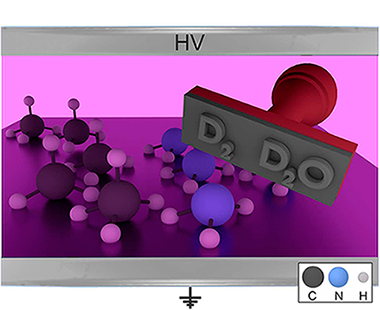
Abstract
Dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasmas and plasma catalysis are becoming an alternative procedure to activate various gas phase reactions. A low-temperature and normal operating pressure are the main advantages of these processes, but a limited energy efficiency and little selectivity control hinder their practical implementation. In this work, we propose the use of isotope labelling to retrieve information about the intermediate reactions that may intervene during the DBD processes contributing to a decrease in their energy efficiency. The results are shown for the wet reforming reaction of methane, using D2O instead of H2O as reactant, and for the ammonia synthesis, using NH3/D-2/N-2 mixtures. In the two cases, it was found that a significant amount of outlet gas molecules, either reactants or products, have deuterium in their structure (e.g., HD for hydrogen, CDxHy for methane, or NDxHy for ammonia). From the analysis of the evolution of the labelled molecules as a function of power, useful information has been obtained about the exchange events of H by D atoms (or vice versa) between the plasma intermediate species. An evaluation of the number of these events revealed a significant progression with the plasma power, a tendency that is recognized to be detrimental for the energy efficiency of reactant to product transformation. The labelling technique is proposed as a useful approach for the analysis of plasma reaction mechanisms.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.3390/catal9010045
Materiales Coloidales
Enhancing Luminescence and X-ray Absorption Capacity of Eu3+:LaF3 Nanoparticles by Bi3+ Codoping
Mancebo, DG; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Moros, M; Balcerzyk, M; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MACS Omega, 4 (2019) 765-774 DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.8b03160
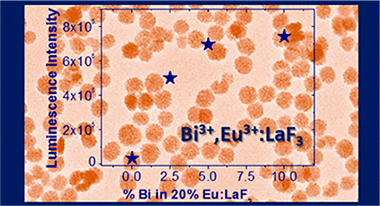
Abstract
Bi3+ codoping has been proposed in this work with a twofold objective, namely, enhancing the luminescence emission of Eu3+:LaF3 nanoparticles (NPs) and increasing their X-ray attenuation capacity, with the purpose of obtaining a bimodal bioprobe for luminescence bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography. The synthesis method, reported here for the first time for LaF3 particles, allowed obtaining uniform, nonaggregated NPs using a homogeneous precipitation in polyol medium at room temperature in just 2 h. The simplicity of the synthesis method allows the large-scale production of NPs. LaF3 NPs with different Eu3+ contents were first synthesized to find the critical Eu3+ concentration, producing the highest emission intensity. This concentration was subsequently used to fabricate Bi3+-Eu3+-codoped LaF3 NPs using the same method. The emission intensity of the codoped NPs increased in more than one order of magnitude, thanks to the possibility of excitation through the Bi3+. Eu3+ energy-transfer band. The luminescence properties of the codoped NPs were analyzed in detail to find the mechanism responsible for the emission enhancement. Finally, it was demonstrated that the high atomic number of Bi3+, higher than that of lanthanides, was an added value of the material because it increased its X-ray attenuation capacity. In summary, the LaF3 NPs codoped with Eu3+ and Bi3+ presented in this work are promising candidates as a bimodal bioprobe for luminescence bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.8b03160
Materiales Coloidales
Biocompatibility assessment of up-and down-converting nanoparticles: implications of interferences with in vitro assays
Pem, Barbara; Gonzalez-Mancebo, Daniel; Moros, Maria; Ocana, Manuel; Becerro, Ana Isabel; Pavicic, Ivan; Selmani, Atida; Babic, Michal; Horak, Daniel; Vinkovic Vrcek, IvanaMethods and Applications in Fluorescence, 7 (2019) 014001 DOI: 10.1088/2050-6120/aae9c8
Abstract
The safety assessment of nanoparticles (NPs) is crucial during their design and development for biomedicine. One of the prerequisite steps during this evaluation is in vitro testing that employs cell-based assays not always validated and well-adapted for NPs. Interferences with in vitro assays may arise due to the nano-related optical, oxidative, fluorescent, surface and catalytic properties of NPs. Thus, proper validation of each assay system has to be performed for each NP type. This study aimed to evaluate the applicability of the most common in vitro cytotoxicity assays for the safety assessment of up- and down-converting lanthanide-doped NPs. Conventional cell viability tests and fluorescence-based assays for oxidative stress response were selected to determine the biological effects of up- and down-converting NPs to human brain cells. Comparison with known silver and iron oxide NPs was made for verification purposes. Both the plate reader and flow cytometric measurements were examined. The obtained results indicated that both types of Ln-doped NPs interfered to a much lesser extent than metallic NPs. In addition, the great potential of both up- and down-converting NPs for biomedicine was manifested due to their biocompatibility and low toxicity.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1088/2050-6120/aae9c8
Reactividad de Sólidos
La0.59Li0.24TiO3 ceramics obtained by spark plasma sintering: Electric behavior analysis
Pereira, JS; Guerrero, F; Romaguera-Barcelay, Y; Anglada-Rivera, J; Sales, JCC; Silva, RS; Zulueta, Y; Poyato, R; Gallardo, A; Almeida, A; Moreira, JA; Leyet, YMaterials Research Express, 6 (2019) art. 015504 DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/aae496
Abstract
This work describes the electric study of Lithium lanthanum titanate (La0.59Li0.24TiO3) ceramics performed by Complex Impedance Spectroscopy. The nanoparticle powders have been synthesized through high energy ball milling and sintered via Spark Plasma Sintering technique. The experimental impedance data have been analyzed using the equivalent circuit model, the Extended Jonscher universal law and the derivative method. From these models, we have determined the dielectric response as well as the grain and grain boundary conductivity. The samples show ionic conductivity values between 10(-5) to 10(-4) S cm(-1) in the studied temperature range, and activation energy values 0.24 eV and 0.48 eV for grain and grain boundary, respectively. These results confirm the Li+ ions mobility through the crystalline structure of the material.
Enero, 2019 · DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/aae496
2018
2018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO/H-2 adsorption on a Ru/Al2O3 model catalyst for Fischer Trospch: Effect of water concentration on the surface species
Jimenez-Barrera, E; Bazin, P; Lopez-Cartes, C; Romero-Sarria, F; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 237 (2018) 986-995 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.053
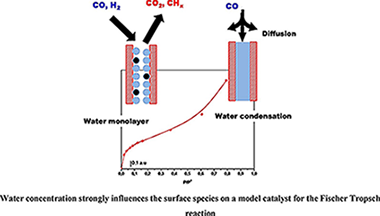
Abstract
Water presence and concentration strongly influence CO conversion and CS+ selectivity in the Fischer Tropsch reaction. In this work, the influence of the water concentration was investigated using a model Ru/Al2O3 (5 wt. %) catalyst. The surface species formed after CO and H-2 adsorption in dry and wet (different water concentrations) conditions were analyzed by FTIR. Firstly, water adsorption was carried out up to complete filling of the pores and then CO was put in contact with the catalyst. The absence of adsorbed CO species in these conditions evidences that CO diffusion in water controls the access of the gas to the active sites and explains the negative effect of high water concentrations reported by some authors. Moreover, the adsorption of a mixture of CO + H-2 + H2O, being the water concentration close to that needed to have a monolayer, and a dry mixture of CO + H-2 were carried out and compared. Results evidence that water in this low concentration, is able to gasify the surface carbon species formed by CO dissociation on the metallic sites. This cleaning effect is related to the positive effect of water on CO conversion detected by some authors.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.053
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Metal Micro-Monoliths for the Kinetic Study and the Intensification of the Water Gas Shift Reaction
Garcia-Moncada, N; Groppi, G; Beretta, A; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysts, 8 (2018) art. 594 DOI: 10.3390/catal8120594
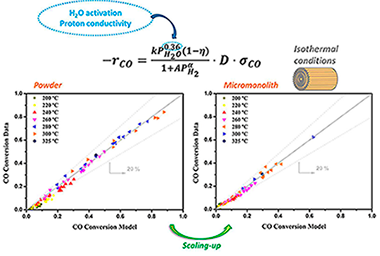
Abstract
A kinetic study of the water gas shift (WGS) reaction has been carried out on a Pt-based catalyst promoted by a Zr-based proton conductor. The investigation was first performed on powders with diluted feed mixtures and then extended to more severe and representative conditions by using a catalyst coated metallic micromonolith. Temperature measurements reveal that isothermal conditions were obtained along the micromonolith during the tested conditions. In addition, the very thin catalytic layer allows for the discarding of intraporous resistances, providing excellent conditions to analyse the kinetics of the WGS reaction under the integral regime. The proposed rate expression accounts for independence on CO concentration, an inhibiting effect of H-2 and a promoting effect of H2O; kinetic orders on CO and H-2 are in line with those reported in the literature for the Pt-based catalyst. Instead, the obtained reaction order of water (0.36) is significantly lower than that reported for unpromoted catalysts (typically 0.77-1.10) in good agreement with the proposed water-enhancer effect of the proton conductor on the rate-limiting step. Metallic micromonoliths turn out to be a powerful tool for the kinetic investigation, due to the absence of mass and heat transport limitations and represent a strategy for the intensification of the WGS unit for future applications of fuel processors in small mobile devices.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.3390/catal8120594
Reactividad de Sólidos
Molten carbonate salts for advanced solar thermal energy power plants: Cover gas effect on fluid thermal stability
Fereres, S; Prieto, C; Gimenez-Gavarrell, P; Rodriguez, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LASolar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 188 (2018) 119-126 DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2018.08.028
Abstract
The eutectic mixture Li2CO3-Na2CO3-K2CO3 is investigated as a high temperature heat transfer fluid and storage medium alternative for molten salt solar thermal power plants. This salt has an operating temperature range of 400–700 °C, enabling the use of higher temperature/efficiency power cycles. However, this carbonate mixture is known to thermally decompose in air. This study evaluates the thermal stability of the salt mixture under different cover gases: air, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and an 80/20 carbon dioxide/air mixture. Initial characterization is performed through thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), followed by larger scale testing in a custom-made reactor to simulate conditions closer to its practical use. The results show improved thermal stability with a CO2 atmosphere. The decomposition kinetics under different cover gases are estimated from TGA data. However, larger-scale, longer duration experiments show much slower decomposition rates compared to the classical TGA approach. These findings indicate that the main contribution to mass loss in TGA is due to vaporization rather than thermal decomposition. Thus, a proper evaluation of the molten salt´s thermal stability can only be obtained from reactor experiments where vaporization is inhibited. Very long induction periods (of the order of days) are observed, suggesting that the kinetic decomposition mechanism is a nucleation and growth type. Other considerations for future plants incorporating these high temperature salts are discussed.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2018.08.028
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Policies and Motivations for the CO2 Valorization through the Sabatier Reaction Using Structured Catalysts. A Review of the Most Recent Advances
Navarro, JC; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JACatalysts, 8 (2018) art. 578 DOI: 10.3390/catal8120578
Abstract
The current scenario where the effects of global warming are more and more evident, has motivated different initiatives for facing this, such as the creation of global policies with a clear environmental guideline. Within these policies, the control of Greenhouse Gase (GHG) emissions has been defined as mandatory, but for carrying out this, a smart strategy is proposed. This is the application of a circular economy model, which seeks to minimize the generation of waste and maximize the efficient use of resources. From this point of view, CO2 recycling is an alternative to reduce emissions to the atmosphere, and we need to look for new business models which valorization this compound which now must be considered as a renewable carbon source. This has renewed the interest in known processes for the chemical transformation of CO2 but that have not been applied at industrial level because they do not offer evident profitability. For example, the methane produced in the Sabatier reaction has a great potential for application, but this depends on the existence of a sustainable supply of hydrogen and a greater efficiency during the process that allows maximizing energy efficiency and thermal control to maximize the methane yield. Regarding energy efficiency and thermal control of the process, the use of structured reactors is an appropriate strategy. The evolution of new technologies, such as 3D printing, and the consolidation of knowledge in the structing of catalysts has enabled the use of these reactors to develop a wide range of possibilities in the field. In this sense, the present review presents a brief description of the main policies that have motivated the transition to a circular economy model and within this, to CO2 recycling. This allows understanding, why efforts are being focused on the development of different reactions for CO2 valorization. Special attention to the case of the Sabatier reaction and in the application of structured reactors for such process is paid.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.3390/catal8120578
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Revealing the substitution mechanism in Eu3+:CaMoO4 and Eu3+,Na+:CaMoO4 phosphors
Becerro, AI; Allix, M; Laguna, M; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Genevois, C; Caballero, A; Lozano, G; Nunez, NO; Ocana, MJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 6 (2018) 47 DOI: 10.1039/c8tc04595j
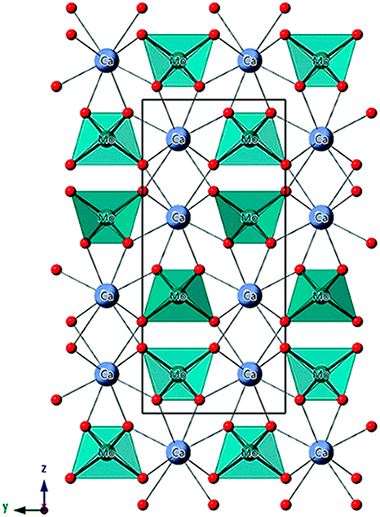
Abstract
Eu3+-Doped calcium molybdate is an excellent phosphor for lighting and display devices due to the very intense pure red emission after UV excitation. It has been reported in the literature that the CaMoO4 unit cell volume expands after Eu3+ doping, in spite of the smaller Eu3+ ionic radius compared with Ca2+. Likewise, several studies found that the emission intensity of the phosphor could be improved by codoping with alkaline ions like Li+, Na+ or K+. None of these studies correlated the apparent volume expansion and luminescence enhancement with the crystal structural details. This paper analyses the aliovalent substitution mechanism and crystal structure of Eu3+:CaMoO4 and Eu3+,Na+:CaMoO4 phosphors using complementary techniques like Raman spectroscopy, EXAFS and SPD. We found that the substitution mechanism was different for both systems, with Ca site vacancies forming in the Eu3+:CaMoO4 phosphors and leading to Ca1-3xEu2xxMoO4 compositions, while the Eu3+,Na+:CaMoO4 phosphors formed Ca1-2xEuxNaxMoO4. SPD showed that the cell volume expansion observed with increasing Eu3+ content is related to the increase of the Mo-O bond distance due to the higher electronegativity of Eu3+ compared with Ca2+. Finally, it was shown that the luminescence properties, i.e. lifetime values and quantum yields (the latter reported here for the first time), do not depend on the presence of monovalent ions in the crystal structure but, exclusively, on the Eu3+ content of the phosphor. The integral and detailed analysis of the materials presented in this paper, ranging from crystal structure to luminescent properties including elemental composition, allows a full picture of the structure-property relationships that had never been addressed before for CaMoO4-based phopshors.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1039/c8tc04595j
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Improving the Bulk Emission Properties of CH3NH3PbBr3 by Modifying the Halide-Related Defect Structure
Tiede, David O.; Calvo, Mauricio E.; Galisteo-Lopez, Juan F.; Miguez, HernanJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 122 (2018) 27250-27255 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b09315 DEC 6 2018
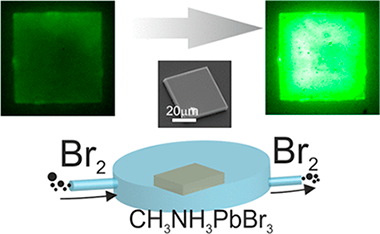
Abstract
The peculiar defect chemistry of hybrid organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites is believed to be partially responsible for the outstanding performance of this solution-processed material in optoelectronic devices. While most effort has been put on the management of halide defects (the ones presenting the highest mobility) for CH3NH3PbI3, its bromide counterpart has not been so widely studied. Although the former is the material of choice for photovoltaics, the latter is present in most light-emitting applications. Here, we report how the exposure of CH3NH3PbBr3 single crystals to a bromine atmosphere strongly affects its emission properties. Such improvement takes place in the absence of apparent signs of degradation and remains for tens of hours. We propose an explanation based on the defect structure for this material where bromine-related defects can act as deep or shallow traps. These results are of relevance for a material expected to be present in a new generation of solution-processed light-emitting devices.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b09315 DEC 6 2018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Understanding the Role of the Acid Sites in 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation to 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid Reaction over Gold Catalysts: Surface Investigation on CexZr1-xO2 Compounds
Megias-Sayago, C; Chakarova, K; Penkova, A; Lolli, A; Ivanova, S; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JAACS Catalysis, 8 (2018) 11154-11164 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b02522 DEC 2018
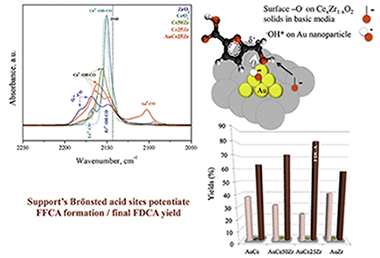
Abstract
A series of CexZr1-xO2 supports with different Ce/Zr molar ratios were utilized for the preparation of gold catalyst used in the selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. The used method of gold deposition allows the preparation of gold particles with homogeneous size and shape distribution, a formulation very useful for studies dedicated to revealing the support participation in the reaction. The supports are characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy using CO as probe molecule, and the sample catalytic activity is thereafter correlated to the support acid site distribution. The possible participation of its Lewis/Bronsted acidity in the reaction mechanism is also proposed.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b02522 DEC 2018
Reactividad de Sólidos
Role of calcium looping conditions on the performance of natural and synthetic Ca-based materials for energy storage
Sarrion, B; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Valverde, JMJournal of CO2 utilization, 28 (2018) 374-384 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.10.018
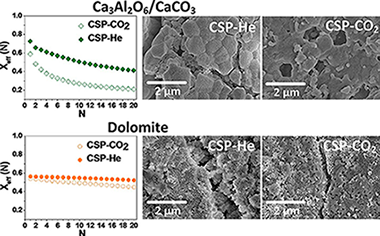
Abstract
In this work, the multicycle activity of natural CaO precursors (limestone and dolomite) and Ca-based composites (Ca3Al2O6/CaCO3 and ZrO2/CaCO3 mixtures) has been studied for Thermochemical Energy Storage (TCES) in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants by means of the Calcium-Looping process (CaL), using two integration schemes proposed elsewhere that differ in the calcination stages. Under CSP-He conditions, calcination for CaO regeneration is performed under pure He at low temperatures (725 degrees C) while under CPS-CO2 conditions calcination is carried out under pure CO2 at high temperatures (950 degrees C). The latter avoids the use of selective membranes to separate He from CO2 even though it requires the use of more expensive materials for solar receptors. Carbonation/calcination conditions drastically affect the multicycle CO2 uptake of the materials tested. Effective multicycle conversion is higher in CSP-He tests due to the mild conditions employed for calcination, which mitigates CaO sintering. On the other hand, the harsh calcination conditions used in CSP-CO2 tests enhance sintering of CaO derived from limestone and the Ca3Al2O6/CaCO3 composite due to the low Tammann temperature of Ca3Al2O6. CaO sintering is hindered by the presence of inert oxides with high Tammann temperatures, such as ZrO2 in the ZrO2/CaCO3 composite and MgO in dolomite. Dolomite derived CaO shows high effective conversion values along the carbonation/calcination cycles when tested under both types of conditions, as compared to limestone and the composites, which suggests that the integration scheme based on CSP-CO2 conditions would be a feasible alternative to CSP-He if natural dolomite were used as CaO precursor.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.10.018
Materiales Avanzados
Degradation of a LDPE film applied as a greenhouse cover design material: the effect of ageing and mechanical modelling
Garzon, Eduardo; Ortiz Rodriguez, Isabel Maria; Castillo, Jose; Jose Sanchez-Soto, PedroRevista de la Construcción, 17 (3) (2018) 457-464 DOI: 10.7764/RDLC.17.3.457 DEC 2018
Abstract
In this work, we studied the mechanical performance of an LDPE film (0.22 mm in thickness) used as a material in the design of greenhouse covers. We investigated the effects of ageing at different periods of its service life and applying chemical substance treatments used as pesticides on greenhouse crops and after breakage using mechanical traction. Numerical simulations were performed using the finite element method. For this purpose, one section of the complete geometry of the greenhouse cover and different load conditions (1-5 kPa) were considered for the modelling. The performance of the polymer was assumed to be linearly elastic to simplify the governing equations. The study demonstrated that the LDPE film used was no longer effective as a greenhouse cover film due to the degradation of its mechanical properties. It was shown that the general performance of this film was in the plastic zone and its performance was non-linear. The results deduced from the present study are of interest because they show the material failure process of greenhouse covers in relation to the degradation process.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.7764/RDLC.17.3.457 DEC 2018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
New concept for old reaction: Novel WGS catalyst design
Garcia-Moncada, N; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 238 (2018) 1-5 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.068
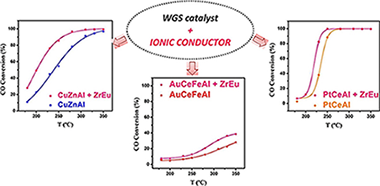
Abstract
The viability of water gas shift catalytic system for mobile application passes through obligatory reactor volume reduction, achieved normally by using less charge of more efficient catalyst. Completely new concept for catalyst design is proposed: a catalytic system including classically reported WGS catalysts of different nature or active phase (Cu, Pt or Au) mechanically mixed with an ionic conductor. The influence of the later on catalyst activity is studied and discussed, more precisely its effect on the rate of the reaction-limiting step and catalysts' efficiency. It is demonstrated with this study, that the presence of an ionic conductor in contact with a WGS catalyst is essential for the water supply (dissociation and transport), thereby potentiating the water activation step, whatever the mechanism and catalyst overall performance.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.068
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
A comparative assessment of the UV-photocatalytic activities of ZnO synthesized by different routes
Jaramillo-Paez, C; Sanchez-Cid, P; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6 (2018) 7161-7171 DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.004
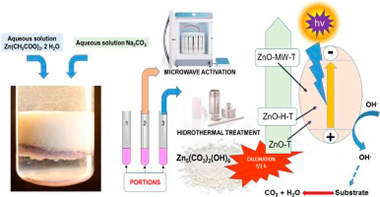
Abstract
ZnO was synthesized by a precipitation procedure, free of template agent, by mixing aqueous solutions of Zn (OAc)(2) and dissolved Na2CO3 at pH ca. 7. This material was calcined at different temperatures (200-600 degrees C for 2 h). In two other alternative procedures, after the precipitation, the suspension was taken to hydrothermal treatments or to microwave treatments, subjecting them to calcination treatments at the same temperatures as the previous material. All materials were characterized using various techniques. The photocatalytic activity was assessed in the degradation of methyl orange and phenol using UV-illumination and evaluating the corresponding percentages of conversion and mineralization. A minimal difference between the relative intensities of the exposed faces (I100I002) related to XRD for the synthesized samples seems to be an important factor in obtaining good photocatalytic properties. This minimum, was achieved with a calcination treatment at 400 degrees C for 2 h. With this calcination treatment, no significant variations were observed in the photocatalytic activities of ZnO obtained by the three procedures, although in all cases the zinc oxides obtained exhibited, for each substrate, higher UV-photocatalytic activities than those obtained with TiO2 (P25) used as a reference catalyst. In all cases, the samples showed no photocatalytic activity in the visible region of the spectrum.
Diciembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.004
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Highly Efficient and Environmentally Stable Flexible Color Converters Based on Confined CH3NH3PbBr3 Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Anaya, M; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Rojas, TC; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10 (2018) 38334-38340 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b11706
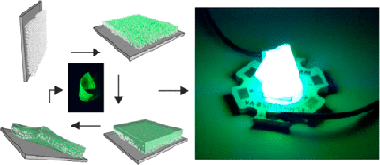
Abstract
In this work, we demonstrate a synthetic route to attain methylammonium lead bromide (CH3NH3PbBr3) perovskite nanocrystals (nc-MAPbBr(3), 1.5 nm < size < 3 nm) and provide them with functionality as highly efficient flexible, transparent, environmentally stable, and adaptable color converting films. We use nanoparticle metal oxide (MOx) thin films as porous scaffolds of controlled nanopores size distribution to synthesize nc-MAPbBr(3) through the infiltration of perovskite liquid precursors. We find that the control over the reaction volume imposed by the nanoporous scaffold gives rise to a strict control of the nanocrystal size, which allows us to observe well-defined quantum confinement effects on the photo-emission, being the luminescence maximum tunable with precision between lambda = 530 nm (green) and lambda = 490 nm (blue). This hybrid nc-MAPbBr(3)/MOx structure presents high mechanical stability and permits subsequent infiltration with an elastomer to achieve a self-standing flexible film, which not only maintains the photo-emission efficiency of the nc-MAPbBr(3) unaltered but also prevents their environmental degradation. Applications as adaptable color-converting layers for light-emitting devices are envisaged and demonstrated.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b11706
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Behavior of High-Strength Polypropylene Fiber-Reinforced Self-Compacting Concrete Exposed to High Temperatures
Rios, JD; Cifuentes, H; Leiva, C; Garcia, C; Alba, MDJournal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 30 (2018) 04018271 DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002491
Abstract
In this study we analyzed the use of high-performance structural concrete reinforced with polypropylene fibers in applications requiring long exposure times to high temperatures, such as thermal energy storage systems. We analyzed the behavior of the concrete at different temperatures (hot tests: 100 degrees C, 300 degrees C, 500 degrees C and 700 degrees C), cooled-down states (cold tests) and exposure times (6, 24, and 48h). We also experimentally determined the thermogravimetric analysis, fracture behavior, compressive strength, Young's modulus, and tensile strength of concrete. Subsequently, we performed a comprehensive analysis of the thermal and mechanical behavior of high-performance concrete under different thermal conditions. We applied longer exposure times to broaden the available results on the behavior of high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete when subjected to high temperatures. Results show that, once thermal and moisture equilibriums are reached, exposure time does not have any influence on mechanical properties. They also provide useful information about the influence of high temperatures on the different parameters of fiber-reinforced concrete and its application for thermal energy storage structures.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002491
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The Role of Surface Recombination on the Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells: Effect of Morphology and Crystalline Phase of TiO2 Contact
Idigoras, J; Contreras-Bernal, L; Cave, JM; Courtier, NE; Barranco, A; Borras, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Anta, JA; Walker, ABAdvanced Materials Interfaces, 5 (2018) art. 1801076 DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801076
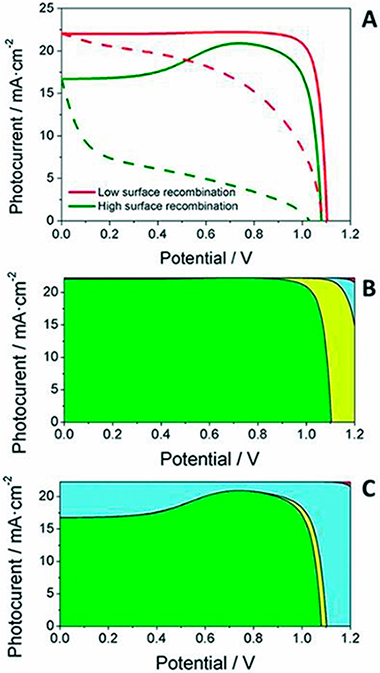
Abstract
Herein, the preparation of 1D TiO2 nanocolumnar films grown by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition is reported as the electron selective layer (ESL) for perovskite solar devices. The impact of the ESL architecture (1D and 3D morphologies) and the nanocrystalline phase (anatase and amorphous) is analyzed. For anatase structures, similar power conversion efficiencies are achieved using an ESL either the 1D nanocolumns or the classical 3D nanoparticle film. However, lower power conversion efficiencies and different optoelectronic properties are found for perovskite devices based on amorphous 1D films. The use of amorphous TiO2 as electron selective contact produces a bump in the reverse scan of the current-voltage curve as well as an additional electronic signal, detected by impedance spectroscopy measurements. The dependence of this additional signal on the optical excitation wavelength used in the IS experiments suggests that it stems from an interfacial process. Calculations using a drift-diffusion model which explicitly considers the selective contacts reproduces qualitatively the main features observed experimentally. These results demonstrate that for a solar cell in which the contact is working properly the open-circuit photovoltage is mainly determined by bulk recombination, whereas the introduction of a "bad contact" shifts the balance to surface recombination.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801076
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Influence of irrigation conditions in the germination of plasma treated Nasturtium seeds
Molina, R; Lopez-Santos, C; Gomez-Ramirez, A; Vilchez, A; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARScientific Reports, 8 (2018) art. 16442 DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34801-0
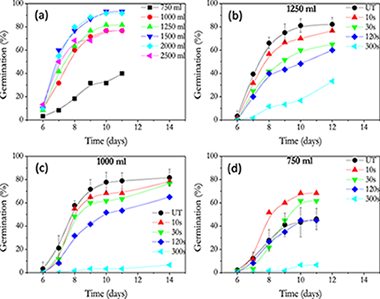
Abstract
Plasma treatments had emerged as a useful technique to improve seed germination. In this work we investigate the influence of different irrigation conditions and plasma treatments on the germination of nasturtium seeds. During plasma treatment, seeds experience a progressive weight loss as a function of treatment time that has been associated to water release, a process that is more pronounced after longer plasma treatment times. Seeds treated for short times (<30 s) are able to germinate more efficiently than untreated specimen under hydric stress (drought conditions), while plasma treatments for longer times (up to 300 s) impaired germination independently on irrigation conditions. Characterization analysis of plasma treated seeds by FTIR-ATR, SEM/EDX and XPS showed that plasma treatment affected the chemical state of pericarp while, simultaneously, induced a considerable increase in the seeds water uptake capacity. The decrease in germination efficiency found after plasma treatment for long times, or for short times under optimum irrigation conditions, has been attributed to that the excess of water accumulated in the pericarp hampers the diffusion up to the embryo of other agents like oxygen which are deemed essential for germination.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34801-0
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
High voltage vacuum-deposited CH3NH3PbI3–CH3NH3PbI3 tandem solar cells
Avila, J; Momblona, C; Boix, P; Sessolo, M; Anaya, M; Lozano, G; Vandewal, K; Miguez, H; Bolink, HJEnergy & Environmental Science, 11 (2018) 3292-3297 DOI: 10.1039/c8ee01936c
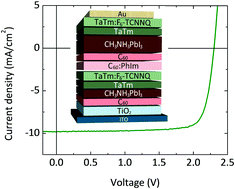
Abstract
The recent success of perovskite solar cells is based on two solid pillars: the rapid progress of their power conversion efficiency and their flexibility in terms of optoelectrical properties and processing methods. That versatility makes these devices ideal candidates for multi-junction photovoltaics. We report an optically optimized double junction CH3NH3PbI3-CH3NH3PbI3 tandem solar cell where the matched short-circuit current is maximized while parasitic absorption is minimized. The use of an additive vacuum-deposition protocol allows us to reproduce calculated stack designs, which comprise several charge selective materials that ensure appropriate band alignment and charge recombination. This rationalized configuration yields an unprecedented open circuit voltage of 2.30 V. Furthermore, this tandem solar cell features efficiencies larger than 18%, higher than those of the individual sub-cells. Low photo-current values allow reducing the losses associated to the series resistance of transparent contacts, which opens the door to the realization of efficient large area modules.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1039/c8ee01936c
Reactividad de Sólidos
Scalable synthesis of potential solar cell absorber Cu2SnS3 (CTS) from nanoprecursors
Hegedus, M; Balaz, M; Tesinsky, M; Sayagues, MJ; Siffalovic, P; Krulakova, M; Kanuchova, M; Briancin, J; Fabian, M; Balaz, PJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 768 (2018) 1006-1015 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.284
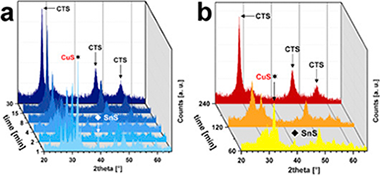
Abstract
The present paper demonstrates an easy and scalable mechanochemical synthesis of ternary sulfide Cu2SnS3 (CTS) as a promising solar cell absorber. For the synthesis, pre-milled nanoparticles of CuS and SnS were used. The pure CTS phase was readily obtained after 60 min of milling in a laboratory planetary ball mill and 240 min in an industrial eccentric vibration industrial mill, respectively. The reaction progress of laboratory scale synthesis was studied by the quantitative Rietveld analysis. The reaction speed reaches its maximum at 4.6 min and the reaction is completed at approximately 60 min, according to the fitted data. The products of the syntheses were further characterized by X-ray powder diffractometry, Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and UV-Vis spectroscopy. The results revealed formation of near-stoichiometric CTS nanoparticles with tetragonal I-42m symmetry. An average crystallites size of approximately 10-15 nm was determined for CTS phase. The SEM images support quintessential polydisperse character of the powders obtained by ball-milling approach. The materials seem to be suitable for photovoltaic applications with the band-gap energies of approximately 1.16-1.19 eV.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.284
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanically induced combustion synthesis of niobium carbonitride nanoparticles
Jalaly, M; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 267 (2018) 106-112 DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2018.08.027
Abstract
Niobium carbonitride [Nb(C,N)] nanoparticles were synthesized by a combustive mechanochemical reaction in the Mg/Nb2O5/C3H6N6 system. High-energy ball milling was used to promote a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). Combustion occurred after a very short milling period of 5 min. X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) analyses revealed that the nature of the product is an intermixed carbonitride material. The formation mechanism of Nb(C,N) resulted from the magnesiothermic reduction of niobium oxide to generate elemental Nb, which then reacted with the species generated from the melamine decomposition.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2018.08.027
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Analysis of the variables that modify the robustness of Ti-SiO2 catalysts for alkene epoxidation: Role of silylation, deactivation and potential solutions
Plata, JJ; Pacheco, LC; Remesal, ER; Masa, MO; Vega, L; Marquez, AM; Odriozola, JA; Sanz, JFMolecular Catalysis, 459 (2018) 55-60 DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.08.010
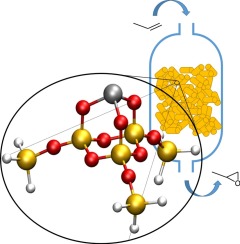
Abstract
Catalytic epoxidation of alkenes plays an essential role in the transformation and synthesis of many organic chemicals. Ti atoms grafted on mesoporous silica, silylated on the surface, is considered the most active and selective catalyst for these reactions. However, the durability and robustness of the active centers remain as the main drawback in industry. In this paper, the characterization of industrial samples is combined with DFT calculations to rationalize the deactivation process of the catalyst and improve its performance. Silylating agents are characterized by experimental and simulated 29Si-NMR and their role in the catalytic mechanism is analysed. Potential deactivation processes are identified before, during and after the reaction. Modifications of the silylating agents and of the active center are proposed to improve the durability of the catalyst.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.08.010
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Environmentally friendly monolithic highly-porous biocarbons as binder-free supercapacitor electrodes
Orlova, TS; Shpeizman, VV; Glebova, NV; Nechitailov, AA; Spitsyn, AA; Ponomarev, DA; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JReviews on Advanced Materials Science, 55 (2018) 50-60 DOI: 10.1515/rams-2018-0027
Abstract
A simple, low-cost and environmentally friendly method has been used to obtain highly porous biomorphic carbon monoliths with a good combination of interconnected macro-, meso- and microporosity, and good electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, making these biocarbon materials interesting for electrochemical applications as binder-free electrodes. Highly porous monolithic biocarbons were obtained from beech wood precursors through pyrolysis and subsequent surface modification in a steam heated to 970 degrees C with different activation times. The obtained biocarbons demonstrated good electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. They were studied as electrodes for supercapacitors in half cell experiments, demonstrating maximum gravimetric capacitance of 200 F g(-1) in a basic media at scan rate 1 mV s(-1). Galvanostatic charge-discharge experiments showed maximum capacitance of 185 F g(-1) at current density of 0.15 A g(-1) and similar to 100 F g(-1) at current density of 0.75 A g(-1). It has been shown that in addition to the developed porous surface, the micropores with diameters exceeding 1 nm play a key role for the enhanced electrochemical capacity. Long-cycling experiments demonstrated excellent stability of the monolithic biocarbon electrodes with no reduction of the initial capacitance values after 600 cycles in voltammetry.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1515/rams-2018-0027
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Sustainable Fabrication of Plant Cuticle-Like Packaging Films from Tomato Pomace Agro-Waste, Beeswax, and Alginate
Tedeschi, G; Benitez, JJ; Ceseracciu, L; Dastmalchi, K; Itin, B; Stark, RE; Heredia, A; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6 (2018) 14955-14966 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03450

Abstract
Plant cuticles have been used as models to produce hydrophobic films composed of sodium alginate, the fatty acid fraction of tomato pomace agrowaste, and beeswax. The fabrication process consisted of the blending of components in green solvents (water and ethanol) and a subsequent thermal treatment (150 degrees C, 8 h) to polymerize unsaturated and polyhydroxylated fatty acids from tomato pomace. When sodium alginate and tomato pomace fatty acids were blended, free-standing films were obtained. These films were characterized to evaluate their morphological (SEM), chemical (solid-state NMR, ATR-FTIR), mechanical (tensile tests), thermal (TGA), and hydrodynamic (water contact angle, uptake, and permeability) properties. A comparison between nonpolymerized and polymerized samples was carried out, revealing that the thermal treatment represents a sustainable route to create structured, composite networks of both components. Finally, beeswax was added to the blend with the same amounts of sodium alginate and tomato pomace fatty acids. The presence of the wax improved the hydrophobicity and the mechanical and water barrier properties as well as decreased the water uptake. These results indicate that polymerized plant cuticle-like films have valuable potential for packaging applications.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03450
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Selective CO methanation with structured RuO2/Al2O3 catalysts
Munoz-Murillo, A; Martinez, LM; Dominguez, MI; Odriozola, JA; Centeno, MAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 236 (2018) 420-427 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.05.020
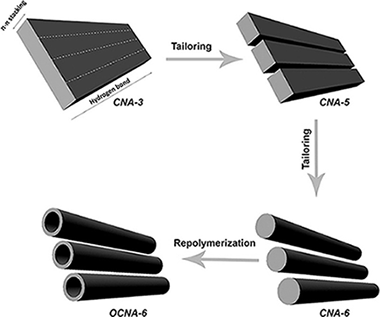
Abstract
Active and selective structured RuO2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO methanation using a flow simulating CO2-rich reformate gases from WGS and PROX units (H-2 excess, CO2 presence and 300 ppm CO concentration) were prepared. Both, the RuO2/Al2O3 powder and the slurry prepared from it for its structuration by washcoating of the metallic micromonolithic structure, were also active and selective. Both the slurry (S-RuAl) and micro monoliths (M-RuAl) were able to completely and selectively methanate CO at much lower temperatures than the parent RuAI powder. The optimal working temperature in which the CO conversion is maximum and the CO2 conversion is minimized was determined to be from 149 degrees C to 239 degrees C for S-RuAl and from 165 degrees C to 232 degrees C for M-RuAl, whilst it was from 217 degrees C to 226 degrees C for RuAI powder. TPR, XRD and TEM measurements confirmed that the changes in the activity and selectivity for CO methanation among the considered catalysts can be related with modifications in the surface particle size of ruthenium and its reducibility. These were ascribed to the metallic substrate, the presence of PVA and colloidal alumina in the slurry preparation, the aqueous and acidic media and the thermal treatment used, resulting in a more active and selective catalysts than the parent powder.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.05.020
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quantitative analysis of Yb 4d photoelectron spectrum of metallic Yb
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Tougaard, SSurface & Coatings Technology, 50 (2018) 1168-1173 DOI: 10.1002/sia.6402
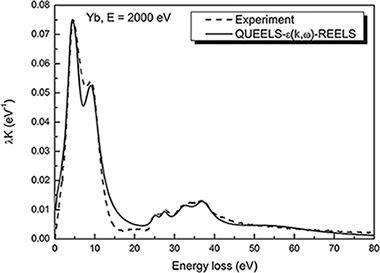
Abstract
The measured Yb 4d(3/2) intensity is larger than the Yb 4d(5/2) in X-ray photoelectron (XPS) emission of metallic Yb, which is unexpected. The shape and intensity of photoelectron peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface (including bulk and surface effects) and to intrinsic excitations due to the sudden creation of the static core hole. To quantitatively extract from experimental XPS the primary excitation spectrum (ie, the initial excitation process) of the considered transition, these effects must be included within the theoretical description. The combined effect of both extrinsic and intrinsic excitations can be described by an effective energy-differential inelastic electron scattering cross section for XPS evaluated by a dielectric response model with the dielectric function as only input. Then, using this cross section, a direct evaluation of the primary excitation spectrum is performed by standard peak shape analysis for thick homogeneous samples. We use this approach in the present paper to determine the Yb 4d photoemission spectrum for metallic Yb. We show that the unexpected larger intensity of Yb 4d(3/2) compared to 4d(5/2) can be fully accounted for by our model and that the total spectrum consists of a sum of symmetric primary excitation peaks.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1002/sia.6402
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Valorization of Tomato Processing by-Products: Fatty Acid Extraction and Production of Bio-Based Materials
Benitez, JJ; Castillo, PM; del Rio, JC; Leon-Camacho, M; Dominguez, E; Heredia, A; Guzman-Puyol, S; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAMaterials, 11 (2018) art. 2211 DOI: 10.3390/ma11112211
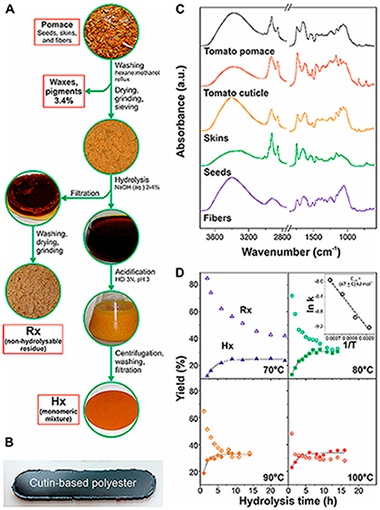
Abstract
A method consisting of the alkaline hydrolysis of tomato pomace by-products has been optimized to obtain a mixture of unsaturated and polyhydroxylated fatty acids as well as a non-hydrolysable secondary residue. Reaction rates and the activation energy of the hydrolysis were calculated to reduce costs associated with chemicals and energy consumption. Lipid and non-hydrolysable fractions were chemically (infrared (IR) spectroscopy, gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC-MS)) and thermally (differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)) characterized. In addition, the fatty acid mixture was used to produce cutin-based polyesters. Freestanding films were prepared by non-catalyzed melt-polycondensation and characterized by Attenuated Total Reflected-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), DSC, TGA, Water Contact Angles (WCA), and tensile tests. These bio-based polymers were hydrophobic, insoluble, infusible, and thermally stable, their physical properties being tunable by controlling the presence of unsaturated fatty acids and oxygen in the reaction. The participation of an oxidative crosslinking side reaction is proposed to be responsible for such modifications.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.3390/ma11112211
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Exotic grain growth law in twinned boron carbide under electric fields
Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Rodriguez, ADJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 38 (2018) 4590-4596 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.06.029
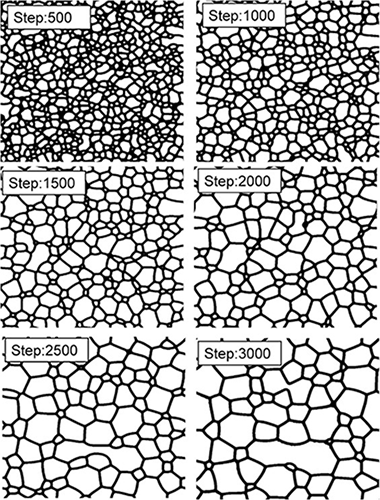
Abstract
Grain growth is a ubiquitous phenomenon in all materials, and it affects both structural and functional properties. Despite its intrinsic importance, a full comprehension of grain growth from a fundamental point of view-i.e., from the nanoscale to the macroscale-is still a pending issue. In practical terms, our knowledge relies on the classical kinetic laws reported sixty years ago.
This paper reports the violation of such classical laws in boron carbide ceramics consolidated by spark plasma sintering. The conjunction of high temperature gradients with large compressive stress when a pulse electric current passes through the ceramic powders gives rise to an intense twinning-detwinning formation. These forming steps at the grain boundaries change the grain mobility drastically. Therefore, a new 'exotic' law for grain-growth kinetics is found and validated at different temperatures and dwell times.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.06.029
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Nanoporous Pt-based catalysts prepared by chemical dealloying of magnetron-sputtered Pt-Cu thin films for the catalytic combustion of hydrogen
Giarratano, F; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Montes, O; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 235 (2018) 168-176 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.04.064
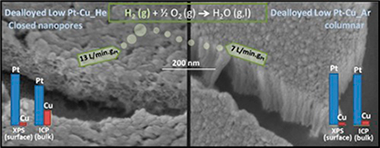
Abstract
In this work, we prepared SiC-supported Pt-Cu thin films by magnetron sputtering for use as catalysts for the combustion of hydrogen under oxidizing conditions. We tested the catalysts as prepared and after chemical dealloying. A methodology is presented to fabricate catalytic thin films of a desired composition with tailored magnetron targets with lower Pt consumption. The deposition gas was changed to prepare columnar (Ar-deposited) and closed-porous (He-deposited) films to study the effect of the microstructure on the activity. The effect of composition was also studied for the columnar samples. The as-prepared Pt-Cu thin films showed significant activity only at temperatures higher than 100 °C. Dealloying permitted an increase in the activity to achieve near room-temperature activity. The dealloyed closed-porous He-deposited sample was the most active, being able to convert as much as 13.15 LH2·min−1 gPt−1 at 70 °C (Ea = 1 kJ mol−1). This sample was preferentially dealloyed on the surface, yielding an almost pure Pt shell (96% at. Pt) and a Cu-depleted interior (71% at. Pt). This compositional inhomogeneity enabled the sample to achieve enhanced activity compared to the Ar-deposited columnar sample (with similar initial composition, but uniformly dealloyed), probably due to the compressive surface lattice strain. The dealloyed closed-porous He-deposited sample was shown to be durable over five cycles.
Noviembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.04.064
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Grain-boundary diffusion coefficient in alpha-Al2O3 from spark plasma sintering tests: Evidence of collective motion of charge disconnections
Tamura, Y; Zapata-Solvas, E; Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ACeramics International, 44 (2018) 19044-19048 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.073
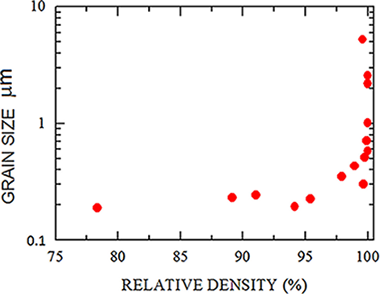
Abstract
The sintering of fine-grained a-alumina by spark plasma sintering (SPS) was performed to study grain growth under SPS conditions. Grain growth is found to be extensive at relative densities above 95%. A grain growth versus dwell time analysis during SPS allows for the determination of the grain-boundary diffusion coefficient. This study shows that the remarkable enhancement of grain-boundary diffusion derived from a previous analysis could be a consequence of the presence of the recently discovered "disconnections" at the grain boundaries of alpha-alumina. Their presence, together with their electric charge and the external electric field at the boundaries, are the key ingredients for a violation of the typical grain growth kinetic law. When they are introduced appropriately, an updated value of the grain-boundary diffusion coefficient is achieved. A comparison with other values reported previously in the literature through other techniques and a critical analysis are also carried out.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.073
Materiales Avanzados
Biomass fly ash and aluminium industry slags-based geopolymers
Perez-Villarejo, L; Bonet-Martinez, E; Eliche-Quesada, D; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Rincon-Lopez, JM; Castro-Galiano, EMaterials Letters, 229 (2018) 6-12 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.06.100
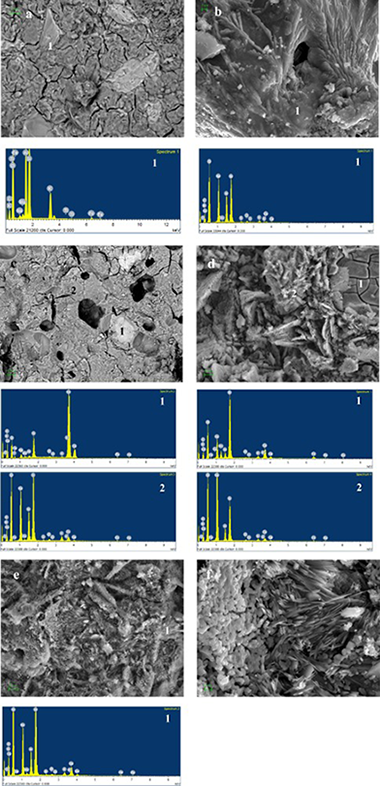
Abstract
Geopolymers are a new class of non-Portland cements produced using an alumino-silicate material and an activating solution, which is mainly composed of sodium or potassium and waterglass to be subsequently cured at relatively low temperatures. Those can be formulated by adding natural minerals, waste and/or industrial by-products. The study investigates the microstructural properties of geopolymers synthesized from metakaolin (MK) and the admixture of fly ash (FBA) and aluminium industry slags (AIS) at different ages of curing. Five different geopolymer compositions were prepared and characterized by XRD, ATR-FTIR and SEM/EDS. The study revealed that geopolymeric gels are identified, which show mainly glassy microstructures, in agreement with the X-ray amorphous diffraction patterns, broad FTIR features and confirmed by SEM/EDS, with promising results prior to an industrial scale.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.06.100
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mesoporous Silica by Solution-Combustion Synthesis Followed by Etching
Salehtash, F; Jalaly, M; Motejadded Emrooz, HB; Gotor, FJ; Sayagués, MJInternational Journal of Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis, 27 (2018) 221–227 DOI: 10.3103/S1061386218040064
Abstract
Mesoporous silica was synthesized through the solution-combustion process followed by etching with aqueous solution of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Combustion products were characterized by XRD, FTIR, SEM, TEM, HRTEM, and BET analysis. After etching, the specific surface, mean pore size, and volume of porous space in silica increased up to 390 m(2)/g, 15 nm, and 1.6 cm(3)/g, respectively. The synthesized mesoporous silica exhibited good performance in the tests on elimination of methylene blue from aqueous solution.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.3103/S1061386218040064
Spanish and Portuguese Gilding Threads: Characterization Using Microscopic Techniques
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Albardonedo, A; Robador, MD; Duran, AMicroscopy and Microanalysis, 24 (2018) 574-590 DOI: 10.1017/S1431927618015167
Abstract
Gilding threads collected from Spanish and Portuguese palaces and from the embroideries and adornments of sculptures of the Virgin and Christ that form part of Sevillian Holy Week were analyzed and compared (20 artifacts were evaluated). The study covered a broad time period with examples from the 13th to 14th centuries, 18th to 20th centuries, and also including modern embroideries. A combination of scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy was used. The knowledge of the layered structures of the threads has provided very valuable information regarding the manufacturing techniques. The different metal threads found in the embroidery studied consisted of gold, silver, copper, and alloys of these metals and aluminium. The fabrication procedures often differed in the different workshops and changed with time. In the modern embroideries, a decrease of precious metal concentration was detected. The threads were wound around a core of silk threads.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1017/S1431927618015167
Materiales Avanzados
Manufacture of sustainable clay ceramic composite with composition SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-K2O materials valuing biomass ash from olive pomace
Bonet-Martinez, E; Perez-Villarejo, L; Eliche-Quesada, D; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Carrasco-Hurtado, B; Castro-Galiano, EMaterials Letters, 229 (2018) 21-25 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.06.105
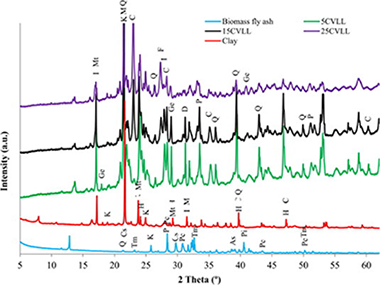
Abstract
Fly ash is a biomass combustion by-product produced by dragging ash from the base of the furnace. Disposing of ash is a growing economic and environmental burden. Based on physical and chemical properties, fly ash could be used in the manufacture of construction materials. This paper investigates the influence of biomass fly ash from olive pomace as additive to manufacture of clay ceramic composite materials. Fired clay brick at 950 degrees C were prepared containing between 0 and 25 wt% fly ash. Final products are studied by water absorption, bulk density, loss of ignition, linear shrinkage, compressive strength and physisorption N-2. The results reveal that the porosity of the materials increases with the level of fly ash replacement (10% up to 25 wt%) resulting in to increased water absorption and decreased compressive strength. Fired clay brick developed in this study can be used for construction materials based on criteria of the current regulations.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.06.105
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
High-temperature oxidation of CrAlYN coatings: Implications of the presence of Y and type of steel
Rojas, TC; Dominguez-Meister, S; Brizuela, M; Sanchez-Lopez, JCSurface & Coatings Technology, 354 (2018) 203-2013 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.09.020
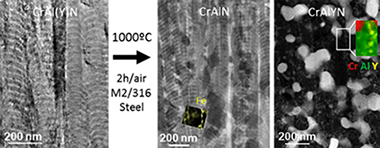
Abstract
Nanolayered CrAIN and CrAIYN/CrAIN (average contents of Al approximate to 25 at.% and Y approximate to 1.6 at. %) coatings are deposited on M2 and 316 steel substrates and heated to 1000 degrees C in air for 2 h to study their oxidation mechanism, the thermal stability and the reactive element (RE) effect of yttrium. CrAIN on M2 develops a Cr2O3/Al2O3 passivation layer that preserves in high degree the fcc-CrAIN structure however iron ions leave the substrate and travel to the surface along the column boundaries. The CrAIYN/CrAIN coatings deposited on steels are not stable at 1000 degrees C, and the initial fcc-CrAIN phase is partially transformed to hcp-Al(O)N and Cr-Fe phases (M2) and Cr2N and Al2O3 (316). The addition of Y changes the predominant scale growth direction. Inward oxygen diffusion becomes dominant but a reduction of the oxide scale thickness as compared to CrAIN is not observed. The advanced microstructural analysis made by transmission electron microscopy combined with electron energy loss spectroscopy determined that yttrium migrates mainly to the oxide scale (forming mixed oxides with substrate elements - V and Mo, either as dispersed particles or segregated at the grain boundaries) in M2, and to the oxide interface and column boundaries (forming Al-Y oxides and YN, respectively) in 316 steel. The benefits of addition of Y in improving the oxidation resistance are discussed comparatively with literature data. The RE effect of yttrium is thus observed to be dependent on the substrate, film architecture and composition.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.09.020
Reactividad de Sólidos
Study of the thermal decomposition of historical metal threads
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Perez-Maqueda, R; Franquelo, ML; Duran, AJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 134 (2018) 15-22 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-017-6924-x
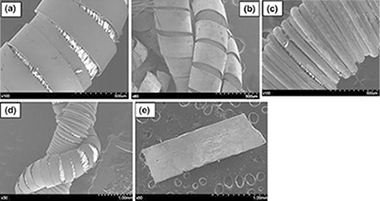
Abstract
In this work, it is reported that thermal analysis techniques such as differential thermal analysis and thermogravimetric analysis are very useful for evaluating metals threads and fibres used in the manufacture of historical artifacts. Thermal analysis has been used to characterize the silk, cotton and linen employed as supports and the copper, silver and aluminium as the metallic components in the studied threads. Other organic compounds, mainly added for the conservation of the threads, have also been characterized.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-017-6924-x
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic H2 production from glycerol aqueous solutions over fluorinated Pt-TiO2 with high {001} facet exposure
V. Vaiano; M.A. Lara; G. Iervolino; M. Matarangolo; J.A. Navío; M.C. HidalgoJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A-Chemistry, 365 (2018) 52-59 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.07.032
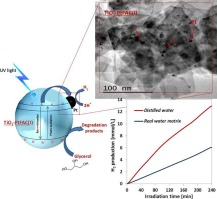
Abstract
An optimized fluorinated TiO2 catalyst with high {001} facet exposure loaded with platinum (TiO2-PtFAC) was tested in the photocatalytic hydrogen production from glycerol solution under UV light irradiation. The samples were synthesized by direct hydrothermal treatment starting from two different types of precursors that are titanium tetraisopropoxide (I) or titanium butoxide (B), while platinisation was performed by photodeposition method. The obtained catalysts were characterised by different techniques (XRD, FESEM, TEM, BET, UV–vis DRS, XRF and XPS) and the results evidenced that anatase is the only crystalline phase present in all TiO2 samples. The morphology of the samples was seen as rectangular platelets particles where Pt particles were was observed all over the surface. The presence of Pt and F in the platinised samples was also confirmed by XRF and XPS analysis. The photocatalytic results have shown that the presence of Pt on TiO2{001}facet surface remarkably enhanced the hydrogen production from aqueous solution at 5 wt % of glycerol. Comparing the results obtained from the photocatalysts prepared by the two different precursors, it was found that the best performances in terms of H2 production was achieved with TiO2-PtFAC(I) (about 13 mmol L−1 after 4 h of irradiation time), while the H2 production was lower for TiO2-PtFAC(B) (about 9 mmol L−1 after 4 h of irradiation time). The effect of the operating conditions using TiO2-PtFAC(I) evidenced that the highest H2 production was obtained with a photocatalyst dosage equal to 1.5 g L−1, initial glycerol concentration at 5 wt% and a pH value equal to 7. Finally, a photocatalytic test was also performed on glycerol solution prepared with a real water matrix. Despite the presence of ions scavengers (chlorides and carbonates) in solution, TiO2-PtFAC(I) was able to reach a photocatalytic H2production of about 6 mmol L−1 after 4 h of UV light irradiation.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.07.032
Reactividad de Sólidos
Isosymmetric structural phase transition of the orthorhombic lanthanum gallate structure as a function of temperature determined by Rietveld analysis
Tang, Y. Q.; Lopez-Cartes, C.; Aviles, M. A.; Cordoba, J. M.CRYSTENGCOMM, 20 (2018) 5562-5569 DOI: 10.1039/c8ce00726h
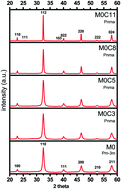
Abstract
High energy planetary ball milling has been used to synthesize pseudo-cubic highly-pure LaGaO3 in one hour from its oxide components in an air atmosphere. Calcination at different temperatures led to the crystallization of lanthanum gallate in an orthorhombic structure with its local lanthanum coordination number environment changing from 12 to 7 when the temperature was increased. This change was attributed to the thermal expansion of the Ga-O bonds that varied non-monotonically inducing GaO6 tilting. Rietveld analysis, Raman spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy were used to elucidate the LaGaO3 structures at different temperatures.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1039/c8ce00726h
Reactividad de Sólidos
Optimizing the homogenization technique for graphene nanoplatelet/yttria tetragonal zirconia composites: Influence on the microstructure and the electrical conductivity
Lopez-Pernia, C; Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Gonzalez-Orellana, C; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 767 (2018) 994-1002 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.199
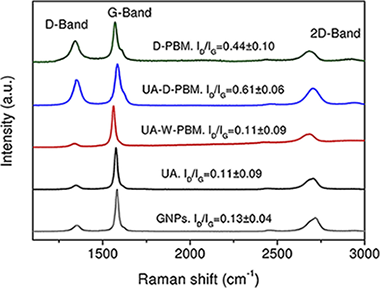
Abstract
3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline (3YTZP) ceramic composite powders with 10 vol% nominal content of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) were prepared using four different homogenization routines: dispersion of the powder mixture by ultrasonication in isopropyl alcohol, homogenization in a high-energy planetary ball mill in wet or dry conditions after ultrasonication, and milling of the powders in a high-energy planetary ball mill in dry conditions. A significant effect of the homogenization routine on the powders particle size distribution was revealed by laser granulometry and Raman spectroscopy. Highly densified composites were obtained after spark plasma sintering (SPS) and remarkable differences on the GNP size, shape and distribution throughout the ceramic matrix and also in the electrical conductivity were observed in the four different composites. The composite with the best performance in terms of electrical conductivity was the one prepared after planetary ball milling of the powders in dry conditions as a consequence of the reduced dimensions of the GNPs and their excellent distribution throughout the ceramic matrix.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.199
Reactividad de Sólidos
The role of carbon nanotubes on the stability of tetragonal zirconia polycrystals
Morales-Rodriguez, A; Poyato, R; Gutierrez-Mora, F; Munoz, A; Gallardo-Lopez, ACeramics International, 44 (2018) 17716-17723 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.238
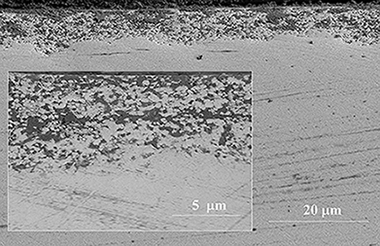
Abstract
The effect of single walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) at zirconia grain boundaries on the stability of a tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline matrix has been explored in as-sintered composites and after low temperature hydro thermal degradation (LTD) experiments. For this purpose, highly-dense 3 mol% Y2O3-doped tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline (3YTZP) ceramics and SWNT/3YTZP composites were prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis and microstructural observations point out that an increasing amount of well-dispersed SWNT bundles surrounding zirconia grains decreases the metastable tetragonal phase retention in the ceramic matrix after sintering. In contrast, the tetragonal ceramic grains in composites with SWNTs are less sensitive to the presence of water, i.e. to undergo a martensitic transformation under LTD conditions, than monolithic 3YTZP ceramics. The SWNT incorporation diminishes micro-cracking due to tetragonal to monoclinic ZrO2 phase transformation in the composites.
Octubre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.238
Materiales Avanzados
Vitrification and derived glass-ceramics from mining wastes containing vermiculite and lithium aluminium phosphate
Rincon, JM; Callejas, P; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Jordan, MMMaterials Letters, 227 (2018) 86-89 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.05.001
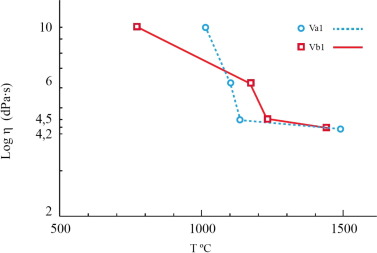
Abstract
The waste vitrification of abandoned open sky vermiculite deposits has been considered by combining with a natural phosphate mineral residue. Several batches haven been designed from the composition system: Li2O-MgO-Al2O3-P2O5-SiO2 including some Fe2O3 and Fluoride. The resulting glasses are transparent and smooth green coloured, giving rise after TTT treatments to several opal, opaque glass-ceramics with iridescent surface. Full characterization has been carried out by XRD and electron microscopy with EDS, as well as by XPS spectroscopies, concluding that the main crystalline phases formed were alpha-cordierite and beta-spodumene. The surface of these glass-ceramics from vermiculiteamblygonite is enriched in Fe2O3. Compared to the parent glasses, the final glass-ceramics exhibited and improvement in fracture toughness.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.05.001
Reactividad de Sólidos
Combined kinetic analysis of multistep processes of thermal decomposition of polydimethylsiloxane silicone
Garcia-Garrido, C; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PEPolymer, 153 (2018) 558-564 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2018.08.045
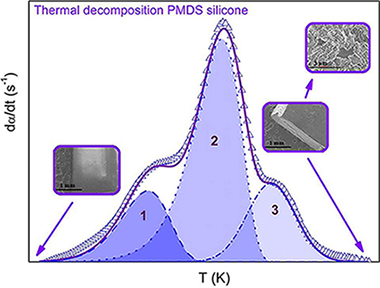
Abstract
In this work, we studied the thermal decomposition of a widely employed silicone elastomer, polydimethylsiloxane, in an inert atmosphere. This silicone elastomer has several applications due to its high thermal stability such as MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) precursors, microfluidic components, adhesives, lubricants, and precursors for non-porous ceramics. Therefore, a reliable description of the thermal decomposition kinetics is important to prevent or control the decomposition in such applications. While the decomposition has been amply reported as a complex process, most kinetic studies published on this system use simplified methods that avoid the fact that the entire process cannot be described by a single kinetic triplet. Here, we have studied the decomposition process by first separating the overall reaction into its three constituent steps which were subsequently analysed independently. The deconvolution was carried out using Fraser-Suzuki function that is capable of fitting an asymmetric peak fitting function. The resulting kinetic parameters proved to be able to reconstruct the original experimental curves but are also capable of producing accurate predictions of curves recorded at heating schedules different from those employed to record the experimental data used in the kinetic analysis. Finally, it was found that the rate limiting step of all stages is the diffusion of the gases released during the polymer decomposition through the transforming polymeric matrix.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2018.08.045
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Operando DRIFTS-MS Study of WGS and rWGS Reaction on Biochar-Based Pt Catalysts: The Promotional Effect of Na
Santos, JL; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAC-Journal of Carbon Research, 4 (2018) 47 DOI: 10.3390/c4030047
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis, characterization and combined kinetic analysis of thermal decomposition of hydrotalcite (Mg6Al2(OH)(16)CO3 center dot 4H(2)O)
Yahyaoui, R; Jimenez, PES; Maqueda, LAP; Nahdi, K; Luque, JMCThermochimica Acta, 667 (2018) 177-184 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2018.07.025
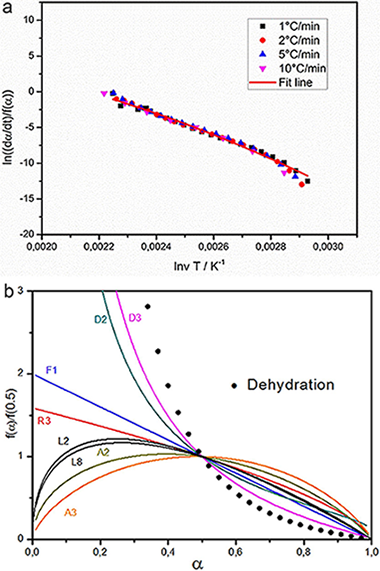
Abstract
Here, a kinetic study of the thermal decomposition of synthesized hydrotalcite, Mg-6 Al-2 CO3(OH)(16)center dot H2O, has been carried out using thermogravimetric experiments in air atmosphere. It is shown that the thermal decomposition occurs in two well differentiated stages. The first one is a single-step dehydration process that comprises the release of four water molecules. On the other hand, the second stage is complex and corresponds to both dehydroxylation and decarbonation processes which occur simultaneously. The kinetic parameters describing all processes were calculated by means of a combined approach comprising isoconversional, model-fitting and deconvolution methods. It was concluded that dehydroxilation and decarbonization cannot be separated by TG experiments and the two stages contributing to the complex process do not apparently match the expected stoichiometry of the process. Therefore, it is proposed that such stages mark a change on the reaction mechanism due to the structural collapse of the laminar double hydroxide.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2018.07.025
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Adhesion enhancement of DLC hard coatings by HiPIMS metal ion etching pretreatment
Santiago, JA; Fernandez-Martinez, I; Wennberg, A; Molina-Aldareguia, JM; Castillo-Rodriguez, M; Rojas, TC; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Gonzalez, MU; Garcia-Martin, JM; Li, H; Bellido-Gonzalez, V; Monclus, MA; Gonzalez-Arrabal, RSurface & Coatings Technology, 349 (2018) 787-796 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.04.090
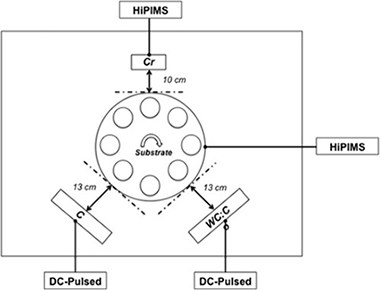
Abstract
Poor adhesion is a recurrent problem for the wider use of diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings in industrial applications. In this work, we investigate the effectiveness of high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) metal ion etching to improve the adhesion of DLC coatings on high speed steel substrates. The influence of HiPIMS pretreatment parameters, the metal ion selection for the process and the addition of bonding layers on the adhesion properties were studied. Daimler-Benz and nanoscratch test methods were used to evaluate the adhesion. The elemental composition, morphology and microstructure of the samples were evaluated by EELS, SEM, AFM and HRTEM. In general, samples pretreated with HiPIMS metal ion etching withstand larger critical loads than those pretreated by conventional Ar + glow discharge and bonding layers. The pretreatment is proven to be very effective at removing surface contaminants and providing a gradual interface. The selection of Cr over Ti contributes to a significant improvement on the adhesion due to the reduction of the oxygen level at the interface thus ensuring an optimal coating-substrate contact and a more compliant structure, which prevents the delamination failure.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.04.090
Materiales Avanzados
An approach to the heating dynamics of residues from greenhouse-crop plant biomass originated by tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum, L.)
Garzon, E; Morales, L; Ortiz-Rodriguez, IM; Sanchez-Soto, PJEnvironmental Science and Pollution Research, 25 (2018) 25880-25887 DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-2577-y
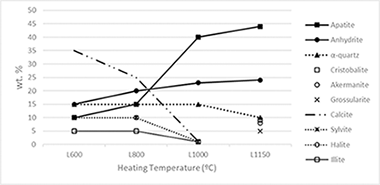
Abstract
The most representative of greenhouse-crop plant biomass residues of tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L.) were selected for this study by using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). The heating dynamics in air in the 600-1150 degrees C range of these residues for the production of renewable energy and the resultant ashes have been investigated. A total of 11 elements were determined by XRF in the biomass ashes and some minor elements. The content of alkaline elements and chlorides decreased as increasing heating temperature and disappeared at 1150 degrees C. Alkaline salts, NaCl and KCl, were volatilized by heating since 800 degrees C. The total contents of S and P in the biomass ashes were associated to CaSO4, and a complex phosphate identified by XRD. CaCO3 present at 600 degrees C was decomposed to CaO with disappearance at 1000 degrees C. By heating, new silicates were formed by solid-state reactions in the biomass residue. The minor elements have been found in a relative proportion lower than 0.9wt.% and they characterized the obtained ashes, with potential use as micronutrients.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-2577-y
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Sensing and biosensing with screen printed electrodes modified with nanostructured nickel oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles
Salazar, P; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochemistry Communications, 94 (2018) 5-8 DOI: 10.1016/j.elecom.2018.07.020
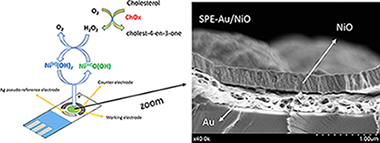
Abstract
This work reports about the sensing and biosensing applications of a novel screen printed electrode (SPE) modified by nanostructured nickel oxide thin films obtained by reactive magnetron sputtering under an oblique angle configuration. Using these films as electrodes we demonstrate their ability to detect hydrogen peroxide under neutral pH conditions. Furthermore, as a proof-of-concept, NiO-modified SPEs have been developed and their cholesterol biosensing properties determined by cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.elecom.2018.07.020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Improving the activity of gold nanoparticles for the water-gas shift reaction using TiO2-Y2O3: an example of catalyst design
Plata, JJ; Romero-Sarria, F; Suarez, JA; Marquez, AM; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JA; Sanz, JFPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 20 (2018) 22076-22083 DOI: 10.1039/c8cp03706j
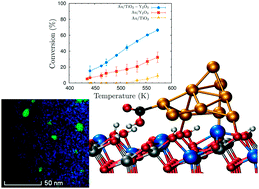
Abstract
In the last ten years, there has been an acceleration in the pace at which new catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction are designed and synthesized. Pt-based catalysts remain the best solution when only activity is considered. However, cost, operation temperature, and deactivation phenomena are important variables when these catalysts are scaled in industry. Here, a new catalyst, Au/TiO2-Y2O3, is presented as an alternative to the less selective Pt/oxide systems. Experimental and theoretical techniques are combined to design, synthesize, characterize and analyze the performance of this system. The mixed oxide demonstrates a synergistic effect, improving the activity of the catalyst not only at large-to-medium temperatures but also at low temperatures. This effect is related to the homogeneous dispersion of the vacancies that act both as nucleation centers for smaller and more active gold nanoparticles and as dissociation sites for water molecules. The calculated reaction path points to carboxyl formation as the rate-limiting step with an activation energy of 6.9 kcal mol(-1), which is in quantitative agreement with experimental measurements and, to the best of our knowledge, it is the lowest activation energy reported for the water-gas shift reaction. This discovery demonstrates the importance of combining experimental and theoretical techniques to model and understand catalytic processes and opens the door to new improvements to reduce the operating temperature and the deactivation of the catalyst.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1039/c8cp03706j
Química de Superficies y Catálisis - Reactividad de Sólidos
A direct in situ observation of water-enhanced proton conductivity of Eu-doped ZrO2: Effect on WGS reaction
Garcia-Moncada, N; Bobadilla, LF; Poyato, R; Lopez-Cartes, C; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 231 (2018) 343-356 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.001
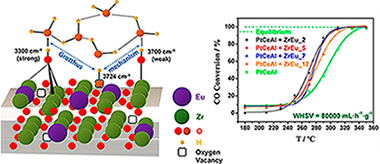
Abstract
Eu-doped ZrO2 solid solutions have been synthesized in order to prepare proton conductors as water-enhancer additives for the WGS reaction. Elemental characterization has been carried out revealing homogeneous dopant distribution resulting in fluorite-type solid solutions for Eu2O3 contents up to similar to 9 mol.%. Representative samples of the Eu-doped ZrO2 series have been analysed by Impedance Spectroscopy (IS) in inert, oxygen and wet conditions. The solid solution with 5 mol.% of Eu2O3 has presented the highest conductivity values for all tested conditions indicating an optimal amount of dopant. Moreover, the presence of vapour pressure results in an increment of the conductivity at temperatures lower than 300 degrees C, meanwhile at higher temperatures the conductivity is the same than that in inert conditions. To elucidate these results, in situ DRIFTS studies were carried out. These experiments evidenced the existence of water dissociation at oxygen vacancies (band at 3724 cm(-1)) as well as the presence of physisorbed water at temperatures up to similar to 300 degrees C where the band at 5248 cm(-1) characteristic of these species disappeared. These results points to a layer model where the physisorbed water interacts with surface hydroxyls generated by dissociated water that improves the proton conductivity through Grotthuss' mechanism in the RT-300 degrees C temperature range. These samples were successfully tested in WGS reaction as additive to a typical Pt-based catalyst. The presence of the mixed oxide reveals an increase of the catalyst' activity assisted by the proton conductor, since improves the water activation step.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.001
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Performance improvement in olive stone's combustion from a previous carbonization transformation
Gomez-Martin, A; Chacartegui, R; Ramirez-Rico, J; Martinez-Fernandez, JFuel, 228 (2018) 254-262 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.04.127
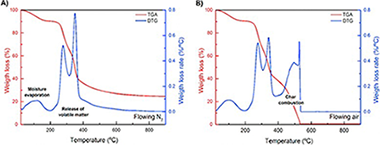
Abstract
Under the framework of circular economy, agricultural wastes are an interesting carbon-based feedstock for thermal energy and power generation. Their use could extend the availability of biomass-based fuel and, at the same time, would reduce negative environmental effects. However, depending on the residues' characteristics, their direct combustion in boilers presents some challenges which could be overcome with a carbonization pretreatment. In this paper, the main mechanisms of thermochemical transformation of an abundant agricultural waste, olive stone, into biochar products via slow carbonization are analyzed, with emphasis on the effect of peak carbonization temperature. Thermogravimetric and differential scanning calorimetry analysis are used to evaluate the performance of the resulting biochars compared to raw olive stone in combustion processes and to assess the correlation between the peak carbonization temperature and compositional and fuel properties. Results show that with a prior treatment up to an optimum temperature of 800 degrees C the energy density is increased up to three times compared to the raw material. These findings suggest that carbonization of olive stones reduces the barriers to their direct use in current biomass boiler technology.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.04.127
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanosynthesis of Sr1-xLaxTiO3 anodes for SOFCs: Structure and electrical conductivity
Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, J; Pueyo, M; Poyato, R; Garcia-Garcia, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 763 (2018) 679-686 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.243
Abstract
Sr1-xLaxTiO3 (SLT; 0 <= x <= 0.5) powder samples were synthesised at room temperature by a mechanochemical method from SrO, La2O3 and TiO2 mixtures in 90 min. The obtained SLT samples as potential anode materials in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) were investigated. The microstructure, electrical conductivity and chemical compatibility with yttria-stabilised zirconia (YSZ) were studied. The powder samples had a nanometric character after milling. After a subsequently heating at 900 degrees C, the particle size slightly increased, but still remained nanometric. At this high temperature, a good chemical compatibility with YSZ was found. The x = 0.2 sample gave the best electrical conductivity values, i.e. 0.23 W cm(-2). These features make such as-obtained samples good candidates to be used as anodes in SOFCs.
Septiembre, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.243
- ‹ anterior
- 15 of 37
- siguiente ›














