Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Strong activation effect on a ru-co-c thin film catalyst for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride
Arzac, GM; Paladini, M; Godinho, V; Beltran, AM; de Haro, MCJ; Fernandez, AScientific Reports, 8 (2018) art. 9755 DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28032-6
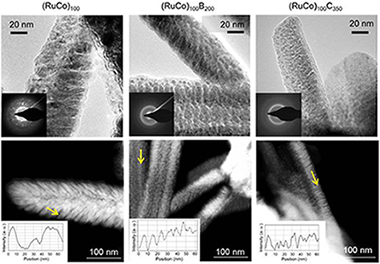
Abstract
In this work, we prepared a series of Ni foam supported Ru-Co, Ru-Co-B and Ru-Co-C catalysts in the form of columnar thin films by magnetron sputtering for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. We studied the activity and durability upon cycling. We found a strong activation effect for the Ru-Co-C sample which was the highest ever reported. This catalyst reached in the second cycle an activity 5 times higher than the initial (maximum activity 9310 ml.min(-1).g(CoRu)(-1) at 25 degrees C). Catalytic studies and characterization of the fresh and used samples permitted to attribute the strong activation effect to the following factors: (i) small column width and amorphous character (ii) the presence of Ru and (iii) dry state before each cycle. The presence of boron in the initial composition is detrimental to the durability. Our studies point out to the idea that after the first cycle the activity is controlled by surface Ru, which is the most active of the two metals. Apart from the activation effect, we found that catalysts deactivated in further cycles. We ascribed this effect to the loss of cobalt in the form of hydroxides, showing that deactivation was controlled by the chemistry of Co, the major surface metal component of the alloy. Alloying with Ru is beneficial for the activity but not for the durability, and this should be improved.
Junio, 2018 · DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28032-6
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Understanding the differences in catalytic performance for hydrogen production of Ni and Co supported on mesoporous SBA-15
Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Pereniguez, R; Caballero, ACatalysts, 307 (2018) 224-230 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.02.020
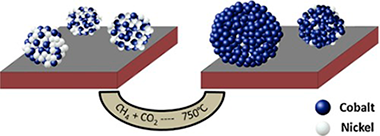
Abstract
Three mono and bimetallic NixCo1-x/SBA-15 catalysts (x = 1, 0.5 and 0) with a total metallic content of 10 wt% have been prepared by a deposition-precipitation (DP) method. The catalytic performances on the dry reforming of methane reaction (DRM) have been determined and correlated with their physical and chemical state before and after the catalytic reaction. So, while the nickel monometallic system presents a high activity and stability in the DRM reaction, the Co/SBA-15 catalytic system turns out completely inactive. For its part, the Ni0.5Co0.5/SBA-15 has initially a catalytic performance similar to the Ni/SBA-15 monometallic system, but rapidly evolving to an inactive system, therefore resembling the behavior of the cobalt-based catalyst. The characterization by TEM and in situ XPS techniques has allowed us to ascribe these differences to the initial state of metallic particles after reduction and their different evolution under reaction conditions. So, while after reduction both nickel containing NixCo1-x/SBA-15 catalysts (x = 1 and 0.5) present a well dispersed metallic phase, the cobalt monometallic catalyst yields big metallic particles with a heterogeneous distribution of sizes. Additionally, unlike the Ni/SBA-15, the NiCo/SBA-15 system increases during reaction the metallic particle sizes.
Besides indicating that the particle size is a major reason determining the catalytic performances, these results suggest that in the Ni-Co system both metals form after reduction a bimetallic phase mainly located inside the mesoporous channels of SBA-15 support. Under DRM reaction conditions, the cobalt is segregated to the surface of the bimetallic particles, which seems to determine the interaction with the support surface SBA-15. This feature gives rise to a much less stable metallic phase which suffers an important sintering process under DRM catalytic conditions.
Junio, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.02.020
Reactividad de Sólidos
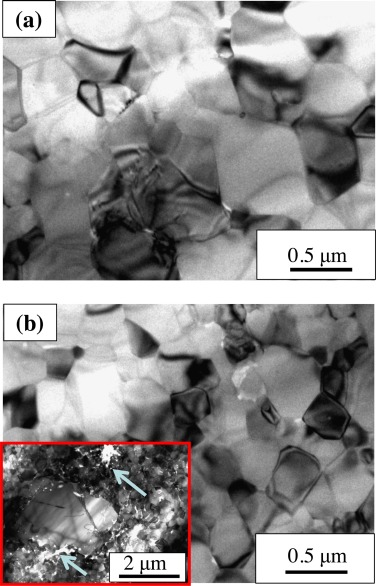
Effects of milling time, sintering temperature, Al content on the chemical nature, microhardness and microstructure of mechanochemically synthesized FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy
Alcala, MD; Real, C; Fombella, I; Trigo, I; Cordoba, JMJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 749 (2018) 834-843 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.358
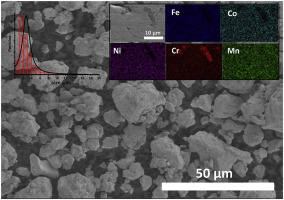
Abstract
FeCoNiCrMn(Al)-based powdered high entropy alloys were synthesized by a short time mechanical alloying process in a high energy planetary ball milling from mixtures of elemental powders, and subsequently sintered by a pressureless procedure. The composition and microstructure of the HEA phases before and after the sintering process were studied by X-ray diffraction, energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) and scanning electron microscopy. The microhardness and tensile strength values for Fe1,8Co1,8Ni1,8Cr1,8Mn1,8Al1,0 HEA sintered at 1400 degrees C sample were 3,7 GPa and 1011 MPa, respectively. Statistical Fisher-Pearson coefficient of skewness and kurtosis were played to determine the optimum synthesis milling time. The use of NaCl as additive led on to a reduction of the as-milled grain size. After sintering, SEM study confirmed a segregation of the initial HEA phase directly related to the melting temperature of the elements. Three melting temperature groups were described (Cr, FeCoNi and Mn) and they agree with the observation in the elemental mapping study. The presence of Al favored the segregation of Cr.
Junio, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.358
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Heteroatom framework distribution and layer charge of sodium Taeniolite
Perdigon, AC; Pesquera, C; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 158 (2018) 246-251 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.03.036
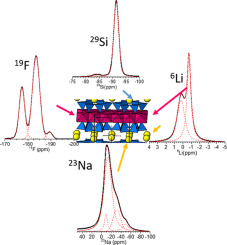
Abstract
The most advanced applications of clays depend crucially on their hydration state and swelling is probably the most important feature of expandable 2:1 layered silicate. Sodium Taeniolite, Na-TAE, a swelling trioctahedral fluormica, has been synthesized and studied using thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and infrared and solid state NMR spectroscopies. The results indicated the formation of a swelling 2:1 phyllosilicate with actual layer charge lower than the nominal one. Herein, a new heteroatom distribution and more accurate composition could be deduced.
Junio, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.03.036
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
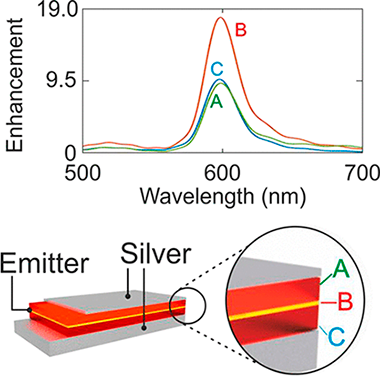
Unexpected Optical Blue Shift in Large Colloidal Quantum Dots by Anionic Migration and Exchange
Acebron, M; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Lopez, C; Herrera, FC; Mizrahi, M; Requejo, FG; Palomares, FJ; Juarez, BHJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 9 (2018) 3124-3130 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b00741
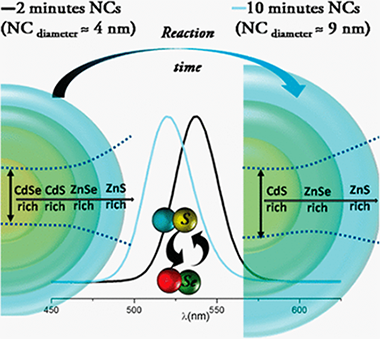
Abstract
Compositional changes taking place during the synthesis of alloyed CdSeZnS nanocrystals (NCs) allow shifting of the optical features to higher energy as the NCs grow. Under certain synthetic conditions, the effect of those changes on the surface/interface chemistry competes with and dominates over the conventional quantum confinement effect in growing NCs. These changes, identified by means of complementary advanced spectroscopic techniques such as XPS (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy) and XAS (X-ray absorption spectroscopy), are understood in the frame of an ion migration and exchange mechanism taking place during the synthesis. Control over the synthetic routes during NC growth represents an alternative tool to tune the optical properties of colloidal quantum dots, broadening the versatility of the wet chemical methods.
Junio, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b00741
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth of nanocolumnar porous TiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering using particle collimators
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alvarez, R; Rico, V; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ASurface & Coatings Technology, 343 (2018) 172-177 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.09.039

Abstract
The selective incorporation of deposition species with preferential directionality is analyzed during the growth of TiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering. Using wisely-designed collimators, tilted nanocolumnar morphologies are grown in a ballistic deposition regime, i.e. when most deposition species arrive at the film surface along well-defined preferential directions, and also in a thermalized deposition regime, when these species follow an isotropic momentum distribution in the plasma gas. The obtained results suggest that the use of particle collimators may promote the growth of porous thin films even in the classical magnetron sputtering configuration, when the target and the substrate are parallel. General insights are given on this approach and, as a proof of concept, its principles applied for the synthesis of nanostructured films in a laboratory-size reactor.
Junio, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.09.039
Reactividad de Sólidos
Pressure Effect on the Multicycle Activity of Natural Carbonates and a Ca/Zr Composite for Energy Storage of Concentrated Solar Power
Sarrion, B; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Valverde, JMACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6 (2018) 7849-7858 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00981
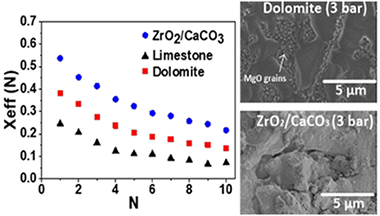
Abstract
This work is focused on the use of the Calcium-Looping process (CaL) in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants for Thermochemical Energy Storage (TCES). Cheap, abundant and nontoxic natural carbonate minerals, such as limestone and dolomite, can be employed in this application to store energy through the cyclic calcination/carbonation of CaCO3. In a recent work, a closed CO2 cycle has been proposed for an efficient CaL-CSP integration in which the CO2 in excess effluent from the carbonator is used to generate electricity by means of a gas turbine. Process simulations show that the thermoelectric efficiency is enhanced as the carbonator pressure and temperature are increased provided that the multicycle CaO conversion is not affected. On the other hand, the use of just one reactor for both calcination and carbonation has been suggested to reduce capital cost. However, the experimental results shown in the present work indicate that sintering is notably enhanced as the pressure in the reactor is increased. Such an adverse effect is mitigated for a ZrO2/CaCO3 composite with a low Zr content as compared to natural carbonates. These results are relevant to process simulations for better assessing the global efficiency of the CaL-CSP integration.
Junio, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00981
Tribología y Protección de Superficies - Materiales Coloidales
Room temperature synthesis of water-dispersible Ln(3+):CeF3 (Ln = Nd, Tb) nanoparticles with different morphology as bimodal probes for fluorescence and CT imaging
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Rojas, TC; Olivencia, A; Corral, A; Balcerzyk, M; Cantelar, E; Cusso, F; Ocana, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 520 (2018) 134-144 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.03.007
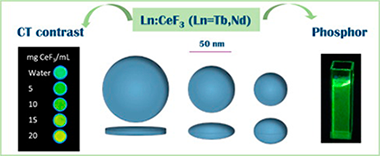
Abstract
The singular properties of lanthanide-based inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) has raised the attention of the scientific community in biotechnological applications. In particular, those systems with two or more functionalities are especially interesting. In this work, an effective and commercially attractive procedure has been developed that renders uniform, water-dispersible Ln(3+):CeF3 (Ln = Tb, Nd) NPs with different shapes and size. The method consists of the homogeneous precipitation, in a mixture of polyol and water, of cations and anions using precursors that allow the controlled release of the latter. The advantages of the reported method are related to the absence of surfactants, dispersing agents or corrosive precursors as well as to the room temperature of the process. The obtained Tb:CeF3 NPs produce an intense emission after excitation through the Ce-Tb energy transfer band located in the UV spectral region, thus being potentially useful as phosphors for in-vitro imaging purposes. On the other hand, the synthesized Nd:CeF3 NPs are good candidates for in-vivo imaging because their excitation and emission wavelengths lie in the biological windows. Finally, the excellent X-ray attenuation efficacy of the Nd:CeF(3)NPs is shown, which confers double functionality to this material as both luminescence bioprobe and contrast agent for X-ray computed-tomography.
Junio, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.03.007
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Multicomponent Au/Cu-ZnO-Al2O3 catalysts: Robust materials for clean hydrogen production
Santos, JL; Reina, TR; Ivanov, I; Penkova, A; Ivanova, S; Tabakova, T; Centeno, MA; Idakiev, V; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 558 (2018) 91-98 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2018.04.002

Abstract
Clean hydrogen production via WGS is a key step in the development of hydrogen fuel processors. Herein, we have designed a new family of highly effective catalysts for low-temperature WGS reaction based on gold modified copper-zinc mixed oxides. Their performance was controlled by catalysts' composition and the Au-Cu synergy. The utilization of hydrotalcite precursors leads to an optimal microstructure that ensures excellent Au and Cu dispersion and favors their strong interaction. From the application perspective these materials succeed to overcome the major drawback of the commercial WGS catalysts: resistance towards start/stop operations, a mandatory requisite for H-2-powered mobile devices.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2018.04.002
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effects of additives on the synthesis of TiCxN1-x by a solid-gas mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Alcala, MD; Cordoba, JMCeramics International, 44 (2018) 7605-7610 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.179
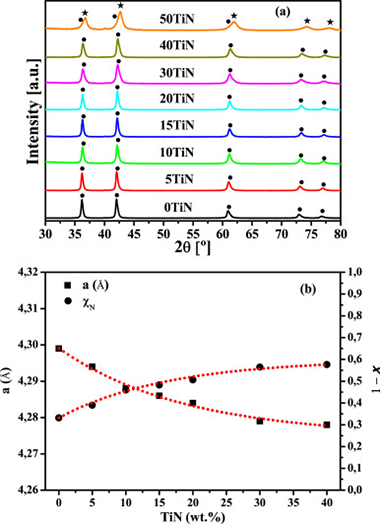
Abstract
The synthesis of TiCxN1-x from Ti/C mixtures in a N-2 atmosphere performed in a high-energy planetary mill was used as example to study the influence of the use of additives in mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) processes. In particular, the effect of the addition of TiN, TiC, Si3N4 and SiC was analyzed. The self-sustaining reaction was extinguished when additive contents of 50, 40, 40 and 30 wt% for TiN, TiC, Si3N4 and SiC, respectively, were employed. These additives cannot be regarded as real inert since they served as an extra solid source for nitrogen and carbon, modifying the final stoichiometry of the TiCxN1-x phase. The adiabatic temperature (T-ad) determined for the mixtures with no MSR effect was well above the empirical limit value of 1800 K adopted as criterion for the occurrence of the self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) process. The ignition time (t(ig)) of the MSR process was practically invariant for low additive contents (approximately 50 min) and tended to increase up to maximum values of 85-95 min for the larger additive contents.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.179
Materiales Avanzados
Thermal behaviour of sericite clays as precursors of mullite materials
Gonzalez-Miranda, FD; Garzon, E; Reca, J; Perez-Villarejo, L; Martinez-Martinez, S; Sanchez-Soto, PJJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 132 (2018) 967-977 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-018-7046-9
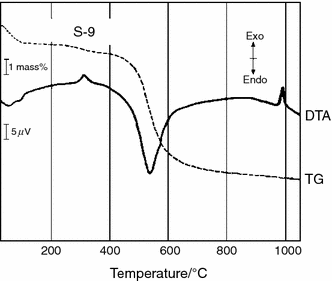
Abstract
Thermal analysis of some sericite clays, from several deposits in Spain, which are not exploited at this time, has been studied. The samples have been previously characterized by mineralogical and chemical analysis. Sericite clays have interesting properties, with implications in ceramics and advanced materials, in particular concerning the formation of mullite by heating. According to this investigation by differential thermal and thermogravimetric analysis (DTA-TG), the sericite clay samples can be classified as: Group (I), sericite-kaolinite clays, with high or medium sericite content, characterized by an endothermic DTA peak of dehydroxylation of kaolinite with mass loss, which overlapped with dehydroxylation of sericite, and Group (II), sericite-kaolinite-pyrophyllite clays, with broader endothermic DTA peaks, in which kaolinite is dehydroxylated first and later sericite and pyrophyllite with the main mass loss, appearing the peaks overlapped. X-ray diffraction analysis of the heated sericite clay samples evidenced the decomposition of dehydroxylated sericite and its disappearance at 1050 A degrees C, with formation of mullite, the progressive disappearance of quartz and the formation of amorphous glassy phase. The vitrification temperature is similar to 1250 A degrees C in all these samples, with slight variations in the temperatures of maximum apparent density (2.41-2.52 g mL(-1)) in the range 1200-1300 A degrees C. The fine-grained sericite content and the presence of some mineralogical components contribute to the formation of mullite and the increase in the glassy phase by heating. Mullite is the only crystalline phase detected at 1400 A degrees C with good crystallinity. SEM revealed the dense network of rod-shaped and elongated needle-like mullite crystals in the thermally treated samples. These characteristics are advantageous when sericite clays are applied as ceramic raw materials.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-018-7046-9
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Engineering of III-Nitride Semiconductors on Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics
Manuel, JM; Jimenez, JJ; Morales, FM; Lacroix, B; Santos, AJ; Garcia, R; Blanco, E; Dominguez, M; Ramirez, M; Beltran, AM; Alexandrov, D; Tot, J; Dubreuil, R; Videkov, V; Andreev, S; Tzaneva, B; Bartsch, H; Breiling, J; Pezoldt, J; Fischer, M; Muller, JScientific Reports, 8 (2018) art. 6879 DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-25416-6
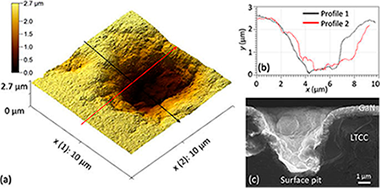
Abstract
This work presents results in the field of advanced substrate solutions in order to achieve high crystalline quality group-III nitrides based heterostructures for high frequency and power devices or for sensor applications. With that objective, Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics has been used, as a non-crystalline substrate. Structures like these have never been developed before, and for economic reasons will represent a groundbreaking material in these fields of Electronic. In this sense, the report presents the characterization through various techniques of three series of specimens where GaN was deposited on this ceramic composite, using different buffer layers, and a singular metal-organic chemical vapor deposition related technique for low temperature deposition. Other single crystalline ceramic-based templates were also utilized as substrate materials, for comparison purposes.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-25416-6
Gildings from Andalusia: Materials used in different types of artworks along centuries
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Robador, MD; Albardonedo, A; Duran, AJournal of Cultural Heritage, 31 (2018) 112-121 DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2017.11.009
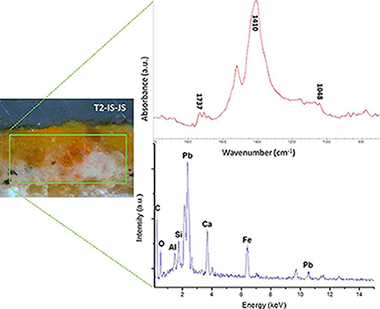
Abstract
The majority of the studied artworks were altarpieces, sculptures and/or wood-based works from different periods. Non-traditional gilding techniques have been first described in this paper, such as those that employ materials as oil in the gilding on bole, glue and bole with lead white in mordant gilding, vermilion in the preparation layers; and brass gilding or those with aluminium, lead chromate, mica or corla trying to imitate the golden hue in restoration or repaint processes. For the determination of the composition of the different gilded layers, spectroscopic techniques, such as FTIR and micro-Raman, and SEM-EDX elemental chemical analyses were successfully used.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2017.11.009
Reactividad de Sólidos
Fabrication and characterization of WC-HEA cemented carbide based on the CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy
Velo, IL; Gotor, FJ; Alcala, MD; Real, C; Cordoba, JMJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 746 (2018) 1-8 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.292
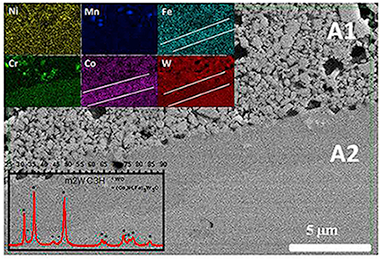
Abstract
A high entropy alloy (HEA, CoCrFeNiMn) synthesized by mechanical alloying was used as the binder for the densification of WC by a pressureless high temperature procedure. Three different WC were used by modifying its microstructure with a high energy ball milling treatment. The alloy content in the HEA-WC mixture was varied from 10 to 30% vol. The microstructure and properties of the sintered composites were studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and microindentation.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.292
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Study of the effectiveness of the flocculation-photocatalysis in the treatment of wastewater coming from dairy industries
Murcia, J.J., Hernández-Laverde, M., Rojas, Muñoz, E., Navío, J.A., Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 358 (2018) 256-264 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.034
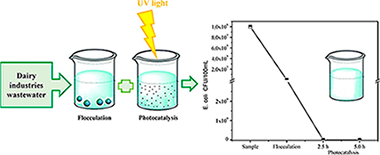
Abstract
The aim of the present work was to evaluate the effectiveness of flocculation-photocatalysis as combined processes in the treatment of dairy industries wastewater. Different commercial and lab prepared flocculants and photocatalysts were evaluated. All the materials prepared were extensively characterized. Commercial materials presented the best physicochemical properties and performance in the treatment of the studied wastewater. On one hand, all the photocatalysts evaluated showed bactericidal activity for E. Coli, total coliforms and other enterobacteriaceae. Total elimination of E. coli was obtained by using commercial TiO2 P25 Evonik, under 120 W/m2 of UV–vis light intensity and 5 h of total illumination time. Other species of bacteria remained after treatment under these conditions. It was also found that the highest light intensity of 120 W/m2 led to increase the Chemical Oxygen Demand and Total Organic Carbon in the samples treated, it can be due to the faster formation of new organic compounds as intermediaries during the photocatalytic reactions at the highest photonic flux. Flocculation pre-treatment of the wastewater samples led to improve the effectiveness of the photocatalytic treatment; thus, the combination of flocculation-photocatalysis treatments at low light intensity of 30 W/m2 leads to achieve the total elimination of E. coli, and under this intensity the elimination of total coliforms and other enterobacteriaceae increased 5.48% compared to the photocatalytic treatment alone. These treatment conditions led to comply the Colombian regulations for dairy wastewater.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.034
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the Mn content on the TiNbxMn alloys with a novel fcc structure
Chicardi, E; Aguilar, C; Sayagues, MJ; Garcia-Garrido, CJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 746 (2018) 601-610 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.306

Abstract
This work studies the structural evolution of TiNbxMn alloys (x: 0-12 wt%) synthetized by mechanical alloying in a planetary ball mill with different milling times between 1 h and 120 h. The specimens were characterized by X-ray diffraction patterns, scanning and transmission electron microscopies and Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. It was observed an evolution of the alloys developed from the raw Ti, Nb and Mn elements to bcc-TiNbxMn alloys and, finally, novel fcc-TiNbxMn alloys, with Fm3m space group symmetry, not previously observed. The presence of Mn promotes other interesting effects: a) the decreasing of the crystallite and the particle sizes, reaching values close to 4 nm and 400 nm, respectively, b) the partial amorphization of the fcc-TiNbxMn alloys due to the combined effect of the Mechanical Alloying and the difference of Mn atomic size in comparison with Ti and Nb and c) the presence of Mn that decreases the Fe amount (from milling media) in the as-milled powders.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.306
Reactividad de Sólidos
Crystallization Kinetics of Nanocrystalline Materials by Combined X-ray Diffraction and Differential Scanning Calorimetry Experiments
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Medina-Carrasco, S; Kupcik, J; Subrt, J; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LACrystal Growth & Design, 18 (2018) 3107-3116 DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.8b00241
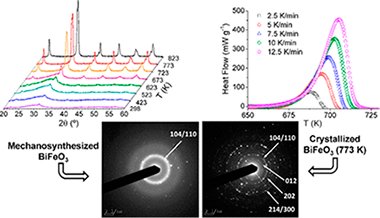
Abstract
Crystallization is one key aspect in the resulting properties of nanocrystalline functional materials, and much effort has been devoted to understanding the physical mechanisms involved in these processes as a function of temperature. The main problems associated with crystallization kinetic studies come from the limitations of the employed techniques, and the obtained results may vary significantly depending on the choice of the measurement method. In this work, a complete description of the thermal crystallization event of nanocrystalline BiFeO3 has been performed by combining the information obtained from three different experimental techniques: in situ high-temperature X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, and differential scanning calorimetry. Interestingly, the kinetic analysis of the X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry data yields almost identical results, although the physical properties measured by both techniques are different. This allows the unambiguous determination of the kinetic parameters. The importance of a proper definition of the conversion degree, which is limited by the employed measurement technique, is also highlighted.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.cgd.8b00241
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photo-induced processes on Nb2O5 synthesized by different procedures
Jaramillo-Páez, C., Sánchez-Fernández, F.J., Navío, J.A., Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 359 (2018) 40-52 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.040
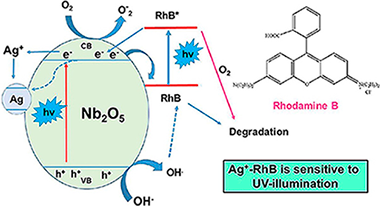
Abstract
The properties of Nb2O5 strongly depend on its synthesis procedure as well as the conditions of ulterior thermal treatment. We report the synthesis of Nb2O5 powders prepared by sol-gel precipitation method using niobium(V) ethoxide as precursor. Two chemical routes were chosen: the presence of tryethyl amine (TEA) as precipitant/template agent, or the oxidant peroxide method. In addition, microwave-assisted activation was also used. The as-prepared samples by the above procedures were amorphous. Structural changes upon heating from room temperature up to 800 °C were investigated by X-ray powder diffraction technique combined with thermogravimetric analysis. The sequential thermal treatment up to 800 °C promotes the crystallization of hexagonal phase to orthorhombic phase whereas the ulterior cooling to room temperature lead to a mixture of both phases. Samples calcined at selected temperatures of either 600 °C or 800 °C for 2 h, were characterized by XRD, SEM, N2-adsorption and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). The synthetic approach routes as well as the combined microwave activation followed by ulterior thermal treatment lead to changes not only on particle size but also on the textural properties of the synthesized catalysts. The catalysts synthesized have been evaluated using Rhodamine B (RhB) as a substrate, under both UV and visible lighting conditions. None of the catalysts synthesized showed activity in the visible. Under UV-illumination conditions, some of the catalysts exhibited a relatively low photoactivity in the degradation of RhB, which is associated with a photo-sensitizing effect. However, the addition of Ag+ ions considerably increased the activity of all the catalysts in the degradation of RhB under UV-illumination conditions. A mechanism is proposed to explain the photo-induced processes obtained, leaving the door open to the possible implications of the observed results in relation to the interaction of RhB dye with noble metal nanoparticles such as silver.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.040
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Chemical CO2 recycling via dry and bi reforming of methane using Ni-Sn/Al2O3 and Ni-Sn/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts
Stroud, T; Smith, TJ; Le Sache, E; Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Arellano-Garcia, H; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TRApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 224 (2018) 125-135 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.047
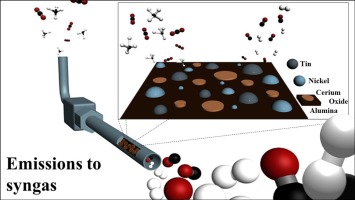
Abstract
Carbon formation and sintering remain the main culprits regarding catalyst deactivation in the dry and bi-reforming of methane reactions (DRM and BRM, respectively). Nickel based catalysts (10 wt.%) supported on alumina (Al2O3) have shown no exception in this study, but can be improved by the addition of tin and ceria. The effect of two different Sn loadings on this base have been examined for the DRM reaction over 20 h, before selecting the most appropriate Sn/Ni ratio and promoting the alumina base with 20 wt.% of CeO2. This catalyst then underwent activity measurements over a range of temperatures and space velocities, before undergoing experimentation in BRM. It not only showed good levels of conversions for DRM, but exhibited stable conversions towards BRM, reaching an equilibrium H-2/CO product ratio in the process. In fact, this work reveals how multicomponent Ni catalysts can be effectively utilised to produce flexible syngas streams from CO2/CH4 mixtures as an efficient route for CO2 utilisation.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.047
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of a novel TiNbTa material potentially suitable for bone replacement implants
Chicardi, E; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, CF; Sayagues, MJ; Garcia-Garrido, CMaterials & Design, 145 (2018) 88-96 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.02.042
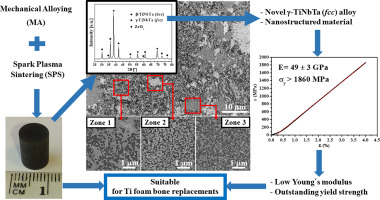
Abstract
A novel (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa alloy has been developed by a combined low energy mechanical alloying (LEMA) and pulsed electric current sintering process (PECS). Microstructurally, this material presents interesting characteristics, such as a submicrometric range of particle size, a body-centered phase (beta-TiNbTa) and, mainly, a novel face-centered cubic Ti-based alloy (gamma-TiNbTa) not previously reported. Related to mechanical performance, the novel (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa shows a lower E (49 +/- 3 GPa) and an outstanding yield strength (sigma(y) 1860 MPa). This combination of original microstructure and properties makes to the (beta + gamma)-TiNbTa a novel material potentially suitable as biomaterial to fabricate bone replacement implants, avoiding the undesirable and detrimental stressshielding problem and even the usual damage on the mechanical strength of Ti-based foams biomaterials.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.02.042
Reactividad de Sólidos
Carbonation of Limestone Derived CaO for Thermochemical Energy Storage: From Kinetics to Process Integration in Concentrating Solar Plants
Ortiz, C; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6 (2018) 6404-6417 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00199
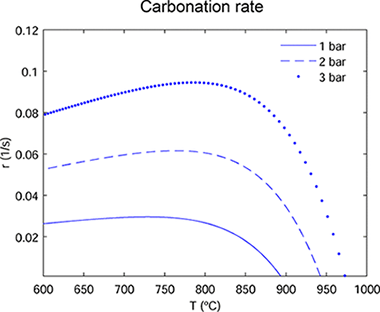
Abstract
Thermochemical energy storage (TCES) is considered as a promising technology to accomplish high energy storage efficiency in concentrating solar power (CSP) plants. Among the various possibilities, the calcium-looping (CaL) process, based on the reversible calcination–carbonation of CaCO3 stands as a main candidate due to the high energy density achievable and the extremely low price, nontoxicity, and wide availability of natural CaO precursors such as limestone. The CaL process is already widely studied for CO2 capture in fossil fuel power plants or to enhance H2 production from methane reforming. Either one of these applications requires particular reaction conditions to which the sorbent performance (reaction kinetics and multicycle conversion) is extremely sensitive. Therefore, specific models based on the conditions of any particular application are needed. To get a grip on the optimum conditions for the carbonation of limestone derived CaO in the CaL-CSP integration, in the present work is pursued a multidisciplinary approach that combines theoretical modeling on reaction kinetics, lab-scale experimental tests at relevant CaL conditions for TCES, process modeling, and simulations. A new analytic equation to estimate the carbonation reaction rate as a function of CO2 partial pressure and temperature is proposed and validated with experimental data. Using the kinetics analysis, a carbonator model is proposed to assess the average carbonation degree of the solids. After that, the carbonator model is incorporated into an overall process integration scheme to address the optimum operation conditions from thermodynamic and kinetics considerations. Results from process simulations show that the highest efficiencies for the CaL-CSP integration are achieved at carbonator absolute pressures of ∼3.5–4 bar, which leads to an overall plant efficiency (net electric power to net solar thermal power) around 41% when carbonation is carried out at 950 °C under pure CO2
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00199
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Tribological properties of TiC/a-C:H nanocomposite coatings prepared via HiPIMS
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Dominguez-Meister, S; Rojas, TC; Colasuonno, M; Bazzan, M; Patelli, AApplied Surface Science, 440 (2018) 458-466 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.135
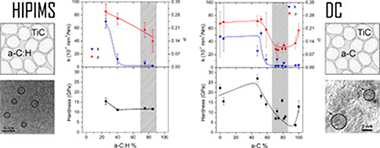
Abstract
High power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) technology has been employed to prepare TiC/a-C:H nanocomposite coatings from a titanium target in acetylene (C2H2) reactive atmospheres. Gas fluxes were varied from 1.3 to 4.4 sccm to obtain C/Ti ratios from 2 to 15 as measured by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA). X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy demonstrate the presence of TiC nanocrystals embedded in an amorphous carbon-based matrix. The hardness properties decrease from 17 to 10 GPa as the carbon content increases. The tribological properties were measured using a pinon-disk tribometer in ambient air (RH = 30-40%) at 10 cm/s with 5 N of applied load against 6-mm 100Cr6 balls. The friction coefficient and the film wear rates are gradually improved from 0.3 and 7 x 10(-6) mm(3)/N m to 0.15 and 2 x 10(-7) mm(3)/N m, respectively, by increasing the C2H2 flux. To understand the tribological processes appearing at the interface and to elucidate the wear mechanism, microstructural and chemical investigations of the coatings were performed before and after the friction test. EPMA, X-ray photoelectron and electron energy-loss spectroscopies were employed to obtain an estimation of the fraction of the a-C:H phase, which can be correlated with the tribological behavior. Examination of the friction counterfaces (ball and track) by Raman microanalysis reveals an increased ordering of the amorphous carbon phase concomitant with friction reduction. The tribological results were compared with similar TiC/a-C(:H) composites prepared by the conventional direct current process.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.135
Reactividad de Sólidos
Obituary Note: Prof. Jose Manuel Criado
Perez-Maqueda, L; Koga, N; Malek, JThermochimica Acta, 663 (2018) A1 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2018.05.004

Abstract
The late Prof. Jose Manuel Criado (1944.6.13–2018.2.27)
It is with the profoundest regret that we must report the passing of Prof. José Manuel Criado on February 27, 2018 at the age of 73. We express our most sincere condolences to his family, colleagues and friends.
Prof. Criado was born in Sevilla, Spain, on June 13th, 1944. He studied chemistry at the University of Seville and recieved his PhD from the same university under the supervision of Prof. Francisco González García and Prof. José María Trillo. He held a position as assistant professor at the Department of Inorganic Chemistry of the University of Seville from 1968 until 1972. Then, he joined the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) or National Research Council of Spain. In this institution he was junior researcher, senior researcher and, from 1986, full professor. Moreover, he has been visiting professor in a number of international institutions such as Stanford University (USA), CNRS Thermodynamics and Microcalorimetry Center in Marseille (France), University of Salford (UK), Macaulay Research Institute (UK), Institute of Inorganic Chemistry (Czech Republic), University of Chile (Chile). He had long-lasting collaborations with scientists from all over the world and visited labs in many countries. For many years, he used to spend some weeks abroad in the frame of collaboration projects with a number of international research groups, of special importance where his projects with the Czech Republic or Chile that lasted for over 20 years. He also served as an editorial board member of Thermochimica Acta for a long time and contributed largely to the further development of our academic field.
First research works of Prof. Criado were done within the field of heterogeneous catalysis, but very soon, he got interested in reactivity of solids and thermal analysis. Thus, most of his scientific career has been devoted to the study of kinetics of solid-state processes and mechanochemisty. He published about 240 papers in international journals. In the field of kinetics of solid-state processes, he made significant contributions, such as showing the limitations of using single linear heating rate experiments for extracting kinetic parameters, the proposal of master curves for discerning the kinetic model followed by the process or the combined analysis of experimental data obtained under different heating schedules. Moreover, after learning about the sample controlled thermal analysis (SCTA) method directly from Prof. Rouquerol in Marseille (France) and Profs. Paulik brothers in Budapest (Hungary), he constructed several of these instruments and extended the use of SCTA to the kinetic analysis of heterogeneous reactions, highlighting its advantages over conventional heating. Additionally, he used the kinetic control of solid-state processes by SCTA for the preparation of a number of functional and structural materials with controlled microstructures and properties. In the field of mechanochemistry, he made substantial contributions to the preparation of materials by gas–solid reaction using high energy planetary ball mills specially modified by him to work under controlled gas atmosphere.
Probably, the main contribution of Prof. Criado as a scientist has been as teacher and mentor for many of us. Despite of spending most of his scientific career in a research center rather than in a university, his laboratories were always full of students, postdocs and visitors from all over the world. He devoted a great effort to motivate and stimulate young people to pursue a career in science. His enthusiasm for science was sincere, as he loved science and research. Thus, he worked until the very last days and, even, when he could not go to the institute because he did not feel well, he worked in a small lab at home. He was very generous and always shared his knowledge with others. Thus, he expended long hours teaching about kinetics, making the complex equations easy to understand. Only those with a deep knowledge have this ability! It is not rare that many of his former students, postdocs and coworkers have permanent positions as professors and scientist in a number of international institutions. Another significant feature of Prof. Criado was his hospitality. He and his wife Maria Jesús Dianez, who joined his research group few years ago, has always his home doors open to any coworker or visitor.
We will all miss him not only as a scientist with a deep knowledge but as a friend we loved so much.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2018.05.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Multicomponent Ni-CeO2 nanocatalysts for syngas production from CO2/CH4 mixtures
le Sache, E.; Santos, J. L.; Smith, T. J.; Centeno, M. A.; Arellano-Garcia, H.; Odriozola, J. A.; Reina, T. R.Journal of CO2 utilization, 25 (2018) 68-78 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.03.012

Abstract
The dry reforming of methane with CO2 is a common route to transform CO2/CH4 mixtures into added value syngas. Ni based catalysts are highly active for this goal but suffer from deactivation, as such promoters need to be introduced to counteract this, and improve performance. In this study, mono- and bi-metallic formulations based on 10 wt.% Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 are explored and compared to a reference 10 wt.% Ni/gamma-Al2O3. The effect of Sn and Pt as promoters of Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 was also investigated. The formulation promoted with Sn looked especially promising, showing CO2 conversions stabilising at 65% after highs of 95%. Its increased performance is attributed to the additional dispersion Sn promotion causes. Changes in the reaction conditions (space velocity and temperature) cement this idea, with the Ni-Sn/CeAl material performing superiorly to the mono-metallic material, showing less deactivation. However, in the long run it is noted that the mono- metallic Ni/CeAl performs better. As such the application is key when deciding which catalyst to employ in the dry reforming process.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.03.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In Vitro Comparative Study of Oxygen Plasma Treated Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic) (PLGA) Membranes and Supported Nanostructured Oxides for Guided Bone Regeneration Processes
Torres-Lagares, D; Castellanos-Cosano, L; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Lopez-Santos, C; Barranco, A; Rodriguez-Gonzalez-Elipe, A; Gutierrez-Perez, JLMaterials, 11 (2018) art. 752 DOI: 10.3390/ma11050752
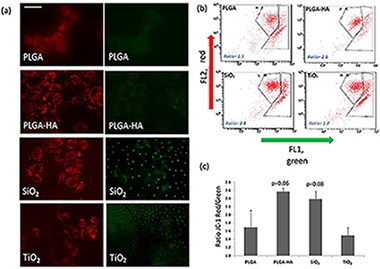
Abstract
(1) Background: The use of physical barriers to prevent the invasion of gingival and connective tissue cells into bone cavities during the healing process is called guided bone regeneration. The objective of this in-vitro study was to compare the growth of human osteoblasts on Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic) (PLGA) membranes modified with oxygen plasma and Hydroxyapatite (HA), silicon dioxide (SiO2), and titanium dioxide (TiO2) composite nanoparticles, respectively. (2) Methods: All the membranes received a common treatment with oxygen plasma and were subsequently treated with HA nanostructured coatings (n = 10), SiO2 (n = 10) and TiO2 (n = 10), respectively and a PLGA control membrane (n = 10). The assays were performed using the human osteoblast line MG-63 acquired from the Center for Scientific Instrumentation (CIC) from the University of Granada. The cell adhesion and the viability of the osteoblasts were analyzed by means of light-field microphotographs of each condition with the inverted microscope Axio Observer A1 (Carl Zeiss). For the determination of the mitochondrial energy balance, the MitoProbe (TM) JC-1 Assay Kit was employed. For the determination of cell growth and the morphology of adherent osteoblasts, two techniques were employed: staining with phalloidin-TRITC and staining with DAPI. (3) Results: The modified membranes that show osteoblasts with a morphology more similar to the control osteoblasts follow the order: PLGA/PO2/HA > PLGA/PO2/SiO2 > PLGA/PO2/TiO2 > PLGA (p < 0.05). When analysing the cell viability, a higher percentage of viable cells bound to the membranes was observed as follows: PLGA/PO2/SiO2 > PLGA/PO2/HA > PLGA/PO2/TiO2 > PLGA (p < 0.05), with a better energy balance of the cells adhered to the membranes PLGA/PO2/HA and PLGA/PO2/SiO2. (4) Conclusion: The membrane in which osteoblasts show characteristics more similar to the control osteoblasts is the PLGA/PO2/HA, followed by the PLGA/PO2/SiO2.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.3390/ma11050752
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
High-temperature compressive creep of novel fine-grained orthorhombic ZrO2 ceramics stabilized with 12 mol% Ta doping
Sponchia, G; Moshtaghioun, BM; Riello, P; Benedetti, A; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Ortiz, ALJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 38 (2018) 2445-2448 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.12.055
Abstract
A novel fine-grained orthorhombic ZrO2 ceramic stabilized with 12 mol% Ta doping was fabricated by spark plasma sintering from home-made powders, and its high-temperature mechanical properties evaluated for the first time by compressive creep tests in both Ar and air. It was found that the high-temperature plasticity of the ceramic deformed in Ar, under which the Ta-doped orthorhombic ZrO2 is a black suboxide with abundant oxygen vacancies in its crystal structure, is controlled by grain boundary sliding (stress exponent similar to 2, and activation energy similar to 780-800 kJ/mol). However, the high-temperature plasticity of the ceramic deformed in air, under which the Ta-doped orthorhombic ZrO2 is a white oxide due to the elimination in situ of oxygen vacancies, is controlled by recovery creep (stress exponent 3, and activation energy similar to 750 kJ/mol). It was also observed that black Ta-doped orthorhombic ZrO2 is more creep resistant than its white counterpart with the same grain size, and that the former deforms as the more conventional Y2O3-stabilized ZrO2 does.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.12.055
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Microemulsion Assisted Sol-Gel Method as Approach to Load a Model Anticancer Drug inside Silica Nanoparticles for Controlled Release Applications
Jaramillo, N; Paucar, C; Fernandez, A; Negrete, CG; Garcia, CCollid and Interface Science Communications, 24 (2018) 13-17 DOI: 10.1016/j.colcom.2018.03.002
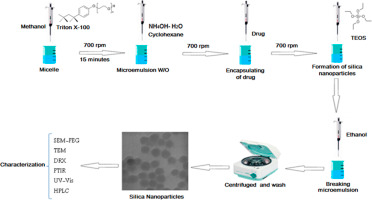
Abstract
Silica nanoparticles are attractive carriers due to their improved safety and effectiveness in drug delivery. Silica nanoparticles were synthesized by using microemulsion assisted sol-gel method, and a model anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) was added to the silica precursor before hydrolysis and condensation reactions start. The obtained materials were characterized by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). Drug encapsulation within silica nanoparticles causes an increase in particle size. However, particle morphology is not affected. The drug release profile was obtained through high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The encapsulation approach showed to be effective for sustaining a continuous and increasing release during testing time (98 h). Further studies were performed to evaluate the cytotoxic effects of silica nanoparticles with loaded 5-FU on Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO-K1). Materials are non-cytotoxic for all concentration tested (5-200 mu g/mL).
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.colcom.2018.03.002
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
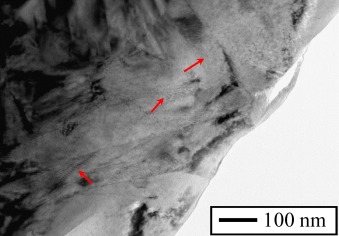
The nanostructure of porous cobalt coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering in helium atmosphere
Lacroix, B; Godinho, V; Fernandez, AMicron, 108 (2018) 49-54 DOI: 10.1016/j.micron.2018.02.004
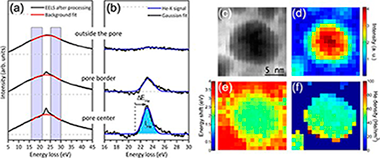
Abstract
In this work, (scanning) transmission electron microscopy has been used to study the nanostructure of porous cobalt coatings obtained by magnetron sputtering using helium as process gas. This nanostructure consists of closed pores of different nanometric size (about 4-20 nm) that are distributed all over a nanocrystalline Co matrix and filled with the deposition gas. Spatially resolved electron energy-loss spectroscopy analysis was applied to measure and map, with high lateral resolution, the relevant physical properties (density, pressure and He-K edge shift) of helium trapped inside these individual nanopores, in order to provide new insights about the growth mechanism involved in such systems. In particular, a coefficient of proportionality, C = 0.039 eV nm(3), between the blue shift of the He K-edge and the He density has been found. In addition, very high He densities (10-100 at./nm(3)) and pressures in the gigapascal range (0.05-5.0 GPa) have been measured. The linear dependence of these parameters as a function of the inverse radii obeying to the Laplace-Young law for most of the pores suggests that their formation during the coating's growth takes place in regime of elastic deformation of the Co matrix.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micron.2018.02.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of gold particle size in Au/C catalysts for base-free oxidation of glucose
Megias-Sayago, C; Santos, JL; Ammari, F; Chenouf, M; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 306 (2018) 183-190 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.01.007
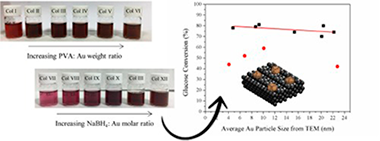
Abstract
A series of gold colloids were prepared and immobilized on commercial activated carbon. The influence of the colloid preparation and stability were studied and related to the gold particle size in the final catalyst. The catalysts show an important activity in the glucose to gluconic acid oxidation reaction, leading to gluconic acid yield close to 90% in base free mild conditions (0.1 MPa O-2 and 40 degrees C). The size-activity correlation and probable mechanism were also discussed. Finally, the viability of the catalyst was tested by recycling it up to four times.
Mayo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.01.007
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Is an alumina-whisker-reinforced alumina composite the most efficient choice for an oxidation-resistant high-temperature ceramic?
Tamura, Y; Moshtaghioun, BM; Zapata-Solvas, E; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Cerecedo-Fernandez, C; Valcarcel-Juarez, VJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 38 (2018) 1812-1818 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.10.006
Abstract
The search of a competitive ceramic material for structural applications demands several requisites: a simple microstructure with easy reproducibility, good intrinsic mechanical properties and most of all, an optimal oxidation resistance. This later point is a challenging point for most ultrahigh refractory materials.
In this work an alumina (Al2O3) whisker-reinforced Al2O3 composite prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) is studied. It will be shown that, although the microstructure is quite similar to that of pure monolithic one, there is a notorious enhancement of the high-temperature deformation resistance, reaching up to one order of magnitude over the pure Al2O3 specimen. On the other hand, the activation energy of these composites increases notably. The results are explained in terms of an original model. A comparison with reported data shows that such composite is as efficient as a SiC-whisker-reinforced Al2O3 composite, with the advantage of its oxidation resistance and much less fabrication cost.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.10.006
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Absorption and Emission of Light in Optoelectronic Nanomaterials: The Role of the Local Optical Environment
Jimenez-Solano, Alberto; Galisteo-Lopez, Juan F.; Miguez, HernanJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 9 (2018) 2077-2084 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b00848
Abstract
Tailoring the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter is central to the development of optoelectronic devices. This becomes particularly relevant for a new generation of devices offering the possibility of solution processing with competitive efficiencies as well as new functionalities. These devices, containing novel materials such as inorganic colloidal quantum dots or hybrid organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites, commonly demand thin (tens of nanometers) active layers in order to perform optimally and thus maximizing the way electromagnetic radiation interacts with these layers is essential. In this Perspective, we discuss the relevance of tailoring the optical environment of the active layer in an optoelectronic device and illustrate it with two real-world systems comprising photovoltaic cells and light emitting devices.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b00848
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Spark plasma sintering of titanium nitride in nitrogen: Does it affect the sinterability and the mechanical properties?
Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 38 (2018) 1190-1196 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.12.029
Abstract
Titanium nitride ceramics have an intrinsic interest due to its optical and structural applications. However, the conditions for sintering of dense pieces are not still clarified. This research work is focused on the spark plasma sintering (SPS) of near-fully dense fine-grained TiN. The main goal is giving a response to a longstanding debate: can the external atmosphere favor sintering? Different sintering atmospheres, either vacuum or a nitrogen flow, have been used during SPS heating to this purpose. X ray diffraction analysis has showed the presence of TiN as the main phase with traces of Ti4O7 in optimal SPS conditions (1600 °C, one minute dwell time). Our results show that the use of a nitrogen flow while heating can improve sinterability very slightly, but mechanical properties are essentially unaltered within the experimental uncertainty. The hardness reaches values as high as 20GPa whereas fracture toughness can be evaluated around 4 MPam1/2.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.12.029
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Bimetallic Ni-Co/SBA-15 catalysts for reforming of ethanol: How cobalt modifies the nickel metal phase and product distribution
Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Caballero, AMolecular Catalysis, 449 (2018) 122-130 DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.02.011

Abstract
In this study, five mono and bimetallic xNi-(10-x)Co/SBA-15 catalysts (x = 10, 8, 5, 2 and 0, with a total metallic content of 10 wt%) have been synthesized using a deposition-precipitation (DP) methodology. Catalytic performances on the steam reforming of ethanol reaction (SRE) have been determined and correlated with their physical and chemical state. A nickel content of 5% or higher yields catalytic systems with good activity, high selectivity to hydrogen and a low production of acetaldehyde (less than 5%). However, in the systems where the cobalt is the main component of the metallic phase (8-10%), the selectivity changes, mainly due to the production of an excess of acetaldehyde, which is also reflected in the larger H-2/CO2 ratio. In agreement with previous findings, this important modification in the selectivity comes from the formation of a cobalt carbide phase, where only takes place in the cobalt enriched systems, and is inhibited with nickel content larger than 5%. The formation of this carbide phase seems to be responsible for the decrease of cobalt particle size during the SRE reaction. Even though this cobalt carbide phase is thermodynamically metastable against decomposition to metallic cobalt and graphite carbon, our results have shown that it only reacts and decomposes after a hydrogen treatment at 600 degrees C.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.02.011
Reactividad de Sólidos
Phase-pure BiFeO3 produced by reaction flash-sintering of Bi2O3 and Fe2O3
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Sayagues, MJ; Raj, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 6 (2018) 5356-5366 DOI: 10.1039/c7ta09239c
Abstract
Mixed powders of Bi2O3 and Fe2O3 are shown to yield single-phase, dense nanostructured polycrystals of BiFeO3 in reaction flash sintering experiments, carried out by applying a field of 50 V cm(-1) and with the current limit set to 35 mA mm(-2). The furnace was heated at a constant rate with the reaction sintering taking place abruptly upon reaching 625 degrees C. Remarkably, an intermediate bismuth-rich phase of the oxide that forms just before reaching the flash temperature transforms, and at the same time sinters, into singlephase BiFeO3 within a few seconds after the onset of the flash. The BiFeO3 so produced is electrically insulating, a property that is critical to its applications. This one-step synthesis of single-phase polycrystals of complex oxides from their basic constituents, by reaction flash sintering, is a significant development in the processing of complex oxides, which are normally difficult to sinter by conventional methods.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1039/c7ta09239c
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cesium adsorption isotherm on swelling high-charged micas from aqueous solutions: Effect of temperature
Osuna, FJ; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDAmerican Mineralogist, 103 (2018) 623-628 DOI: 10.2138/am-2018-6203
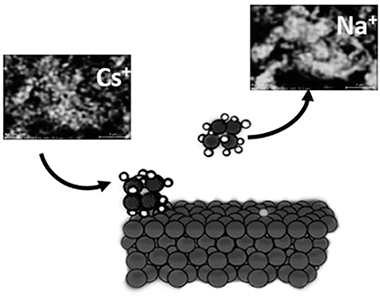
Abstract
The potential use of a new family of synthetic swelling micas for cesium immobilization from aqueous solution was evaluated and the structural modifications after adsorption were analyzed. The results have revealed that they are good cesium adsorbents compared to natural clays and as the layer charge increases, the adsorption capacity and affinity increase. The cesium ions are adsorbed through a cation exchange mechanism, but an inner sphere complex with the basal O atoms of the tetrahedral sheet is favored. These findings imply that is possible to design minerals with improved environmental applications.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.2138/am-2018-6203
Materiales Coloidales
Photoluminescence quenching of dye molecules near a resonant silicon nanoparticle
Zyuzin, MV; Baranov, DG; Escudero, A; Chakraborty, I; Tsypkin, A; Ushakova, EV; Kraus, F; Parak, WJ; Makarov, SVScientific Reports, 8 (2018) art. 6107 DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-24492-y
Abstract
Luminescent molecules attached to resonant colloidal particles are an important tool to study light-matter interaction. A traditional approach to enhance the photoluminescence intensity of the luminescent molecules in such conjugates is to incorporate spacer-coated plasmonic nanoantennas, where the spacer prevents intense non-radiative decay of the luminescent molecules. Here, we explore the capabilities of an alternative platform for photoluminescence enhancement, which is based on low-loss Mie-resonant colloidal silicon particles. We demonstrate that resonant silicon particles of spherical shape are more efficient for photoluminescence enhancement than their plasmonic counterparts in spacer-free configuration. Our theoretical calculations show that significant enhancement originates from larger quantum yields supported by silicon particles and their resonant features. Our results prove the potential of high-index dielectric particles for spacer-free enhancement of photoluminescence, which potentially could be a future platform for bioimaging and nanolasers.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-24492-y
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhancing Moisture and Water Resistance in Perovskite Solar Cells by Encapsulation with Ultrathin Plasma Polymers
Idigoras, J; Aparicio, FJ; Contreras-Bemal, L; Ramos-Terron, S; Alcaire, M; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Anta, JAACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10 (2018) 11587-11594 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b17824
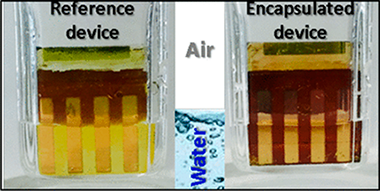
Abstract
A compromise between high power conversion efficiency and long-term stability of hybrid organic inorganic metal halide perovskite solar cells is necessary for their outdoor photovoltaic application and commercialization. Herein, a method to improve the stability of perovskite solar cells under water and moisture exposure consisting of the encapsulation of the cell with an ultrathin plasma polymer is reported. The deposition of the polymer is carried out at room temperature by the remote plasma vacuum deposition of adamantane powder. This encapsulation method does not affect the photovoltaic performance of the tested devices and is virtually compatible with any device configuration independent of the chemical composition. After 30 days under ambient conditions with a relative humidity (RH) in the range of 35-60%, the absorbance of encapsulated perovskite films remains practically unaltered. The deterioration in the photovoltaic performance of the corresponding encapsulated devices also becomes significantly delayed with respect to devices without encapsulation when vented continuously with very humid air (RH > 85%). More impressively, when encapsulated solar devices were immersed in liquid water, the photovoltaic performance was not affected at least within the first 60 s. In fact, it has been possible to measure the power conversion efficiency of encapsulated devices under operation in water. The proposed method opens up a new promising strategy to develop stable photovoltaic and photocatalytic perovskite devices.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b17824
Materiales Avanzados
Synthesis of vaterite CaCO3 as submicron and nanosized particles using inorganic precursors and sucrose in aqueous medium
Perez-Villarejo, L; Takabait, F; Mahtout, L; Carrasco-Hurtado, B; Eliche-Quesada, D; Sanchez-Soto, PJCeramics International, 44 (2018) 5291-5296 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.142
Abstract
It is reported the synthesis of CaCO3 vaterite as stable nanoparticles and submicron-sized by a simple and relatively rapid procedure. XRD, SEM and FTIR techniques have been used to characterize the precipitated products. The synthesis is based on chemical precipitation of inorganic salt precursors, calcium nitrate tetra hydrate and sodium bicarbonate, and using the disaccharide sucrose as an additive in aqueous medium. The role of the disaccharide sucrose is to control the vaterite precipitation after nucleation and growth. It has been found that an increase in sugar concentration promotes the crystal precipitation of vaterite with spherulitic morphology, as revealed by SEM, and changed the surface of the precipitated particles. There is a significant difference between CaCO3 precipitation in the absence and presence of sucrose. Addition of 0% of sucrose leads to 83% of calcite as identified by XRD methods. In contrast, addition of 67% of sucrose in aqueous medium produces 100% vaterite. The present results may be useful to provide a quick, simple, inexpensive and novel method for the controlled synthesis of new advanced biomaterials based on vaterite particles without hazardous chemicals and inert atmosphere, with great possibilities for industrial scale production.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.142
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrophoretic deposition of mixed copper oxide/GO as cathode and N-doped GO as anode for electrochemical energy storage
Jafari, EA; Moradi, M; Hajati, S; Kiani, MA; Espinos, JPElectrochimica Acta, 268 (2018) 392-402 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.02.122
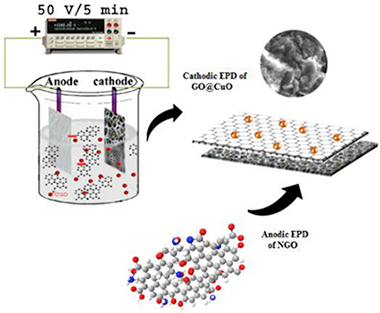
Abstract
In this work, energy storage properties of mixed copper oxide wrapped by reduced graphene oxide and nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide were investigated. First, co-electrophoretic deposition technique was used to coat GO@CuO on nickel foam; followed by electrochemical phase transformation to rGO@CuxO. Electron spectroscopy analyses (XPS, REELS and UPS) confirm the phase transformation and electrochemical reduction. Then, an electrophoretic deposition was carried out for coating nitrogen-doped graphene oxide on nickel foam coupled to its electrochemical reduction to the NrGO. The cathode and anode performances were studied by galvanostatic charge-discharge, cyclic voltammetry and impedance spectroscopy. The rGO@CuxO and NrGO exhibit a favorable specific capacity of 267.2 and 332.6 C g(-1) at 2 A g(-1), respectively. High electrochemical activity and elimination of polymer binders with a maximum potential of 1.6 V are among the advantages of rGO@CuxO//NrGO electrochemical charge storage device. Furthermore, fabricated device provided a maximum specific power and specific energy of 11917.24 W kg(-1) and 14.15 Wh kg(-1), respectively, with 86% capacity retention after 2000 cycles.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.02.122
Reactividad de Sólidos
Self-propagating mechanosynthesis of HfB2 nanoparticles by a magnesiothermic reaction
Jalaly, M; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 101 (2018) 1412-1419 DOI: 10.1111/jace.15297
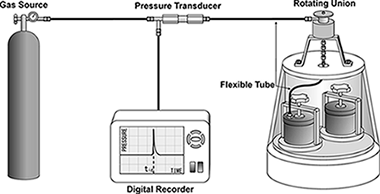
Abstract
A mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) was used to synthesize hafnium diboride nanoparticles. Along this route, magnesium was selected as a robust reducing agent for co-reduction in boron and hafnium oxides in a combustive manner. Combustion occurred after a short milling period of 12 minutes. The hafnium diboride nanoparticles had a polygonal faceted morphology and were 50-250 nm in diameter. The assessment of the processing mechanism revealed that the initial combustive reduction in B2O3 to elemental B by Mg was the major step for progressing the overall reaction. After that, HfO2 can be reduced to elemental Hf, followed by the synthesis of HfB2 phase.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.15297
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Colorimetric energy sensitive scintillator detectors based on luminescent multilayer designs
Ferrer, FJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, FSensors and Actuators A-Physical, 272 (2018) 217-222 DOI: 10.1016/j.sna.2018.01.062
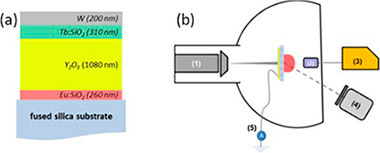
Abstract
In this work we present a new concept for energy sensitive radiation-beam scintillator detectors based on a luminescent multilayer design, where each layer within the stack consists of a rare-earth-doped highly transparent oxide. For a given type of particle beam (i.e., protons, a particles, etc.), its penetration depth, and therefore its energy loss at a particular buried layer, depends on its initial kinetic energy. Relying on this principle and since the intensity of the luminescent response of each layer and substrate should be proportional to the energy deposited by the radiation beam, we prove that a characteristic energy dependent color emission is obtained depending on both the phosphors integrated in the luminescent stack and on the primary energy and type of particle beam. Phosphor doping, emission efficiency, layer thickness, and multilayer structure design are key parameters to achieve a broad gamut in colorimetric response. The developed scintillators are designed to operate in a transmission geometry (light detection from the opposite side of the incident radiation) which is well suited for high energy particle detection in fields such as oncotherapy, space radiation, or of fusion studies. The principles of the method are illustrated with a case example typical of ion beam accelerators devoted to materials analysis. It is obtained that the kinetic energy of protons/alpha particle beams can be distinguished and evaluated with a sensitivity of 0.06/0.25 chromaticity units per MeV in the 0.7-2.0 MeV range.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.sna.2018.01.062
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Silver-modified ZnO highly UV-photoactive
Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Navío, J.C.; Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 356 (2018) 112-122 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.12.044
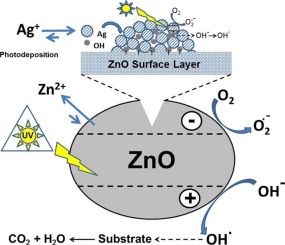
Abstract
ZnO nanoparticles were successfully synthesized by a controlled precipitation procedure by mixing aqueous solutions of Zn(II) acetate and dissolved Na2CO3 at pH ca. 7.0 without template addition and ulterior calcination at 400 °C for 2 h. The Ag-ZnO catalysts (ranging from 0.5 to 10 Ag wt.-%) were obtained by photochemical deposition method at the surface of the prepared ZnO sample, using AgNO3 as precursor. The as-prepared catalysts (with and without silver) were characterized by XRD, BET, FE-SEM, TEM, and XPS and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). The effect of Ag-phodeposition on the photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanoparticles was investigated. Three different probe molecules were used to evaluate the photocatalytic properties under UV-illumination and visible illumination: Methyl Orange and Rhodamine B were chosen as hazardous dyes and Phenol as a transparent substrate. For each of the chosen substrates, it was observed that the UV-photocatalytic properties of ZnO improved with the amount of Ag deposited, up to an optimum percentage around 1–5 wt.-% Ag, being even better than the commercial Evonik-TiO2(P25) in the same conditions. Above this amount, the UV-photocatalytic properties of the Ag-ZnO samples remain unchanged, indicating a maximum for Ag-deposition. While ZnO and Ag-ZnO catalysts can photodegrade Rhodamine B, Methyl Orange and Phenol totally within 60 min under UV-illumination, the process is slightly faster for the case of Ag–ZnO nanoparticles. Under Vis-illumination, the silver-metalized samples did not present photocatalytic activity in the degradation of Methyl Orange. However, a very low photoactivity was present for phenol degradation (10% conversion) and a moderate conversion of ca. 70% for Rhodamine B degradation, after 120 min of Visible-illumination. High conversion values and a total organic carbon (TOC) removal of 86–97% were obtained over the Ag-ZnO photocatalysts after 120 min of UV-illumination, suggesting that these Ag-modified ZnO nanoparticles may have good applications in wastewater treatment, due to its reuse properties.
Abril, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.12.044
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO2 reforming of methane over Ni-Ru supported catalysts: On the nature of active sites by operando DRIFTS study
Alvarez, A; Bobadilla, LF; Garcilaso, V; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of CO2 utilization, 24 (2018) 509-515 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.01.027
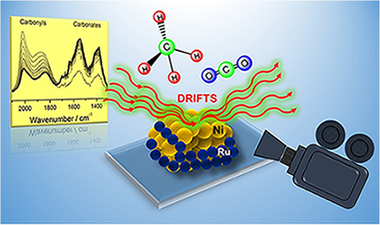
Abstract
The present paper addresses the nature of the active sites of a bimetallic Ni-Ru supported catalyst on the dry reforming of methane (DRM). The structural characterization by XRD and Raman spectroscopy, along with the reducibility study (TPR-H-2) of the samples, evidenced the existence of a strong Ni-Ru interaction in the bimetallic system. We have assumed that Ru atoms block the most reactive Ni sites (step-edge sites) leaving less reactive centers for methane activation (terraces). In this way, operando DRIFTS measurements revealed that Ru decreases the catalytic activity but favors the carbon gasification and prevents the CO dissociation.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.01.027
Materiales Avanzados
Investigation of use of coal fly ash in eco-friendly construction materials: fired clay bricks and silica-calcareous non fired bricks
Eliche-Quesada, D; Sandalio-Perez, JA; Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Sanchez-Soto, PJCeramics International, 44 (2018) 4400-4412 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.039
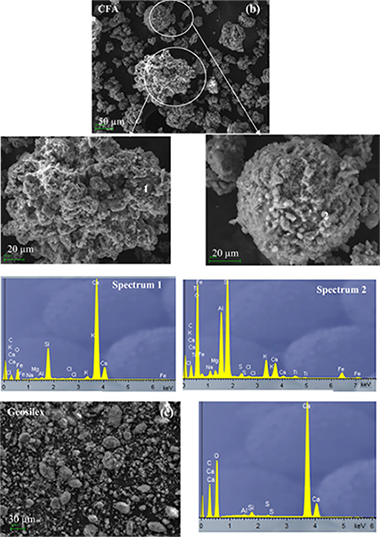
Abstract
The use of coal fly ash (CFA) as raw material for the manufacture of two construction materials, fired clay bricks and silica-calcareous non-fired bricks, was investigated. Fired clay bricks were manufactured using a commercial clay and different waste ratios (0-50 wt%), moulded at 10 MPa and fired at 1000 degrees C (4 h). Silica-calcareous non fired bricks were prepared using two wastes as raw material: CFA and "geosilex"(G), a hidrated lime residue which comes entirely from acetylene industry waste. Different proportions CFA (80-30 wt%) G (20-70 wt%) were investigated. Raw materials were moulded at 10 MPa and cured in water at room temperature during 28 days. The results indicated that the incorporation of up to 20 wt% of CFA produced fired clay bricks with physical and mechanical properties similar to control bricks without waste. However, additions of a higher amount (30-50 wt%) of residue resulted in a more pronounced decrease in mechanical properties (between 25-50%) due to an increase in open porosity. The technological characterization of the silica-calcareous non fired bricks showed a reduction in the values of bulk density and water absorption when the coal fly ash content decreases. Silica-calcareous non-fired bricks containing between 40 and 60 wt% of CFA had the highest values of compressive strength in the range 46-43 MPa. These silica-calcareous non-fired bricks, 60CFA-40 G, 50CFA-50 G and 40CFA-60 G, presented the optimum amount of pozzolanic materials (SiO2 and Al2O3) in the coal fly ash and calcium hydroxide in the geosilex to give rise to the formation of calcium silicate hydrates and calcium aluminate hydrates, the phases responsible for the mechanical resistance increase of the construction materials. Therefore, CFA-clay fired bricks and silica-calcareous CFA-Geosilex non-fired bricks presented optimal technological properties that attain the quality standards.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.039
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Epimerization of glucose over ionic liquid/phosphomolybdate hybrids: structure-activity relationship
Megias-Sayago, C; Alvarez, E; Ivanova, S; Odriozola, JAGreen Chemistry, 20 (2018) 1042-1049 DOI: 10.1039/c7gc03738d
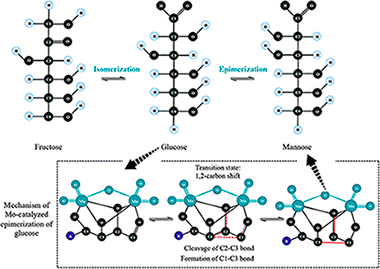
Abstract
The influence of the crystal structure and chemical nature of some ionic liquid/phosphomolybdate hybrids on their catalytic activity in the epimerization of glucose was studied. A clear evidence of structure-activity relationship was found. The inorganic part of the hybrid ensured the availability of active sites for the reaction, while the organic cation part organized the structure and controled the diffusion of the reactants. This study can be used as a first approach to predict the symmetry, long range order and availability of active sites in the presented class of imidazolium based polyoxometalate hybrids.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1039/c7gc03738d
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Dye Giant Absorption and Light Confinement Effects in Porous Bragg Microcavities
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gil-Rostra, J; Simonsen, AC; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Photonics, 5 (2018) 984-991 DOI: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01283
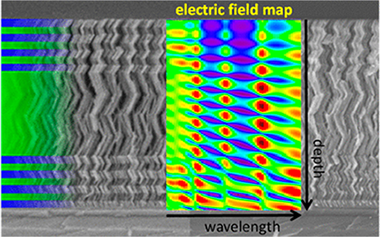
Abstract
This work presents a simple experimental procedure to probe light confinement effects in photonic structures. Two types of porous 1D Bragg microcavities with two resonant peaks in the reflection gap were prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angle configurations and then infiltrated with dye solutions of increasing concentrations. The unusual position shift and intensity drop of the transmitted resonant peak observed when it was scanned through the dye absorption band have been accounted for by the effect of the light trapped at their optical defect layer. An experimentally observed giant absorption of the dye molecules and a strong anomalous dispersion in the refractive index of the solution are claimed as the reasons for the observed variations in the Bragg microcavity resonant feature. Determining the giant absorption of infiltrated dye solutions is proposed as a general and simple methodology to experimentally assess light trapping effects in porous photonic structures.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01283
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
LaFeO3 ceramics as selective oxygen sensors at mild temperature
Jaouali, I; Hamrouni, H; Moussa, N; Nsib, MF; Centeno, MA; Bonavita, A; Neri, G; Leonardi, SGCeramics International, 44 (2018) 4183-4189 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.221

Abstract
In this study, an investigation about the oxygen sensing properties of lanthanum orthoferrite (LaFeO3) ceramics is reported. LaFeO3 nanoparticles were synthesized by using tartaric sol-gel route and annealed in air at different temperatures (500, 700 and 900 degrees C). The samples have been characterized by using thermal analysis (TA), BET surface area and porosity, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Results of sensing tests indicate that LaFeO3 nanoparticles exhibit good response to oxygen at mild temperatures (300-450 degrees C). The effect of annealing temperature on gas sensing performance was investigated, demonstrating that LaFeO3 ceramics obtained after annealing at 500 degrees C display better characteristics with respect to others. The oxygen sensor developed shows also high stability in humid environment and excellent selectivity to oxygen over other interfering gases such as CO, NO2, CO2, H-2 and ethanol.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.221
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass promotes angiogenesis in an in vivo zebrafish model
Romero-Sanchez, LB; Mari-Beffa, M; Carrillo, P; Medina, MA; Diaz-Cuenca, AActa Biomaterialia, 68 (2018) 272-285 DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.12.032
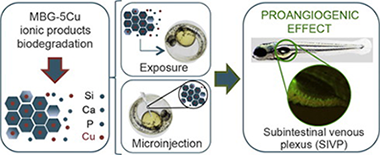
Abstract
The osteogenic and angiogenic responses of organisms to the ionic products of degradation of bioactive glasses (BGs) are being intensively investigated. The promotion of angiogenesis by copper (Cu) has been known for more than three decades. This element can be incorporated to delivery carriers, such as BGs, and the materials used in biological assays. In this work, Cu-containing mesoporous bioactive glass (MBG) in the SiO2-CaO-P2O5compositional system was prepared incorporating 5% mol Cu (MBG-5Cu) by replacement of the corresponding amount of Ca. The biological effects of the ionic products of MBG biodegradation were evaluated on a well-known endothelial cell line, the bovine aorta endothelial cells (BAEC), as well as in an in vivo zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo assay. The results suggest that ionic products of both MBG (Cu free) and MBG-5Cu materials promote angiogenesis. In vitro cell cultures show that the ionic dissolution products of these materials are not toxic and promote BAEC viability and migration. In addition, the in vivo assay indicates that both exposition and microinjection of zebrafish embryos with Cu free MBG material increase vessel number and thickness of the subintestinal venous plexus (SIVP), whereas assays using MBG-5Cu enhance this effect.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.12.032
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Biodegradabiliy of spherical mesoporous silica particles (MCM-41) in simulated body fluid (SBF)
Boccardi, E; Philippart, A; Beltran, AM; Schmidt, J; Liverani, L; Peukert, W; Boccaccini, ARAmerican Mineralogist, 103 (2018) 350-354 DOI: 10.2138/am-2018-6281
Abstract
Mesoporous silica particles of type MCM-41 (Mobile Composition of Matter No. 41), exhibiting highly ordered mesoporosity (pores with diameter between 2 and 50 nm) and surface roughness, are developed and used as a functional coating on bioactive glass-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. The degradability and the mesostructure stability of these novel MCM-41 particles were evaluated. The particles are immersed in simulated body fluid (SBF) for up to 28 days at 37 degrees C, and the variation of the ordered porosity, surface characteristics, and chemical composition of the particles are assessed by SEM-EDX, HRTEM, FTIR, ICP-OES, and pH measurements. The results indicate that the MCM-41 particles are affected by immersion in SBF only during the first few days; however, the surface and the mesopore structure of the particles do not change further with increasing time in SBF. The pore channel diameter increased slightly, confirming the stability of the developed material. The release of dissolved Si-species, which reached a maximum of 260 mg SiO2 per gram of material, could play a key role in gene activation of osteoblast cells and in inducing new bone matrix formation.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.2138/am-2018-6281
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Tailoring structured WGS catalysts: Impact of multilayered concept on the water surface interactions
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Le Sache, E; Ivanova, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 222 (2018) 124-132 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.018
Abstract
A novel multilayer approach for designing structured WGS catalyst is employed in this study as a response to the lack of new strategies in the literature. The approach proposes the use of two successive layers with different functionalities on metallic micromonolith substrate. The WGS catalyst behavior is modulated by the nature of the inner layer which determines the active species surface population by acting on the water activation step. The catalytic promotion attained by introducing inner ceria containing solids with increasing number of oxygen defects is intensely analyzed through FT-IR and H2O-TPD. Several evidences about the participation of the oxygen vacancies, as key sites, for water absorption processes are established. Besides, remarkable relationships between the water absorption strengths and the water splitting processes within their influence on the catalyst performance are also discussed.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Numerical study of the accuracy of temperature measurement by thermocouples in small-scale reactors
Blay, V; Bobadilla, LFChemical Engineering Research & Design, 131 (2018) 545-556 DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2017.06.003
Abstract
Proper temperature measurement is imperative in any laboratory study if reliable data are to be obtained, particularly in the field of chemical kinetics. In this paper we analyze in silico some typical thermowell configurations used in small-scale reactors by coupling computational fluid dynamics (CFD) with conjugated heat transfer phenomena. This allows us to identify deviations in measurements arising from thermal radiation and self-conductivity in mid and high temperature ranges, in addition to radial temperature gradients. A novel design is proposed and optimized by additional simulation, showing potential for faster and more accurate temperature measurements.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2017.06.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Robust polarization active nanostructured 1D Bragg Microcavities as optofluidic label-free refractive index sensor
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 256 (2018) 590-599 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.060
Abstract
In this work we report the use of polarization active porous 1D Bragg microcavities (BM) prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles for the optofluidic analysis of liquid solutions. These photonic structures consist of a series of stacked highly porous layers of two materials with different refractive indices and high birefringence. Their operational principle implies filling the pores with the analyzed liquid while monitoring with linearly polarized light the associated changes in optical response as a function of the solution refractive index. The response of both polarization active and inactive BMs as optofluidic sensors for the determination of glucose concentration in water solutions has been systematically compared. Different methods of detection, including monitoring the BM wave retarder behavior, are critically compared for both low and high glucose concentrations. Data are taken in transmission and reflection modes and different options explored to prove the incorporation of these nanostructured transducers into microfluidic systems and/or onto the tip of an optical fiber. This analysis has proven the advantages of the polarization active transducer sensors for the optofluidic analysis of liquids and their robustness even in the presence of light source instabilities or misalignments of the optical system used for detection.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.060
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthesis of Pd-Al/biomorphic carbon catalysts using cellulose as carbon precursor
Cazana, F; Galetti, A; Meyer, C; Sebastian, V; Centeno, MA; Romeo, E; Monzon, ACatalysis Today, 301 (2018) 226-238 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.05.026

Abstract
This work presents the results obtained with novel Pd and Pd-Al catalysts supported on carbon, which have been prepared using a biomorphic mineralization technique. The catalyst synthesis procedure includes a stage of thermal decomposition under reductive atmosphere of cellulose previously impregnated with the metallic precursors. We have studied the influence of the temperature and time of decomposition, and of the Al precursor addition, on the textural and catalytic properties. The characterisation results indicate that the preparation method used leads to the formation of carbonaceous supports with a high microporosity (up to 97% micropore volume) and values of the BET surface up to 470 m2/g while maintaining the original external structure. The use of low temperatures (ca. 600 °C) during the decomposition step allows the preparation of highly dispersed catalysts with narrow Pd particle size distributions. However, the thermal decomposition at elevated temperatures (ca. 800 °C) increases the Pd particle size due to the sintering of the metallic phase. This phenomenon is augmented with the decomposition time and is not affected by the presence of Al. Consequently, the catalytic activity of these materials in cyclohexene hydrogenation is strongly affected by the operational conditions used during the thermal decomposition step. Unexpectedly, the more sintered catalysts, i.e. those prepared at 800 °C, show the highest activity. According to the characterization results, this fact can be explained considering that the smaller Pd particles obtained after preparation at e.g. 600 °C are quite inactive because they are confined in the internal structure of the micropores of the support and/or embedded inside the carbon matrix. In contrast, after decomposition at 800 °C, the larger Pd particles formed are placed at the external surface of the catalyst, being accessible to the reactants. In addition, for the specific conditions under which the Pd is accessible, the presence of Al favours the cyclohexene conversion due to the enhancement of the adsorption on the Pd surface as a consequence of a charge transfer phenomenon. These results can serve as a guideline for the preparation of these catalysts based on raw lignocellulosic materials in order to maximize their catalytic performance.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.05.026
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold catalyst recycling study in base-free glucose oxidation reaction
Megias-Sayago, C.; Bobadilla, L. F.; Ivanova, S.; Penkova, A.; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Catalysis Today, 301 (2018) 72-77 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.03.022
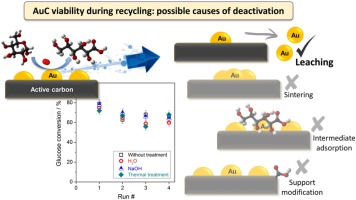
Abstract
This work is devoted to the study of viability of immobilized gold colloids on carbon as catalysts for the base-free glucose oxidation reaction with a special emphasis made on catalysts' recycling, operational life and possible routes for deactivation/reactivation under batch conditions. The observed catalytic behavior is related to all possible manners of deactivation, like gold metal state changes (particle size agglomeration or leaching), support modifications or active sites blocking by intermediates. In an attempt to recover the initial catalytic activity, the samples are subjected to different treatments such as H2O and NaOH washings and calcination. The failure of the regeneration procedures to recover the initial activity and after detailed catalyst' characterization allows us to find out the main cause of deactivation
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.03.022
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and optical properties of environmentally benign and highly uniform NaCe(MoO4)(2) based yellow nanopigments
Laguna, M; Nuñez, NO; Fernandez, M; Ocaña, MJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 739 (2018) 542-548 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.158
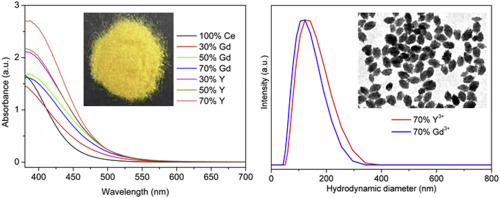
Abstract
A method for the synthesis of uniform and aggregation free NaCeMoO4 based nanospheroids with tunable size is reported. The procedure is based on a precipitation reaction at 120 degrees C for 20 h from solutions containing Na2MoO4, sodium citrate and Ce(NO3)(3) and different amounts of Y(NO3)(3) or Gd(NO3)(3). The role played by the later compounds on the formation of the particles and their morphological and structural characteristics is analyzed through the analysis of the mechanism of particle formation. The chromaticity coordinates of the obtained samples are also evaluated showing that the here reported nanoparticles constitute an ecofriendly alternative to more toxic commercial yellow pigments. The synthesized nanoparticles are also free of aggregation in water suspensions and might be suitable for injet-printing technologies.
Marzo, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.158
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Experimental measurement of the filtration efficiency and pressure drop of wall-flow diesel particulate filters (DPF) made of biomorphic Silicon Carbide using laboratory generated particles
Orihuela, MP; Gomez-Martin, A; Miceli, P; Becerra, JA; Chacartegui, R; Fino, DApplied Thermal Engineering, 131 (2018) 41-53 DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.149
Abstract
Biomorphic Silicon Carbide (bioSiC) has been recently introduced in the scope of porous ceramic substrates for hot gas filtration applications, where it has demonstrated to have good thermal and mechanical properties, and a high potential to meet the requirements for current Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF). In this experimental study, a small wall-flow bioSiC diesel filter was characterized using a soot generator, the particle size distribution of which being similar to the one generated by a diesel engine. The bioSiC samples were manufactured from Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) following a general manufacturing procedure for bioSiC ceramics, but paying special attention in the mechanizing stage to the geometry and optimal design of the honeycomb structure required for diesel engine applications. The samples had a cell density of 57.59 cell/cm(2) (371.6 cpsi), a square cross section of 9.2 x 9.2 mm, and a length of 31 mm. To generate the particle laden stream and perform the filtration tests, a synthetic Soot Generator (SG) was used. Tests were performed under controlled and reproducible conditions, with a fixed gas flow rate of 5 LPM and a soot mass flow rate of 4 mg/h. The filtration efficiency was determined with the aid of a Scanning Mobility Particle Sizer (SMPS) from the measurements of the particle concentration upstream and downstream the filter samples. During the soot loading process, the pressure drop was also monitored. The results show that, in the initial stage (clean filter), bioSiC wall-flow DPFs may have a filtration efficiency between 0.7 and 0.85 and a pressure drop of around 2 kPa for a normalized wall velocity of 0.01 m/s at ambient temperature. The filtration performance of wall-flow bioSiC particle filters showed in this work can help us to better understand their real potential for automotive applications.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.149
Materiales Coloidales
Laterally and Temporally Controlled Intracellular Staining by Light-Triggered Release of Encapsulated Fluorescent Markers
Kantner, K; Rejman, J; Kraft, KVL; Soliman, MG; Zyuzin, MV; Escudero, A; del Pino, P; Parak, WJChemistry-A European Journal, 24 (2018) 2098-2102 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201706135
Abstract
Fluorescent molecular markers were encapsulated. The capsules were additionally modified with plasmonic nanoparticles. The encapsulated markers were endocytosed by cells. Upon light stimulation the plasmonic nanoparticles generated heat, which opened the encapsulation and transiently perforated the endosomal/lysosomal membrane surrounding the capsule, thus allowing for release of the marker into the cytosol. Fluorescence labeling of different intracellular compartments was demonstrated in this way. Most important, the cells do not need to be fixed and perforated, as the molecular markers are introduced into cells by endocytosis and subsequent light-induced release. Thus this technique allows for intracellular fluorescence labeling of living cells.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1002/chem.201706135
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Basicity on the Hydrolysis of the Bi(III) Aqua Ion in Solution: An Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Study
Ayala, R; Martinez, JM; Pappalardo, RR; Refson, K; Marcos, ESJournal of Physical Chemistry A, 122 (2018) 1905-1915 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b12402
Abstract
Hydrolysis of the Bi(III) aqua ion under a range of solution conditions has been studied by means of ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. While the Bi(III) aqua ion is stable in pure water, there is an increasing degree of hydrolysis with the number of hydroxide anions in the medium. This is accompanied by a monotonic decrease of the total coordination number to an asymptotic value of similar to 6, reached under extreme basicity conditions. Comparison of the simulated Bi(III) hydrolyzed species with the experimental species distribution at different degrees of basicity suggests that, at the PBE/DFT level of theory here employed, liquid water shows an overly acidic character. Predictions of theoretical EXAFS and XANES spectra were generated from the AIMD trajectories for different Bi hydrolyzed species, [Bi(HO)(m)(H2O)(n)](3-m+), m = 0-3 and n = 7-2. Comparison with available experimental spectra is presented. Spectral features joined to the degree of hydrolysis and hydration are analyzed.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b12402
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Self-Assembly of the Nonplanar Fe(III) Phthalocyanine Small-Molecule: Unraveling the Impact on the Magnetic Properties of Organic Nanowires
Filippin, AN; Lopez-Flores, V; Rojas, TC; Saghi, Z; Rico, VJ; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Espinos, JP; Zitolo, A; Viret, M; Midgley, PA; Barranco, A; Borras, AChemistry of Materials, 30 (2018) 879-887 DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04515
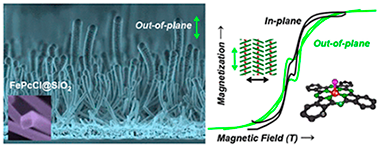
Abstract
In this article we show for the first time the formation of magnetic supported organic nanowires (ONWs) driven by self-assembly of a nonplanar Fe(III) phthalocyanine chloride (FePcCl) molecule. The ONWs grow by a crystallization mechanism on roughness-tailored substrates. The growth methodology consists of a vapor deposition under low vacuum and mild temperature conditions. The structure, microstructure, and chemical composition of the FePcCl NWs are thoroughly elucidated and compared with those of Fe(II) phthalocyanine NWs by a consistent and complementary combination of advanced electron microscopies and X-ray spectroscopies. In a further step, we vertically align the NWs by conformal deposition of a SiO2 shell. Such orientation is critical to analyze the magnetic properties of the FePcCl and FePc supported NWs. A ferromagnetic behavior below 30 K with an easy axis perpendicular to the phthalocyanine plane was observed in the two cases with the FePcCl nanowires presenting a wider hysteresis. These results open the path to the fabrication of nanostructured one-dimensional small-molecule spintronic devices.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04515
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In situ monitoring of the phenomenon of electrochemical promotion of catalysis
Espinos, JP; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; de Lucas-Consuegra, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Catalysis, 358 (2018) 27-34 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.11.027
Abstract
In this work we investigate by in-situ near-ambient pressure photoemission (NAPP) spectroscopy the phenomenon of Electrochemical Promotion of Catalysis (EPOC). We studied the reduction and diffusion kinetics of alkaline ions in a solid electrolyte cell formed by a nickel electrode supported on K+-beta-alumina electrolyte. Experiments in ultra-high vacuum and in the presence of steam showed that the amount of potassium atoms supplied to the surface is probably affected by nickel electronic modifications induced by adsorbed OH- groups. It was also deduced that part of the segregated potassium would be adsorbed at inner interfaces where it would be inaccessible to the photoelectron analyzer. A migration mechanism of the promoter is proposed consisting in: (i) the electrochemical reduction of the alkali ions (potassium) at the Ni/solid electrolyte/gas interface; (ii) the spillover of potassium atoms onto the Ni gas-exposed surface; and (iii) the diffusion of potassium atoms to Ni inner grain boundary interfaces.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.11.027
- ‹ anterior
- 16 of 37
- siguiente ›














