Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Improving the direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide from hydrogen and oxygen over Au-Pd/SBA-15 catalysts by selective functionalization
Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Platero, F; Caballero, A; Colon, GMolecular Catalysis, 445 (2018) 142-151 DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.10.034
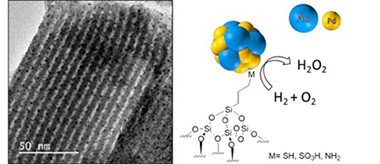
Abstract
A series of gold-palladium catalysts supported in a mesoporous surface functionalized silica SBA-15 was studied for H2O2 direct synthesis. Support functionalization was performed using different organic groups (namely-SO3H, -NH2 and-SH) while metal was then supported by an ion exchanged method. Different Au-Pd/SBA-15 catalysts were tested in the Direct Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide (DSHP). Organic functional groups (-SH, -SO3H and-NH2) with acid-base properties acted as anchoring sites controlling both the dispersion of the metallic active phase and the chemical state of gold and palladium species as Au+ and Pd2+, respectively. Compared to a Au-Pd/SBA-15 system prepared by incipient wetness impregnation over non-functionalized SBA-15, catalytic performance is improved upon functionalization, increasing hydrogen peroxide rate in sulfonic-SBA-15 systems and reducing the hydrogenation/decomposition activity by adding amine groups. The occurrence of amine groups clearly suppresses the support microporosity and probably condition the metal cluster size. The analysis of particle size by TEM showed that sulfonated samples lead to a Pd size compromise which improves the H2O2 production hindering the competitive side reactions, particularly suppressed by the presence of amine groups.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.10.034
Reactividad de Sólidos - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
High {0 0 1} faceted TiO2 nanoparticles for the valorization of oxygenated compounds present in aqueous biomass-derived feedstocks
Fernández-Arroyo, A.; Lara, M.A.; Domine, M.E.; Sayagués, M.J.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Catalysts, 358 (2018) 266-276 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.12.018
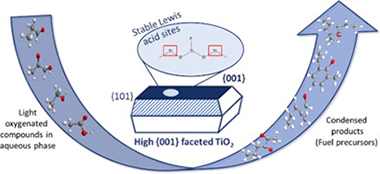
Abstract
{0 0 1} faceted TiO2 catalysts are hydrothermally synthesized by using titanium(IV) isopropoxide and butoxide precursors (ISO and BUT TiO2samples) together with HF addition. Their activity and stability are evaluated in the catalytic condensation of light oxygenated organic compounds present in an aqueous model mixture simulating a real bio-refinery effluent, under moderate operation conditions. High {0 0 1} faceted TiO2 catalysts show organic products yields superior to those attained with other TiO2 samples (anatase, rutile, and P25). This enhanced catalytic activity relates to their physico-chemical and textural properties, such as high surface area (≈100 m2/g), regular morphology (platelets conformed by partially agglomerated TiO2 nanoparticles), and adequate Lewis acidity. XRD and Raman measurements evidence the unique presence of anatase crystalline phase in both ISO and BUT materials, in which the use of HF during synthesis produces the preferential growth of TiO2 crystals mainly exposing the {0 0 1} plane. This effective {0 0 1} facet exposition directly determines catalytic results. Moreover, TiO2 ISO catalyst shows outstanding stability under reaction conditions, maintaining practically unaltered their activity after several re-uses. In particular, Lewis acid sites present in TiO2 faceted materials are more stable in the presence of organic acids under aqueous environments. This opens new possibilities for the application of these materials in the valorization of light oxygenated compounds present in biomass-derived aqueous effluents.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.12.018
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of temperature on the biaxial strength of cemented carbides with different microstructures
Chicardi, E; Bermejo, R; Gotor, FJ; Llanes, L; Torres, YInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 71 (2018) 82-91 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.11.003
Abstract
The effect of the temperature on the mechanical strength of WC-Co cemented carbides with different microstructures (grain size and binder content) was evaluated. Biaxial flexural tests were performed on three cemented carbide grades at 600 °C using the ball-on-three-balls (B3B) method. Results were interpreted by Weibull statistics and compared to biaxial strength results at room temperature. A detailed fractographic analysis, supported by Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics, was performed to differentiate the nature and size of critical defects and the mechanism responsible for the fracture. A significant decrease in the mechanical strength (around 30%) was observed at 600 °C for all grades of cemented carbides. This fact was ascribed to the change in the critical flaw population from sub-surface (at room temperature) to surface defects, associated with the selective oxidation of Co. Additionally, an estimation of the fracture toughness at 600 °C was attempted for the three cemented carbides, based upon the B3B strength results, the corresponding number of the tested specimens fragments and the macroscopic area of the B3B fracture surfaces. The fracture toughness was not affected by the temperature, at least up to 600 °C. In addition, the good agreement with the Single Edge Notch Beam toughness data suggests the possibility of employing this approach for fracture toughness evaluation of brittle materials under different testing conditions.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.11.003
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Experimental measurement of the filtration efficiency and pressure drop of wall-flow diesel particulate filters (DPF) made of biomorphic Silicon Carbide using laboratory generated particles
Orihuela, MP; Gomez-Martin, A; Miceli, P; Becerra, JA; Chacartegui, R; Fino, DApplied Thermal Engineering, 131 (2018) 41-53 DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.149
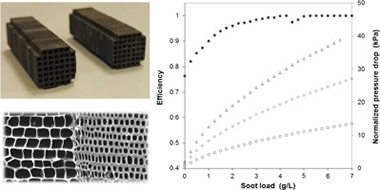
Abstract
Biomorphic Silicon Carbide (bioSiC) has been recently introduced in the scope of porous ceramic substrates for hot gas filtration applications, where it has demonstrated to have good thermal and mechanical properties, and a high potential to meet the requirements for current Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF). In this experimental study, a small wall-flow bioSiC diesel filter was characterized using a soot generator, the particle size distribution of which being similar to the one generated by a diesel engine. The bioSiC samples were manufactured from Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) following a general manufacturing procedure for bioSiC ceramics, but paying special attention in the mechanizing stage to the geometry and optimal design of the honeycomb structure required for diesel engine applications. The samples had a cell density of 57.59 cell/cm(2) (371.6 cpsi), a square cross section of 9.2 x 9.2 mm, and a length of 31 mm. To generate the particle laden stream and perform the filtration tests, a synthetic Soot Generator (SG) was used. Tests were performed under controlled and reproducible conditions, with a fixed gas flow rate of 5 LPM and a soot mass flow rate of 4 mg/h. The filtration efficiency was determined with the aid of a Scanning Mobility Particle Sizer (SMPS) from the measurements of the particle concentration upstream and downstream the filter samples. During the soot loading process, the pressure drop was also monitored. The results show that, in the initial stage (clean filter), bioSiC wall-flow DPFs may have a filtration efficiency between 0.7 and 0.85 and a pressure drop of around 2 kPa for a normalized wall velocity of 0.01 m/s at ambient temperature. The filtration performance of wall-flow bioSiC particle filters showed in this work can help us to better understand their real potential for automotive applications.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.149
Materiales Coloidales
Laterally and Temporally Controlled Intracellular Staining by Light-Triggered Release of Encapsulated Fluorescent Markers
Kantner, K; Rejman, J; Kraft, KVL; Soliman, MG; Zyuzin, MV; Escudero, A; del Pino, P; Parak, WJChemistry-A European Journal, 24 (2018) 2098-2102 DOI: 10.1002/chem.201706135
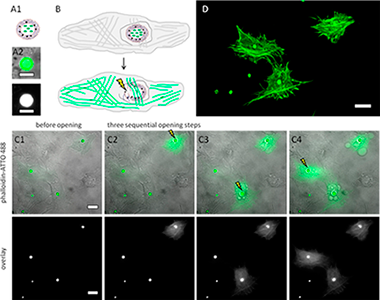
Abstract
Fluorescent molecular markers were encapsulated. The capsules were additionally modified with plasmonic nanoparticles. The encapsulated markers were endocytosed by cells. Upon light stimulation the plasmonic nanoparticles generated heat, which opened the encapsulation and transiently perforated the endosomal/lysosomal membrane surrounding the capsule, thus allowing for release of the marker into the cytosol. Fluorescence labeling of different intracellular compartments was demonstrated in this way. Most important, the cells do not need to be fixed and perforated, as the molecular markers are introduced into cells by endocytosis and subsequent light-induced release. Thus this technique allows for intracellular fluorescence labeling of living cells.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1002/chem.201706135
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Basicity on the Hydrolysis of the Bi(III) Aqua Ion in Solution: An Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Study
Ayala, R; Martinez, JM; Pappalardo, RR; Refson, K; Marcos, ESJournal of Physical Chemistry A, 122 (2018) 1905-1915 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b12402
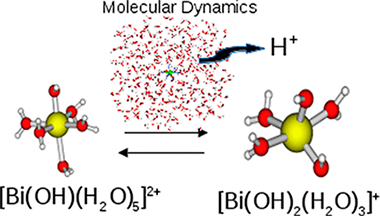
Abstract
Hydrolysis of the Bi(III) aqua ion under a range of solution conditions has been studied by means of ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. While the Bi(III) aqua ion is stable in pure water, there is an increasing degree of hydrolysis with the number of hydroxide anions in the medium. This is accompanied by a monotonic decrease of the total coordination number to an asymptotic value of similar to 6, reached under extreme basicity conditions. Comparison of the simulated Bi(III) hydrolyzed species with the experimental species distribution at different degrees of basicity suggests that, at the PBE/DFT level of theory here employed, liquid water shows an overly acidic character. Predictions of theoretical EXAFS and XANES spectra were generated from the AIMD trajectories for different Bi hydrolyzed species, [Bi(HO)(m)(H2O)(n)](3-m+), m = 0-3 and n = 7-2. Comparison with available experimental spectra is presented. Spectral features joined to the degree of hydrolysis and hydration are analyzed.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b12402
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Self-Assembly of the Nonplanar Fe(III) Phthalocyanine Small-Molecule: Unraveling the Impact on the Magnetic Properties of Organic Nanowires
Filippin, AN; Lopez-Flores, V; Rojas, TC; Saghi, Z; Rico, VJ; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Espinos, JP; Zitolo, A; Viret, M; Midgley, PA; Barranco, A; Borras, AChemistry of Materials, 30 (2018) 879-887 DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04515
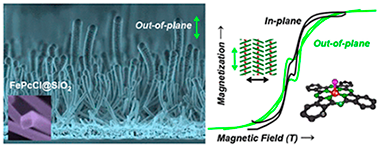
Abstract
In this article we show for the first time the formation of magnetic supported organic nanowires (ONWs) driven by self-assembly of a nonplanar Fe(III) phthalocyanine chloride (FePcCl) molecule. The ONWs grow by a crystallization mechanism on roughness-tailored substrates. The growth methodology consists of a vapor deposition under low vacuum and mild temperature conditions. The structure, microstructure, and chemical composition of the FePcCl NWs are thoroughly elucidated and compared with those of Fe(II) phthalocyanine NWs by a consistent and complementary combination of advanced electron microscopies and X-ray spectroscopies. In a further step, we vertically align the NWs by conformal deposition of a SiO2 shell. Such orientation is critical to analyze the magnetic properties of the FePcCl and FePc supported NWs. A ferromagnetic behavior below 30 K with an easy axis perpendicular to the phthalocyanine plane was observed in the two cases with the FePcCl nanowires presenting a wider hysteresis. These results open the path to the fabrication of nanostructured one-dimensional small-molecule spintronic devices.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04515
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In situ monitoring of the phenomenon of electrochemical promotion of catalysis
Espinos, JP; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; de Lucas-Consuegra, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Catalysis, 358 (2018) 27-34 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.11.027
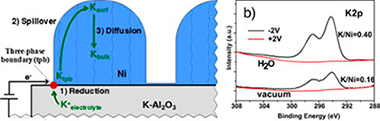
Abstract
In this work we investigate by in-situ near-ambient pressure photoemission (NAPP) spectroscopy the phenomenon of Electrochemical Promotion of Catalysis (EPOC). We studied the reduction and diffusion kinetics of alkaline ions in a solid electrolyte cell formed by a nickel electrode supported on K+-beta-alumina electrolyte. Experiments in ultra-high vacuum and in the presence of steam showed that the amount of potassium atoms supplied to the surface is probably affected by nickel electronic modifications induced by adsorbed OH- groups. It was also deduced that part of the segregated potassium would be adsorbed at inner interfaces where it would be inaccessible to the photoelectron analyzer. A migration mechanism of the promoter is proposed consisting in: (i) the electrochemical reduction of the alkali ions (potassium) at the Ni/solid electrolyte/gas interface; (ii) the spillover of potassium atoms onto the Ni gas-exposed surface; and (iii) the diffusion of potassium atoms to Ni inner grain boundary interfaces.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.11.027
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping performance of mechanically modified Al2O3-CaO composites for energy storage and CO2 capture
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 334 (2018) 2343-2355 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.183
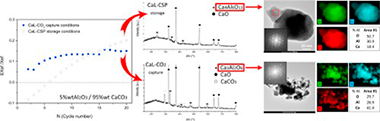
Abstract
This work reports the Calcium-Looping (CaL) multicycle performance under energy storage and CO2 capture conditions of different Al-composites prepared by milling mixtures of nanoalumina and natural limestone powders. The micro-and nanostructure of the composites have been analyzed by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy as affected by the type of CaL conditions employed, either for energy storage in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants or for post-combustion CO2 capture. Two types of calcium aluminates are formed under these diverse CaL conditions. A calcium aluminate with ratio Ca/Al < 1 (Ca4Al6O13) is formed under CaL-CSP conditions, which helps stabilize the CaO microstructure and mitigate pore-plugging. On the other hand, a crystalline phase Ca3Al2O6 is formed (Ca/Al > 1) under CaL-CO2 capture conditions presumably due to the higher calcination temperature, which withdraws from the sorbent a relatively higher amount of active Ca. Moreover, the addition of nano-alumina, and the consequent generation of calcium aluminate, affects in a diverse way the microstructure and morphology of the CaO particles as depending on the CaL application, which critically modifies the performance of the composites.
Febrero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.183
Reactividad de Sólidos
Corrigendum to “Dense graphene nanoplatelet/yttria tetragonal zirconia composites: Processing, hardness and electrical conductivity” [Ceram. Int. 43 (2017) 11743–11752]
Gallardo-Lopez, A; Marquez-Abril, I; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Munoz, A; Poyato, RCeramics International, 44 (2018) 1225-1225 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.015 (Correction)
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Packing Defects in Fatty Amine Self-Assembled Monolayers on Mica as Revealed from AFM Techniques
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; San-Miguel, MA; Galloway, HCJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 122 (2018) 493-499 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b03603
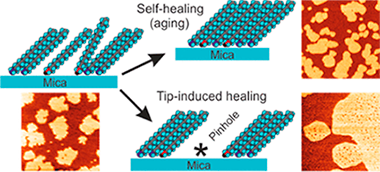
Abstract
Self-assembled monolayers of n-octadecylamine (ODA-SAMs) on mica have been prepared and studied by contact and jumping mode atomic force microscopy (AFM). Adhesion and friction data show that the compactness of the monolayers spontaneously increases as they are allowed to ripen. Molecular packing can also be induced by the controlled mechanical perturbation exerted by the probe when getting into and out of contact intermittently. Under these conditions, defects and vacancies aggregate giving rise to detectable pinholes uniformly distributed in AFM images. Created pinhole density was found to decrease with ripening time, thus confirming the proposed spontaneous self-healing mechanism. Pinhole density is also suggested as a parameter characterizing the packing degree of ODA-SAMs, and it has been related to their tribological properties. Additionally, molecular dynamics simulations were used to corroborate the compatibility between the packing degree and the observed topography of ODA-SAMs on mica.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b03603
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of a novel fcc structure for an amorphous-nanocrystalline Ti-33Nb-4Mn (at.%) ternary alloy
Chicardi, E; Garcia-Garrido, C; Sayagues, MJ; Torres, Y; Amigo, V; Aguilar, CMaterials Characterization, 135 (2018) 46-56 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.11.021
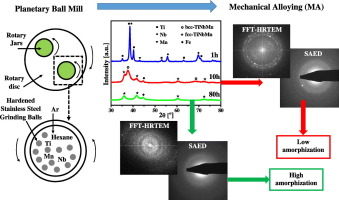
Abstract
In this work, a novel amorphous-nanocrystalline titanium-niobium-manganese solid solution ternary alloy with a Ti-33Nb-4Mn (at.%) nominal composition was developed by a High-Energy Mechanical Alloying. Nb and Mn were added to the elemental Ti as a beta-phase (bcc) stabilizer and an amorphization promoter, respectively. The system evolved from the elemental Ti, Nb and Mn raw materials to a body centred cubic (bcc) TiNbMn alloy and, finally, to the formation of an original and stable face centred cubic (fcc) nanocrystalline TiNbMn alloy, not reported until now, at short milling time (20 h). This alloy remains invariant until 120 h. In turn, the partial amorphization of the system occurs and increases until at intermediate milling time (80 h). The production of both original fcc and the amorphous TiNbMn alloy may be beneficial for reducing the Young's modulus and improving the mechanical strength pursued for the Ti alloy. The optimal milling time respect to the amorphization, nanocrystalline size and Fe mount from milling media was 60 h and 80 h (TiNbMn60h and TiNbMn80h), with > 50 wt% of an amorphous phase and a crystalline domain size of approximately 5 nm.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.11.021
Reactividad de Sólidos - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
A facile shape-controlled synthesis of highly photoactive fluorine containing TiO2 nanosheets with high {001} facet exposure
Lara, M.A.; Sayagués, M.J.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Journal of Materials Science, 53 (2018) 435-446 DOI: 10.1007/s1085
Abstract
Surface-fluorinated TiO2 materials with high {001} facet exposure were prepared by a simple and high-yield preparation procedure. Faceted/fluorinated samples showed a high photocatalytic performance not only in oxidation processes, tested in phenol and methyl orange degradation, but also in a reduction process as Cr(VI) photoreduction. Reaction rates for these materials greatly exceeded the ones obtained for materials prepared without fluorine addition and for commercial TiO2 Degussa (Evonik) P25 used as reference photocatalyst. A broad characterisation of the samples allowed us to estimate the percentages of different facets and the amount and form in which the fluorine is found on the surfaces. Good photocatalytic behaviour can be ascribed to both high {001} facet exposure and adsorbed fluorine on the photocatalysts surfaces.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1007/s1085
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
High temperature creep of 20 vol%. SiC-HfB2 UHTCs up to 2000 degrees C and the effect of La2O3 addition
Zapata-Solvas, E; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Lee, WEJournal of the European Ceramic Society. 38 (2018) 47-56 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.08.028
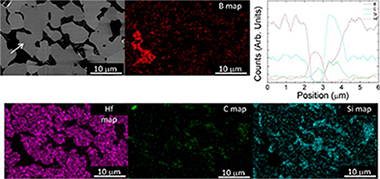
Abstract
High temperature compressive creep of SiC-HfB2 UHTCs up to 2000 °C has been studied. Microstructural analysis after deformation reveals formation of new phases in the Hf-B-Si and Hf-B-Si-C systems, which are responsible for the poor creep resistance. RE oxide additions have a negative effect reducing the creep resistance of SiC-HfB2 UHTCs. A simplistic analysis for the required creep resistance is described, indicating that only SiC-HfB2 UHTCs could withstand re-entry conditions for 5 min in a single use. However, RE oxide addition to SiC-HfB2UHTCs does not provide the required creep resistance for them to be candidate materials for hypersonic applications.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.08.028
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Enhanced photocatalytic removal of phenol from aqueous solutions using ZnO modified with Ag
Vaiano, V.; Matarangolo, M.; Murcia, J.J.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 225 (2018) 197-206 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.075
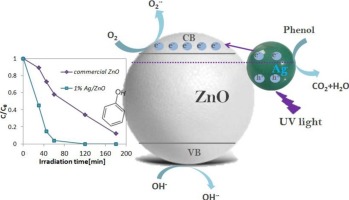
Abstract
Different photocatalysts based on commercial ZnO modified by silver photodeposition were prepared in this work. The samples were characterized by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), specific surface area (SSA), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and UV–vis diffuse reflectance (UV–vis DRS). XRD and XPS showed that Ag/ZnO samples are composed of metallic Ag (Ag0) and ZnO structure was identified. Furthermore, TEM analysis evidenced that the number of silver particles increased with the Ag content. At last, UV–vis DRS results revealed a reflectance band for Ag/ZnO samples, ascribed to the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) absorption of metal silver particles. Commercial ZnO and Ag/ZnO samples were evaluated in the phenol removal under UV light irradiation. It was observed an enhancement of photocatalytic phenol removal from aqueous solutions by silver addition in comparison to commercial ZnO. In particular, the phenol removal increased with the silver content from 0.14 to 0.88 wt%, after this content (i.e 1.28 wt%) the phenol degradation significantly decreased indicating that the optimal Ag content was equal to 0.88 wt%. The influence of the best photocatalyst dosage and the change of the initial phenol concentration in solution were also investigated in this work and the best photocatalytic performance was obtained by using 50 mg L−1 of phenol initial concentration and 0.15 g L−1 of photocatalyst dosage. Finally, the optimized Ag/ZnO photocatalyst was employed for the treatment of a real drinking wastewater containing phenol in which the almost total phenol removal was achieved after 180 min of UV irradiation time.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.075
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nickel/Copper Bilayer-modified Screen Printed Electrode for Glucose Determination in Flow Injection Analysis
Salazar, P.; Rico, V.; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Electroanalysis, 30 (2018) 187-193 DOI: 10.1002/elan.201700592
Abstract
This work reports about the performance of a Ni/Cu-modified screen printed electrodes (SPE/Ni/Cu), prepared by physical vapor deposition (PVD) in an oblique angle configuration (OAD), for non-enzymatic glucose sensing applications. SPE/Ni/Cu electrodes showed an excellent reversibility and a catalytic behavior for detection of glucose that were controlled by the diffusion of reactants up to the active sites at the electrode surface. The study with a flow injection analysis (FIA) setup of the main experimental variables affecting the detection process has shown that the developed electrode system had an excellent glucose sensitivity of 1.04AM(-1)cm(-2) (R-2:0.999), a linear response up to 1mM, a limit of detection of 0.33M and a time of analysis of ca. 30s per sample. The selectivity of the sensor was checked against various interferences, including ascorbic acid, uric acid, acetaminophen and other sugars, in all cases with excellent results. The feasibility of using this sensor for practical applications was successfully confirmed by determining the glucose concentration in different commercial beverages.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1002/elan.201700592
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Outstanding performance of rehydrated Mg-Al hydrotalcites as heterogeneous methanolysis catalysts for the synthesis of biodiesel
Navajas, A; Campo, I; Moral, A; Echave, J; Sanz, O; Montes, M; Odriozola, JA; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LMFuel, 211 (2018) 173-181 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.09.061
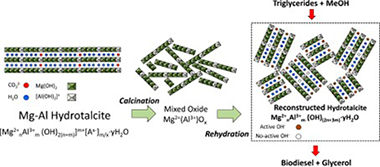
Abstract
There is still a need for active, selective and stable heterogeneous catalysts for the synthesis of biodiesel. In this work, magnesium-aluminium hydrotalcites with Mg/Al molar ratios within the 1.5-5 range were synthesized by coprecipitation and used as transesterification catalysts for the synthesis of biodiesel. The mixed oxides obtained after calcination recovered the hydrotalcite structure in the form of meixnerite after rehydration in boiling water. The solids were characterized by XRD, TGA, N-2 adsorption-desorption, and SEM. Basic properties were assessed by means of Hammett indicators and CO2-TPD. Rehydrated materials with the highest Mg/Al ratios showed some distinctive features: low surface area, well defined flake-like crystals, high basicity and strong basic sites with H_ values above 11. They were also the most active catalysts allowing to achieve 51-75% sunflower oil methanolysis conversion after 8 h of reaction under mild conditions (60 degrees C, 1 atm), methanol/oil molar ratio of 12 using between 2 and 6 wt% of catalyst. The conversion increased up to 96% (92% fatty acid methyl esters yield) using 2 wt% catalyst and methanol/oil molar ratio of 48. Catalyst leaching was not a serious problem with these solids that could be reutilized maintaining very good activities. A general accordance between solids basic properties and their catalytic performance has been observed. These results are among the best reported in the literature for heterogeneous methanolysis catalysts and have been attributed to the high basicity of the rehydrated solids and the presence of strong and accessible basic sites probably consisting in interlayer hydroxide anions at the edges of the crystals.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.09.061
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Ir-Catalysed Nitrous oxide (N2O) Decomposition: Effect of Ir Particle Size and Metal-Support Interactions
Yentekakis, IV; Goula, G; Kampouri, S; Betsi-Argyropoulou, I; Panagiotopoulou, P; Taylor, MJ; Kyriakou, G; Lambert, RMCatalysis Letters, 148 (2019) 341-347 DOI: 10.1007/s10562-017-2233-z
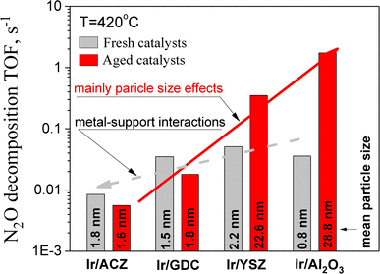
Abstract
The effect of the morphology of Ir particles supported on.-Al2O3, 8 mol% Y2O3-stabilized -ZrO2 (YSZ), 10 mol%Gd2O3-doped CeO2 (GDC) and 80 wt%Al2O3-10 wt%CeO2-10 wt%ZrO2 (ACZ) on their stability on oxidative conditions, the associated metal-support interactions and activity for catalytic decomposition of N2O has been studied. Supports with intermediate or high oxygen ion lability (GDC and ACZ) effectively stabilized Ir nanoparticles against sintering, in striking contrast to supports offering negligible or low oxygen ion lability (gamma-Al2O3 and YSZ). Turnover frequency studies using size-controlled Ir particles showed strong structure sensitivity, de-N2O catalysis being favoured on large catalyst particles. Although metallic Ir showed some de-N2O activity, IrO2 was more active, possibly present as a superficial overlayer on the iridium particles under reaction conditions. Support-induced turnover rate modifications, resulted from an effective double layer [O delta--delta(+)](Ir) on the surface of iridium nanoparticles, via O2- backspillover from the support, were significant in the case of GDC and ACZ.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1007/s10562-017-2233-z
Reactividad de Sólidos
Core-rim structure formation in TiC-Ni based cermets fabricated by a combined thermal explosion/hot-pressing process
Lemboub, S; Boudebane, S; Gotor, FJ; Haouli, S; Mezrag, S; Bouhedja, S; Hesser, G; Chadli, H; Chouchane, TInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 70 (2018) 84-92 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.09.014
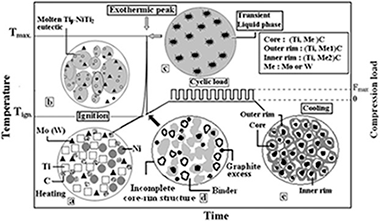
Abstract
TiC-Ni-based cermets were obtained by thermal explosion from different elemental mixtures (Ti, C, Ni and X, where X = Cr, Mo or W) and subsequently densified by hot-pressing under a cyclic load. The whole process was performed in a single stage in the same experimental device according to the following thermal and pressure procedure: a heating rate ramp up to 1573 K without applying any load followed by an isothermal dwelling under a compressive cyclic load of 32 MPa. The thermal explosion synthesis occurred during the heating ramp at a temperature close to 1273 K that was practically independent of the starting nominal composition. The influence of different refractory elements on the chemical composition and microstructure of cermets was studied. SEM characterization showed that only with Mo and W, the cermets developed the characteristic core-rim structure. A high densification was achieved, but decreased when the refractory elements were added. Nevertheless, in these cases higher hardness values were obtained.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.09.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
A new combustion route for synthesis of TaB2 nanoparticles
Jalaly, M; Gotor, FJCeramics International, 44 (2018) 1142-1146 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.074

Abstract
Tantalum diboride (TaB2) nanoparticles were synthesized through a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). In this method, the ternary system of Mg/Ta2O5/B was employed in which, magnesium was used as a reducing agent for reduction of tantalum oxides in a combustive regime. The processing route of TaB2 by the solid-state combustion was very short-term and the product purification was extremely easy and rapid. The synthesis mechanism was studied and revealed that magnesiothermic reduction of tantalum oxide is the initiator of the total reaction, while borothermic reduction of the oxide may occur in parallel.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.074
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Flexible and Adaptable Light-Emitting Coatings for Arbitrary Metal Surfaces based on Optical Tamm Mode Coupling
Jiménez-Solano, A.; Galisteo-López, J.; Míguez, H.Advanced Optical Materials, 6 (2018) 1700560 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700560
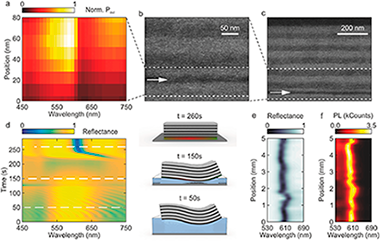
Abstract
This study demonstrates a design that maximizes the power radiated into free space from a monolayer of nanoemitters embedded in a flexible distributed Bragg reflector conformably attached to a metal surface. This is achieved by positioning the light source at the precise depth within the multilayer for which optical Tamm states provide enhanced quantum yield and outcoupling efficiency, which are combined to optimize the luminous power radiated by the surface of the ensemble. This approach, based on the adhesion of flexible multilayer stacks onto metal surfaces with an arbitrary curvature, is versatile and permits the realization of spectrally narrow monodirectional or self-focusing light-emitting surfaces.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700560
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Nanostructured hybrid device mimicking bone extracellular matrix as local and sustained antibiotic delivery system
Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Romero-Sanchez, LB; Blazquez, J; Diaz-Cuenca, AMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 256 (2018) 165-176 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.08.010
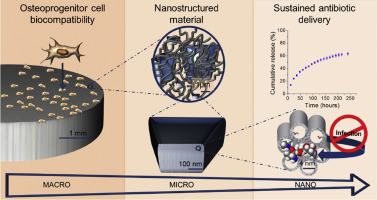
Abstract
A fluidic permeable and stable in wet media, MBG-NfGel, device consisting of a mesoporous ceramic embodied in a nanofibrillar biodegradable polymer has been processed using appropriate thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) processing variables of 5.4% (wt/v) gelatin in 50/50 water/ethanol (v/v) ratio. The device comprises high surface area mesoporous bioactive glass (MBG) microparticles within a fibrous matrix of 170 nm average diameter nanofibers gelatin, forming a meshwork of 0.2-1.6 mu m range voids. Gentamicin sulphate (GS) antibiotic high loading capacity and sustained release ability, as well as in vitro bioactivity and osteoprogenitor cells biocompatibility supports long-term antibacterial and bone growth stimulation properties. Antibiotic local delivery functionality in vitro of this device has been analysed and discussed in relation to other systems previously reported. The presented device properties as well as its industrial scalability potential, in terms of process reliability and absence of toxic chemical agents, low raw material biopolymer cost and immunogenicity, are other important advantages. These advantages rank MBG-NfGel device as a potential candidate to further development for application as local antibiotic device in bone surgery and therapy.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.08.010
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Phase-Contact Engineering in Mono- and Bimetallic Cu-Ni Co-catalysts for Hydrogen Photocatalytic Materials
Munoz-Batista, MJ; Meira, DM; Colon, G; Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, MAngewandte Chemie-International Edition, 57 (2018) 1199-1203 DOI: 10.1002/anie.201709552
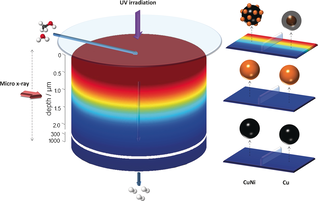
Abstract
Understanding how a photocatalyst modulates its oxidation state, size, and structure during a photocatalytic reaction under operando conditions is strongly limited by the mismatch between (catalyst) volume sampled by light and, to date, the physicochemical techniques and probes employed to study them. A synchrotron micro-beam X-ray absorption spectroscopy study together with the computational simulation and analysis (at the X-ray cell) of the light-matter interaction occurring in powdered TiO2-based monometallic Cu, Ni and bimetallic CuNi catalysts for hydrogen production from renewables was carried out. The combined information unveils an unexpected key catalytic role involving the phase contact between the reduced and oxidized non-noble metal phases in all catalysts and, additionally, reveals the source of the synergistic Cu-Ni interaction in the bimetallic material. The experimental method is applicable to operando studies of a wide variety of photocatalytic materials.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1002/anie.201709552
Reactividad de Sólidos
The dizinc bond as a ligand: A computational study of elongated dizinc bonds
Ayala, R; Carmona, E; Galindo, AInorganic Chimica Acta, 470 (2018) 197-205 DOI: 10.1016/j.ica.2017.06.008
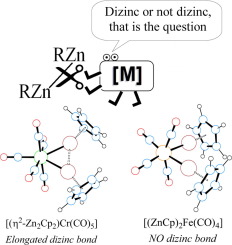
Abstract
Following the synthesis of [Zn-2(eta(2)-C5Me5)(2)] (in short [Zn2Cp*(2)]) many complexes of the directly bonded Zn-Zn unit were prepared and characterized, leading to the recognition of an isolobal analogy between the Zn-Zn bond and the molecule of dihydrogen. Prompted by these results, we have investigated eta(2)-eta(2)-coordination of [Zn2Cp2] and [Zn2Ph2] (Cp = C5H5, Ph = C6H5) to several selected transition metal fragments and report herein the results of a QTAIM study of complexes [(ZnR)(2)Fe(CO)(4)], [(eta(2)-Zn2R2)M(CO)(5)]] and [(eta(2)-Zn2R2)Pd(PR'(3))(2)] (for R = Cp, Ph; M = Cr, Mo, W; and R' = F, H, Me). A decrease of rho(BCP), Delta(2) rho(BCP) and delocalization indexes delta(Zn, Zn), relative to corresponding values in the parent molecules of [Zn2Cp2] and [Zn2Ph2], accompanied dizinc coordination. In most cases the computed d(Zn, Zn) parameters were indicative of significant electron density sharing between the two Zn atoms. Nevertheless, the interaction with [Fe(CO)(4)] resulted in oxidative cleavage of the coordinated Zn-Zn bond, due to high pi backdonation to the sigma* Zn-2 MO as deduced from the delta(M, O-CO) index. The Zn-Zn bond critical points identified in our study are discussed. The computed Zn-Zn contacts concentrate in the range 2.44-2.58 angstrom, and we propose that this interval corresponds to elongated dizinc bonds.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ica.2017.06.008
Reactividad de Sólidos
Low-cost Ca-based composites synthesized by biotemplate method for thermochemical energy storage of concentrated solar power
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maquecla, LAApplied Energy, 210 (2018) 108-116 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.10.109
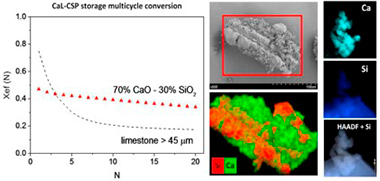
Abstract
An ever more environmentally conscious society demands the use of green, sustainable and high-efficiency renewable energy resources. However, large-scale energy storage remains a challenge for a deep penetration of power produced from renewables into the grid. The Calcium-Looping (CaL) process, based on the reversible carbonation/calcination of CaO, is a promising technology for thermochemical energy storage (TCES) in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants. Natural limestone to be used as CaO precursor is cheap, non-toxic and abundant. Nevertheless, recent works have shown that carbonation of CaO derived limestone at optimum conditions for TCES is limited by pore-plugging, which leads to severe deactivation for large enough particles to be employed in practice. In our work, we have synthesized inexpensive CaO/SiO2 composites by means of a biotemplate method using rice husk as support. The morphological and compositional features of the biomorphic materials synthesized help improve the CaO multicycle activity under optimum CSP storage conditions and for particles sufficiently large to be managed in practical processes.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.10.109
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Nickel Particles Selectively Confined in the Mesoporous Channels of SBA-15 Yielding a Very Stable Catalyst for DRM Reaction
Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Pereniguez, R; Caballero, AJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 122 (2018) 500-510 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b03835
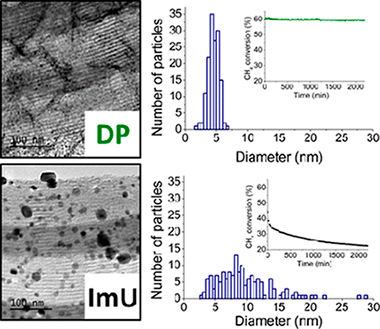
Abstract
A series of four Ni catalysts supported on SBA-15 and on a high SiO2 surface area have been prepared by modified impregnation (ImU) and deposition-precipitation (DP) methods. The catalysts have been extensively characterized, including in situ XAS (bulk sensitive) and XPS (surface sensitive) techniques, and their catalytic activities evaluated in the dry reforming reaction of methane (DRM). The combined use of XPS and XAS has allowed us to determine the location of nickel particles on each catalyst after reduction at high temperature (750 degrees C). Both Ni/SiO2-DP and Ni/SBA-15-DP catalysts yield well-dispersed and homogeneous metallic phases mainly located in the mesoporosity of both supports. On the contrary, the Ni/SiO2-ImU and Ni/SBA-15-ImU catalysts present a bimodal distribution of the reduced nickel phase, with nickel metallic particles located out and into the mesoporous structure of SiO2 or the SBA-15 channels. The Ni/SBA-15-DP catalyst was found the most stable and performing system, with a very low level of carbon deposition, about an order of magnitude lower than the equivalent ImU catalyst. This outstanding performance comes from the confinement of small and homogeneous nickel particles in the mesoporous channels of SBA-15, which, in strong interaction with the support, are resistant to sintering and coke deposition during the demanding reaction conditions of DRM.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b03835
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Microstructural engineering and use of efficient poison resistant Au-doped Ni-GDC ultrathin anodes in methane-fed solid oxide fuel cells
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lambert, RMInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 43 (2018) 885-893 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.11.020
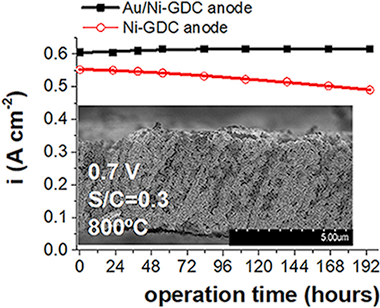
Abstract
Ultrathin porous solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) anodes consisting of nickel-gadolinia-dopedceria (Ni-GDC) cermets with a unique porous micro-columnar architecture with intimate contact between the GDC and the Ni phases were made by magnetron sputtering at an oblique deposition angle and characterised in detail by a variety of methods prior to use in hydrogen or methane-fuelled SOFCs. These Ni-GDC anodes exhibited excellent transport properties, were robust under thermal cycling and resistant to delamination from the underlying yttria-stabilised zirconia electrolyte. Similarly prepared Au-doped Ni-GDC anodes exhibited the same morphology, porosity and durability. The gold associated exclusively with the Ni component in which it was present as a surface alloy. Strikingly, whatever their treatment, a substantial amount of Ce3+ persisted in the anodes, even after operation at 800 degrees C under fuel cell conditions. With hydrogen as fuel, the un-doped and Au doped Ni-GDC anodes exhibited identical electrochemical performances, comparable to that of much thicker commercial state-of-the-art Ni-GDC anodes. However, under steam reforming conditions with CH4/H(2)0 mixtures the behaviour of the Au-doped Ni-GDC anodes were far superior, exhibiting retention of good power density and dramatically improved resistance to deactivation by carbon deposition. Thus two distinct beneficial effects contributed to overall performance: persistence of Ce3+ in the working anodes could induce a strong metal-support interaction with Ni that enhanced the catalytic oxidation of methane, while formation of a Ni Au surface alloy that inhibited carbonisation and poisoning of the active nickel surface.
Enero, 2018 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.11.020
2017
2017
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Fluorescent Humidity Sensors Based on Photonic Resonators
Szendrei, K; Jimenez-Solano, A; Lozano, G; Lotsch, BV; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) 1700663 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700663
Abstract
Among the different approaches to humidity sensing available, those based on fluorescent signals are gathering a great deal of attention due to their fast response and versatility of detection and design. So far, all proposals have focused on the use of luminescent probes whose emission is either triggered or inhibited by the presence of water that reacts or alters their chemical environment, hence inducing the signal change. Here, a novel concept in fluorescent humidity sensing based on combining stimuli-responsive photonic resonators with molecular fluorescent probes is introduced. The resonator is assembled from humidity-swellable antimony phosphate nanosheets embedding a planar light-emitting probe, whose emission is dramatically modified by the changes that ambient humidity causes in its photonic environment. Guided by "in silico" optical design of the resonator architecture and subsequent experimental realization, two embodiments of fluorescent photonic humidity sensors featuring turn-on and turn-off detection schemes are presented. The interplay between the luminescent properties of an emitter and its photonic environment implies a fundamental advantage as the emitters are not chemically altered during the detection process. At the same time, it paves the way toward a new generation of photonic humidity sensors which can conveniently be interfaced with common fluorescence detection schemes.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700663
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping performance of steel and blast furnace slags for thermochemical energy storage in concentrated solar power plants
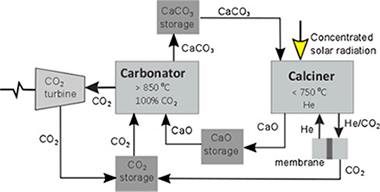
Valverde, JM; Miranda-Pizarro, J; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of CO2 Utilization, 22 (2017) 143-154 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2017.09.021
Abstract
The Calcium Looping (CaL) process, based on the carbonation/calcination of CaO, has been proposed as a feasible technology for Thermochemical Energy Storage (TCES) in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants. The CaL process usually employs limestone as CaO precursor for its very low cost, non-toxicity, abundance and wide geographical distribution. However, the multicycle activity of limestone derived CaO under relevant CaL conditions for TCES in CSP plants can be severely limited by pore plugging. In this work, the alternative use of calcium-rich steel and blast furnace slags after treatment with acetic acid is investigated. A main observation is that the calcination temperature to regenerate the CaO is significantly reduced as compared to limestone. Furthermore, the multicycle activity of some of the slags tested at relevant CaL conditions for TCES remains high and stable if the treated samples are subjected to filtration. This process serves to remove silica grains, which helps decrease the porosity of the CaO resulting from calcination in the mesoporous range thus mitigating pore plugging.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2017.09.021
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Photochemical methane partial oxidation to methanol assisted by H2O2
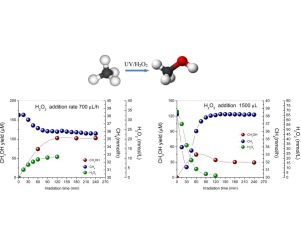
López Martin, A.; Caballero, A.; Colón, G.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 349 (2017) 216-223 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.09.039
Abstract
The photochemical conversion of methane into methanol from H2O2 aqueous solution as well as the effect of the addition mode were studied. Direct addition of different amounts H2O2 leads to increasing methanol production at the first stage of the reaction. The excess of H2O2 would lead to the reactive oxygen species scavenging and the subsequent O2 production. It was also corroborated that extra hydroxyl radicals in the aqueous medium do not improve the formation of methanol but a noticeable increase in the formation of HCOOH with respect to methanol was evidenced. In contrast, dosing addition at relatively low rates leads to constant methane consumption towards methanol. Methanol formation would be in this case in equilibrium with further oxidation to HCOOH or CO2. This suggests that only a controlled constant availability of HO’s at low concentration can enhance the performance of methanol generation in the photochemical process.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.09.039
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Silver and gold nanoparticles in nanometric confined templates: synthesis and alloying within the anisotropic pores of oblique angle deposited films
Parra-Barranco, J., Sánchez-Valencia, J.R., Barranco, A., González-Elipe, A.R.Nanotechnology, 28 (2017) 485602 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa92af
Abstract
In this work we have developed an infiltration methodology to incorporate metal nanoparticles (NPs) of controlled size and shape into the open voids available in oblique angle deposited thin films. These NPs exhibited well-defined surface plasmon resonances (SPRs). The nanometric confined space provided by their porous microstructure has been used as a template for the growth of anisotropic NPs with interesting SPR properties. The fabrication methodology has been applied for the preparation of films with embedded Ag and Au NPs with two associated plasmon resonance features that developed a dichroic behaviour when examined with linearly polarized light. A confined alloying process was induced by near IR nanosecond laser irradiation yielding bimetallic NPs with SPR features covering a large zone of the electromagnetic spectrum. The possibilities of the method for the tailored fabrication of a wide range colour palette based on SPR features are highlighted.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa92af
Reactividad de Sólidos
Chalcogenide Quaternary Cu2FeSnS4 Nanocrystals for Solar Cells: Explosive Character of Mechanochemical Synthesis and Environmental Challenge
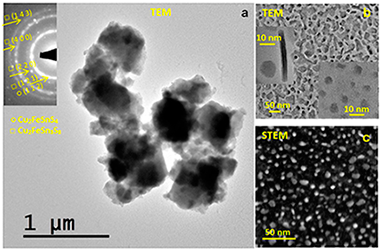
Balaz, P; Balaz, M; Sayagues, MJ; Eliyas, A; Kostova, NG; Kanuchova, M; Dutkova, E; Zorkovska, ACrystals, 7 (2017) art. 367 DOI: 10.3390/cryst7120367
Abstract
In this study we demonstrate the synthesis of quaternary semiconductor nanocrystals of stannite Cu2FeSnS4/rhodostannite Cu2FeSn3S8 (CFTS) via mechanochemical route using Cu, Fe, Sn and S elements as precursors in one-pot experiments. Methods of X-ray diffraction (XRD), nitrogen adsorption, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were applied to characterize properties of the unique nanostructures. Mechanochemical route of synthesis induced new phenomena like explosive character of reaction, where three stages could be identified and the formation of nanostructures 5-10 nm in size. By using XPS method, Cu(I), Fe(II), Sn(IV) and S(-II) species were identified on the surface of CFTS. The value of optical band gap 1.27 eV is optimal for semiconductors applicable as absorbers in solar cells. The significant photocatalytic activity of the CFTS nanocrystals was also evidenced. The obtained results confirm the excellent properties of the quaternary semiconductor nanocrystals synthesized from earth-abundant elements.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.3390/cryst7120367
Materiales Coloidales
Local Disorder and Tunable Luminescence in Sr1–x/2Al2–xSixO4 (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) Transparent Ceramics
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Al Saghir, K; Veron, E; Becerro, AI; Porcher, F; Wisniewsld, W; Matzen, G; Fayon, F; Allix, MInorganic Chemistry, 56 (2017) 14446-14458 DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b01881
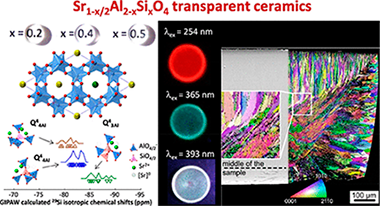
Abstract
Eu-doped Sr1–x/2Al2–xSixO4 (x = 0.2, 0.4, and 0.5) transparent ceramics have been synthesized by full and congruent crystallization from glasses prepared by aerodynamic levitation and laser-heating method. Structural refinements from synchrotron and neutron powder diffraction data show that the ceramics adopt a 1 × 1 × 2 superstructure compared to the SrAl2O4 hexagonal polymorph. While the observed superstructure reflections indicate a long-range ordering of the Sr vacancies in the structure, 29Si and 27Al solid-state NMR measurements associated with DFT computations reveal a significant degree of disorder in the fully polymerized tetrahedral network. This is evidenced through the presence of Si–O–Si bonds, as well as Si(OAl)4 units at remote distances of the Sr vacancies and Al(OAl)4 units in the close vicinity of Sr vacancies departing from local charge compensation in the network. The transparent ceramics can be doped by europium to induce light emission arising from the volume under UV excitation. Luminescence measurements then reveal the coexistence of Eu2+ and Eu3+ in the samples, thereby allowing tuning the emission color depending on the excitation wavelength and suggesting possible applications such as solid state lighting.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b01881
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of acid-treatment and colloidal-processing conditions on the room temperature mechanical and electrical properties of 3YTZP/MWNT ceramic nanocomposites
Poyato, R.; Morales-Rodríguez, A.; Gutiérrez-Mora, F.; Muñoz, A.; Gallardo-López, A.Ceramics International, 43 (2017) 16560-16568 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.043
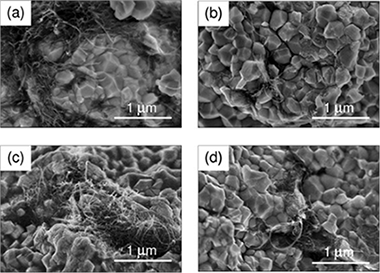
Abstract
Different colloidal powder processing routines have been used to prepare composites of 3 mol% Y2O3 -ZrO2 (tetragonal zirconia polycrystals, 3YTZP) with 2.5 vol% multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWNT) with the aim of achieving a homogeneous distribution of the MWNTs in the ceramic, eliminating agglomerates but also minimizing carbon nanotube (CNT) damage during processing. Modifications of the acid treatment applied to the nanotubes, including subjecting them to stirring or ultrasonic agitation, and use of acid or basic pH during composite powder mixing have been approached.
No MWNT damage during processing was detected by Raman spectroscopy. CNT bundles were found in all the composites forming different patterns depending on the processing route. Similar values of hardness were obtained for all the composites, while different anisotropy in fracture propagation was found when studying parallel and perpendicular directions to the sintering pressing axis on the cross sections of the composites due to the MWNT preferential alignment. The CNT bundles were found to act as fracture short paths. A similar anisotropic behavior was observed for the electrical conductivity. These results have been correlated to the different microstructures obtained in the composites prepared with different processing routines.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.043
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
High temperature compressive strength and creep behavior of Si-Ti-C-O fiber-bonded ceramics
Vera, MC; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, M; Ramirez-Rico, JJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 37 (2017) 4442-4448 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.06.037
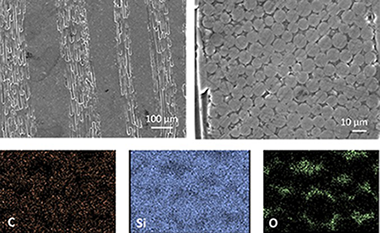
Abstract
Fiber bonded silicon carbide ceramic materials provide cost-advantage over traditional ceramic matrix composites and require fewer processing steps. Despite their interest in extreme environment thermostructural applications no data on long term mechanical reliability other than static fatigue is available for them. We studied the high temperature compressive strength and creep behavior of a fiber bonded SiC material obtained by hot-pressing of Si Ti-C-O fibers. The deformation mechanism and onset of plasticity was evaluated and compared with other commercial SiC materials. Up to 1400 degrees C, plasticity is very limited and any macroscopic deformation proceeds by crack formation and damage propagation. A transient viscous creep stage is observed due to flow in the silica matrix and once steady state is established, a stress exponent n similar to 4 and an activation energy Q similar to 700 kJ mol(-1) are found. These results are consistent with previous data on creep of polymer derived SiC fibers and polycrystals.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.06.037
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Micron-scale wedge thin films prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition
Lopez-Santos, MC; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Borras, A; del Campo, RC; Holgado, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 14 (2017) e1700043 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201700043
Abstract
Wedge-shaped materials are currently employed for optical analyses and sensing applications. In this paper, we present an easy to implement plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition procedure to grow wedge-shaped thin films with controlled slope at the scale of few hundred microns. The method relies on the use of few tenths micron height obstacles to alter the laminar flow of precursor gas during deposition and is applied for the fabrication of wedge-shaped ZnO thin films. Local interference patterns, refractive index, and birefringence of the films have been measured with one micron resolution using a specially designed optical set-up. Their micro- and nano-structures have been characterized by means of scanning electron microscopy and theoretically reproduced by Monte Carlo calculations.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201700043
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Performance of biomorphic Silicon Carbide as particulate filter in diesel boilers
Orihuela, M Pilar; Gomez-Martin, Aurora; Becerra, Jose A; Chacartegui, Ricardo; Ramirez-Rico, JoaquinJournal of Environmental Management, 203 (2017) 907-919 DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.003
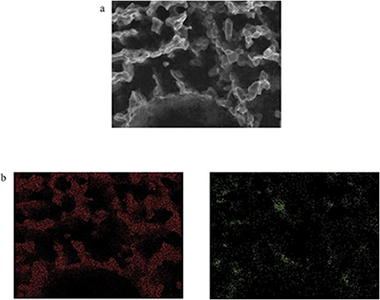
Abstract
Biomorphic Silicon Carbide (bioSiC) is a novel porous ceramic material with excellent mechanical and thermal properties. Previous studies have demonstrated that it may be a good candidate for its use as particle filter media of exhaust gases at medium or high temperature. In order to determine the filtration efficiency of biomorphic Silicon Carbide, and its adequacy as substrate for diesel particulate filters, different bioSiC-samples have been tested in the flue gases of a diesel boiler. For this purpose, an experimental facility to extract a fraction of the boiler exhaust flow and filter it under controlled conditions has been designed and built. Several filter samples with different microstructures, obtained from different precursors, have been tested in this bench. The experimental campaign was focused on the measurement of the number and size of particles before and after placing the samples. Results show that the initial efficiency of filters made from natural precursors is severely determined by the cutting direction and associated microstructure. In biomorphic Silicon Carbide derived from radially cut wood, the initial efficiency of the filter is higher than 95%. Nevertheless, when the cut of the wood is axial, the efficiency depends on the pore size and the permeability, reaching in some cases values in the range 70–90%. In this case, the presence of macropores in some of the samples reduces their efficiency as particle traps. In continuous operation, the accumulation of particles within the porous media leads to the formation of a soot cake, which improves the efficiency except in the case when extra-large pores exist. For all the samples, after a few operation cycles, capture efficiency was higher than 95%. These experimental results show the potential for developing filters for diesel boilers based on biomorphic Silicon Carbide.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.003
Materiales Coloidales
Microemulsion-Mediated Synthesis and Properties of Uniform Ln:CaWO4 (Ln = Eu, Dy) Nanophosphors with Multicolor Luminescence for Optical and CT Imaging
Laguna, M; Nuñez, NO; Garcia, FJ; Corral, A; Parrado-Gallego, A; Balcerzyk, M; Becerro, AI; Ocaña, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 44 (2017) 5158-5168 DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201700650
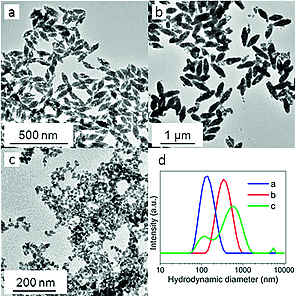
Abstract
A new room-temperature method has been developed that yields, for the first time in the literature, uniform and well-dispersed CaWO4 nanospindles. This method is based on the use of microemulsions consisting of aqueous solutions of Ca2+ and WO42- precursors, cyclohexane as the organic medium, Triton X-100 as the surfactant, and n-octanol as the cosurfactant. We show that the formation of uniform nanospindles requires a restrictive set of experimental conditions. These particles crystallize into the tetragonal CaWO4 phase and emit blue-green luminescence when excited by UV radiation. The reported method is also useful for doping the CaWO4 spindles with Eu3+ or Dy3+ cations, resulting in multicolor emissions (red for Eu3+; white for Dy3+). The luminescence is much stronger when excited through a WO42--Ln(3+) (Ln = Eu or Dy) energy-transfer band than through the f-f transition bands of the Ln(3+) cations. Interestingly, because of the white luminescence associated with the Dy:CaWO4 nanophosphor, it might be useful for LED technologies. Luminescence dynamics and energy-transfer efficiency have been analyzed to determine the optimum phosphors. Finally, the Eu-doped CaWO4 nanospindles also showed excellent X-ray attenuation efficacy, which confers double functionality to this material as both a luminescence bioprobe and as a contrasting agent for X-ray computed-tomography.
Diciembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201700650
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Over Zr-Promoted Co/gamma-Al2O3 Catalysts
Barrientos, J; Garcilaso, V; Venezia, B; Aho, A; Odriozola, JA; Boutonnet, M; Jaras, STopics in Catalysis, 60 (2017) 1285-1298 DOI: 10.1007/s11244-017-0813-1
Abstract
Two Zr-modified alumina supports were synthetized containing the same amount of Zr but a different distribution of this modifier over the alumina surface. These supports, together with the unmodified alumina carrier, were used to prepare three cobalt-based catalysts which were characterized and tested under relevant Fischer-Tropsch conditions. The three catalysts presented very similar porosity and cobalt dispersion. The addition of Zr nor its distribution enhanced the catalyst reducibility. The catalyst activity was superior when using a carrier consisting of large ZrO2 islands over the alumina surface. The use of a carrier with a homogeneous Zr distribution had however, a detrimental effect. Moreover, a faster initial deactivation rate was observed for the Zr-promoted catalysts, fact that may explain this contradictory effect of Zr on activity. Finally, the addition of Zr showed a clear enhancement of the selectivity to long chain hydrocarbons and ethylene, especially when Zr was well dispersed.
Noviembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1007/s11244-017-0813-1
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Determination of the thickness of the embedding phase in 0D nanocomposites
Martinez-Martinez, D; Sanchez-Lopez, JCApplied Surface Science, 421 (2017) 179-184 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.081
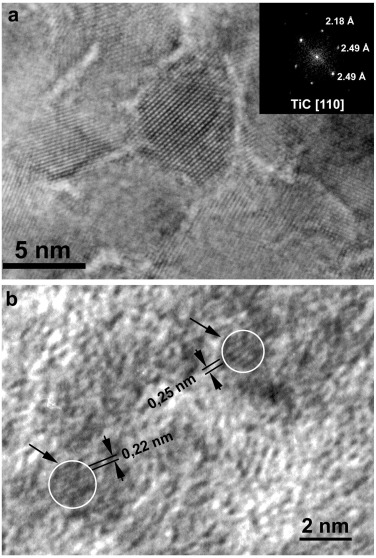
Abstract
0D nanocomposites formed by small nanoparticles embedded in a second phase are very interesting systems which may show properties that are beyond those observed in the original constituents alone. One of the main parameters to understand the behavior of such nanocomposites is the determination of the separation between two adjacent nanoparticles, in other words, the thickness of the embedding phase. However, its experimental measurement is extremely complicated. Therefore, its evaluation is performed by an indirect approach using geometrical models. The ones typically used represent the nanoparticles by cubes or spheres.
In this paper the used geometrical models are revised, and additional geometrical models based in other parallelohedra (hexagonal prism, rhombic and elongated dodecahedron and truncated octahedron) are presented. Additionally, a hybrid model that shows a transition between the spherical and tessellated models is proposed. Finally, the different approaches are tested on a set of titanium carbide/amorphous carbon (TiC/a-C) nanocomposite films to estimate the thickness of the a-C phase and explain the observed hardness properties.
Noviembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.081
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Redox and Catalytic Properties of Promoted NiO Catalysts for the Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Ethane
Delgado, D; Solsona, B; Ykrelef, A; Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Caballero, A; Rodriguez-Aguado, E; Rodriguez-Castellon, E; Nieto, JMLJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 121 (2017) 25132-25142 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b07066
Abstract
NiO and metal-promoted NiO catalysts (M-NiO, with a M/(M+Ni) atomic ratio of 0.08, with M = Nb, Sn, or La) have been prepared, tested in the oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of ethane, and characterized by means of XRD, TPR, HRTEM, Raman, XPS, and in situ XAS (using H-2/He, air or C2H6/He mixtures). The selectivity to ethylene during the ODH of ethane decreases according to the following trend: Nb NiO Sn NiO > La NiO > NiO, whereas the catalyst reducibility (determined by both TPR and XAS using H-2/He mixtures) shows the opposite trend. However, different reducibility and catalytic behavior in the absence of oxygen (ethane/He mixtures) have been observed, especially when comparing Nb- and Sn-promoted NiO samples. These differences can be ascribed mainly to a different phase distribution of the promoter. The results presented here are discussed in terms of the nature of active and selective sites for ODH of ethane in selective and unselective catalysts, but also the role of promoters and the importance of their phase distribution.
Noviembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b07066
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Structural control in porous/compact multilayer systems grown by magnetron sputtering
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Alvarez, R; Rico, V; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ANanotechnology, 28 (2017) 46 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa8cf4
Abstract
In this work we analyze a phenomenon that takes place when growing magnetron sputtered porous/compact multilayer systems by alternating the oblique angle and the classical configuration geometries. We show that the compact layers develop numerous fissures rooted in the porous structures of the film below, in a phenomenon that amplifies when increasing the number of stacked layers. We demonstrate that these fissures emerge during growth due to the high roughness of the porous layers and the coarsening of a discontinuous interfacial region. To minimize this phenomenon, we have grown thin interlayers between porous and compact films under the impingement of energetic plasma ions, responsible for smoothing out the interfaces and inhibiting the formation of structural fissures. This method has been tested in practical situations for compact TiO2/porous SiO2 multilayer systems, although it can be extrapolated to other materials and conditions.
Noviembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa8cf4
Materiales Avanzados
Characterization of ashes from greenhouse crops plant biomass residues using X-ray fluorescence analysis and X-ray diffraction
Garzon, E; Morales, L; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Sanchez-Soto, PJX-ray spectrometry, 46 (2017) 569-578 DOI: 10.1002/xrs.2801
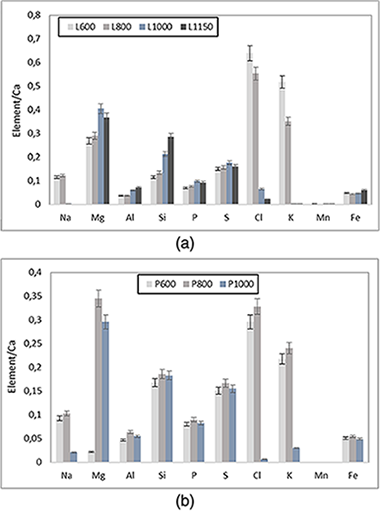
Abstract
A characterization of ashes obtained by thermal treatments on greenhouse crops plant biomass residues is presented. The chemical analysis, by X-ray fluorescence (wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence), and phase analysis, by X-ray diffraction, of the resultant ashes are reported. Thermal treatments of selected samples of these residues increase the relative amounts of inorganic Mg, Si, P, and S in the ashes, being these amounts as high as increasing temperature. As an opposite effect, Na, Cl, and K contents decrease as increasing temperature by a volatilization process of the chlorides, as confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The crystalline phase analysis of the ashes demonstrates the formation of inorganic constituents of the biomass, including alkaline chlorides and calcium salts (calcite, anhydrite, and apatite). Progressive thermal treatments induce the formation of new silicate phases (akermanite and grossularite) and silica (-quartz and cristobalite). Furthermore, the particle size of the starting biomass samples does not influence the evolution of the crystalline phases by thermal treatments. In contrast, a previous leaching using water and subsequent heating at 1,000 degrees C produces the formation of periclase (MgO), lime (CaO), and the silicate gehlenite, without the presence of anhydrite. This study is interesting for future investigations on the residues as a profitable biomass source for energy production and sustainable large-scale management. Some potential applications of the resultant ashes can be proposed.
Noviembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/xrs.2801
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effect of the crystal chemistry on the hydration mechanism of swelling micas
Pavon, E; Alba, MD; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pazos, MCGeochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 217 (2017) 231-239 DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.08.028
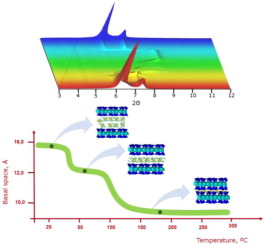
Abstract
Swelling and dehydration under minor changes in temperature and water vapor pressure is an important property that clays and clay minerals exhibit. In particular, their interlayer space, the solid-water interface and the layers' collapse and re-expansion have received much attention because it affects to the dynamical properties of interlayer cations and thus the transfer and fate of water and pollutants. In this contribution, the dehydration and rehydration mechanism of a swelling high-charge mica family is examined by in situ X-ray Diffraction. The effect of the aluminosilicate layer charge and the physicochemical properties of the interlayer cations on these processes are analyzed. The results showed that the dehydration temperature and the number of steps involved in this process are related to the layer charge of the silicate and the physicochemical properties of the interlayer cations. Moreover, the ability to adsorb water molecules in a confined space with high electric field by the interlayer cations does not only depend on their hydration enthalpy but also on the electrostatic parameters of these cations.
Noviembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.08.028
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Incorporation of Calcium Containing Mesoporous (MCM-41-Type) Particles in Electrospun PCL Fibers by Using Benign Solvents
Liverani, L.;Boccardi, E.; Beltrán, A.M.; Boccaccini, A.R.Polymers, 9 (2017) 487 DOI: 10.3390/polym9100487
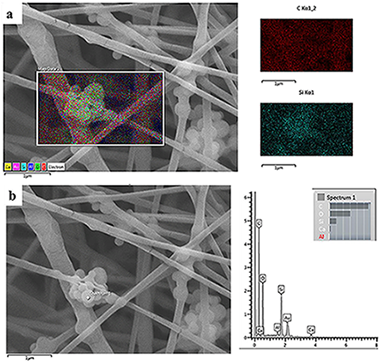
Abstract
The electrospinning technique is a versatile method for the production of fibrous scaffolds able to resemble the morphology of the native extra cellular matrix. In the present paper, electrospinning is used to fabricate novel SiO2particles (type MCM-41) containing poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers. The main aims of the present work are both the optimization of the particle synthesis and the fabrication of composite fibers, obtained using benign solvents, suitable as drug delivery systems and scaffolds for soft tissue engineering applications. The optimized synthesis and characterization of calcium-containing MCM-41 particles are reported. Homogeneous bead-free composite electrospun mats were obtained by using acetic acid and formic acid as solvents; neat PCL electrospun mats were used as control. Initially, an optimization of the electrospinning environmental parameters, like relative humidity, was performed. The obtained composite nanofibers were characterized from the morphological, chemical and mechanical points of view, the acellular bioactivity of the composite nanofibers was also investigated. Positive results were obtained in terms of mesoporous particle incorporation in the fibers and no significant differences in terms of average fiber diameter were detected between the neat and composite electrospun fibers. Even if the Ca-containing MCM-41 particles are bioactive, this property is not preserved in the composite fibers. In fact, during the bioactivity assessment, the particles were released confirming the potential application of the composite fibers as a drug delivery system. Preliminary in vitro tests with bone marrow stromal cells were performed to investigate cell adhesion on the fabricated composite mats, the positive obtained results confirmed the suitability of the composite fibers as scaffolds for soft tissue engineering.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.3390/polym9100487
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cellulose-polyhydroxylated fatty acid ester-based bioplastics with tuning properties: Acylation via a mixed anhydride system
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Goldoni, L; Benitez, JJ; Davis, A; Ceseracciu, L; Cingolani, R; Bayer, IS; Heinze, T; Koschella, A; Heredia, A; Athanassiou, ACarbohydrate Polymers, 173 (2017) 312-320 DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.068
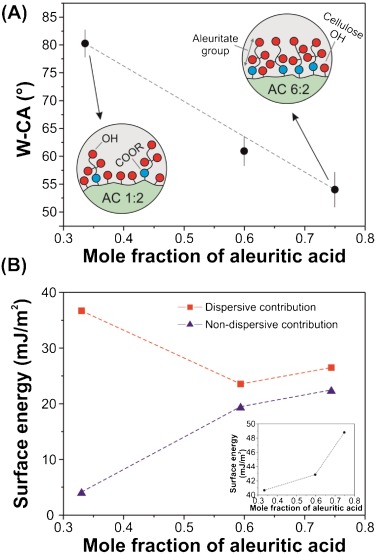
Abstract
The synthesis of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and 9,10,16-hydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid ester-based bioplastics was investigated through acylation in a mixed anhydride (trifluoroacetic acid (TFA)/trifluoroacetic acid anhydride (TFAA)), chloroform co-solvent system. The effects of chemical interactions and the molar ratio of aleuritic acid to the anhydroglucose unit (AGU) of cellulose were investigated. The degree of substitution (DS) of new polymers were characterized by two-dimensional solution-state NMR and ranged from 0.51 to 2.60. The chemical analysis by attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) confirmed the presence of aleuritate groups in the structure induces the formation of new H-bond networks. The tensile analysis and the contact angle measurement confirmed the ductile behavior and the hydrophobicity of the prepared bioplastics. By increasing the aleuritate amounts, the glass transition temperature decreased and the solubility of bioplastic films in most common solvents was improved. Furthermore, this new polymer exhibits similar properties compared to commercial cellulose derivatives.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.068
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthesis and characterization of Rh/MnO2-CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO-PrOx reaction
Martinez, TLM; Laguna, OH; Lopez-Cartes, C; Centeno, MAMolecular Catalysis, 440 (2017) 9-18 DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.06.018
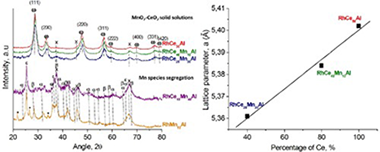
Abstract
Rh/MnO2-CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts with different manganese-to-ceria ratios have been synthesized, characterized and tested in CO-PrOx reaction. The physicochemical properties of the solids were studied by XRD, Raman spectroscopy, BET surface area, H-2-TPR, TGA-DTG and TEM. The differences observed in the textural, structural and redox properties were related to the Mn-to-ceria ratio of the samples. The segregation of Mn species was observed at high Mn-to-Ce ratios. In opposite way, MnO2-CeO2 solid solutions were obtained at low Mn to Ce ones. In this last case, the physicochemical properties of the solids were favored by the intimate Rh-Ce-Mn contact. The effect of the Mn-Ce presence on Rh catalysts which promotes the catalytic behavior towards selective CO oxidation was observed to be better at low temperatures. At higher temperatures, Mn species promote the Reverse Water Gas Shift reaction, whilst ceria promotes the H-2 oxidation in the whole range of working temperatures.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.06.018
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Towards Extending Solar Cell Lifetimes: Addition of a Fluorous Cation to Triple Cation-Based Perovskite Films
Salado, M; Fernandez, MA; Holgado, JP; Kazim, S; Nazeeruddin, MK; Dyson, PJ; Ahmad, SChemsuschem, 10 (2017) 3846-3853 DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201700797
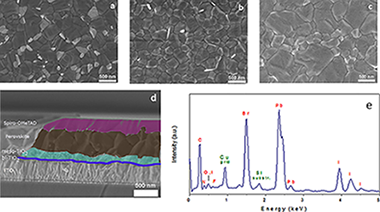
Abstract
Organohalide perovskites have emerged as highly promising replacements for thin-film solar cells. However, their poor stability under ambient conditions remains problematic, hindering commercial exploitation. The addition of a fluorous-functionalized imidazolium cation during the preparation of a highly stable cesium-based mixed perovskite material Cs-0.05(MA(0.15)FA(0.85))(0.95)Pb(I0.85Br0.15)(3) (MA= methylammonium; FA= formamidinium) has been shown to influence its stability. The resulting materials, which vary according to the amount of the fluorous-functionalized imidazolium cation present during fabrication, display a prolonged tolerance to atmospheric humidity (> 100 days) along with power conversion efficiencies exceeding 16%. This work provides a general route that can be implemented in a variety of perovskites and highlights a promising way to increase perovskite solar cell stability.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201700797
Reactividad de Sólidos
Dense graphene nanoplatelet/yttria tetragonal zirconia composites: Processing, hardness and electrical conductivity
Gallardo-Lopez, A; Marquez-Abril, I; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Munoz, A; Poyato, RCeramics International, 43 (2017) 11743-11752 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.06.007

Abstract
Yttria tetragonal zirconia ceramic composites with 1, 2.5, 5 and 10 vol% nominal contents of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) were fabricated and characterized. First, the GNP dispersion in isopropanol was optimized to de-agglomerate the GNPs without damaging their structure. Then, submicrometric fully dense composites were obtained via spark plasma sintering (SPS) at 1250 degrees C with a 5 min holding time. The processing routine produced a nearly homogeneous GNP dispersion in the ceramic matrix, and the GNPs preferential orientation was perpendicular to the sintering compression axis. A ceramic grain refinement due to the GNPs was also detected. The Vickers hardness measured on the plane perpendicular to the sintering compression axis (basal plane) was lower than on the cross sections. This anisotropy increased with the increasing GNP content, while the average hardness decreased. The electrical conductivity was also highly anisotropic, up to seven times higher for the basal planes. The electrical percolation threshold for these composites was estimated to be between 2.2 and 4.4 vol% of the GNP measured content.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.06.007
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Vapor and liquid optical monitoring with sculptured Bragg microcavities
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gil-Rostra, J; Lopez-Santos, MC; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, FJournal of Nanophotonics, 11 (2017) 046009 DOI: 10.1117/1.JNP.11.046009
Abstract
Sculptured porous Bragg microcavities (BMs) formed by the successive stacking of columnar SiO2 and TiO2 thin films with a zig-zag columnar microstructure are prepared by glancing angle deposition. These BMs act as wavelength-dependent optical retarders. This optical behavior is attributed to a self-structuration of the stacked layers involving the lateral association of nanocolumns in the direction perpendicular to the main flux of particles during the multilayer film growth, as observed by focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy. The retardance of these optically active BMs can be modulated by dynamic infiltration of their open porosity with vapors, liquids, or solutions with different refractive indices. The tunable birefringence of these nanostructured photonic systems has been successfully simulated with a simple model that assumes that each layer within the BMs stack has uniaxial birefringence. The sculptured BMs have been incorporated as microfluidic chips for optical transduction for label-free vapor and liquid sensing. Several examples of the detection performance of these chips, working either in reflection or transmission configuration, for the optical monitoring of vapor and liquids of different refractive indices and aqueous solutions of glucose flowing through the microfluidic chips are described.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1117/1.JNP.11.046009
Tribología y Protección de Superficies - Materiales Coloidales
HoF3 and DyF3 Nanoparticles as Contrast Agents for High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Gonzalez-Mancebo, Daniel; Becerro, Ana I.; Rojas, T. Cristina; Garcia-Martin, Maria L.; de la Fuente, Jesus M.; Ocana, ManuelParticle & particle systems characterization, 34 (2017) art. 1700116 DOI: 10.1002/ppsc.201700116
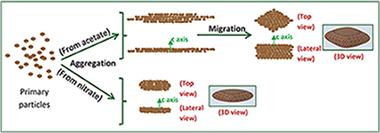
Abstract
Clinical contrast agents (CAs) currently used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at low fields are less effective at high magnetic fields. The development of new CAs is mandatory to improve diagnostic capabilities of the new generation of high field MRI scanners. The purpose of this study is to synthesize uniform, water dispersible LnF3 (Ln = Ho, Dy) nanoparticles (NPs) and to evaluate their relaxivity at high magnetic field (9.4 T) as a function of size and composition. Two different types of HoF3 NPs are obtained by homogeneous precipitation in ethylene glycol at 120 °C. The use of holmium acetate as holmium precursor leads to rhombus-like nanoparticles, while smaller, ellipsoid-like nanoparticles are obtained when nitrate is used as the holmium salt. To explain this behavior, the mechanism of formation of both kinds of particles is analyzed in detail. Likewise, rhombus-like DyF3 nanoparticles are prepared following the same method as for the rhombus-like HoF3 nanoparticles. We have found, to the best of knowledge, the highest transverse relaxivity values at 9.4 T described in the literature for this kind of CAs. Finally, the LnF3 NPs have shown negligible cytotoxicity for C6 rat glioma cells for concentrations up to 0.1 mg mL−1.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/ppsc.201700116
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Facile Synthesis of Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Perovskite Microcubes of Optical Quality Using Polar Antisolvents
Li, Yuelong; Galisteo-Lopez, Juan F.; Calvo, Mauricio E.; Miguez, HernanACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9 (2017) 35505-35510 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b08431
Abstract
Herein, we demonstrate a synthetic approach producing highly crystalline methylammonium lead bromide perovskite (MAPbBr3) microcubes at room temperature by injecting a perovskite precursor solution into an environmentally friendly antisolvent (isopropyl alcohol). Confirmed by X-ray and electron diffraction, as well as electron microscopy, these MAPbBr3 microcubes are single crystals and have perfect cubic structure, with sizes varying between 1 and 15 μm depending on the synthesis conditions. The stoichiometry of the MAPbBr3 crystal is proven by energy-dispersive X-ray analysis. Finally, optical analysis carried out by means of laser scanning confocal microscopy evidences how the crystalline quality of the microcubes translates into a homogeneous photoluminescence throughout the cube volume.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b08431
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructure characterization of multifunctional As4S4/Fe3O4 nanocomposites prepared by high-energy mechanical milling
Shpotyuk, O; Bujnakova, Z; Sayagues, MJ; Balaz, P; Ingram, A; Shpotyuk, Y; Demchenko, PMaterials Characterization, 132 (20187) 303-311 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.08.028
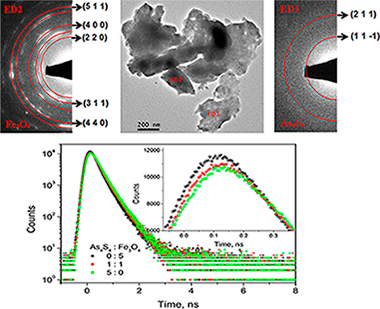
Abstract
Multifunctional As4S4/Fe3O4 nanocomposites prepared by high-energy mechanical milling are probed by complementary methods of positron annihilation lifetime (PAL) spectroscopy, supported by microstructure characterization using X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) with analysis applied to the first sharp diffraction peak (FSDP), morphology studies by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and high-resolution TEM (HRTEM).
These nanocomposites are shown to consist of Fe3O4 crystallites with particle sizes of 8-21 nm, and far separated beta-As4S4 crystallites surrounded by amorphous As-S phase. In respect to PAL data, the effect of milling is identified as possible conversion from Ps traps to positron-trapping sites depending on preferential chemistry of atomic surrounding. So, the interfacial triple junctions at the intersections of Fe3O4 crystallites are identified as principal positron traps in As4S4/Fe3O4 nanocomposites with competitive influence from free-volume defects of amorphous As-S phase.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.08.028
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Materials chemistry approaches to the control of the optical features of perovskite solar cells
Calvo, Mauricio E.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 5 (2017) 20561-20578 DOI: 10.1039/c7ta05666d
Abstract
Perovskite solar cells have revolutionized the field of photovoltaics. Apart from their impressive photo-conversion efficiencies, the ease of their fabrication – principally when carried out by solution processing – has permitted addition of new functionalities to the photovoltaic cell. Some of these features are related to the optical properties. In this review, the different materials chemistry approaches that allow controlling the spectral absorption of ABX3 perovskite layers and the changes that they produce in the visual aspect of the solar cell will be covered. These modifications can be done either by playing with the composition of the precursors or by integrating different types of nanostructures. Spectral bandgap tuning, semitransparency, color and enhancement of light absorption are examples of how these modifications operate in the core of ABX3 perovskite solar cells. These optical features bring benefits in terms of photo-conversion efficiencies or else in the aesthetical integration of perovskite solar cells with architectonic elements for building integrated photovoltaics. Additionally, surface passivation approaches are covered to show its effect over the photo-conversion efficiency and stability of the cell.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/c7ta05666d
Reactividad de Sólidos
Defect chemistry and electrical properties of BiFeO3
Schrade, M; Maso, N; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; West, ARJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 5 (2017) 10077-10086 DOI: 10.1039/c7tc03345a
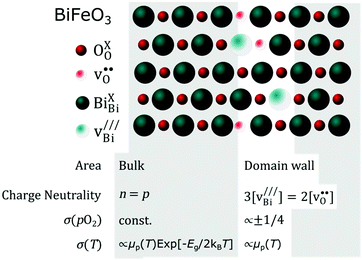
Abstract
BiFeO3 attracts considerable attention for its rich functional properties, including room temperature coexistence of magnetic order and ferroelectricity and more recently, the discovery of conduction pathways along ferroelectric domain walls. Here, insights into the defect chemistry and electrical properties of BiFeO3 are obtained by in situ measurements of electrical conductivity, sigma, and Seebeck coefficient, a, of undoped, cation-stoichiometric BiFeO3 and acceptor-doped Bi1-xCaxFeO3-delta ceramics as a function of temperature and oxygen partial pressure pO(2). Bi1-xCaxFeO3-delta exhibits p-type conduction; the dependencies of s and a on pO(2) show that Ca dopants are compensated mainly by oxygen vacancies. By contrast, undoped BiFeO3 shows a simultaneous increase of s and a with increasing pO(2), indicating intrinsic behavior with electrons and holes as the main defect species in almost equal concentrations. The pO(2)-dependency of s and a cannot be described by a single point defect model but instead, is quantitatively described by a combination of intrinsic and acceptor-doped characteristics attributable to parallel conduction pathways through undoped grains and defect-containing domain walls; both contribute to the total charge transport in BiFeO3. Based on this model, we discuss the charge transport mechanism and carrier mobilities of BiFeO3 and show that several previous experimental findings can readily be explained within the proposed model.
Octubre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/c7tc03345a
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhanced green fluorescent protein in optofluidic Fabry-Perot microcavity to detect laser induced temperature changes in a bacterial culture
Lahoz, F; Martin, IR; Walo, D; Freire, R; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARApplied Physics Letters, 111 (2017) 111103 DOI: 10.1063/1.4990870

Abstract
Thermal therapy using laser sources can be used in combination with other cancer therapies to eliminate tumors. However, high precision temperature control is required to avoid damage in healthy surrounding tissues. Therefore, in order to detect laser induced temperature changes, we have used the fluorescence signal of the enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein (eGFP) over-expressed in an E. coli bacterial culture. For that purpose, the bacteria expressing eGFP are injected in a Fabry-Perot (FP) optofluidic planar microcavity. In order to locally heat the bacterial culture, external infrared or ultraviolet lasers were used. Shifts in the wavelengths of the resonant FP modes are used to determine the temperature increase as a function of the heating laser pump power. Laser induced local temperature increments up to 6-7 degrees C were measured. These results show a relatively easy way to measure laser induced local temperature changes using a FP microcavity and using eGFP as a molecular probe instead of external nanoparticles, which could damage/alter the cell. Therefore, we believe that this approach can be of interest for the study of thermal effects in laser induced thermal therapies.
Septiembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1063/1.4990870
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of milling parameters on the solid-gas synthesis of TiCxN1-x by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Alcala, MD; Cordoba, JMPowder Technology, 319 (2017) 12-18 DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.06.035
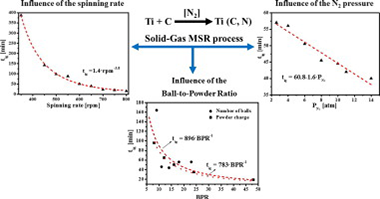
Abstract
The synthesis of a titanium carbonitride solid solution (TiCxN1 − x) performed in a high-energy planetary mill by a solid-gas Mechanically induced Self-sustaining Reaction (MSR) was used to study the influence of a full set of experimental milling parameters on the ignition time (tig) as a measure of the mechanical dose rate provided by the mill. The highly exothermic Ti-C-N mixture was selected to ensure no competitiveness between MSR and diffusion-controlled routes under the milling conditions employed. The results showed that the dependence of tig on the spinning rate followed a potential function, with a potential factor higher than the value of 3 that would be obtained if a perfect collision model is assumed. The scalability of milling processes performed using planetary mills was confirmed. The results suggested that to define a milling experiment, it is necessary to provide not only the Ball-to-Powder mass Ratio (BPR) and spinning rate values, as is usually performed, but also the full set of milling parameters including the nature of the milling media (vial and balls), the number and size of balls, the mass of the powder charge, the pressure of the reactive gas and even the volume of the vial.
Septiembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.06.035
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Carbon nanofibers replacing graphene oxide in ceramic composites as a reinforcing-phase: Is it feasible?
Cano-Crespo, Rafael; Malmal Moshtaghioun, Bibi; Gomez-Garcia, Diego; Dominguez-Rodriguez, Arturo; Moreno, RodrigoJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 37 (2017) 3791-3796 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.03.027
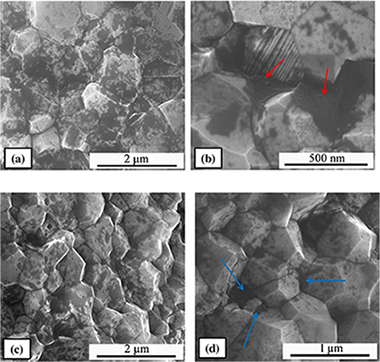
Abstract
In recent years, the interest of graphene and graphene-oxide has increased extraordinarily due to the outstanding properties concurring in this material. In ceramic science, the possibility of combining excellent electrical conductivities together with an enhancement of mechanical properties has motivated the research in fabrication of graphene oxide-reinforced ceramic composites despite the intrinsic difficulties for sintering. In this work a comparison is made between graphene oxide-reinforced alumina composites and carbon nanofiber-reinforced alumina ones. It will be concluded that the improvement of mechanical properties is scarce, if any. Since carbon nanofibers have also a good electrical conductivity their importance for future applications as a replacement of more sophisticated but expensive graphene-based ceramic composites will be stressed.
Septiembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.03.027
Reactividad de Sólidos
Multicycle activity of natural CaCO3 minerals for thermochemical energy storage in Concentrated Solar Power plants
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LASolar Energy, 153 (2017) 188-199 DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2017.05.068
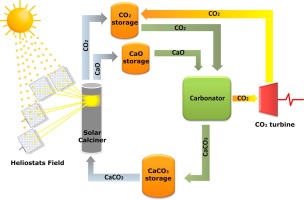
Abstract
Thermochemical energy storage in Concentrated Solar Power plants by means of the Calcium-Looping process is a promising novel technology that would allow for a higher share of renewables. A main benefit of this technology is the use of widely available, non-toxic and environmentally friendly calcium carbonate minerals as raw materials to store energy. Efficient integration of the Calcium-Looping process into Concentrated Solar Power plants involves the endothermic calcination of CaCO3 in the solar receiver while the exothermic carbonation of CaO is carried out at high temperature under high CO2 partial pressure. The heat released by this reaction is carried out by the excess CO2 and employed for power generation by means of a closed CO2 cycle. This work explores the multicycle Calcium-Looping performance of naturally occurring CaCO3 minerals such as limestone, chalk and marble for thermochemical energy storage in Concentrated Solar Power plants. Despite their similar composition (almost pure CaCO3), these minerals exhibit a significant difference in their Calcium-Looping multicycle activity, which may be attributed to differences in particle size and microstructure. Pore plugging at the Calcium-Looping conditions for thermochemical energy storage tested in our work is a main limiting mechanism on the multicycle CaO carbonation activity.
Septiembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2017.05.068
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
High performance novel gadolinium doped ceria/yttria stabilized zirconia/nickel layered and hybrid thin film anodes for application in solid oxide fuel cells
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Beltran, AM; Yubero, E; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lambert, RMJournal of Power Sources, 363 (2017) 251-259 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.07.085
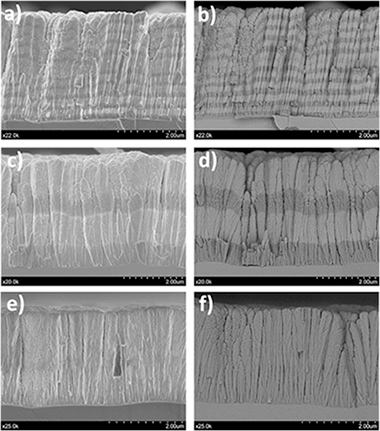
Abstract
Magnetron sputtering under oblique angle deposition was used to produce Ni-containing ultra thin film anodes comprising alternating layers of,gadolinium doped ceria (GDC) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) of either 200 nm or 1000 nm thickness. The evolution of film structure from initial deposition, through calcination and final reduction was examined by XRD, SEM, TEM and TOF-SIMS. After subsequent fuel cell usage, the porous columnar architecture of the two-component layered thin film anodes was maintained and their resistance to delamination from the underlying YSZ electrolyte was superior to that of corresponding single component Ni-YSZ and Ni-GDC thin films. Moreover, the fuel cell performance of the 200 nm layered anodes compared favorably with conventional commercially available thick anodes. The observed dependence of fuel cell performance on individual layer thicknesses prompted study of equivalent but more easily fabricated hybrid anodes consisting of simultaneously deposited Ni-GDC and Ni-YSZ, which procedure resulted in exceptionally intimate mixing and interaction of the components. The hybrids exhibited very unusual and favorable I-V characteristics, along with exceptionally high power densities at high currents. Their discovery is the principal contribution of the present work.
Septiembre, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.07.085
- ‹ anterior
- 17 of 37
- siguiente ›














