Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Environmentally Tight TiO2-SiO2 Porous 1D-Photonic Structures
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Rico, V; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Materials Interfaces, 6 (2019) art. 1801212
Show abstract ▽
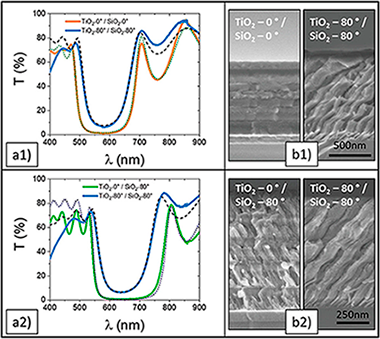
Although thin film porosity is the basis of many optical sensors, it can be deleterious for a stable optical behavior of passive optical elements due to the condensation of water and other vapors in their pores. This paper proposes a new strategy for the magnetron sputtering (MS) fabrication of environmentally tight SiO2-TiO2 porous multilayers. Thin films of these two oxides deposited in an oblique angle configuration (MS-OAD) present a nanocolumnar and highly porous nanostructure and, as a consequence, experience significant changes in their optical properties when exposed to water vapor. Similarly, the optical properties of Bragg reflectors and Bragg microcavities made of the stacking of porous and compact SiO2 and TiO2 thin films experience reversible changes when these 1D-photonic structures are exposed to water pressure. A key finding of this work is that a very thin capping layer of SiO2 deposited on the surface of porous SiO2 films in the stack, at the interlayer between the two oxides, efficiently seals the pores making the photonic structures environmentally tight. This capping layer approach is a useful strategy to incorporate porosity as an additional parameter to design the optical behavior of planar photonic structures while preserving optical and environmental stability.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801212
Amber, beads and social interaction in the Late Prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula: an update
Odriozola, CP; Sousa, AC; Mataloto, R; Boaventura, R; Andrade, M; Garcia, RV; Garrido-Cordero, JA; Rodriguez, E; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Aviles, MA; Daura, J; Sanz, M; Riquelme, JAArchaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 11 (2019) 567-595
Show abstract ▽
The identification of archaeological amber has been used in Iberian prehistory to evidence long-distance exchanges and engage Iberia in networks that connect western Europe with central and northern Europe, the emergence of social complexity, and the consolidation of trade networks. However, until now, no comprehensive analytical study of the Iberian amber has been produced to support any of the interpretive models currently in use. This paper approaches the analysis of Iberian Peninsula amber artefacts by considering their provenance (based on FTIR characterization), chronology, and spatial relationship with other exotica. Our work increases the number of analyzed artefacts to 156 (24%), out of the c. 647 currently known for the Iberian Peninsula. Based on these new data and a review of Murillo-Barroso and Martinon-Torres (2012), this overview outlines amber consumption patterns from the 6th to 2nd millennia BCE and demonstrates long-distance amber exchange connecting Iberia with the Mediterranean region from the Neolithic period onwards.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1007/s12520-017-0549-7
Reactividad de Sólidos
Insight into the BiFeO3 flash sintering process by in-situ energy dispersive X-ray diffraction (ED-XRD)
Perez-Maqueda, LA; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Wassel, MA; Jha, SK; Perejon, A; Charalambous, H; Okasinski, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Tsakalakos, TCeramics International, 45 (2019) 2828-2834
Show abstract ▽
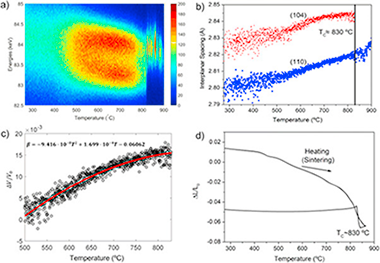
The sintering mechanism of BiFeO3 has been investigated in-situ by energy dispersive X-ray diffraction (ED-XRD) using a high-energy white collimated X-ray beam from the Advanced Photon Source (Argonne National Laboratories). Such radiation is very penetrating thereby allowing measurements of the sample even when placed inside the flash sintering set up. Additionally, the fast ED-XRD measurements permit monitoring the flash sintering process by providing information about phase composition and sample temperature in real time. Moreover, profile scans, obtained by moving the stage vertically while recording the ED-XRD spectra, permit investigating the homogeneity of the flash for the entire length of the sample. All experiments have been complemented by ex-situ studies. It has been concluded that flash sintering of BiFeO3 is a homogeneous process without any directionality effects. Furthermore, flash sintering takes place at quite low temperatures (below the Tc ≈ 830 °C), which may be related to the high quality of the samples, as pure, highly insulating ceramics without evidence of secondary phases with a homogenous nanostructured grain size distribution are obtained by this technique. Moreover, it is also evidenced that the rapid heating of the sample does not seem to justify, at least by itself, the densification process. Therefore, it appears that the electric current should play a role in the enhanced mobility during the sintering process.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.293
Reactividad de Sólidos
Production of Ag-ZnO powders by hot mechanochemical processing
Guzman, D; Aguilar, C; Rojas, P; Criado, JM; Dianez, MJ; Espinoza, R; Guzman, A; Martinez, CTransactions of nonferrous metals society of China, 29 (2019) 365-373
Show abstract ▽
Ag-CdO composites are still one of the most commonly used electrical contact materials in low-voltage applications owing to their excellent electrical and mechanical properties. Nevertheless, considering the restriction on using Cd due to its toxicity, it is necessary to find alternative materials that can replace these composites. In this study, the synthesis of Ag-ZnO alloys from Ag-Zn solid solutions was investigated by hot mechanochemical processing. The hot mechanochemical processing was conducted in a modified attritor mill at 138 degrees C under flowing O-2 at 1200 cm(3)/min for 3.0 h. The microstructure and phase evolution were investigated using X-ray diffractometry, field emission gun scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The results suggest that it is possible to complete the oxidation of Ag-Zn solid solution by hot mechanochemical processing at a low temperature and short time. This novel synthesis route can produce Ag-ZnO composites with a homogeneous distribution of nanoscale ZnO precipitates, which is impossible to achieve using the conventional material processing methods. Considering the fact that the fundamental approach to improving electric contact material performance resides in obtaining uniform dispersion of the second-phase in the Ag matrix, this new processing route could open the possibility for Ag-ZnO composites to replace non-environmentally friendly Ag-CdO.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64946-0
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Fluorinated and Platinized Titania as Effective Materials in the Photocatalytic Treatment of Dyestuffs and Stained Wastewater Coming from Handicrafts Factories
Murcia, J.J.; Cely, A.C.; Rojas, H.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navío, J.A.Catalysts, 9 (2019) 179
Show abstract ▽
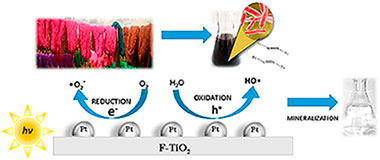
In this study, commercial and lab-prepared TiO2 were modified by fluorination and platinum photodeposition; and the effect of these modifications over the physicochemical and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 was evaluated. It was found that F and Pt addition leads to the modification of the optical and textural properties of TiO2. The materials prepared were tested in the photocatalytic degradation of different organic dyestuffs such as methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO); the degradation of commercial anilines employed in the staining of natural fibers was also evaluated. Photocatalysis was also studied in this work as an eco-friendly treatment of wastewater coming from handicrafts factories. In general it was observed that the effectiveness of the photocatalytic treatment strongly depends on the substrate to be degraded, thus, fluorinated and platinized commercial Titania (Pt-F-P25) showed the best photocatalytic performance in the MB and MO photodegradation and in contrast, in the case of the anilines the highest degradation was obtained over commercial TiO2 fluorinated (F-P25). These results can be explained by differences observed in the structure and in the adsorption of these dyestuffs over the photocatalysts surfaces. F-P25 photocatalyst also demonstrated to be the best material for the treatment of real wastewater coming from handicrafts factories.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/catal9020179
- ‹ anterior
- 143 of 420
- siguiente ›














