Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Reactividad de Sólidos
Tailoring the Band Gap in the ZnS/ZnSe System: Solid Solutions by a Mechanically Induced Self-Sustaining Reaction
Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJInorganic Chemistry, 58 (2019) 2565-2575
Show abstract ▽
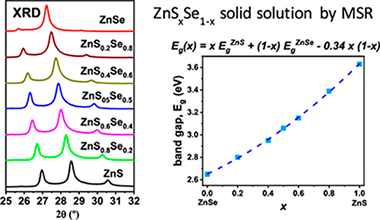
The complete ZnSxSe1-x solid solution was successfully obtained by the mechanochemical process denoted as a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction. Excellent control of the chemical stoichiometry of the solid solution was possible by adjusting the atomic ratio of the starting Zn/S/Se elemental mixture subjected to milling. A mixture of both wurtzite-2H (hexagonal) and zinc blende (cubic) structures was always obtained, although for a similar milling time the proportion of the zinc blende structure increased with the Se content in the solid solution. However, wurtzite was the major phase for S-rich compositions when milling was stopped just after ignition. It was demonstrated that milling induces the wurtzite-to-zinc blende phase transition. The 8H hexagonal polytype was also observed in samples subjected to long milling times. Variation of the lattice parameters for both structures with the x value in the solid solution presented an excellent linearity, confirming the validity of Vegard's law. However, variation of the band-gap energy (E-g) with x was not perfectly linear, and a small bowing parameter of 0.34 was obtained. It was possible to tune the E-g value between those of the end members of the solid solution in a continuous manner by adjusting the stoichiometry of the solid solution. The morphology and crystalline domain size can also be controlled by adjusting, in this case, the postignition milling time of the mechanochemical process.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b03183
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid over TiO2(B)/anatase nanobelts and Au-TiO2(B)/anatase nanobelts
Chenchana, A.; Nemamcha, A.; Moumeni, H.; Doña Rodríguez, J.M.; Araña, J.; Navío, J.A.; González Díaz, O.; Pulido Melián, E.Applied Surface Science, 467-468 (2019) 1076-1087
Show abstract ▽
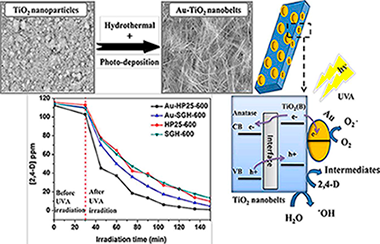
In this work, novel TiO2-based nanobelts with various phases were synthesized: biphasic TiO2(B)/anatase, pure TiO2(B) and pure anatase. These catalysts were obtained via hydrothermal reaction using two nanoparticulated TiO2 photocatalysts as precursors: Aeroxide TiO2 P25 (P25) and TiO2 synthesized via a sol-gel process (SG). In addition, the surface of the photocatalysts was modified with gold using a photodeposition method. A characterization study of the different photocatalysts was performed with X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), UV–Vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectrum analysis (XPS) and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller measurements (BET). The photocatalytic reaction of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) was investigated under UVA irradiation. A toxicity analysis was performed with the marine bioluminescent bacteria Vibrio fischeri. The highest 2,4-D removal efficiency of 99.2% was obtained with the biphasic Au-TiO2(TiO2(B)/anatase) nanobelts with anatase as predominant phase. Toxicity was mainly due to the intermediate 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) which was eliminated in 4 h. The TiO2 nanobelt phase structure is shown to have a significant effect on photocatalytic activity.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.175
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study of the Interface of the Early Stages of Growth under Quasi-Equilibrium Conditions of ZnO on Graphene/Cu and Graphite
Morales, C; Black, A; Urbanos, FJ; Granados, D; Mendez, J; del Campo, A; Yubero, F; Soriano, LAdvanced Materials Interfaces, 6 (2019) art. 1801689
Show abstract ▽
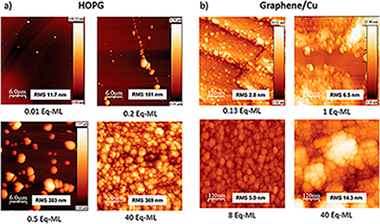
The study of the early stages of growth of ZnO on graphene supported on Cu and on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite by means of reactive thermal evaporation of metallic Zn at room temperature is presented. This growth method allows to go in depth in the study of the fundamental interaction between ZnO and graphene at the interface in quasi-equilibrium conditions. Quantitative, chemical, and morphological analysis is performed using photoemission spectroscopy, atomic force, and scanning microscopies as experimental characterization techniques and factor analysis and inelastic peak shape analysis as modeling techniques. The growth of ZnO on a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite substrate is also studied using the same growth method for comparison. The results show that, in spite that the first atomic layer of both substrates is identical, the growth kinetics and morphology of the deposits are completely different. A model for the kinetics of the growth of ZnO on both substrates is proposed.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/admi.201801689
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical combustion synthesis of vanadium carbide (VC), niobium carbide (NbC) and tantalum carbide (TaC) nanoparticles
Jalaly, M; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 79 (2019) 177-184
Show abstract ▽
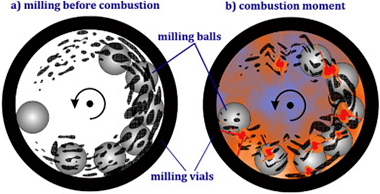
The nanoparticles of vanadium, niobium, and tantalum carbides were synthesized by a mechanically induced magnesiothermic combustion in the separate Mg/V2O5/C, Mg/Nb2O5/C, and Mg/Ta2O5/C systems. Initial materials in these systems ignited after short milling times of 10, 10, and 23 min, respectively. X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and elemental mapping techniques were employed to characterize the combustion products. In this process, magnesium reduces initial oxides to generate elemental V/Nb/Ta to react with carbon, forming the carbide phases.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.12.011
Reactividad de Sólidos
Multicycle CO2 capture activity and fluidizability of Al-based synthesized CaO sorbents
Azimi, B; Tahmasebpoor, M; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 358 (2019) 679-690
Show abstract ▽
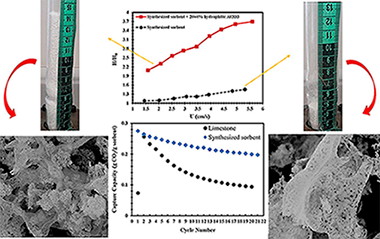
CaO-based materials have been identified as promising sorbents for highly efficient pre-combustion and post-combustion CO2 capture in fluidized beds operated at high temperatures by means of the Calcium Looping (CaL) process. However, Ca-based sorbents suffer from a decline of the capture capacity over multiple sorption/desorption cycles, mainly due to sintering, and from a markedly heterogeneous fluidization behavior due to the strength of interparticle attractive forces as compared to particle weight. The present study is focused on the development of novel synthetic CaO/Al2O3 sorbents for CO2capture with enhanced CaL performance and fluidizability by dry mixing with flow conditioner nanopowders. The influence of initial precursors on the sorbents multicycle activity at realistic CaL conditions has been investigated. The formation of a stable Ca9Al6O18 mixed-phase during the preparation of the sorbents promotes the multicycle capture capacity. The type of Ca and Al precursors, either soluble or insoluble, can significantly affect the dispersion of this stabilizer (Ca9Al6O18) in the sorbent matrix and, consequently, may affect the carbonation activity of the materials. The sorbent prepared from soluble aluminum nitrate and calcium nitrate precursors by sol-gel method exhibits a very stable multicycle capture capacity with a capture capacity around 0.2 g of CO2/g of sorbent after 21 cycles keeping a 72% of its initial capture capacity. The fluidizability of this promising sorbent was also investigated as affected by the addition of three different flow conditioners. Fluidization experiments confirmed the positive effect of using hydrophilic alumina and hydrophobic silica nanoparticles on improving the fluidizability of the synthesized sorbents.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.061
- ‹ anterior
- 144 of 420
- siguiente ›














