Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical combustion synthesis of vanadium carbide (VC), niobium carbide (NbC) and tantalum carbide (TaC) nanoparticles
Jalaly, M; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 79 (2019) 177-184
Show abstract ▽
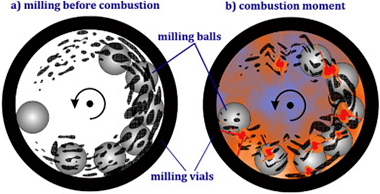
The nanoparticles of vanadium, niobium, and tantalum carbides were synthesized by a mechanically induced magnesiothermic combustion in the separate Mg/V2O5/C, Mg/Nb2O5/C, and Mg/Ta2O5/C systems. Initial materials in these systems ignited after short milling times of 10, 10, and 23 min, respectively. X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and elemental mapping techniques were employed to characterize the combustion products. In this process, magnesium reduces initial oxides to generate elemental V/Nb/Ta to react with carbon, forming the carbide phases.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.12.011
Reactividad de Sólidos
Multicycle CO2 capture activity and fluidizability of Al-based synthesized CaO sorbents
Azimi, B; Tahmasebpoor, M; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 358 (2019) 679-690
Show abstract ▽
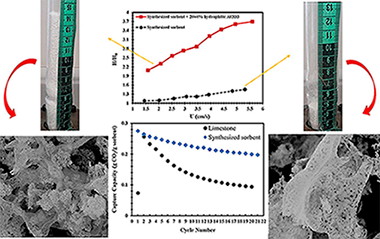
CaO-based materials have been identified as promising sorbents for highly efficient pre-combustion and post-combustion CO2 capture in fluidized beds operated at high temperatures by means of the Calcium Looping (CaL) process. However, Ca-based sorbents suffer from a decline of the capture capacity over multiple sorption/desorption cycles, mainly due to sintering, and from a markedly heterogeneous fluidization behavior due to the strength of interparticle attractive forces as compared to particle weight. The present study is focused on the development of novel synthetic CaO/Al2O3 sorbents for CO2capture with enhanced CaL performance and fluidizability by dry mixing with flow conditioner nanopowders. The influence of initial precursors on the sorbents multicycle activity at realistic CaL conditions has been investigated. The formation of a stable Ca9Al6O18 mixed-phase during the preparation of the sorbents promotes the multicycle capture capacity. The type of Ca and Al precursors, either soluble or insoluble, can significantly affect the dispersion of this stabilizer (Ca9Al6O18) in the sorbent matrix and, consequently, may affect the carbonation activity of the materials. The sorbent prepared from soluble aluminum nitrate and calcium nitrate precursors by sol-gel method exhibits a very stable multicycle capture capacity with a capture capacity around 0.2 g of CO2/g of sorbent after 21 cycles keeping a 72% of its initial capture capacity. The fluidizability of this promising sorbent was also investigated as affected by the addition of three different flow conditioners. Fluidization experiments confirmed the positive effect of using hydrophilic alumina and hydrophobic silica nanoparticles on improving the fluidizability of the synthesized sorbents.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.061
Materiales Coloidales
Enhancing Luminescence and X-ray Absorption Capacity of Eu3+:LaF3 Nanoparticles by Bi3+ Codoping
Mancebo, DG; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Moros, M; Balcerzyk, M; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MACS Omega, 4 (2019) 765-774
Show abstract ▽
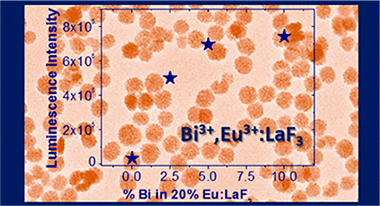
Bi3+ codoping has been proposed in this work with a twofold objective, namely, enhancing the luminescence emission of Eu3+:LaF3 nanoparticles (NPs) and increasing their X-ray attenuation capacity, with the purpose of obtaining a bimodal bioprobe for luminescence bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography. The synthesis method, reported here for the first time for LaF3 particles, allowed obtaining uniform, nonaggregated NPs using a homogeneous precipitation in polyol medium at room temperature in just 2 h. The simplicity of the synthesis method allows the large-scale production of NPs. LaF3 NPs with different Eu3+ contents were first synthesized to find the critical Eu3+ concentration, producing the highest emission intensity. This concentration was subsequently used to fabricate Bi3+-Eu3+-codoped LaF3 NPs using the same method. The emission intensity of the codoped NPs increased in more than one order of magnitude, thanks to the possibility of excitation through the Bi3+. Eu3+ energy-transfer band. The luminescence properties of the codoped NPs were analyzed in detail to find the mechanism responsible for the emission enhancement. Finally, it was demonstrated that the high atomic number of Bi3+, higher than that of lanthanides, was an added value of the material because it increased its X-ray attenuation capacity. In summary, the LaF3 NPs codoped with Eu3+ and Bi3+ presented in this work are promising candidates as a bimodal bioprobe for luminescence bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.8b03160
Reactividad de Sólidos
La0.59Li0.24TiO3 ceramics obtained by spark plasma sintering: Electric behavior analysis
Pereira, JS; Guerrero, F; Romaguera-Barcelay, Y; Anglada-Rivera, J; Sales, JCC; Silva, RS; Zulueta, Y; Poyato, R; Gallardo, A; Almeida, A; Moreira, JA; Leyet, YMaterials Research Express, 6 (2019) art. 015504
Show abstract ▽
This work describes the electric study of Lithium lanthanum titanate (La0.59Li0.24TiO3) ceramics performed by Complex Impedance Spectroscopy. The nanoparticle powders have been synthesized through high energy ball milling and sintered via Spark Plasma Sintering technique. The experimental impedance data have been analyzed using the equivalent circuit model, the Extended Jonscher universal law and the derivative method. From these models, we have determined the dielectric response as well as the grain and grain boundary conductivity. The samples show ionic conductivity values between 10(-5) to 10(-4) S cm(-1) in the studied temperature range, and activation energy values 0.24 eV and 0.48 eV for grain and grain boundary, respectively. These results confirm the Li+ ions mobility through the crystalline structure of the material.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/aae496
Materiales Coloidales
Biocompatibility assessment of up-and down-converting nanoparticles: implications of interferences with in vitro assays
Pem, Barbara; Gonzalez-Mancebo, Daniel; Moros, Maria; Ocana, Manuel; Becerro, Ana Isabel; Pavicic, Ivan; Selmani, Atida; Babic, Michal; Horak, Daniel; Vinkovic Vrcek, IvanaMethods and Applications in Fluorescence, 7 (2019) 014001
Show abstract ▽
The safety assessment of nanoparticles (NPs) is crucial during their design and development for biomedicine. One of the prerequisite steps during this evaluation is in vitro testing that employs cell-based assays not always validated and well-adapted for NPs. Interferences with in vitro assays may arise due to the nano-related optical, oxidative, fluorescent, surface and catalytic properties of NPs. Thus, proper validation of each assay system has to be performed for each NP type. This study aimed to evaluate the applicability of the most common in vitro cytotoxicity assays for the safety assessment of up- and down-converting lanthanide-doped NPs. Conventional cell viability tests and fluorescence-based assays for oxidative stress response were selected to determine the biological effects of up- and down-converting NPs to human brain cells. Comparison with known silver and iron oxide NPs was made for verification purposes. Both the plate reader and flow cytometric measurements were examined. The obtained results indicated that both types of Ln-doped NPs interfered to a much lesser extent than metallic NPs. In addition, the great potential of both up- and down-converting NPs for biomedicine was manifested due to their biocompatibility and low toxicity.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1088/2050-6120/aae9c8
- ‹ anterior
- 145 of 420
- siguiente ›














