Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Highly Efficient Transparent Nanophosphor Films for Tunable White-Light-Emitting Layered Coatings
Geng, DL; Lozano, G; Miguez, HACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 11 (4) (2019) 4219-4225
Show abstract ▽
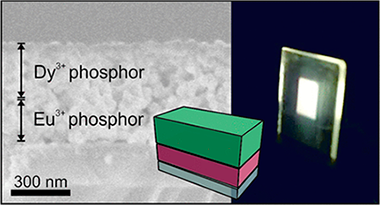
Bright luminescence in rare-earth (RE) nanocrystals, the so-called nanophosphors, is generally achieved by choosing a host that enables an effective excitation of the RE activator through charge or energy transfer. Although tungstate, molybdate, or vanadate compounds provide the aforementioned transfer, a comparative analysis of the efficiency of such emitters remains elusive. Herein, we perform a combined structural and optical analysis, which reveals that the tetragonal GdVO4 matrix gives rise to the highest efficiency among the different transparent nanophosphor films compared. Then, we demonstrate that by a sequential stacking of optical quality layers made of Eu3+- and Dy3+-doped nanocrystals, it is possible to attain highly transparent white-light-emitting coatings of tunable shade with photoluminescence quantum yields above 35%. Layering provides a precise dynamic tuning of the chromaticity based on the photoexcitation wavelength dependence of the emission of the nanophosphor ensemble without altering the chemical composition of the emitters or degrading their efficiency. The total extinction of the incoming radiation along with the high quantum yields achieved makes these thin-layered phosphors one of the most efficient transparent white converter coatings ever developed.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b17368
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Influence of Al and Y content on the oxidation resistance of CrAlYN protective coatings for high temperature applications: New insights about the Y role
Rojas, TC; Dominguez-Meister, S; Brizuela, M; Sanchez-Lopez, JCJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 777 (2019) 1172-1181
Show abstract ▽
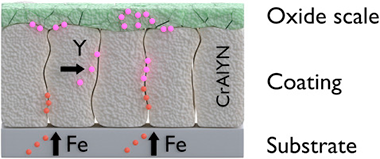
CrAlYN hard coatings with two different average Al contents: similar to 16 at.% and similar to 25 at.%, and Y concentration varying between 1.2 and 5.7 at.% were deposited by direct current reactive magnetron co-sputtering of mixed Cr-Al and Y targets on commercial M2 steel substrates. The samples were heated to 1000 degrees C in air during 2 h to study their oxidation resistance and thermal stability. The Y content is critical and the coatings present different behaviour depending on the Al content. The best oxidation resistance and thermal stability are obtained for the coating with similar to 16 at.% Al and 3.4 at.% Y. The initial film microstructure and the cubic phase (fcc-CrAlN) were retained, and a thin (Cr,Al)(2)O-3 oxide protective scale was formed. At lower Y content (1.2 at.%) iron, from the substrate crosses the coating, while a higher content (4.6 at.%) avoided the iron diffusion at the expense of a thicker oxide scale with new oxide phases. The coatings with higher Al content (similar to 25 at. %) were not thermally stable at 1000 degrees C. A good oxidation resistance was obtained for 2.6 at.% of Y although new phases (hcp-AlN and Cr-Fe) were formed. Higher amount of yttrium (similar to 5.7 at. %) led to the complete oxidation of the coating.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.280
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Coupling of Ag2CO3 to an optimized ZnO photocatalyst: Advantages vs. disadvantages
P. Sánchez-Cid; C. Jaramillo-Páez; J.A. Navío; A.N. Martín-Gómez; M.C. HidalgoJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 369 (2019) 119-132
Show abstract ▽

With the aim of improving the photocatalytic properties of a previously optimized zinc oxide photocatalyst, the effect of the incorporation of different amounts of Ag2CO3 on the aforementioned ZnO has been studied. For this purpose we report the synthesis, by means of simple precipitation procedures, of bare ZnO and Ag2CO3 samples as well as the coupled materials ZnO/Ag2CO3 (X) (where X = 1%, 2%, 4% and 5% in molar percentages). Both, single and coupled materials have been characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, N2-absorption, SEM, TEM, UV–vis/DRS and XPS). To assess the advantages or disadvantages that Ag2CO3 addition could have over the optimized ZnO, the photocatalytic properties have been established by following the photo-degradation of selected toxic molecules, both in the UV and in the visible, as well as using complementary techniques of liquid medium analyses (TOC and Atomic Emission Spectrometry with plasma ICP). Three selected substrates were chosen: Rhodamine B (RhB) as a dye, and phenol and caffeine as colourless recalcitrant toxic molecules.
Our results suggest that although the use of Ag2CO3 could be beneficial to implement the optical absorption towards the visible region, however, other effects have to be bore in mind, such as the photo-corrosion of Ag2CO3 and the chemical structure of the chosen substrate, to elucidate whether the addition of Ag2CO3 has beneficial or detrimental effects on the photocatalytic properties of the coupled ZnO/Ag2CO3 materials.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.10.024
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO-ZrO2 Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic Degradation and Mineralization of Phenol
Lopez, MCU; Lemus, MAA; Hidalgo, MC; Gonzalez, RL; Owen, PQ; Oros-Ruiz, S; Lopez, SAU; Acosta, JJournal of Nanomaterials (2019) art. 1015876, 12 pages
Show abstract ▽
ZnO-ZrO2 nanocomposites using zinc (II) acetylacetonate and different ZnO contents (13, 25, 50, and 75% mol) were synthesized through sol-gel method. The synthesis process was strongly related to nanocomposite properties especially on their structural composition. The obtained ZnO-ZrO2 nanomaterials presented tetragonal crystalline structure for zirconia whereas hexagonal one was formed in ZnO. Raman spectroscopy and XRD patterns confirmed the formation of tetragonal zirconia whereas inhibition of monoclinic structure was observed. Addition of ZnO affected the pore size distribution of the composite, and the measured specific surface areas were from 10 m2/g (for pure ZnO) to 46 m2/g (pristine ZrO2). Eg values of ZrO2 were modified by ZnO addition, since calculated values using Kubelka-Munk’s function varied from 4.73 to 3.76 eV. The morphology and size of the nanomaterials investigated by electron microscopy showed formation of nanorods for ZnO with sizes ranging from 50 nm to 300 nm while zirconia was formed by smaller particles (less than 50 nm). The main advantage of using the nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of phenol was the mineralization degree, since 75ZnO-ZrO2 nanocomposite surpassed mineralization reached by pure ZnO and also inhibited formation of undesirable intermediates.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1155/2019/1015876
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Flexible nanophosphor films doped with Mie resonators for enhanced out-coupling of the emission
Miranda-Munoz, JM; Geng, DL; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 7 (2019) 267-274
Show abstract ▽
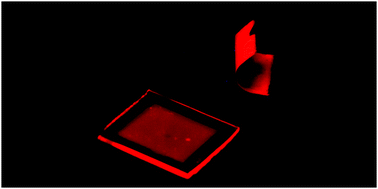
Herein, we present a general method to prepare self-standing flexible photoluminescent coatings of controlled opacity for integration into light-emitting diodes (LEDs) employing cost-effective solution-processing methods. From colloidal suspensions of nano-sized phosphors, we fabricate light-emitting transparent films that can be doped with spherical scatterers, which act as Mie resonators that trigger a controlled photoluminescence enhancement, evidenced by the reduction of the guided light along the layer. This results in an enhanced emission compared to that extracted from a bare phosphor layer. We show not only that emission is visible under ultraviolet-LED illumination for both rigid and flexible versions of the coatings, but we also prove the feasibility of the integration of these flexible conversion layers into such devices. We believe these results can contribute to develop more efficient and cost-effective illumination sources by providing efficient and easy-to-handle conversion layers susceptible to excitation by LEDs emitting at wavelengths in the near UV region.
Enero, 2019 | DOI:
- ‹ anterior
- 146 of 420
- siguiente ›














