Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Flexible nanophosphor films doped with Mie resonators for enhanced out-coupling of the emission
Miranda-Munoz, JM; Geng, DL; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 7 (2019) 267-274
Show abstract ▽
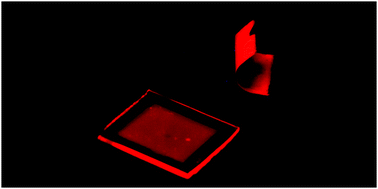
Herein, we present a general method to prepare self-standing flexible photoluminescent coatings of controlled opacity for integration into light-emitting diodes (LEDs) employing cost-effective solution-processing methods. From colloidal suspensions of nano-sized phosphors, we fabricate light-emitting transparent films that can be doped with spherical scatterers, which act as Mie resonators that trigger a controlled photoluminescence enhancement, evidenced by the reduction of the guided light along the layer. This results in an enhanced emission compared to that extracted from a bare phosphor layer. We show not only that emission is visible under ultraviolet-LED illumination for both rigid and flexible versions of the coatings, but we also prove the feasibility of the integration of these flexible conversion layers into such devices. We believe these results can contribute to develop more efficient and cost-effective illumination sources by providing efficient and easy-to-handle conversion layers susceptible to excitation by LEDs emitting at wavelengths in the near UV region.
Enero, 2019 | DOI:
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Isotope Labelling for Reaction Mechanism Analysis in DBD Plasma Processes
Navascues, P; Obrero-Perez, JM; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, ACatalysts, 9(1) (2019) 45
Show abstract ▽
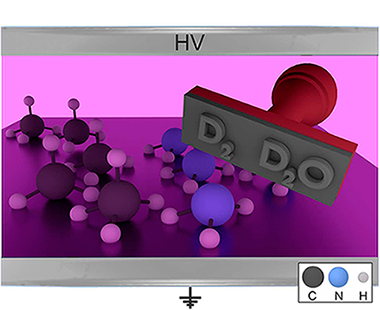
Dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasmas and plasma catalysis are becoming an alternative procedure to activate various gas phase reactions. A low-temperature and normal operating pressure are the main advantages of these processes, but a limited energy efficiency and little selectivity control hinder their practical implementation. In this work, we propose the use of isotope labelling to retrieve information about the intermediate reactions that may intervene during the DBD processes contributing to a decrease in their energy efficiency. The results are shown for the wet reforming reaction of methane, using D2O instead of H2O as reactant, and for the ammonia synthesis, using NH3/D-2/N-2 mixtures. In the two cases, it was found that a significant amount of outlet gas molecules, either reactants or products, have deuterium in their structure (e.g., HD for hydrogen, CDxHy for methane, or NDxHy for ammonia). From the analysis of the evolution of the labelled molecules as a function of power, useful information has been obtained about the exchange events of H by D atoms (or vice versa) between the plasma intermediate species. An evaluation of the number of these events revealed a significant progression with the plasma power, a tendency that is recognized to be detrimental for the energy efficiency of reactant to product transformation. The labelling technique is proposed as a useful approach for the analysis of plasma reaction mechanisms.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/catal9010045
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Coupling of Ag2CO3 to an optimized ZnO photocatalyst: Advantages vs. disadvantages
P. Sánchez-Cid; C. Jaramillo-Páez; J.A. Navío; A.N. Martín-Gómez; M.C. HidalgoJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 369 (2019) 119-132
Show abstract ▽

With the aim of improving the photocatalytic properties of a previously optimized zinc oxide photocatalyst, the effect of the incorporation of different amounts of Ag2CO3 on the aforementioned ZnO has been studied. For this purpose we report the synthesis, by means of simple precipitation procedures, of bare ZnO and Ag2CO3 samples as well as the coupled materials ZnO/Ag2CO3 (X) (where X = 1%, 2%, 4% and 5% in molar percentages). Both, single and coupled materials have been characterized by different techniques (XRD, XRF, N2-absorption, SEM, TEM, UV–vis/DRS and XPS). To assess the advantages or disadvantages that Ag2CO3 addition could have over the optimized ZnO, the photocatalytic properties have been established by following the photo-degradation of selected toxic molecules, both in the UV and in the visible, as well as using complementary techniques of liquid medium analyses (TOC and Atomic Emission Spectrometry with plasma ICP). Three selected substrates were chosen: Rhodamine B (RhB) as a dye, and phenol and caffeine as colourless recalcitrant toxic molecules.
Our results suggest that although the use of Ag2CO3 could be beneficial to implement the optical absorption towards the visible region, however, other effects have to be bore in mind, such as the photo-corrosion of Ag2CO3 and the chemical structure of the chosen substrate, to elucidate whether the addition of Ag2CO3 has beneficial or detrimental effects on the photocatalytic properties of the coupled ZnO/Ag2CO3 materials.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.10.024
Materiales Coloidales
Enhancing Luminescence and X-ray Absorption Capacity of Eu3+:LaF3 Nanoparticles by Bi3+ Codoping
Mancebo, DG; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Moros, M; Balcerzyk, M; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MACS Omega, 4 (2019) 765-774
Show abstract ▽
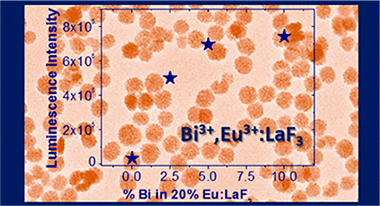
Bi3+ codoping has been proposed in this work with a twofold objective, namely, enhancing the luminescence emission of Eu3+:LaF3 nanoparticles (NPs) and increasing their X-ray attenuation capacity, with the purpose of obtaining a bimodal bioprobe for luminescence bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography. The synthesis method, reported here for the first time for LaF3 particles, allowed obtaining uniform, nonaggregated NPs using a homogeneous precipitation in polyol medium at room temperature in just 2 h. The simplicity of the synthesis method allows the large-scale production of NPs. LaF3 NPs with different Eu3+ contents were first synthesized to find the critical Eu3+ concentration, producing the highest emission intensity. This concentration was subsequently used to fabricate Bi3+-Eu3+-codoped LaF3 NPs using the same method. The emission intensity of the codoped NPs increased in more than one order of magnitude, thanks to the possibility of excitation through the Bi3+. Eu3+ energy-transfer band. The luminescence properties of the codoped NPs were analyzed in detail to find the mechanism responsible for the emission enhancement. Finally, it was demonstrated that the high atomic number of Bi3+, higher than that of lanthanides, was an added value of the material because it increased its X-ray attenuation capacity. In summary, the LaF3 NPs codoped with Eu3+ and Bi3+ presented in this work are promising candidates as a bimodal bioprobe for luminescence bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography.
Enero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.8b03160
2018
2018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Understanding the Role of the Acid Sites in 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation to 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid Reaction over Gold Catalysts: Surface Investigation on CexZr1-xO2 Compounds
Megias-Sayago, C; Chakarova, K; Penkova, A; Lolli, A; Ivanova, S; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JAACS Catalysis, 8 (2018) 11154-11164
Show abstract ▽
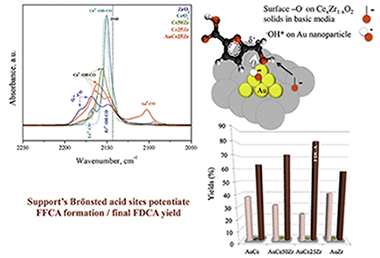
A series of CexZr1-xO2 supports with different Ce/Zr molar ratios were utilized for the preparation of gold catalyst used in the selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. The used method of gold deposition allows the preparation of gold particles with homogeneous size and shape distribution, a formulation very useful for studies dedicated to revealing the support participation in the reaction. The supports are characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy using CO as probe molecule, and the sample catalytic activity is thereafter correlated to the support acid site distribution. The possible participation of its Lewis/Bronsted acidity in the reaction mechanism is also proposed.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b02522 DEC 2018
- ‹ anterior
- 147 of 420
- siguiente ›














