Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales Avanzados
Degradation of a LDPE film applied as a greenhouse cover design material: the effect of ageing and mechanical modelling
Garzon, Eduardo; Ortiz Rodriguez, Isabel Maria; Castillo, Jose; Jose Sanchez-Soto, PedroRevista de la Construcción, 17 (3) (2018) 457-464
Show abstract ▽
In this work, we studied the mechanical performance of an LDPE film (0.22 mm in thickness) used as a material in the design of greenhouse covers. We investigated the effects of ageing at different periods of its service life and applying chemical substance treatments used as pesticides on greenhouse crops and after breakage using mechanical traction. Numerical simulations were performed using the finite element method. For this purpose, one section of the complete geometry of the greenhouse cover and different load conditions (1-5 kPa) were considered for the modelling. The performance of the polymer was assumed to be linearly elastic to simplify the governing equations. The study demonstrated that the LDPE film used was no longer effective as a greenhouse cover film due to the degradation of its mechanical properties. It was shown that the general performance of this film was in the plastic zone and its performance was non-linear. The results deduced from the present study are of interest because they show the material failure process of greenhouse covers in relation to the degradation process.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.7764/RDLC.17.3.457 DEC 2018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
New concept for old reaction: Novel WGS catalyst design
Garcia-Moncada, N; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 238 (2018) 1-5
Show abstract ▽
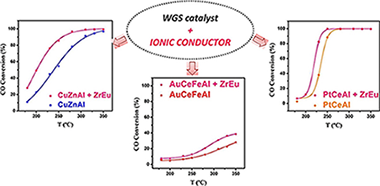
The viability of water gas shift catalytic system for mobile application passes through obligatory reactor volume reduction, achieved normally by using less charge of more efficient catalyst. Completely new concept for catalyst design is proposed: a catalytic system including classically reported WGS catalysts of different nature or active phase (Cu, Pt or Au) mechanically mixed with an ionic conductor. The influence of the later on catalyst activity is studied and discussed, more precisely its effect on the rate of the reaction-limiting step and catalysts' efficiency. It is demonstrated with this study, that the presence of an ionic conductor in contact with a WGS catalyst is essential for the water supply (dissociation and transport), thereby potentiating the water activation step, whatever the mechanism and catalyst overall performance.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.068
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
A comparative assessment of the UV-photocatalytic activities of ZnO synthesized by different routes
Jaramillo-Paez, C; Sanchez-Cid, P; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6 (2018) 7161-7171
Show abstract ▽
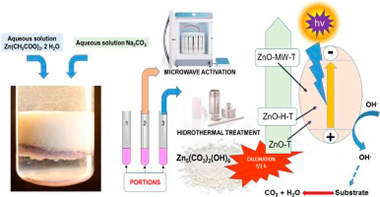
ZnO was synthesized by a precipitation procedure, free of template agent, by mixing aqueous solutions of Zn (OAc)(2) and dissolved Na2CO3 at pH ca. 7. This material was calcined at different temperatures (200-600 degrees C for 2 h). In two other alternative procedures, after the precipitation, the suspension was taken to hydrothermal treatments or to microwave treatments, subjecting them to calcination treatments at the same temperatures as the previous material. All materials were characterized using various techniques. The photocatalytic activity was assessed in the degradation of methyl orange and phenol using UV-illumination and evaluating the corresponding percentages of conversion and mineralization. A minimal difference between the relative intensities of the exposed faces (I100I002) related to XRD for the synthesized samples seems to be an important factor in obtaining good photocatalytic properties. This minimum, was achieved with a calcination treatment at 400 degrees C for 2 h. With this calcination treatment, no significant variations were observed in the photocatalytic activities of ZnO obtained by the three procedures, although in all cases the zinc oxides obtained exhibited, for each substrate, higher UV-photocatalytic activities than those obtained with TiO2 (P25) used as a reference catalyst. In all cases, the samples showed no photocatalytic activity in the visible region of the spectrum.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO/H-2 adsorption on a Ru/Al2O3 model catalyst for Fischer Trospch: Effect of water concentration on the surface species
Jimenez-Barrera, E; Bazin, P; Lopez-Cartes, C; Romero-Sarria, F; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 237 (2018) 986-995
Show abstract ▽
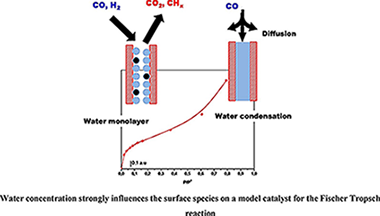
Water presence and concentration strongly influence CO conversion and CS+ selectivity in the Fischer Tropsch reaction. In this work, the influence of the water concentration was investigated using a model Ru/Al2O3 (5 wt. %) catalyst. The surface species formed after CO and H-2 adsorption in dry and wet (different water concentrations) conditions were analyzed by FTIR. Firstly, water adsorption was carried out up to complete filling of the pores and then CO was put in contact with the catalyst. The absence of adsorbed CO species in these conditions evidences that CO diffusion in water controls the access of the gas to the active sites and explains the negative effect of high water concentrations reported by some authors. Moreover, the adsorption of a mixture of CO + H-2 + H2O, being the water concentration close to that needed to have a monolayer, and a dry mixture of CO + H-2 were carried out and compared. Results evidence that water in this low concentration, is able to gasify the surface carbon species formed by CO dissociation on the metallic sites. This cleaning effect is related to the positive effect of water on CO conversion detected by some authors.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.053
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Metal Micro-Monoliths for the Kinetic Study and the Intensification of the Water Gas Shift Reaction
Garcia-Moncada, N; Groppi, G; Beretta, A; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysts, 8 (2018) art. 594
Show abstract ▽
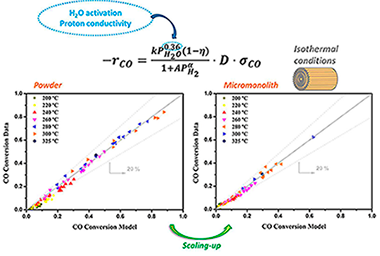
A kinetic study of the water gas shift (WGS) reaction has been carried out on a Pt-based catalyst promoted by a Zr-based proton conductor. The investigation was first performed on powders with diluted feed mixtures and then extended to more severe and representative conditions by using a catalyst coated metallic micromonolith. Temperature measurements reveal that isothermal conditions were obtained along the micromonolith during the tested conditions. In addition, the very thin catalytic layer allows for the discarding of intraporous resistances, providing excellent conditions to analyse the kinetics of the WGS reaction under the integral regime. The proposed rate expression accounts for independence on CO concentration, an inhibiting effect of H-2 and a promoting effect of H2O; kinetic orders on CO and H-2 are in line with those reported in the literature for the Pt-based catalyst. Instead, the obtained reaction order of water (0.36) is significantly lower than that reported for unpromoted catalysts (typically 0.77-1.10) in good agreement with the proposed water-enhancer effect of the proton conductor on the rate-limiting step. Metallic micromonoliths turn out to be a powerful tool for the kinetic investigation, due to the absence of mass and heat transport limitations and represent a strategy for the intensification of the WGS unit for future applications of fuel processors in small mobile devices.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.3390/catal8120594
- ‹ anterior
- 148 of 420
- siguiente ›














