Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Improving the Bulk Emission Properties of CH3NH3PbBr3 by Modifying the Halide-Related Defect Structure
Tiede, David O.; Calvo, Mauricio E.; Galisteo-Lopez, Juan F.; Miguez, HernanJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 122 (2018) 27250-27255
Show abstract ▽
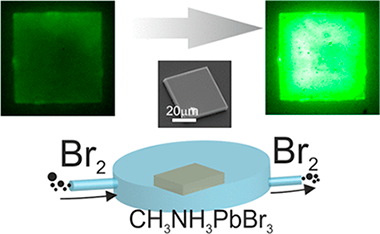
The peculiar defect chemistry of hybrid organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites is believed to be partially responsible for the outstanding performance of this solution-processed material in optoelectronic devices. While most effort has been put on the management of halide defects (the ones presenting the highest mobility) for CH3NH3PbI3, its bromide counterpart has not been so widely studied. Although the former is the material of choice for photovoltaics, the latter is present in most light-emitting applications. Here, we report how the exposure of CH3NH3PbBr3 single crystals to a bromine atmosphere strongly affects its emission properties. Such improvement takes place in the absence of apparent signs of degradation and remains for tens of hours. We propose an explanation based on the defect structure for this material where bromine-related defects can act as deep or shallow traps. These results are of relevance for a material expected to be present in a new generation of solution-processed light-emitting devices.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b09315 DEC 6 2018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Understanding the Role of the Acid Sites in 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation to 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid Reaction over Gold Catalysts: Surface Investigation on CexZr1-xO2 Compounds
Megias-Sayago, C; Chakarova, K; Penkova, A; Lolli, A; Ivanova, S; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JAACS Catalysis, 8 (2018) 11154-11164
Show abstract ▽
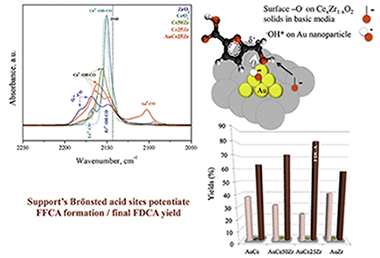
A series of CexZr1-xO2 supports with different Ce/Zr molar ratios were utilized for the preparation of gold catalyst used in the selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. The used method of gold deposition allows the preparation of gold particles with homogeneous size and shape distribution, a formulation very useful for studies dedicated to revealing the support participation in the reaction. The supports are characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy using CO as probe molecule, and the sample catalytic activity is thereafter correlated to the support acid site distribution. The possible participation of its Lewis/Bronsted acidity in the reaction mechanism is also proposed.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.8b02522 DEC 2018
Reactividad de Sólidos
Role of calcium looping conditions on the performance of natural and synthetic Ca-based materials for energy storage
Sarrion, B; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Valverde, JMJournal of CO2 utilization, 28 (2018) 374-384
Show abstract ▽
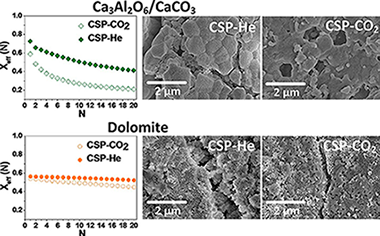
In this work, the multicycle activity of natural CaO precursors (limestone and dolomite) and Ca-based composites (Ca3Al2O6/CaCO3 and ZrO2/CaCO3 mixtures) has been studied for Thermochemical Energy Storage (TCES) in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants by means of the Calcium-Looping process (CaL), using two integration schemes proposed elsewhere that differ in the calcination stages. Under CSP-He conditions, calcination for CaO regeneration is performed under pure He at low temperatures (725 degrees C) while under CPS-CO2 conditions calcination is carried out under pure CO2 at high temperatures (950 degrees C). The latter avoids the use of selective membranes to separate He from CO2 even though it requires the use of more expensive materials for solar receptors. Carbonation/calcination conditions drastically affect the multicycle CO2 uptake of the materials tested. Effective multicycle conversion is higher in CSP-He tests due to the mild conditions employed for calcination, which mitigates CaO sintering. On the other hand, the harsh calcination conditions used in CSP-CO2 tests enhance sintering of CaO derived from limestone and the Ca3Al2O6/CaCO3 composite due to the low Tammann temperature of Ca3Al2O6. CaO sintering is hindered by the presence of inert oxides with high Tammann temperatures, such as ZrO2 in the ZrO2/CaCO3 composite and MgO in dolomite. Dolomite derived CaO shows high effective conversion values along the carbonation/calcination cycles when tested under both types of conditions, as compared to limestone and the composites, which suggests that the integration scheme based on CSP-CO2 conditions would be a feasible alternative to CSP-He if natural dolomite were used as CaO precursor.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.10.018
Materiales Avanzados
Degradation of a LDPE film applied as a greenhouse cover design material: the effect of ageing and mechanical modelling
Garzon, Eduardo; Ortiz Rodriguez, Isabel Maria; Castillo, Jose; Jose Sanchez-Soto, PedroRevista de la Construcción, 17 (3) (2018) 457-464
Show abstract ▽
In this work, we studied the mechanical performance of an LDPE film (0.22 mm in thickness) used as a material in the design of greenhouse covers. We investigated the effects of ageing at different periods of its service life and applying chemical substance treatments used as pesticides on greenhouse crops and after breakage using mechanical traction. Numerical simulations were performed using the finite element method. For this purpose, one section of the complete geometry of the greenhouse cover and different load conditions (1-5 kPa) were considered for the modelling. The performance of the polymer was assumed to be linearly elastic to simplify the governing equations. The study demonstrated that the LDPE film used was no longer effective as a greenhouse cover film due to the degradation of its mechanical properties. It was shown that the general performance of this film was in the plastic zone and its performance was non-linear. The results deduced from the present study are of interest because they show the material failure process of greenhouse covers in relation to the degradation process.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.7764/RDLC.17.3.457 DEC 2018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
New concept for old reaction: Novel WGS catalyst design
Garcia-Moncada, N; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 238 (2018) 1-5
Show abstract ▽
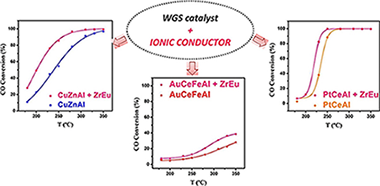
The viability of water gas shift catalytic system for mobile application passes through obligatory reactor volume reduction, achieved normally by using less charge of more efficient catalyst. Completely new concept for catalyst design is proposed: a catalytic system including classically reported WGS catalysts of different nature or active phase (Cu, Pt or Au) mechanically mixed with an ionic conductor. The influence of the later on catalyst activity is studied and discussed, more precisely its effect on the rate of the reaction-limiting step and catalysts' efficiency. It is demonstrated with this study, that the presence of an ionic conductor in contact with a WGS catalyst is essential for the water supply (dissociation and transport), thereby potentiating the water activation step, whatever the mechanism and catalyst overall performance.
Diciembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.068
- ‹ anterior
- 149 of 420
- siguiente ›














