Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quantitative analysis of Yb 4d photoelectron spectrum of metallic Yb
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Tougaard, SSurface & Coatings Technology, 50 (2018) 1168-1173
Show abstract ▽
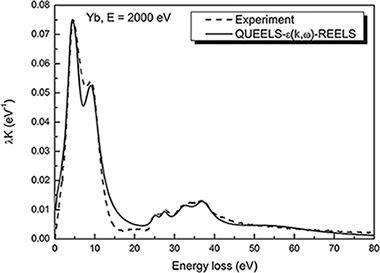
The measured Yb 4d(3/2) intensity is larger than the Yb 4d(5/2) in X-ray photoelectron (XPS) emission of metallic Yb, which is unexpected. The shape and intensity of photoelectron peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface (including bulk and surface effects) and to intrinsic excitations due to the sudden creation of the static core hole. To quantitatively extract from experimental XPS the primary excitation spectrum (ie, the initial excitation process) of the considered transition, these effects must be included within the theoretical description. The combined effect of both extrinsic and intrinsic excitations can be described by an effective energy-differential inelastic electron scattering cross section for XPS evaluated by a dielectric response model with the dielectric function as only input. Then, using this cross section, a direct evaluation of the primary excitation spectrum is performed by standard peak shape analysis for thick homogeneous samples. We use this approach in the present paper to determine the Yb 4d photoemission spectrum for metallic Yb. We show that the unexpected larger intensity of Yb 4d(3/2) compared to 4d(5/2) can be fully accounted for by our model and that the total spectrum consists of a sum of symmetric primary excitation peaks.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.6402
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Valorization of Tomato Processing by-Products: Fatty Acid Extraction and Production of Bio-Based Materials
Benitez, JJ; Castillo, PM; del Rio, JC; Leon-Camacho, M; Dominguez, E; Heredia, A; Guzman-Puyol, S; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAMaterials, 11 (2018) art. 2211
Show abstract ▽
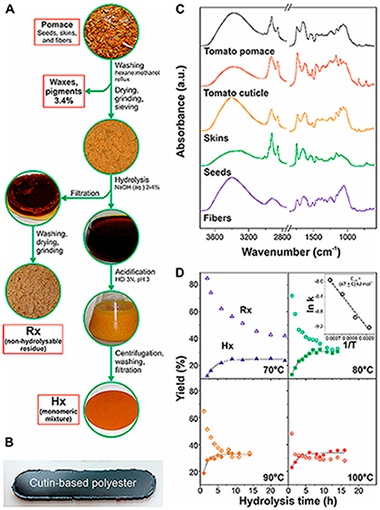
A method consisting of the alkaline hydrolysis of tomato pomace by-products has been optimized to obtain a mixture of unsaturated and polyhydroxylated fatty acids as well as a non-hydrolysable secondary residue. Reaction rates and the activation energy of the hydrolysis were calculated to reduce costs associated with chemicals and energy consumption. Lipid and non-hydrolysable fractions were chemically (infrared (IR) spectroscopy, gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC-MS)) and thermally (differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)) characterized. In addition, the fatty acid mixture was used to produce cutin-based polyesters. Freestanding films were prepared by non-catalyzed melt-polycondensation and characterized by Attenuated Total Reflected-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), DSC, TGA, Water Contact Angles (WCA), and tensile tests. These bio-based polymers were hydrophobic, insoluble, infusible, and thermally stable, their physical properties being tunable by controlling the presence of unsaturated fatty acids and oxygen in the reaction. The participation of an oxidative crosslinking side reaction is proposed to be responsible for such modifications.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.3390/ma11112211
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Exotic grain growth law in twinned boron carbide under electric fields
Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Rodriguez, ADJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 38 (2018) 4590-4596
Show abstract ▽
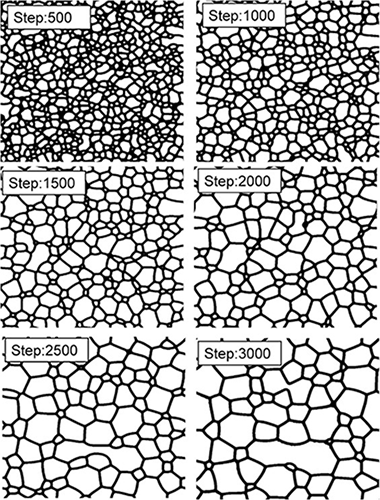
Grain growth is a ubiquitous phenomenon in all materials, and it affects both structural and functional properties. Despite its intrinsic importance, a full comprehension of grain growth from a fundamental point of view-i.e., from the nanoscale to the macroscale-is still a pending issue. In practical terms, our knowledge relies on the classical kinetic laws reported sixty years ago.
This paper reports the violation of such classical laws in boron carbide ceramics consolidated by spark plasma sintering. The conjunction of high temperature gradients with large compressive stress when a pulse electric current passes through the ceramic powders gives rise to an intense twinning-detwinning formation. These forming steps at the grain boundaries change the grain mobility drastically. Therefore, a new 'exotic' law for grain-growth kinetics is found and validated at different temperatures and dwell times.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.06.029
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Nanoporous Pt-based catalysts prepared by chemical dealloying of magnetron-sputtered Pt-Cu thin films for the catalytic combustion of hydrogen
Giarratano, F; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Montes, O; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 235 (2018) 168-176
Show abstract ▽
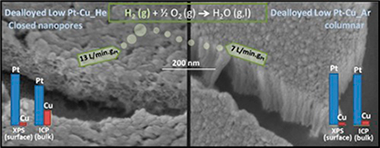
In this work, we prepared SiC-supported Pt-Cu thin films by magnetron sputtering for use as catalysts for the combustion of hydrogen under oxidizing conditions. We tested the catalysts as prepared and after chemical dealloying. A methodology is presented to fabricate catalytic thin films of a desired composition with tailored magnetron targets with lower Pt consumption. The deposition gas was changed to prepare columnar (Ar-deposited) and closed-porous (He-deposited) films to study the effect of the microstructure on the activity. The effect of composition was also studied for the columnar samples. The as-prepared Pt-Cu thin films showed significant activity only at temperatures higher than 100 °C. Dealloying permitted an increase in the activity to achieve near room-temperature activity. The dealloyed closed-porous He-deposited sample was the most active, being able to convert as much as 13.15 LH2·min−1 gPt−1 at 70 °C (Ea = 1 kJ mol−1). This sample was preferentially dealloyed on the surface, yielding an almost pure Pt shell (96% at. Pt) and a Cu-depleted interior (71% at. Pt). This compositional inhomogeneity enabled the sample to achieve enhanced activity compared to the Ar-deposited columnar sample (with similar initial composition, but uniformly dealloyed), probably due to the compressive surface lattice strain. The dealloyed closed-porous He-deposited sample was shown to be durable over five cycles.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.04.064
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Highly Efficient and Environmentally Stable Flexible Color Converters Based on Confined CH3NH3PbBr3 Nanocrystals
Rubino, A; Anaya, M; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Rojas, TC; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10 (2018) 38334-38340
Show abstract ▽
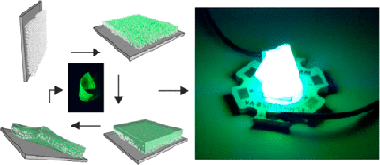
In this work, we demonstrate a synthetic route to attain methylammonium lead bromide (CH3NH3PbBr3) perovskite nanocrystals (nc-MAPbBr(3), 1.5 nm < size < 3 nm) and provide them with functionality as highly efficient flexible, transparent, environmentally stable, and adaptable color converting films. We use nanoparticle metal oxide (MOx) thin films as porous scaffolds of controlled nanopores size distribution to synthesize nc-MAPbBr(3) through the infiltration of perovskite liquid precursors. We find that the control over the reaction volume imposed by the nanoporous scaffold gives rise to a strict control of the nanocrystal size, which allows us to observe well-defined quantum confinement effects on the photo-emission, being the luminescence maximum tunable with precision between lambda = 530 nm (green) and lambda = 490 nm (blue). This hybrid nc-MAPbBr(3)/MOx structure presents high mechanical stability and permits subsequent infiltration with an elastomer to achieve a self-standing flexible film, which not only maintains the photo-emission efficiency of the nc-MAPbBr(3) unaltered but also prevents their environmental degradation. Applications as adaptable color-converting layers for light-emitting devices are envisaged and demonstrated.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b11706
- ‹ anterior
- 151 of 420
- siguiente ›














