Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Sustainable Fabrication of Plant Cuticle-Like Packaging Films from Tomato Pomace Agro-Waste, Beeswax, and Alginate
Tedeschi, G; Benitez, JJ; Ceseracciu, L; Dastmalchi, K; Itin, B; Stark, RE; Heredia, A; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6 (2018) 14955-14966
Show abstract ▽

Plant cuticles have been used as models to produce hydrophobic films composed of sodium alginate, the fatty acid fraction of tomato pomace agrowaste, and beeswax. The fabrication process consisted of the blending of components in green solvents (water and ethanol) and a subsequent thermal treatment (150 degrees C, 8 h) to polymerize unsaturated and polyhydroxylated fatty acids from tomato pomace. When sodium alginate and tomato pomace fatty acids were blended, free-standing films were obtained. These films were characterized to evaluate their morphological (SEM), chemical (solid-state NMR, ATR-FTIR), mechanical (tensile tests), thermal (TGA), and hydrodynamic (water contact angle, uptake, and permeability) properties. A comparison between nonpolymerized and polymerized samples was carried out, revealing that the thermal treatment represents a sustainable route to create structured, composite networks of both components. Finally, beeswax was added to the blend with the same amounts of sodium alginate and tomato pomace fatty acids. The presence of the wax improved the hydrophobicity and the mechanical and water barrier properties as well as decreased the water uptake. These results indicate that polymerized plant cuticle-like films have valuable potential for packaging applications.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03450
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Selective CO methanation with structured RuO2/Al2O3 catalysts
Munoz-Murillo, A; Martinez, LM; Dominguez, MI; Odriozola, JA; Centeno, MAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 236 (2018) 420-427
Show abstract ▽
Active and selective structured RuO2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO methanation using a flow simulating CO2-rich reformate gases from WGS and PROX units (H-2 excess, CO2 presence and 300 ppm CO concentration) were prepared. Both, the RuO2/Al2O3 powder and the slurry prepared from it for its structuration by washcoating of the metallic micromonolithic structure, were also active and selective. Both the slurry (S-RuAl) and micro monoliths (M-RuAl) were able to completely and selectively methanate CO at much lower temperatures than the parent RuAI powder. The optimal working temperature in which the CO conversion is maximum and the CO2 conversion is minimized was determined to be from 149 degrees C to 239 degrees C for S-RuAl and from 165 degrees C to 232 degrees C for M-RuAl, whilst it was from 217 degrees C to 226 degrees C for RuAI powder. TPR, XRD and TEM measurements confirmed that the changes in the activity and selectivity for CO methanation among the considered catalysts can be related with modifications in the surface particle size of ruthenium and its reducibility. These were ascribed to the metallic substrate, the presence of PVA and colloidal alumina in the slurry preparation, the aqueous and acidic media and the thermal treatment used, resulting in a more active and selective catalysts than the parent powder.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.05.020
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
High voltage vacuum-deposited CH3NH3PbI3–CH3NH3PbI3 tandem solar cells
Avila, J; Momblona, C; Boix, P; Sessolo, M; Anaya, M; Lozano, G; Vandewal, K; Miguez, H; Bolink, HJEnergy & Environmental Science, 11 (2018) 3292-3297
Show abstract ▽
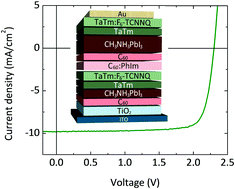
The recent success of perovskite solar cells is based on two solid pillars: the rapid progress of their power conversion efficiency and their flexibility in terms of optoelectrical properties and processing methods. That versatility makes these devices ideal candidates for multi-junction photovoltaics. We report an optically optimized double junction CH3NH3PbI3-CH3NH3PbI3 tandem solar cell where the matched short-circuit current is maximized while parasitic absorption is minimized. The use of an additive vacuum-deposition protocol allows us to reproduce calculated stack designs, which comprise several charge selective materials that ensure appropriate band alignment and charge recombination. This rationalized configuration yields an unprecedented open circuit voltage of 2.30 V. Furthermore, this tandem solar cell features efficiencies larger than 18%, higher than those of the individual sub-cells. Low photo-current values allow reducing the losses associated to the series resistance of transparent contacts, which opens the door to the realization of efficient large area modules.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1039/c8ee01936c
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quantitative analysis of Yb 4d photoelectron spectrum of metallic Yb
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Tougaard, SSurface & Coatings Technology, 50 (2018) 1168-1173
Show abstract ▽
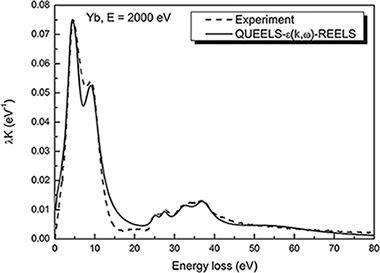
The measured Yb 4d(3/2) intensity is larger than the Yb 4d(5/2) in X-ray photoelectron (XPS) emission of metallic Yb, which is unexpected. The shape and intensity of photoelectron peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface (including bulk and surface effects) and to intrinsic excitations due to the sudden creation of the static core hole. To quantitatively extract from experimental XPS the primary excitation spectrum (ie, the initial excitation process) of the considered transition, these effects must be included within the theoretical description. The combined effect of both extrinsic and intrinsic excitations can be described by an effective energy-differential inelastic electron scattering cross section for XPS evaluated by a dielectric response model with the dielectric function as only input. Then, using this cross section, a direct evaluation of the primary excitation spectrum is performed by standard peak shape analysis for thick homogeneous samples. We use this approach in the present paper to determine the Yb 4d photoemission spectrum for metallic Yb. We show that the unexpected larger intensity of Yb 4d(3/2) compared to 4d(5/2) can be fully accounted for by our model and that the total spectrum consists of a sum of symmetric primary excitation peaks.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.6402
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Valorization of Tomato Processing by-Products: Fatty Acid Extraction and Production of Bio-Based Materials
Benitez, JJ; Castillo, PM; del Rio, JC; Leon-Camacho, M; Dominguez, E; Heredia, A; Guzman-Puyol, S; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAMaterials, 11 (2018) art. 2211
Show abstract ▽
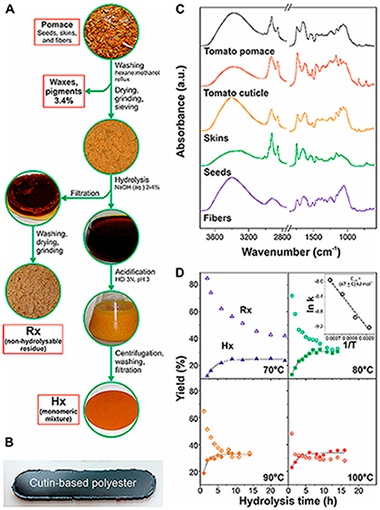
A method consisting of the alkaline hydrolysis of tomato pomace by-products has been optimized to obtain a mixture of unsaturated and polyhydroxylated fatty acids as well as a non-hydrolysable secondary residue. Reaction rates and the activation energy of the hydrolysis were calculated to reduce costs associated with chemicals and energy consumption. Lipid and non-hydrolysable fractions were chemically (infrared (IR) spectroscopy, gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC-MS)) and thermally (differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)) characterized. In addition, the fatty acid mixture was used to produce cutin-based polyesters. Freestanding films were prepared by non-catalyzed melt-polycondensation and characterized by Attenuated Total Reflected-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), DSC, TGA, Water Contact Angles (WCA), and tensile tests. These bio-based polymers were hydrophobic, insoluble, infusible, and thermally stable, their physical properties being tunable by controlling the presence of unsaturated fatty acids and oxygen in the reaction. The participation of an oxidative crosslinking side reaction is proposed to be responsible for such modifications.
Noviembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.3390/ma11112211
- ‹ anterior
- 152 of 420
- siguiente ›














