Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Absorption enhancement in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite solar cells with embedded arrays of dielectric particles
Jimenez-Solano, A; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HOptics Express, 26 (2018) A865-A878
Show abstract ▽
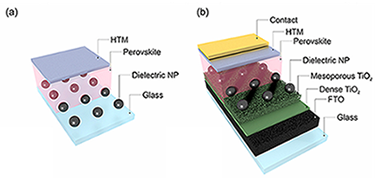
In the field of hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite based photovoltaics, there is a growing interest in the exploration of novel and smarter ways to improve the cells light harvesting efficiency at targeted wavelength ranges within the minimum volume possible, as well as in the development of colored and/or semitransparent devices that could pave the way both to their architectonic integration and to their use in the flowering field of tandem solar cells. The work herein presented targets these different goals by means of the theoretical optimization of the optical design of standard opaque and semitransparent perovskite solar cells. In order to do so, we focus on the effect of harmless, compatible and commercially available dielectric inclusions within the absorbing material, methylammonium lead iodide (MAPI). Following a gradual and systematic process of analysis, we are capable of identifying the appearance of collective and hybrid (both localized and ex tended) photonic resonances which allow to significantly improve light harvesting and thus the overall efficiency of the standard device by above 10% with respect to the reference value while keeping the semiconductor film thickness to a minimum. We believe our results will be particularly relevant in the promising field of perovskite solar cell based tandem photovoltaic devices, which has posed new challenges to the solar energy community in order to maximize the performance of semitransparent cells, but also for applications focusing on architectonic integration.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1364/OE.26.00A865
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanostructural Analysis of Porous Oblique Angle Deposited (OAD) Multilayer Systems by Grazing-Incidence Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2018) 1800530
Show abstract ▽
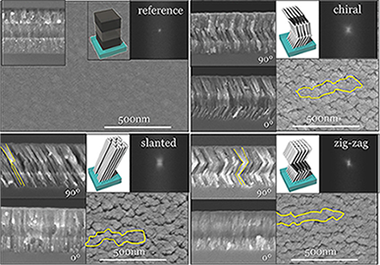
This work reports a thorough characterization analysis of various porous thin film multilayers by means of grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering (GISAXS). Alternated TiO2/SiO2 nanocolumnar layers deposited at oblique angles are fabricated in slanted, chiral, and zig-zag configurations by rotating azimuthally the substrate from one layer to the next. Multilayer systems formed by the stacking of 3 and 15 alternant thin films of these two oxides are morphologically characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and structurally by GISAXS. This technique has provided a means to determine various vertical and lateral correlation lengths and to assess the anisotropic electron density distribution along the structural elements existing in the multilayers. This information can be systematically used to account for the actual arrangement of nanostructural elements in multilayer systems.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/admi.201800530
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
ZnO and Pt-ZnO photocatalysts: Characterization and photocatalytic activity assessing by means of three substrates
Jaramillo, C; Navio, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Macías, M.Catalysis Today, 313 (2018) 12-19
Show abstract ▽
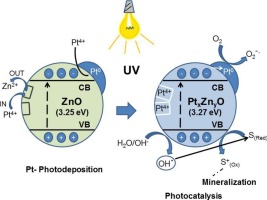
ZnO nanoparticles have been previously synthesized by a facile precipitation procedure by mixing aqueous solutions of Zn(II) acetate and dissolved Na2CO3 at pH ca. 7.0 without the addition of a template. The as-prepared ZnO material was anealed at 400 °C in air for 2 h. The Pt-ZnO catalysts (0.5 or 1.0 Pt wt.%) were obtained by photochemical deposition method on the surface of the prepared ZnO sample, using hexachloroplatinic acid (H2PtCl6). It has been shown that Zn2+ is lost from the photocatalyst to the medium and a replacement of the cationic vacancies of Zn2+ by Pt4+ cations occurs during the platinization process of the ZnO samples, regardless of whether the platinum metal photodeposition process. The as-prepared catalysts were characterized by XRD, BET, FE-SEM, TEM, XPS and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). Three different probe molecules were used to evaluate the photocatalytic properties under UV-illumination: Methyl Orange and Rhodamine B were chosen as dye substrates and Phenol as a transparent substrate. High conversion values (ca. 100%) and a total organic carbon (TOC) removal of 90–96%, were obtained over these photocatalysts after 160 min of UV illumination. In general, it was observed that the presence of Pt on ZnO affects the lattice parameters and the crystallite size. Although ZnO can completely degrade RhB, MO and Phenol totally in ca. 60 min, the process is more efficient for Pt–ZnO photocatalysts.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.12.009
Materiales Avanzados
Vitrification and derived glass-ceramics from mining wastes containing vermiculite and lithium aluminium phosphate
Rincon, JM; Callejas, P; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Jordan, MMMaterials Letters, 227 (2018) 86-89
Show abstract ▽
The waste vitrification of abandoned open sky vermiculite deposits has been considered by combining with a natural phosphate mineral residue. Several batches haven been designed from the composition system: Li2O-MgO-Al2O3-P2O5-SiO2 including some Fe2O3 and Fluoride. The resulting glasses are transparent and smooth green coloured, giving rise after TTT treatments to several opal, opaque glass-ceramics with iridescent surface. Full characterization has been carried out by XRD and electron microscopy with EDS, as well as by XPS spectroscopies, concluding that the main crystalline phases formed were alpha-cordierite and beta-spodumene. The surface of these glass-ceramics from vermiculiteamblygonite is enriched in Fe2O3. Compared to the parent glasses, the final glass-ceramics exhibited and improvement in fracture toughness.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.05.001
Reactividad de Sólidos
Combined kinetic analysis of multistep processes of thermal decomposition of polydimethylsiloxane silicone
Garcia-Garrido, C; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PEPolymer, 153 (2018) 558-564
Show abstract ▽
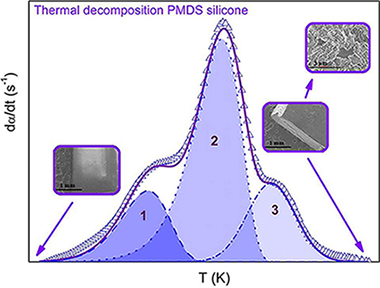
In this work, we studied the thermal decomposition of a widely employed silicone elastomer, polydimethylsiloxane, in an inert atmosphere. This silicone elastomer has several applications due to its high thermal stability such as MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) precursors, microfluidic components, adhesives, lubricants, and precursors for non-porous ceramics. Therefore, a reliable description of the thermal decomposition kinetics is important to prevent or control the decomposition in such applications. While the decomposition has been amply reported as a complex process, most kinetic studies published on this system use simplified methods that avoid the fact that the entire process cannot be described by a single kinetic triplet. Here, we have studied the decomposition process by first separating the overall reaction into its three constituent steps which were subsequently analysed independently. The deconvolution was carried out using Fraser-Suzuki function that is capable of fitting an asymmetric peak fitting function. The resulting kinetic parameters proved to be able to reconstruct the original experimental curves but are also capable of producing accurate predictions of curves recorded at heating schedules different from those employed to record the experimental data used in the kinetic analysis. Finally, it was found that the rate limiting step of all stages is the diffusion of the gases released during the polymer decomposition through the transforming polymeric matrix.
Septiembre, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2018.08.045
- ‹ anterior
- 156 of 420
- siguiente ›














